Drug Detail:Brineura (Cerliponase alfa [ ser-lip-oh-nase-al-fa ])
Generic Name: CERLIPONASE ALFA 150mg in 5mL;
Dosage Form: kit
Drug Class: Lysosomal enzymes
Important Preparation and Administration Information
-
Aseptic technique must be strictly observed during preparation and administration.
-
Brineura should be administered by, or under the direction of, a physician experienced in intraventricular administration.
-
Prior to each infusion of Brineura, inspect the scalp for signs of intraventricular access device leakage, failure or potential infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
-
Prior to each infusion of Brineura and when clinically indicated, obtain a sample of CSF for cell count and culture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
Brineura is administered into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by infusion via a surgically implanted reservoir and catheter (intraventricular access device). Brineura is intended to be administered via the Codman® HOLTER RICKHAM Reservoirs (Part Numbers: 82-1625, 82-1621, 82-1616) with the Codman® Ventricular Catheter (Part Number: 82-1650). The intraventricular access device must be implanted prior to the first infusion. It is recommended that the first dose be administered at least 5 to 7 days after device implantation.
-
Brineura is intended to be administered with the B Braun Perfusor® Space Infusion Pump System (Product Code: 8713030U). If an alternative pump must be used, the essential performance requirements for this syringe pump used to deliver Brineura are as follows:
-
Delivery rate of 2.5 mL/hr with delivery accuracy of +/- 1 mL/hr
-
Compatible with 20 mL syringes provided in the Administration Kit for use with Brineura
-
Occlusion alarm setting to ≤ 281 mm Hg
-
Cleared for intraventricular route of administration
-
-
Administer Brineura and the Intraventricular Electrolytes using the provided Administration Kit for use with Brineura components [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
2.2 Dosage
The recommended dosage of Brineura in pediatric patients 3 years of age and older is 300 mg administered once every other week by intraventricular infusion. Administer Brineura first followed by infusion of the Intraventricular Electrolytes each at an infusion rate of 2.5 mL/hr. The complete Brineura infusion, including the required infusion of Intraventricular Electrolytes, is approximately 4.5 hours.
Pre-treatment of patients with antihistamines with or without antipyretics or corticosteroids is recommended 30 to 60 minutes prior to the start of infusion.
2.3 Method of Administration
Brineura and the Intraventricular Electrolytes must only be administered by the intraventricular route, using the provided Administration Kit for use with Brineura. Each vial of Brineura and Intraventricular Electrolytes is intended for a single dose only.
Each infusion consists of 10 mL of Brineura followed by 2 mL of Intraventricular Electrolytes. The complete infusion must be administered using an infusion set with a 0.2 micron inline filter. The Intraventricular Electrolytes are used to flush the infusion line, port needle, and intraventricular access device in order to fully administer Brineura and to maintain patency of the intraventricular access device.
Preparation for Infusion
Gather supplies:
-
Brineura and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection vials (package 1 of 2) [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]
-
Administration Kit for use with Brineura (package 2 of 2) [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]
-
Syringe pump (not supplied)
Inspect the Administration Kit infusion components to ensure the components are in the individual packages and have not been compromised.
Thaw Brineura and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection vials at room temperature for approximately 60 minutes. Do not thaw or warm vials any other way. Do not shake vials. Condensation will occur during thawing period. Do not re‑freeze vials or freeze syringes containing Brineura or Intraventricular Electrolytes.
Inspect fully thawed Brineura and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection vials. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Brineura is a clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow solution. Intraventricular Electrolytes is a clear to colorless solution. Do not use if the solutions are discolored or if there is other foreign particulate matter in the solutions. Brineura vials may occasionally contain thin translucent fibers or opaque particles. These naturally occurring particles are cerliponase alfa. These particles are removed via the 0.2 micron inline filter without having a detectable effect on the purity or strength of Brineura. Intraventricular Electrolytes may contain particles, which appear during the thaw period; however, these dissolve when the solution reaches room temperature.
Intraventricular Infusion Procedure
Intraventricular Infusion of Brineura
Figure 1 represents the intraventricular infusion system set up. Use aseptic technique during the infusion. Follow the steps below to proceed with the intraventricular infusion.
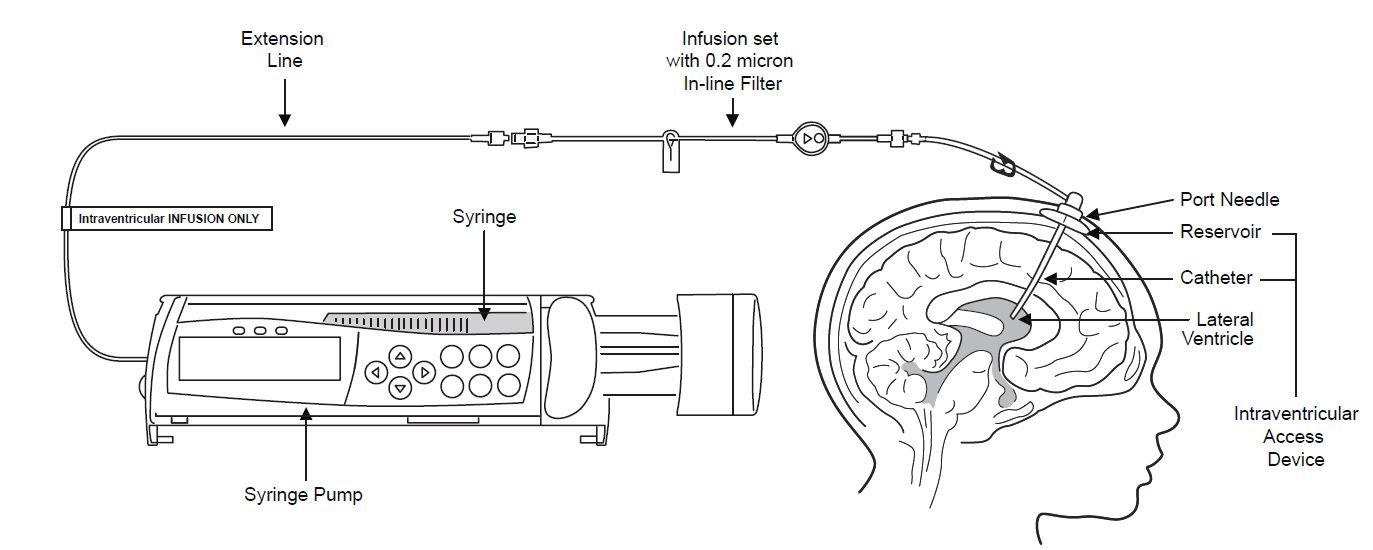
Figure 1
1. Use aseptic technique when preparing the Brineura syringe for infusion. Label one sterile syringe “Brineura” and attach the syringe needle. Remove the green flip-off caps from the two Brineura vials. Use the “Brineura” labeled syringe to withdraw a total of 10 mL from the Brineura vials. Do not dilute Brineura. Do not mix Brineura with any other drug.
2. Label the infusion line “intraventricular infusion only” (see Figure 1).
3. Attach the syringe containing Brineura to the extension line (see Figure 2). Then connect the extension line to the infusion set with a 0.2 micron inline filter (see Figure 1).
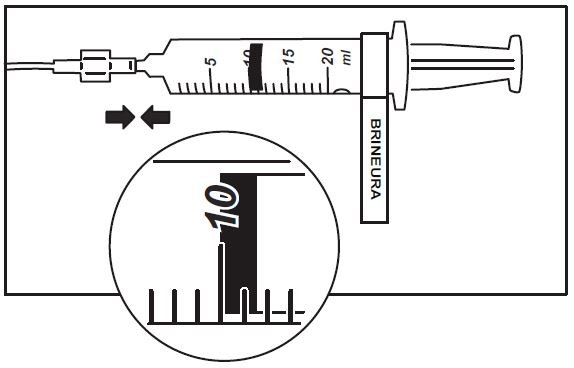
Figure 2
4. Prime the infusion components with Brineura.
5. Inspect scalp for signs of intraventricular access device leakage or failure and for potential infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
6. Prepare the scalp for intraventricular infusion per institution standard of care.
7. Insert port needle into intraventricular access device (see Figure 3).
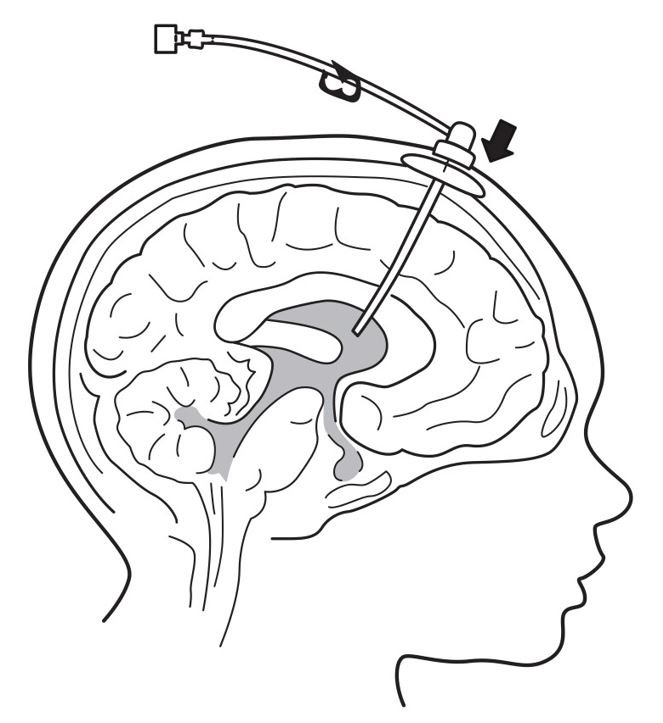
Figure 3
8. Connect a separate empty sterile single-use luer lock syringe, no larger than 3 mL (not provided) to the port needle. Withdraw 0.5 mL to 1 mL of CSF to check patency of intraventricular access device (see Figure 4) and send specimen for culture.
- Do not return CSF to intraventricular access device.
- Routinely send CSF samples for infection monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].

Figure 4
9. Attach the infusion set with 0.2 micron inline filter to the port needle (see Figure 1).
- Secure the components per institution standard of care.
10. Place the syringe containing Brineura into the syringe pump and program pump to deliver at an infusion rate of 2.5 mL per hour. Set the occlusion alarm setting to alert at pressure ≤ 281 mm Hg. See syringe pump operating manual for details. Do not deliver as a bolus or manually.
11. Administer pre-medication 30 to 60 minutes prior to the start of infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
12. Monitor vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate) prior to the start of infusion, periodically during infusion, and post-infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
13. Initiate infusion of Brineura at a rate of 2.5 mL per hour.
14. Periodically inspect the infusion system during the infusion for signs of leakage or delivery failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
15. When the Brineura infusion is complete, detach and remove the empty syringe from the pump and disconnect from the tubing (see Figure 5). Proceed to Step 16 for Intraventricular Electrolytes infusion.
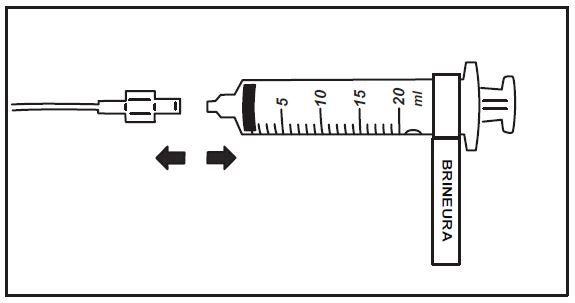
Figure 5
Intraventricular Infusion of Intraventricular Electrolytes
Administer the Intraventricular Electrolytes provided after Brineura infusion is complete.
16. Use aseptic technique when preparing the Intraventricular Electrolytes syringe for infusion. Label one sterile syringe “Intraventricular Electrolytes” and attach the syringe needle. Remove the yellow flip-off cap from the Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection vial. Withdraw 2 mL of Intraventricular Electrolytes. Discard the remaining unused portion.
17. Attach the syringe to the extension line (see Figure 6).
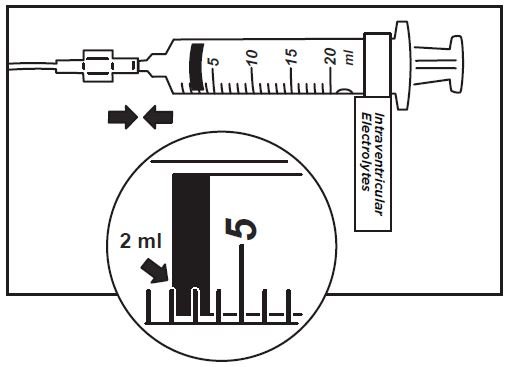
Figure 6
18. Place the syringe containing Intraventricular Electrolytes into the syringe pump and program pump to deliver at an infusion rate of 2.5 mL per hour. Set the occlusion alarm setting to alert at pressure ≤ 281 mm Hg. See syringe pump operating manual for details. Do not deliver as a bolus or manually.
19. Initiate infusion of Intraventricular Electrolytes at a rate of 2.5 mL per hour.
20. Periodically inspect the infusion system during the infusion for signs of leakage or delivery failure.
21. When the Intraventricular Electrolytes infusion is complete, detach and remove the empty syringe from the pump and disconnect from the infusion line.
22. Remove the port needle. Apply gentle pressure and bandage the infusion site per institution standard of care.
Dispose of the infusion components, needles, unused solutions and other waste materials in accordance with local requirements.
Storage of Thawed Product
Use thawed Brineura and Intraventricular Electrolytes immediately. If not used immediately, store unopened vials in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C and use within 24 hours.
Storage of Product in Syringes
Use product held in labeled syringes immediately. If not used immediately, store product held in labeled syringes in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C up to 4 hours prior to infusion.
The following adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
-
Meningitis and Other Intraventricular Access Device-Related Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
Intraventricular Access Device-Related Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
-
Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
-
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of Brineura was evaluated in 24 patients with CLN2 disease who received at least one dose of Brineura in a clinical study with extension of up to 161 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Table 1 summarizes the most common adverse reactions that occurred in Brineura-treated patients through 96 weeks.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥ 8% of Symptomatic Pediatric Patients with CLN2 Disease in the Brineura Single-Arm Clinical Study with Extension at Week 96
| Adverse Reaction |
Patients Treated with Brineura n=24 (%) |
| Pyrexia1 | 17 (71) |
| ECG abnormalities2 | 17 (71) |
| Decreased CSF protein | 17 (71) |
| Vomiting | 15 (63) |
| Seizures3 | 12 (50) |
| Device-related complications4 | 12 (50) |
| Hypersensitvity5 | 11 (46) |
| Increased CSF protein | 5 (21) |
| Hematoma | 5 (21) |
| Headache | 4 (17) |
| Irritability | 4 (17) |
| Pleocytosis | 4 (17) |
| Device-related infection6 | 2 (8) |
| Bradycardia | 2 (8) |
| Feeling jittery | 2 (8) |
| Hypotension | 2 (8) |
1Pyrexia includes: pyrexia and increased body temperature
2ECG abnormalities include: non-specific repolarization abnormality, notched QRS, ST segment elevation, biphasic T wave abnormality, supraventricular extrasystoles, bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, and intraventricular conduction delay
3Seizures include: atonic, generalized tonic-clonic, focal, and absence
4Device-related complications include device-related infection, delivery system-related complications (needle issues, device leakage, device malfunction, device difficult to use, etc.) and pleocytosis.
5Hypersensitivity includes: immune reactions and signs and symptoms observed concomitantly with hypersensitivity reactions including pyrexia, vomiting, pleocytosis or irritability [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6Device-related infections include:Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis
Description of Selected Adverse Reactions
Seizures
Seizures were reported in 12 of 24 (50%) patients. The seizure types reported include atonic, generalized tonic-clonic, focal, and absence. Seizures were managed with standard anti-convulsive therapies and did not result in discontinuation of Brineura treatment.
Device-Related Complications
Adverse reactions related to the device were observed in 12 of 24 (50%) of patients. Device-related adverse reactions include infection, delivery system-related complications, and pleocytosis. Nine out of 24 patients (38%) experienced adverse reactions, which involved complications of the non-implanted delivery system components. Four out of 24 patients (16%) had device-related adverse reactions, which required medical intervention, including two patients (8%) with intraventricular access device-related CNS infections, and one patient (4%) each with leakage of the intraventricular access device and pleocytosis. Device-related infections were diagnosed by increased CSF pleocytosis and microbiology culture and organism identification, without accompanying signs and symptoms of meningitis. Intraventricular access devices were replaced and infections were treated with antibiotics. Device-related complications did not result in discontinuation of Brineura treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
Hematoma
Hematoma adverse reactions were reported in 5 (21%) patients treated with Brineura and presented as hematoma, post procedural hematoma, traumatic hematoma and subdural hematoma. Hematomas did not require treatment and did not interfere with Brineura infusion.
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity reactions were reported in 11 out of 24 patients (46%) treated with Brineura during or within 24 hours after completion of the Brineura infusion, despite pre-medication with antihistamines with or without antipyretics or corticosteroids [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. The most common manifestations observed concomitantly with hypersensitivity included pyrexia with vomiting, pleocytosis, or irritability, which are not consistent with classic immune mediated hypersensitivity. Symptoms resolved over time or with administration of antipyretics, antihistamines and/or corticosteroids and no patient discontinued treatment with Brineura.
One patient experienced hypoxia (decreased oxygen saturation less than 88% by pulse oximeter), 8 hours after Brineura infusion, followed by a low mean arterial pressure at 15 hours post infusion. Symptoms resolved after oxygen administration, airway repositioning and normal saline infusion. One patient reported decreased oxygen saturation (90% by pulse oximeter), 45 minutes after starting Brineura with associated low diastolic blood pressures. Hypoxia resolved after oxygen administration. No treatment was administered for the low diastolic blood pressure, which returned to normal while the patient continued to receive Brineura infusion without change to the infusion rate or dose.
Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to cerliponase alfa in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
Anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) to cerliponase alfa were detected in both serum and CSF in 79% and 33%, respectively, of patients treated with Brineura for up to 161 weeks. Patients who experienced hypersensitivity adverse reactions were tested for drug-specific IgE and found to be negative, including three patients for whom grade 3 (severe) hypersensitivity adverse reactions were reported. No association was found between serum or CSF ADA titers and incidence or severity of hypersensitivity. Drug-specific neutralizing antibodies (NAb) have not been evaluated.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Brineura. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Infections and infestations: Bacterial meningitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Immune system disorders: Anaphylactic reaction characterized by acute pyrexia, respiratory distress (bronchospasm, hypoxemia, perioral cyanosis), tachycardia, hypotension, diarrhea, and rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].




