Generic Name: HUMAN IMMUNOGLOBULIN G 100mg in 1mL
Dosage Form: injection, solution
Drug Class: Immune globulins
Dosage
|
Dose |
Initial Infusion rate |
Maintenance Infusion rate |
|
Intravenous Administration |
||
|
Primary Immunodeficiency |
||
|
300 to 600 milligram/kg every 3 to 4 weeks based on clinical response |
0.5 mL/kg/hr (0.8 milligram/kg/min) for 30 minutes |
Increase every 30 minutes |
|
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy |
||
|
Dose range 0.5 to 2.4 grams/kg/month based on clinical response (14) |
0.5 mL/kg/hr (0.8 milligram/kg/min) |
Infusion rate may be increased if tolerated up to 5.4 mL/kg/hr |
|
Subcutaneous Administration: |
||
|
Primary Immunodeficiency |
||
|
Initial Dose is 1.37 × previous intravenous dose divided by # of weeks between intravenous doses. Maintenance dose is based on clinical response and target IgG trough level (2.2). |
40 kg BW and greater: 30 mL/site at 20 mL/hr/site. Under 40 kg BW: |
40 kg BW and greater: Under 40 kg BW: |
Dose Adjustments for Intravenous Administration in Patients with PI
Adjust dose according to IgG levels and clinical response, as the frequency and dose of immune globulin may vary from patient to patient.
No randomized controlled clinical studies are available to determine an optimum trough serum IgG level for intravenous treatment. If a patient misses a dose, administer the missed dose as soon as possible, and then resume scheduled treatments every 3 or 4 weeks, as applicable.
Prior to switching from intravenous to subcutaneous treatment, obtain the patient's serum IgG trough level to guide subsequent dose adjustments. Start the initial subcutaneous dose approximately one week after the last intravenous infusion.
Dose Adjustments for Intravenous Administration in MMN
The dose may need to be adjusted to achieve the desired clinical response. In the clinical study, the dose ranged between 0.5 to 2.4 grams/kg/month (See Table 1). While receiving GAMMAGARD LIQUID, 9% of subjects in the clinical study experienced neurological decompensation that required an increase in dose. In order to avoid worsening of muscle weakness in patients, dose adjustment may be necessary.
Dose Adjustments for Subcutaneous Administration for PI only
Based on the results of clinical studies, the expected increase in serum IgG trough level during weekly subcutaneous treatment at the dose adjusted to provide a comparable AUC, is approximately 281 milligram/dL higher than the last trough level during prior stable intravenous treatment. To calculate the target trough IgG level for subcutaneous treatment, add 281 milligram/dL to the IgG trough level obtained after the last intravenous treatment.
To guide dose adjustment, calculate the difference between the patient's target serum IgG trough level and the IgG trough level during subcutaneous treatment. Find this difference in the columns of Table 2 and the corresponding amount (in mL) by which to increase (or decrease) the weekly dose based on the patient's body weight. If the difference between measured and target trough levels is less than 100 milligram/dL then no adjustment is necessary. However, the patient's clinical response should be the primary consideration in dose adjustment.
|
||||
|
Difference between Measured and Target IgG Trough Levels |
||||
|
Body Weight |
100 mg/dL |
200 mg/dL |
300 mg/dL |
400 mg/dL |
|
10 kg |
2 mL |
4 mL |
6 mL |
8 mL |
|
20 kg |
4 mL |
8 mL |
11 mL |
15 mL |
|
30 kg |
6 mL |
11 mL |
17 mL |
23 mL |
|
40 kg |
8 mL |
15 mL |
23 mL |
30 mL |
|
50 kg |
9 mL |
19 mL |
28 mL |
38 mL |
|
60 kg |
11 mL |
23 mL |
34 mL |
45 mL |
|
70 kg |
13 mL |
26 mL |
40 mL |
53 mL |
|
80 kg |
15 mL |
30 mL |
45 mL |
60 mL |
|
90 kg |
17 mL |
34 mL |
51 mL |
68 mL |
|
100 kg |
19 mL |
38 mL |
57 mL |
75 mL |
|
110 kg |
21 mL |
42 mL |
62 mL |
83 mL |
|
120 kg |
23 mL |
45 mL |
68 mL |
91 mL |
|
130 kg |
25 mL |
49 mL |
74 mL |
98 mL |
|
140 kg |
26 mL |
53 mL |
79 mL |
106 mL |
Example 1: A patient with a body weight of 80 kg has a measured IgG trough level of 800 milligram/dL and the target trough level is 1000 milligram/dL. The desired target trough level difference is 200 milligram/dL (1000 milligram/dL minus 800 milligram/dL). The weekly dose of GAMMAGARD LIQUID should be increased by 30 mL (3.0 gm).
Example 2: A patient with a body weight of 60 kg has a measured IgG trough of 1000 milligram/dL and the target trough level is 800 milligram/dL. The desired target trough level difference is 200 milligram/dL (800 milligram/dL minus 1000 milligram/dL). The weekly dose of GAMMAGARD LIQUID should be decreased by 23 mL (2.3 gm).
Dose Adjustments for Measles Exposure
If a patient has been exposed to measles, it may be prudent to administer an extra dose of GAMMAGARD LIQUID as soon as possible and within 6 days of exposure. A dose of 400 mg/kg should provide a serum level > 240 mIU/mL of measles antibodies for at least two weeks.
If a patient is at risk of future measles exposure and receives a dose of less than 530 mg/kg every 3-4 weeks, the dose should be increased to at least 530 mg/kg. This should provide a serum level of 240 mIU/mL of measles antibodies for at least 22 days after infusion.
Preparation and Handling
- ▪
- Inspect the drug product visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. GAMMAGARD LIQUID is a clear or slightly opalescent, colorless or pale yellow solution. Do not use if the solution is cloudy, turbid, or if it contains particulates.
- ▪
- GAMMAGARD LIQUID vial is for single use only. Any vial that has been entered should be used promptly. Partially used vials should be discarded. GAMMAGARD LIQUID contains no preservative.
- ▪
- Allow refrigerated product to come to room temperature before use. DO NOT MICROWAVE.
- ▪
- Do not shake.
- ▪
- Do not mix with other products.
- ▪
- Do not use normal saline as a diluent. If dilution is desired, 5% dextrose in water (D5W) should be used as a diluent.
- ▪
- The infusion line may be flushed with normal saline. An in-line filter is optional.
- ▪
- Record the name and lot number of the product in the recipient's records.
Administration
Intravenous
|
PI |
MMN |
|
|
Initial |
0.5 mL/kg/hr (0.8 milligram/kg/min) for 30 minutes |
Increasing rates of infusion starting at 0.5mL/kg/h (0.8 milligram/kg/min) |
|
Subsequent |
Increase every 30 minutes |
Increasing to a maximum rate of 5.4 mL/kg/hr if tolerated (9 milligram/kg/min) |
Monitor patient vital signs throughout the infusion. Certain adverse reactions such as headaches, flushing, and changes in pulse rate and blood pressure may be related to the rate of infusion. Slow or stop infusion if adverse reactions occur. If symptoms subside promptly, the infusion may be resumed at a lower rate that does not result in recurrence of the symptoms.
Adverse reactions may occur more frequently in patients receiving immune globulin for the first time, upon switching brands or if there has been a long interval since the previous infusion.2 In such cases, start at lower infusion rates and gradually increase as tolerated.
Ensure that patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency are not volume depleted. For patients over 65 years of age or judged to be at risk for renal dysfunction or thrombotic events, administer GAMMAGARD LIQUID at the minimum infusion rate practicable. In such cases, the maximal rate should be less than 3.3 milligram/kg/min (<2mL/kg/hr); consider discontinuation of administration if renal function deteriorates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4) and Use In Specific Populations (8.5)].
Subcutaneous for PI
|
40 kg BW and greater |
Under 40 kg BW |
|
|
Initial |
30 mL/site at a rate of 20 mL/hr/site |
20 mL/site at a rate of 15 mL/hr/site |
|
Maintenance |
30 mL/site at a rate of 20 to 30 mL/hr/site |
20 mL/site at a rate of 15 to 20 mL/hr/site |
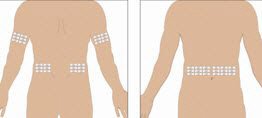
Selection of Infusion Site: Suggested areas for subcutaneous infusion of GAMMAGARD LIQUID are abdomen, thighs, upper arms, or lower back. Infusion sites should be at least two inches apart, avoiding bony prominences. Rotate sites each week.
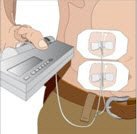
Volume per Site: The weekly dose (mL) should be divided by 30 or 20, based on patient weight above, to determine the number of sites required. Simultaneous subcutaneous infusion at multiple sites can be facilitated by use of a multi-needle administration set.
Rate of Infusion for Patients 40 kg and greater (88 lbs): If multiple sites are used, the rate set on the pump should be the rate per site multiplied by the number of sites (e.g., 30 mL x 4 sites = 120 mL/hr). The number of simultaneous sites should be limited to 8, or maximum infusion rate of 240 mL/hr.
Rate of Infusion for Patients under 40 kg (88 lbs): If multiple sites are used, the rate set on the pump should be the rate per site multiplied by the number of sites (e.g., 20 mL x 3 sites = 60 mL/hr). The number of simultaneous sites should be limited to 8, or maximum infusion rate of 160 mL/hr.
Instructions for Subcutaneous Administration: Instruct patients to observe the following procedures:
- 1.
- Aseptic technique - Use aseptic technique when preparing and infusing GAMMAGARD LIQUID.
- 2.
- Assemble supplies - Set up a clean work area and gather all supplies necessary for the subcutaneous infusion: vial(s) of GAMMAGARD LIQUID, ancillary supplies, sharps container and pump. If GAMMAGARD LIQUID has already been pooled into a bag or a syringe, skip to Step 5.
- 3.
- Product preparation - Remove the protective cap from the vial to expose the center of the vial. Wipe the stopper with an alcohol pad and allow to dry.
- 4.
- Withdraw GAMMAGARD LIQUID from the vials - Attach a sterile syringe to a needle and draw air into the syringe barrel equal to the amount of product to be withdrawn. Inject the air into the vial and withdraw the desired volume of GAMMAGARD LIQUID. If multiple vials are required to achieve the desired dose, repeat this step.
- 5.
- Prepare the infusion pump and tubing - Follow the manufacturer's instructions for preparing the pump and administration tubing, if needed. Be sure to prime the pump tubing to ensure that no air is left in the tubing and needle.
- 6.
- Select the infusion sites - Select the number of infusion sites depending on the volume of the total dose. [See Dosage and Administration (2.3)] for recommended maximum volumes and rates. Potential sites for infusion include the back of arms, abdomen, thighs, and lower back (see Figure below). Ensure sites are at least 2 inches apart; avoid bony prominences.
- 7.
- Cleanse the infusion site(s) - Cleanse the infusion site(s) with an antiseptic skin preparation (e.g., alcohol pad) using a circular motion working from the center of the site and moving to the outside. Allow to dry.
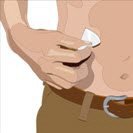
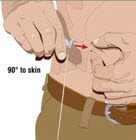
- 8.
- Insert the needle - Choose the correct needle length to assure that GAMMAGARD LIQUID is delivered into the subcutaneous space. Grasp the skin and pinch at least one inch of skin between two fingers. Insert needle at a 90-degree angle with a darting motion into the subcutaneous tissue. Secure the needle.
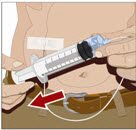
- 9.
- Check for proper needle placement - Prior to the start of infusion, check each needle for correct placement to make sure that a blood vessel has not been punctured. Gently pull back on the attached syringe plunger and monitor for any blood return in the needle set. If you see any blood, remove and discard the needle set. Repeat priming and needle insertion steps in a different infusion site with a new needle set.
- 10.
- Secure the needle to the skin - Secure the needle(s) in place by applying a sterile protective dressing over the site.
- 11.
- Start infusion of GAMMAGARD LIQUID - Follow the manufacturer's instructions to turn pump on.
- 12.
- Document the infusion - Remove the peel-off label with product lot number and expiration date from the GAMMAGARD LIQUID vial and place in treatment diary/log book to keep track of the product lots used. Keep the treatment diary/log book current by recording the time, date, dose, product label and any reactions after each infusion.
- 13.
- Remove needle set - After the infusion is complete, remove the needle set and gently press a small piece of gauze over the needle insertion site and cover with a protective dressing. Discard any unused solution and disposable supplies in accordance with local requirements,