Drug Detail:Arikayce (Amikacin liposome [ am-i-kay-sin ])
Drug Class: Aminoglycosides
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ARIKAYCE® (amikacin liposome inhalation suspension), for oral inhalation use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
LIMITED POPULATION
WARNING: RISK OF INCREASED RESPIRATORY ADVERSE REACTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
ARIKAYCE has been associated with a risk of increased respiratory adverse reactions, including, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, hemoptysis, bronchospasm, and exacerbation of underlying pulmonary disease that have led to hospitalizations in some cases. (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4)
Recent Major Changes
| Warnings and Precautions, Ototoxicity (5.6) | 2/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Arikayce
LIMITED POPULATION: ARIKAYCE is an aminoglycoside antibacterial indicated in adults who have limited or no alternative treatment options, for the treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) lung disease as part of a combination antibacterial drug regimen in patients who do not achieve negative sputum cultures after a minimum of 6 consecutive months of a multidrug background regimen therapy. As only limited clinical safety and effectiveness data for ARIKAYCE are currently available, reserve ARIKAYCE for use in adults who have limited or no alternative treatment options. This drug is indicated for use in a limited and specific population of patients. (1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on achieving sputum culture conversion (defined as 3 consecutive negative monthly sputum cultures) by Month 6. Clinical benefit has not yet been established. (1)
Limitation of Use:
ARIKAYCE has only been studied in patients with refractory MAC lung disease defined as patients who did not achieve negative sputum cultures after a minimum of 6 consecutive months of a multidrug background regimen therapy. The use of ARIKAYCE is not recommended for patients with non-refractory MAC lung disease.
Arikayce Dosage and Administration
- For oral inhalation use only. (2.1)
- Use ARIKAYCE vials only with the Lamira Nebulizer System. (2.1)
- Pre-treatment with inhaled bronchodilator should be considered in patients with a history of hyperreactive airway disease. (2.1)
- The recommended dosage in adults is once daily oral inhalation of the contents of one 590 mg/8.4 mL ARIKAYCE vial. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
ARIKAYCE is supplied as a sterile, aqueous, liposome suspension for oral inhalation in a unit-dose glass vial containing amikacin 590 mg/8.4 mL. (3)
Contraindications
ARIKAYCE is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to any aminoglycoside. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Reported with ARIKAYCE treatment; if hypersensitivity pneumonitis occurs, discontinue ARIKAYCE and manage patients as medically appropriate. (5.1)
- Hemoptysis: Higher frequency of hemoptysis has been reported with ARIKAYCE treatment. If hemoptysis occurs, manage the patients as medically appropriate. (5.2)
- Bronchospasm: Higher frequency of bronchospasm has been reported with ARIKAYCE treatment. Treat patients as medically appropriate if this occurs during treatment with ARIKAYCE. (5.3)
- Exacerbations of Underlying Pulmonary Disease: Higher frequency of exacerbations of underlying pulmonary disease has been reported with ARIKAYCE treatment. Treat patients as medically appropriate if this occurs during treatment with ARIKAYCE. (5.4)
- Anaphylaxis and Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious and potentially life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in patients taking ARIKAYCE. If anaphylaxis or a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue ARIKAYCE and institute appropriate supportive measures. (5.5)
- Ototoxicity: Higher frequency of ototoxicity has been reported with ARIKAYCE treatment. Closely monitor patients with known or suspected auditory or vestibular dysfunction. If patients develop tinnitus this may be an early symptom of ototoxicity. (5.6)
- Nephrotoxicity: Nephrotoxicity was observed during the clinical trials of ARIKAYCE in patients with MAC lung disease but not at a higher frequency than the background regimen alone. Aminoglycosides have been associated with nephrotoxicity. Close monitoring of patients with known or suspected renal dysfunction may be needed when prescribing ARIKAYCE. (5.7)
- Neuromuscular Blockade: Aminoglycosides may aggravate muscle weakness by blocking the release of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions. Closely monitor patients with known or suspected neuromuscular disorders, such as myasthenia gravis. If neuromuscular blockade occurs, it may be reversed by the administration of calcium salts but mechanical respiratory assistance may be necessary. (5.8)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Aminoglycosides can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Aminoglycosides, including ARIKAYCE, may be associated with total, irreversible, bilateral congenital deafness in pediatric patients exposed in utero. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. (5.9, 8.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥10% and higher than control) in the patients with refractory MAC lung disease were: dysphonia, cough, bronchospasm, hemoptysis, musculoskeletal pain, upper airway irritation, ototoxicity, fatigue/asthenia, exacerbation of underlying pulmonary disease, diarrhea, nausea, and headache. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Insmed Incorporated at 1-844-4-INSMED or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 2/2023
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISK OF INCREASED RESPIRATORY ADVERSE REACTIONS
ARIKAYCE has been associated with an increased risk of respiratory adverse reactions including, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, hemoptysis, bronchospasm, exacerbation of underlying pulmonary disease that have led to hospitalizations in some cases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4)].
1. Indications and Usage for Arikayce
LIMITED POPULATION: ARIKAYCE® is indicated in adults, who have limited or no alternative treatment options, for the treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) lung disease as part of a combination antibacterial drug regimen in patients who do not achieve negative sputum cultures after a minimum of 6 consecutive months of a multidrug background regimen therapy. As only limited clinical safety and effectiveness data for ARIKAYCE are currently available, reserve ARIKAYCE for use in adults who have limited or no alternative treatment options. This drug is indicated for use in a limited and specific population of patients.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on achieving sputum culture conversion (defined as 3 consecutive negative monthly sputum cultures) by Month 6. Clinical benefit has not yet been established [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
2. Arikayce Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
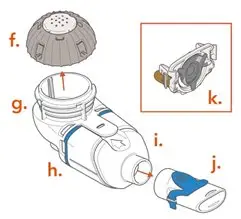
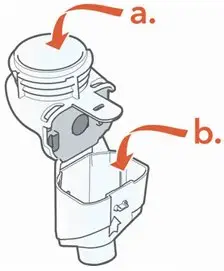
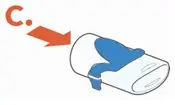
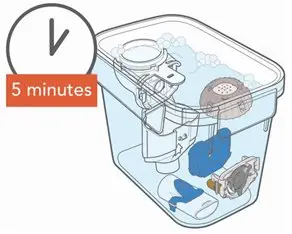
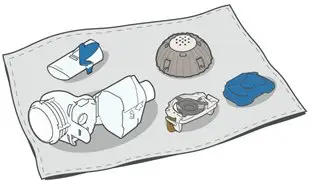
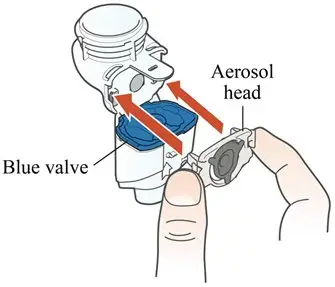
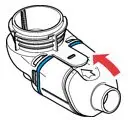
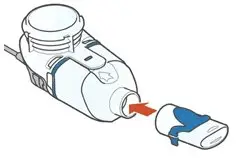
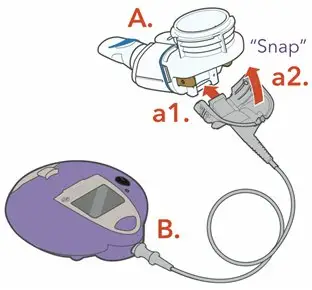
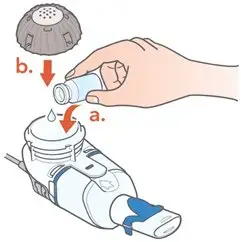
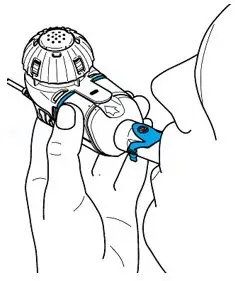
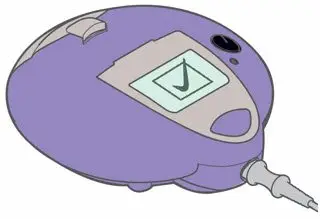
ARIKAYCE is for oral inhalation use only. Administer by nebulization only with the Lamira® Nebulizer System. Refer to the Instructions for Use for full administration information on use of ARIKAYCE with the Lamira Nebulizer System.
Instruct patients using a bronchodilator (‘reliever’) to first use the bronchodilator following the bronchodilator leaflet for use information before using ARIKAYCE.
Pre-treatment with short-acting selective beta-2 agonists should be considered for patients with known hyperreactive airway disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, or bronchospasm [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of ARIKAYCE in adults is once daily inhalation of the contents of one 590 mg/8.4 mL ARIKAYCE vial (590 mg of amikacin) using the Lamira Nebulizer System [see Clinical Studies (14)].
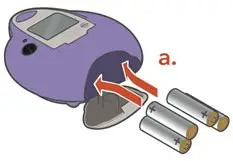
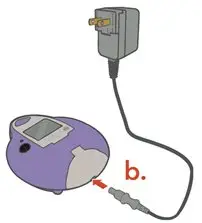
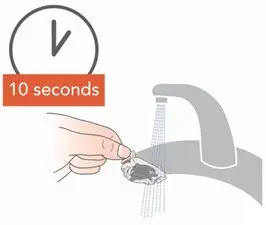
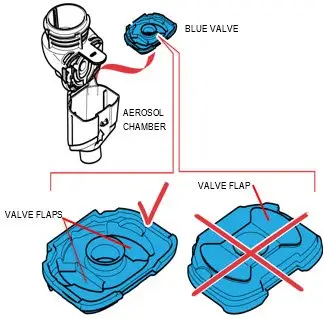
Administer ARIKAYCE with the Lamira Nebulizer System only. ARIKAYCE should be at room temperature before use. Prior to opening, shake the ARIKAYCE vial well for at least 10 to 15 seconds until the contents appear uniform and well mixed. The ARIKAYCE vial is opened by flipping up the plastic top of the vial then pulling downward to loosen the metal ring. The metal ring and the rubber stopper should be removed carefully. The contents of the ARIKAYCE vial can then be poured into the medication reservoir of the nebulizer handset.
If a daily dose of ARIKAYCE is missed, administer the next dose the next day. Do NOT double the dose to make up for the missed dose.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
ARIKAYCE is supplied as a sterile, white, milky, aqueous, liposome suspension for oral inhalation in a unit-dose glass vial containing amikacin 590 mg/8.4 mL (equivalent to amikacin sulfate 623 mg/8.4 mL).
4. Contraindications
ARIKAYCE is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to any aminoglycoside.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis has been reported with the use of ARIKAYCE in the clinical trials. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (reported as allergic alveolitis, pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease, allergic reaction to ARIKAYCE) was reported at a higher frequency in patients treated with ARIKAYCE plus a background regimen (3.1%) compared to patients treated with a background regimen alone (0%). Most patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis discontinued treatment with ARIKAYCE and received treatment with corticosteroids [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
If hypersensitivity pneumonitis occurs, discontinue ARIKAYCE and manage the patient as medically appropriate.
5.2 Hemoptysis
Hemoptysis has been reported with the use of ARIKAYCE in the clinical trials. Hemoptysis was reported at a higher frequency in patients treated with ARIKAYCE plus a background regimen (18.4%) compared to patients treated with a background regimen alone (13.4%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. If hemoptysis occurs, manage the patients as medically appropriate.
5.3 Bronchospasm
Bronchospasm has been reported with the use of ARIKAYCE in the clinical trials. Bronchospasm (reported as asthma, bronchial hyperreactivity, bronchospasm, dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, prolonged expiration, throat tightness, wheezing) was reported at a higher frequency in patients treated with ARIKAYCE plus a background regimen (28.7%) compared to patients treated with a background regimen alone (10.7%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. If bronchospasm occurs during the use of ARIKAYCE, treat the patients as medically appropriate.
5.4 Exacerbation of Underlying Pulmonary Disease
Exacerbations of underlying pulmonary disease have been reported with the use of ARIKAYCE in the clinical trials. Exacerbations of underlying pulmonary disease (reported as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, infective exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, infective exacerbation of bronchiectasis) have been reported at a higher frequency in patients treated with ARIKAYCE plus a background regimen (15.2%) compared to patients treated with background regimen alone (9.8%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. If exacerbations of underlying pulmonary disease occur during the use of ARIKAYCE, treat the patients as medically appropriate.
5.5 Anaphylaxis and Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious and potentially life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in patients taking ARIKAYCE. Signs and symptoms include acute onset of skin and mucosal tissue hypersensitivity reactions (hives, itching, flushing, swollen lips/tongue/uvula), respiratory difficulty (shortness of breath, wheezing, stridor, cough), gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, crampy abdominal pain), and cardiovascular signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis (tachycardia, low blood pressure, syncope, incontinence, dizziness). Before therapy with ARIKAYCE is instituted, evaluate for previous hypersensitivity reactions to aminoglycosides. If anaphylaxis or a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue ARIKAYCE and institute appropriate supportive measures.
5.7 Nephrotoxicity
Nephrotoxicity was observed during the clinical trials of ARIKAYCE in patients with MAC lung disease but not at a higher frequency than the background regimen alone [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Nephrotoxicity has been associated with the aminoglycosides. Close monitoring of patients with known or suspected renal dysfunction may be needed when prescribing ARIKAYCE.
5.8 Neuromuscular Blockade
Patients with neuromuscular disorders were not enrolled in ARIKAYCE clinical trials. Aminoglycosides may aggravate muscle weakness by blocking the release of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions. Closely monitor patients with known or suspected neuromuscular disorders, such as myasthenia gravis. If neuromuscular blockade occurs, it may be reversed by the administration of calcium salts but mechanical respiratory assistance may be necessary.
5.9 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Aminoglycosides can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Aminoglycosides, including ARIKAYCE, may be associated with total, irreversible, bilateral congenital deafness in pediatric patients exposed in utero. Patients who use ARIKAYCE during pregnancy, or become pregnant while taking ARIKAYCE should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described in greater detail in other sections of labeling:
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hemoptysis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Bronchospasm [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Exacerbation of Underlying Pulmonary Disease [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Anaphylaxis and Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Ototoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Nephrotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Neuromuscular Blockade [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Common Adverse Reactions
The incidence of adverse reactions in Trial 1 are displayed in Table 1. Only those adverse reactions with a rate of at least 5% in the ARIKAYCE plus background regimen group and greater than the background regimen alone group, are shown.
| Adverse Reaction | ARIKAYCE plus Background Regimen | Background Regimen Alone |
|---|---|---|
| (N=223) n (%) | (N=112) n (%) |
|
|
||
| Dysphonia* | 106 (48) | 2 (2) |
| Cough† | 88 (40) | 19 (17) |
| Bronchospasm‡ | 64 (29) | 12 (11) |
| Hemoptysis | 41 (18) | 15 (13) |
| Musculoskeletal pain§ | 40 (18) | 10 (9) |
| Upper airway irritation¶ | 39 (18) | 2 (2) |
| Ototoxicity# | 38 (17) | 11 (10) |
| Fatigue and asthenia | 36 (16) | 11 (10) |
| Exacerbation of underlying pulmonary diseaseÞ | 34 (15) | 11 (10) |
| Diarrhea | 28 (13) | 5 (5) |
| Nausea | 26 (12) | 4 (4) |
| Headache | 22 (10) | 5 (5) |
| Pneumoniaß | 20 (9) | 10 (9) |
| Pyrexia | 17 (8) | 5 (5) |
| Weight decreased | 16 (7) | 1 (1) |
| Vomitingà | 15 (7) | 4 (4) |
| Rashè | 14 (6) | 1 (1) |
| Change in sputumð | 13 (6) | 1 (1) |
| Chest discomfort | 12 (5) | 3 (3) |
Selected adverse drug reactions that occurred in <5% of patients and at higher frequency in ARIKAYCE-treated patients in Trial 1 are presented in Table 2.
| Adverse Reaction | ARIKAYCE plus Background Regimen N=223 n (%) | Background Regimen Alone N=112 n (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Anxiety* | 10 (5) | 0 (0) |
| Oral fungal infection† | 9 (4) | 2 (2) |
| Bronchitis | 8 (4) | 3 (3) |
| Dysgeusia | 7 (3) | 0 (0) |
| Hypersensitivity pneumonitis‡ | 7 (3) | 0 (0) |
| Dry mouth | 6 (3) | 0 (0) |
| Epistaxis | 6 (3) | 1 (1) |
| Respiratory failure§ | 6 (3) | 2 (2) |
| Pneumothorax¶ | 5 (2) | 1 (1) |
| Exercise tolerance decreased | 3 (1) | 0 (0) |
| Balance disorder | 3 (1) | 0 (0) |
| Neuromuscular disorder# | 2 (1) | 0 (0) |
Refer to Table 1 and Table 2 for the incidence rate of hypersensitivity pneumonitis, bronchospasm, cough, dysphonia, exacerbation of underlying disease, hemoptysis, ototoxicity, upper airway irritation, and neuromuscular disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.6, 5.7)].
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified from postmarketing surveillance. Because these adverse reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, precise estimates of frequency cannot be made and a causal relationship to drug exposure cannot be established.
Immune System Disorders: hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
7. Drug Interactions
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ARIKAYCE in pediatric patients below 18 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the NTM clinical trials, of the total number of patients receiving ARIKAYCE, 208 (51.5%) were ≥ 65 years and 59 (14.6%) were ≥ 75 years. No overall differences in safety and effectiveness were observed between elderly subjects and younger subjects. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
ARIKAYCE has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment. No dose adjustments based on hepatic impairment are required since amikacin is not hepatically metabolized [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
ARIKAYCE has not been studied in patients with renal impairment. Given the low systemic exposure to amikacin following administration of ARIKAYCE, clinically relevant accumulation of amikacin is unlikely to occur in patients with renal impairment. However, renal function should be monitored in patients with known or suspected renal impairment, including elderly patients with potential age-related decreases in renal function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
10. Overdosage
Adverse reactions specifically associated with overdose of ARIKAYCE have not been identified. Acute toxicity should be treated with immediate withdrawal of ARIKAYCE, and baseline tests of renal function should be undertaken.
Hemodialysis may be helpful in removing amikacin from the body.
In all cases of suspected overdosage, physicians should contact the Regional Poison Control Center for information about effective treatment. In the case of any overdosage, the possibility of drug interactions with alterations in drug disposition should be considered.
11. Arikayce Description
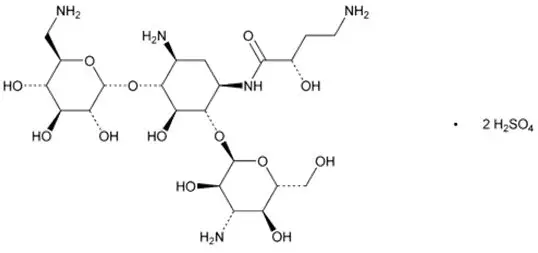
The active ingredient in ARIKAYCE (amikacin liposome inhalation suspension) is amikacin sulfate USP, an aminoglycoside antibacterial. Its chemical name is D-Streptamine, O-3-amino-3-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-[6-amino-6-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-N1-(4-amino-2-hydroxy-1-oxobutyl)-2-deoxy-, (S)-, sulfate (1:2) salt with a chemical formula of C22H43N5O13∙2H2SO4 with a molecular weight of 781.76. Its structural formula is:
ARIKAYCE is a white milky suspension consisting of amikacin sulfate encapsulated in liposomes and is supplied in a unit-dose 10 mL clear glass vial containing amikacin 590 mg/8.4 mL (equivalent to amikacin sulfate 623 mg/8.4 mL) as a sterile aqueous liposomal suspension for oral inhalation. ARIKAYCE consists of amikacin sulfate encapsulated in liposomes at a targeted concentration of 70 mg amikacin/mL with the pH range of 6.1 to 7.1 and lipid to amikacin weight ratio in the range of 0.60 to 0.79. The inactive ingredients are cholesterol, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), and water for injection.
ARIKAYCE is administered only using a Lamira Nebulizer System [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Like all other nebulized treatments, the amount delivered to the lungs will depend upon patient factors. Under standardized in vitro testing per USP<1601> adult breathing pattern (500 mL tidal volume, 15 breaths per minute, and inhalation: exhalation ratio of 1:1), the mean delivered dose from the mouthpiece was approximately 312 mg of amikacin sulfate (53% of label claim). The mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) of the nebulized aerosol droplets is about 4.7 µm (4.1 – 5.3 µm) as determined using the Next Generation Impactor (NGI) method. A percentage of the amikacin in the liposome is released by the nebulization process, thus nebulized ARIKAYCE delivers a combination of free and liposomal amikacin.
12. Arikayce - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
ARIKAYCE exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year inhalation carcinogenicity study, rats were exposed to ARIKAYCE for 15-25, 50-70, or 155-170 minutes per day for 96-104 weeks. These provided approximate inhaled doses of 5, 15, and 45 mg/kg/day. Squamous cell carcinoma was observed in the lungs of 2 of 120 rats administered the highest dose tested. Maximum serum AUC levels of amikacin in the rats at steady state were approximately 1.3, 2.8, and 7.6 mcg∙hr/mL at the low, mid, and high doses, respectively, compared with 23.5 mcg∙hr/mL (8.0 to 46.5 mcg∙hr/mL) measured in humans. The squamous cell carcinomas may be the result of a high lung burden of particulates from ARIKAYCE in the rat lung. The relevance of the lung tumor findings with regards to humans receiving ARIKAYCE is unknown.
No evidence of mutagenicity or genotoxicity was observed in a battery of in vitro and in vivo genotoxicity studies with a liposome-encapsulated amikacin formulation similar to ARIKAYCE (in vitro microbial mutagenesis test, in vitro mouse lymphoma mutation assay, in vitro chromosomal aberration study, and an in vivo micronucleus study in rats).
No fertility studies were conducted with ARIKAYCE. Intraperitoneal administration of amikacin to male and female rats at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day prior to mating through Day 7 of gestation were not associated with impairment of fertility or adverse effects on early embryonic development.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
To provide information about chronic dosing of ARIKAYCE to another animal species, a 9-month inhalation toxicology study was conducted in dogs. Foamy alveolar macrophages associated with clearance of the inhaled product were present at dose-related incidence and severity, but they were not associated with inflammation, tissue hyperplasia, or the presence of preneoplastic or neoplastic changes. Dogs were exposed to ARIKAYCE for up to 90 minutes per day, providing inhaled amikacin doses of approximately 5, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day.
14. Clinical Studies
Trial 1 (NCT#02344004) was an open-label, randomized (2:1), multi-center trial in patients with refractory Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) lung disease as confirmed by at least 2 sputum culture results. Patients were considered to have refractory MAC lung disease if they did not achieve negative sputum cultures after a minimum duration of 6 consecutive months of background regimen therapy that was either ongoing or stopped no more than 12 months before the screening visit. Patients were randomized to either ARIKAYCE plus a background regimen or background regimen alone. The surrogate endpoint for assessing efficacy was based on achieving culture conversion (3 consecutive monthly negative sputum cultures) by Month 6. The date of conversion was defined as the date of the first of the 3 negative monthly cultures, which had to be achieved by Month 4 in order to meet the endpoint by Month 6. Patients who achieved culture conversion by Month 6 were continued on study drug (ARIKAYCE plus background regimen or background regimen alone based on their randomization) for a total of 12 months after the first negative sputum culture.
A total of 336 patients were randomized (ARIKAYCE plus background regimen, n=224; background regimen alone, n=112) (ITT population), with a mean age of 64.7 years and there was a higher percentage of females (69.3%) than males (30.7%) in the study. At the time of enrollment, of the 336 subjects in the ITT population, 302 (89.9%) were either on a guideline-based regimen for MAC or off guideline-based therapy for MAC for less than 3 months while 34 (10.1%) were off treatment for 3 to 12 months prior to enrollment. At screening, patients were stratified by smoking status (current smoker or not) and by whether patients were on treatment or off treatment for at least 3 months. Most patients at screening were not current smokers (89.3%) and had underlying bronchiectasis (62.5%). At baseline, 329 patients were on a multidrug background regimen that included a macrolide (93.3%), a rifamycin (86.3%), or ethambutol (81.4%). Overall, 55.6% of subjects were receiving a triple-drug background regimen consisting of a macrolide, a rifamycin and ethambutol.
The proportion of patients achieving culture conversion (3 consecutive monthly negative sputum cultures) by Month 6 was significantly (p<0.0001) greater for ARIKAYCE plus background regimen (65/224, 29.0%) compared to background regimen alone (10/112, 8.9%). Of those receiving ARIKAYCE plus background regimen, 18.3% (41/224) achieved culture conversion by Month 6 and sustained sputum culture conversion (defined as consecutive negative sputum cultures with no positive culture on solid media or no more than 2 consecutive positive cultures on liquid media following culture conversion) for up to 12 months of treatment after the first culture that defined culture conversion, compared to 2.7% (3/112) of patients receiving background regimen alone (p<0.0001). At 3 months after the completion of treatment, 16.1% (36/224) of patients who had received ARIKAYCE plus background regimen maintained durable culture conversion, compared to 0% of patients who had received background regimen alone (p<0.0001).
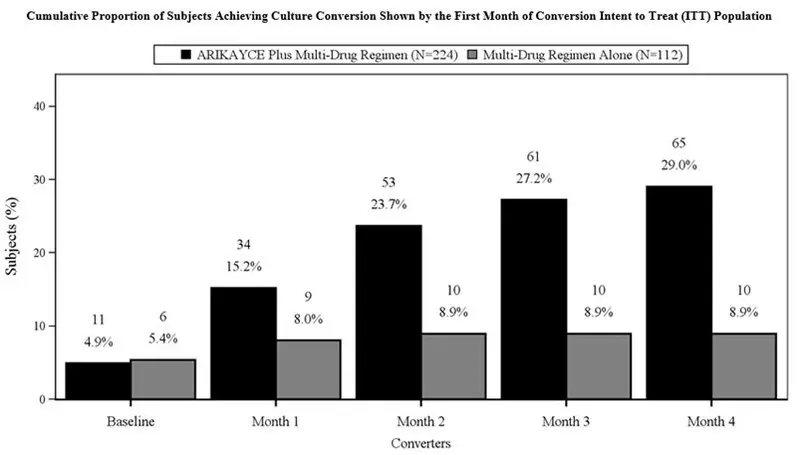
In Trial 1, 23/224 (10.3%) of patients had MAC isolates that developed MIC of > 64 mcg/mL while receiving treatment with ARIKAYCE. In the background regimen alone arm, 4/112 (3.6%) of patients had MAC isolates that developed amikacin MIC of > 64 mcg/mL.
Additional endpoints to assess the clinical benefit of ARIKAYCE, for example, change from baseline in six-minute walk test distance and the Saint George's Respiratory Questionnaire, did not demonstrate clinical benefit by Month 6.
16. How is Arikayce supplied
16.1 How Supplied
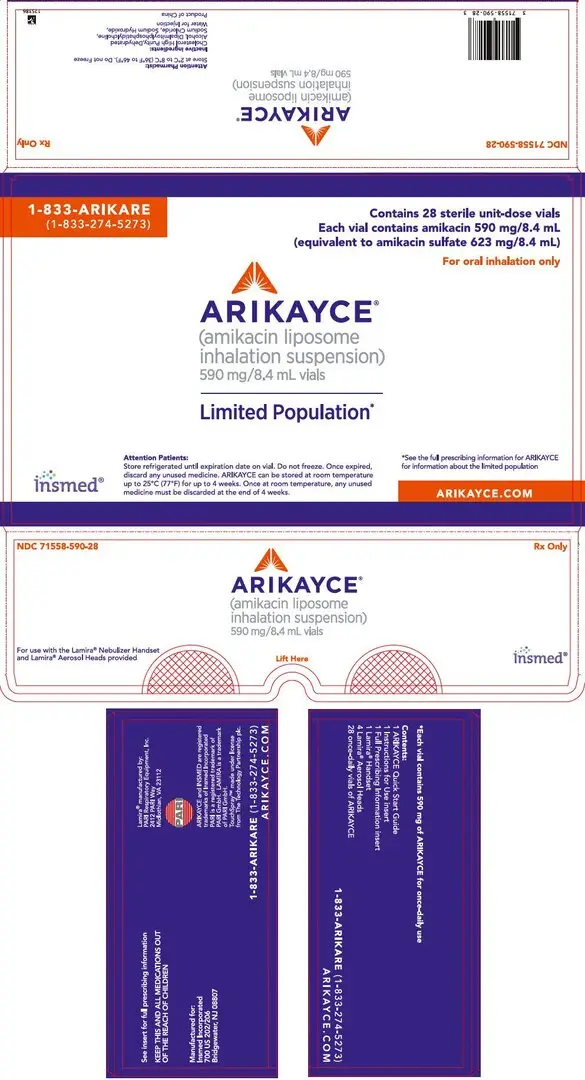
ARIKAYCE (amikacin liposome inhalation suspension), 590 mg/8.4 mL, is supplied in a sterile, unit-dose 10-mL glass vial. The product is dispensed as a 28-vial kit.
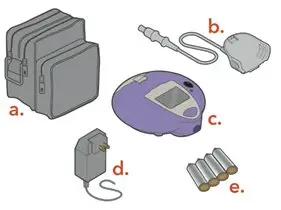
Each carton contains a 28-day supply of medication (28 vials). In addition to the ARIKAYCE vials in the carton, one Lamira Nebulizer Handset and four Lamira Aerosol Heads are provided.
NDC 71558-590-28
The Lamira Nebulizer System contains a controller, a spare Aerosol Head, a spare Handset, Power Cord and accessories.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store ARIKAYCE vials refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) until expiration date on vial. Do not freeze. Once expired, discard any unused drug.
ARIKAYCE can be stored at room temperature up to 25°C (77°F) for up to 4 weeks. Once at room temperature, any unused drug must be discarded at the end of 4 weeks.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Patient Instructions for Use).
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Issued 2/2023 | |||
| MEDICATION GUIDE ARIKAYCE (ar' i kase) LIMITED POPULATION (amikacin liposome inhalation suspension) for oral inhalation use |
||||
| Important: For oral inhalation only. | ||||
| What is the most important information I should know about ARIKAYCE? | ||||
ARIKAYCE can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
|
| |||
|
||||
|
| |||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
| ||
| While using ARIKAYCE these side effects may become serious enough that treatment in a hospital is needed. | ||||
| Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have any of these serious side effects while taking ARIKAYCE. Your healthcare provider may ask you to stop using ARIKAYCE for a short period of time or completely stop using ARIKAYCE. | ||||
| What is ARIKAYCE? | ||||
| ARIKAYCE is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with refractory (difficult to treat) Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) lung disease as part of a combination antibacterial drug treatment plan (regimen). | ||||
| It is not known if ARIKAYCE is safe and effective in children younger than 18 years of age. | ||||
| This product was approved by FDA using the Limited Population pathway. This means FDA has approved this drug for a limited and specific patient population, and studies on the drug may have only answered focused questions about its safety and effectiveness. | ||||
Do not use ARIKAYCE if you:
|
||||
Before using ARIKAYCE, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription medicines and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | ||||
How should I use ARIKAYCE?
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of ARIKAYCE? | ||||
ARIKAYCE may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
| The most common side effects of ARIKAYCE include: | ||||
|
|
| ||
| These are not all of the possible side effects of ARIKAYCE. | ||||
| Call your doctor or pharmacist for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||||
How should I store ARIKAYCE?
|
||||
| Keep ARIKAYCE and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||||
| General information about safe and effective use of ARIKAYCE | ||||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use ARIKAYCE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ARIKAYCE to other people even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ARIKAYCE that is written for health professionals. | ||||
| What are the ingredients in ARIKAYCE? | ||||
| Active ingredient: amikacin sulfate | ||||
| Inactive ingredients: Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), cholesterol, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), and water for injection | ||||
| Manufactured for: Insmed Incorporated, 700 US Highway 202/206, Bridgewater, NJ 08807-1704 | ||||
| Insmed Incorporated, All rights reserved. | ||||
| For more information, call Insmed Arikares Support at: 1- 833-ARIKARE (1-833-274-5273) | ||||
| ARIKAYCE
amikacin suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Insmed Incorporated (183470066) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACS Dobfar S.p.A. | 366662773 | API MANUFACTURE(71558-590) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resilience Biotechnologies Inc. | 243669426 | MANUFACTURE(71558-590) , ANALYSIS(71558-590) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| LabCorp Early Development Laboratories Limited | 213137276 | ANALYSIS(71558-590) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wickham Micro Limited | 228216353 | ANALYSIS(71558-590) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcami Carolinas Corporation | 831351445 | ANALYSIS(71558-590) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharp Packaging Services, LLC | 143696495 | PACK(71558-590) , LABEL(71558-590) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPD Development Ireland Ltd | 985036175 | ANALYSIS(71558-590) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charles River Laboratories Ireland Limited | 988712659 | ANALYSIS(71558-590) | |