Drug Detail:Asmanex hfa (Mometasone inhalation [ moe-met-a-sone ])
Drug Class: Inhaled corticosteroids
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ASMANEX® HFA (mometasone furoate) inhalation aerosol, for
oral inhalation use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1987
Indications and Usage for Asmanex HFA
ASMANEX HFA is a corticosteroid indicated for:
- Maintenance treatment of asthma as prophylactic therapy in patients 5 years of age and older. (1.1)
Important limitations:
- Not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm. (1.1)
Asmanex HFA Dosage and Administration
For oral inhalation only. (2.1)
- Treatment of asthma in patients 12 years of age and older: 2 inhalations twice daily of ASMANEX HFA 100 mcg or 200 mcg. Starting dosage is based on prior asthma therapy. (2.2)
- Treatment of asthma in patients aged 5 to less than 12 years: 2 inhalations twice daily of ASMANEX HFA 50 mcg. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Inhalation aerosol containing 50 mcg, 100 mcg, or 200 mcg of mometasone furoate per actuation. (3)
Contraindications
- Primary treatment of status asthmaticus or acute episodes of asthma requiring intensive measures. (4.1)
- Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients of ASMANEX HFA. (4.2)
Warnings and Precautions
- Deterioration of asthma and acute episodes: ASMANEX HFA should not be used for relief of acute symptoms. Patients require immediate re-evaluation during rapidly deteriorating asthma. (5.1)
- Localized infections: Candida albicans infection of the mouth and throat may occur. Monitor patients periodically for signs of adverse effects on the oral cavity. After dosing, advise patients to rinse their mouth with water and spit out contents without swallowing. (5.2)
- Immunosuppression: Potential worsening of existing tuberculosis, fungal, bacterial, viral, or parasitic infection; or ocular herpes simplex infections. More serious or even fatal course of chickenpox or measles can occur in susceptible patients. Use with caution in patients with these infections because of the potential for worsening of these infections. (5.3)
- Transferring patients from systemic corticosteroids: Risk of impaired adrenal function when transferring from oral steroids. Wean patients slowly from systemic corticosteroids if transferring to ASMANEX HFA. (5.4)
- Hypercorticism and adrenal suppression: May occur with very high dosages or at the regular dosage in susceptible individuals. If such changes occur, discontinue ASMANEX HFA slowly. (5.5)
- Strong cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir): Risk of increased systemic corticosteroid effects. Exercise caution when used with ASMANEX HFA. (5.6)
- Paradoxical bronchospasm: Discontinue ASMANEX HFA and institute alternative therapy if paradoxical bronchospasm occurs. (5.7)
- Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis: Hypersensitivity reactions, such as urticaria, flushing, allergic dermatitis, bronchospasm, rash, pruritus, angioedema, and anaphylactic reaction may occur. Discontinue ASMANEX HFA if such reactions occur. (5.8)
- Decreases in bone mineral density: Monitor patients with major risk factors for decreased bone mineral content. (5.9)
- Effects on growth: Monitor growth of pediatric patients. (5.10)
- Glaucoma and cataracts: Consider referral to an ophthalmologist in patients who develop ocular symptoms or use ASMANEX HFA long term. (5.11)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (reported in greater than or equal to 3% of patients) included:
- nasopharyngitis, headache, sinusitis, bronchitis, and influenza. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Organon LLC, a subsidiary of Organon & Co., at 1-844-674-3200 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Strong cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir): Use with caution. May cause increased systemic corticosteroid effects. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
- Hepatic impairment: Monitor patients for signs of increased drug exposure. (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2021
Related/similar drugs
Symbicort, Dupixent, Breo Ellipta, Ventolin, Ventolin HFA, XopenexFull Prescribing Information
2. Asmanex HFA Dosage and Administration
2.1 Administration Information
Administer ASMANEX HFA only by the orally inhaled route [see Instructions for Use in the Patient Information leaflet]. After each dose, advise patients to rinse their mouth with water and, without swallowing, spit out the contents to help reduce the risk of oropharyngeal candidiasis.
Remove the cap from the mouthpiece of the actuator before using ASMANEX HFA.
Prime ASMANEX HFA before using for the first time by releasing 4 test sprays into the air, away from the face, shaking well before each spray. In cases where the inhaler has not been used for more than 5 days, prime the inhaler again by releasing 4 test sprays into the air, away from the face, shaking well before each spray.
Only use the ASMANEX HFA canister with the ASMANEX HFA actuator. Do not use the ASMANEX HFA actuator with any other inhalation drug product. Do not use actuators from other products with the ASMANEX HFA canister.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Administer ASMANEX HFA as two inhalations twice daily every day (morning and evening) by the orally inhaled route. Shake well prior to each inhalation. If symptoms arise between doses, use an inhaled short-acting beta2-agonist for immediate relief. The maximum benefit may not be achieved for 1 week or longer after beginning treatment. Individual patients may experience a variable time to onset and degree of symptom relief.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
ASMANEX HFA is a pressurized metered dose inhaler (MDI) that is available in 2 strengths (100 mcg and 200 mcg) for adult and adolescent patients aged 12 years and older; and 1 strength (50 mcg) for pediatric patients aged 5 to less than 12 years.
ASMANEX HFA 50 mcg delivers 50 mcg of mometasone furoate per actuation.
ASMANEX HFA 100 mcg delivers 100 mcg of mometasone furoate per actuation.
ASMANEX HFA 200 mcg delivers 200 mcg of mometasone furoate per actuation.
Each strength of ASMANEX HFA is supplied with a blue colored actuator and pink dust cap [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.1)].
4. Contraindications
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Deterioration of Asthma and Acute Episodes
ASMANEX HFA is not indicated for the relief of acute symptoms, i.e., as rescue therapy for the treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm. An inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist, not ASMANEX HFA, should be used to relieve acute symptoms such as shortness of breath. When prescribing ASMANEX HFA, the physician must also provide the patient with an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist (e.g., albuterol) for treatment of acute symptoms, despite regular twice-daily (morning and evening) use of ASMANEX HFA. Instruct patients to contact their physician immediately if episodes of asthma that are not responsive to bronchodilators occur during the course of treatment with ASMANEX HFA. During such episodes, patients may require therapy with oral corticosteroids.
5.2 Local Effects
In clinical trials, the development of localized infections of the mouth and pharynx with Candida albicans have occurred in patients treated with ASMANEX HFA. If oropharyngeal candidiasis develops, treat with appropriate local or systemic (i.e., oral) antifungal therapy while remaining on treatment with ASMANEX HFA therapy, but at times therapy with ASMANEX HFA may need to be interrupted. To reduce the risk of oropharyngeal candidiasis, after dosing with ASMANEX HFA, advise patients to rinse their mouth with water and spit out the contents without swallowing.
5.3 Immunosuppression
Persons who are using drugs that suppress the immune system are more susceptible to infections than healthy individuals.
Chickenpox and measles, for example, can have a more serious or even fatal course in susceptible children or adults using corticosteroids. In such children or adults who have not had these diseases or who are not properly immunized, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. How the dose, route, and duration of corticosteroid administration affect the risk of developing a disseminated infection is not known. The contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid treatment to the risk is also not known. If exposed to chickenpox, prophylaxis with varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) or pooled intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) may be indicated. If exposed to measles, prophylaxis with pooled intramuscular immunoglobulin (IG) may be indicated. (See the respective package inserts for complete VZIG and IG prescribing information.) If chickenpox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered.
Inhaled corticosteroids should be used with caution, if at all, in patients with active or quiescent tuberculosis infection of the respiratory tract, untreated systemic fungal, bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections; or ocular herpes simplex.
5.4 Transferring Patients from Systemic Corticosteroid Therapy
Particular care is needed for patients who are transferred from systemically active corticosteroids to ASMANEX HFA because deaths due to adrenal insufficiency have occurred in asthmatic patients during and after transfer from systemic corticosteroids to less systemically available inhaled corticosteroids. After withdrawal from systemic corticosteroids, a number of months are required for recovery of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) function.
Patients who have been previously maintained on 20 mg or more per day of prednisone (or its equivalent) may be most susceptible, particularly when their systemic corticosteroids have been almost completely withdrawn. During this period of HPA suppression, patients may exhibit signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency when exposed to trauma, surgery, or infection (particularly gastroenteritis) or other conditions associated with severe electrolyte loss. Although ASMANEX HFA may improve control of asthma symptoms during these episodes, in recommended doses it supplies less than normal physiological amounts of corticosteroid systemically and does NOT provide the mineralocorticoid activity necessary for coping with these emergencies.
During periods of stress or severe asthma attack, patients who have been withdrawn from systemic corticosteroids should be instructed to resume oral corticosteroids (in large doses) immediately and to contact their physicians for further instruction. These patients should also be instructed to carry a medical identification card indicating that they may need supplementary systemic corticosteroids during periods of stress or severe asthma attack.
Patients requiring oral or other systemic corticosteroids should be weaned slowly from oral or other systemic corticosteroid use after transferring to ASMANEX HFA. Lung function (FEV1 or PEF), beta-agonist use, and asthma symptoms should be carefully monitored during withdrawal of oral or other systemic corticosteroids. In addition to monitoring asthma signs and symptoms, patients should be observed for signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency such as fatigue, lassitude, weakness, nausea and vomiting, and hypotension.
Transfer of patients from systemic corticosteroid therapy to ASMANEX HFA may unmask allergic conditions previously suppressed by the systemic corticosteroid therapy, e.g., rhinitis, conjunctivitis, eczema, arthritis, and eosinophilic conditions.
During withdrawal from oral corticosteroids, some patients may experience symptoms of systemically active corticosteroid withdrawal, e.g., joint and/or muscular pain, lassitude, and depression, despite maintenance or even improvement of respiratory function.
5.5 Hypercorticism and Adrenal Suppression
ASMANEX HFA will often help control asthma symptoms with less suppression of HPA function than therapeutically equivalent oral doses of prednisone. Since mometasone furoate is absorbed into the circulation and can be systemically active at higher doses, the beneficial effects of ASMANEX HFA in minimizing HPA dysfunction may be expected only when recommended dosages are not exceeded and individual patients are titrated to the lowest effective dose.
Because of the possibility of systemic absorption of inhaled corticosteroids, patients treated with ASMANEX HFA should be observed carefully for any evidence of systemic corticosteroid effects. Particular care should be taken in observing patients postoperatively or during periods of stress for evidence of inadequate adrenal response.
It is possible that systemic corticosteroid effects such as hypercorticism and adrenal suppression (including adrenal crisis) may appear in a small number of patients, particularly when mometasone furoate is administered at higher than recommended doses over prolonged periods of time. If such effects occur, the dosage of ASMANEX HFA should be reduced slowly, consistent with accepted procedures for reducing systemic corticosteroids and for management of asthma symptoms.
5.6 Drug Interactions with Strong Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitors
Caution should be exercised when considering the coadministration of ASMANEX HFA with ketoconazole, and other known strong cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, cobicistat-containing products, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, saquinavir, telithromycin) because adverse effects related to increased systemic exposure to mometasone furoate may occur [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.7 Paradoxical Bronchospasm and Upper Airway Symptoms
ASMANEX HFA may produce inhalation induced bronchospasm with an immediate increase in wheezing after dosing that may be life-threatening. If inhalation induced bronchospasm occurs, it should be treated immediately with an inhaled, short-acting bronchodilator. ASMANEX HFA should be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted.
5.8 Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
Hypersensitivity reactions such as urticaria, flushing, allergic dermatitis, and bronchospasm, may occur after administration of ASMANEX HFA. Discontinue ASMANEX HFA if such reactions occur [see Contraindications (4.2)].
The following additional hypersensitivity reactions, such as rash, pruritus, angioedema, and anaphylactic reaction, have been reported after administration of mometasone furoate dry powder inhaler (DPI) [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.9 Reduction in Bone Mineral Density
Decreases in bone mineral density (BMD) have been observed with long-term administration of products containing inhaled corticosteroids, including mometasone furoate. The clinical significance of small changes in BMD with regard to long-term outcomes, such as fracture, is unknown. Patients with major risk factors for decreased bone mineral content, such as prolonged immobilization, family history of osteoporosis, or chronic use of drugs that can reduce bone mass (e.g., anticonvulsants and corticosteroids) should be monitored and treated with established standards of care.
In a 2-year double-blind study in 103 male and female asthma patients 18 to 50 years of age previously maintained on bronchodilator therapy (Baseline FEV1 85%-88% predicted), treatment with mometasone furoate dry powder inhaler 200 mcg twice daily resulted in significant reductions in lumbar spine (LS) BMD at the end of the treatment period compared to placebo. The mean change from Baseline to Endpoint in the lumbar spine BMD was -0.015 (-1.43%) for the mometasone furoate dry powder inhaler group compared to 0.002 (0.25%) for the placebo group. In another 2-year double-blind study in 87 male and female asthma patients 18 to 50 years of age previously maintained on bronchodilator therapy (Baseline FEV1 82%-83% predicted), treatment with mometasone furoate dry powder inhaler 400 mcg twice daily demonstrated no statistically significant changes in lumbar spine BMD at the end of the treatment period compared to placebo. The mean change from Baseline to Endpoint in the lumbar spine BMD was -0.018 (-1.57%) for the mometasone furoate group compared to -0.006 (-0.43%) for the placebo group.
5.10 Effect on Growth
Orally inhaled corticosteroids, including ASMANEX HFA, may cause a reduction in growth velocity when administered to pediatric patients. Monitor the growth of pediatric patients receiving ASMANEX HFA routinely (e.g., via stadiometry). To minimize the systemic effects of orally inhaled corticosteroids, including ASMANEX HFA, titrate each patient's dose to the lowest dosage that effectively controls his/her symptoms [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.11 Glaucoma and Cataracts
Glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure, and cataracts have been reported following the use of long-term administration of inhaled corticosteroids, including mometasone furoate. Consider referral to an ophthalmologist in patients who develop ocular symptoms or use ASMANEX HFA long term [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Systemic and local corticosteroid use may result in the following:
- Candida albicans infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Immunosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypercorticism and adrenal suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Growth effects in pediatrics [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Glaucoma and cataracts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Adult and Adolescent Patients Aged 12 Years and Older
The safety of ASMANEX HFA was evaluated in 2 randomized placebo and active-controlled trials of 12 and 26 weeks' duration, conducted as part of a mometasone furoate/formoterol fumarate combination product asthma program, which enrolled 1509 patients with persistent asthma. Patient ages ranged from 12 to 84 years of age, 41% were male and 59% female, 73% were Caucasian and 27% non-Caucasian. Of the total population enrolled in the 2 trials, 432 patients received two inhalations twice daily of either ASMANEX HFA, 100 mcg or 200 mcg/actuation. In the 26-week trial (Trial 1) 192 patients received two inhalations twice daily of ASMANEX HFA 100 mcg/actuation and 196 patients received placebo. In the 12 week trial (Trial 2) 240 patients received two inhalations twice daily of ASMANEX HFA 200 mcg/actuation and 233 and 255 patients received mometasone furoate and formoterol fumarate 100 mcg/5 mcg and 200 mcg/5 mcg/actuation combination products, respectively, as comparators.
In these trials, the proportion of patients who discontinued study treatment early due to adverse reactions was 3% and 2% for ASMANEX HFA 100 and 200 mcg treated patients, respectively, and 4% for placebo-treated patients. Serious adverse reactions, whether considered drug-related or not by the investigators, which occurred more frequently in ASMANEX HFA-treated patients included colitis ulcerative, colonic polyp, chest pain, gastroenteritis, endometriosis, asthma, and hemoptysis; all events occurred at rates less than 1%.
The incidence of treatment emergent adverse events associated with ASMANEX HFA are shown in Tables 1 and 2. These are based upon data from each of the 2 clinical trials of 12 or 26 weeks in duration in patients 12 years and older treated with two inhalations twice daily of ASMANEX HFA (100 mcg or 200 mcg), mometasone furoate/formoterol fumarate (100 mcg/5 mcg or 200 mcg/5 mcg), or placebo.
| ASMANEX HFA 100 mcg N=192 n (%) | Placebo N=196 n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Nasopharyngitis | 15 (8) | 7 (4) |
| Headache | 10 (5) | 7 (4) |
| Influenza | 7 (4) | 5 (3) |
| Sinusitis | 6 (3) | 2 (1) |
| ASMANEX HFA 200 mcg N=240 n (%) | MF/F*
100/5 mcg N=233 n (%) | MF/F*
200/5 mcg N=255 n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Nasopharyngitis | 13 (5) | 8 (3) | 12 (5) |
| Headache | 8 (3) | 10 (4) | 5 (2) |
| Bronchitis | 6 (3) | 2 (1) | 7 (3) |
Oral candidiasis has been reported in clinical trials at an incidence of 0.5% in patients using ASMANEX HFA 100 mcg, 0.8% in patients using ASMANEX HFA 200 mcg and 0.5% in the placebo group.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
There are no postmarketing adverse experiences reported to date with ASMANEX HFA. However, the postmarketing safety experience with mometasone furoate dry powder inhaler is relevant to ASMANEX HFA since they contain the same active ingredient. The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of mometasone furoate dry powder inhaler. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Eye disorders: Vision blurred [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Immune System Disorders: Immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions including rash, pruritus, angioedema and anaphylactic reaction [see Contraindications (4.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: Asthma aggravation, which may include cough, dyspnea, wheezing and bronchospasm.
7. Drug Interactions
In clinical trials, concurrent administration of ASMANEX HFA and other drugs, such as short-acting beta2-agonist and intranasal corticosteroids have not resulted in an increased frequency of adverse drug reactions. No formal drug interaction studies have been performed with ASMANEX HFA.
7.1 Inhibitors of Cytochrome P450 3A4
The main route of metabolism of corticosteroids, including mometasone furoate, is via CYP3A4. After oral administration of ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4, the mean plasma concentration of orally inhaled mometasone furoate increased. Concomitant administration of CYP3A4 inhibitors may inhibit the metabolism of, and increase the systemic exposure to, mometasone furoate and potentially increase the risk for systemic corticosteroid side effects. Caution should be exercised when considering the coadministration of ASMANEX HFA with long-term ketoconazole and other known strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, cobicistat-containing products, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, saquinavir, telithromycin) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Consider the benefit of coadministration versus the potential risk of systemic corticosteroid effects, in which case patients should be monitored for systemic corticosteroid side effects.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ASMANEX HFA have been established in patients 12 years of age and older in 2 clinical trials of 12 and 26 weeks in duration. In the 2 clinical trials, 32 patients 12 to 17 years of age were treated with ASMANEX HFA. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between patients in this age group compared to those observed in patients 18 years of age and older. There were no obvious differences in the type or frequency of adverse reactions reported in this age group compared to patients 18 years of age and older.
The safety and effectiveness of ASMANEX HFA 50 mcg, two inhalations twice daily, have been established in patients with asthma aged 5 to less than 12 years in clinical trials up to 24 weeks of treatment duration. The safety profile and overall effectiveness in this age group were consistent with that observed in patients aged 12 years and older who also received ASMANEX HFA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of ASMANEX HFA have not been established in children younger than 5 years of age.
Controlled clinical studies have shown that inhaled corticosteroids may cause a reduction in growth velocity in pediatric patients. In these studies, the mean reduction in growth velocity was approximately 1 cm per year (range 0.3 to 1.8 per year) and appears to depend upon dose and duration of exposure. This effect was observed in the absence of laboratory evidence of HPA axis suppression, suggesting that growth velocity is a more sensitive indicator of systemic corticosteroid exposure in pediatric patients than some commonly used tests of HPA axis function. The long-term effects of this reduction in growth velocity associated with orally inhaled corticosteroids, including the impact on final adult height, are unknown. The potential for "catch-up" growth following discontinuation of treatment with orally inhaled corticosteroids has not been adequately studied.
The growth of children and adolescents receiving orally inhaled corticosteroids, including ASMANEX HFA, should be monitored routinely (e.g., via stadiometry). If a child or adolescent on any corticosteroid appears to have growth suppression, the possibility that he/she is particularly sensitive to this effect should be considered. The potential growth effects of prolonged treatment should be weighed against clinical benefits obtained and the risks associated with alternative therapies. To minimize the systemic effects of orally inhaled corticosteroids, including ASMANEX HFA, each patient should be titrated to his/her lowest effective dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
A total of 38 patients 65 years of age and older (3 of whom were 75 years and older) have been treated with ASMANEX HFA in 2 clinical trials of 12 and 26 weeks in duration. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. Based on available data for ASMANEX HFA, no adjustment of dosage in geriatric patients is warranted.
10. Overdosage
Chronic overdosage may result in signs/symptoms of hypercorticism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Single oral doses up to 8000 mcg of mometasone furoate have been studied on adult subjects with no adverse reactions reported.
11. Asmanex HFA Description
ASMANEX HFA is a metered dose inhaler for oral inhalation only, consisting of 50 mcg, 100 mcg, or 200 mcg of mometasone furoate per actuation.
Mometasone furoate, the active component of ASMANEX HFA, is a corticosteroid having the chemical name 9,21-dichloro-11(Beta),17-dihydroxy-16 (alpha)-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 17-(2-furoate) with the following chemical structure:
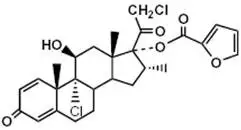
Mometasone furoate is a white powder with an empirical formula of C27H30Cl2O6, and molecular weight 521.44. It is practically insoluble in water; slightly soluble in methanol, ethanol, and isopropanol; soluble in acetone.
ASMANEX HFA 50 mcg, 100 mcg, and 200 mcg are each formulated as a hydrofluoroalkane (HFA-227: 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane) propelled pressurized metered dose inhaler containing sufficient amount of drug for 120 actuations [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]. After priming, each actuation of the inhaler delivers 60, 115, or 225 mcg of mometasone furoate in 69.6 mg of suspension from the valve and delivers 50, 100, or 200 mcg of mometasone furoate from the actuator. The actual amount of drug delivered to the lung may depend on patient factors, such as the coordination between actuation of the device and inspiration through the delivery system. ASMANEX HFA also contains ethanol as a cosolvent and oleic acid as a surfactant.
ASMANEX HFA should be primed before using for the first time by releasing 4 test sprays into the air, away from the face, shaking well before each spray. In cases where the inhaler has not been used for more than 5 days, prime the inhaler again by releasing 4 test sprays into the air, away from the face, shaking well before each spray.
12. Asmanex HFA - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mometasone furoate is a corticosteroid demonstrating potent anti-inflammatory activity. The precise mechanism of corticosteroid action on asthma is not known. Inflammation is an important component in the pathogenesis of asthma. Corticosteroids have been shown to have a wide range of inhibitory effects on multiple cell types (e.g., mast cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes) and mediators (e.g., histamine, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, and cytokines) involved in inflammation and in the asthmatic response. These anti-inflammatory actions of corticosteroids may contribute to their efficacy in asthma.
Mometasone furoate has been shown in vitro to exhibit a binding affinity for the human glucocorticoid receptor, which is approximately 12 times that of dexamethasone, 7 times that of triamcinolone acetonide, 5 times that of budesonide, and 1.5 times that of fluticasone. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Systemic effects of inhaled corticosteroids are related to systemic exposure. Pharmacokinetic data have demonstrated that, in adults, systemic exposure to mometasone furoate administered by MDI is the same or lower than that of equivalent doses of inhaled mometasone furoate administered via DPI [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Based upon the pharmacokinetic data, the systemic effects (e.g., HPA-axis suppression and growth retardation) of mometasone furoate delivered by MDI in adult and pediatric patients would be expected to be no greater than what is reported for inhaled mometasone furoate when administered at comparable doses via DPI [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
As no evidence of a pharmacokinetic drug interaction between mometasone furoate and formoterol was observed when the two drugs were administered from a mometasone furoate/formoterol fumarate combination product, the pharmacokinetics information from the combination product is applicable to ASMANEX HFA.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in Sprague Dawley rats, mometasone furoate demonstrated no statistically significant increase in the incidence of tumors at inhalation doses up to 67 mcg/kg (approximately 14 times the MRHD on an AUC basis). In a 19-month carcinogenicity study in Swiss CD-1 mice, mometasone furoate demonstrated no statistically significant increase in the incidence of tumors at inhalation doses up to 160 mcg/kg (approximately 9 times the MRHD on an AUC basis).
Mometasone furoate increased chromosomal aberrations in an in vitro Chinese hamster ovary cell assay, but did not have this effect in an in vitro Chinese hamster lung cell assay. Mometasone furoate was not mutagenic in the Ames test or mouse lymphoma assay, and was not clastogenic in an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay, a rat bone marrow chromosomal aberration assay, or a mouse male germ-cell chromosomal aberration assay. Mometasone furoate also did not induce unscheduled DNA synthesis in vivo in rat hepatocytes.
In reproductive studies in rats, impairment of fertility was not produced by subcutaneous doses up to 15 mcg/kg (approximately 8 times the MRHD on an AUC basis).
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Asthma
16. How is Asmanex HFA supplied
16.1 How Supplied
ASMANEX HFA is available in three strengths and supplied in the following package size (TABLE 3):
| Package | NDC | Strength Identifier (Color Band)* |
|---|---|---|
|
||
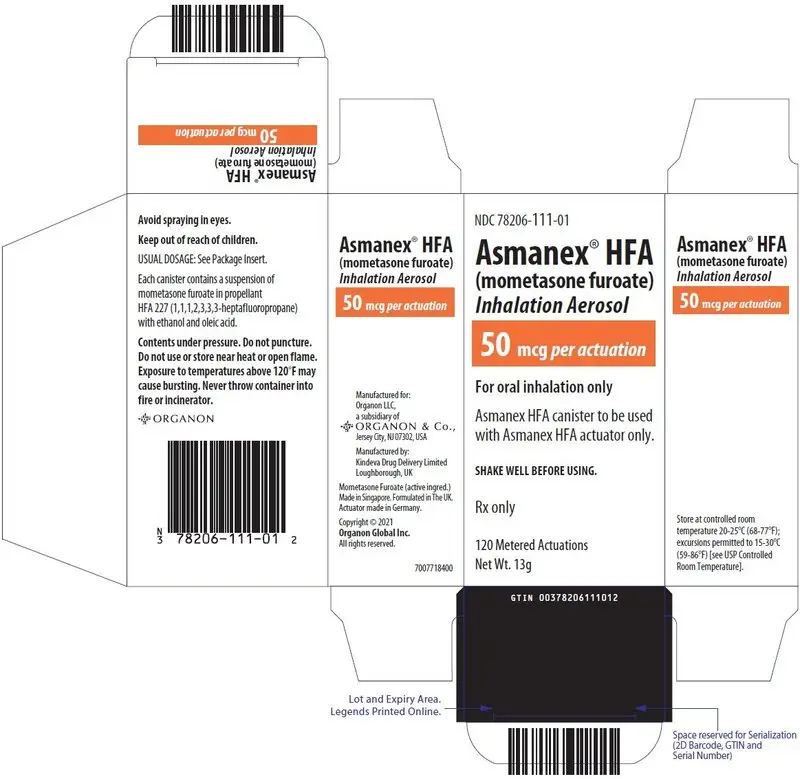
| ASMANEX HFA 50 mcg 120 metered actuations | 78206-111-01 | Orange |
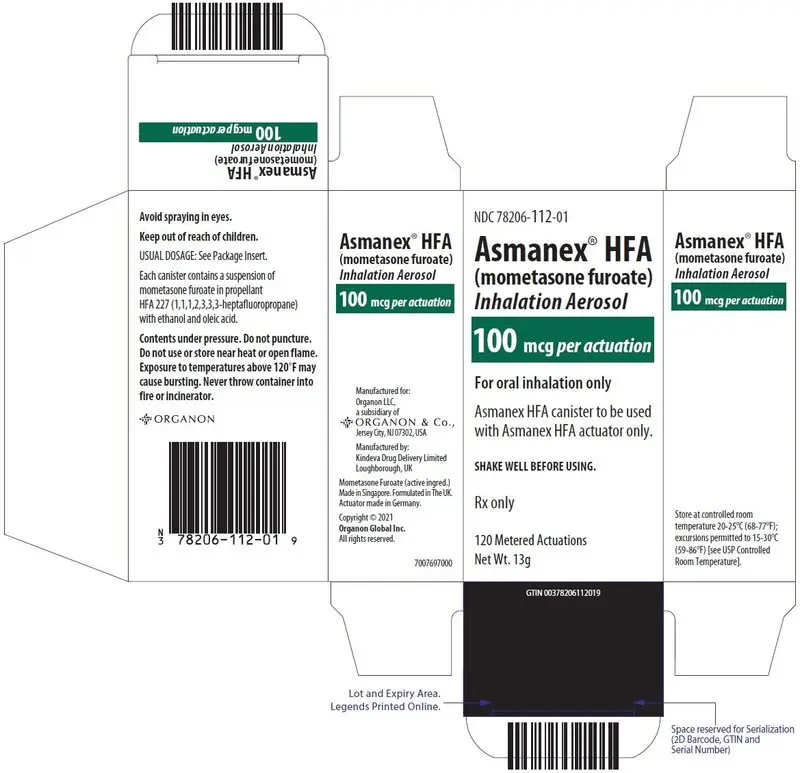
| ASMANEX HFA 100 mcg 120 metered actuations | 78206-112-01 | Green |
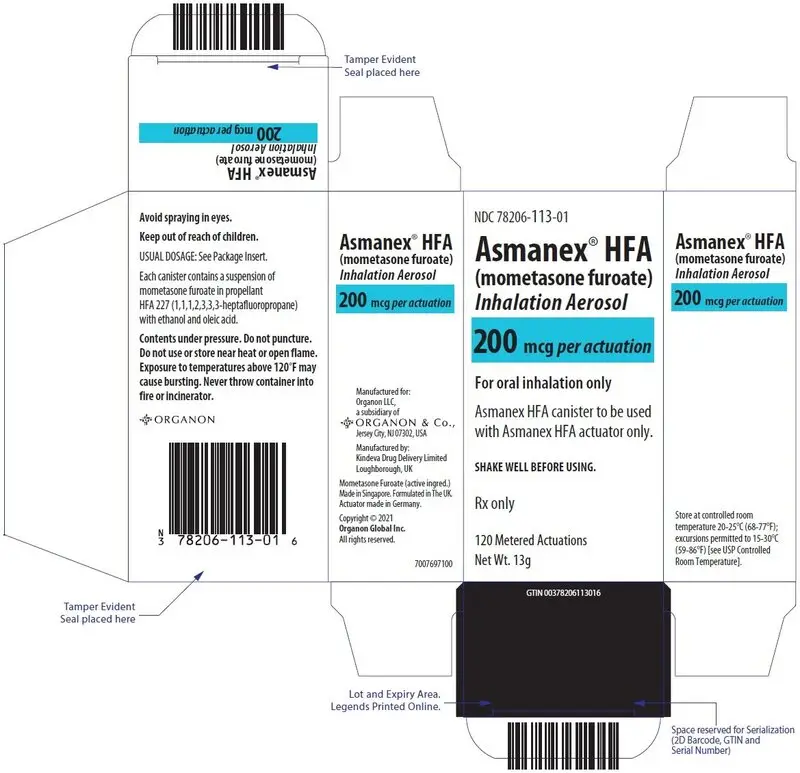
| ASMANEX HFA 200 mcg 120 metered actuations | 78206-113-01 | Blue |
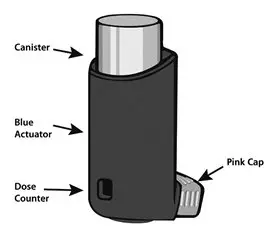
Each strength is supplied as a pressurized aluminum canister that has a blue plastic actuator integrated with a dose counter and a pink dust cap. Each canister has a net fill weight of 13 grams. Each inhaler is placed into a carton. Each carton contains 1 inhaler.
Initially the dose counter will display "124" actuations. After the initial priming with 4 actuations, the dose counter will read "120" and the inhaler is now ready for use.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Only use the ASMANEX HFA canister with the ASMANEX HFA actuator. Do not use the ASMANEX HFA actuator with any other inhalation drug product. Do not use actuators from other products with the ASMANEX HFA canister.
Do not remove the canister from the actuator because the correct amount of medication may not be discharged; the dose counter may not function properly; reinsertion may cause the dose counter to count down by 1 and discharge a puff.
The correct amount of medication in each inhalation cannot be ensured after the labeled number of actuations from the canister has been used, even though the inhaler may not feel completely empty and may continue to operate. Discard the inhaler when the labeled number of actuations has been used (the dose counter will read "0").
Store at controlled room temperature 20°C-25°C (68°F-77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C-30°C (59°F-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
For best results, keep the canister at room temperature before use. Shake well and remove the cap from the mouthpiece of the actuator before using. Keep out of reach of children. Avoid spraying in eyes.
Contents Under Pressure: Do not puncture. Do not use or store near heat or open flame. Exposure to temperatures above 120°F may cause bursting. Never throw container into fire or incinerator.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
| Patient Information ASMANEX® HFA (AZ-ma-neks) 50 mcg ASMANEX® HFA 100 mcg ASMANEX® HFA 200 mcg (mometasone furoate) Inhalation Aerosol |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised Date: 6/2021 | |||||
| What is ASMANEX HFA?
ASMANEX HFA is an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) prescription medicine used as maintenance treatment for the prevention and control of asthma symptoms in people 5 years of age and older.
|
||||||
| Who should not use ASMANEX HFA? Do not use ASMANEX HFA:
|
||||||
| What should I tell my doctor before and during treatment with ASMANEX HFA? Before you use ASMANEX HFA, tell your healthcare provider if you:
ASMANEX HFA may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how ASMANEX HFA works. Especially, tell your healthcare provider if you take antifungal medicines, antibiotic medicines, or anti-HIV medicines such as: |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if any of your medicines are the kinds listed above. For some medicines (including medicines for HIV such as ritonavir, cobicistat-containing products, and certain antifungals and antibiotics) your doctor may wish to monitor you carefully. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine. |
||||||
| How should I use ASMANEX HFA? Read the step-by-step instructions for using ASMANEX HFA in the Instructions for Use.
|
||||||
| What are the possible side effects of ASMANEX HFA? ASMANEX HFA can cause serious side effects, including |
||||||
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
||||||
| The most common side effects reported while using ASMANEX HFA include: | ||||||
|
|
|
||||
| Other side effects: Worsening asthma or sudden asthma attacks have been reported with the use of inhaled mometasone furoate. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the side effects with ASMANEX HFA. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||||
How should I store ASMANEX HFA?
|
||||||
| General Information about the safe and effective use of ASMANEX HFA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ASMANEX HFA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give your ASMANEX HFA to other people, even if they have the same condition that you have. It may harm them. This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about ASMANEX HFA. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about ASMANEX HFA that was written for healthcare professionals. For more information about ASMANEX HFA go to www.ASMANEX.com, or to report side effects call 1-844-674-3200. |
||||||
| What are the ingredients in ASMANEX HFA?
Active ingredient: mometasone furoate Inactive ingredients: hydrofluoroalkane (HFA-227: 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane), ethanol and oleic acid |
||||||
Instructions for Use
ASMANEX® HFA (AZ-ma-neks) 50 mcg
ASMANEX® HFA 100 mcg
ASMANEX® HFA 200 mcg
(mometasone furoate)
Inhalation Aerosol
Read these Instructions for Use before you start using ASMANEX HFA and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
The parts of your ASMANEX HFA:
There are 2 main parts to your ASMANEX HFA inhaler: the metal canister that holds the medicine and the blue plastic actuator that sprays the medicine from the canister.
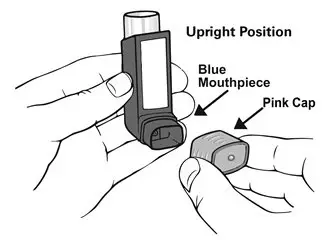
- The inhaler also has a pink cap that covers the mouthpiece of the actuator (see Figure 1). The cap from the mouthpiece must be removed before use. The inhaler contains "120" actuations (puffs).
- The inhaler comes with a dose counter located on the plastic actuator (see Figure 1). The counter display will show the number of actuations (puffs) of medicine remaining. The first time you use ASMANEX HFA the dose counter will show "124" actuations remaining. Each time you press the canister, a puff of medicine is released and the counter will count down by 1. The counter will stop counting at 0.
Important Information:
- Use ASMANEX HFA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to. Adults may assist children with using ASMANEX HFA as prescribed. Children may use ASMANEX HFA with or without a spacer device.
- Remove the cap from the mouthpiece of the actuator before using ASMANEX HFA.
-
Do not remove the canister from the actuator because:
- you may not receive the correct amount of medication.
- the dose counter may not function properly.
- if you try to insert the canister back into the actuator this may cause the dose counter to count down by 1 and may discharge a puff.
- Use the ASMANEX HFA canister only with the actuator supplied with the product. Do not use parts of the ASMANEX HFA inhaler with parts from any other inhalation medicine.
Before using your ASMANEX HFA:
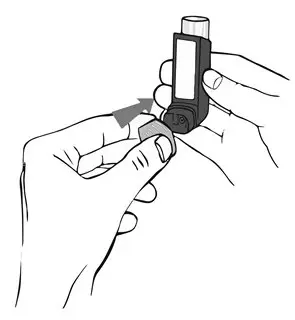
Remove the cap from the mouthpiece of the actuator before using ASMANEX HFA (see Figure 2). Check the mouthpiece for objects before use. Make sure the canister is fully inserted into the actuator.
Priming your ASMANEX HFA Inhaler:
Before you use ASMANEX HFA for the first time, you must prime the inhaler.
- 1.
- To prime the inhaler, hold it in the upright position away from your face, and press down firmly and fully on the top of the canister until it stops moving in the actuator. Do this 4 times to release a total of 4 actuations (puffs) into the air.
- 2.
- Shake the inhaler well before each of the priming actuations. After priming 4 times, the dose counter should read "120".
- 3.
- If you do not use your ASMANEX HFA for more than 5 days, you will need to prime it again before use.
Using your ASMANEX HFA:
- 4.
- Confirm that the strength indicated on the actuator and canister labels matches the prescribed dosage.
- 5.
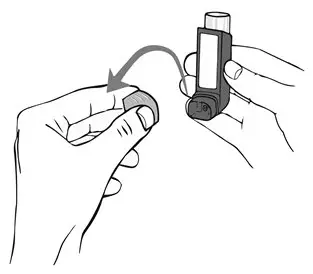
- Remove the cap from the mouthpiece of the actuator (see Figure 3). Check the mouthpiece for objects before use. Make sure the canister is fully inserted into the actuator.
- 6.
- Shake the inhaler well before each use.
- 7.
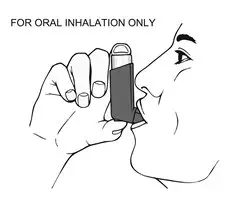
- Breathe out as fully as you comfortably can through your mouth. Push out as much air from your lungs as possible. Hold the inhaler in the upright position and place the mouthpiece into your mouth (see Figure 4). Close your lips around the mouthpiece.
- 8.
- Take a deep breath (inhale) in slowly through your mouth. While doing this, press down firmly and fully on the top of the canister until it stops moving in the actuator. Take your finger off the canister.
- 9.
- When you have finished breathing in, hold your breath as long as you comfortably can, up to 10 seconds. Then remove the inhaler from your mouth and breathe out through your nose, while keeping your lips closed.
- 10.
- Wait at least 30 seconds to take your second puff of ASMANEX HFA.
- 11.
- Shake the inhaler well again and repeat steps 6 through 8 to take your second puff of ASMANEX HFA.
After using your ASMANEX HFA inhaler:
- 12.
- Replace the cap over the mouthpiece right away after use (see Figure 5).
- 13.
- After you finish taking ASMANEX HFA (2 puffs), rinse your mouth with water.
Reading the counter:
- The dose counter identifies the number of inhalations (puffs) left in your inhaler (see Figure 6).
- The counter will count down each time you release a puff of medicine (either when preparing your ASMANEX HFA inhaler for use or when using the medicine).
When to replace your ASMANEX HFA:
- It is important that you pay attention to the number of inhalations (puffs) left in your ASMANEX HFA inhaler by reading the counter.
- When the counter reads "20", you should refill your prescription or ask your healthcare provider if you need a new prescription for ASMANEX HFA.
- Throw away ASMANEX HFA after the counter reaches "0", indicating that you have used the number of actuations on the product label and box. Your inhaler may not feel empty and it may continue to operate, but you will not get the right amount of medicine if you keep using it.
- Never try to change the numbers on the counter or remove the counter from the actuator.
- Do not use the inhaler after the expiration date.
How to clean your ASMANEX HFA:
The mouthpiece should be cleaned using a dry wipe after every 7 days of use.
Routine cleaning instructions:
- Remove the cap off the mouthpiece. Wipe the inside and outside surfaces of the actuator mouthpiece with a clean, dry, lint-free tissue or cloth. Do not wash or put any parts of your inhaler in water. Put the cap back on the mouthpiece after cleaning.
- Do not remove the canister from the actuator.
- Do not attempt to unblock the actuator with a sharp object, such as a pin.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
| ASMANEX HFA
mometasone furoate aerosol |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASMANEX HFA
mometasone furoate aerosol |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASMANEX HFA
mometasone furoate aerosol |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Organon LLC (117494753) |