Drug Detail:Asparlas (Calaspargase pegol [ kal-as-par-jase-peg-ol ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antineoplastics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ASPARLAS® (calaspargase pegol-mknl) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration, Recommended Premedication (2.2) | 12/2021 |
| Dosage and Administration, Recommended Monitoring and Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions (2.3) | 12/2021 |
Indications and Usage for Asparlas
ASPARLAS is an asparagine specific enzyme indicated as a component of a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in pediatric and young adult patients age 1 month to 21 years. (1.1)
Asparlas Dosage and Administration
- Recommended Dosage: 2,500 units/m2 intravenously no more frequently than every 21 days. (2.1)
- See Full Prescribing Information for important details regarding dosing modifications and preparation and administration. (2.2, 2.3, 2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 3,750 units/5 mL (750 units/mL) in a single-dose vial. (3)
Contraindications
- History of serious hypersensitivity reactions to pegylated L-asparaginase. (4)
- History of serious thrombosis during L-asparaginase therapy. (4)
- History of serious pancreatitis related to previous L-asparaginase treatment. (4)
- History of serious hemorrhagic events during previous L-asparaginase therapy. (4)
- Severe hepatic impairment. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity: Observe patients for one hour after administration. Discontinue ASPARLAS in patients with serious hypersensitivity reactions. (5.1)
- Pancreatitis: Discontinue ASPARLAS in patients with pancreatitis. Monitor blood glucose. (5.2)
- Thrombosis: Discontinue ASPARLAS for severe or life-threatening thrombosis. (5.3)
- Hemorrhage: Discontinue ASPARLAS for severe or life-threatening hemorrhage. Evaluate for etiology and treat. (5.4)
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor for toxicity through recovery from cycle. Discontinue ASPARLAS for severe liver toxicity. (5.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common (incidence ≥10%) grade ≥3 adverse reactions were elevated transaminase, bilirubin increased, pancreatitis, and abnormal clotting studies. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Servier Pharmaceuticals LLC at 1-800-807-6124 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2022
Related/similar drugs
methotrexate, imatinib, doxorubicin, mercaptopurine, Sprycel, GleevecFull Prescribing Information
2. Asparlas Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of ASPARLAS is 2,500 units/m2 given intravenously no more frequently than every 21 days.
2.2 Recommended Premedication
Premedicate patients with acetaminophen, an H-1 receptor blocker (such as diphenhydramine), and an H-2 receptor blocker (such as famotidine) 30-60 minutes prior to administration of ASPARLAS to decrease the risk and severity of both infusion and hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.3 Recommended Monitoring and Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Monitor patients at least weekly with bilirubin, transaminases, glucose, and clinical examinations until recovery from the cycle of therapy. If an adverse reaction should occur, modify treatment according to Table 1.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity* | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Infusion Reaction/ Hypersensitivity Reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Grade 1 |
|
| Grade 2 |
|
|
| Grade 3 to 4 |
|
|
| Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grades 3 to 4 |
|
| Thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Uncomplicated deep vein thrombosis |
|
| Severe or life-threatening thrombosis |
|
|
| Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | Grade 3 to 4 |
|
| Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | Total bilirubin more than 3 times to no more than 10 times the ULN |
|
| Total bilirubin more than 10 times the ULN |
|
|
2.4 Preparation and Administration
ASPARLAS is a clear and colorless solution. Visually inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter, cloudiness, or discoloration prior to administration. If any of these are present, discard the vial. Do not administer if ASPARLAS has been shaken or vigorously agitated, frozen, or stored at room temperature for more than 48 hours.
- Dilute ASPARLAS in 100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP using sterile/aseptic technique. Discard any unused portion left in a vial.
- After dilution, administer immediately into a running infusion of either 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose, respectively.
- Administer the dose over a period of 1 hour.
- Do not infuse other drugs through the same intravenous line during administration of ASPARLAS.
- The diluted solution may be stored for up to 4 hours at room temperature (15°C to 25°C [59°F to 77°F]) or refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 24 hours.
- Protect from light. Do not shake or freeze.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 3,750 units/5 mL (750 units/mL) clear, colorless solution in a single-dose vial.
4. Contraindications
ASPARLAS is contraindicated in patients with:
- History of serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, to pegylated L-asparaginase therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- History of serious pancreatitis during previous L-asparaginase therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- History of serious thrombosis during previous L-asparaginase therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- History of serious hemorrhagic events during previous L-asparaginase therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Severe hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity
Grade 3 and 4 hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in clinical trials with ASPARLAS with an incidence between 7 and 21% [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Hypersensitivity reactions observed with other asparaginases include angioedema, lip swelling, eye swelling, erythema, blood pressure decreased, bronchospasm, dyspnea, pruritus, and rash [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Premedicate patients 30-60 minutes prior to administration of ASPARLAS [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Because of the risk of serious allergic reactions (e.g., life-threatening anaphylaxis), administer ASPARLAS in a clinical setting with resuscitation equipment and other agents necessary to treat anaphylaxis (e.g., epinephrine, oxygen, intravenous steroids, antihistamines) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] and observe patients for 1 hour after administration. Discontinue ASPARLAS in patients with serious hypersensitivity reactions.
5.2 Pancreatitis
Cases of pancreatitis have been reported in clinical trials with ASPARLAS with an incidence between 12 and 16% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis have been reported with other asparaginases.
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of pancreatitis, which, if left untreated, could be fatal. Assess serum amylase and/or lipase levels to identify early signs of pancreatic inflammation. Discontinue ASPARLAS if pancreatitis is suspected; if pancreatitis is confirmed, do not resume ASPARLAS [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Thrombosis
Serious thrombotic events, including sagittal sinus thrombosis, have been reported in clinical trials with ASPARLAS with an incidence of 9 to 12%. Discontinue ASPARLAS in patients experiencing serious thrombotic events [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.4 Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage associated with increased prothrombin time (PT), increased partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and hypofibrinogenemia have been reported in patients receiving ASPARLAS [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Evaluate patients with signs and symptoms of hemorrhage with coagulation parameters including PT, PTT, fibrinogen. Consider appropriate replacement therapy in patients with severe or symptomatic coagulopathy [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.5 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity and abnormal liver function, including elevations of transaminase, bilirubin (direct and indirect), reduced serum albumin, and plasma fibrinogen can occur. Evaluate bilirubin and transaminases at least weekly, during cycles of treatment that include ASPARLAS through 6 weeks after the last dose of ASPARLAS. In the event of serious liver toxicity, discontinue treatment with ASPARLAS and provide supportive care [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to ASPARLAS in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other asparaginase products may be misleading.
Immunogenicity was assessed using enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) in Study DFCI 11-001. Of 98 evaluable patients treated with ASPARLAS, 15 (15%) patients developed new or an increased titer of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) during treatment; 14 of these 15 patients were positive for anti-PEG antibodies. The presence of ADA correlated with the occurrence of hypersensitivity reactions. There is insufficient information to determine whether the development of antibodies is associated with altered pharmacokinetics (i.e., loss of asparaginase activity).
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
ASPARLAS can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ASPARLAS in the treatment of ALL have been established in pediatric patients 1 month to <17 years (no data for the age group <1 month old). Use of ASPARLAS in these age groups is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled trial with additional safety from a second trial. The trials included 208 children with ALL or lymphoblastic lymphoma treated with ASPARLAS; there were 19 infants (1 month to <2 years old), 128 children (2 years to <12 years old), and 61 adolescents (12 years to <17 years old). There were no clinically meaningful differences in safety or nadir serum asparaginase activity across age groups [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14)].
11. Asparlas Description
Calaspargase pegol-mknl contains an asparagine specific enzyme derived from Escherichia coli, as a conjugate of L-asparaginase (L-asparagine amidohydrolase) and monomethoxypolyethylene glycol (mPEG) with a succinimidyl carbonate (SC) linker. The SC linker is a chemically stable carbamate bond between the mPEG moiety and the lysine groups of L-asparaginase.
L-asparaginase is a tetrameric enzyme that is produced endogenously by E. coli and consists of identical 34.5 kDa subunits. Approximately 31 to 39 molecules of SC-PEG are linked to L-asparaginase; the molecular weight of each SC-PEG molecule is about 5 kDa. The activity of ASPARLAS is expressed in units (U).
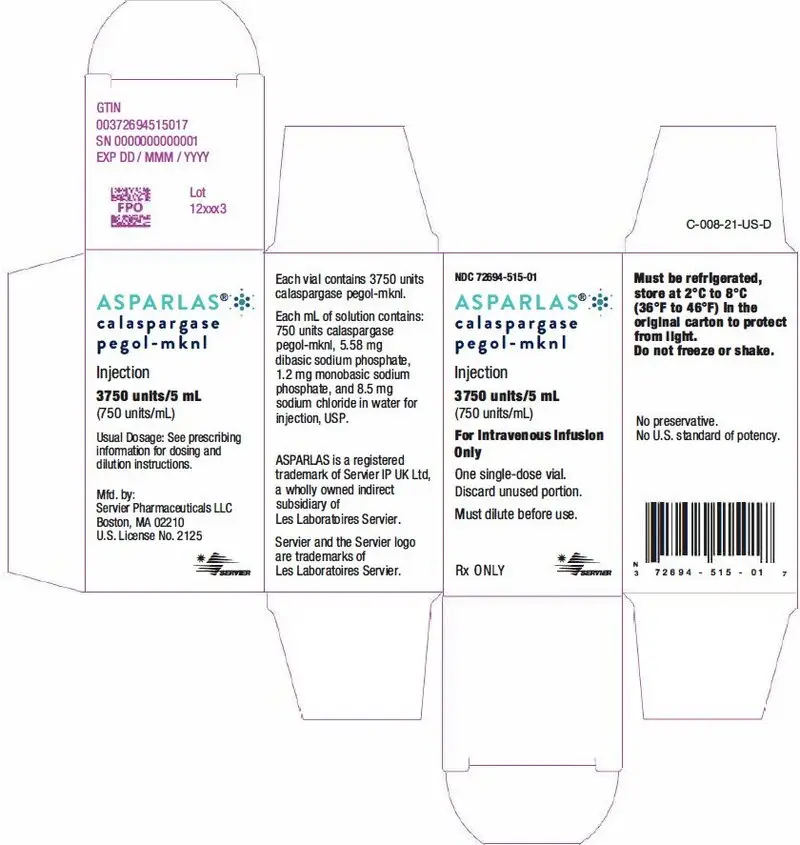
ASPARLAS injection is supplied as a clear, colorless, preservative-free, isotonic sterile solution in phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.3 that requires dilution prior to intravenous infusion. Each vial of ASPARLAS contains 3,750 units in 5 mL of solution. Each milliliter contains 750 units of calaspargase pegol-mknl; dibasic sodium phosphate, USP (5.58 mg); monobasic sodium phosphate, USP (1.20 mg); and sodium chloride, USP (8.50 mg) in water for injection, USP.
12. Asparlas - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
L-asparaginase is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of the amino acid L-asparagine into aspartic acid and ammonia. The pharmacological effect of ASPARLAS is thought to be based on the killing of leukemic cells due to depletion of plasma asparagine. Leukemic cells with low expression of asparagine synthetase have a reduced ability to synthesize asparagine, and therefore depend on an exogenous source of asparagine for survival.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Calaspargase pegol-mknl pharmacodynamic (PD) response was assessed through measurement of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) asparagine concentrations via an LC-MS/MS assay.
Asparagine concentrations in plasma (N=41) were maintained below the assay limit of quantification for more than 18 days following a single dose of ASPARLAS 2,500 U/m2 during the induction phase. Mean CSF asparagine concentrations decreased from a pretreatment concentration of 0.8 µg/mL (N=10) to 0.2 µg/mL on Day 4 (N=37) and remained decreased at 0.2 µg/mL (N=35) 25 days after the administration of a single dose of ASPARLAS 2,500 U/m2 in the induction phase.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Calaspargase pegol-mknl pharmacokinetics (PK) were assessed through measurement of plasma asparaginase activity via a coupled enzymatic assay.
The plasma asparaginase activity pharmacokinetics were characterized in 43 patients (1 to 26 years) with newly diagnosed high risk B-precursor ALL treated with a multidrug backbone therapy. Table 3 summarizes the plasma asparaginase activity pharmacokinetic parameters after a single dose of ASPARLAS 2,500 U/m2 in the induction phase.
| Parameter | Arithmetic Mean (%CV) N=43 |
|---|---|
|
|
| General | |
| Cmax (U/mL) | 1.62 (23.0) |
| AUC0-25day (day∙U/mL) | 16.9 (23.2)* |
| AUC0∞ (day∙U/mL)† | 25.5 (30.4)* |
| Absorption | |
| Tmax (h)† | 1.17 (1.05, 5.47)‡ |
| Distribution | |
| Vss (L) | 2.96 (84.3)* |
| Elimination | |
| t1/2 (day)§ | 16.1 (51.9)* |
| Clearance (L/day) | 0.147 (76.1)* |
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
The determination of efficacy was based on a demonstration of the achievement and maintenance of nadir serum asparaginase activity (NSAA) above the level of 0.1 U/mL using ASPARLAS 2500 U/m2 intravenously every 3 weeks. The pharmacokinetics of ASPARLAS were studied when used in combination with multiagent chemotherapy in 124 patients with B-cell lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Among these patients, the median age was 11.5 years (range, 1-26); 62 (50%) were male, 102 (82%) white, 6 (5%) Asian, 5 (4%) Black or African American, 2 (2%) Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander and 9 (7%) other or unknown. The results showed that 123 (99%, 95% CI: 96%-100%) of the 124 patients maintained NSAA >0.1 U/mL at weeks 6, 12, 18, 24, and 30.
16. How is Asparlas supplied
ASPARLAS (calaspargase pegol-mknl) injection is supplied as a clear, colorless, preservative-free sterile solution in a single-dose vial containing 3,750 units of calaspargase pegol-mknl per 5 mL solution (NDC 72694-515-01).
| ASPARLAS
calaspargase pegol injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Servier Pharmaceuticals LLC (116608503) |