Drug Detail:Atryn (Antithrombin [recombinant])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous coagulation modifiers
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ATRYN (antithrombin (Recombinant))
Lyophilized powder for solution for intravenous injection
Initial U.S. Approval: 2009
Recent Major Changes
Dosage and Administration (2.3) 5/2017
Indications and Usage for ATryn
ATryn (antithrombin (Recombinant)) is a recombinant antithrombin indicated for the prevention of peri-operative and peri-partum thromboembolic events in hereditary antithrombin deficient patients. (1)
It is not indicated for treatment of thromboembolic events in hereditary antithrombin deficient patients.
ATryn Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use after reconstitution only.
- The dosage of ATryn is individualized for each patient. Treatment goal is to restore and maintain functional antithrombin (AT) activity levels between 80% - 120% (0.8 - 1.2 IU/mL) of normal. (2.2)
- Administer loading dose as a 15-minute intravenous infusion immediately followed by continuous infusion of the maintenance dose. (2.2)
- AT activity monitoring is required for proper treatment. Check AT activity once or twice per day with dose adjustments made as recommended. (2.2)
- Continue administration of ATryn until adequate follow-on anticoagulation has been established. (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
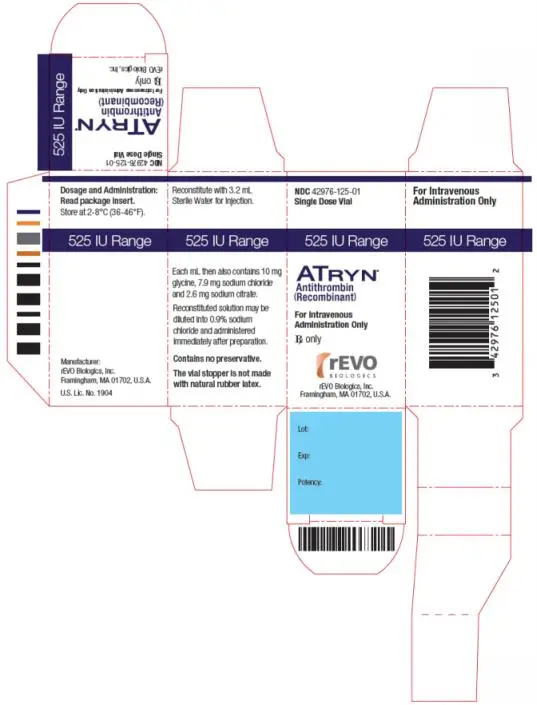
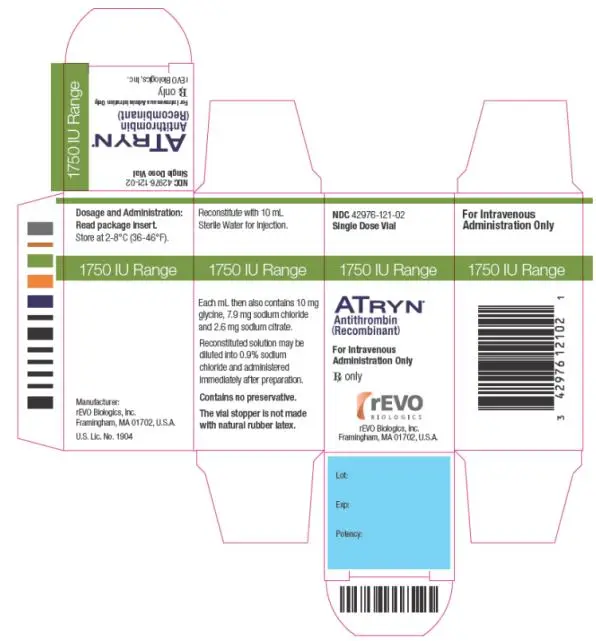
- ATryn is a sterile lyophilized powder for reconstitution. Each single dose vial of ATryn contains the potency as stated on the label, which is approximately 525 IU or 1750 IU. (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to goat and goat milk proteins. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Anaphylaxis and severe hypersensitivity reactions are possible. Should symptoms occur, treatment with the product should be discontinued, and emergency treatment should be administered. (5.1)
- The anticoagulant effect of drugs that use antithrombin to exert their anticoagulation may be altered when ATryn is added or withdrawn. To avoid excessive or insufficient anticoagulation, regularly perform coagulation tests suitable for the anticoagulant used, at close intervals, especially in the first hours following the start or withdrawal of ATryn and monitor patients for bleeding or thrombosis. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials at a frequency of ≥ 5% were hemorrhage and infusion site reaction. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact rEVO Biologics, Inc. at 1-800-610-3776 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- ATryn enhances anticoagulant effect of heparin and low molecular weight heparin. (7)
- The half-life of ATryn may be altered by concomitant treatment with anticoagulants that use antithrombin to exert their anticoagulant effect. (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: ATryn administered during the third trimester of pregnancy has not shown an increased risk of fetal abnormalities. No data is available for use of ATryn in earlier stages of pregnancy. (8.1)
- Lactation: ATryn administered by infusion will be present in breast milk at estimated concentrations 1/50 to 1/100 that of concentration in blood. Use only if clearly needed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2021
Related/similar drugs
Thrombate III, antithrombin iiiFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for ATryn
ATryn® is a recombinant antithrombin indicated for the prevention of peri-operative and peri-partum thromboembolic events in hereditary antithrombin deficient patients1.
It is not indicated for treatment of thromboembolic events in hereditary antithrombin deficient patients.
2. ATryn Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use after reconstitution only.
2.1 Dose and Schedule
- ATryn dosage is to be individualized based on the patient’s pre-treatment functional AT activity level (expressed in percent of normal) and body weight (expressed in kilograms) and using therapeutic drug monitoring (Table 1).
- Treatment goal is to restore and maintain functional antithrombin (AT) activity levels between 80% - 120% of normal (0.8 - 1.2 IU/mL).
- Treatment should be initiated prior to delivery or approximately 24 hours prior to surgery to ensure that the plasma antithrombin level is in the target range at that time.
- A different dosing formula is used for the treatment of surgical and pregnant patients. Pregnant women who need a surgical procedure other than Cesarean section should be treated according to the dosing formula for pregnant patients.
- A loading dose should be administered as a 15-minute intravenous infusion, immediately followed by a continuous infusion of the maintenance dose.
- AT activity monitoring and dose adjustments should be made according to Table 2.
- Treatment should be continued until adequate follow-on anticoagulation is established.
| Surgical Patients | ||
| Loading Dose (IU) | (100 – baseline AT activity level) 2.3 | x Body Wt (kg) |
| Maintenance Dose (IU/hour) | (100 – baseline AT activity level) 10.2 | x Body Wt (kg) |
| Pregnant Women | ||
| Loading Dose (IU) | (100 – baseline AT activity level) 1.3 | x Body Wt (kg) |
| Maintenance Dose (IU/hour) | (100 – baseline AT activity level) 5.4 | x Body Wt (kg) |
AT Activity Monitoring and Dose Adjustment
AT activity monitoring is required for proper treatment. Check AT activity once or twice per day with dose adjustments made according to Table 2.
| Initial MonitorTime | AT Level | Dose Adjustment | Recheck AT Level |
| < 80% | Increase 30% | 2 hours after each dose adjustment | |
| 2 hours after initiation of treatment | 80% to 120% | None | 6 hours after initiation of treatment or dose adjustment |
| > 120% | Decrease 30% | 2 hours after each dose adjustment |
As surgery or delivery may rapidly decrease the AT activity levels, check the AT level just after surgery or delivery. If AT activity level is below 80%, an additional bolus dose may be administered to rapidly restore decreased AT activity level. In such instances, the loading dose formula in Table 1 should be used, utilizing in the calculation the last available AT activity result. Thereafter, restart the maintenance dose at the same rate of infusion as before the bolus.
2.2 Preparation
- Bring vials to room temperature no more than 3 hours prior to reconstitution.
- For the 525 IU vial, reconstitute with 3.2 mL Sterile Water for Injection [(WFI) not supplied with ATryn] immediately prior to use. Do not shake.
- For the 1750 IU vial, reconstitute with 10 mL Sterile Water for Injection [(WFI) not supplied with ATryn] immediately prior to use. Do not shake.
- Do not use solution containing visible particulates or if it is discolored or cloudy.
- Draw solution from one or more vials into a sterile disposable syringe for intravenous administration or add solution to an infusion bag containing 0.9% sterile sodium chloride for injection (e.g., dilute solution to obtain a concentration of 100 IU/mL).
2.3 Administration
- Administer using an infusion set with a 0.22 micron pore-size, in-line filter.
- Administer contents of infusion syringes or diluted solution within 24 hours of preparation when stored at room temperature (68-77°F (20-25°C)).
- Discard unused product in accordance with local requirements.
- Administer ATryn alone without mixing with other agents, with the exception of the medications in Table 3, which demonstrated compatibility with ATryn in an in vitro mixing study2 when co-infused at selected doses and infusion rates in the same IV tubing with 100 IU/mL of ATryn.
- Do not co-infuse ATryn in the same IV line with vecuronium or labetalol, since these medications demonstrated IV incompatibility (i.e., precipitation and/or reduction in ATryn activity).
| Dexmedetomidine | Magnesium Sulfate |
| Dopamine | Midazolam |
| Epinephrine | Milrinone |
| Fentanyl | Nicardipine |
| Hydralazine | Nitroprusside |
| Hydrocortisone | Norepinephrine |
| Furosemide | Vasopressin |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
ATryn is a sterile white to off white lyophilized powder supplied in single-use vials containing nominal potencies of 525 IU or 1750 IU. The actual potency is labeled on each vial and carton.
4. Contraindications
ATryn is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to goat and goat milk proteins.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Allergic-type hypersensitivity reactions are possible. Patients must be closely monitored and carefully observed for any symptoms throughout the infusion period. Patients should be informed of the early signs of hypersensitivity reactions including hives, generalized urticaria, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension, and anaphylaxis. If these symptoms occur during administration, treatment must be discontinued immediately and emergency treatment should be administered.
5.2 Coagulation Monitoring Tests
The anticoagulant effect of drugs that use antithrombin to exert their anticoagulation may be altered when ATryn is added or withdrawn. To avoid excessive or insufficient anticoagulation, coagulation tests suitable for the anticoagulant used (e.g., aPTT and anti-Factor Xa activity) are to be performed regularly, at close intervals, and in particular in the first hours following the start or withdrawal of ATryn. Additionally, monitor the patients for the occurrence of bleeding or thrombosis in such situation.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials at a frequency of ≥ 5% are hemorrhage and infusion site reaction. The serious adverse reaction that has been reported in clinical studies is hemorrhage (intra-abdominal, hemarthrosis and post procedural).
7. Drug Interactions
The anticoagulant effect of heparin and low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is enhanced by antithrombin. The half-life of antithrombin may be altered by concomitant treatment with these anticoagulants due to an altered antithrombin turnover. Thus, concurrent administration of antithrombin with heparin, low molecular weight heparin, or other anticoagulants that use antithrombin to exert their anticoagulant effect must be monitored clinically and biologically. To avoid excessive anticoagulation, regular coagulation tests (aPTT, and where appropriate, anti-Factor Xa activity) are to be performed at close intervals, with adjustment in dosage of the anticoagulant as necessary.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
ATryn is indicated for the treatment of pregnant women during the peri-partum period. Pregnant patients who need a surgical procedure other than Cesarean section are to be treated according to the dosing formula for pregnant patients.
In rats, a dose of 210 mg/kg/day ATryn (5-6 times the human dose for pregnant women) administered during most of the pregnancy and entire lactation showed a slight but statistically significant increase in pup mortality in day one through day four when compared to concurrent control (90% compared to 94% viability index for 210 mg/kg/day versus control). This slight statistical difference does not reflect a true treatment-related effect. This same dose was shown to be safe in a second rat study when administered around parturition and during lactation where the no adverse effect level for dam and pups was 210 mg/kg/day.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Studies in pregnant women have not shown that ATryn increases the risk of fetal abnormalities if administered during the third trimester of pregnancy. In clinical trials in hereditary AT deficient patients, 22 pregnant women have been treated with ATryn around parturition.
No adverse reactions were reported in 22 neonates born from pregnant women treated with ATryn during clinical trials.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
ATryn is present in breast milk at levels estimated to be 1/50 to 1/100 of its concentration in the blood. This level is the same as that estimated to be present in breast milk of normal lactating women which is not known to be harmful to breastfed neonates. However, caution should be exercised when ATryn is administered to a nursing woman. Use only if clearly needed.
In 2 reproductive toxicology studies performed in rats, antithrombin (Recombinant) was administered to pregnant dams at doses up to 210 mg/kg/day, resulting in supraphysiologic plasma levels of antithrombin. Pups were allowed to breastfeed and were monitored for changes in prothrombin (PT) or aPTT, as well as pup viability, body weight at birth, growth, and development. In these studies, there were no adverse effects in offspring who consumed milk from dams treated with ATryn.
| ATRYN
antithrombin recombinant injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| ATRYN
antithrombin recombinant injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - rEVO Biologics, Inc. (807934260) |