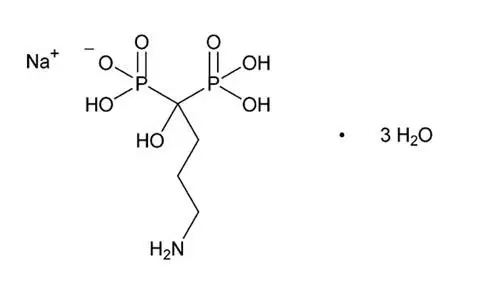
Drug Detail:Binosto (Alendronate [ a-len-dro-nate ])
Drug Class: Bisphosphonates
Highlights of Prescribing Information
BINOSTO (alendronate sodium) effervescent tablets for oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 1995
Recent Major Changes
- Dosage and Administration ( 2.3) 06/2020
- Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7) 06/2020
Indications and Usage for Binosto
BINOSTO is a bisphosphonate indicated for:
- Treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women ( 1.1)
- Treatment to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis ( 1.2)
Limitation of use:
Optimal duration
of use has not been determined. For patients at low-risk for fracture,
consider drug discontinuation after 3 to 5 years of use. (
1.3)
Binosto Dosage and Administration
- 70 mg BINOSTO effervescent tablet once weekly. ( 2.1, 2.2)
- Instruct patients to: (
2.3)
- Dissolve one tablet of BINOSTO in approximately half a glass of plain room temperature water (4 oz). Wait at least 5 minutes after the effervescence stops, stir the solution for approximately 10 seconds and consume contents.
- Swallow solution at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or medication of the day.
- Avoid lying down for at least 30 minutes after taking BINOSTO and until after the first food of the day.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Effervescent tablets, 70 mg ( 3)
Contraindications
- Abnormalities of the esophagus which delay emptying such as stricture or achalasia ( 4, 5.1)
- Inability to stand/sit upright for at least 30 minutes ( 4, 5.1)
- Increased risk of aspiration. ( 4)
- Hypocalcemia ( 4, 5.2)
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this product ( 4, 6.2)
Warnings and Precautions
- Upper Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions can occur. Instruct patients to follow dosing instructions. Discontinue if new or worsening symptoms occur. ( 5.1)
- Hypocalcemia can worsen and must be corrected prior to use. ( 5.2)
- Severe Bone, Joint, Muscle Pain may occur. Discontinue use if severe symptoms develop. ( 5.3)
- Osteonecrosis of the Jaw has been reported. ( 5.4)
- Atypical Femur Fractures have been reported. Patients with new thigh or groin pain should be evaluated to rule out a femoral fracture. ( 5.5)
- Sodium Content: Each tablet contains 603 mg sodium, equivalent to 1532 mg NaCl. Use caution in patients on sodium restriction. ( 5.7)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 3%) are abdominal pain, acid regurgitation, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, musculoskeletal pain, and nausea. (
6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact ASCEND Therapeutics at 1-877-204-1013 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
- Calcium supplements, antacids or oral medications containing multivalent cations interfere with absorption of alendronate. ( 7.1)
- Use caution when co-prescribing aspirin/nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that may worsen gastrointestinal irritation. ( 7.2, 7.3)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Discontinue when pregnancy is recognized. ( 8.1)
- BINOSTO is not indicated for use in pediatric patients. ( 8.4)
- BINOSTO is not recommended in patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 35 mL/min). ( 5.6, 8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2021
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Binosto
2. Binosto Dosage and Administration
2.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
The recommended dosage is one 70 mg effervescent tablet once weekly.
2.2 Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men With Osteoporosis
The recommended dosage is one 70 mg effervescent tablet once weekly.
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
i. Take BINOSTO upon arising for the day and at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or medication of the day.
• Patients should not swallow the undissolved effervescent tablet, should not chew the effervescent tablet or allow the effervescent tablet to dissolve in their mouths because of the risk for oropharyngeal irritation [see Warnings and Precautions (
5.1)].
Dissolve the effervescent tablet in 4 ounces room temperature plain water only (not mineral water or flavored water).
ii. Wait at least 5 minutes after the effervescence stops and then stir the buffered solution for approximately 10 seconds and ingest.
iii. Avoid lying down for at least 30 minutes after taking BINOSTO and until after their first food of the day.
iv. Do not take BINOSTO at bedtime or before arising for the day.
Failure to follow these instructions may increase the risk of esophageal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (
5.1)].
4. Contraindications
BINOSTO is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions:
- Abnormalities of the esophagus which delay esophageal emptying such as stricture or achalasia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)]
- Inability to stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.3); Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)]
Do not administer BINOSTO to patients at increased risk of aspiration
- Hypocalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)]
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this product. Hypersensitivity reactions including urticaria and angioedema have been reported [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.2)] .
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.4 Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), which can occur spontaneously, is generally associated with tooth extraction and/or local infection with delayed healing, and has been reported in patients taking bisphosphonates, including alendronate sodium. Known risk factors for osteonecrosis of the jaw include invasive dental procedures (e.g., tooth extraction, dental implants, boney surgery), diagnosis of cancer, concomitant therapies (e.g., chemotherapy, corticosteroids, angiogenesis inhibitors), poor oral hygiene, and co-morbid disorders (e.g., periodontal and/or other pre-existing dental disease, anemia, coagulopathy, infection, ill-fitting dentures). The risk of ONJ may increase with duration of exposure to bisphosphonates.
For patients requiring invasive dental procedures, discontinuation of bisphosphonate treatment may reduce the risk for ONJ. Clinical judgment of the treating physician and/or oral surgeon should guide the management plan of each patient based on individual benefit/risk assessment.
Patients who develop osteonecrosis of the jaw while on bisphosphonate therapy should receive care by an oral surgeon. In these patients, extensive dental surgery to treat ONJ may exacerbate the condition. Discontinuation of bisphosphonate therapy should be considered based on individual benefit/risk assessment.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
| * 10 mg/day for three years
** 5 mg/day for 2 years and 10 mg/day for either 1 or 2 additional years |
||||
| United States/Multinational Studies | Fracture Intervention Trial | |||
| Alendronate
Sodium* % (N=196) | Placebo
% (N=397) | Alendronate
Sodium** % (N=3236) | Placebo
% (N=3223) |
|
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Abdominal pain | 6.6 | 4.8 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Nausea | 3.6 | 4.0 | 1.1 | 1.5 |
| Dyspepsia | 3.6 | 3.5 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| Constipation | 3.1 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| Diarrhea | 3.1 | 1.8 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| Flatulence | 2.6 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Acid regurgitation | 2.0 | 4.3 | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| Esophageal ulcer | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Vomiting | 1.0 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Dysphagia | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Abdominal distention | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Gastritis | 0.5 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| Musculoskeletal | ||||
| Musculoskeletal (bone, muscle or joint) pain | 4.1 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Muscle cramp | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Nervous system/psychiatric | ||||
| Headache | 2.6 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Dizziness | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Special senses | ||||
| Taste perversion | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Once Weekly
Alendronate Sodium 70 mg % (N=519) | Once Daily
Alendronate Sodium 10 mg % (N=370) |
|
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Abdominal pain | 3.7 | 3.0 |
| Dyspepsia | 2.7 | 2.2 |
| Acid regurgitation | 1.9 | 2.4 |
| Nausea | 1.9 | 2.4 |
| Abdominal distention | 1.0 | 1.4 |
| Constipation | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| Flatulence | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| Gastritis | 0.2 | 1.1 |
| Gastric ulcer | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Musculoskeletal | ||
| Musculoskeletal (bone, muscle, joint) pain | 2.9 | 3.2 |
| Muscle cramp | 0.2 | 1.1 |
| Two-Year Study | One-Year Study | |||
| Once Daily
Alendronate Sodium 10 mg % (N=146) | Placebo
% (N=95) | Once Weekly
Alendronate Sodium 70 mg % (N=109) | Placebo
% (N=58) |
|
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Acid regurgitation | 4.1 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Flatulence | 4.1 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 0.7 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 0.0 |
| Dyspepsia | 3.4 | 0.0 | 2.8 | 1.7 |
| Diarrhea | 1.4 | 1.1 | 2.8 | 0.0 |
| Abdominal pain | 2.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 3.4 |
| Nausea | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
7. Drug Interactions
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Available data on the use of BINOSTO in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Discontinue BINOSTO when pregnancy is recognized.
In animal reproduction studies, daily oral administration of alendronate to rats from before mating through the end of gestation or lactation showed decreased postimplantation survival and decreased pup body weight gain starting at doses equivalent to less than half of the highest recommended 40 mg clinical daily dose (based on body surface area, mg/m 2). Oral administration of alendronate to rats during organogenesis resulted in reduced fetal ossification starting at doses 3 times the 40 mg clinical daily dose. No similar fetal effects were observed in pregnant rabbits dosed orally during organogenesis at doses equivalent to approximately 10 times the 40 mg clinical daily dose.
Delayed or failed delivery of offspring, protracted parturition, and late pregnancy maternal and fetal deaths due to maternal hypocalcemia occurred in rats at oral doses as low as one tenth the 40 mg clinical daily dose (See Data).
Bisphosphonates are incorporated into the bone matrix, from which they are gradually released over a period of years. The amount of bisphosphonate incorporated into adult bone and available for release into the systemic circulation is directly related to the dose and duration of bisphosphonate use. Consequently, based on the mechanism of action of bisphosphonates, there is a potential risk of fetal harm, predominantly skeletal, if a woman becomes pregnant after completing a course of bisphosphonate therapy. The impact of variables such as time between cessation of bisphosphonate therapy to conception, the particular bisphosphonate used, and the route of administration (intravenous versus oral) on the risk has not been studied.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 4% and 15 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Reproduction studies in rats dosed orally from before mating to the end of gestation or lactation showed decreased postimplantation survival starting at 2 mg/kg/day and decreased body weight gain starting at 1 mg/kg/day, doses equivalent to less than half the 40 mg clinical daily dose based on body surface area, mg/m 2. Incidence of incomplete fetal ossification in vertebral, skull, and sternebral bones were increased in rats dosed orally during organogenesis starting at 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 times the 40 mg clinical daily dose). No similar fetal effects were observed in pregnant rabbits dosed orally during organogenesis at up to 35 mg/kg/day (equivalent to approximately 10 times the 40 mg clinical daily dose).
Both total and ionized calcium decreased in pregnant rats dosed orally with 15 mg/kg/day alendronate (approximately 4 times the 40 mg clinical daily dose) resulting in delays and failures of delivery. Protracted parturition due to maternal hypocalcemia was observed when rats were treated from before mating through gestation starting at 0.5 mg/kg/day (approximately one tenth the 40 mg clinical daily dose). Maternotoxicity (late pregnancy deaths) also occurred in female rats treated orally with 15 mg/kg/day (approximately 4 times the 40 mg clinical daily dose) for varying gestational time periods. These maternal deaths were lessened but not eliminated by cessation of treatment. Calcium supplementation in the drinking water or by subcutaneous minipump to rats dosed orally with 15 mg/kg/day alendronate could not ameliorate the hypocalcemia or prevent the dystocia-related maternal and neonatal deaths. However, intravenous calcium supplementation prevented maternal, but not neonatal deaths.
8.2 Lactation
It is not known whether alendronate is present in human breast milk, affects human milk production, or has effects on the breastfed infant. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for BINOSTO and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from BINOSTO or from the underlying maternal condition.
12. Binosto - Clinical Pharmacology
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
Fracture Intervention Trial: Three-Year Study (patients with at least one baseline radiographic vertebral fracture)
| *Number evaluable for vertebral fractures: alendronate, n=984; placebo, n=966
†p<0.001, ‡p=0.007, §p<0.01, ¶p<0.05 |
||||
| Percent of Patients | ||||
| Alendronate
Sodium (N=1022) | Placebo
(N=1005) | Absolute
Reduction in Fracture Incidence | Relative
Reduction in Fracture Risk % |
|
| Patients with:
Vertebral fractures (diagnosed by X-ray)* | ||||
| ≥1 new vertebral fracture | 7.9 | 15.0 | 7.1 | 47 † |
| ≥2 new vertebral fractures | 0.5 | 4.9 | 4.4 | 90 † |
| Clinical (symptomatic) fractures | ||||
| Any clinical (symptomatic) fracture | 13.8 | 18.1 | 4.3 | 26 ‡ |
| ≥1 clinical (symptomatic) vertebral fracture | 2.3 | 5.0 | 2.7 | 54 § |
| Hip fracture | 1.1 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 51 ¶ |
| Wrist (forearm) fracture | 2.2 | 4.1 | 1.9 | 48 ¶ |
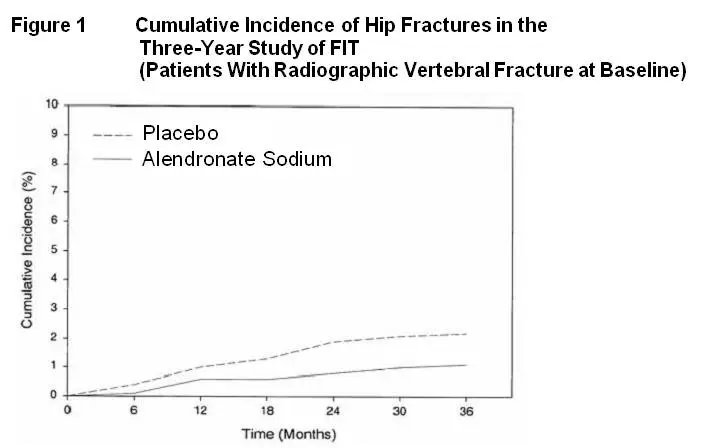
Fracture Intervention Trial: Four-Year Study (patients with low bone mass but without a baseline radiographic vertebral fracture)
| *Baseline femoral neck BMD at least 2 SD below the
mean for young adult women
†Number evaluable for vertebral fractures: alendronate, n=1426; placebo, n=1428 ‡p<0.001, §p=0.035, ¶p=0.01 #Not significant. This study was not powered to detect differences at these sites. |
||||
| Percent of Patients | ||||
| Alendronate
Sodium (n=1545) | Placebo
(n=1521) | Absolute
Reduction in Fracture Incidence | Relative
Reduction in Fracture Risk (%) |
|
| Patients with:
Vertebral fractures (diagnosed by X-ray)† | ||||
| ≥1 new vertebral fracture | 2.5 | 4.8 | 2.3 | 48 ‡ |
| ≥2 new vertebral fractures | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 78 § |
| Clinical (symptomatic) fractures | ||||
| Any clinical (symptomatic) fracture | 12.9 | 16.2 | 3.3 | 22 ¶ |
| ≥1 clinical (symptomatic) vertebral fracture | 1.0 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 41 (NS) # |
| Hip fracture | 1.0 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 29 (NS) # |
| Wrist (forearm) fracture | 3.9 | 3.8 | -0.1 | NS # |
Effect on Bone Mineral Density
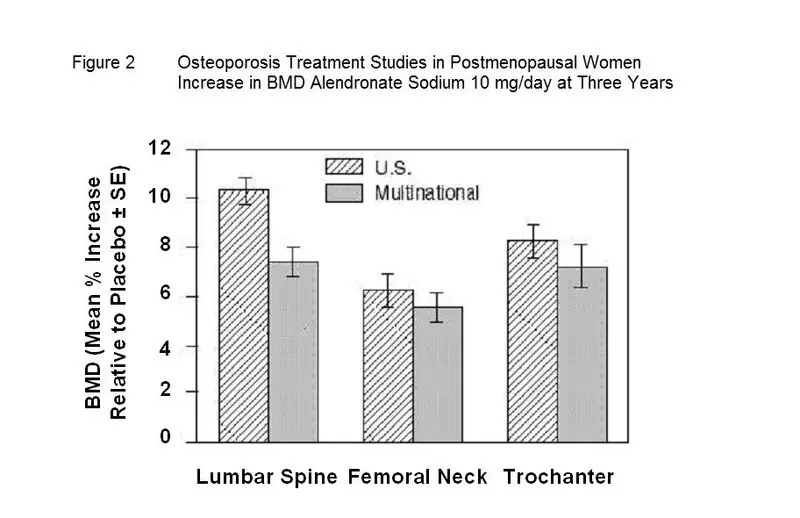
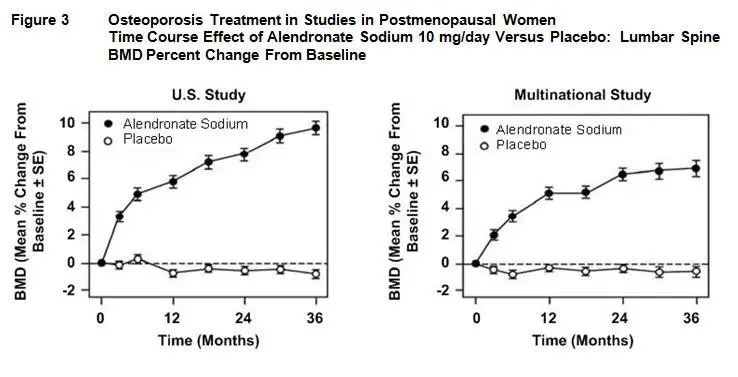
At 3 years significant increases in BMD, relative both to baseline and placebo, were seen at each measurement site in each study in patients who received alendronate 10 mg/day. Total body BMD also increased significantly in each study, suggesting that the increases in bone mass of the spine and hip did not occur at the expense of other skeletal sites. Increases in BMD were evident as early as 3 months and continued throughout the 3 years of treatment. ( See figures below for lumbar spine results.) In the 2-year extension of these studies, treatment of 147 patients with alendronate sodium 10 mg/day resulted in continued increases in BMD at the lumbar spine and trochanter (absolute additional increases between years 3 and 5: lumbar spine, 0.94%; trochanter, 0.88%). BMD at the femoral neck, forearm and total body were maintained. Alendronate sodium was similarly effective regardless of age, race, baseline rate of bone turnover, and baseline BMD in the range studied (at least 2 standard deviations below the premenopausal mean).
17. Patient Counseling Information
17.2 Dosing Instructions
Instruct patients that it is necessary to follow all dosing instructions for BINOSTO:
- BINOSTO should only be taken upon arising for the day and must be taken at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or medication of the day. Instruct patients not attempt to swallow, chew, or suck on the tablet because of a potential for oropharyngeal ulceration.
- Instruct patients to dissolve the effervescent tablet in 4 ounces room temperature plain water only (not mineral water or flavored water).
- Instruct patients to wait at least 5 minutes after the effervescence stops and then stir the solution for approximately 10 seconds and then consume the contents.
- Instruct patients to avoid lying down for at least 30 minutes after taking BINOSTO and until after their first food of the day.
- Instruct patients not to take BINOSTO at bedtime or before arising for the day.
- Instruct patients that waiting less than 30 minutes, or taking BINOSTO with food, beverages (other than plain water) or other medications will lessen the effect of BINOSTO by decreasing its absorption into the body [see Drug Interactions ( 7.1)] . Even dosing with orange juice or coffee has been shown to markedly reduce the absorption of BINOSTO [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)].
- Inform patients that failure to follow these instructions may increase their risk of esophageal problems [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)] .
Medication Guide
Medication Guide
BINOSTO
® (BIN
-oss-tow
)
(alendronate sodium)
Effervescent Tablets
What is the most important information I should know about BINOSTO Effervescent Tablet?
BINOSTO Effervescent Tablet can cause serious side effects, including:
- Esophagus problems
- Low calcium levels in your blood (hypocalcemia)
- Bone, joint, or muscle pain
- Severe jaw bone problems (osteonecrosis)
- Unusual thigh bone fractures
-
Esophagus problems.
Some people who take BINOSTO may develop problems in the esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth and the stomach). These problems include irritation, inflammation, or ulcers of the esophagus which may sometimes bleed.
● It is important that you take BINOSTO exactly as prescribed to help lower your chance of getting esophagus problems. (See the section “How should I take BINOSTO?”)
● Stop taking BINOSTO and call your doctor right away if you get chest pain, new or worsening heartburn, or have trouble or pain when you swallow. -
Low calcium levels in your blood (hypocalcemia).
BINOSTO may lower the calcium levels in your blood. If you have low blood calcium before you start taking BINOSTO, it may get worse during treatment. Your low blood calcium must be treated before you take BINOSTO. Most people with low blood calcium levels do not have symptoms, but some people may have symptoms. Call your doctor right away if you have symptoms of low blood calcium such as:
● Spasms, twitches, or cramps in your muscles
● Numbness or tingling in your fingers, toes, or around your mouth
Your doctor may prescribe calcium and vitamin D to help prevent low calcium levels in your blood, while you take BINOSTO. Take calcium and vitamin D as your doctor tells you to. -
Bone, joint, or muscle pain.
Some people who take BINOSTO develop severe bone, joint, or muscle pain. -
Severe jaw bone problems (osteonecrosis).
Severe jaw bone problems may happen when you take BINOSTO. Your doctor should examine your mouth before you start BINOSTO. Your doctor may tell you to see your dentist before you start BINOSTO. It is important for you to practice good mouth care during treatment with BINOSTO. -
Unusual thigh bone fractures.
Some people have developed unusual fractures in their thigh bone. Symptoms of a fracture may include new or unusual pain in your hip, groin, or thigh.
Call your doctor right away if you have any of these side effects.
What is BINOSTO Effervescent Tablet?
BINOSTO is a prescription medicine used to:
- Treat thinning of your bones (osteoporosis) in women after menopause. BINOSTO helps reduce the chance of having a hip or spinal fracture (break).
- Increase bone mass in men who have osteoporosis.
BINOSTO is not for use in children.
Who should not take BINOSTO Effervescent Tablet?
- Have certain problems with your esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth with your stomach
- Cannot stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes
- Have trouble swallowing liquids
- Have low levels of calcium in your blood
- Are allergic to BINOSTO or any of its ingredients. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in BINOSTO.
What should I tell my doctor before taking BINOSTO Effervescent Tablet?
- Have problems with swallowing
- Have stomach or digestive problems
- Have low blood calcium
- Plan to have dental surgery or teeth removed
- Have kidney problems
- Have been told you have trouble absorbing minerals in your stomach or intestines (malabsorption syndrome)
- Have been told to lower your salt intake
- Are pregnant, planning to become pregnant or suspect that you are pregnant. If you become pregnant while taking BINOSTO, stop taking it and contact your doctor. It is not known if BINOSTO can harm your unborn baby.
- Are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if BINOSTO passes into your milk and may harm your baby.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- calcium
- antacids
- aspirin
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory (NSAID) medicines
How should I take BINOSTO Effervescent Tablet?
- Take BINOSTO exactly as your doctor tells you.
- BINOSTO is taken 1 time each week. Choose the day of the week that best fits your schedule, then take BINOSTO on the same day every week.
- BINOSTO works only if you take it on an empty stomach.
- Take BINOSTO after you get up for the day and 30 minutes before taking your first food, drink, or other medicine.
- Take BINOSTO while you are sitting or standing.
- Do not swallow, chew or suck on a BINOSTO tablet.
-
Do not dissolve BINOSTO in:
- mineral or flavored water
- coffee
- tea
- soda
- juice
-
You must dissolve your BINOSTO effervescent tablet in plain water at room temperature before you take it. To prepare your BINOSTO liquid medicine:
Step 1. Place the BINOSTO tablet in about a half glass (4 ounces) of plain water. The water should not be cold or hot, and should be at room temperature.
Step 2. Wait at least 5 minutes after the bubbling (effervescence) stops for the BINOSTO tablet to completely dissolve in the water.
Step 3. Stir the liquid medicine for about 10 seconds.
Step 4. Drink all of the BINOSTO liquid medicine in the glass.
After you take BINOSTO, wait at least 30 minutes before you:
- lie down. You may sit, stand or walk, and do normal activities like reading.
- take your first food or drink, except for plain water.
- take other medicines, including antacids, calcium, and other supplements and vitamins.
Do not lie down until after you eat your first food of the day.
- If you miss a dose of BINOSTO, do not take it later in the day. Take your missed dose on the next morning after you remember and then return to your normal schedule. Do not take 2 doses on the same day.
- If you think you took more than your prescribed dose of BINOSTO, drink a full glass of milk and call your doctor right away. Do not try to vomit. Do not lie down.
What should I avoid while taking BINOSTO Effervescent Tablet?
What are the possible side effects of BINOSTO Effervescent Tablet?
BINOSTO may cause serious side effects.
- See “What is the most important information I should know about BINOSTO?”
The most common side effects of BINOSTO are:
- Stomach area (abdominal) pain
- Heartburn
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Upset stomach
- Pain in your bones, joints, or muscles
- Nausea
You may get allergic reactions, such as hives, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Tell your doctor about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the side effects with BINOSTO. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How should I store BINOSTO Effervescent Tablet?
- Store BINOSTO at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep BINOSTO tablets in their original blister pack until you use them.
- Protect BINOSTO from moisture.
Keep BINOSTO and all medicines out of the reach of children.
For more information, go to BINOSTO.com, or call 1-877-204-1013.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
| BINOSTO
alendronate sodium tablet, effervescent |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - ASCEND Therapeutics U.S., LLC (133780051) |
| Registrant - ASCEND Therapeutics (133780051) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| SwissCo Services AG | 480086560 | manufacture(17139-400) | |