Drug Detail:Brixadi (Buprenorphine)
Drug Class:
Highlights of Prescribing Information
BRIXADI™ (buprenorphine) extended-release injection for subcutaneous use CIII
Initial U.S. Approval: 2002
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS HARM OR DEATH WITH INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION; BRIXADI RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Serious harm or death could result if administered intravenously. (5.1)
- BRIXADI is only available through a restricted program called the BRIXADI REMS. Healthcare settings and pharmacies that order and dispense BRIXADI must be certified in this program and comply with the REMS requirements. (5.2)
Indications and Usage for Brixadi Injection
BRIXADI contains buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist.
BRIXADI is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe opioid use disorder in patients who have initiated treatment with a single dose of a transmucosal buprenorphine product or who are already being treated with buprenorphine. (1)
BRIXADI should be used as part of a complete treatment plan that includes counseling and psychosocial support. (1)
Brixadi Injection Dosage and Administration
- Only healthcare providers should prepare and administer BRIXADI. (2.1)
- BRIXADI (weekly) and BRIXADI (monthly) are different formulations. Doses of BRIXADI (weekly) cannot be combined to yield an equivalent BRIXADI (monthly) dose. (2.1)
- BRIXADI should be injected slowly, into the subcutaneous tissue of the buttock, thigh, abdomen, or upper arm (2.1)
- Strongly consider prescribing naloxone at the time BRIXADI is initiated or renewed because patients being treated for opioid use disorder have the potential for relapse, putting them at risk for opioid overdose. (2.2)
- Injection sites for BRIXADI (weekly) should be alternated/rotated for each injection. (2.7)
See Full Prescribing Information for administration instructions. (2.7)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
BRIXADI is a weekly and monthly injection provided in a pre-filled single-dose syringe with a 23 gauge ½ inch needle. (3)
- BRIXADI (weekly) is available in 8 mg/0.16 mL, 16 mg/0.32 mL, 24 mg/0.48 mL, and 32 mg/0.64 mL;
- BRIXADI (monthly) is available in 64 mg/0.18 mL, 96 mg/0.27 mL, and 128 mg/0.36 mL.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to buprenorphine or any other ingredients in BRIXADI. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse: Buprenorphine can be abused in a manner similar to other opioids. Monitor patients for conditions indicative of diversion or progression of opioid dependence and addictive behaviors. (5.3)
- Respiratory Depression: Life-threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in association with buprenorphine. Warn patients of the potential danger of self-administration of benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants while under treatment with BRIXADI. (5.4, 5.5)
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome: Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS) is an expected and treatable outcome of prolonged use of opioids during pregnancy. (5.6)
- Adrenal Insufficiency: If diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement of corticosteroids, and wean patient off of the opioid. (5.7)
- Risk of Opioid Withdrawal with Abrupt Discontinuation: If treatment with BRIXADI is discontinued, monitor patients for withdrawal and treat appropriately. (5.8)
- Risk of Hepatitis, Hepatic Events: Monitor liver function tests prior to and during treatment. (5.9)
- Latex Allergy: The packaging of this product contains natural rubber latex which may cause allergic reactions. (5.10)
- Risk of Withdrawal in Patients Dependent on Full Agonist Opioids: Administer a test dose of transmucosal buprenorphine and monitor for precipitated withdrawal before injecting BRIXADI. (5.11)
- Treatment of Emergent Acute Pain: Treat pain with a non-opioid analgesic whenever possible. If opioid therapy is required, monitor patients closely because higher doses may be required for analgesic effect. (5.12)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Adverse reactions commonly associated with BRIXADI administration (in ≥5% of patients) were injection site pain, headache, constipation, nausea, injection site erythema, injection site pruritus, insomnia, and urinary tract infection. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Braeburn at 1-833-274-9234 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors and Inducers: Monitor patients starting or ending CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers for potential over or under dosing. (7)
- Serotonergic Drugs: If concomitant use is warranted, monitor for serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment initiation, and during dose adjustment of the serotonergic drug. (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Buprenorphine passes into the mother's milk. (8.2)
- Geriatric Patients: Monitor for sedation or respiratory depression. (8.5)
- Moderate to Severe Hepatic Impairment: Not recommended. (5.14, 8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 5/2023
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS HARM OR DEATH WITH INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION; BRIXADI RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY
- Serious harm or death could result if administered intravenously. BRIXADI forms a liquid crystalline gel upon contact with body fluids and may cause occlusion, local tissue damage, and thrombo‐embolic events, including life-threatening pulmonary emboli, if administered intravenously. (5.1)
- Because of the risk of serious harm or death that could result from intravenous self‐administration, BRIXADI is only available through a restricted program called the BRIXADI REMS. Healthcare settings and pharmacies that order and dispense BRIXADI must be certified in this program and comply with the REMS requirements. (5.2)
1. Indications and Usage for Brixadi Injection
BRIXADI is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe opioid use disorder in patients who have initiated treatment with a single dose of a transmucosal buprenorphine product or who are already being treated with buprenorphine.
BRIXADI should be used as part of a complete treatment plan that includes counseling and psychosocial support.
2. Brixadi Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
FOR SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION ONLY. DO NOT ADMINISTER BRIXADI INTRAVENOUSLY, INTRAMUSCULARLY, OR INTRADERMALLY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Instructions for Use (2.6)].
- BRIXADI exists in two formulations.
- Doses of BRIXADI (weekly) cannot be combined to yield a monthly dose.
- Only healthcare providers should prepare and administer BRIXADI.
- Administer BRIXADI as a single injection. Do not divide.
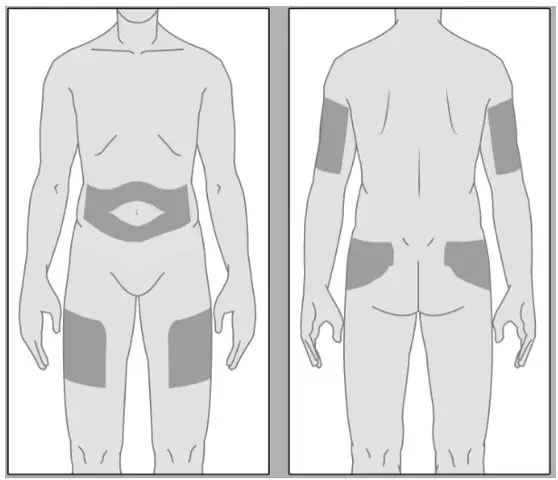
- BRIXADI should be injected slowly, into the subcutaneous tissue of the buttock, thigh, abdomen, or upper arm.
- In patients who are not currently receiving buprenorphine treatment, for BRIXADI (weekly), the upper arm site should only be used after steady-state has been achieved (4 consecutive doses) [see Instructions for Use (2.6)]. Injection in the arm site was associated with approximately 10% lower plasma levels than other sites.
- Injection sites should be alternated/rotated between injections for BRIXADI (weekly) [see Instructions for Use (2.6)].
- For all patients, the dose of BRIXADI must be individualized based on patient tolerability and/or efficacy.
- BRIXADI (weekly) should be administered in 7-day intervals.
- BRIXADI (monthly) should be administered in 28-day intervals.
- For patients not currently receiving buprenorphine treatment, begin with a test dose of 4 mg transmucosal buprenorphine to establish that buprenorphine is tolerated without precipitated withdrawal, and then transition to BRIXADI (weekly). Initiating treatment with BRIXADI as the first buprenorphine product has not been studied. Initiating treatment with BRIXADI (monthly) in new entrants to treatment has not been studied [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Patients who are currently being treated with other buprenorphine-containing products can start treatment with either BRIXADI (weekly) or BRIXADI (monthly) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Administer each injection using only the syringe and safety needle included with the product [see Instructions for Use (2.6)]. Caution: The BRIXADI needle cap is synthetically derived from natural rubber latex which may cause allergic reactions in latex-sensitive individuals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
To avoid missed doses, the weekly dose may be administered up to 2 days before or after the weekly time point, and the monthly dose may be administered up to 1 week before or after the monthly time point.
If a dose is missed, the next dose should be administered as soon as practically possible.
2.2 Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid Overdose
Discuss the availability of naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose with the patient and caregiver. Because patients being treated for opioid use disorder have the potential for relapse, putting them at risk for opioid overdose, strongly consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose, both when initiating and renewing treatment with BRIXADI. Also consider prescribing naloxone if the patient has household members (including children) or other close contacts at risk for accidental ingestion or opioid overdose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Advise patients and caregivers that naloxone may also be administered for a known or suspected overdose with buprenorphine itself. Higher than normal doses and repeated administration of naloxone may be necessary due to the long duration of action of buprenorphine and its affinity for the mu receptor [see Overdosage (10)].
Inform patients and caregivers of their options for obtaining naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program) [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
2.3 Recommended Dosing
Patients Transitioning Between BRIXADI (weekly) and BRIXADI (monthly)
Patients may be transitioned from weekly to monthly or from monthly to weekly dosing of BRIXADI based on clinical judgment (see Table 2).
| BRIXADI (weekly) | BRIXADI (monthly) |
|---|---|
| 16 mg | 64 mg |
| 24 mg | 96 mg |
| 32 mg | 128 mg |
A patient who misses a dose of BRIXADI should receive the next dose as soon as possible. BRIXADI (weekly) should be administered in 7-day intervals. BRIXADI (monthly) should be administered in 28-day intervals.
2.4 Patient Selection
Patients appropriate for BRIXADI (weekly) are:
- adults who have tolerated a single 4 mg dose of a transmucosal buprenorphine-containing product. The test dose of transmucosal buprenorphine-containing product should be administered based on instructions in the appropriate product label.
- adults who are currently being treated with a transmucosal buprenorphine-containing product.
Patients appropriate for BRIXADI (monthly) are adults who are currently being treated with a transmucosal buprenorphine-containing product. BRIXADI (monthly) is not intended for patients who are not currently receiving buprenorphine treatment.
2.5 Clinical Supervision
Periodic assessment is necessary to determine effectiveness of the treatment plan and overall patient progress. When evaluating the patient, examine the injection site for signs of infection or evidence of tampering or attempts to remove the depot.
Due to the chronic nature of opioid use disorder, the need for continuing medication-assisted treatment should be re-evaluated periodically. There is no maximum recommended duration of maintenance treatment. For some patients, treatment may continue indefinitely. If considering stopping treatment, the clinical status of the patient should be considered.
If BRIXADI is discontinued, its extended-release characteristics should be considered, and the patient should be monitored for several months for signs and symptoms of withdrawal and treated appropriately. After steady-state has been achieved, which is 4 weeks for BRIXADI (weekly) and 4 months for BRIXADI (monthly), patients discontinuing BRIXADI may have detectable plasma levels of buprenorphine for approximately 1 month for BRIXADI (weekly) and for approximately 4 months for BRIXADI (monthly). The correlation between plasma concentrations of buprenorphine and those detectable in urine is not known.
2.6 Instructions for Use
Prior to injecting BRIXADI, carefully read the instructions as well as the full prescribing information.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION:
- For subcutaneous injection only [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- To be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider only.
- Read the instructions carefully before handling the product.
- As a universal precaution, always wear gloves and inject BRIXADI under aseptic conditions.
- BRIXADI should be injected slowly, into the subcutaneous tissue of the buttock, thigh, abdomen, or upper arm.
- In patients who are not currently receiving buprenorphine treatment, for BRIXADI (weekly), the upper arm site should only be used after steady-state has been achieved (4 consecutive doses). Injection in the arm site was associated with approximately 10% lower plasma levels than other sites.
- Discard BRIXADI if the liquid contains visible particles or is cloudy. Discard BRIXADI after the expiration date shown on the carton or on the safety syringe label.
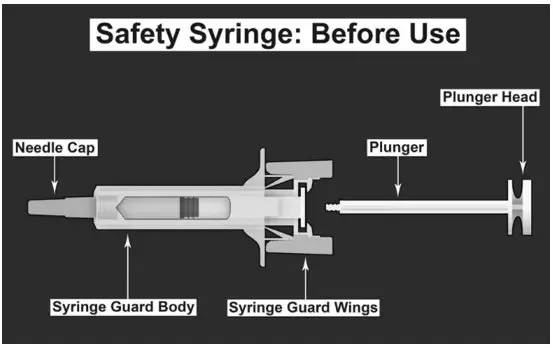
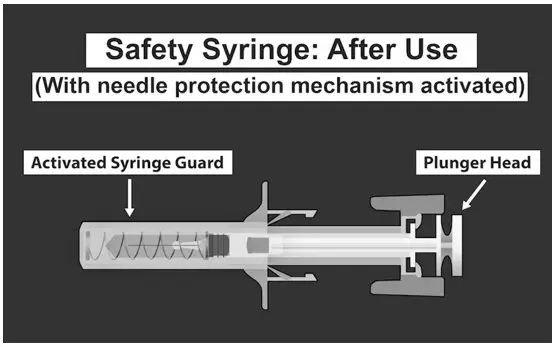
| SAFETY SYRINGE PARTS (see Figures 1, 2, and 3 below) |
|
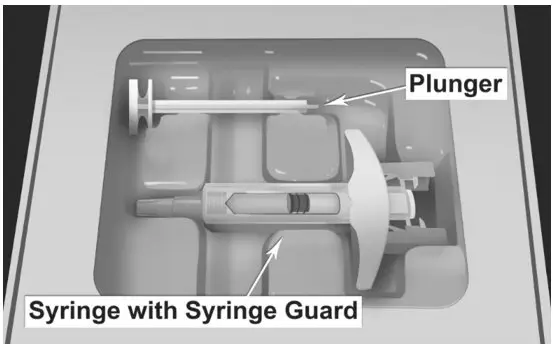
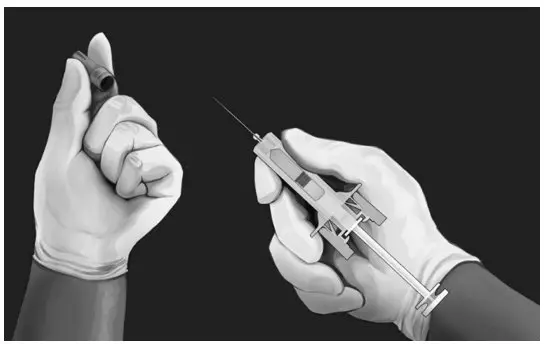
| MATERIALS NEEDED FOR INJECTION
Illustrated in Figure 4.
| Figure 4.
|
| SELECTING AN INJECTION SITE
The areas for subcutaneous injection are highlighted in Figure 5. BRIXADI should not be administered to the same site of injection for at least 8 weeks for BRIXADI (weekly). No injection site rotation is required for BRIXADI (monthly). BRIXADI should be injected slowly, into the subcutaneous tissue of the buttock, thigh, abdomen, or upper arm. In patients who are not currently receiving buprenorphine treatment, for BRIXADI (weekly), the upper arm site should only be used after steady-state has been achieved (after 4 consecutive doses) [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. | Figure 5.
|
| PREPARE THE SAFETY SYRINGE
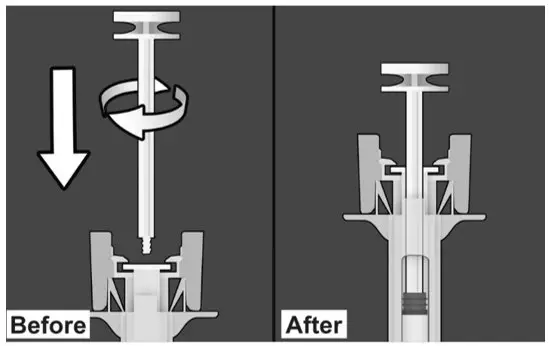
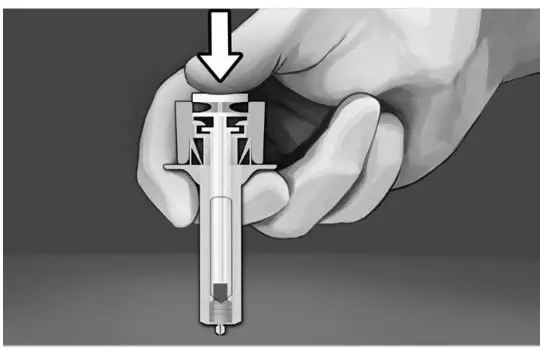
Step 1: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water prior to handling the safety syringe. Step 2: Remove the safety syringe components from the carton. Assemble the safety syringe. While holding the syringe guard body, insert the plunger into the body of the syringe and rotate clockwise until it is attached to the stopper inside the syringe as illustrated in Figure 6. | Figure 6.
|
| Step 3:
Inspect the safety syringe closely: Do not use the safety syringe after the expiration date shown on the carton or on the safety syringe label.
| |
| PREPARATION OF SITE
Step 4:
| |
| ADMINISTERING INJECTION
Step 5:
| |
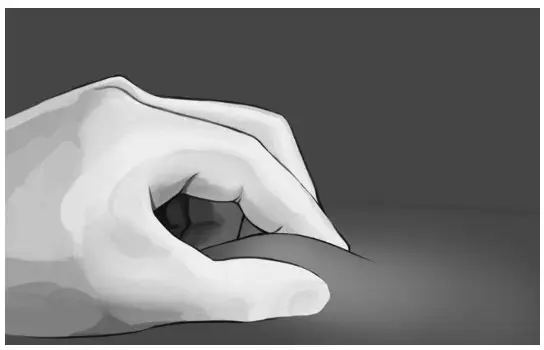
| Step 6:
Pinch the skin at the injection site between your thumb and index finger as shown in Figure 8. | |
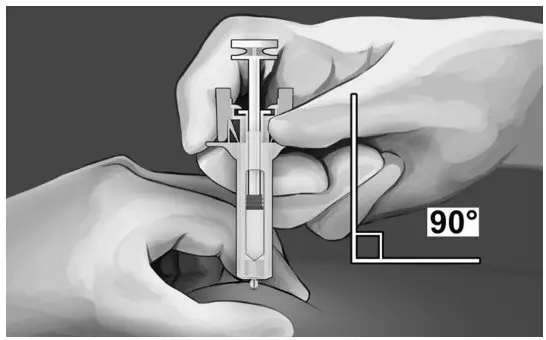
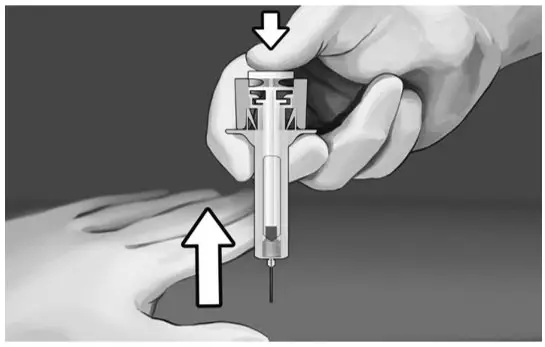
| Step 7:
Hold the syringe, as shown, and insert the needle at an angle of approximately 90° (see Figure 9). The needle is designed to inject into the subcutaneous space. It is important to fully insert the needle. | |
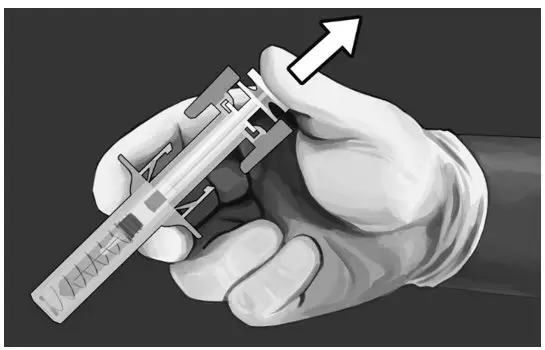
Step 8:
| |
Step 9:
| |
Step 10:
| |
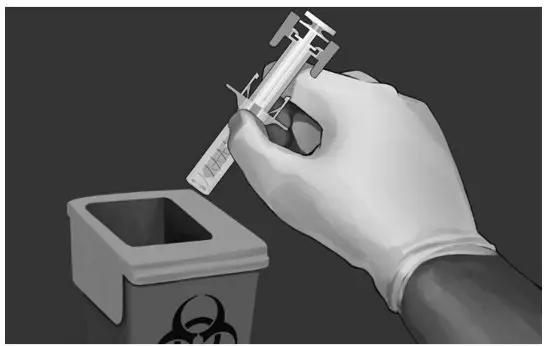
| DISPOSAL OF USED SAFETY SYRINGE
Step 11: Put the used safety syringe immediately into a sharps container (see Figure 13). POST INJECTION CARE
|
2.7 Limits on Distribution
BRIXADI is subject to a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) program that includes, among other elements, a restricted distribution program. The purpose of the restricted distribution program is to ensure that BRIXADI is only administered by a healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
BRIXADI is a sterile, yellowish to yellow-clear liquid solution and is provided as two different formulations, one for weekly and one for monthly administration in pre-filled, single-dose, syringes, with 23 gauge ½ inch needles, available in the following dosage strengths.
| BRIXADI (weekly) 50 mg/mL buprenorphine | |
|---|---|
| Dosage Strength | Dosage Volume |
| 8 mg | 0.16 mL |
| 16 mg | 0.32 mL |
| 24 mg | 0.48 mL |
| 32 mg | 0.64 mL |
| BRIXADI (monthly) 356 mg/mL buprenorphine | |
|---|---|
| Dosage Strength | Dosage Volume |
| 64 mg | 0.18 mL |
| 96 mg | 0.27 mL |
| 128 mg | 0.36 mL |
4. Contraindications
BRIXADI is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic shock) to buprenorphine, or any other ingredients in the solution for injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risk of Serious Harm or Death with Intravenous Administration
Intravenous injection presents significant risk of serious harm or death as BRIXADI forms a liquid crystalline gel upon contact with body fluids. Occlusion, local tissue damage, and thrombo-embolic events, including life-threatening pulmonary emboli, could result if administered intravenously [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2)]. Do not administer intravenously, intramuscularly, or intradermally.
5.2 BRIXADI Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS)
BRIXADI is available only through a restricted program called the BRIXADI REMS because of the risk of serious harm or death that could result from intravenous self-administration. The goal of the REMS is to mitigate serious harm or death that could result from intravenous self-administration by ensuring that healthcare settings and pharmacies are certified and only dispense BRIXADI directly to a healthcare provider for administration by a healthcare provider.
Notable requirements of the BRIXADI REMS include the following:
- Healthcare Settings and Pharmacies that order and dispense BRIXADI must be certified in the BRIXADI REMS.
- Certified Healthcare Settings and Pharmacies must establish processes and procedures to verify BRIXADI is provided directly to a healthcare provider for administration by a healthcare provider, and the drug is not dispensed to the patient.
- Certified Healthcare Settings and Pharmacies must not distribute, transfer, loan, or sell BRIXADI.
Further information is available at www.BRIXADIREMS.com or by calling 1-833-274-9234.
5.3 Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
BRIXADI contains buprenorphine, a Schedule III controlled substance that can be abused in a manner similar to other opioids. Buprenorphine is sought by people with opioid use disorder and is subject to criminal diversion. Monitor all patients for progression of opioid use disorder and addictive behaviors [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2)].
5.4 Risk of Life-Threatening Respiratory and Central Nervous System (CNS) Depression
Buprenorphine has been associated with life-threatening respiratory depression and death. Many, but not all, postmarketing reports regarding coma and death involved misuse by self-injection or were associated with the concomitant use of buprenorphine and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressant drugs including alcohol. Warn patients of the potential danger of self-administration of benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants while under treatment with BRIXADI [see Drug Interactions (7), Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Use BRIXADI with caution in patients with compromised respiratory function (e.g., chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cor pulmonale, decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or pre-existing respiratory depression).
Due to its extended-release characteristics, if BRIXADI is discontinued as a result of compromised respiratory function, monitor patients for ongoing buprenorphine effects for approximately 1 month for BRIXADI (weekly) and for approximately 4 months for BRIXADI (monthly).
Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize respiratory depression and emphasize the importance of calling 911 or getting emergency medical help right away in the event of a known or suspected overdose [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Opioids can cause sleep-related breathing disorders including central sleep apnea (CSA) and sleep related hypoxemia. Opioid use increases the risk of CSA in a dose-dependent fashion. In patients who present with CSA, monitor patient during treatment and consider dose reduction using best practices for opioid taper. [see Clinical Supervision (2.6)].
5.5 Managing Risks From Concomitant Use of Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants with Buprenorphine
Concomitant use of buprenorphine and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants increases the risk of adverse reactions including respiratory depression, overdose, and death. Medication-assisted treatment of opioid use disorder, however, should not be categorically denied to patients taking these drugs. Prohibiting or creating barriers to treatment can pose an even greater risk of morbidity and mortality due to the opioid use disorder alone.
As a routine part of orientation to buprenorphine treatment, educate patients about the risks of concomitant use of benzodiazepines sedatives, opioid analgesics, and alcohol.
Develop strategies to manage use of prescribed or illicit benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants at initiation of buprenorphine treatment, or if it emerges as a concern during treatment. Adjustments to induction procedures and additional monitoring may be required. There is no evidence to support dose limitations or arbitrary caps of buprenorphine as a strategy to address benzodiazepine use in buprenorphine-treated patients. However, if a patient is sedated at the time of buprenorphine dosing, delay or omit the buprenorphine dose if appropriate.
Cessation of benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants is preferred in most cases of concomitant use with buprenorphine. In some cases, monitoring in a higher level of care for taper may be appropriate. In others, gradually tapering a patient off of a prescribed benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant or decreasing to the lowest effective dose may be appropriate.
For patients in buprenorphine treatment, benzodiazepines are not the treatment of choice for anxiety or insomnia. Before co-prescribing benzodiazepines, ensure that patients are appropriately diagnosed and consider alternative medications and non-pharmacologic treatments to address anxiety or insomnia. Ensure that other healthcare providers prescribing benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants are aware of the patients' buprenorphine treatment and coordinate care to minimize the risks associated with concomitant use.
If concomitant use is warranted, strongly consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose, as is recommended for all patients in buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
In addition, take measures to confirm that patients are taking their medications as prescribed and are not diverting or supplementing with illicit drugs. Toxicology screening should test for prescribed and illicit benzodiazepines [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.6 Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS) is an expected and treatable outcome of prolonged use of opioids during pregnancy, whether that use is medically-authorized or illicit. Unlike opioid withdrawal syndrome in adults, NOWS may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated in the neonate. Healthcare providers should observe newborns for signs of NOWS and manage accordingly [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise pregnant women receiving opioid addiction treatment with BRIXADI of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. This risk must be balanced against the risk of untreated opioid addiction which often results in continued or relapsing illicit opioid use and is associated with poor pregnancy outcomes. Therefore, prescribers should discuss the importance and benefits of management of opioid addiction throughout pregnancy.
5.7 Adrenal Insufficiency
Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use. Presentation of adrenal insufficiency may include non-specific symptoms and signs including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. If adrenal insufficiency is suspected, confirm the diagnosis with diagnostic testing as soon as possible. If adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids. Wean the patient off of the opioid to allow adrenal function to recover and continue corticosteroid treatment until adrenal function recovers. Other opioids may be tried as some cases reported use of a different opioid without recurrence of adrenal insufficiency. The information available does not identify any particular opioids as being more likely to be associated with adrenal insufficiency.
5.8 Risk of Opioid Withdrawal with Abrupt Discontinuation of BRIXADI Treatment
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu-opioid receptor and chronic administration produces physical dependence of the opioid type, characterized by withdrawal signs and symptoms upon abrupt discontinuation or rapid taper. The withdrawal syndrome is milder than that seen with full agonists and may be delayed in onset [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
Patients who elect to discontinue BRIXADI treatment should be monitored for withdrawal signs and symptoms with consideration given to the product's extended-release characteristics [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Consider transmucosal buprenorphine if needed to treat withdrawal after discontinuing BRIXADI.
5.9 Risk of Hepatitis, Hepatic Events
Cases of cytolytic hepatitis and hepatitis with jaundice have been observed in individuals receiving buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid use disorder, both in clinical trials and through postmarketing adverse event reports.
The spectrum of abnormalities ranges from transient asymptomatic elevations in hepatic transaminases to case reports of death, hepatic failure, hepatic necrosis, hepatorenal syndrome, and hepatic encephalopathy. In many cases, the presence of pre-existing liver enzyme abnormalities, infection with hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus, concomitant usage of other potentially hepatotoxic drugs, and ongoing injection drug abuse may have played a causative or contributory role. In other cases, insufficient data were available to determine the etiology of the abnormality. Withdrawal of buprenorphine has resulted in amelioration of acute hepatitis in some cases; however, in other cases no dose reduction was necessary. The possibility exists that buprenorphine had a causative or contributory role in the development of the hepatic abnormality in some cases.
Liver function tests are recommended prior to initiation of treatment to establish a baseline. Periodic monitoring of liver function during treatment is also recommended. A biological and etiological evaluation is recommended when a hepatic event is suspected. Monitor patients with declining hepatic function for side effects resulting from increased exposure to buprenorphine.
5.10 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Cases of hypersensitivity to buprenorphine containing products have been reported both in clinical trials and in the postmarketing experience. Cases of bronchospasm, angioneurotic edema, and anaphylactic shock have been reported. The most common signs and symptoms include rashes, hives, and pruritus. A history of hypersensitivity to buprenorphine or other components is a contraindication to the use of BRIXADI [see Contraindications (4)].
5.11 Precipitation of Opioid Withdrawal Signs and Symptoms
Because of the partial agonist properties of buprenorphine, BRIXADI injection may precipitate opioid withdrawal signs and symptoms in individuals physically dependent on full opioid agonists such as heroin, morphine, or methadone before the effects of the full opioid agonist have subsided.
In patients who are new entrants to treatment, administer a test dose of transmucosal buprenorphine and monitor for precipitated withdrawal and treat appropriately [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.12 Risks Associated with Treatment of Emergent Acute Pain
While on BRIXADI, situations may arise where patients need acute pain management, or may require anesthesia. Treat patients receiving BRIXADI with non-opioid analgesic whenever possible. Patients requiring opioid therapy for analgesia may be treated with a high-affinity full opioid analgesic under the supervision of a healthcare provider, with particular attention to respiratory function. Higher doses may be required for analgesic effect. Therefore, a higher potential for toxicity exists with opioid administration. If opioid therapy is required as part of anesthesia, patients should be continuously monitored in an anesthesia care setting by persons not involved in the conduct of the surgical or diagnostic procedure. The opioid therapy should be provided by individuals specifically trained in the use of anesthetic drugs and the management of the respiratory effects of potent opioids, specifically the establishment and maintenance of a patent airway and assisted ventilation.
Advise patients of the importance of instructing their family members, in the event of emergency, to inform the treating healthcare provider or emergency room staff that the patient is physically dependent on an opioid and that the patient is being treated with BRIXADI [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Please refer to Section 2.5 for further details on duration of exposure following discontinuation for both weekly and monthly BRIXADI formulations. [see Clinical Supervision (2.5)].
5.13 Use in Opioid Naïve Patients
There have been reported deaths of opioid naïve individuals who received a 2 mg dose of buprenorphine as a sublingual tablet. BRIXADI is not appropriate for use in opioid naïve patients.
5.14 Use in Patients With Impaired Hepatic Function
In a pharmacokinetic study with transmucosal buprenorphine, buprenorphine plasma levels were found to be higher and the half-life was found to be longer in subjects with moderate and severe hepatic impairment, but not in subjects with mild hepatic impairment. The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of BRIXADI, has not been studied.
Because of the long-acting nature of the product, adjustments to dosages of BRIXADI are not rapidly reflected in plasma buprenorphine levels. Because buprenorphine levels cannot be rapidly decreased, patients with pre-existing moderate to severe hepatic impairment are not candidates for treatment with BRIXADI.
Patients who develop moderate to severe hepatic impairment while being treated with BRIXADI should be monitored for several months for signs and symptoms of toxicity or overdose caused by increased levels of buprenorphine and patients may require a dose adjustment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.15 QTc Prolongation
Thorough QT studies with buprenorphine products have demonstrated QT prolongation ≤ 15 msec. This QTc prolongation effect does not appear to be mediated by hERG channels. Based on these two findings, buprenorphine is unlikely to be pro-arrhythmic when used alone in patients without risk factors. The risk of combining buprenorphine with other QT- prolonging agents is not known.
Consider these observations in clinical decisions when prescribing BRIXADI to patients with risk factors such as hypokalemia, bradycardia, recent conversion from atrial fibrillation, congestive heart failure, digitalis therapy, baseline QT prolongation, subclinical long-QT syndrome, or severe hypomagnesemia. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
5.16 Impairment of Ability to Drive and Operate Machinery
BRIXADI may impair the mental or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially dangerous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery, especially for the first few days following treatment and dose adjustment. Buprenorphine plasma levels accumulate during the BRIXADI (weekly) or BRIXADI (monthly) injections, which achieves steady-state at the fourth weekly or monthly injection. Caution patients about driving or operating hazardous machinery until they are reasonably certain that BRIXADI does not adversely affect their ability to engage in such activities. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.17 Orthostatic Hypotension
Buprenorphine may produce orthostatic hypotension in ambulatory patients.
5.18 Elevation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure
Buprenorphine may elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure and should be used with caution in patients with head injury, intracranial lesions, and other circumstances where cerebrospinal pressure may be increased. Buprenorphine can produce miosis and changes in the level of consciousness that may interfere with patient evaluation.
5.19 Elevation of Intracholedochal Pressure
Buprenorphine has been shown to increase intracholedochal pressure, as do other opioids, and thus should be administered with caution to patients with dysfunction of the biliary tract.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Respiratory and CNS Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Adrenal Insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Opioid Withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8, 5.11)]
- Hepatitis, Hepatic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Orthostatic Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17)]
- Elevation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)]
- Elevation of Intracholedochal Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.19)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of BRIXADI was evaluated in 440 opioid-dependent patients across two, Phase 3 clinical studies: one double-blind, active-control (n=213) and one open-label (n=227). In these studies, a total of 305 patients were exposed to BRIXADI for at least 24 weeks and 132 patients were exposed for at least 48 weeks.
In the first 12-week phase of the double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled study, patients received BRIXADI (weekly) (16, 24, 32 mg) or matching placebo injections after a one-week titration. In the second 12-week phase of the study, patients remaining in the study received BRIXADI (monthly) (64, 96, 128, or 160 mg) or matching placebo injections. The 160 mg monthly dose is not an approved dose. Those randomized to receiving placebo injections were the active control groups and received sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablets at corresponding doses to BRIXADI. Patients receiving active BRIXADI injections also received placebo sublingual tablets.
Adverse reactions led to premature discontinuation in 10 (4.7%) patients in the group receiving BRIXADI compared to 5 (2.3%) patients in the sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone group, during the double-blind study.
Adverse reactions commonly reported after BRIXADI administration (≥5%, regardless of dose and regimen) in the double-blind study, were injection site pain (9.9%), headache (7.5%), constipation (7.5%), nausea (7.0%), injection site erythema (6.6%), injection site pruritus (6.1%), Insomnia (5.6%), and urinary tract infection (5.2%).
Table 5 shows the adverse reactions for BRIXADI compared with the active-control group (SL BPN/NX) in the double-blind study.
| System Organ Class (SOC) | BRIXADI Total* | SL BPN/NX† |
|---|---|---|
| Preferred Term (PT)‡ | (N=213) n(%) | (N=215) n(%) |
|
||
| Cardiac disorders | 6 (2.8%) | 9 (4.2%) |
| Tachycardia | 5 (2.3) | 5 (2.3) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 43 (20.2%) | 45 (20.9%) |
| Constipation | 16 (7.5) | 16 (7.4) |
| Diarrhea | 6 (2.8) | 7 (3.3) |
| Nausea | 15 (7.0) | 17 (7.9) |
| Vomiting | 9 (4.2) | 8 (3.7) |
| Infections and infestations | 42 (19.7%) | 50 (23.3%) |
| Urinary tract infection | 11 (5.2) | 10 (4.7) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 9 (4.2) | 9 (4.2) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | 20 (9.4%) | 22 (10.2%) |
| Arthralgia | 7 (3.3) | 3 (1.4) |
| Nervous system disorders | 27 (12.7%) | 27 (12.6%) |
| Headache | 16 (7.5) | 17 (7.9) |
| Psychiatric disorders | 20 (9.4%) | 20 (9.3%) |
| Anxiety | 6 (2.8) | 7 (3.3) |
| Insomnia | 12 (5.6) | 6 (2.8) |
Injection site reactions in the double-blind study are presented in Table 6 below. The majority of injection site-related adverse events were mild or moderate in severity. No injection site reactions were reported as severe intensity.
| Preferred Term (PT)* | BRIXADI Total†
(N=213) n(%) | SL BPN/NX‡
(N=215) n(%) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Administration site reactions§ | 44 (20.7%) | 49 (22.8%) |
| Injection site pain | 21 (9.9%) | 17 (7.9%) |
| Injection site erythema | 14 (6.6%) | 12 (5.6%) |
| Injection site pruritus | 13 (6.1%) | 13 (6.0%) |
| Injection site swelling | 10 (4.7%) | 7 (3.3%) |
| Injection site reaction | 9 (4.2%) | 7 (3.3%) |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of buprenorphine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The most frequently reported postmarketing adverse event observed with buprenorphine sublingual tablets, excluding drug exposure during pregnancy, was drug misuse or abuse.
Serotonin syndrome: Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of opioids with serotonergic drugs.
Adrenal insufficiency: Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use.
Anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis has been reported with buprenorphine [see Contraindications (4)].
Androgen deficiency: Cases of androgen deficiency have occurred with chronic use of opioids [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of an identical buprenorphine extended-release injection for subcutaneous use outside of the United States and are not described elsewhere in the label. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Injection site mass, abscess, ulceration, and necrosis: Cases of injection site abscess, ulceration and necrosis have been reported after treatment initiation. Some cases have required debridement and antibiotic treatment. The likelihood of serious injection site reactions may be increased with inadvertent intramuscular or intradermal administration.
Insufficient dosing: Cases of drug withdrawal reactions consistent with insufficient drug dosing have been reported, often occurring at or after two weeks of treatment initiation and resolving upon dose increase.
7. Drug Interactions
| Benzodiazepines and other Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants | |
| Clinical Impact: | Due to additive pharmacologic effects, the concomitant use of benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, increases the risk of respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death. |
| Intervention: | Cessation of benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants is preferred in most cases of concomitant use. In some cases, monitoring in a higher level of care for taper may be appropriate. In others, gradually tapering a patient off a prescribed benzodiazepine or CNS depressant or decreasing to the lowest effective dose may be appropriate. Similarly, cessation of other CNS depressants is preferred when possible. Before co-prescribing benzodiazepines for anxiety or insomnia, ensure that patients are appropriately diagnosed and consider alternative medications and non-pharmacologic treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. If concomitant use is warranted, strongly consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose, as is recommended for all patients in treatment for opioid use disorder [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. |
| Examples: | Alcohol, non-benzodiazepine sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, and other opioids. |
| Inhibitors of CYP3A4 | |
| Clinical Impact: | The effects on buprenorphine exposure in patients treated with BRIXADI have not been studied, and the effects may be dependent on the route of administration. Buprenorphine is metabolized to norbuprenorphine primarily by CYP3A4; therefore, potential interactions may occur when BRIXADI is given concurrently with agents that affect CYP3A4 activity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The concomitant use of buprenorphine and CYP3A4 inhibitors can increase the plasma concentration of buprenorphine, resulting in increased or prolonged opioid effects, particularly when an inhibitor is added after a stable dose of BRIXADI is achieved. |
| Intervention: | Patients Converted to BRIXADI Treatment from a Regimen of Transmucosal Buprenorphine used Concomitantly with CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Monitor to ensure that the plasma buprenorphine level provided by BRIXADI is adequate. Patients Already on BRIXADI who Require Newly-Initiated Treatment with a CYP3A4 Inhibitor: Monitor for signs and symptoms of over-medication. If signs and symptoms of buprenorphine toxicity or overdose occur but the concomitant medication cannot be reduced or discontinued, reduce the dose of BRIXADI. If available doses do not permit achievement of the desired dose, it may be necessary to discontinue treatment with BRIXADI and treat the patient with a formulation of buprenorphine that permits more precise dose adjustments. Patients Stabilized on BRIXADI in the Setting of Concomitant Medication That is a CYP3A4 Inhibitor, and the Concomitant Medication is Discontinued: Monitor for withdrawal and consider a dosage adjustment of BRIXADI. If the dose of BRIXADI cannot be adjusted to an adequate level in the absence of the concomitant medication, transition the patient back to a formulation of buprenorphine that permits more precise dose adjustments. |
| Examples: | azole antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole), macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin), and protease inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, indinavir, and saquinavir) |
| CYP3A4 Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact: | The effects of co-administered CYP3A4 inducers on buprenorphine exposure in patients treated with BRIXADI have not been studied. Buprenorphine is metabolized to norbuprenorphine primarily by CYP3A4; therefore, potential interactions may occur when BRIXADI is given concurrently with agents that affect CYP3A4 activity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. CYP3A4 inducers may induce metabolism of buprenorphine and, therefore, may cause increased clearance of the drug which could lead to a decrease in buprenorphine plasma concentrations, lack of efficacy or, possibly, development of an abstinence syndrome. |
| Intervention: | Patients Converted to BRIXADI Treatment from a Regimen of Transmucosal Buprenorphine used Concomitantly with CYP3A4 Inducers: Monitor to ensure that the plasma buprenorphine level provided by BRIXADI is adequate. Patients Already on BRIXADI who Require Newly-Initiated Treatment with a CYP3A4 Inducer: Monitor for withdrawal. If the dose of BRIXADI is not adequate in the presence of the concomitant medication, and the concomitant medication cannot be reduced or discontinued, adjust the dose of BRIXADI. If the dose of BRIXADI cannot be adjusted to an adequate level, transition the patient back to a formulation of buprenorphine that permits more precise dose adjustments. Patients Stabilized on BRIXADI in the setting of Concomitant Medication that is a CYP3A4 Inducer, and the Concomitant Medication is Discontinued: Monitor for signs and symptoms of over-medication. If the dose provided by BRIXADI is excessive in the absence of the concomitant inducer, consider reducing the dose of BRIXADI. If the dose of BRIXADI cannot be adjusted to an adequate level, transition the patient back to a formulation of buprenorphine that permits more precise dose adjustments [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Examples: | Rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital |
| Antiretrovirals: Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) | |
| Clinical Impact: | Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are metabolized principally by CYP3A4. Efavirenz, nevirapine, and etravirine are known CYP3A4 inducers, whereas delaviridine is a CYP3A4 inhibitor. Significant pharmacokinetic interactions between NNRTIs (e.g., efavirenz and delviradine) and buprenorphine have been shown in clinical studies, but these pharmacokinetic interactions did not result in any significant pharmacodynamics effects. |
| Intervention: | It is recommended that patients who are on BRIXADI treatment have their dose monitored for increase or decrease in therapeutic effects if NNRTIs are added to their treatment regimen. |
| Examples: | Efavirenz, nevirapine, etravirine, delavirdine |
| Antiretrovirals: Protease Inhibitors (PIs) | |
| Clinical Impact: | Studies have shown some antiretroviral protease inhibitors (PIs) with CYP3A4 inhibitory activity (e.g., nelfinavir, lopinavir/ritonavir, ritonavir) have little effect on buprenorphine pharmacokinetics and no significant pharmacodynamics effects. Other PIs with CYP3A4 inhibitory activity (e.g., atazanavir and atazanavir/ritonavir) resulted in elevated levels of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine and patients in one study reported increased sedation. Symptoms of opioid excess have been found in postmarketing reports of patients receiving buprenorphine and atazanavir with and without ritonavir concomitantly. |
| Intervention: | If treatment with atazanavir with and without ritonavir must be initiated in a patient already treated with BRIXADI, the patient should be monitored for signs and symptoms of over-medication. It may be necessary to discontinue treatment with BRIXADI and treat the patient with a sublingual buprenorphine product that permits rapid dose adjustments. |
| Examples: | Atazanavir, ritonavir |
| Antiretrovirals: Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) | |
| Clinical impact: | Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) do not appear to induce or inhibit the P450 enzyme pathway, thus no interactions with buprenorphine are expected. |
| Intervention: | None |
| Serotonergic Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of opioids with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system has resulted in serotonin syndrome. |
| Intervention: | If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation, and during dose adjustment of the serotonergic drug. Discontinue BRIXADI if serotonin syndrome is suspected. |
| Examples: | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), triptans, S-HT3 receptor antagonists, drugs that affect serotonin neurotransmitter system (e.g., mirtazapine, trazodone, tramadol), certain muscle relaxants (i.e. cyclobenzaprine, metaxalone), and monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue). |
| Monomaine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) | |
| Clinical Impact: | MAOI interactions with opioids may manifest as serotonin syndrome or opioid toxicity (e.g., respiratory depression, coma). |
| Intervention: | The use of BRIXADI is not recommended for patients taking MAOIs or within 14 days of stopping such treatment. |
| Examples: | Phenelzine, tranylcypromine, linezolid |
| Muscle Relaxants | |
| Clinical Impact: | Buprenorphine may enhance the neuromuscular blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produce an increased degree of respiratory depression. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients receiving muscle relaxants and BRIXADI for signs of respiratory depression that may be greater than otherwise expected and decrease the dosage of the muscle relaxant as necessary. Due to the risk of respiratory depression with concomitant use of skeletal muscle relaxants and opioids, strongly consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.5)]. |
| Diuretics | |
| Clinical Impact: | Opioids can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing the release of antidiuretic hormone. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients for signs of diminished diuresis and/or effects on blood pressure and increase the dosage of the diuretic needed. |
| Anticholinergic Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs may increase the risk of urinary retention and/or severe constipation, which may lead to paralytic ileus. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients for signs of urinary retention or reduced gastric motility when BRIXADI is used concomitantly with anticholinergic drugs. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of BRIXADI have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of BRIXADI did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 or older to determine whether they respond differently to the drug than younger patients. Other reported clinical experience with buprenorphine has not identified differences in responses between the geriatric and younger patients.
Due to possible decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy in geriatric patients, the decision to prescribe BRIXADI should be made cautiously in individuals 65 years of age or older and these patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of toxicity or overdose.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of BRIXADI has not been studied.
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of sublingual buprenorphine has been evaluated in a pharmacokinetic study. While no clinically significant changes were observed in subjects with mild hepatic impairment, the plasma levels have been shown to be higher and half-life values have been shown to be longer for buprenorphine in subjects with moderate and severe hepatic impairment.
Because of the long-acting nature of the product, adjustments to dosages of BRIXADI are not rapidly reflected in plasma buprenorphine levels. Therefore, patients with pre-existing moderate to severe hepatic impairment are not candidates for treatment with BRIXADI.
Patients who develop moderate to severe hepatic impairment while being treated with BRIXADI should be monitored for signs and symptoms of toxicity or overdose caused by increased levels of buprenorphine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
BRIXADI contains buprenorphine, a Schedule III substance under the Controlled Substances Act.
9.2 Abuse
Abuse is the intentional, non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its desirable psychological or physiological effects. Misuse is the intentional use, for therapeutic purposes, of a drug by an individual in a way other than prescribed by a healthcare provider or for whom it was not prescribed.
BRIXADI contains buprenorphine, a Schedule III controlled substance that can be abused similar to other opioids. Patients who continue to misuse, abuse, or divert buprenorphine products or other opioids should be provided with or referred for more intensive and structured treatment. Abuse of buprenorphine poses a risk of overdose and death. This risk is increased with the abuse of buprenorphine and alcohol and other substances, especially benzodiazepines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
BRIXADI is distributed through a restricted distribution program, which is intended to prevent the direct distribution to a patient. BRIXADI should only be dispensed directly to a healthcare provider for administration by a healthcare provider. It is supplied in prefilled syringes and is intended for administration only by subcutaneous injection by a healthcare provider. The entire contents of the prefilled syringe should be administered. After administration, a small amount of BRIXADI may remain in the needle and syringe should be properly disposed of [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
Upon injection, BRIXADI spontaneously transforms from a low viscous solution to a liquid crystalline gel that encapsulates buprenorphine and releases it at a steady rate as the depot biodegrades [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Clinical monitoring for evidence at the injection site of tampering or attempting to remove the depot should be ongoing throughout treatment. No attempts to remove BRIXADI have been reported in clinical trials.
9.3 Dependence
Physical dependence is a state that develops as a result of physiological adaptation in response to repeated drug use, manifested by withdrawal signs and symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug.
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu-opioid receptor and chronic administration produces physical dependence of the opioid type, characterized by moderate withdrawal signs and symptoms upon abrupt discontinuation or rapid taper. The withdrawal syndrome is typically milder than seen with full agonists and may be delayed in onset. Monitor patients during discontinuation of BRIXADI for symptoms of withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Due to the long-acting nature of BRIXADI, withdrawal signs and symptoms may not be evident immediately following the discontinuation of treatment.
Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS) is an expected and treatable outcome of prolonged use of opioids during pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
11. Brixadi Injection Description
BRIXADI (buprenorphine) extended-release injection is a sterile, yellowish to yellow clear liquid provided in a single-dose, pre-filled syringe intended for subcutaneous injection only. BRIXADI is designed to deliver buprenorphine at a controlled rate over either one week or one month.
The active ingredient in BRIXADI is buprenorphine free base, a partial opioid agonist.
BRIXADI is provided in multiple doses with two durations (weekly and monthly).
- BRIXADI (weekly; 8, 16, 24, 32 mg) consists of 50 mg/mL buprenorphine base, 10% w/w anhydrous ethanol and soybean phosphatidylcholine/glycerol dioleate in a weight ratio 50/50 to final volume.
- BRIXADI (monthly; 64, 96, 128 mg) consists of 356 mg/mL buprenorphine base, 30% w/w N-methyl pyrrolidine and soybean phosphatidylcholine/glycerol dioleate in weight ratio 40/60 to final volume.
Upon injection, BRIXADI spontaneously transforms from a low viscous solution to a liquid crystalline gel that encapsulates buprenorphine and releases it at a steady rate as the depot biodegrades.
Different drug product strengths, or doses, are accomplished by different syringe fill volumes [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3)].
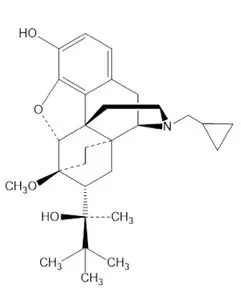
The molecular weight of buprenorphine free base is 467.65 g/mol, and its molecular formula is C29H41NO4. Chemically, buprenorphine is: (2S)-2-[17-(Cyclopropylmethyl)-4,5α-epoxy-3-hydroxy-6α,14-ethano-14α-morphinan-7α-yl]-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol.
The structural formula is:
12. Brixadi Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
BRIXADI contains buprenorphine, a partial agonist at the mu-opioid receptor and an antagonist at the kappa-opioid receptor.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
14. Clinical Studies
The key studies from the BRIXADI clinical development program that support its use in the treatment of moderate to severe opioid use disorder are a Phase 3, double-blind, active control (sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone), efficacy and safety study (NCT02651584), and an opioid blockade study (NCT02611752). Additionally, a Phase 3, open-label safety study (NCT0267211) provides data to support the safety of converting from daily transmucosal buprenorphine, buprenorphine/naloxone or generic equivalents.
14.1 Opioid Blockade Study, NCT02611752
The opioid blockade study assessed the blockade of subjective opioid effects, PK, and safety of BRIXADI weekly in 47 patients with moderate or severe opioid use disorder. Forty-six patients completed the study. Subjects were randomized to receive two injections of BRIXADI (weekly) once weekly for 2 weeks either at a 24 mg or 32 mg dose level.
After stabilization on immediate-release morphine, all patients completed a 3-day qualification/baseline hydromorphone (HM) challenge session, which included intramuscular administration of 3 doses of HM (0 mg [placebo], 6 mg and 18 mg) once daily for 3 consecutive days. Patients were not exposed to buprenorphine during the baseline/qualification phase.
Following the qualification phase, eligible patients were randomly assigned to receive 2 doses of either 24 mg (22 patients) or 32 mg (24 patients) BRIXADI (weekly) with each dose administered one week apart. Two HM challenge sessions (Days 1-3 and 4-6 for the first session and Days 8-10 and 11-13 for the second session, respectively) were conducted after each dose of BRIXADI (weekly).
The primary endpoint was the peak effect (Emax) on a 100-mm bipolar (i.e., 50=neutral response) "Drug Liking" Visual Analog Scale (VAS). The pre-defined upper bound of the 95% CI for complete blockade of drug liking was an 11 mm difference between VAS Emax scores obtained for HM doses compared with placebo.
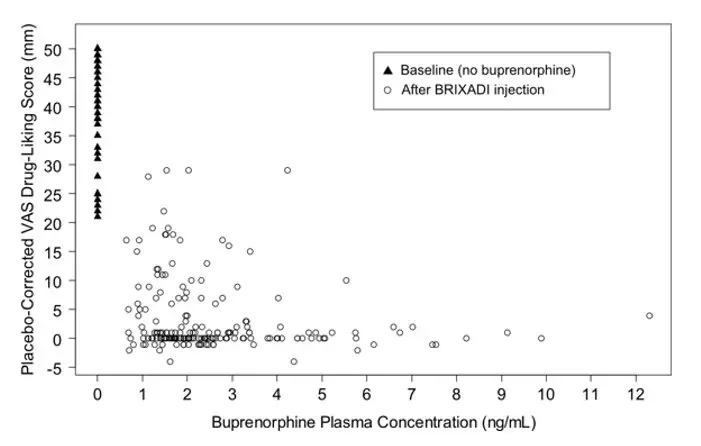
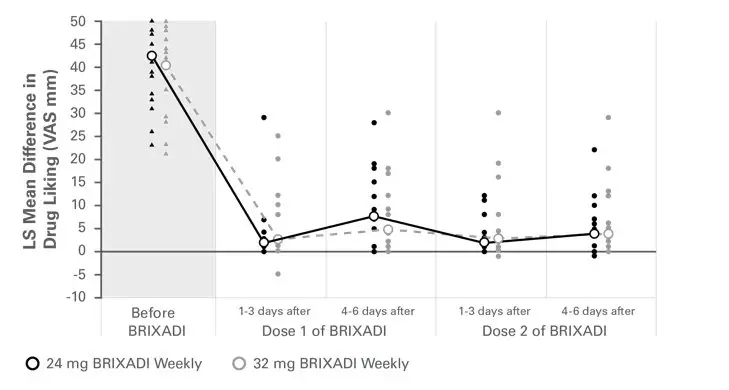
During the qualification/baseline phase, mean Emax scores for placebo were neutral while intramuscular hydromorphone 6 and 18 mg produced dose-related increases in the scores. Beginning with the first injection of BRIXADI (weekly) 24 mg or 32 mg weekly, no active intramuscular hydromorphone dose resulted in a mean drug liking VAS Emax score of 11 mm or greater when compared to placebo, which demonstrated complete blockade that was sustained throughout the first and second dosing intervals (see Figure 15). Individual subject scores are shown in Figure 16.
Figure 15: Mean Difference in Placebo-Corrected Peak Drug Liking
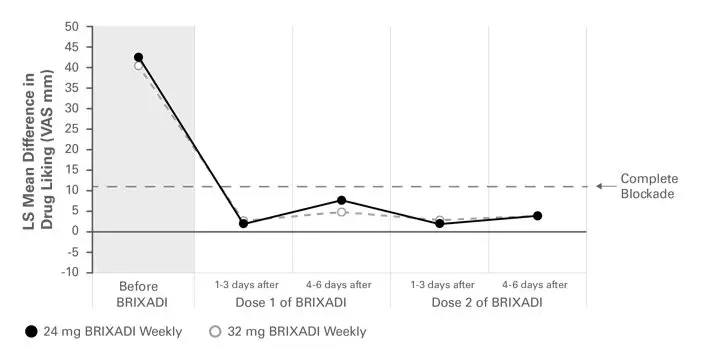
Figure 16: Mean Difference in Placebo-Corrected Peak Drug Liking with Individual Scores
14.2 Phase 3 Double-Blind Study, NCT02651584
The efficacy and safety of BRIXADI for the treatment of opioid use disorder was evaluated in a Phase 3, 24-Week, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active controlled, multicenter study in patients who met the DSM-5 criteria for moderate or severe opioid use disorder and who were actively seeking but not currently receiving buprenorphine treatment. Patients were randomized to receive either BRIXADI injections with placebo sublingual tablets or sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone (SL BPN/NX) tablets with placebo injections. All patients received individual drug counseling for the duration of the study.
On the first day of treatment patients received an open-label 4 mg test dose of sublingual buprenorphine. Patients who tolerated the test dose (two patients did not tolerate the test dose) were randomized and given a 16 mg injection of BRIXADI (weekly) or matched placebo. During the next 6 days patients were allowed up to two further 8 mg injections as needed. Patients received an injection of 16, 24, or 32 mg on Day 8 matched to the dose they received in the previous seven days. Patients received injections weekly (every 7 days +/- 2-day window) for twelve weeks total and then transitioned to an equivalent dose of BRIXADI (monthly) (every 28 days, +/- 7-day window) for the remaining twelve weeks. Dose adjustments were permitted for the duration of the study. Supplemental 8 mg BRIXADI (weekly) injections were allowed during the second phase of the study and were also used in the active-controlled group. Overall, supplemental 8 mg injections were given to 14 patients (6.6%) in the BRIXADI arm and 17 patients (7.9%) in the SL BPN/NX arm. Table 8 shows the doses of BRIXADI (weekly) administered following the initial titration period and at the final visit before transition to BRIXADI (monthly) was allowed. Table 9 shows the first and final BRIXADI (monthly) dose administered to each patient.
| BRIXADI (weekly) Dose | Following Titration Period | End of Weekly Phase |
|---|---|---|
| 16 mg | 2 | 6 |
| 24 mg | 128 | 84 |
| 32 mg | 54 | 64 |
| BRIXADI (monthly) Dose | First BRIXADI (monthly) dose | Final BRIXADI (monthly) dose |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| 64 mg | 8 | 11 |
| 96 mg | 84 | 83 |
| 128 mg | 66 | 56 |
| 160 mg* | 0 | 8 |
For the first twelve weeks patients completed weekly visits. For the final twelve weeks patients were transitioned to monthly visits. Patients were also required to complete three additional randomly scheduled visits during the final twelve weeks. Efficacy was evaluated using urine drug screens combined with self-reported use of illicit opioid use. Missing urine drug screen samples and/or self-reports were counted as positive for illicit opioids.
A total of 428 patients were randomized equally (215 patients in the SL BPN/NX group and 213 in the BRIXADI group). Of the randomized patients, 69.0% (147/213) of the patients in BRIXADI treatment group and 72.6% (156/215) of the patients in the SL BPN/NX treatment group completed the 24-week period. Patient demographics and baseline characteristics are provided in Table 10.
| BRIXADI (N=213) | SL BPN/NX (N=215) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Mean Age (Years) | 38.7 | 38.0 |
| Sex % | ||
| Male | 56.8 | 66.0 |
| Female | 43.2 | 34.0 |
| Race or Ethnicity % | ||
| White | 74.6 | 76.3 |
| Black or African American | 22.1 | 22.3 |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| Asian | 0.5 | 0 |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 0.5 | 0 |
| Other | 1.4 | 0.9 |
| Primary Opioid of Use at Initiation % | ||
| Heroin | 71.4 | 70.2 |
| Prescription Pain Reliever | 28.6 | 29.8 |
| Injectable Route % | 53.5 | 51.2 |
| Substance Use by Urine Toxicology Prior to Randomization % | ||
| Amphetamines | 22.1 | 18.6 |
| Barbiturates | 1.4 | 0.5 |
| Benzodiazepine | 21.1 | 21.9 |
| Cocaine | 30.5 | 32.6 |
| Cannabinoids | 34.3 | 36.3 |
| Fentanyl | 29.1 | 22.8 |
| Phencyclidine | 1.9 | 0.5 |
| Medical History % | ||
| Anxiety | 14.1 | 18.6 |
| Back Pain | 15.5 | 18.6 |
| Depression | 11.7 | 13.0 |
Table 11 below illustrates the proportion of patients who were considered to be responders. A patient was a responder if they met all of the following criteria:
- Negative opioid assessment (urinalysis and self-report) during week 12 (evaluated during week 13 visit).
- No more than one positive opioid assessment in the three illicit opioid use assessments performed during week 9 to 11 (evaluated during visits at weeks 10 to 12).
- Negative opioid assessment during the final month of the study.
- No more than one positive opioid assessment at the three scheduled monthly visits and three random site visits.
This responder definition was designed to identify patients who were successfully treated with both BRIXADI (weekly) (administered in the first 12 weeks of treatment) and BRIXADI (monthly) (administered in the second 12 weeks of treatment). Therefore, patients were required to have negative opioid assessments at the end of each treatment phase. Each phase also included an allowable grace period (an initial period of time when positive opioid assessments were not taken into account) and the definition also allowed for sporadic positive assessments. Based on the results of this trial, the efficacy of BRIXADI was demonstrated. Table 11 shows the response rate for each treatment arm along with the associated 95% confidence interval for their difference.
| BRIXADI Injection with placebo sublingual tablets (N=213) | SL BPN/NX Tablets with Placebo Injections (N=215) | Treatment Difference (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| 36 (16.9%) | 30 (14.0%) | 2.9% (-3.9%, 9.8%)* |
The cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the percentage of negative opioid assessments (urine samples negative for illicit opioid use combined with self-reports negative for illicit opioid use) from Week 4 through Week 24 are shown in Figure 17 and Table 12. The figure and table are cumulative, so that a patient whose percentage of opioid-free assessments is, for example 50%, is also included at every level of negative opioid assessments below 50%. Missing values and values after premature discontinuation were considered positive. Based on the CDF of the percentage of negative opioid assessments, superiority was demonstrated with BRIXADI with statistical significance compared with SL BPN/NX. However, on the right-hand side of the curves where patients were reporting mostly negative opioid assessments (80% or greater) there was little to no difference between BRIXADI and SL BPN/NX.
Figure 17: Patients Achieving Varying Percentages of Negative Opioid Assessments (urine and self-report) in weeks 4 through 24
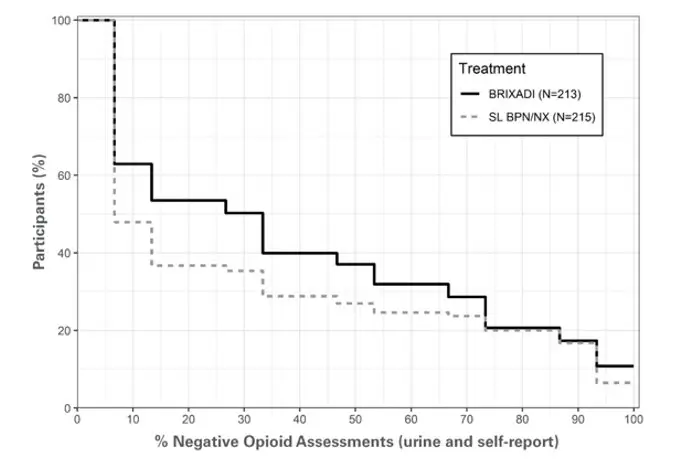
| Percentage of Opioid-Negative Assessments (Urine and Self Report) | Number (%) of Patients | |
|---|---|---|
| BRIXADI N=213 | SL BPN/NX N=215 |
|
| ≥ 0% | 213 (100.0) | 215 (100.0) |
| ≥ 10% | 121 (56.8) | 87 (40.5) |
| ≥ 20% | 114 (53.5) | 79 (36.7) |
| ≥ 30% | 95 (44.6) | 67 (31.2) |
| ≥ 40% | 85 (39.9) | 62 (28.8) |
| ≥ 50% | 74 (34.7) | 56 (26.0) |
| ≥ 60% | 68 (31.9) | 53 (24.7) |
| ≥ 70% | 51 (23.9) | 49 (22.8) |
| ≥ 80% | 44 (20.7) | 43 (20.0) |
| ≥ 90% | 28 (13.1) | 27 (12.6) |
| ≥ 100% | 23 (10.8) | 14 (6.5) |
16. How is Brixadi Injection supplied
Weekly and monthly BRIXADI is available as a sterile, yellowish to yellow clear liquid solution in a single dose, prefilled safety syringe.
The BRIXADI needle cap is synthetically derived from natural rubber latex, which may cause allergic reactions in latex sensitive individuals.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Instruct patients to read the Medication Guide each time BRIXADI is administered because new information may be available.
Safe Use
Before initiating treatment with BRIXADI, explain the points listed below to patients and caregivers.
|
Medication Guide BRIXADI™ (brix-a-dee) (buprenorphine) extended-release injection, for subcutaneous use (CIII) |
|
|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U. S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: 05/2023 |
What is the most important information I should know about BRIXADI?
|
|
| What is BRIXADI?
BRIXADI is a prescription medicine used to treat moderate to severe opioid addiction (dependence) to opioid drugs (prescription or illegal) in people:
|
|
| Who should not receive BRIXADI? Do not receive BRIXADI if you are allergic to buprenorphine or any ingredients in BRIXADI. See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of ingredients in BRIXADI . |
|
Before receiving BRIXADI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you have:
|
|
How will I receive BRIXADI?
|
|
What should I avoid while receiving BRIXADI?
|
|
| What are the possible side effects of BRIXADI? BRIXADI can cause serious side effects, including:
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of BRIXADI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information that is written for healthcare professionals. |
|
| What are the ingredients in BRIXADI? Active ingredient: buprenorphine Inactive ingredients: BRIXADI weekly: anhydrous ethanol and soybean phosphatidylcholine/glycerol dioleate. BRIXADI monthly: N-methyl pyrrolidine and soybean phosphatidylcholine/glycerol dioleate. |
|
| Distributed by Braeburn, Inc., Plymouth Meeting, PA 19462, USA. © 2023 Braeburn, Inc. BRIXADI™ is a trademark of Braeburn Inc. Manufactured by: Pharmaceutics International, Inc. (Pii), Cockeysville MD 21030 For more information, go to www.BRIXADI.com or call 1-833-274-9234 | |
Carton - Single-dose Prefilled Syringe Kit - 8 mg Weekly Dose - BRIXADI
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Brixadi™
(buprenorphine) extended-release
injection for subcutaneous use
CIII
WEEKLY
For Subcutaneous Use Only
8 mg
0.16 mL
of a 50 mg/mL solution
per syringe (Weekly)
WARNING: SERIOUS HARM OR DEATH COULD
RESULT IF INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY.
SINGLE-DOSE PREFILLED SYRINGE KIT
CONTENTS:
- One (1) sterile prefilled syring with needle shield. 8 mg (buprenorphine) per syringe
- One (1) plunger rod
- Prescribing Information
- Instructions for Use
- Medication Guide
For Healthcare Provider
Administration Only.
Do Not Dispense to Patient.
Attention: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Giude to each patient.
Rx ONLY
Distributed by: Braeburn Inc.
Plymouth Meeting, PA 19462
Properly dispose of BRIXADI™ syringes per facility
procedure for a Schedule III drug product, and per
applicable federal, state, and local regulations.
Once-weekly subcutaneous injection for
treatment of opiod use disorder. For questions,
call 1-833-274-9234.
05/23 126980
NDC 58284-208-01

Carton - Single-dose Prefilled Syringe Kit - 16 mg Weekly Dose - BRIXADI
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Brixadi™
(buprenorphine) extended-release
injection for subcutaneous use
CIII
WEEKLY
For Subcutaneous Use Only
16 mg
0.32 mL
of a 50 mg/mL solution
per syringe (Weekly)
WARNING: SERIOUS HARM OR DEATH COULD
RESULT IF INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY.
SINGLE-DOSE PREFILLED SYRINGE KIT
CONTENTS:
- One (1) sterile prefilled syring with needle shield. 16 mg (buprenorphine) per syringe
- One (1) plunger rod
- Prescribing Information
- Instructions for Use
- Medication Guide
For Healthcare Provider
Administration Only.
Do Not Dispense to Patient.
Attention: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Giude to each patient.
Rx ONLY
Distributed by: Braeburn Inc.
Plymouth Meeting, PA 19462
Properly dispose of BRIXADI™ syringes per facility
procedure for a Schedule III drug product, and per
applicable federal, state, and local regulations.
Once-weekly subcutaneous injection for
treatment of opiod use disorder. For questions,
call 1-833-274-9234.
05/23 126981
NDC 58284-216-01

Carton - Single-dose Prefilled Syringe Kit - 24 mg Weekly Dose - BRIXADI
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Brixadi™
(buprenorphine) extended-release
injection for subcutaneous use
CIII
WEEKLY
For Subcutaneous Use Only
24 mg
0.48 mL
of a 50 mg/mL solution
per syringe (Weekly)
WARNING: SERIOUS HARM OR DEATH COULD
RESULT IF INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY.
SINGLE-DOSE PREFILLED SYRINGE KIT
CONTENTS:
- One (1) sterile prefilled syring with needle shield. 24 mg (buprenorphine) per syringe
- One (1) plunger rod
- Prescribing Information
- Instructions for Use
- Medication Guide
For Healthcare Provider
Administration Only.
Do Not Dispense to Patient.
Attention: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Giude to each patient.
Rx ONLY
Distributed by: Braeburn Inc.
Plymouth Meeting, PA 19462
Properly dispose of BRIXADI™ syringes per facility
procedure for a Schedule III drug product, and per
applicable federal, state, and local regulations.
Once-weekly subcutaneous injection for
treatment of opiod use disorder. For questions,
call 1-833-274-9234.
05/23 126982
NDC 58284-224-01

Carton - Single-dose Prefilled Syringe Kit - 32 mg Weekly Dose - BRIXADI
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Brixadi™
(buprenorphine) extended-release
injection for subcutaneous use
CIII
WEEKLY
For Subcutaneous Use Only
32 mg
0.64 mL
of a 50 mg/mL solution
per syringe (Weekly)
WARNING: SERIOUS HARM OR DEATH COULD
RESULT IF INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY.
SINGLE-DOSE PREFILLED SYRINGE KIT
CONTENTS:
- One (1) sterile prefilled syring with needle shield. 32 mg (buprenorphine) per syringe
- One (1) plunger rod
- Prescribing Information
- Instructions for Use
- Medication Guide
For Healthcare Provider
Administration Only.
Do Not Dispense to Patient.
Attention: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Giude to each patient.
Rx ONLY
Distributed by: Braeburn Inc.
Plymouth Meeting, PA 19462
Properly dispose of BRIXADI™ syringes per facility
procedure for a Schedule III drug product, and per
applicable federal, state, and local regulations.
Once-weekly subcutaneous injection for
treatment of opiod use disorder. For questions,
call 1-833-274-9234.
05/23 126983
NDC 58284-232-01

Carton - Single-dose Prefilled Syringe Kit - 64 mg Monthly Dose - BRIXADI
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Brixadi™
(buprenorphine) extended-release
injection for subcutaneous use
CIII
MONTHLY
For Subcutaneous Use Only
64 mg
0.18 mL
of a 356 mg/mL solution
per syringe (Monthly)
WARNING: SERIOUS HARM OR DEATH COULD
RESULT IF INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY.
SINGLE-DOSE PREFILLED SYRINGE KIT
CONTENTS:
- One (1) sterile prefilled syring with needle shield. 64 mg (buprenorphine) per syringe
- One (1) plunger rod
- Prescribing Information
- Instructions for Use
- Medication Guide
For Healthcare Provider
Administration Only.
Do Not Dispense to Patient.
Attention: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Giude to each patient.
Rx ONLY
Distributed by: Braeburn Inc.
Plymouth Meeting, PA 19462
Properly dispose of BRIXADI™ syringes per facility
procedure for a Schedule III drug product, and per
applicable federal, state, and local regulations.
Once-monthly subcutaneous injection for
treatment of opiod use disorder. For questions,
call 1-833-274-9234.
05/23 126984
NDC 58284-264-01

Carton - Single-dose Prefilled Syringe Kit - 96 mg Monthly Dose - BRIXADI
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Brixadi™
(buprenorphine) extended-release
injection for subcutaneous use
CIII
MONTHLY
For Subcutaneous Use Only
96 mg
0.27 mL
of a 356 mg/mL solution
per syringe (Monthly)
WARNING: SERIOUS HARM OR DEATH COULD
RESULT IF INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY.
SINGLE-DOSE PREFILLED SYRINGE KIT
CONTENTS:
- One (1) sterile prefilled syring with needle shield. 96 mg (buprenorphine) per syringe
- One (1) plunger rod
- Prescribing Information
- Instructions for Use
- Medication Guide
For Healthcare Provider
Administration Only.
Do Not Dispense to Patient.
Attention: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Giude to each patient.
Rx ONLY
Distributed by: Braeburn Inc.
Plymouth Meeting, PA 19462
Properly dispose of BRIXADI™ syringes per facility
procedure for a Schedule III drug product, and per
applicable federal, state, and local regulations.
Once-monthly subcutaneous injection for
treatment of opiod use disorder. For questions,
call 1-833-274-9234.
05/23 126985
NDC 58284-296-01

Carton - Single-dose Prefilled Syringe Kit - 128 mg Monthly Dose - BRIXADI
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Brixadi™
(buprenorphine) extended-release
injection for subcutaneous use
CIII
MONTHLY
For Subcutaneous Use Only
128 mg
0.36 mL
of a 356 mg/mL solution
per syringe (Monthly)
WARNING: SERIOUS HARM OR DEATH COULD
RESULT IF INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY.
SINGLE-DOSE PREFILLED SYRINGE KIT
CONTENTS:
- One (1) sterile prefilled syring with needle shield. 128 mg (buprenorphine) per syringe
- One (1) plunger rod
- Prescribing Information
- Instructions for Use
- Medication Guide
For Healthcare Provider
Administration Only.
Do Not Dispense to Patient.
Attention: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Giude to each patient.
Rx ONLY
Distributed by: Braeburn Inc.
Plymouth Meeting, PA 19462
Properly dispose of BRIXADI™ syringes per facility
procedure for a Schedule III drug product, and per
applicable federal, state, and local regulations.
Once-monthly subcutaneous injection for
treatment of opiod use disorder. For questions,
call 1-833-274-9234.
05/23 126986
NDC 58284-228-01

| BRIXADI
buprenorphine injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| BRIXADI
buprenorphine injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| BRIXADI
buprenorphine injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| BRIXADI
buprenorphine injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| BRIXADI
buprenorphine injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| BRIXADI
buprenorphine injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| BRIXADI
buprenorphine injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Braeburn Inc. (078763433) |
| Registrant - Braeburn Inc. (078763433) |