Drug Detail:Brukinsa (Zanubrutinib)
Drug Class: BTK inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
BRUKINSA® (zanubrutinib) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1.4) | 1/2023 |
| Dosage and Administration (2.3) | 1/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.5) | 1/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Brukinsa
BRUKINSA is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy. (1.1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial. - Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM). (1.2)
- Relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) who have received at least one anti–CD20-based regimen. (1.3)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial. - Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). (1.4)
Brukinsa Dosage and Administration
- Recommended dosage: 160 mg orally twice daily or 320 mg orally once daily; swallow whole with water and with or without food. (2.1)
- Reduce BRUKINSA dose in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (2.2, 8.7)
- Advise patients not to open, break, or chew capsules. (2.1)
- Manage toxicity using treatment interruption, dose reduction, or discontinuation. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules: 80 mg. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hemorrhage: Monitor for bleeding and manage appropriately. (5.1)
- Infections: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection, including opportunistic infections, and treat as needed. (5.2)
- Cytopenias: Monitor complete blood counts during treatment. (5.3)
- Second Primary Malignancies: Other malignancies have developed including skin cancers and non-skin carcinomas. Monitor and advise patients to use sun protection. (5.4)
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: Monitor for signs and symptoms of arrhythmias and manage appropriately. (5.5)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (≥30%), including laboratory abnormalities, are neutrophil count decreased, upper respiratory tract infection, platelet count decreased, hemorrhage, and musculoskeletal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact BeiGene at 1-877-828-5596 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- CYP3A Inhibitors: Modify BRUKINSA dose with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors as described. (2.3, 7.1)
- CYP3A Inducers: Avoid coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers. Dose adjustment may be recommended with moderate CYP3A inducers. (2.3, 7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Brukinsa
1.1 Mantle Cell Lymphoma
BRUKINSA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
1.2 Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia
BRUKINSA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
1.3 Marginal Zone Lymphoma
BRUKINSA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) who have received at least one anti–CD20-based regimen.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
2. Brukinsa Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of BRUKINSA is 160 mg taken orally twice daily or 320 mg taken orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
BRUKINSA can be taken with or without food. Advise patients to swallow capsules whole with water. Advise patients not to open, break, or chew the capsules. If a dose of BRUKINSA is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible on the same day with a return to the normal schedule the following day.
2.2 Dosage Modification for Use in Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dosage of BRUKINSA for patients with severe hepatic impairment is 80 mg orally twice daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Recommended dosage modifications of BRUKINSA for drug interactions are provided in Table 1 [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
| Coadministered Drug | Recommended BRUKINSA Dosage (Starting Dose: 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily) |
|---|---|
| Strong CYP3A inhibitor | 80 mg once daily. Interrupt dose as recommended for adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. |
| Moderate CYP3A inhibitor | 80 mg twice daily. Modify dose as recommended for adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. |
| Strong CYP3A inducer | Avoid concomitant use. |
| Moderate CYP3A inducer | Avoid concomitant use. If these inducers cannot be avoided, increase BRUKINSA dose to 320 mg twice daily. |
After discontinuation of a CYP3A inhibitor or moderate CYP3A4 inducer, resume previous dose of BRUKINSA [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Recommended dosage modifications of BRUKINSA for Grade 3 or higher adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
| Adverse Reaction | Adverse Reaction Occurrence | Dosage Modification (Starting Dose: 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Hematological toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | ||
| Grade 3 or Grade 4 febrile neutropenia Platelet count decreased to 25,000-50,000/mm3 with significant bleeding Neutrophil count decreased to <500/mm3 (lasting more than 10 consecutive days) Platelet count decreased to <25,000/mm3 (lasting more than 10 consecutive days) | First | Interrupt BRUKINSA Once toxicity has resolved to Grade 1 or lower or baseline: Resume at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily. |
| Second | Interrupt BRUKINSA Once toxicity has resolved to Grade 1 or lower or baseline: Resume at 80 mg twice daily or 160 mg once daily. |
|
| Third | Interrupt BRUKINSA Once toxicity has resolved to Grade 1 or lower or baseline: Resume at 80 mg once daily. |
|
| Fourth | Discontinue BRUKINSA | |
| Non-hematological toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | ||
| Severe or life-threatening non-hematological toxicities* | First | Interrupt BRUKINSA Once toxicity has resolved to Grade 1 or lower or baseline: Resume at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily.* |
| Second | Interrupt BRUKINSA Once toxicity has resolved to Grade 1 or lower or baseline: Resume at 80 mg twice daily or 160 mg once daily. |
|
| Third | Interrupt BRUKINSA Once toxicity has resolved to Grade 1 or lower or baseline: Resume at 80 mg once daily. |
|
| Fourth | Discontinue BRUKINSA | |
Asymptomatic lymphocytosis should not be regarded as an adverse reaction, and these patients should continue taking BRUKINSA.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules: Each 80 mg capsule is a size 0, white to off-white opaque capsule marked with "ZANU 80" in black ink.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hemorrhage
Fatal and serious hemorrhage has occurred in patients with hematological malignancies treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. Grade 3 or higher hemorrhage including intracranial and gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hematuria, and hemothorax was reported in 3.6% of patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy in clinical trials, with fatalities occurring in 0.3% of patients. Bleeding of any grade, excluding purpura and petechiae, occurred in 30% of patients.
Bleeding has occurred in patients with and without concomitant antiplatelet or anticoagulation therapy. Coadministration of BRUKINSA with antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications may further increase the risk of hemorrhage.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Discontinue BRUKINSA if intracranial hemorrhage of any grade occurs. Consider the benefit-risk of withholding BRUKINSA for 3-7 days pre and post surgery depending upon the type of surgery and the risk of bleeding.
5.2 Infections
Fatal and serious infections (including bacterial, viral, or fungal infections) and opportunistic infections have occurred in patients with hematological malignancies treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. Grade 3 or higher infections occurred in 24% of patients, most commonly pneumonia (11%), with fatal infections occurring in 2.9% of patients. Infections due to hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation have occurred.
Consider prophylaxis for herpes simplex virus, pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, and other infections according to standard of care in patients who are at increased risk for infections. Monitor and evaluate patients for fever or other signs and symptoms of infection and treat appropriately.
5.3 Cytopenias
Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias, including neutropenia (22%), thrombocytopenia (8%), and anemia (7%) based on laboratory measurements, developed in patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Grade 4 neutropenia occurred in 11% of patients, and Grade 4 thrombocytopenia occurred in 2.8% of patients.
Monitor complete blood counts regularly during treatment and interrupt treatment, reduce the dose, or discontinue treatment as warranted [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Treat using growth factor or transfusions, as needed.
5.4 Second Primary Malignancies
Second primary malignancies, including non-skin carcinoma, have occurred in 13% of patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. The most frequent second primary malignancy was non-melanoma skin cancer, reported in 7% of patients. Other second primary malignancies included malignant solid tumors (5%), melanoma (1.2%), and hematologic malignancies (0.5%). Advise patients to use sun protection and monitor patients for the development of second primary malignancies.
5.5 Cardiac Arrhythmias
Serious cardiac arrhythmias have occurred in patients treated with BRUKINSA. Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter were reported in 3.7% of 1550 patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy, including Grade 3 or higher cases in 1.7% of patients. Patients with cardiac risk factors, hypertension, and acute infections may be at increased risk. Grade 3 or higher ventricular arrhythmias were reported in 0.2% of patients.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of cardiac arrhythmias (e.g., palpitations, dizziness, syncope, dyspnea, chest discomfort), manage appropriately [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)], and consider the risks and benefits of continued BRUKINSA treatment.
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals, BRUKINSA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Administration of zanubrutinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused embryo-fetal toxicity, including malformations at exposures that were 5 times higher than those reported in patients at the recommended dose of 160 mg twice daily. Advise women to avoid becoming pregnant while taking BRUKINSA and for 1 week after the last dose. Advise men to avoid fathering a child during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cytopenias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Second Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cardiac Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to BRUKINSA as a single-agent in nine clinical trials, administered at 160 mg twice daily in 1445 patients and at 320 mg once daily in 105 patients. Among these 1550 patients, the median duration of exposure was 26 months, 80% of patients were exposed for at least 12 months, and 58% of patients were exposed for at least 24 months.
In this pooled safety population, the most common adverse reactions (≥30%), including laboratory abnormalities, included neutrophil count decreased (42%), upper respiratory tract infection (39%), platelet count decreased (34%), hemorrhage (30%), and musculoskeletal pain (30%).
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on BRUKINSA
| Moderate and Strong CYP3A Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or management |
|
| Moderate and Strong CYP3A Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or management |
|
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
BRUKINSA can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1550 patients with MCL, MZL, WM, and CLL/SLL in clinical studies with BRUKINSA, 61% were ≥65 years of age, and 22% were ≥75 years of age. Patients ≥65 years of age had numerically higher rates of Grade 3 or higher adverse reactions and serious adverse reactions (63% and 47%, respectively) than patients <65 years of age (57% and 36%, respectively). No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between younger and older patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage modification is recommended in patients with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment (CLcr ≥15 mL/min, estimated by Cockcroft-Gault). Monitor for BRUKINSA adverse reactions in patients on dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Dosage modification of BRUKINSA is recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. The safety of BRUKINSA has not been evaluated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. No dosage modification is recommended in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Monitor for BRUKINSA adverse reactions in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11. Brukinsa Description
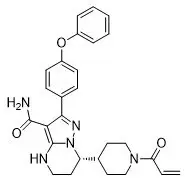
BRUKINSA (zanubrutinib) is a kinase inhibitor. The empirical formula of zanubrutinib is C27H29N5O3 and the chemical name is (S)-7-(1-acryloylpiperidin-4-yl)-2-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxamide. Zanubrutinib is a white to off-white powder, with a pH of 7.8 in saturated solution. The aqueous solubility of zanubrutinib is pH dependent, from very slightly soluble to practically insoluble.
The molecular weight of zanubrutinib is 471.55 Daltons.
Zanubrutinib has the following structure:
Each BRUKINSA capsule for oral administration contains 80 mg zanubrutinib and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and sodium lauryl sulfate. The capsule shell contains edible black ink, gelatin, and titanium dioxide.
12. Brukinsa - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Zanubrutinib is a small-molecule inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK). Zanubrutinib forms a covalent bond with a cysteine residue in the BTK active site, leading to inhibition of BTK activity. BTK is a signaling molecule of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) and cytokine receptor pathways. In B-cells, BTK signaling results in activation of pathways necessary for B-cell proliferation, trafficking, chemotaxis and adhesion. In nonclinical studies, zanubrutinib inhibited malignant B-cell proliferation and reduced tumor growth.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Zanubrutinib maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the plasma drug concentration over time curve (AUC) increase proportionally over a dosage range from 40 mg to 320 mg (0.13 to 1 time the recommended total daily dose). Limited systemic accumulation of zanubrutinib was observed following repeated administration.
The geometric mean (%CV) zanubrutinib steady-state daily AUC is 2,099 (42%) ng∙h/mL following 160 mg twice daily and 1,917 (59%) ng∙h/mL following 320 mg once daily. The geometric mean (%CV) zanubrutinib steady-state Cmax is 295 (55%) ng/mL following 160 mg twice daily and 537 (55%) ng/mL following 320 mg once daily.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with zanubrutinib.
Zanubrutinib was not mutagenic in a bacterial mutagenicity (Ames) assay, was not clastogenic in a chromosome aberration assay in mammalian (CHO) cells, nor was it clastogenic in an in vivo bone marrow micronucleus assay in rats.
A combined male and female fertility and early embryonic development study was conducted in rats at oral zanubrutinib doses of 30 to 300 mg/kg/day. Male rats were dosed 4 weeks prior to mating and through mating and female rats were dosed 2 weeks prior to mating and to gestation day 7. No effect on male or female fertility was noted but at the highest dose tested, morphological abnormalities in sperm and increased post-implantation loss were noted. The high dose of 300 mg/kg/day is approximately 10 times the human recommended dose, based on body surface area.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Mantle Cell Lymphoma
The efficacy of BRUKINSA was assessed in BGB-3111-206 [NCT03206970], a Phase 2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 previously treated patients with MCL who had received at least one prior therapy. BRUKINSA was given orally at a dose of 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The median age of patients was 60.5 years (range: 34 to 75) and the majority were male (78%). The median time since diagnosis to study entry was 30 months (range: 3 to 102) and the median number of prior therapies was 2 (range: 1 to 4). The most common prior regimens were CHOP-based (91%) followed by rituximab-based (74%). The majority of patients had extranodal involvement (71%) and refractory disease (52%). Blastoid variant of MCL was present in 14% of patients. The MIPI score was low in 58%, intermediate in 29%, and high risk in 13%.
The efficacy of BRUKINSA was also assessed in BGB-3111-AU-003 [NCT02343120], a Phase 1/2, open-label, dose-escalation, global, multicenter, single-arm trial of B cell malignancies including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with BRUKINSA. BRUKINSA was given orally at doses of 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg daily. The median age of patients with previously treated MCL was 70 years (range: 42 to 86) and 38% of patients were ≥75 years old. Most patients were male (69%) and Caucasian (78%). The MIPI score was low in 28%, intermediate in 41%, and high risk in 31%.
Tumor response was according to the 2014 Lugano Classification for both studies, and the primary efficacy endpoint was overall response rate as assessed by an Independent Review Committee.
| Study BGB-3111-206 (N=86) | Study BGB-3111-AU-003 (N=32) |
|
|---|---|---|
| ORR: overall response rate, CR: complete response, PR: partial response, DoR: duration of response, CI: confidence interval, NE: not estimable. | ||
|
||
| ORR (95% CI) | 84% (74, 91) | 84% (67, 95) |
| CR | 59% | 22%* |
| PR | 24% | 62% |
| Median DoR in months (95% CI) | 19.5 (16.6, NE) | 18.5 (12.6, NE) |
14.2 Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia
The efficacy of BRUKINSA was evaluated in ASPEN [NCT03053440], a randomized, active control, open-label trial, comparing BRUKINSA and ibrutinib in patients with MYD88 L265P mutation (MYD88MUT) WM. Patients in Cohort 1 (n=201) were randomized 1:1 to receive BRUKINSA 160 mg twice daily or ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Randomization was stratified by number of prior therapies (0 versus 1-3 versus >3) and CXCR4 status (presence or absence of a WHIM-like mutation as measured by Sanger assay).
The major efficacy outcome was the response rate defined as PR or better as assessed by IRC based on standard consensus response criteria from the International Workshop on Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia (IWWM)-6 criteria. An additional efficacy outcome measure was duration of response (DOR).
The median age was 70 years (range: 38 to 90) and 68% were male. Of those enrolled, 2% were Asian, 91% were White, and 7% were of unknown race. ECOG performance status of 0 or 1 was present in 93% patients at baseline and 7% had a baseline ECOG performance status of 2. A total of 82% had relapsed/refractory disease with 85% having received prior alkylating agents and 91% prior anti-CD20 therapy. The median number of prior therapies in those with relapsed/refractory disease was 1 (range: 1 to 8). A total of 91 (45%) patients had International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) high WM.
The study did not meet statistical significance for the prespecified efficacy outcome of superior CR+VGPR as assessed by IRC, tested first in patients with R/R disease in ASPEN.
Table 18 shows the response rates in ASPEN based on IRC assessment.
| Standard IWWM-6* | Modified IWWM-6† | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response Category | BRUKINSA (N=102) | Ibrutinib (N=99) | BRUKINSA (N=102) | Ibrutinib (N=99) |
|
||||
| Response rate (CR+VGPR+PR), (%) | 79 (77.5) | 77 (77.8) | 79 (77.5) | 77 (77.8) |
| 95% CI (%)‡ | (68.1, 85.1) | (68.3, 85.5) | (68.1, 85.1) | (68.3, 85.5) |
| Complete Response (CR) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Very Good Partial Response (VGPR) | 16 (15.7) | 7 (7.1) | 29 (28.4) | 19 (19.2) |
| Partial Response (PR), (%) | 63 (61.8) | 70 (70.7) | 50 (49.0) | 58 (58.6) |
| Duration of response (DOR), Event-free at 12 months (95% CI)§ | 94.4% (85.8, 97.9) | 87.9% (77.0, 93.8) | 94.4% (85.8, 97.9) | 87.9% (77.0, 93.8) |
14.3 Marginal Zone Lymphoma
The efficacy of BRUKINSA was assessed in Study BGB-3111-214 [NCT03846427], an open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial that evaluated 66 patients with MZL who received at least one prior anti–CD20-based therapy. BRUKINSA was given orally at a dosage of 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median age was 70 years (range: 37 to 85); 55% were male; 38% had extranodal MZL, 38% nodal, 18% splenic and 6% had unknown subtype. The median number of prior systemic therapies was 2 (range: 1 to 6), with 27% having 3 or more lines of systemic therapy; 88% had prior rituximab-based chemotherapy; 32% had refractory disease at study entry.
The efficacy of BRUKINSA was also assessed in BGB-3111-AU-003 [NCT02343120], an open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial that included 20 patients with previously treated MZL (45% having extranodal MZL, 25% nodal, 30% splenic). BRUKINSA was given orally at dosages of 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily. The median age was 70 years (range: 52 to 85); 50% were male. The median number of prior systemic therapies was 2 (range: 1 to 5), with 20% having 3 or more lines of systemic therapy; 95% had prior rituximab-based chemotherapy.
Efficacy was based on overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response as assessed by an Independent Review Committee (IRC) using 2014 Lugano criteria (Table 19).
| Parameter | Study BGB-3111-214 (N=66) | Study BGB-3111-AU-003 (N=20) |
|---|---|---|
| ORR: overall response rate, CR: complete response, PR: partial response, DoR: duration of response, CI: confidence interval, NE: not estimable. | ||
|
||
| Overall Response Rate (CT-based)* | ||
| ORR, n | 37 (56%) | 16 (80%) |
| (95% CI, %) | (43, 68) | (56, 94) |
| CR, n | 13 (20%) | 4 (20%) |
| PR, n | 24 (36%) | 12 (60%) |
| Time to Response | ||
| Median (range), months | 2.9 (1.8, 11.1) | 2.9 (2.6, 23.1) |
| Duration of Response† | ||
| Median DoR (95% CI), months | NE (NE, NE) | NE (8.4, NE) |
| Rate at 12 months (95% CI) | 85% (67, 93) | 72% (40, 88) |
In study BGB-3111-214, ORR prioritizing PET-CT when available (55 patients, with the remainder assessed by CT scan) was 67% (95% CI: 54, 78) with a CR rate of 26%.
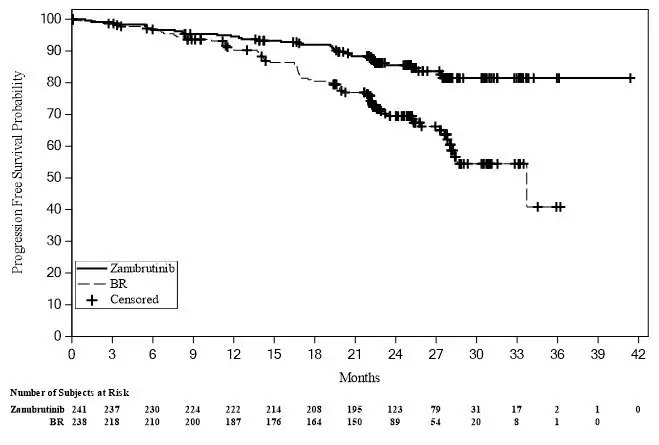
14.4 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
The efficacy of BRUKINSA in patients with CLL/SLL was evaluated in two randomized controlled trials.
| BRUKINSA
zanubrutinib capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - BEIGENE USA, INC. (081210042) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| AndersonBrecon Inc. | 053217022 | PACK(72579-011) , LABEL(72579-011) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Changzhou SynTheAll Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | 544385021 | ANALYSIS(72579-011) , API MANUFACTURE(72579-011) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalent CTS, LLC | 962674474 | ANALYSIS(72579-011) , MANUFACTURE(72579-011) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beigene (Suzhou) Co.,Ltd | 543941083 | ANALYSIS(72579-011) | |