Drug Detail:Campath (Alemtuzumab [ al-em-tooz-ue-mab ])
Drug Class: CD52 monoclonal antibodies
Highlights of Prescribing Information
CAMPATH® (alemtuzumab) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001
WARNING: CYTOPENIAS, INFUSION-RELATED REACTIONS, AND INFECTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Serious, including fatal, cytopenias, infusion-related reactions, and infections can occur (5.1–5.3).
- Limit doses to 30 mg (single) and 90 mg (cumulative weekly); higher doses increase risk of pancytopenia. (2.1)
- Escalate dose gradually and monitor patients during infusion. Withhold therapy for Grade 3 or 4 infusion-related reactions. (5.2)
- Administer prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) and herpes virus infections. (2.2, 5.3)
Indications and Usage for Campath
CAMPATH is a CD52-directed cytolytic antibody indicated as a single agent for the treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). (1)
Campath Dosage and Administration
- Administer as an intravenous infusion over 2 hours. (2.1)
- Escalate to recommended dose of 30 mg/day three times per week for 12 weeks. (2.1)
- Premedicate with oral antihistamine and acetaminophen. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 30 mg/1 mL single-dose vial (3)
Contraindications
None (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Cytopenias: Obtain complete blood counts (CBC) and platelet counts at weekly intervals during therapy and CD4 counts after therapy until recovery to ≥200 cells/µL. Withhold for severe cytopenias. Discontinue for autoimmune or severe hematologic adverse reactions. (2.2, 5.1)
- Immunosuppression/Infections: CAMPATH induces severe and prolonged lymphopenia and increases risk of infection. If a serious infection occurs, withhold treatment until infection resolves. (5.3)
- Immunization: Do not administer live viral vaccines to patients who have recently received CAMPATH. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥10%): cytopenias, infusion-related reactions, cytomegalovirus (CMV) and other infections, nausea, emesis, diarrhea, and insomnia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genzyme Corporation at 1-877-4-CAMPATH (1-877-422-6728) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 4/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Campath
CAMPATH is indicated as a single agent for the treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL).
2. Campath Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosing Schedule and Administration
- Administer as an intravenous infusion over 2 hours. Do not administer as intravenous push or bolus.
- Recommended Dosing Regimen
- Gradually escalate to the maximum recommended single dose of 30 mg. Escalation is required at initiation of dosing or if dosing is held ≥7 days during treatment. Escalation to 30 mg ordinarily can be accomplished in 3 to 7 days.
- Escalation Strategy:
- –
- Administer 3 mg daily until infusion-related reactions are ≤ Grade 2 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- –
- Then administer 10 mg daily until infusion-related reactions are ≤ Grade 2.
- –
- Then administer 30 mg/day three times per week on alternate days (e.g., Mon-Wed-Fri). The total duration of therapy, including dose escalation, is 12 weeks.
- Single doses of greater than 30 mg or cumulative doses greater than 90 mg per week increase the incidence of pancytopenia.
2.2 Recommended Concomitant Medications
- Premedicate with diphenhydramine (50 mg) and acetaminophen (500–1000 mg) 30 minutes prior to first infusion and each dose escalation. Institute appropriate medical management (e.g., glucocorticoids, epinephrine, meperidine) for infusion-related reactions as needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- Administer trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole double strength (DS) twice daily 3 times per week (or equivalent) as Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) prophylaxis.
- Administer famciclovir 250 mg BID or equivalent as herpetic prophylaxis.
Continue PCP and herpes viral prophylaxis for a minimum of 2 months after completion of CAMPATH or until the CD4+ count is ≥200 cells/µL, whichever occurs later [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.3 Dosage Modification
- Withhold CAMPATH during serious infection or other serious adverse reactions until resolution.
- Discontinue CAMPATH for autoimmune anemia or autoimmune thrombocytopenia.
- There are no dose modifications recommended for lymphopenia.
| Hematologic Values | Dosage Modification* |
|---|---|
|
|
| ANC <250/μL and/or platelet count ≤25,000/μL | |
| For first occurrence: | Withhold CAMPATH therapy. Resume CAMPATH at 30 mg when ANC ≥500/μL and platelet count ≥50,000/μL. |
| For second occurrence: | Withhold CAMPATH therapy. Resume CAMPATH at 10 mg when ANC ≥500/μL and platelet count ≥50,000/μL. |
| For third occurrence: | Discontinue CAMPATH therapy. |
| ≥50% decrease from baseline in patients initiating therapy with a baseline ANC ≤250/μL and/or a baseline platelet count ≤25,000/μL | |
| For first occurrence: | Withhold CAMPATH therapy. Resume CAMPATH at 30 mg upon return to baseline value(s). |
| For second occurrence: | Withhold CAMPATH therapy. Resume CAMPATH at 10 mg upon return to baseline value(s). |
| For third occurrence: | Discontinue CAMPATH therapy. |
2.4 Preparation and Administration
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. If particulate matter is present or the solution is discolored, discard the vial. DO NOT SHAKE VIAL.
Use aseptic technique during the preparation and administration of CAMPATH. Withdraw the necessary amount of CAMPATH from the vial into a syringe.
- To prepare the 3 mg dose, withdraw 0.1 mL into a 1 mL syringe calibrated in increments of 0.01 mL.
- To prepare the 10 mg dose, withdraw 0.33 mL into a 1 mL syringe calibrated in increments of 0.01 mL.
- To prepare the 30 mg dose, withdraw 1 mL in either a 1 mL or 3 mL syringe calibrated in 0.1 mL increments.
Inject syringe contents into 100 mL sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride USP or 5% Dextrose in Water USP. Gently invert the bag to mix the solution. Discard syringe.
The vial contains no preservatives and is intended for single use only. DISCARD VIAL including any unused portion after withdrawal of dose.
Use within 8 hours after dilution. Store diluted CAMPATH at room temperature between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) or refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Protect from light.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 30 mg/1 mL as a clear, colorless solution in single-dose vial
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cytopenias
Severe, including fatal, autoimmune anemia and thrombocytopenia, and prolonged myelosuppression have been reported in patients receiving CAMPATH.
In addition, hemolytic anemia, pure red cell aplasia, bone marrow aplasia, and hypoplasia have been reported after treatment with CAMPATH at the recommended dose. Single doses of CAMPATH greater than 30 mg or cumulative doses greater than 90 mg per week increase the incidence of pancytopenia.
Withhold CAMPATH for severe cytopenias (except lymphopenia). Discontinue for autoimmune cytopenias or recurrent/persistent severe cytopenias (except lymphopenia) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. No data exist on the safety of CAMPATH resumption in patients with autoimmune cytopenias or marrow aplasia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Obtain complete blood counts (CBC) at weekly intervals during CAMPATH therapy and more frequently if worsening anemia, neutropenia, or thrombocytopenia occurs. Assess CD4+ counts after treatment until recovery to ≥200 cells/µL [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.2 Infusion-Related Reactions
Adverse reactions occurring during or shortly after CAMPATH infusion include pyrexia, chills/rigors, nausea, hypotension, urticaria, dyspnea, rash, emesis, and bronchospasm [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In clinical trials, the frequency of infusion-related reactions was highest in the first week of treatment. Monitor for the signs and symptoms listed above and withhold infusion for Grade 3 or 4 infusion-related reactions.
The following serious, including fatal, infusion-related reactions have been identified in postmarketing reports: syncope, pulmonary infiltrates, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), respiratory arrest, cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, acute cardiac insufficiency, cardiac arrest, angioedema, and anaphylactoid shock.
Initiate CAMPATH according to the recommended dose-escalation scheme [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Premedicate patients with an antihistamine and acetaminophen prior to each dose. Institute appropriate medical management (e.g., glucocorticoids, epinephrine, meperidine) for infusion-related reactions as needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. If therapy is interrupted for 7 or more days, reinstitute CAMPATH with gradual dose escalation [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
5.3 Immunosuppression/Infections
CAMPATH treatment results in severe and prolonged lymphopenia with a concomitant increased incidence of opportunistic infections [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Administer PCP and herpes viral prophylaxis during treatment with CAMPATH and for a minimum of 2 months after completion of CAMPATH or until the CD4+ count is ≥200 cells/µL, whichever occurs later [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Prophylaxis does not eliminate these infections.
Routinely monitor patients for CMV infection during treatment with CAMPATH and for at least 2 months following completion of CAMPATH. Withhold CAMPATH for serious infections and during antiviral treatment for CMV infection or confirmed CMV viremia (defined as polymerase chain reaction [PCR] positive CMV in ≥2 consecutive samples obtained 1 week apart). Initiate therapeutic ganciclovir (or equivalent) for CMV infection or confirmed CMV viremia.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, including severe and fatal EBV-associated hepatitis, has been reported in patients who received CAMPATH.
Monitor for sign and symptoms of EBV infections. Withhold CAMPATH for EBV reactivation or severe infection.
Administer only irradiated blood products to avoid transfusion associated Graft versus Host Disease (TAGVHD), unless emergent circumstances dictate immediate transfusion.
In patients who received CAMPATH as initial therapy, recovery of CD4+ counts to ≥200 cells/µL occurred by 6 months following completion of CAMPATH; however, at 2 months post treatment, the median was 183 cells/µL. In previously treated patients who received CAMPATH, the median time to recovery of CD4+ counts to ≥200 cells/µL was 2 months; however, full recovery (to baseline) of CD4+ and CD8+ counts may take more than 12 months [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.4 Immunization
The safety of immunization with live viral vaccines following CAMPATH therapy has not been studied. Do not administer live viral vaccines to patients or infants born to patients receiving CAMPATH. The ability to generate an immune response to any vaccine following CAMPATH therapy has not been studied.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Cytopenias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Immunosuppression/Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data below reflect exposure to CAMPATH in 296 patients with CLL of whom 147 were previously untreated and 149 received at least 2 prior chemotherapy regimens. The median duration of exposure was 11.7 weeks for previously untreated patients and 8 weeks for previously treated patients.
The most common adverse reactions with CAMPATH are: infusion-related reactions (pyrexia, chills, hypotension, urticaria, nausea, rash, tachycardia, dyspnea), cytopenias (neutropenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia), infections (CMV viremia, CMV infection, other infections), gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, emesis, abdominal pain), and neurological symptoms (insomnia, anxiety). The most common serious adverse reactions are cytopenias, infusion-related reactions, and immunosuppression/infections.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The incidence of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies with the incidence of antibodies to other alemtuzumab products may be misleading.
Using an ELISA assay, anti-human antibodies (HAHA) were detected in 11 of 133 (8.3%) previously untreated patients. In addition, two patients were weakly positive for neutralizing activity. Limited data suggest that the anti-CAMPATH antibodies did not adversely affect tumor response. Four of 211 (1.9%) previously treated patients were found to have antibodies to CAMPATH following treatment.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Data
Alemtuzumab was detected in the milk of lactating huCD52 transgenic mice following intravenous administration of alemtuzumab at a dose of 10 mg/kg on postpartum days 8–12. Serum levels of alemtuzumab were similar in lactating mice and offspring on postpartum day 13 and were associated with evidence of pharmacological activity (decrease in lymphocyte counts) in the offspring.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
CAMPATH may cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of CAMPATH have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of 147 previously untreated B-CLL patients treated with CAMPATH, 35% were ≥ age 65 and 4% were ≥ age 75. Of 149 previously treated patients with B-CLL, 44% were ≥65 years of age and 10% were ≥75 years of age. Clinical studies of CAMPATH did not include sufficient number of subjects age 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
10. Overdosage
Across all clinical experience, the reported maximum single dose received was 90 mg. Bone marrow aplasia, infections, or severe infusion-related reactions occurred in patients who received a dose higher than recommended.
One patient who received an 80 mg dose intravenously experienced acute bronchospasm, cough, and dyspnea, followed by anuria and death. Another patient received two 90 mg doses intravenously one day apart during the second week of treatment and experienced a rapid onset of bone marrow aplasia.
There is no known specific antidote for CAMPATH overdosage. Discontinue CAMPATH and provide supportive therapy.
11. Campath Description
Alemtuzumab, a CD52-directed cytolytic antibody, is a recombinant DNA-derived humanized monoclonal antibody (CAMPATH-1H). CAMPATH-1H is an IgG1 kappa antibody with human variable framework and constant regions, and complementarity-determining regions from a murine (rat) monoclonal antibody (CAMPATH-1G). The CAMPATH-1H antibody has an approximate molecular weight of 150 kD. CAMPATH is produced in mammalian cell (Chinese hamster ovary) suspension culture in a medium containing neomycin. Neomycin is not detectable in the final product.
CAMPATH (alemtuzumab) injection is a sterile, clear, colorless, isotonic solution (pH 6.8–7.4) in a single-dose vial for intravenous use. Each single-dose vial of CAMPATH contains 30 mg alemtuzumab, 8.0 mg sodium chloride, 1.44 mg dibasic sodium phosphate, 0.2 mg potassium chloride, 0.2 mg monobasic potassium phosphate, 0.1 mg polysorbate 80, and 0.0187 mg disodium edetate dihydrate. No preservatives are added.
12. Campath - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
CAMPATH binds to CD52, an antigen present on the surface of B and T lymphocytes, a majority of monocytes, macrophages, NK cells, and a subpopulation of granulocytes. A proportion of bone marrow cells, including some CD34+ cells, express variable levels of CD52. The proposed mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cellular-mediated lysis following cell surface binding of CAMPATH to the leukemic cells.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies to assess the carcinogenic or genotoxic potential of CAMPATH have not been conducted.
In fertility studies, alemtuzumab (3 or 10 mg/kg intravenously) was administered to huCD52 transgenic male mice on 5 consecutive days prior to cohabitation with untreated wild-type females. No effect on fertility or reproductive performance was observed. However, adverse effects on sperm parameters (including abnormal morphology [detached/no head] and reduced total count and motility) were observed at both doses tested.
When alemtuzumab (3 or 10 mg/kg intravenously) was administered to huCD52 transgenic female mice for 5 consecutive days prior to cohabitation with untreated wild-type males, there was a decrease in the average number of corpora lutea and implantation sites and an increase in postimplantation loss, resulting in fewer viable embryos at the higher dose tested.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Previously Untreated B-CLL Patients
CAMPATH was evaluated in an open-label, randomized (1:1) active-controlled study in previously untreated patients with B-CLL, Rai Stage I–IV, with evidence of progressive disease requiring therapy. Patients received either CAMPATH 30 mg intravenously 3 times per week for a maximum of 12 weeks or chlorambucil 40 mg/m2 orally once every 28 days for a maximum of 12 cycles.
Of the 297 patients randomized, the median age was 60 years, 72% were male, 99% were Caucasian, 96% had a WHO performance status 0–1, 23% had maximum lymph node diameter ≥5 cm, 34% were Rai Stage III/IV, and 8% were treated in the U.S.
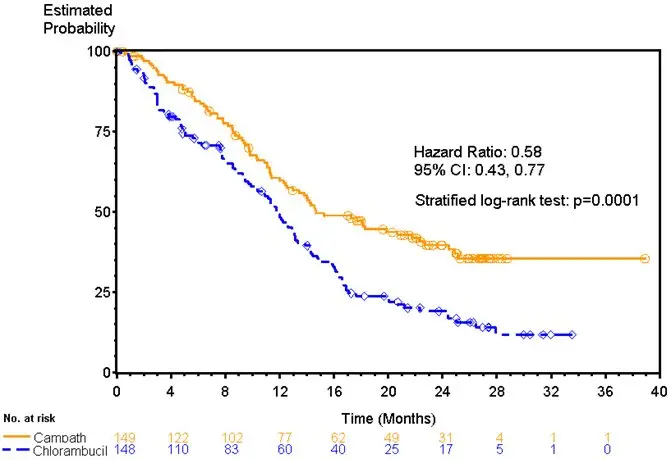
Patients randomized to receive CAMPATH experienced longer progression free survival (PFS) compared to those randomized to receive chlorambucil (median PFS 14.6 months vs. 11.7 months, respectively). The overall response rates were 83% and 55% (p <0.0001) and the complete response rates were 24% and 2% (p <0.0001) for CAMPATH and chlorambucil arms, respectively. The Kaplan-Meier curve for PFS is shown in Figure 1.
| Figure 1: Progression Free Survival in Previously Untreated B-CLL Patients* |
|---|
|
|
|
14.2 Previously Treated B-CLL Patients
CAMPATH was evaluated in three multicenter, open-label, single-arm studies of 149 patients with B-CLL previously treated with alkylating agents, fludarabine, or other chemotherapies. Patients were treated with the recommended dose of CAMPATH 30 mg intravenously 3 times per week for up to 12 weeks. Partial response rates of 21% to 31% and complete response rates of 0% to 2% were observed.
16. How is Campath supplied
CAMPATH (alemtuzumab) is supplied in clear glass single-dose vial containing 30 mg of alemtuzumab in 1 mL of solution. Each carton contains three CAMPATH vials (NDC 58468-0357-3) or one CAMPATH vial (NDC 58468-0357-1).
| CAMPATH
alemtuzumab injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Genzyme Corporation (025322157) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG | 340700520 | ANALYSIS(58468-0357) , API MANUFACTURE(58468-0357) , MANUFACTURE(58468-0357) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH | 313218430 | ANALYSIS(58468-0357) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUROAPI UK LIMITED | 229522842 | PACK(58468-0357) , LABEL(58468-0357) | |