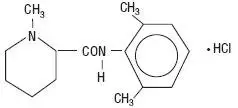
Drug Detail:Carbocaine hcl (Mepivacaine [ me-piv-a-kane ])
Drug Class: Local injectable anesthetics
Contraindications
CARBOCAINE is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to amide-type local anesthetics.
Precautions
The safety and effectiveness of mepivacaine depend upon proper dosage, correct technique, adequate precautions, and readiness for emergencies.
The lowest dose that results in effective anesthesia should be used to avoid high plasma levels and possible adverse effects. Injection of repeated doses of Mepivacaine may cause significant increases in blood levels with each repeated dose due to slow accumulation of the drug or its metabolites, or due to slower metabolic degradation than normal.
Tolerance varies with the status of the patient. Debilitated, elderly patients, acutely ill patients, and children should be given reduced doses commensurate with their weight and physical status.
Mepivacaine should be used with caution in patients with a history of severe disturbances of cardiac rhythm or heart block.
INJECTIONS SHOULD ALWAYS BE MADE SLOWLY WITH ASPIRATION TO AVOID INTRAVASCULAR INJECTION AND THEREFORE SYSTEMIC REACTION TO BOTH LOCAL ANESTHETIC AND VASOCONSTRICTOR.
If sedatives are employed to reduce patient apprehension, use reduced doses, since local anesthetic agents, like sedatives, are central nervous system depressants which in combination may have an additive effect. Young children should be given minimal doses of each agent.
Changes in sensorium such as excitation, disorientation or drowsiness may be early indications of a high blood level of the drug and may occur following inadvertent intravascular administration or rapid absorption of mepivacaine.
Local anesthetic procedures should be used with caution when there is inflammation and/or sepsis in the region of the proposed injection.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Reactions to CARBOCAINE are characteristic of those associated with other amide-type local anesthetics. Systemic adverse reactions involving the central nervous system and the cardiovascular system usually result from high plasma levels (which may be due to excessive dosage, rapid absorption, inadvertent intravascular injection, or slow metabolic degradation), injection technique, or volume of injection.
A small number of reactions may result from hypersensitivity, idiosyncrasy or diminished tolerance to normal dosage on the part of the patient.
Persistent paresthesias of the lips, tongue, and oral tissues have been reported with the use of mepivacaine, with slow, incomplete, or no recovery. These post-markeing events have been reported chiefly following nerve blocks in the mandible and have involved the trigeminal nerve and its branches.
Reactions involving the central nervous system are characterized by excitation and/or depression. Nervousness, dizziness, blurred vision, or tremors may occur followed by drowsiness, convulsions, unconsciousness, and possible respiratory arrest. Since excitement may be transient or absent, the first manifestations may be drowsiness merging into unconsciousness and respiratory arrest.
Cardiovascular reactions are depressant. They may be the result of direct drug effect or more commonly in dental practice, the result of vasovagal reaction, particularly if the patient is in the sitting position. Failure to recognize premonitory signs such as sweating, feeling of faintness, changes in pulse or sensorium may result in progressive cerebral hypoxia and seizure or serious cardiovascular catastrophe. Management consists of placing the patient in the recumbent position and administration of oxygen. Vasoactive drugs such as Ephedrine or Methoxamine may be administered intravenously.
Allergic reactions are rare and may occur as a result of sensitivity to the local anesthetic and are characterized by cutaneous lesions of delayed onset or urticaria, edema and other manifestations of allergy. The detection of sensitivity by skin testing is of limited value. As with other local anesthetics, anaphylactoid reactions to Mepivacaine have occurred rarely. The reaction may be abrupt and severe and is not usually dose related. Localized puffiness and swelling may occur.
Carbocaine Dosage and Administration
As with all local anesthetics, the dose varies and depends upon the area to be anesthetized, the vascularity of the tissues, individual tolerance and the technique of anesthesia. The lowest dose needed to provide effective anesthesia should be administered. For specific techniques and procedures refer to standard dental manuals and textbooks.
For infiltration and block injections in the upper or lower jaw, the average dose of 1 cartridge will usually suffice.
Each cartridge contains 1.7 mL (34 mg of 2% or 51 mg of 3%).
5.3 cartridges (180 mg of the 2% solution or 270 mg of the 3% solution) are usually adequate to effect anesthesia of the entire oral cavity. Whenever a larger dose seems to be necessary for an extensive procedure, the maximum dose should be calculated according to the patient's weight. A dose of up to 3 mg per pound of body weight may be administered. At any single dental sitting the total dose for all injected sites should not exceed 400 mg in adults.
The maximum pediatric dose should be carefully calculated.
| Maximum dose for pediatric population = | ||
| Child's Weight (lbs.) | × | Maximum Recommended Dose for Adults (400 mg) |
| 150 | ||
The following table, approximating these calculations, may also be used as a guide. This table is based upon a recommended maximum for larger pediatric population of 5.3 cartridges (the maximum recommended adult dose) during any single dental sitting, regardless of the pediatric patient's weight or (for 2% mepivacaine) calculated maximum amount of drug:
| 3% Mepivacaine (Plain) | 2% Mepivacaine 1:20,000 Levonordefrin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 mg/lb (270 mg max.) | 3mg/lb (180 mg max.) | |||
| Weight (lb.) | mg | Number of Cartridges | mg | Number of Cartridges |
|
||||
| 20 | 60 | 1.2 | 60 | 1.8 |
| 30 | 90 | 1.8 | 90 | 2.6 |
| 40 | 120 | 2.3 | 120 | 3.5 |
| 50 | 150 | 2.9 | 150 | 4.4 |
| 60 | 180 | 3.5 | 180 | 5.3 |
| 80 | 240 | 4.7 | 180 | 5.3 |
| 100 | 270 | 5.3 | 180 | 5.3 |
| 120 | 270 | 5.3 | 180 | 5.3 |
When using CARBOCAINE for infiltration or regional block anesthesia, injection should always be made slowly and with frequent aspiration.
Any unused portion of a cartridge should be discarded.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
| CARBOCAINE
mepivacaine hydrochloride injection, solution |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Septodont, Inc. (627058738) |
| Registrant - Novocol Pharmaceutical of Canada, Inc. (201719960) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novocol Pharmaceutical of Canada, Inc. | 201719960 | MANUFACTURE(0362-0753) | |




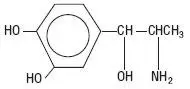
 -(1-Aminoethyl)-3, 4-dihydroxybenzyl alcohol with the following structural formula:
-(1-Aminoethyl)-3, 4-dihydroxybenzyl alcohol with the following structural formula: