Drug Detail:Cimzia (Certolizumab [ ser-toe-liz-oo-mab ])
Drug Class: TNF alfa inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
CIMZIA (certolizumab pegol) for injection, for subcutaneous use
CIMZIA (certolizumab pegol) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2008
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS AND MALIGNANCY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Increased risk of serious infections leading to hospitalization or death including tuberculosis (TB), bacterial sepsis, invasive fungal infections (such as histoplasmosis), and infections due to other opportunistic pathogens ( 5.1).
- CIMZIA should be discontinued if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis ( 5.1).
- Perform test for latent TB; if positive, start treatment for TB prior to starting CIMZIA ( 5.1).
- Monitor all patients for active TB during treatment, even if initial latent TB test is negative ( 5.1)
- Lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children and adolescent patients treated with TNF blockers, of which CIMZIA is a member ( 5.2) . CIMZIA is not indicated for use in pediatric patients. ( 8.4)
Indications and Usage for Cimzia
CIMZIA is a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker indicated for:
- Reducing signs and symptoms of Crohn's disease and maintaining clinical response in adult patients with moderately to severely active disease who have had an inadequate response to conventional therapy ( 1.1)
- Treatment of adults with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis ( 1.2)
- Treatment of adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis. ( 1.3)
- Treatment of adults with active ankylosing spondylitis ( 1.4)
- Treatment of adults with active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis with objective signs of inflammation ( 1.5)
- Treatment of adults with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy ( 1.6)
Cimzia Dosage and Administration
CIMZIA is administered by subcutaneous injection. The recommended initial dose of CIMZIA is 400 mg (given as two subcutaneous injections of 200 mg) ( 2).
Crohn's Disease (2.1)
- 400 mg initially and at Weeks 2 and 4. If response occurs, follow with 400 mg every four weeks
Rheumatoid Arthritis (2.2)
- 400 mg initially and at Weeks 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every other week; for maintenance dosing, 400 mg every 4 weeks can be considered
Psoriatic Arthritis (2.3)
- 400 mg initially and at week 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every other week; for maintenance dosing, 400 mg every 4 weeks can be considered.
Ankylosing Spondylitis (2.4)
- 400 mg (given as 2 subcutaneous injections of 200 mg each) initially and at weeks 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every other week or 400 mg every 4 weeks.
Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis (2.5)
- 400 mg (given as 2 subcutaneous injections of 200 mg each) initially and at weeks 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every other week or 400 mg every 4 weeks.
Plaque Psoriasis (2.6, 14.6)
- 400 mg (given as 2 subcutaneous injections of 200 mg each) every other week. For some patients (with body weight ≤ 90 kg), a dose of 400 mg (given as 2 subcutaneous injections of 200 mg each) initially and at Weeks 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every other week may be considered.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- For injection: 200 mg lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial ( 3)
- Injection: 200 mg/mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe ( 3)
Contraindications
Serious hypersensitivity reaction to certolizumab pegol or to any of the excipients. ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Serious Infections: CIMZIA should not be initiated in patients with an active infection. Monitor for infection during and after treatment; discontinue if a serious infection develops. If invasive fungal infection develops in patients who reside or travel to regions where mycoses are endemic, consider empiric antifungal therapy. ( 5.1)
- Malignancies: Cases of lymphoma and other malignancies have been observed among patients receiving TNF blockers, including CIMZIA. ( 5.2)
- Heart Failure: Monitor patients for new onset or worsening congestive heart failure. ( 5.3)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Discontinue CIMZIA and institute appropriate therapy if anaphylaxis or other serious hypersensitivity reactions occur. ( 5.4)
- Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation: Test for HBV infection before starting CIMZIA. Monitor HBV carriers during and several months after therapy. If reactivation occurs, stop CIMZIA and begin anti-viral therapy ( 5.5)
- Neurologic Reactions: Exacerbation or new onset demyelinating disease may occur; use caution in patients with pre-existing or recent-onset demyelinating disorders. ( 5.6)
- Hematological Reactions (including leukopenia, pancytopenia and thrombocytopenia): Use with caution in patients who have ongoing, or a history of, significant hematologic abnormalities. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms develop; consider discontinuing CIMZIA in patients with confirmed abnormalities. ( 5.7)
- Use with Anakinra, Abatacept, Rituximab and Natalizumab: Increased risk of serious infections; concomitant use is not recommended. ( 5.8, 7.1)
- Autoimmunity: Discontinue CIMZIA if lupus-like syndrome develops. ( 5.9)
- Live vaccines: Avoid use with CIMZIA ( 5.10, 7.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥7%): upper respiratory tract infection, rash, and urinary tract infection (
6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact UCB, Inc. at 1-866-822-0068 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Laboratory Tests: May cause erroneously elevated aPTT results. ( 7.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2022
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS AND MALIGNANCY
SERIOUS INFECTIONS
Patients treated with CIMZIA are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids.
CIMZIA should be discontinued if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis.
Reported infections include:
- Active tuberculosis, including reactivation of latent tuberculosis. Patients with tuberculosis have frequently presented with disseminated or extrapulmonary disease. Patients should be tested for latent tuberculosis before CIMZIA use and during therapy. Treatment for latent infection should be initiated prior to CIMZIA use.
- Invasive fungal infections, including histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, candidiasis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, and pneumocystosis. Patients with histoplasmosis or other invasive fungal infections may present with disseminated, rather than localized disease. Antigen and antibody testing for histoplasmosis may be negative in some patients with active infection. Empiric anti-fungal therapy should be considered in patients at risk for invasive fungal infections who develop severe systemic illness.
- Bacterial, viral and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens, including Legionella and Listeria.
The risks and benefits of treatment with CIMZIA should be carefully considered prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection.
Patients should be closely monitored for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with CIMZIA, including the possible development of tuberculosis in patients who tested negative for latent tuberculosis infection prior to initiating therapy. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
MALIGNANCY
Lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children and adolescent patients treated with TNF blockers, of which CIMZIA is a member [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. CIMZIA is not indicated for use in pediatric patients.
1. Indications and Usage for Cimzia
1.1 Crohn's Disease
CIMZIA is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms of Crohn's disease and maintaining clinical response in adult patients with moderately to severely active disease who have had an inadequate response to conventional therapy.
1.2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
CIMZIA is indicated for the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
1.3 Psoriatic Arthritis
CIMZIA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
1.4 Ankylosing Spondylitis
CIMZIA is indicated for the treatment of adults with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS). [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]
2. Cimzia Dosage and Administration
CIMZIA is administered by subcutaneous injection . Injection sites should be rotated and injections should not be given into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red or hard. When a 400 mg dose is needed (given as two subcutaneous injections of 200 mg), injections should occur at separate sites in the thigh or abdomen.
The solution should be carefully inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The solution should be a clear colorless to yellow liquid, essentially free from particulates and should not be used if cloudy or if foreign particulate matter is present. CIMZIA does not contain preservatives; therefore, unused portions of drug remaining in the syringe or vial should be discarded.
2.1 Crohn's Disease
The recommended initial adult dose of CIMZIA is 400 mg (given as two subcutaneous injections of 200 mg) initially, and at Weeks 2 and 4. In patients who obtain a clinical response, the recommended maintenance regimen is 400 mg every four weeks.
2.2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
The recommended dose of CIMZIA for adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis is 400 mg (given as two subcutaneous injections of 200 mg) initially and at Weeks 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every other week. For maintenance dosing, CIMZIA 400 mg every 4 weeks can be considered [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] .
2.3 Psoriatic Arthritis
The recommended dose of CIMZIA for adult patients with psoriatic arthritis is 400 mg (given as 2 subcutaneous injections of 200 mg each) initially and at week 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every other week. For maintenance dosing, CIMZIA 400 mg every 4 weeks can be considered [see Clinical Studies (14.3)] .
2.4 Ankylosing Spondylitis
The recommended dose of CIMZIA for adult patients with ankylosing spondylitis is 400 mg (given as 2 subcutaneous injections of 200 mg each) initially and at weeks 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every 2 weeks or 400 mg every 4 weeks.
2.5 Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis
The recommended dose of CIMZIA for adult patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis is 400 mg (given as 2 subcutaneous injections of 200 mg each) initially and at weeks 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every 2 weeks or 400 mg every 4 weeks.
2.6 Plaque Psoriasis
The recommended dose of CIMZIA for adults with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis is 400 mg (given as 2 subcutaneous injections of 200 mg each) every other week.
For some patients (with body weight ≤ 90 kg), CIMZIA 400 mg (given as 2 subcutaneous injections of 200 mg each) initially and at Weeks 2 and 4, followed by 200 mg every other week can be considered [see Clinical Studies (14.6)] .
2.7 Preparation and Administration of CIMZIA Using the Lyophilized Powder for Injection
CIMZIA Lyophilized powder should be prepared and administered by a health care professional. CIMZIA is provided in a package that contains everything required to reconstitute and inject the drug [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)] . Step-by-step preparation and administration instructions are provided below.
Preparation and Storage
- If refrigerated, remove CIMZIA from the refrigerator and allow the vial(s) to sit at room temperature for 30 minutes before reconstituting. Do not warm the vial in any other way. Use appropriate aseptic technique when preparing and administering CIMZIA.
- Reconstitute the vial(s) of CIMZIA with 1 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP using the 20-gauge needle provided. The sterile water for injection should be directed at the vial wall rather than directly on CIMZIA.
- Gently swirl each vial of CIMZIA for about one minute without shaking, assuring that all of the powder comes in contact with the Sterile Water for Injection. The swirling should be as gentle as possible in order to avoid creating a foaming effect.
- Continue swirling every 5 minutes as long as non-dissolved particles are observed. Full reconstitution may take as long as 30 minutes. The final reconstituted solution contains 200 mg/mL and should be clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow liquid essentially free from particulates.
- Once reconstituted, CIMZIA can be stored in the vials for up to 24 hours between 2° to 8° C (36° to 46° F) prior to injection. Do not freeze.
Administration
- Prior to injecting, reconstituted CIMZIA should be at room temperature but do not leave reconstituted CIMZIA at room temperature for more than two hours prior to administration.
- Withdraw the reconstituted solution into a separate syringe for each vial using a new 20-gauge needle for each vial so that each syringe contains 1 mL of CIMZIA (200 mg of certolizumab pegol).
- Replace the 20-gauge needle(s) on the syringes with a 23-gauge(s) for administration.
- Inject the full contents of the syringe(s) subcutaneously, by pinching the skin of the thigh or abdomen. Where a 400 mg dose is required, two injections are required, therefore, separate sites should be used for each 200 mg injection.
2.8 Preparation and Administration of CIMZIA Using the Prefilled Syringe
After proper training in subcutaneous injection technique, a patient may self-inject with the CIMZIA Prefilled Syringe if a physician determines that it is appropriate.
- If refrigerated, remove the prefilled syringe from the carton and let it warm to room temperature.
- Inspect the liquid in the prefilled syringe. It should be clear and colorless to yellow and free from particulates. Discard the syringe if cloudy, discolored or contains particulates.
- Suitable sites for injection include the thigh or abdomen at least 2 inches away from the navel. Inject at least 1 inch from the previous site.
- Do not inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red or hard, or where there are scars or stretch marks.
The needle shield inside the removable cap of the CIMZIA prefilled syringe contains a derivative of natural rubber latex which may cause allergic reactions and should be handled with caution by latex-sensitive individuals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] .
2.9 Monitoring to Assess Safety
Before initiation of therapy with CIMZIA, all patients must be evaluated for both active and inactive (latent) tuberculosis infection. The possibility of undetected latent tuberculosis should be considered in patients who have immigrated from or traveled to countries with a high prevalence of tuberculosis or had close contact with a person with active tuberculosis. Appropriate screening tests (e.g. tuberculin skin test and chest x-ray) should be performed in all patients.
4. Contraindications
CIMZIA is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reaction to certolizumab pegol or to any of the excipients. Reactions have included angioedema, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, and urticaria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] .
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risk of Serious Infections
Patients treated with CIMZIA are at an increased risk for developing serious infections involving various organ systems and sites that may lead to hospitalization or death.
Opportunistic infections due to bacterial, mycobacterial, invasive fungal, viral, parasitic, or other opportunistic pathogens including aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, legionellosis, listeriosis, pneumocystosis and tuberculosis have been reported with TNF blockers. Patients have frequently presented with disseminated rather than localized disease.
Treatment with CIMZIA should not be initiated in patients with an active infection, including clinically important localized infections. Patients greater than 65 years of age, patients with co-morbid conditions, and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressants (e.g. corticosteroids or methotrexate) may be at a greater risk of infection. The risks and benefits of treatment should be considered prior to initiating therapy in patients:
- with chronic or recurrent infection
- who have been exposed to tuberculosis
- with a history of an opportunistic infection
- who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses, such as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, or blastomycosis
- with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection
5.2 Malignancies
In the controlled portions of clinical studies of some TNF blockers, more cases of malignancies have been observed among patients receiving TNF blockers compared to control patients. During controlled and open-labeled portions of CIMZIA studies of Crohn's disease and other diseases, malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer) were observed at a rate (95% confidence interval) of 0.5 (0.4, 0.7) per 100 patient-years among 4,650 CIMZIA-treated patients versus a rate of 0.6 (0.1, 1.7) per 100 patient-years among 1,319 placebo-treated patients. During CIMZIA studies of psoriasis, malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer) were observed corresponding to an incidence rate of 0.5 (0.2, 1.0) per 100 subject-years among a total of 995 subjects who received CIMZIA. The size of the control group and limited duration of the controlled portions of the studies precludes the ability to draw firm conclusions.
Malignancies, some fatal, have been reported among children, adolescents, and young adults who received treatment with TNF-blocking agents (initiation of therapy ≤ 18 years of age), of which CIMZIA is a member. Approximately half the cases were lymphomas, including Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The other cases represented a variety of different malignancies and included rare malignancies usually associated with immunosuppression and malignancies that are not usually observed in children and adolescents. The malignancies occurred after a median of 30 months of therapy (range 1 to 84 months). Most of the patients were receiving concomitant immunosuppressants. These cases were reported post-marketing and are derived from a variety of sources including registries and spontaneous post-marketing reports. CIMZIA is not indicated for use in pediatric patients.
In the controlled portions of clinical trials of all the TNF blockers, more cases of lymphoma have been observed among patients receiving TNF blockers compared to control patients. In controlled studies of CIMZIA for Crohn's disease and other investigational uses, there was one case of lymphoma among 2,657 Cimzia-treated patients and one case of Hodgkin's lymphoma among 1,319 placebo-treated patients.
In the CIMZIA RA clinical trials (placebo-controlled and open label) a total of three cases of lymphoma were observed among 2,367 patients. This is approximately 2-fold higher than expected in the general population. Patients with RA, particularly those with highly active disease, are at a higher risk for the development of lymphoma. In the CIMZIA PsO clinical trials (placebo-controlled and open label) there was one case of Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Rates in clinical studies for CIMZIA cannot be compared to the rates of clinical trials of other TNF blockers and may not predict the rates observed when CIMZIA is used in a broader patient population. Patients with Crohn's disease that require chronic exposure to immunosuppressant therapies may be at higher risk than the general population for the development of lymphoma, even in the absence of TNF blocker therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . The potential role of TNF blocker therapy in the development of malignancies in adults is not known.
Postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL), a rare type of T-cell lymphoma that has a very aggressive disease course and is usually fatal, have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers, including CIMZIA. The majority of reported TNF blocker cases occurred in adolescent and young adult males with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. Almost all of these patients had received treatment with the immunosuppressants azathioprine and/or 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) concomitantly with a TNF blocker at or prior to diagnosis. It is uncertain whether the occurrence of HSTCL is related to use of a TNF blocker or a TNF blocker in combination with these other immunosuppressants. The potential risk of using a TNF blocker in combination with azathioprine or 6-MP should be carefully considered.
Cases of acute and chronic leukemia have been reported in association with post-marketing TNF-blocker use in RA and other indications. Even in the absence of TNF-blocker therapy, patients with RA may be at a higher risk (approximately 2-fold) than the general population for the development of leukemia.
Melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers, including CIMZIA. Periodic skin examinations are recommended for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer.
5.3 Heart Failure
Cases of worsening congestive heart failure (CHF) and new onset CHF have been reported with TNF blockers, including CIMZIA. CIMZIA has not been formally studied in patients with CHF; however, in clinical studies in patients with CHF with another TNF blocker, worsening congestive heart failure (CHF) and increased mortality due to CHF were observed. Exercise caution in patients with heart failure and monitor them carefully [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
The following symptoms that could be compatible with hypersensitivity reactions have been reported rarely following CIMZIA administration to patients: angioedema, anaphylaxis, dyspnea, hypotension, rash, serum sickness, and urticaria. Some of these reactions occurred after the first administration of CIMZIA. If such reactions occur, discontinue further administration of CIMZIA and institute appropriate therapy. There are no data on the risks of using CIMZIA in patients who have experienced a severe hypersensitivity reaction towards another TNF blocker; in these patients caution is needed [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
The needle shield inside the removable cap of the CIMZIA prefilled syringe contains a derivative of natural rubber latex which may cause an allergic reaction in individuals sensitive to latex.
5.5 Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation
Use of TNF blockers, including CIMZIA, has been associated with reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in patients who are chronic carriers of this virus. In some instances, HBV reactivation occurring in conjunction with TNF blocker therapy has been fatal. The majority of reports have occurred in patients concomitantly receiving other medications that suppress the immune system, which may also contribute to HBV reactivation.
Test patients for HBV infection before initiating treatment with CIMZIA. For patients who test positive for HBV infection, consultation with a physician with expertise in the treatment of hepatitis B is recommended. Adequate data are not available on the safety or efficacy of treating patients who are carriers of HBV with anti-viral therapy in conjunction with TNF blocker therapy to prevent HBV reactivation. Patients who are carriers of HBV and require treatment with CIMZIA should be closely monitored for clinical and laboratory signs of active HBV infection throughout therapy and for several months following termination of therapy.
In patients who develop HBV reactivation, discontinue CIMZIA and initiate effective anti-viral therapy with appropriate supportive treatment. The safety of resuming TNF blocker therapy after HBV reactivation is controlled is not known. Therefore, exercise caution when considering resumption of CIMZIA therapy in this situation and monitor patients closely.
5.6 Neurologic Reactions
Use of TNF blockers, of which CIMZIA is a member, has been associated with rare cases of new onset or exacerbation of clinical symptoms and/or radiographic evidence of central nervous system demyelinating disease, including multiple sclerosis, and with peripheral demyelinating disease, including Guillain-Barré syndrome. Exercise caution in considering the use of CIMZIA in patients with pre-existing or recent-onset central or peripheral nervous system demyelinating disorders. Rare cases of neurological disorders, including seizure disorder, optic neuritis, and peripheral neuropathy have been reported in patients treated with CIMZIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
5.7 Hematological Reactions
Rare reports of pancytopenia, including aplastic anemia, have been reported with TNF blockers. Adverse reactions of the hematologic system, including medically significant cytopenia (e.g., leukopenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia) have been infrequently reported with CIMZIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . The causal relationship of these events to CIMZIA remains unclear.
Although no high risk group has been identified, exercise caution in patients being treated with CIMZIA who have ongoing, or a history of, significant hematologic abnormalities. Advise all patients to seek immediate medical attention if they develop signs and symptoms suggestive of blood dyscrasias or infection (e.g., persistent fever, bruising, bleeding, pallor) while on CIMZIA. Consider discontinuation of CIMZIA therapy in patients with confirmed significant hematologic abnormalities.
5.8 Use with Biological Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (Biological DMARDs)
Serious infections were seen in clinical studies with concurrent use of anakinra (an interleukin-1 antagonist) and another TNF blocker, etanercept, with no added benefit compared to etanercept alone. A higher risk of serious infections was also observed in combination use of TNF blockers with abatacept and rituximab. Because of the nature of the adverse events seen with this combination therapy, similar toxicities may also result from the use of CIMZIA in this combination. Therefore, the use of CIMZIA in combination with other biological DMARDs is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.9 Autoimmunity
Treatment with CIMZIA may result in the formation of autoantibodies and rarely, in the development of a lupus-like syndrome. If a patient develops symptoms suggestive of a lupus-like syndrome following treatment with CIMZIA, discontinue treatment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
5.10 Immunizations
Patients treated with CIMZIA may receive vaccinations, except for live or live attenuated vaccines. No data are available on the response to live vaccinations or the secondary transmission of infection by live vaccines in patients receiving CIMZIA.
In a placebo-controlled clinical trial of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, no difference was detected in antibody response to vaccine between CIMZIA and placebo treatment groups when the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine and influenza vaccine were administered concurrently with CIMZIA. Similar proportions of patients developed protective levels of anti-vaccine antibodies between CIMZIA and placebo treatment groups; however patients receiving CIMZIA and concomitant methotrexate had a lower humoral response compared with patients receiving CIMZIA alone. The clinical significance of this is unknown.
5.11 Immunosuppression
Since TNF mediates inflammation and modulates cellular immune responses, the possibility exists for TNF blockers, including CIMZIA, to affect host defenses against infections and malignancies. The impact of treatment with CIMZIA on the development and course of malignancies, as well as active and/or chronic infections, is not fully understood [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.5) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . The safety and efficacy of CIMZIA in patients with immunosuppression has not been formally evaluated.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most serious adverse reactions were:
- Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Neurologic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hematologic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Autoimmunity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Immunosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying and controlled conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug, and may not predict the rates observed in a broader patient population in clinical practice.
In premarketing controlled trials of all patient populations combined the most common adverse reactions (≥ 8%) were upper respiratory infections (18%), rash (9%) and urinary tract infections (8%).
Controlled Studies with Rheumatoid Arthritis
CIMZIA was studied primarily in placebo-controlled trials and in long-term follow-up studies. The data described below reflect the exposure to CIMZIA in 2,367 RA patients, including 2,030 exposed for at least 6 months, 1,663 exposed for at least one year and 282 for at least 2 years; and 1,774 in adequate and well-controlled studies. In placebo-controlled studies, the population had a median age of 53 years at entry; approximately 80% were females, 93% were Caucasian and all patients were suffering from active rheumatoid arthritis, with a median disease duration of 6.2 years. Most patients received the recommended dose of CIMZIA or higher.
Table 1 summarizes the reactions reported at a rate of at least 3% in patients treated with CIMZIA 200 mg every other week compared to placebo (saline formulation), given concomitantly with methotrexate.
| Adverse Reaction
(Preferred Term) | Placebo+ MTX
* (%)
N =324 | CIMZIA 200 mg EOW + MTX(%)
N =640 |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 2 | 6 |
| Headache | 4 | 5 |
| Hypertension | 2 | 5 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 1 | 5 |
| Back pain | 1 | 4 |
| Pyrexia | 2 | 3 |
| Pharyngitis | 1 | 3 |
| Rash | 1 | 3 |
| Acute bronchitis | 1 | 3 |
| Fatigue | 2 | 3 |
Hypertensive adverse reactions were observed more frequently in patients receiving CIMZIA than in controls. These adverse reactions occurred more frequently among patients with a baseline history of hypertension and among patients receiving concomitant corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Patients receiving CIMZIA 400 mg as monotherapy every 4 weeks in rheumatoid arthritis controlled clinical trials had similar adverse reactions to those patients receiving CIMZIA 200 mg every other week.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of CIMZIA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate reliably their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Vascular disorder: systemic vasculitis has been identified during post-approval use of TNF blockers.
Skin: case of severe skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, new or worsening psoriasis (all sub-types including pustular and palmoplantar), and lichenoid skin reaction have been identified during post-approval use of TNF blockers.
Immune System Disorders: sarcoidosis
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps): Melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma (neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Use with Anakinra, Abatacept, Rituximab, and Natalizumab
An increased risk of serious infections has been seen in clinical studies of other TNF-blocking agents used in combination with anakinra or abatacept, with no added benefit. Formal drug interaction studies have not been performed with rituximab or natalizumab. Because of the nature of the adverse events seen with these combinations with TNF blocker therapy, similar toxicities may also result from the use of CIMZIA in these combinations. There is not enough information to assess the safety and efficacy of such combination therapy. Therefore, the use of CIMZIA in combination with anakinra, abatacept, rituximab, or natalizumab is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)] .
7.2 Live Vaccines
Avoid use of live (including attenuated) vaccines concurrently with CIMZIA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] .
7.3 Laboratory Tests
Interference with certain coagulation assays has been detected in patients treated with CIMZIA. Certolizumab pegol may cause erroneously elevated activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) assay results in patients without coagulation abnormalities. This effect has been observed with the PTT-Lupus Anticoagulant (LA) test and Standard Target Activated Partial Thromboplastin time (STA-PTT) Automate tests from Diagnostica Stago, and the HemosIL APTT-SP liquid and HemosIL lyophilized silica tests from Instrumentation Laboratories. Other aPTT assays may be affected as well. Interference with thrombin time (TT) and prothrombin time (PT) assays has not been observed. There is no evidence that CIMZIA therapy has an effect on in vivo coagulation.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Data
A multicenter clinical study designed to evaluate breast milk was conducted in 17 lactating women who were at least 6 weeks post-partum and had received at least 3 consecutive doses of CIMZIA 200 mg every 2 weeks or 400 mg every 4 weeks for rheumatological disease or Crohn's disease. The effects of certolizumab pegol on milk production were not studied. The concentration of certolizumab pegol in breast milk was not measurable in 77 (56 %) of the 137 samples taken over the dosing periods using an assay that can measure certolizumab pegol concentrations at or above 0.032 mcg/mL. The median of the estimated average daily infant doses was 0.0035 mg/kg/day (range: 0 to 0.01 mg/kg/day). The percentage of the maternal dose (200 mg CIMZIA dosed once every 2 weeks), that reaches an infant ranged from 0.56% to 4.25% based on samples with measurable certolizumab pegol concentration. No serious adverse reactions were noted in the 17 breastfed infants in the study.
In a separate study, plasma certolizumab pegol concentrations were collected 4 weeks after birth in 9 breastfed infants whose mothers had been currently taking CIMZIA (regardless of being exclusively breastfed or not). Certolizumab pegol in infant plasma was not measurable i.e., below 0.032 mcg/mL.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
CIMZIA was evaluated for the treatment of pediatric patients with moderately to severely active Crohn's disease. Efficacy was not demonstrated in an open-label, randomized, parallel-group, multiple dose study for a period of up to 62 weeks in 99 subjects aged 6 to 17 years. The study was ended prematurely because of a high number of patient discontinuations.
Due to its inhibition of TNFα, CIMZIA administered during pregnancy could affect immune responses in the in utero-exposed newborn and infant [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of CIMZIA did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. Population pharmacokinetic analyses of patients enrolled in CIMZIA clinical studies concluded that there was no apparent difference in drug concentration regardless of age. Because there is a higher incidence of infections in the elderly population in general, use caution when treating the elderly with CIMZIA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
11. Cimzia Description
Certolizumab pegol is a TNF blocker. CIMZIA is a recombinant, humanized antibody Fab' fragment, with specificity for human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), conjugated to an approximately 40kDa polyethylene glycol (PEG2MAL40K). The Fab' fragment is manufactured in E. coli and is subsequently subjected to purification and conjugation to PEG2MAL40K, to generate certolizumab pegol. The Fab' fragment is composed of a light chain with 214 amino acids and a heavy chain with 229 amino acids. The molecular weight of certolizumab pegol is approximately 91 kiloDaltons.
CIMZIA (certolizumab pegol) for injection is supplied as a sterile white, lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for subcutaneous use. After reconstitution of the lyophilized powder with 1 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, the final concentration is 200 mg/mL with a deliverable volume of 1 mL (200 mg) and a pH of approximately 5.2. Each single-dose vial provides 200 mg certolizumab pegol, lactic acid (0.9 mg), polysorbate (0.1 mg), and sucrose (100 mg).
CIMZIA (certolizumab pegol) injection is supplied as a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution that may contain particulates in a single-dose prefilled syringe for subcutaneous use. Each prefilled syringe delivers 1 mL of solution containing 200 mg certolizumab pegol, sodium acetate (1.36 mg), sodium chloride (7.31 mg), and Water for Injection, USP.
12. Cimzia - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Certolizumab pegol binds to human TNFα with a KD of 90pM. TNFα is a key pro-inflammatory cytokine with a central role in inflammatory processes. Certolizumab pegol selectively neutralizes TNFα (IC 90 of 4 ng/mL for inhibition of human TNFα in the in vitro L929 murine fibrosarcoma cytotoxicity assay) but does not neutralize lymphotoxin α (TNFβ). Certolizumab pegol cross-reacts poorly with TNF from rodents and rabbits, therefore in vivo efficacy was evaluated using animal models in which human TNFα was the physiologically active molecule.
Certolizumab pegol was shown to neutralize membrane-associated and soluble human TNFα in a dose-dependent manner. Incubation of monocytes with certolizumab pegol resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of LPS-induced TNFα and IL-1β production in human monocytes.
Certolizumab pegol does not contain a fragment crystallizable (Fc) region, which is normally present in a complete antibody, and therefore does not fix complement or cause antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. It does not induce apoptosis in vitro in human peripheral blood-derived monocytes or lymphocytes, nor does certolizumab pegol induce neutrophil degranulation.
A tissue reactivity study was carried out ex vivo to evaluate potential cross-reactivity of certolizumab pegol with cryosections of normal human tissues. Certolizumab pegol showed no reactivity with a designated standard panel of normal human tissues.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Biological activities ascribed to TNFα include the upregulation of cellular adhesion molecules and chemokines, upregulation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II molecules, and direct leukocyte activation. TNFα stimulates the production of downstream inflammatory mediators, including interleukin-1, prostaglandins, platelet activating factor, and nitric oxide. Elevated levels of TNFα have been implicated in the pathology of Crohn's disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Certolizumab pegol binds to TNFα, inhibiting its role as a key mediator of inflammation. TNFα is strongly expressed in the bowel wall in areas involved by Crohn's disease and fecal concentrations of TNFα in patients with Crohn's disease have been shown to reflect clinical severity of the disease. After treatment with certolizumab pegol, patients with Crohn's disease demonstrated a decrease in the levels of C-reactive protein (CRP). Increased TNFα levels are found in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients and play an important role in the joint destruction that is a hallmark of this disease.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies of CIMZIA have not been conducted to assess its carcinogenic potential. Certolizumab pegol was not genotoxic in the Ames test, the human peripheral blood lymphocytes chromosomal aberration assay, or the mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Since certolizumab pegol does not cross-react with mouse or rat TNFα, reproduction studies were performed in rats using a rodent anti-murine TNFα pegylated Fab fragment (cTN3 PF), similar to certolizumab pegol. The cTN3 PF had no effects on the fertility and general reproductive performance of male and female rats at intravenous doses up 100 mg/kg, administered twice weekly.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Crohn's Disease
The efficacy and safety of CIMZIA were assessed in two double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled studies in patients aged 18 years and older with moderately to severely active Crohn's disease, as defined by a Crohn's Disease Activity Index (CDAI) of 220 to 450 points, inclusive. CIMZIA was administered subcutaneously at a dose of 400 mg in both studies. Stable concomitant medications for Crohn's disease were permitted.
Study CD1
Study CD1 was a randomized placebo-controlled study in 662 patients with active Crohn's disease. CIMZIA or placebo was administered at Weeks 0, 2, and 4 and then every four weeks to Week 24. Assessments were done at Weeks 6 and 26. Clinical response was defined as at least a 100-point reduction in CDAI score compared to baseline, and clinical remission was defined as an absolute CDAI score of 150 points or lower.
The results for Study CD1 are provided in Table 3. At Week 6, the proportion of clinical responders was statistically significantly greater for CIMZIA-treated patients compared to controls. The difference in clinical remission rates was not statistically significant at Week 6. The difference in the proportion of patients who were in clinical response at both Weeks 6 and 26 was also statistically significant, demonstrating maintenance of clinical response.
| Timepoint | % Response or Remission (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Placebo
(N = 328) | CIMZIA 400 mg
(N = 331) |
|
|
||
| Week 6 | ||
| Clinical Response * | 27% (22%, 32%) | 35% (30%, 40%) † |
| Clinical Remission * | 17% (13%, 22%) | 22% (17%, 26%) |
| Week 26 | ||
| Clinical Response | 27% (22%, 31%) | 37% (32%, 42%) † |
| Clinical Remission | 18% (14%, 22%) | 29% (25%, 34%) † |
| Both Weeks 6 & 26 | ||
| Clinical Response | 16% (12%, 20%) | 23% (18%, 28%) † |
| Clinical Remission | 10% (7%, 13%) | 14% (11%, 18%) |
Study CD2
Study CD2 was a randomized treatment-withdrawal study in patients with active Crohn's disease. All patients who entered the study were dosed initially with CIMZIA 400 mg at Weeks 0, 2, and 4 and then assessed for clinical response at Week 6 (as defined by at least a 100-point reduction in CDAI score). At Week 6, a group of 428 clinical responders was randomized to receive either CIMZIA 400 mg or placebo, every four weeks starting at Week 8, as maintenance therapy through Week 24. Non-responders at Week 6 were withdrawn from the study. Final evaluation was based on the CDAI score at Week 26. Patients who withdrew or who received rescue therapy were considered not to be in clinical response. Three randomized responders received no study injections, and were excluded from the ITT analysis.
The results for clinical response and remission are shown in Table 4. At Week 26, a statistically significantly greater proportion of Week 6 responders were in clinical response and in clinical remission in the CIMZIA-treated group compared to the group treated with placebo.
| % Response or Remission (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|
| CIMZIA 400 mg ×3 + Placebo
N = 210 | CIMZIA
400 mg N = 215 |
|
|
||
| Week 26 | ||
| Clinical Response * | 36% (30%, 43%) | 63% (56%, 69%) † |
| Clinical Remission * | 29% (22%, 35%) | 48% (41%, 55%) † |
Baseline use of immunosuppressants or corticosteroids had no impact on the clinical response to CIMZIA.
14.2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
The efficacy and safety of CIMZIA were assessed in four randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies (RA-I, RA-II, RA-III, and RA-IV) in patients ≥ 18 years of age with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed according to the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria. Patients had ≥ 9 swollen and tender joints and had active RA for at least 6 months prior to baseline. CIMZIA was administered subcutaneously in combination with MTX at stable doses of at least 10 mg weekly in Studies RA-I, RA-II, and RA-III. CIMZIA was administered as monotherapy in Study RA-IV.
Study RA-I and Study RA-II evaluated patients who had received MTX for at least 6 months prior to study medication, but had an incomplete response to MTX alone. Patients were treated with a loading dose of 400 mg at Weeks 0, 2 and 4 (for both treatment arms) or placebo followed by either 200 mg or 400 mg of CIMZIA or placebo every other week, in combination with MTX for 52 weeks in Study RA-I and for 24 weeks in Study RA-II. Patients were evaluated for signs and symptoms and structural damage using the ACR20 response at Week 24 (RA-I and RA-II) and modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) at Week 52 (RA-I). The open-label extension follow-up study enrolled 846 patients who received 400 mg of CIMZIA every other week.
Study RA-III evaluated 247 patients who had active disease despite receiving MTX for at least 6 months prior to study enrollment. Patients received 400 mg of CIMZIA every four weeks for 24 weeks without a prior loading dose. Patients were evaluated for signs and symptoms of RA using the ACR20 at Week 24.
Study RA-IV (monotherapy) evaluated 220 patients who had failed at least one DMARD use prior to receiving CIMZIA. Patients were treated with CIMZIA 400 mg or placebo every 4 weeks for 24 weeks. Patients were evaluated for signs and symptoms of active RA using the ACR20 at Week 24.
Clinical Response
The percent of CIMZIA-treated patients achieving ACR20, 50, and 70 responses in Studies RA-I and RA-IV are shown in Table 5. CIMZIA-treated patients had higher ACR20, 50 and 70 response rates at 6 months compared to placebo-treated patients. The results in study RA-II (619 patients) were similar to the results in RA-I at Week 24. The results in study RA-III (247 patients) were similar to those seen in study RA-IV. Over the one-year Study RA-I, 13% of CIMZIA-treated patients achieved a major clinical response, defined as achieving an ACR70 response over a continuous 6-month period, compared to 1% of placebo-treated patients.
| Study RA-I
Methotrexate Combination (24 and 52 weeks) | Study RA-IV
Monotherapy (24 weeks) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response | Placebo + MTX | CIMZIA
* 200 mg + MTX
q 2 weeks | CIMZIA * 200 mg + MTX - Placebo + MTX | Placebo | CIMZIA
† 400 mg
q 4 weeks | CIMZIA † 400 mg - Placebo |
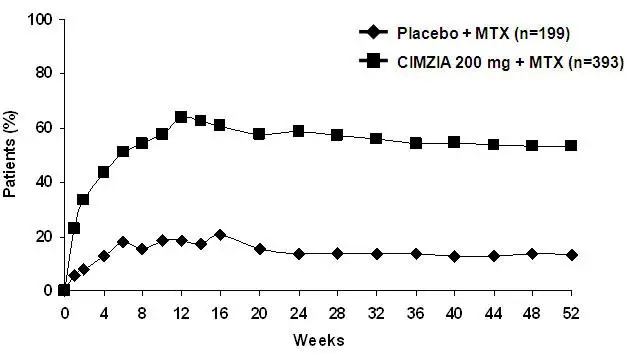
| N=199 | N=393 | (95% CI) ‡ | N=109 | N=111 | (95% CI) ‡ | |
|
||||||
| ACR20 | ||||||
| Week 24 | 14% | 59% | 45% (38%, 52%) | 9% | 46% | 36% (25%, 47%) |
| Week 52 | 13% | 53% | 40% (33%, 47%) | N/A | N/A | |
| ACR50 | ||||||
| Week 24 | 8% | 37% | 30% (24%, 36%) | 4% | 23% | 19% (10%, 28%) |
| Week 52 | 8% | 38% | 30% (24%, 37%) | N/A | N/A | |
| ACR70 | ||||||
| Week 24 | 3% | 21% | 18% (14%, 23%) | 0% | 6% | 6% (1%, 10%) |
| Week 52 | 4% | 21% | 18% (13%, 22%) | N/A | N/A | |
| Major Clinical Response § | 1% | 13% | 12% (8%, 15%) | |||
| Study RA-I | Study RA-IV | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter * | Placebo +
MTX N=199 | CIMZIA
† 200 mg + MTX q 2 weeks
N=393 | Placebo
N=109 | CIMZIA
‡ 400 mg q 4 weeks
Monotherapy N=111 |
||||
| Baseline | Week 24 | Baseline | Week 24 | Baseline | Week 24 | Baseline | Week 24 | |
|
||||||||
| Number of tender joints (0-68) | 28 | 27 | 29 | 9 | 28 (12.5) | 24 (15.4) | 30 (13.7) | 16 (15.8) |
| Number of swollen joints (0-66) | 20 | 19 | 20 | 4 | 20 (9.3) | 16 (12.5) | 21 (10.1) | 12 (11.2) |
| Physician global assessment § | 66 | 56 | 65 | 25 | 4 (0.6) | 3 (1.0) | 4 (0.7) | 3 (1.1) |
| Patient global assessment § | 67 | 60 | 64 | 32 | 3 (0.8) | 3 (1.0) | 3 (0.8) | 3 (1.0) |
| Pain §¶ | 65 | 60 | 65 | 32 | 55 (20.8) | 60 (26.7) | 58 (21.9) | 39 (29.6) |
| Disability index (HAQ) # | 1.75 | 1.63 | 1.75 | 1.00 | 1.55 (0.65) | 1.62 (0.68) | 1.43 (0.63) | 1.04 (0.74) |
| CRP (mg/L)
| 16.0 | 14.0 | 16.0 | 4.0 | 11.3 | 13.5 | 11.6 | 6.4 |
The percent of patients achieving ACR20 responses by visit for Study RA-I is shown in Figure 1. Among patients receiving CIMZIA, clinical responses were seen in some patients within one to two weeks after initiation of therapy.
|
| Figure 1 Study RA-I ACR20 Response Over 52 Weeks * |
|
|
Radiographic Response
In Study RA-I, inhibition of progression of structural damage was assessed radiographically and expressed as the change in modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) and its components, the Erosion Score (ES) and Joint Space Narrowing (JSN) score, at Week 52, compared to baseline. CIMZIA inhibited the progression of structural damage compared to placebo plus MTX after 12 months of treatment as shown in Table 7. In the placebo group, 52% of patients experienced no radiographic progression (mTSS ≤0.0) at Week 52 compared to 69% in the CIMZIA 200 mg every other week treatment group. Study RA-II showed similar results at Week 24.
| Placebo + MTX
N=199 Mean (SD) | CIMZIA 200 mg + MTX
N=393 Mean (SD) | CIMZIA 200 mg + MTX –
Placebo + MTX Mean Difference |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| An ANCOVA was fitted to the ranked change from baseline for each measure with region and treatment as factors and rank baseline as a covariate. | |||
| mTSS | |||
| Baseline | 40 (45) | 38 (49) | -- |
| Week 24 | 1.3 (3.8) | 0.2 (3.2) | -1.1 |
| Week 52 | 2.8 (7.8) | 0.4 (5.7) | -2.4 |
| Erosion Score | |||
| Baseline | 14 (21) | 15 (24) | -- |
| Week 24 | 0.7 (2.1) | 0.0 (1.5) | -0.7 |
| Week 52 | 1.5 (4.3) | 0.1 (2.5) | -1.4 |
| JSN Score | |||
| Baseline | 25 (27) | 24 (28) | -- |
| Week 24 | 0.7 (2.4) | 0.2 (2.5) | -0.5 |
| Week 52 | 1.4 (5.0) | 0.4 (4.2) | -1.0 |
14.3 Psoriatic Arthritis
The efficacy and safety of CIMZIA were assessed in a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial (PsA001) in 409 patients aged 18 years and older with active psoriatic arthritis despite DMARD therapy. Patients in this study had ≥ 3 swollen and tender joints and adult-onset PsA of at least 6 months' duration as defined by the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) criteria, and increased acute phase reactants. Patients had failed one or more DMARDs. Previous treatment with one anti-TNF biologic therapy was allowed, and 20% of patients had prior anti-TNF biologic exposure. Patients receiving concomitant NSAIDs and conventional DMARDs were 73% and 70 % respectively.
Patients received a loading dose of CIMZIA 400 mg at Weeks 0, 2 and 4 (for both treatment arms) or placebo followed by either CIMZIA 200 mg every other week or CIMZIA 400 mg every 4 weeks or placebo every other week. Patients were evaluated for signs and symptoms and structural damage using the ACR20 response at Week 12 and modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) at Week 24.
Clinical Response
The percentage of CIMZIA-treated patients achieving ACR20, 50 and 70 responses in study PsA001 are shown in Table 8. ACR20 response rates at weeks 12 and 24 were higher for each CIMZIA dose group relative to placebo (95% confidence intervals for CIMZIA 200 mg minus placebo at weeks 12 and 24 of (23%, 45%) and (30%, 51%), respectively and 95% confidence intervals for CIMZIA 400 mg minus placebo at weeks 12 and 24 of (17%, 39%) and (22%, 44%), respectively). The results of the components of the ACR response criteria are shown in Table 9.
Patients with enthesitis at baseline were evaluated for mean improvement in Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI). CIMZIA-treated patients receiving either 200 mg every 2 weeks or 400 mg every 4 weeks showed a reduction in enthesitis of 1.8 and 1.7, respectively as compared with a reduction in placebo-treated patients of 0.9 at week 12. Similar results were observed for this endpoint at week 24. Treatment with CIMZIA resulted in improvement in skin manifestations in patients with PsA.
| Response * | Placebo | CIMZIA
†200 mg
Q2W | CIMZIA
‡ 400 mg
Q4W |
|---|---|---|---|
| N=136 | N=138 | N=135 | |
|
|||
| ACR20 | |||
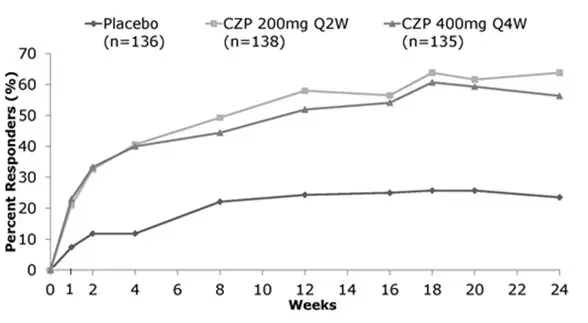
| Week 12 | 24% | 58% | 52% |
| Week 24 | 24% | 64% | 56% |
| ACR50 | |||
| Week 12 | 11% | 36% | 33% |
| Week 24 | 13% | 44% | 40% |
| ACR70 | |||
| Week 12 | 3% | 25% | 13% |
| Week 24 | 4% | 28% | 24% |
| Parameter | Placebo
*
N=136 | CIMZIA
† 200 mg Q2W
N=138 | CIMZIA
‡ 400 mg Q4W
N=135 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 12 | Baseline | Week 12 | Baseline | Week 12 | |
| All values presented represent the mean | ||||||
| Results are from the randomized set (either with imputation or observed case) | ||||||
|
||||||
| Number of tender joints (0-68) § | 20 | 17 | 22 | 11 | 20 | 11 |
| Number of swollen joints (0-66) § | 10 | 9 | 11 | 4 | 11 | 5 |
| Physician global assessment §, ¶ | 59 | 44 | 57 | 25 | 58 | 29 |
| Patient global assessment §, ¶ | 57 | 50 | 60 | 33 | 60 | 40 |
| Pain §, # | 60 | 50 | 60 | 33 | 61 | 39 |
| Disability index (HAQ) §, Þ | 1.30 | 1.15 | 1.33 | 0.87 | 1.29 | 0.90 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 18.56 | 14.75 | 15.36 | 5.67 | 13.71 | 6.34 |
The percent of patients achieving ACR20 responses by visit for PsA001 is shown in Figure 2.
| Randomized Set. Non-responder imputation used for patients with missing data or those who escaped therapy. |
|
| Figure 2: Study PsA001-ACR20 Response Over 24 Weeks * |
|
|
14.4 Ankylosing Spondylitis
The efficacy and safety of CIMZIA were assessed in one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (AS-1) in 325 patients ≥18 years of age with adult-onset active axial spondyloarthritis for at least 3 months. The majority of patients in the study had active AS.
Patients had active disease as defined by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≥4, and spinal pain ≥4 on a 0 to 10 Numerical Rating Scale (NRS). Patients must have been intolerant to or had an inadequate response to at least one NSAID. Patients were treated with a loading dose of CIMZIA 400 mg at Weeks 0, 2 and 4 (for both treatment arms) or placebo followed by either 200 mg of CIMZIA every 2 weeks or 400 mg of CIMZIA every 4 weeks or placebo. Concomitant NSAIDs were received by 91% of the AS patients. The primary efficacy variable was the proportion of patients achieving an ASAS20 response at Week 12.
Clinical Response
In study AS-1, at Week 12, a greater proportion of AS patients treated with CIMZIA 200 mg every 2 weeks or 400 mg every 4 weeks achieved ASAS 20 response compared to AS patients treated with placebo (Table 10). Responses were similar in patients receiving CIMZIA 200 mg every 2 weeks and CIMZIA 400 mg every 4 weeks. The results of the components of the ASAS response criteria and other measures of disease activity are shown in Table 11.
| Parameters | Placebo
N=57 | CIMZIA
* 200 mg every 2 weeks
N=65 | CIMZIA
† 400 mg every 4 weeks
N=56 |
|---|---|---|---|
| All percents reflect the proportion of patients who responded in the full analysis set | |||
|
|||
| ASAS20 | |||
| Week 12 | 37% | 57% | 64% |
| Week 24 | 33% | 68% | 70% |
| ASAS40 | |||
| Week 12 | 19% | 40% | 50% |
| Week 24 | 16% | 48% | 59% |
| Placebo
N=57 | CIMZIA
* 200 mg every 2 weeks
N=65 | CIMZIA
† 400 mg every 4 weeks
N=56 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 12 | Baseline | Week 12 | Baseline | Week 12 | |
| All values presented represent the mean in the full analysis set | ||||||
|
||||||
| ASAS20 response criteria | ||||||
| -Patient Global Assessment (0-10) | 6.9 | 5.6 | 7.3 | 4.2 | 6.8 | 3.8 |
| -Total spinal pain (0-10) | 7.3 | 5.8 | 7.0 | 4.3 | 6.9 | 4.0 |
| -BASFI (0-10) ‡ | 6.0 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 3.8 | 5.7 | 3.8 |
| -Inflammation (0-10) | 6.7 | 5.5 | 6.7 | 3.8 | 6.4 | 3.4 |
| BASDAI (0-10) § | 6.4 | 5.4 | 6.5 | 4.0 | 6.2 | 3.7 |
| BASMI ¶ | 4.8 | 4.4 | 4.2 | 3.6 | 4.3 | 3.9 |
The percent of AS patients achieving ASAS20 responses by visit for Study AS001 is shown in Figure 3. Among patients receiving CIMZIA, clinical responses were seen in some AS patients within one to two weeks after initiation of therapy.
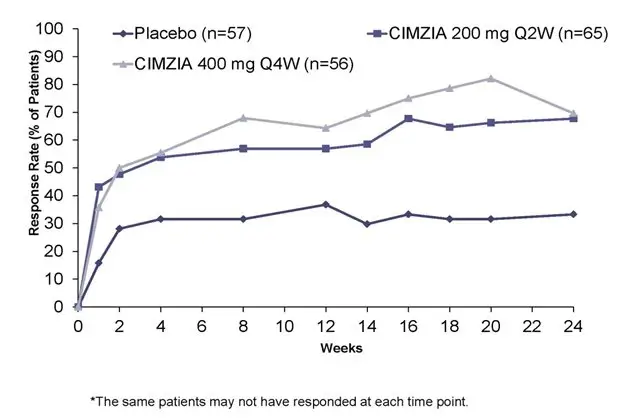
Figure 3: Study AS-1: ASAS20 response over 24 weeks in AS patients *
14.5 Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis
The efficacy and safety of CIMZIA were assessed in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (nr-axSpA-1) (NCT02552212) in 317 subjects ≥18 years of age with adult-onset active axial spondyloarthritis for at least 12 months. Patients must have had objective signs of inflammation indicated by C-reactive protein (CRP) levels above the upper limit of normal and/or sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), indicative of inflammatory disease [positive CRP (> ULN) and/or positive MRI], but without definitive radiographic evidence of structural damage on sacroiliac joints. Patients had active disease as defined by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≥4, and spinal pain ≥4 on a 0 to 10 Numerical Rating Scale (NRS). Patients must have been intolerant to or had an inadequate response to at least two NSAIDs. Patients were treated with a loading dose of CIMZIA 400 mg at Weeks 0, 2 and 4 or placebo followed by 200 mg of CIMZIA every 2 weeks or placebo. Utilization and dose adjustment of concomitant medications (including NSAIDs, DMARDs, corticosteroids, opioids) were permitted at any time. Patients were allowed to transition to use of open-label CIMZIA at any time at the discretion of the investigator. However, no patients transitioned before Week 12. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving an Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score-Major Improvement (ASDAS-MI) response at Week 52. The ASDAS is a composite weighted scoring system that assesses disease activity, including patient-reported outcomes and CRP levels. A response in ASDAS-Major Improvement (MI) is indicated by a change from baseline of ≥2.0 in the ASDAS and/or reaching the lowest possible ASDAS value.
Clinical Response
In study nr-axSpA-1, at Week 52, a greater proportion of nr-axSpA patients treated with CIMZIA had ASDAS-MI response compared to patients treated with placebo. At both Weeks 12 and 52, ASAS40 responses were greater for patients treated with CIMZIA compared to patients treated with placebo (Table 12). The components of the ASDAS-MI and ASAS response criteria are shown in Table 13.
| Parameters | Placebo | CIMZIA * 200 mg every 2 weeks | CIMZIA 200 mg versus Placebo Odds ratio
(95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N=158 | N=159 | ||
|
|||
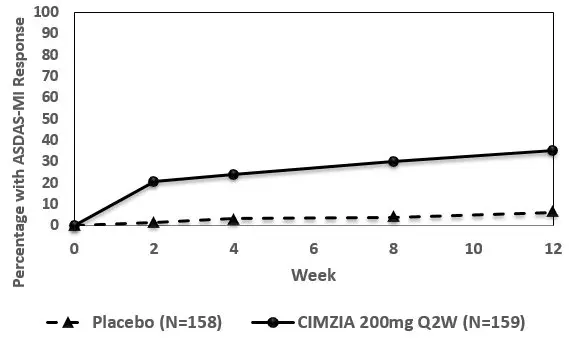
| ASDAS-MI | |||
| Week 52 | 7% | 47% | 15.2
(7.3 , 31.6) |
| ASAS-40 | |||
| Week 12 | 11% | 48% | 7.4
(4.1, 13.4) |
| Week 52 | 16% | 57% | 7.4
(4.3, 12.6) |
| Placebo | CIMZIA * 200 mg every 2 weeks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N=158 | N=159 | |||
| Baseline
(SD) | Week 12
(SD) | Baseline
(SD) | Week 12
(SD) |
|
| Mean and standard deviation in parenthesis were presented based on full analysis set. | ||||
|
||||
| Total Spinal Pain (0-10) | 6.9 (1.8) | 6.0 (2.3) | 7.0 (1.9) | 3.9 (2.6) |
| Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity (0-10) | 6.7 (2.0) | 5.9 (2.4) | 6.8 (1.9) | 3.8 (2.6) |
| C-Reactive Protein (mg/L) | 15.8 (17.7) | 13.2 (17.2) | 15.8 (17.8) | 6.7 (15.1) |
| BASDAI (0-10) † | 6.8 (1.3) | 5.7 (2.1) | 6.9 (1.4) | 3.9 (2.2) |
| - Back Pain | 7.4 (1.3) | 6.2 (2.1) | 7.4 (1.4) | 4.1 (2.5) |
| - Peripheral pain and swelling (0-10) | 6.2 (2.2) | 5.3 (2.5) | 6.3 (2.3) | 3.7 (2.4) |
| - Inflammation ‡ | 6.7 (1.8) | 5.5 (2.4) | 6.9 (1.8) | 3.6 (2.4) |
| BASFI (0-10) § | 5.4 (2.2) | 4.9 (2.4) | 5.4 (2.1) | 3.2 (2.3) |
| BASMI ¶ | 2.8 (1.4) | 2.7 (1.4) | 3.0 (1.3) | 2.6 (1.4) |
The percentage of nr-axSpA patients achieving ASDAS-MI response by visit for study nr-axSpA-1 is shown in Figure 4.
|
|
Figure 4: Study nr-axSpA-1: ASDAS-MI response over 12 weeks * |
|
|
In study AS-1, at Week 12, patients with nr-axSpA treated with CIMZIA 200 mg every 2 weeks and CIMZIA 400 mg every 4 weeks had an ASAS 20 response of 42% and 47%, respectively, compared to 20% of patients treated with placebo. The ASAS 40 response in patients treated with CIMZIA 200 mg every 2 weeks and 400 mg every 4 weeks was 30% and 37%, respectively, compared to 11% of patients treated with placebo at Week 12 (see Section 14.4).
14.6 Plaque Psoriasis
Three multicenter, randomized, double-blind studies (Study PS-1 [NCT02326298], Study PS-2 [NCT02326272], and Study PS-3 [NCT02346240]) enrolled subjects 18 years of age or older with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis who were eligible for systemic therapy or phototherapy. Subjects had a Physician Global Assessment (PGA) of ≥ 3 ("moderate") on a 5-category scale of overall disease severity, a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score ≥ 12, and body surface area (BSA) involvement of ≥ 10%.
Studies PS-1 (234 subjects) and PS-2 (227 subjects) randomized subjects to placebo, CIMZIA 200 mg every other week (following a loading dose of CIMZIA 400 mg at Weeks 0, 2, and 4), or CIMZIA 400 mg every other week. Studies PS-1 and PS-2 assessed the co-primary endpoints of the proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 75 and PGA of "clear" or "almost clear" with at least a 2-point improvement at Week 16. Other evaluated outcomes were PASI 90 at Week 16 and maintenance of efficacy to Week 48.
Study PS-3 randomized 559 subjects to receive placebo, CIMZIA 200 mg every other week (following a loading dose of CIMZIA 400 mg at Weeks 0, 2, and 4), CIMZIA 400 mg every other week up to Week 16, or a biologic comparator (up to Week 12). Study PS-3 assessed the proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 75 at Week 12 as the primary endpoint. Other evaluated outcomes were PGA of "clear" or "almost clear" at Week 16, PASI 75 at Week 16, PASI 90 at Week 16, and maintenance of efficacy to Week 48.
Of the 850 subjects randomized to receive placebo or CIMZIA in these placebo-controlled studies, 29% of patients were naïve to prior systemic therapy for the treatment of psoriasis, 47% had received prior phototherapy or chemophototherapy, and 30% had received prior biologic therapy for the treatment of psoriasis. Of the 850 subjects, 14% had received at least one TNF alpha agent and 16% had received an anti-IL agent. Eighteen percent of subjects reported a history of psoriatic arthritis at baseline.
Across all studies and treatment groups, the mean PASI score at baseline was 20 and ranged from 12 to 69. The baseline PGA score ranged from moderate (70%) to severe (30%). Mean baseline BSA was 25% and ranged from 10% to 96%. Subjects were predominantly men (64%) and White (94%), with a mean age of 46 years.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use)
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: April 2020 | |||
| MEDICATION GUIDE
CIMZIA ® (CIM-zee-uh) (certolizumab pegol) injection for subcutaneous use |
||||
| What is the most important information I should know about CIMZIA?
CIMZIA may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
|
|
|||
|
||||
| Stop using CIMZIA, and tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the symptoms of an infection listed above. | ||||
|
||||
| What is CIMZIA?
CIMZIA is a prescription medicine called a Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) blocker used in adults to:
|
||||
Before receiving CIMZIA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
||||
How will I receive CIMZIA?
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of CIMZIA?
CIMZIA can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
|
|
|||
|
||||
|
|
|||
The most common side effects of CIMZIA include upper respiratory infections (flu, cold), rash, urinary tract infections (bladder infections). These are not all of the possible side effects of CIMZIA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||
How should I store CIMZIA?
|
||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of CIMZIA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use CIMZIA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give CIMZIA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about CIMZIA that is written for health professionals. |
||||
| What are the ingredients in CIMZIA?
CIMZIA lyophilized powder: Active ingredient: certolizumab pegol Inactive ingredients: lactic acid, polysorbate, sucrose CIMZIA lyophilized powder is mixed with sterile Water for Injection. CIMZIA prefilled syringe: Active ingredient: certolizumab pegol Inactive ingredients: sodium acetate, sodium chloride, Water for Injection CIMZIA has no preservatives. Product manufactured by: UCB, Inc. 1950 Lake Park Drive Smyrna, GA 30080 US License No. 1736 For more information, go to www.CIMZIA.com or call 1-866-424-6942. |
||||
Instructions for Use
CIMZIA
® (CIM-zee-uh)
(certolizumab pegol)
injection for subcutaneous use
Prefilled Syringes
Read this Instructions for Use booklet that comes with CIMZIA before you start receiving it, and before each injection of CIMZIA. This Instructions for Use booklet does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. These instructions are for 1 injection only. You may need more than 1 injection at a time depending on your prescribed dose of CIMZIA.
| Do not share your CIMZIA Prefilled Syringe with needle attached with another person. You may give another person an infection or get an infection from them.
Important: The plastic needle shield inside the removable cap contains natural rubber. Tell your healthcare provider if you are allergic to latex. Supplies you will need to give your CIMZIA injection: See Figure A and Figure B.
CIMZIA comes in a tray containing 2 prefilled glass syringes. Use a new CIMZIA syringe for each injection. |
|
Storage information:
|
|
| Setting up for your CIMZIA injection:
Step 1. If refrigerated, take the carton containing the prefilled syringes of CIMZIA out of the refrigerator. Check the expiration date on the syringe carton and label. See Figure C. |
|
| If the expiration date has passed,
do not use the syringe. Call your pharmacist for questions about the expiration date. Do not use CIMZIA if the carton has been opened or tampered with.
|
|
| Step 2.
Remove the prefilled syringe from the carton and let it warm to room temperature, this will take about 30 minutes. Do not warm the syringe in any other way. If you are not using the second syringe, put the carton containing the remaining prefilled syringe back in the refrigerator. |
|
| Step 3.
Find a clean, flat work surface, such as a table. |
|
| Step 4.
Make sure the liquid medicine in the prefilled syringe is clear and colorless to yellow and free from particles. Do not inject the medicine if it is cloudy, discolored, or contains particles. Call your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions about your CIMZIA prefilled syringe. |
|
| Step 5.
Gather all the supplies you will need for your injection. |
|
| Step 6.
Wash your hands with soap and warm water and dry with a clean towel. |
|
| Selecting and preparing your injection site:
|
|
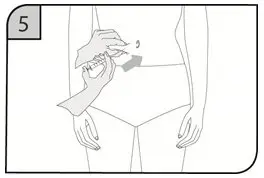
| Step 7.
Choose your injection site(s) on your stomach or upper thighs. See Figure D. 
|
|
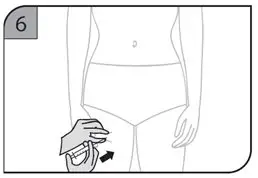
| Step 8.
Clean your injection site with an alcohol swab. Let the area dry completely. |
|
| Giving your CIMZIA injection:
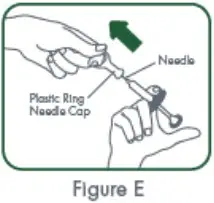
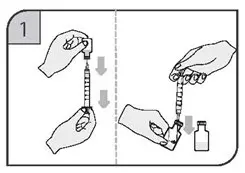
Step 9. Pick up the prefilled syringe with 1 hand and hold it with the needle pointing up. You may see air bubbles. This is normal. There is no need to remove air bubbles before giving your injection. Injecting the solution with air bubbles will not harm you. With your other hand, remove the plastic ring needle cap by pulling straight up on the plastic ring. See Figure E. |
|
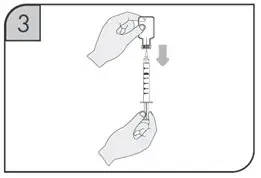
| Do not touch the needle and do not let the needle touch any surface.
Do not bend the needle. Place the plastic ring needle cap to the side. |
|
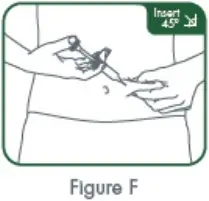
| Step 10.
With your other hand, gently pinch a fold of skin at the cleaned injection site. See Figure F. |
|
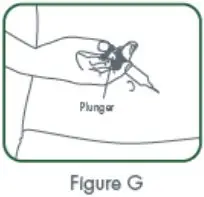
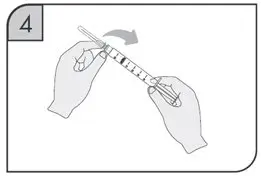
| Step 11.
With a quick, "dart-like" motion, insert the needle into your skin at about a 45 degree angle. Release the pinched skin, keeping the syringe in position. Slowly push on the plunger all the way down until the syringe is empty. See Figure G. |
|
| Step 12.
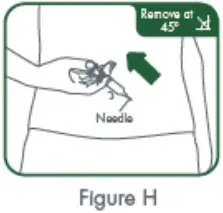
When the syringe is empty, pull the needle out of your skin while carefully keeping the needle at the same angle as inserted. See Figure H. |
|
| Step 13.
Place a dry cotton ball or gauze pad over the injection site for several seconds. See Figure I. |
|
 |
|
| Do not rub the injection site. Do not use an alcohol swab as it may cause stinging. If there is a little bleeding, cover the injection site with a small bandage.
To avoid a needle-stick injury, do not try to recap the needle. Do not reuse any of your injection supplies. |
|
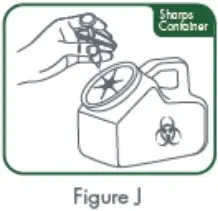
| Do not throw away (dispose of) loose syringes and needles in your household trash. |
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out
- upright and stable during use
- leak-resistant
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Product manufactured by:
UCB, Inc.
1950 Lake Park Drive
Smyrna, GA 30080
Revised: 04/2020
| CIMZIA
certolizumab pegol kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CIMZIA
certolizumab pegol injection, solution |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - UCB, Inc. (028526403) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unither Manufacturing LLC | 079176615 | manufacture(50474-700, 50474-710) , label(50474-700, 50474-710) , pack(50474-700, 50474-710) , analysis(50474-700, 50474-710) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| UCB Pharma S.A. | 372274485 | analysis(50474-700, 50474-710) , manufacture(50474-700, 50474-710) , label(50474-700, 50474-710) | |