Drug Detail:Coartem (Artemether and lumefantrine [ ar-tem-e-ther-and-loo-me-fan-treen ])
Drug Class: Antimalarial combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
COARTEM® (artemether and lumefantrine) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2009
Indications and Usage for Coartem
- Coartem Tablets are a combination of artemether and lumefantrine, both antimalarials, indicated for treatment of acute, uncomplicated malaria infections due to Plasmodium falciparum (P. falciparum) in patients 2 months of age and older with a bodyweight of 5 kg and above. (1)
- Coartem Tablets have been shown to be effective in geographical regions where resistance to chloroquine has been reported. (1)
Limitations of Use: (1)
- Coartem Tablets are not approved for patients with severe or complicated P. falciparum malaria.
- Coartem Tablets are not approved for the prevention of malaria.
Coartem Dosage and Administration
- Coartem Tablets should be taken with food. (2.1, 5.2)
- Tablets may be crushed and mixed with 1 to 2 teaspoons of water immediately prior to administration to patients, including children. (2.1)
- Coartem Tablets should be administered over 3 days for a total of 6 doses: an initial dose, second dose after 8 hours, and then twice-daily (morning and evening) for the following 2 days. (2.2, 2.3)
- The adult dosage for patients with bodyweight of 35 kg and above is 4 tablets per dose for a total of 6 doses. (2.2)
- The number of tablets per dose for children is determined by bodyweight, as shown in the chart below. (2.3)
| 5 to < 15 kg | 1 tablet |
| 15 to < 25 kg | 2 tablets |
| 25 to < 35 kg | 3 tablets |
| 35 kg and over | 4 tablets |
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets are scored and contain 20 mg artemether and 120 mg lumefantrine. (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to artemether, lumefantrine, or to any of the excipients. (4)
- Coadministration of strong inducers of CYP3A4 such as rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, and St. John’s wort with Coartem Tablets. (4, 7.1, 12.3)
Warnings and Precautions
- Avoid use in patients with known QT prolongation, those with hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, and those taking other drugs that prolong the QT interval. (5.1, 12.6)
- Halofantrine and Coartem Tablets should not be administered within one month of each other due to potential additive effects on the QT interval. (5.1, 5.2, 12.3)
- Antimalarials should not be given concomitantly, unless there is no other treatment option, due to limited safety data. (5.2)
- QT prolonging drugs, including quinine and quinidine, should be used cautiously following Coartem Tablets. (5.1, 5.2, 7.7, 12.3)
- Substrates, inhibitors, or inducers of CYP3A4, including antiretroviral medications, should be used cautiously with Coartem Tablets, due to a potential loss of efficacy of the concomitant drug or additive QT prolongation. (5.3, 7.2, 7.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions in adults (greater than 30%) are headache, anorexia, dizziness, asthenia, arthralgia, and myalgia. The most common adverse reactions in children (greater than 12%) are pyrexia, cough, vomiting, anorexia, and headache. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inducers: Potential for loss of antimalarial efficacy. (4, 5.3, 7.1, 12.3)
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Use cautiously due to potential for QT prolongation. (5.3, 7.2, 12.3)
- Antiretrovirals: Use cautiously due to potential for QT prolongation, loss of antiviral efficacy, or loss of antimalarial efficacy of Coartem Tablets. (5.3, 7.3, 12.3)
- Mefloquine: If used immediately before treatment, monitor for decreased efficacy of Coartem Tablets and encourage food consumption. (2.1, 7.4, 12.3)
- Hormonal Contraceptives: Effectiveness may be reduced; use an additional method of birth control. (5.3, 7.5, 12.3)
- CYP2D6 Substrates: Monitor for adverse reactions and potential QT prolongation. (5.1, 5.4, 7.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2019
Related/similar drugs
doxycycline, clindamycin, hydroxychloroquine, Plaquenil, CleocinFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Coartem
Coartem Tablets are indicated for treatment of acute, uncomplicated malaria infections due to Plasmodium falciparum (P. falciparum) in patients 2 months of age and older with a bodyweight of 5 kg and above. Coartem Tablets have been shown to be effective in geographical regions where resistance to chloroquine has been reported [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Limitations of Use:
- Coartem Tablets are not approved for patients with severe or complicated P. falciparum malaria.
- Coartem Tablets are not approved for the prevention of malaria.
2. Coartem Dosage and Administration
2.1 Administration Instructions
Coartem Tablets should be taken with food. Patients with acute malaria are frequently averse to food. Patients should be encouraged to resume normal eating as soon as food can be tolerated since this improves absorption of artemether and lumefantrine.
For patients who are unable to swallow the tablets such as infants and children, Coartem Tablets may be crushed and mixed with a small amount of water (1 to 2 teaspoons) in a clean container for administration immediately prior to use. The container can be rinsed with more water and the contents swallowed by the patient. The crushed tablet preparation should be followed whenever possible by food/drink (e.g., milk, formula, pudding, broth, and porridge).
In the event of vomiting within 1 to 2 hours after administration, a repeat dose should be taken. If the repeat dose is vomited, the patient should be given an alternative antimalarial for treatment.
2.2 Dosage in Adult Patients (greater than 16 years of age)
A 3-day treatment schedule with a total of 6 doses is recommended for adult patients with a bodyweight of 35 kg and above:
Four tablets as a single initial dose, 4 tablets again after 8 hours, and then 4 tablets twice-daily (morning and evening) for the following 2 days (total course of 24 tablets).
For patients weighing less than 35 kg, [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
2.3 Dosage in Pediatric Patients
A 3-day treatment schedule with a total of 6 doses is recommended as below:
5 kg to less than 15 kg bodyweight: One tablet as an initial dose, 1 tablet again after 8 hours, and then 1 tablet twice daily (morning and evening) for the following 2 days (total course of 6 tablets).
15 kg to less than 25 kg bodyweight: Two tablets as an initial dose, 2 tablets again after 8 hours, and then 2 tablets twice daily (morning and evening) for the following 2 days (total course of 12 tablets).
25 kg to less than 35 kg bodyweight: Three tablets as an initial dose, 3 tablets again after 8 hours, and then 3 tablets twice daily (morning and evening) for the following 2 days (total course of 18 tablets).
35 kg bodyweight and above: Four tablets as a single initial dose, 4 tablets again after 8 hours, and then 4 tablets twice daily (morning and evening) for the following 2 days (total course of 24 tablets).
2.4 Dosage in Patients With Hepatic or Renal Impairment
No specific pharmacokinetic studies have been carried out in patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Most patients with acute malaria present with some degree of related hepatic and/or renal impairment. In clinical studies, the adverse event profile did not differ in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment compared to patients with normal hepatic function. No specific dose adjustments are needed for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment.
In clinical studies, the adverse event profile did not differ in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment compared to patients with normal renal function. There were few patients with severe renal impairment in clinical studies. There is no significant renal excretion of lumefantrine, artemether, and dihydroartemisinin (DHA) in healthy volunteers and while clinical experience in this population is limited, no dose adjustment is recommended.
Caution should be exercised when administering Coartem Tablets in patients with severe hepatic or renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Coartem Tablets contain 20 mg of artemether and 120 mg of lumefantrine. Coartem Tablets are supplied as yellow, round, flat tablets with beveled edges and scored on one side. Tablets are imprinted with “N/C” on one side and “CG” on the other side.
4. Contraindications
Hypersensitivity
Known hypersensitivity to artemether, lumefantrine, or to any of the excipients of Coartem Tablets [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Coadministration of strong inducers of CYP3A4 such as rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, and St. John’s wort with Coartem Tablets can result in decreased concentrations of artemether and/or lumefantrine and loss of antimalarial efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Prolongation of the QT Interval
Some antimalarials (e.g., halofantrine, quinine, quinidine) including Coartem Tablets have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram (ECG).
Coartem Tablets should be avoided in patients:
- With congenital prolongation of the QT interval (e.g., long QT syndrome) or any other clinical condition known to prolong the QTc interval such as patients with a history of symptomatic cardiac arrhythmias, with clinically relevant bradycardia or with severe cardiac disease.
- With a family history of congenital prolongation of the QT interval or sudden death.
- With known disturbances of electrolyte balance, e.g., hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia.
- Receiving other medications that prolong the QT interval, such as Class IA (quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide), or Class III (amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents; antipsychotics (pimozide, ziprasidone); antidepressants; certain antibiotics (macrolide antibiotics, fluoroquinolone antibiotics, imidazole, and triazole antifungal agents) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.6)].
- Receiving medications that are metabolized by the cytochrome enzyme CYP2D6, which also have cardiac effects (e.g., flecainide, imipramine, amitriptyline, clomipramine) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.2 Use of QT Prolonging Drugs and Other Antimalarials
Halofantrine and Coartem Tablets should not be administered within 1 month of each other due to the long elimination half-life of lumefantrine (3 to 6 days) and potential additive effects on the QT interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Antimalarials should not be given concomitantly with Coartem Tablets, unless there is no other treatment option, due to limited safety data.
Drugs that prolong the QT interval, including antimalarials such as quinine and quinidine, should be used cautiously following Coartem Tablets, due to the long elimination half-life of lumefantrine (3 to 6 days) and the potential for additive effects on the QT interval; ECG monitoring is advised if use of drugs that prolong the QT interval is medically required [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
If mefloquine is administered immediately prior to Coartem Tablets, there may be a decreased exposure to lumefantrine, possibly due to a mefloquine-induced decrease in bile production. Therefore, patients should be monitored for decreased efficacy and food consumption should be encouraged while taking Coartem Tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Drug Interactions (7.4), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.3 Drug Interactions With CYP3A4
When Coartem Tablets are coadministered with substrates of CYP3A4, it may result in decreased concentrations of the substrate and potential loss of substrate efficacy. When Coartem Tablets are coadministered with an inhibitor of CYP3A4, including grapefruit juice, it may result in increased concentrations of artemether and/or lumefantrine and potentiate QT prolongation. When Coartem Tablets are coadministered with inducers of CYP3A4, it may result in decreased concentrations of artemether and/or lumefantrine and loss of antimalarial efficacy [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Drugs that have a mixed effect on CYP3A4, especially antiretroviral drugs such as HIV protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and those that have an effect on the QT interval should be used with caution in patients taking Coartem Tablets [see Drug Interactions (7.3, 7.7)].
Coartem Tablets may reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives. Therefore, patients using hormonal contraceptives should be advised to use an alternative non-hormonal contraceptive method or add a barrier method of contraception during treatment with Coartem [see Drug Interactions (7.5)].
5.4 Drug Interactions With CYP2D6
Administration of Coartem Tablets with drugs that are metabolized by CYP2D6 may significantly increase plasma concentrations of the coadministered drug and increase the risk of adverse effects. Many of the drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 can prolong the QT interval and should not be administered with Coartem Tablets due to the potential additive effect on the QT interval (e.g., flecainide, imipramine, amitriptyline, clomipramine) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.5 Recrudescence
Food enhances absorption of artemether and lumefantrine following administration of Coartem Tablets. Patients who remain averse to food during treatment should be closely monitored as the risk of recrudescence may be greater [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
In the event of recrudescent P. falciparum infection after treatment with Coartem Tablets, patients should be treated with a different antimalarial drug.
5.6 Hepatic and Renal Impairment
Coartem Tablets have not been studied for efficacy and safety in patients with severe hepatic and/or renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.7 Plasmodium vivax Infection
Coartem Tablets have been shown in limited data (43 patients) to be effective in treating the erythrocytic stage of P. vivax infection. However, relapsing malaria caused by P. vivax requires additional treatment with other antimalarial agents to achieve radical cure i.e., eradicate any hypnozoites forms that may remain dormant in the liver.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious and otherwise important adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Contraindications (4)]
- Prolongation of the QT Interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Use of QT Prolonging Drugs and Other Antimalarials [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Drug Interactions with CYP3A4 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Drug Interactions with CYP2D6 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rate observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to a 6-dose regimen of Coartem Tablets in 1979 patients including 647 adults (older than 16 years) and 1332 children (16 years and younger). For the 6-dose regimen, Coartem Tablets was studied in active-controlled (366 patients) and noncontrolled, open-label trials (1613 patients). The 6-dose Coartem Tablets population was patients with malaria between ages 2 months and 71 years: 67% (1332) were 16 years and younger and 33% (647) were older than 16 years. Males represented 73% and 53% of the adult and pediatric populations, respectively. The majority of adult patients were enrolled in studies in Thailand, while the majority of pediatric patients were enrolled in Africa.
Tables 1 and 2 show the most frequently reported adverse reactions (greater than or equal to 3%) in adults and children respectively who received the 6-dose regimen of Coartem Tablets. Adverse reactions collected in clinical trials included signs and symptoms at baseline, but only treatment emergent adverse events, defined as events that appeared or worsened after the start of treatment, are presented below. In adults, the most frequently reported adverse reactions were headache, anorexia, dizziness, and asthenia. In children, the adverse reactions were pyrexia, cough, vomiting, anorexia, and headache. Most adverse reactions were mild, did not lead to discontinuation of study medication, and resolved.
In limited comparative studies, the adverse reaction profile of Coartem Tablets appeared similar to that of another antimalarial regimen.
Discontinuation of Coartem Tablets due to adverse drug reactions occurred in 1.1% of patients treated with the 6-dose regimen overall: 0.2% (1/647) in adults and 1.6% (21/1332) in children.
| *Adult patients defined as greater than 16 years of age. | ||
| System Organ Class | Preferred Term | Adults*
N = 647 (%) |
| Nervous system disorders | Headache | 360 (56) |
| Dizziness | 253 (39) | |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Anorexia | 260 (40) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Asthenia | 243 (38) |
| Pyrexia | 159 (25) | |
| Chills | 147 (23) | |
| Fatigue | 111 (17) | |
| Malaise | 20 (3) | |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Arthralgia | 219 (34) |
| Myalgia | 206 (32) | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Nausea | 169 (26) |
| Vomiting | 113 (17) | |
| Abdominal pain | 112 (17) | |
| Diarrhea | 46 (7) | |
| Psychiatric disorders | Sleep disorder | 144 (22) |
| Insomnia | 32 (5) | |
| Cardiac disorders | Palpitations | 115 (18) |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | Hepatomegaly | 59 (9) |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Splenomegaly | 57 (9) |
| Anemia | 23 (4) | |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Cough | 37 (6) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Pruritus | 24 (4) |
| Rash | 21 (3) | |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders | Vertigo | 21 (3) |
| Infections and infestations | Malaria | 18 (3) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 17 (3) | |
| *Children defined as patients less than or equal to 16 years of age. | ||
| System Organ Class | Preferred Term | Children*
N = 1332 (%) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Pyrexia | 381 (29) |
| Chills | 72 (5) | |
| Asthenia | 63 (5) | |
| Fatigue | 46 (3) | |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Cough | 302 (23) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Vomiting | 242 (18) |
| Abdominal pain | 112 (8) | |
| Diarrhea | 100 (8) | |
| Nausea | 61 (5) | |
| Infections and infestations | Plasmodium falciparum infection | 224 (17) |
| Rhinitis | 51 (4) | |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Anorexia | 175 (13) |
| Nervous system disorders | Headache | 168 (13) |
| Dizziness | 56 (4) | |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Splenomegaly | 124 (9) |
| Anemia | 115 (9) | |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | Hepatomegaly | 75 (6) |
| Investigations | Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 51 (4) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Arthralgia | 39 (3) |
| Myalgia | 39 (3) | |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Rash | 38 (3) |
Clinically significant adverse reactions reported in adults and/or children treated with the 6-dose regimen of Coartem Tablets, which occurred in clinical studies at less than 3% regardless of causality are listed below:
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: eosinophilia
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: tinnitus
Eye Disorders: conjunctivitis
Gastrointestinal Disorders: constipation, dyspepsia, dysphagia, peptic ulcer
General Disorders: gait disturbance
Infections and Infestations: abscess, acrodermatitis, bronchitis, ear infection, gastroenteritis, helminthic infection, hook-worm infection, impetigo, influenza, lower respiratory tract infection, malaria, nasopharyngitis, oral herpes, pneumonia, respiratory tract infection, subcutaneous abscess, upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection
Investigations: alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, hematocrit decreased, lymphocyte morphology abnormal, platelet count decreased, platelet count increased, white blood cell count decreased, white blood cell count increased
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: hypokalemia
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: back pain
Nervous System Disorders: ataxia, clonus, fine motor delay, hyperreflexia, hypoesthesia, nystagmus, tremor
Psychiatric Disorders: agitation, mood swings
Renal and Urinary Disorders: hematuria, proteinuria
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: asthma, pharyngo-laryngeal pain
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: urticaria
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of Coartem Tablets. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: anaphylaxis, urticaria, angioedema, and serious skin reactions (bullous eruption) have been reported.
- Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Cases of delayed hemolytic anemia have been reported following treatment with artemether-lumefantrine, mostly when used for treatment of severe malaria in patients initially treated with IV/parenteral artesunate. Coartem Tablets should not be used to treat severe malaria as it is not an approved indication.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Rifampin
Oral administration of rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, with Coartem Tablets resulted in significant decreases in exposure to artemether, DHA (metabolite of artemether), and lumefantrine by 89%, 85%, and 68%, respectively, when compared to exposure values after Coartem Tablets alone. Concomitant use of strong inducers of CYP3A4 such as rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, and St. John’s wort is contraindicated with Coartem Tablets [see Contraindications (4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Ketoconazole
Concurrent oral administration of ketoconazole, a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor, with a single dose of Coartem Tablets resulted in a moderate increase in exposure to artemether, DHA, and lumefantrine in a study of 15 healthy subjects. No dose adjustment of Coartem Tablets is necessary when administered with ketoconazole or other potent CYP3A4 inhibitors. However, due to the potential for increased concentrations of lumefantrine which could lead to QT prolongation, Coartem Tablets should be used cautiously with drugs that inhibit CYP3A4 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Antiretroviral Drugs
Both artemether and lumefantrine are metabolized by CYP3A4. Antiretroviral drugs, such as protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, are known to have variable patterns of inhibition, induction or competition for CYP3A4. Therefore, the effects of antiretroviral drugs on the exposure to artemether, DHA, and lumefantrine are also variable [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Coartem Tablets should be used cautiously in patients on antiretroviral drugs because decreased artemether, DHA, and/or lumefantrine concentrations may result in a decrease of antimalarial efficacy of Coartem Tablets, and increased lumefantrine concentrations may cause QT prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
7.4 Prior Use of Mefloquine
Administration of 3 doses of mefloquine followed 12 hours later by a 6-dose regimen of Coartem Tablets in 14 healthy volunteers demonstrated no effect of mefloquine on plasma concentrations of artemether or the artemether/DHA ratio. However, exposure to lumefantrine was reduced, possibly due to lower absorption secondary to a mefloquine-induced decrease in bile production. Patients should be monitored for decreased efficacy and food consumption should be encouraged with administration of Coartem Tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.5 Hormonal Contraceptives
In vitro, the metabolism of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel was not induced by artemether, DHA, or lumefantrine. However, artemether has been reported to weakly induce, in humans, the activity of CYP2C19, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4. Therefore, Coartem Tablets may potentially reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives. Patients using hormonal contraception should be advised to use an alternative non-hormonal contraceptive method or add a barrier method of contraception during treatment with Coartem [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.6 CYP2D6 Substrates
Lumefantrine inhibits CYP2D6 in vitro. Administration of Coartem Tablets with drugs that are metabolized by CYP2D6 may significantly increase plasma concentrations of the coadministered drug and increase the risk of adverse effects. Many of the drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 can prolong the QT interval and should not be administered with Coartem Tablets due to the potential additive effect on the QT interval (e.g., flecainide, imipramine, amitriptyline, clomipramine) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.7 Sequential Use of Quinine
A single dose of intravenous quinine (10 mg/kg bodyweight) concurrent with the final dose of a 6-dose regimen of Coartem Tablets demonstrated no effect of intravenous quinine on the systemic exposure of DHA or lumefantrine. Quinine exposure was also not altered. Exposure to artemether was decreased. This decrease in artemether exposure is not thought to be clinically significant. However, quinine and other drugs that prolong the QT interval should be used cautiously following treatment with Coartem Tablets due to the long elimination half-life of lumefantrine and the potential for additive QT effects; ECG monitoring is advised if use of drugs that prolong the QT interval is medically required [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.8 Interaction With Drugs That are Known to Prolong the QT Interval
Coartem Tablets are to be used with caution when coadministered with drugs that may cause prolonged QT interval such as antiarrhythmics of Classes IA and III, neuroleptics and antidepressant agents, certain antibiotics including some agents of the following classes: macrolides, fluoroquinolones, imidazole, and triazole antifungal agents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Published data from clinical studies and pharmacovigilance data have not established an association with artemether/lumefantrine use during pregnancy and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Malaria during and after pregnancy increases the risk for adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes, including maternal anemia, severe malaria, spontaneous abortion, stillbirths, preterm delivery, low birth weight, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital malaria, and maternal and neonatal mortality.
Data
Human Data
While available studies cannot definitively establish the absence of risk, a meta-analysis of observational studies including over 500 artemether-lumefantrine exposed women in their first trimester of pregnancy, data from observational, and open label studies including more than 1200 pregnant women in their second- or third trimester exposed to artemether-lumefantrine compared to other antimalarials, and pharmacovigilance data have not demonstrated an increase in major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Published epidemiologic studies have important methodological limitations which hinder interpretation of data, including inability to control for confounders, such as underlying maternal disease, and maternal use of concomitant medications and missing information on the dose and duration of use.
Animal Data
Pregnant rats dosed orally during the period of organogenesis [gestational days (GD) 7 through 17] at 50 mg/kg/day artemether-lumefantrine combination (corresponding to 7 mg/kg/day artemether or higher, a dose of less than half the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 1120 mg artemether-lumefantrine per day (based on body surface area (BSA) comparisons), showed increases in fetal loss, early resorptions, and postimplantation loss. No adverse effects were observed in animals dosed at 25 mg/kg/day artemether-lumefantrine (corresponding to 3.6 mg/kg/day of artemether), about one-third the MRHD (based on BSA comparison). Similarly, oral dosing in pregnant rabbits during organogenesis (GD 7 through GD 19) at 175 mg/kg/day, (corresponding to 25 mg/kg/day artemether) about 3 times the MRHD (based on BSA comparisons) resulted in abortions, preimplantation loss, post implantation loss and decreases in the number of live fetuses. No adverse reproductive effects were detected in rabbits at 105 mg/kg/day artemether-lumefantrine (corresponding to 15 mg/kg/day artemether), about 2 times the MRHD. Artemether and other artemisinins are associated with maternal toxicity and embryotoxicity and malformations in animals at clinically relevant exposures; however, lumefantrine doses as high as 1000 mg/kg/day, showed no evidence to suggest maternal, embryo- or fetotoxicity or teratogenicity in rats and rabbits. The relevance of the findings from the animal reproductive studies to human risk is unclear.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of artemether or lumefantrine in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. Artemether and lumefantrine are transferred into rat milk. When a drug is transferred into animal milk, it is likely that the drug will also be transferred into human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Coartem and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Coartem or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Use of Coartem may reduce the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives. Advise patients using hormonal contraceptives to use an alternative non-hormonal contraceptive method or add a barrier method of contraception during treatment with Coartem [see Drug Interactions (7.5)].
Infertility
In animal fertility studies, administration of repeated doses of artemether-lumefantrine combination to female rats (for 2 to 4 weeks) resulted in pregnancy rates that were reduced by one half. In male rats dosed for approximately 3 months with artemether-lumefantrine combination, abnormal sperm cells, decreased sperm motility, and increased testes weight were observed [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Coartem Tablets have been established in pediatric patients aged 2 months and older with a bodyweight of 5 kg and above for the treatment of acute, uncomplicated malaria [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The safety and effectiveness of Coartem Tablets have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 2 months old or who weigh less than 5 kg. Pediatric patients from non-endemic countries were not included in clinical trials.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Coartem Tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy in elderly patients should be considered when prescribing Coartem Tablets.
8.6 Hepatic and Renal Impairment
No specific pharmacokinetic studies have been performed in patients with either hepatic or renal impairment. Coartem Tablets have not been studied for efficacy and safety in patients with severe hepatic and/or renal impairment. Based on the pharmacokinetic data in 16 healthy subjects showing no or insignificant renal excretion of lumefantrine, artemether, and DHA, no dose adjustment for the use of Coartem Tablets in patients with renal impairment is advised. No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
10. Overdosage
There is no information on overdoses of Coartem Tablets higher than the doses recommended for treatment.
In cases of suspected overdosage, symptomatic and supportive therapy, which would include ECG and blood electrolyte monitoring, should be given as appropriate.
11. Coartem Description
Coartem Tablets contain a fixed combination of 2 antimalarial active ingredients, artemether, an artemisinin derivative, and lumefantrine. Both components are blood schizontocides. The chemical name of artemether is (3R,5aS,6R,8aS,9R,10S,12R,12aR)-10-methoxy-3,6,9-trimethyldecahydro-3,12-epoxypyrano[4,3-j]-1,2-benzodioxepine. Artemether is a white, crystalline powder that is freely soluble in acetone, soluble in methanol and ethanol, and practically insoluble in water. It has the empirical formula C16H26O5 with a molecular weight of 298.4 g/mol, and the following structural formula:
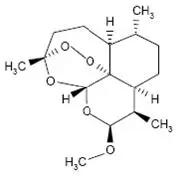
The chemical name of lumefantrine is (1RS)-2-(dibutylamino)-1-{(9Z)-2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylene]-9H-fluorene-4-yl}ethanol. Lumefantrine is a yellow, crystalline powder that is freely soluble in N,N-dimethylformamide, chloroform, and ethyl acetate; soluble in dichloromethane; slightly soluble in ethanol and methanol; and insoluble in water. It has the empirical formula C30H32Cl3NO with a molecular weight of 528.9 g/mol, and the following structural formula:
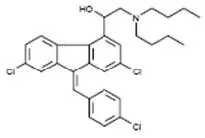
Coartem Tablets are for oral administration. Each Coartem Tablet contains 20 mg of artemether and 120 mg lumefantrine. The inactive ingredients are colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and polysorbate 80.
12. Coartem - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Coartem Tablets, a fixed dose combination of artemether and lumefantrine in the ratio of 1:6, is an antimalarial agent [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following administration of Coartem Tablets to healthy volunteers and patients with malaria, artemether is absorbed with peak plasma concentrations reached about 2 hours after dosing. Absorption of lumefantrine, a highly lipophilic compound, starts after a lag-time of up to 2 hours, with peak plasma concentrations about 6 to 8 hours after administration. The single dose (4 tablets) pharmacokinetic parameters for artemether, DHA, an active antimalarial metabolite of artemether, and lumefantrine in adult Caucasian healthy volunteers are given in Table 3. Multiple dose data after the 6-dose regimen of Coartem Tablets in adult malaria patients are given in Table 4.
| Abbreviations: DHA, dihydroartemisinin; SD, standard deviation; AUC, area under the curve. aMean ± SD Cmax, AUClast, t½ and Median Tmax. |
||
| Study 2102
(n = 50) | Study 2104
(n = 48) |
|
| Artemether | ||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 60.0 ± 32.5 | 83.8 ± 59.7 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.50 | 2.00 |
| AUClast (ng·h/mL) | 146 ± 72.2 | 259 ± 150 |
| t½ (h) | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 1.9 |
| DHA | ||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 104 ± 35.3 | 90.4 ± 48.9 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.76 | 2.00 |
| AUClast (ng·h/mL) | 284 ± 83.8 | 285 ± 98.0 |
| t½ (h) | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 2.2 ± 1.5 |
| Lumefantrine | ||
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 7.38 ± 3.19 | 9.80 ± 4.20 |
| Tmax (h) | 6.01 | 8.00 |
| AUClast (µg·h/mL) | 158 ± 70.1 | 243 ± 117 |
| t½ (h) | 101 ± 35.6 | 119 ± 51.0 |
Food enhances the absorption of both artemether and lumefantrine. In healthy volunteers, the relative bioavailability of artemether was increased between 2- to 3-fold, and that of lumefantrine 16-fold when Coartem Tablets were taken after a high-fat meal compared under fasted conditions. Patients should be encouraged to take Coartem Tablets with a meal as soon as food can be tolerated [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Distribution
Artemether and lumefantrine are both highly bound to human serum proteins in vitro (95.4% and 99.7%, respectively). Dihydroartemisinin (DHA) is also bound to human serum proteins (47% to 76%). Protein binding to human plasma proteins is linear.
Biotransformation
In human liver microsomes and recombinant CYP450 enzymes, the metabolism of artemether was catalyzed predominantly by CYP3A4/5. Dihydroartemisinin (DHA) is an active metabolite of artemether. The metabolism of artemether was also catalyzed to a lesser extent by CYP2B6, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19. In vitro studies with artemether at therapeutic concentrations revealed no significant inhibition of the metabolic activities of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4/5, and CYP4A9/11. In vitro studies with artemether, DHA, and lumefantrine at therapeutic concentrations revealed no significant induction of the metabolic activities of CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, or CYP3A5.
During repeated administration of Coartem Tablets, systemic exposure of artemether decreased significantly, while concentrations of DHA increased, although not to a statistically significant degree. The artemether/DHA area under the curve (AUC) ratio is 1.2 after a single dose and 0.3 after 6 doses given over 3 days. This suggests that there was induction of enzymes responsible for the metabolism of artemether.
In human liver microsomes and in recombinant CYP450 enzymes, lumefantrine was metabolized mainly by CYP3A4 to desbutyl-lumefantrine. The systemic exposure to the metabolite desbutyl-lumefantrine was less than 1% of the exposure to the parent compound. In vitro, lumefantrine significantly inhibits the activity of CYP2D6 at therapeutic plasma concentrations.
Caution is recommended when combining Coartem Tablets with substrates, inhibitors, or inducers of CYP3A4, especially antiretroviral drugs and those that prolong the QT interval (e.g., macrolide antibiotics, pimozide) [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3), and Drug Interactions (7)].
Coadministration of Coartem Tablets with CYP2D6 substrates may result in increased plasma concentrations of the CYP2D6 substrate and increase the risk of adverse reactions. In addition, many of the drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 can prolong the QT interval and should not be administered with Coartem Tablets due to the potential additive effect on the QT interval (e.g., flecainide, imipramine, amitriptyline, clomipramine) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.4) and Drug Interactions (7.6)].
Elimination
Artemether and DHA are cleared from plasma with an elimination half-life of about 2 hours. Lumefantrine is eliminated more slowly, with an elimination half-life of 3 to 6 days in healthy volunteers and in patients with falciparum malaria. Demographic characteristics such as sex and weight appear to have no clinically relevant effects on the pharmacokinetics of artemether and lumefantrine.
In 16 healthy volunteers, neither lumefantrine nor artemether was found in the urine after administration of Coartem Tablets, and urinary excretion of DHA amounted to less than 0.01% of the artemether dose.
Specific Populations
Hepatic and Renal Impairment
No specific pharmacokinetic studies have been performed in patients with either hepatic or renal impairment. There is no significant renal excretion of lumefantrine, artemether, and DHA in healthy volunteers and while clinical experience in this population is limited, no dose adjustment in renal impairment is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Pediatric Patients
The PK of artemether, DHA, and lumefantrine were obtained in 2 pediatric studies by sparse sampling using a population-based approach. PK estimates derived from a composite plasma concentration profile for artemether, DHA, and lumefantrine are provided in Table 4.
Systemic exposure to artemether, DHA, and lumefantrine, when dosed on an mg/kg body weight basis in pediatric patients (greater than or equal to 5 to less than 35 kg body weight), is comparable to that of the recommended dosing regimen in adult patients.
| Adults1 | Pediatric Patients (body weight, kg)2 | |||
| Drug | 5 to < 15 | 15 to < 25 | 25 to < 35 | |
| Lumefantrine | ||||
| Mean Cmax, range (mcg/mL) | 5.60-9.0 | 4.71–12.6 | Not Available | |
| Mean AUClast, range (mcg·h/mL) | 410-561 | 372–699 | Not Available | |
| Artemether | ||||
| Mean Cmax ± SD (ng/mL) | 186 ± 125 | 223 ± 309 | 198 ± 179 | 174 ± 145 |
| Dihydroartemisinin | ||||
| Mean Cmax ± SD (ng/mL) | 101 ± 58 | 54.7 ± 58.9 | 79.8 ± 80.5 | 65.3 ± 23.6 |
| Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; DHA, dihydroartemisinin; SD, standard deviation. 1There are a total of 181 adults for lumefantrine pharmacokinetic parameters and a total of 25 adults for artemether and dihydroartemisinin pharmacokinetic parameters. 2There are 477 children for the lumefantrine pharmacokinetic parameters; for artemether and dihydroartemisinin pharmacokinetic parameters there are 55, 29, and 8 children for the 5 to less than 15, 15 to less than 25 and the 25 to less than 35 kg groups, respectively. |
||||
Geriatric Patients
No specific pharmacokinetic studies have been performed in patients older than 65 years of age.
Drug Interaction Studies
Rifampin (strong CYP3A4 inducer)
Oral administration of rifampin (600 mg daily), a strong CYP3A4 inducer, with Coartem Tablets (6-dose regimen over 3 days) in 6 HIV-1 and tuberculosis co-infected adults without malaria resulted in significant decreases in exposure, in terms of AUC, to artemether, DHA and lumefantrine by 89%, 85%, and 68%, respectively, when compared to exposure values after Coartem Tablets alone. Concomitant use of strong inducers of CYP3A4 such as rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, and St. John’s wort is contraindicated with Coartem Tablets [see Contraindications (4)].
Ketoconazole (potent CYP3A4 inhibitor)
Concurrent oral administration of ketoconazole (400 mg on day 1 followed by 200 mg on Days 2, 3, 4, and 5) with Coartem Tablets (single-dose of 4 tablets of 20 mg artemether/120 mg lumefantrine per tablet) with a meal led to an increase in exposure, in terms of AUC, of artemether (2.3-fold), DHA (1.5-fold), and lumefantrine (1.6-fold) in 13 healthy subjects. The pharmacokinetics of ketoconazole was not evaluated. Based on this study, dose adjustment of Coartem Tablets is considered unnecessary when administered with ketoconazole or other CYP3A4 inhibitors. However, due to the potential for increased concentrations of lumefantrine, which could lead to QT prolongation, Coartem Tablets should be used cautiously with other drugs that inhibit CYP3A4 (e.g., antiretroviral drugs, macrolide antibiotics, antidepressants, imidazole antifungal agents) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3)].
Antimalarials
The oral administration of mefloquine in 14 healthy volunteers administered as 3 doses of 500 mg, 250 mg, and 250 mg, followed 12 hours later by Coartem Tablets (6 doses of 4 tablets of 20 mg artemether/120 mg lumefantrine per tablet), had no effect on plasma concentrations of artemether or the artemether/DHA ratio. In the same study, there was a 30% reduction in Cmax and 40% reduction in AUC of lumefantrine, possibly due to lower absorption secondary to a mefloquine-induced decrease in bile production.
Intravenous administration of a single dose of quinine (10 mg/kg bodyweight) concurrent with the last dose of a 6-dose regimen of Coartem Tablets had no effect on systemic exposure of DHA, lumefantrine, or quinine in 14 healthy volunteers. Mean AUC of artemether were 46% lower when administered with quinine compared to Coartem Tablets alone. This decrease in artemether exposure is not thought to be clinically significant. However, quinine should be used cautiously in patients following treatment with Coartem Tablets due to the long elimination half-life of lumefantrine and the potential for additive effects on the QT interval; ECG monitoring is advised if use of quinine is medically required [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Antiretroviral Drugs
The oral administration of lopinavir/ritonavir (400 mg/100 mg twice daily for 26 days) in 10 healthy volunteers coadministered with Coartem Tablets (6-dose regimen over 3 days), resulted in a decrease in systemic exposures, in terms of AUC, to artemether and DHA by approximately 40%, but an increase in exposure to lumefantrine by approximately 2.3-fold. The oral administration of efavirenz (600 mg once daily for 26 days) in 12 healthy volunteers coadministered with Coartem Tablets (6-dose regimen over 3 days), resulted in a decrease in exposures to artemether, DHA, and lumefantrine by approximately 50%, 45%, and 20%, respectively. Exposures to lopinavir/ritonavir and efavirenz were not significantly affected by concomitant use of Coartem Tablets. Coartem Tablets should be used cautiously in patients on antiretroviral drugs such as HIV protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors because decreased artemether, DHA, and/or lumefantrine concentrations may result in a decrease of antimalarial efficacy of Coartem Tablets, and increased lumefantrine concentrations may cause QT prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Hormonal Contraceptives
No clinical drug-drug interaction studies between Coartem Tablets and hormonal contraceptives have been performed. In vitro studies revealed that the metabolism of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel was not induced by artemether, DHA, or lumefantrine. However, artemether has been reported to weakly induce, in humans, the activity of CYP2C19, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4. Therefore, coadministration of Coartem Tablets may potentially reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Drug Interactions (7.5)].
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Coartem Tablets, a fixed ratio of 1:6 parts of artemether and lumefantrine, respectively, is an antimalarial agent. Artemether is rapidly metabolized into an active metabolite DHA. The antimalarial activity of artemether and DHA has been attributed to endoperoxide moiety. The exact mechanism by which lumefantrine exerts its antimalarial effect is not well defined. Available data suggest lumefantrine inhibits the formation of β-hematin by forming a complex with hemin. Both artemether and lumefantrine were shown to inhibit nucleic acid and protein synthesis.
Activity In Vitro and In Vivo
Artemether and lumefantrine are active against the erythrocytic stages of P. falciparum.
Drug Resistance
There is a potential for development of resistance to artemether and lumefantrine. Strains of P. falciparum with a moderate decrease in susceptibility to artemether or lumefantrine alone can be selected in vitro or in vivo, but not maintained in the case of artemether. Alterations in some genetic regions of P. falciparum [multidrug resistant 1 (pfmdr1), chloroquine resistance transporter (pfcrt), and kelch 13 (K13)] based on in vitro testing and/or identification of isolates in endemic areas where artemether/lumefantrine treatment was administered, have been reported. The clinical relevance of these findings are not known.
12.6 Effects on the Electrocardiogram
In a healthy adult volunteer parallel-group study including a placebo and moxifloxacin control-group (n = 42 per group), the administration of the 6-dose regimen of Coartem Tablets was associated with prolongation of QTcF (Fridericia). Following administration of a 6-dose regimen of Coartem Tablets consisting of 4 tablets per dose (total of 4 tablets of 80 mg artemether/480 mg lumefantrine) taken with food, the maximum mean change from baseline and placebo adjusted QTcF was 7.5 msec (1-sided 95% upper confidence interval: 11 msec). There was a concentration-dependent increase in QTcF for lumefantrine.
In clinical trials conducted in children, no patient had QTcF greater than 500 msec. Over 5% of patients had an increase in QTcF of over 60 msec.
In clinical trials conducted in adults, QTcF prolongation of greater than 500 msec was reported in 3 (0.3%) patients. Over 6% of adults had a QTcF increase of over 60 msec from baseline.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies were not conducted.
Mutagenesis
No evidence of mutagenicity was detected. The artemether-lumefantrine combination was evaluated using the Salmonella and Escherichia/mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test, the gene mutation test with Chinese hamster cells V79, the cytogenetic test on Chinese hamster cells in vitro, and the rat micronucleus test, in vivo.
Impairment of Fertility
Pregnancy rates were reduced by about one-half in female rats dosed for 2 to 4 weeks with the artemether-lumefantrine combination at 1000 mg/kg (about 9 times the clinical dose based on BSA comparisons). Male rats dosed for 89 to 93 days showed increases in abnormal sperm (87% abnormal) at 30 mg/kg doses (about one-third the clinical dose). Higher doses (about 9 times the MRHD) resulted in increased testes weights, decreased sperm motility, and 100% abnormal sperm cells.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Neonatal rats (7 to 21 days old) were more sensitive to the toxic effects of artemether (a component of Coartem Tablets) than older juvenile rats or adults. Mortality and severe clinical signs were observed in neonatal rats at doses which were well tolerated in pups above 22 days old.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Treatment of Acute, Uncomplicated P. falciparum Malaria
The efficacy of Coartem Tablets was evaluated for the treatment of acute, uncomplicated malaria caused by P. falciparum in HIV negative patients in 8 clinical studies. Uncomplicated malaria was defined as symptomatic P. falciparum malaria without signs and symptoms of severe malaria or evidence of vital organ dysfunction. Baseline parasite density ranged from 500/mcL to 200,000/mcL (0.01% to 4% parasitemia) in the majority of patients. Studies were conducted in partially immune and non-immune adults and children (greater than or equal to 5 kg body weight) with uncomplicated malaria in China, Thailand, sub-Saharan Africa, Europe, and South America. Patients who had clinical features of severe malaria, severe cardiac, renal, or hepatic impairment were excluded.
The studies include two 4-dose studies assessing the efficacy of the components of the regimen, a study comparing a 4-dose versus a 6-dose regimen, and 5 additional 6-dose regimen studies.
Coartem Tablets were administered at 0, 8, 24, and 48 hours in the 4-dose regimen, and at 0, 8, 24, 36, 48, and 60 hours in the 6-dose regimen. Efficacy endpoints consisted of:
- 28-day cure rate, defined as clearance of asexual parasites (the erythrocytic stage) within 7 days without recrudescence by Day 28
- parasite clearance time (PCT), defined as time from first dose until first total and continued disappearance of asexual parasite which continues for a further 48 hours
- fever clearance time (FCT), defined as time from first dose until the first time body temperature fell below 37.5°C and remained below 37.5°C for at least a further 48 hours (only for patients with temperature greater than 37.5°C at baseline)
The modified intent-to-treat (mITT) population includes all patients with malaria diagnosis confirmation who received at least 1 dose of study drug. Evaluable patients generally are all patients who had a Day 7 and a Day 28 parasitological assessment or experienced treatment failure by Day 28.
Studies 1 and 2: The 2 studies, which assessed the efficacy of Coartem Tablets (4 doses of 4 tablets of 20 mg artemether/120 mg lumefantrine) compared to each component alone, were randomized, double-blind, comparative, single center, conducted in China. The efficacy results (Table 5) support that the combination of artemether and lumefantrine in Coartem Tablets had a significantly higher 28-day cure rate compared to artemether and had a significantly faster PCT and FCT compared to lumefantrine.
| Study No.
Region/patient ages | 28-day cure rate2
n/N (%) patients | Median FCT3
[25th, 75th percentile] | Median PCT
[25th, 75th percentile] |
| Study 1
China, ages 13 to 57 years | |||
| Coartem Tablets | 50/51 (98.0) | 24 hours [9, 48] | 30 hours [24, 36] |
| Artemether4 | 24/52 (46.2) | 21 hours [12, 30] | 30 hours [24, 33] |
| Lumefantrine5 | 47/52 (90.4) | 60 hours [36, 78] | 54 hours [45, 66] |
| Study 2
China, ages 12 to 65 years | |||
| Coartem Tablets | 50/52 (96.2) | 21 hours [6, 33] | 30 hours [24, 36] |
| Lumefantrine6 | 45/51 (88.2) | 36 hours [12, 60] | 48 hours [42, 60] |
| Abbreviations: FCT, fever clearance time; mITT, modified intent-to-treat; PCT, parasite clearance time. 1In mITT analysis, patients whose status was uncertain were classified as treatment failures. 2Efficacy cure rate based on blood smear microscopy. 3For patients who had a body temperature greater than 37.5°C at baseline only. 495% Confidence Interval (Coartem Tablets–artemether) on 28-day cure rate: 37.8%, 66.0%. 5P-value comparing Coartem Tablets to lumefantrine on PCT and FCT: < 0.001. 6P-value comparing Coartem Tablets to lumefantrine on PCT: < 0.001 and on FCT: < 0.05. |
|||
Results of 4-dose studies conducted in areas with high resistance such as Thailand during 1995-96 showed lower efficacy results than the above studies. Therefore, Study 3 was conducted.
Study 3: Study 3 was a randomized, double-blind, 2-center study conducted in Thailand in adults and children (aged greater than or equal to 2 years), which compared the 4-dose regimen (administered over 48 hours) of Coartem Tablets to a 6-dose regimen (administered over 60 hours). Twenty-eight day cure rate in mITT subjects was 81% (96/118) for the Coartem Tablets 6-dose arm as compared to 71% (85/120) in the 4-dose arm.
Studies 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8: In these studies, Coartem Tablets were administered as the 6-dose regimen.
In study 4, a total of 150 adults and children aged greater than or equal to 2 years received Coartem Tablets. In study 5, a total 164 adults and children greater than or equal to 12 years received Coartem Tablets. Both studies were conducted in Thailand.
Study 6 was a study of 165 non-immune adults residing in regions non-endemic for malaria (Europe and Colombia) who contracted acute uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria when traveling in endemic regions.
Study 7 was conducted in Africa in 310 infants and children aged 2 months to 9 years, weighing 5 kg to 25 kg, with an axillary temperature greater than or equal to 37.5ºC.
Study 8 was conducted in Africa in 452 infants and children, aged 3 months to 12 years, weighing 5 kg to less than 35 kg, with fever (greater than or equal to 37.5°C axillary or greater than or equal to 38°C rectally) or history of fever in the preceding 24 hours.
Results of 28-day cure rate, median PCT, and FCT for Studies 3 to 8 are reported in Table 6.
| Study No. Region/ages | 28-day cure rate1 n/N (%) Patients | Median FCT2
[25th, 75th percentile] | Median PCT
[25th, 75th percentile] |
|
| mITT3 | Evaluable | |||
| Study 3 Thailand, ages 3–62 years | 96/118 (81.4) | 93/96 (96.9) | 35 hours [20, 46] | 44 hours [22, 47] |
| Early failure4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Late failure5 | 4 (3.4) | 3 (3.1) | ||
| Lost to follow-up | 18 (15.3) | |||
| Other6 | 0 | |||
| Study 4 Thailand, ages 2–63 years | 130/149 (87.2) | 130/134 (97.0) | 22 hours [19, 44] | NA |
| Early failure4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Late failure5 | 4 (2.7) | 4 (3.0) | ||
| Lost to follow-up | 13 (8.7) | |||
| Other6 | 2 (1.3) | |||
| Study 5 Thailand, ages 12–71 years | 148/164 (90.2) | 148/155 (95.5) | 29 hours [8, 51] | 29 hours [18, 40] |
| Early failure4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Late failure5 | 7 (4.3) | 7 (4.5) | ||
| Lost to follow-up | 9 (5.5) | |||
| Other6 | 0 | |||
| Study 6
Europe/Columbia, ages 16–66 years | 120/162 (74.1) | 119/124 (96.0) | 37 hours [18, 44] | 42 hours [34, 63] |
| Early failure4 | 6 (3.7) | 1 (0.8) | ||
| Late failure5 | 3 (1.9) | 3 (2.4) | ||
| Lost to follow-up | 17 (10.5) | |||
| Other6 | 16 (9.9) | 1 (0.8) | ||
| Study 7 Africa, ages 2 months–9 years | 268/310 (86.5) | 267/300 (89.0) | 8 hours [8, 24] | 24 hours [24, 36] |
| Early failure4 | 2 (0.6) | 0 | ||
| Late failure5 | 34 (11.0) | 33 (11.0) | ||
| Lost to follow-up | 2 (0.6) | |||
| Other6 | 4 (1.3) | |||
| Study 8 Africa, ages 3 months–12 years | 374/452 (82.7) | 370/419 (88.3) | 8 hours [8, 23] | 35 hours [24, 36] |
| Early failure4 | 13 (2.9) | 0 | ||
| Late failure5 | 49 (10.8) | 49 (11.7) | ||
| Lost to follow-up | 6 (1.3) | |||
| Other6 | 10 (2.2) | |||
| Abbreviations: FCT, fever clearance time; mITT, modified intent-to-treat; PCT, parasite clearance time; NA, not applicable. 1Efficacy cure rate based on blood smear microscopy. 2For patients who had a body temperature greater than 37.5°C at baseline only. 3In mITT analysis, patients whose status was uncertain were classified as treatment failures. 4Early failures were usually defined as patients withdrawn for unsatisfactory therapeutic effect within the first 7 days or because they received another antimalarial medication within the first 7 days. 5Late failures were defined as patients achieving parasite clearance within 7 days but having parasite reappearance including recrudescence or new infection during the 28-day follow-up period. 6Other includes withdrawn due to protocol violation or non-compliance, received additional medication after day 7, withdrew consent, missing day 7 or 28 assessment. |
||||
In all studies, patients’ signs and symptoms of malaria resolved when parasites were cleared.
In studies conducted in areas with high transmission rates, such as Africa, reappearance of P. falciparum parasites may be due to recrudescence or a new infection.
The efficacy by body weight category for studies 7 and 8 is summarized in Table 7.
| Study No.
Age category | Coartem Tablets 6-dose Regimen | ||
| mITT Population1 | Evaluable Population | ||
| Median PCT
[25th, 75th percentile] | 28-day cure rate2
n/N (%) patients | 28-day cure rate2
n/N (%) patients |
|
| Study 7 | |||
| 5 to < 10 kg | 24 [24, 36] | 133/154 (86.4) | 133/149 (89.3) |
| 10 to < 15 kg | 35 [24, 36] | 94/110 (85.5) | 94/107 (87.9) |
| 15 to 25 kg | 24 [24, 36] | 41/46 (89.1) | 40/44 (90.9) |
| Study 83 | |||
| 5 to < 10 kg | 36 [24, 36] | 61/83 (73.5) | 61/69 (88.4) |
| 10 to < 15 kg | 35 [24, 36] | 160/190 (84.2) | 157/179 (87.7) |
| 15 to < 25 kg | 35 [24, 36] | 123/145 (84.8) | 123/140 (87.9) |
| 25 to < 35 kg | 26 [24, 36] | 30/34 (88.2) | 29/31 (93.5) |
| Abbreviations: mITT, modified intent-to-treat; PCT, parasite clearance time. 1In mITT analysis, patients whose status was uncertain were classified as treatment failures. 2Efficacy cure rate based on blood smear microscopy. 3Coartem Tablets administered as crushed tablets. |
|||
The efficacy of Coartem Tablets for the treatment P. falciparum infections mixed with P. vivax was assessed in a small number of patients. Coartem Tablets are only active against the erythrocytic phase of P. vivax malaria. Of the 43 patients with mixed infections at baseline, all cleared their parasitemia within 48 hours. However, parasite relapse occurred commonly (14/43; 33%). Relapsing malaria caused by P. vivax requires additional treatment with other antimalarial agents to achieve radical cure i.e., eradicate any hypnozoite forms that may remain dormant in the liver.
16. How is Coartem supplied
Coartem (artemether/lumefantrine) Tablets
20 mg/120 mg Tablets - yellow, round flat tablets with beveled edges and scored on one side. Tablets are imprinted with “N/C” on one side and “CG” on the other.
Bottle of 24 NDC 0078-0568-45
Store at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF); excursions permitted to 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in tight container (USP).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise patients to read the FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information).
Administration Instructions
Instruct patients to take Coartem Tablets with food. Patients who do not have an adequate intake of food are at risk for recrudescence of malaria [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Hypersensitivity
Patients with known hypersensitivity to artemether, lumefantrine, or to any of the excipients should not receive Coartem Tablets [see Contraindications (4)].
Prolongation of the QT Interval
- Instruct patients to inform their physician of any personal or family history of QT prolongation or proarrhythmic conditions such as hypokalemia, bradycardia, or recent myocardial ischemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Instruct patients to inform their physician if they are taking any other medications that prolong the QT interval, such as Class IA (quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide), or Class III (amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents; antipsychotics (pimozide, ziprasidone); antidepressants; certain antibiotics (macrolide antibiotics, fluoroquinolone antibiotics, imidazole, and triazole antifungal agents) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Instruct patients to notify their physicians if they have any symptoms of prolongation of the QT interval, including prolonged heart palpitations or a loss of consciousness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Drug Interactions With CYP2D6
Instruct patients to avoid medications that are metabolized by the cytochrome enzyme CYP2D6 while receiving Coartem Tablets since these drugs also have cardiac effects (e.g., flecainide, imipramine, amitriptyline, clomipramine) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Contraception
Advise patients that use of Coartem may reduce the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives. Advise patients using hormonal contraceptive to use an alternative non-hormonal contraceptive method or add a barrier method of contraception during treatment with Coartem [see Drug Interactions (7.5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Use of QT Prolonging Drugs and Other Antimalarials
Halofantrine and Coartem Tablets should not be administered within 1 month of each other due to potential additive effects on the QT interval. Antimalarials should not be given concomitantly with Coartem Tablets, unless there is no other treatment option, due to limited safety data [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Sequential Use of Quinine
QT prolonging drugs, including quinine and quinidine, should be used cautiously following Coartem Tablets due to the long elimination half-life of lumefantrine and the potential for additive effects on the QT interval. ECG monitoring is advised if use of drugs that prolong the QT interval is medically required [see Drug Interactions (7.7)].
Prior Use of Mefloquine
Closely monitor food intake in patients who received mefloquine immediately prior to treatment with Coartem Tablets [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
Drug Interactions With CYP3A4
Use Coartem Tablets cautiously in patients receiving other drugs that are substrates, inhibitors or inducers of CYP3A4, including grapefruit juice, especially those that prolong the QT interval or are antiretroviral drugs. Coadministration of strong inducers of CYP3A4 such as rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, and St. John’s wort is contraindicated with Coartem Tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that Coartem Tablets can cause hypersensitivity reactions. Instruct patients to discontinue the drug at the first sign of a skin rash, hives or other skin reactions, a rapid heartbeat, difficulty in swallowing or breathing, any swelling suggesting angioedema (e.g., swelling of the lips, tongue, face, tightness of the throat, hoarseness), or other symptoms of an allergic reaction [see Contraindications (4)].
T2019-88
| COARTEM
artemether and lumefantrine tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |





