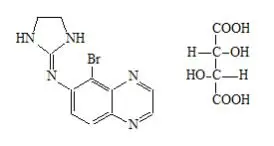
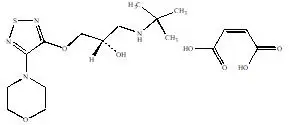
Drug Detail:Combigan (Brimonidine and timolol ophthalmic [ bri-moe-ni-deen-and-tim-oh-lol-off-thal-mik ])
Drug Class: Ophthalmic glaucoma agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
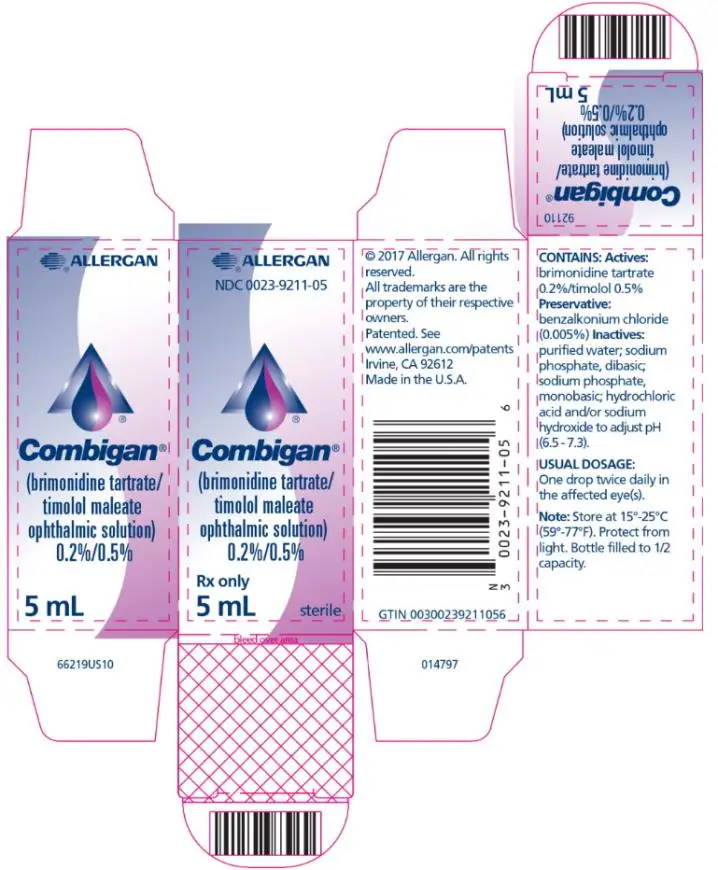
COMBIGAN® (brimonidine tartrate/timolol maleate ophthalmic solution) 0.2%/0.5%, for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2007
Recent Major Changes
- Contraindications, Reactive Airway Disease Including Asthma, COPD (4.1) 10/2015
- Warnings and Precautions, Potential for Severe Respiratory or Cardiac Reactions (5.1) 10/2015
Indications and Usage for Combigan
COMBIGAN® is an alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist with a beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitor indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension who require adjunctive or replacement therapy due to inadequately controlled IOP; the IOP-lowering of COMBIGAN® dosed twice a day was slightly less than that seen with the concomitant administration of timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, 0.5% dosed twice a day and brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution, 0.2% dosed three times per day. (1)
Combigan Dosage and Administration
One drop in the affected eye(s), twice daily approximately 12 hours apart. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Solution containing 2 mg/mL brimonidine tartrate and 5 mg/mL timolol. (3)
Contraindications
- Bronchial asthma, a history of bronchial asthma, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. (4.1, 5.1, 5.3)
- Sinus bradycardia, atrioventricular block, overt cardiac failure, cardiogenic shock. (4.2, 5.2)
- Neonates and infants (under the age of 2 years). (4.3)
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this product. (4.4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Potential for Severe Respiratory or Cardiac Reactions (5.1)
- Cardiac Failure (5.2)
- Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (5.3)
- Potentiation of Vascular Insufficiency (5.4)
- Increased Reactivity to Allergens (5.5)
- Potentiation of Muscle Weakness (5.6)
- Masking of Hypoglycemic Symptoms in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus (5.7)
- Masking of Thyrotoxicosis (5.8)
- Ocular Hypersensitivity (5.9)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions occurring in approximately 5 to 15% of patients included allergic conjunctivitis, conjunctival folliculosis, conjunctival hyperemia, eye pruritus, ocular burning, and stinging. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Allergan at 1-800-433-8871 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Antihypertensives/cardiac glycosides may lower blood pressure. (7.1)
- Concomitant use with systemic beta-blockers may potentiate systemic beta-blockade. (7.2)
- Oral or intravenous calcium antagonists may cause atrioventricular conduction disturbances, left ventricular failure, and hypotension. (7.3)
- Catecholamine-depleting drugs may have additive effects and produce hypotension and/or marked bradycardia. (7.4)
- Use with CNS depressants may result in an additive or potentiating effect. (7.5)
- Digitalis and calcium antagonists may have additive effects in prolonging atrioventricular conduction time. (7.6)
- CYP2D6 inhibitors may potentiate systemic beta-blockade. (7.7)
- Tricyclic antidepressants may potentially blunt the hypotensive effect of systemic clonidine. (7.8)
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors may result in increased hypotension. (7.9)
Use In Specific Populations
Not for use in children below the age of 2 years. Use with caution in children ≥ 2 years of age. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2015
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Combigan
COMBIGAN® (brimonidine tartrate/timolol maleate ophthalmic solution) 0.2%/0.5% is an alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist with a beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitor indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension who require adjunctive or replacement therapy due to inadequately controlled IOP; the IOP-lowering of COMBIGAN® dosed twice a day was slightly less than that seen with the concomitant administration of 0.5% timolol maleate ophthalmic solution dosed twice a day and 0.2% brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution dosed three times per day.
2. Combigan Dosage and Administration
The recommended dose is one drop of COMBIGAN® in the affected eye(s) twice daily approximately 12 hours apart. If more than one topical ophthalmic product is to be used, the different products should be instilled at least 5 minutes apart.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Solution containing 2 mg/mL brimonidine tartrate and 5 mg/mL timolol (6.8 mg/mL timolol maleate).
4. Contraindications
4.1 Reactive Airway Disease Including Asthma, COPD
COMBIGAN® is contraindicated in patients with reactive airway disease including bronchial asthma; a history of bronchial asthma; severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3)].
4.2 Sinus Bradycardia, AV Block, Cardiac Failure, Cardiogenic Shock
COMBIGAN® is contraindicated in patients with sinus bradycardia; second or third degree atrioventricular block; overt cardiac failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]; cardiogenic shock.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Potential for Severe Respiratory or Cardiac Reactions
COMBIGAN® contains timolol maleate; and although administered topically can be absorbed systemically. Therefore, the same types of adverse reactions found with systemic administration of beta-adrenergic blocking agents may occur with topical administration. For example, severe respiratory reactions and cardiac reactions including death due to bronchospasm in patients with asthma, and rarely death in association with cardiac failure have been reported following systemic or ophthalmic administration of timolol maleate [see Contraindications (4.1)]. Additionally, ophthalmic beta-blockers may impair compensatory tachycardia and increase risk of hypotension.
5.2 Cardiac Failure
Sympathetic stimulation may be essential for support of the circulation in individuals with diminished myocardial contractility, and its inhibition by beta-adrenergic receptor blockade may precipitate more severe failure.
In patients without a history of cardiac failure, continued depression of the myocardium with beta-blocking agents over a period of time can, in some cases, lead to cardiac failure. At the first sign or symptom of cardiac failure, COMBIGAN® should be discontinued [see Contraindications (4.2)].
5.3 Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (e.g., chronic bronchitis, emphysema) of mild or moderate severity, bronchospastic disease, or a history of bronchospastic disease (other than bronchial asthma or a history of bronchial asthma, in which COMBIGAN® is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4.1)]) should, in general, not receive beta-blocking agents, including COMBIGAN®.
5.4 Potentiation of Vascular Insufficiency
COMBIGAN® may potentiate syndromes associated with vascular insufficiency. COMBIGAN® should be used with caution in patients with depression, cerebral or coronary insufficiency, Raynaud’s phenomenon, orthostatic hypotension, or thromboangiitis obliterans.
5.5 Increased Reactivity to Allergens
While taking beta-blockers, patients with a history of atopy or a history of severe anaphylactic reactions to a variety of allergens may be more reactive to repeated accidental, diagnostic, or therapeutic challenge with such allergens. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat anaphylactic reactions.
5.6 Potentiation of Muscle Weakness
Beta-adrenergic blockade has been reported to potentiate muscle weakness consistent with certain myasthenic symptoms (e.g., diplopia, ptosis, and generalized weakness). Timolol has been reported rarely to increase muscle weakness in some patients with myasthenia gravis or myasthenic symptoms.
5.7 Masking of Hypoglycemic Symptoms in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents should be administered with caution in patients subject to spontaneous hypoglycemia or to diabetic patients (especially those with labile diabetes) who are receiving insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents may mask the signs and symptoms of acute hypoglycemia.
5.8 Masking of Thyrotoxicosis
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents may mask certain clinical signs (e.g., tachycardia) of hyperthyroidism. Patients suspected of developing thyrotoxicosis should be managed carefully to avoid abrupt withdrawal of beta-adrenergic blocking agents that might precipitate a thyroid storm.
5.9 Ocular Hypersensitivity
Ocular hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solutions 0.2%, with some reported to be associated with an increase in intraocular pressure [see Contraindications (4.4)].
5.10 Contamination of Topical Ophthalmic Products After Use
There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple-dose containers of topical ophthalmic products. These containers had been inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent corneal disease or a disruption of the ocular epithelial surface [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
COMBIGAN®
In clinical trials of 12 months duration with COMBIGAN®, the most frequent reactions associated with its use occurring in approximately 5% to 15% of the patients included: allergic conjunctivitis, conjunctival folliculosis, conjunctival hyperemia, eye pruritus, ocular burning, and stinging. The following adverse reactions were reported in 1% to 5% of patients: asthenia, blepharitis, corneal erosion, depression, epiphora, eye discharge, eye dryness, eye irritation, eye pain, eyelid edema, eyelid erythema, eyelid pruritus, foreign body sensation, headache, hypertension, oral dryness, somnolence, superficial punctate keratitis, and visual disturbance.
Other adverse reactions that have been reported with the individual components are listed below.
Brimonidine Tartrate (0.1%-0.2%)
Abnormal taste, allergic reaction, blepharoconjunctivitis, blurred vision, bronchitis, cataract, conjunctival blanching, conjunctival edema, conjunctival hemorrhage, conjunctivitis, cough, dizziness, dyspepsia, dyspnea, fatigue, flu syndrome, follicular conjunctivitis, gastrointestinal disorder, hypercholesterolemia, hypotension, infection (primarily colds and respiratory infections), hordeolum, insomnia, keratitis, lid crusting, lid disorder, muscular pain, nasal dryness, ocular allergic reaction, pharyngitis, photophobia, rash, rhinitis, sinus infection, sinusitis, superficial punctate keratopathy, tearing, upper respiratory symptoms, visual field defect, vitreous detachment, vitreous disorder, vitreous floaters, and worsened visual acuity.
Timolol (Ocular Administration)
Body as a whole: chest pain; Cardiovascular: Arrhythmia, bradycardia, cardiac arrest, cardiac failure, cerebral ischemia, cerebral vascular accident, claudication, cold hands and feet, edema, heart block, palpitation, pulmonary edema, Raynaud’s phenomenon, syncope, and worsening of angina pectoris; Digestive: anorexia, diarrhea, nausea; Immunologic: Systemic lupus erythematosus; Nervous System/Psychiatric: Increase in signs and symptoms of myasthenia gravis, insomnia, nightmares, paresthesia, behavioral changes and psychic disturbances including confusion, hallucinations, anxiety, disorientation, nervousness, and memory loss; Skin: Alopecia, psoriasiform rash or exacerbation of psoriasis; Hypersensitivity: Signs and symptoms of systemic allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, and generalized and localized rash; Respiratory: Bronchospasm (predominantly in patients with pre-existing bronchospastic disease) [see Contraindications (4.1)], dyspnea, nasal congestion, respiratory failure, upper respiratory infections; Endocrine: Masked symptoms of hypoglycemia in diabetes patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]; Special Senses: diplopia, choroidal detachment following filtration surgery, cystoid macular edema, decreased corneal sensitivity, pseudopemphigoid, ptosis, refractive changes, tinnitus; Urogenital: Decreased libido, impotence, Peyronie’s disease, retroperitoneal fibrosis.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Antihypertensives/Cardiac Glycosides
Because COMBIGAN® may reduce blood pressure, caution in using drugs such as antihypertensives and/or cardiac glycosides with COMBIGAN® is advised.
7.2 Beta-adrenergic Blocking Agents
Patients who are receiving a beta-adrenergic blocking agent either orally or intravenously and COMBIGAN® should be observed for potential additive effects of beta-blockade, both systemic and on intraocular pressure. The concomitant use of two topical beta-adrenergic blocking agents is not recommended.
7.3 Calcium Antagonists
Caution should be used in the co-administration of beta-adrenergic blocking agents, such as COMBIGAN®, and oral or intravenous calcium antagonists because of possible atrioventricular conduction disturbances, left ventricular failure, and hypotension. In patients with impaired cardiac function, co-administration should be avoided.
7.4 Catecholamine-depleting Drugs
Close observation of the patient is recommended when a beta blocker is administered to patients receiving catecholamine-depleting drugs such as reserpine, because of possible additive effects and the production of hypotension and/or marked bradycardia, which may result in vertigo, syncope, or postural hypotension.
7.5 CNS Depressants
Although specific drug interaction studies have not been conducted with COMBIGAN®, the possibility of an additive or potentiating effect with CNS depressants (alcohol, barbiturates, opiates, sedatives, or anesthetics) should be considered.
7.6 Digitalis and Calcium Antagonists
The concomitant use of beta-adrenergic blocking agents with digitalis and calcium antagonists may have additive effects in prolonging atrioventricular conduction time.
7.7 CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Potentiated systemic beta-blockade (e.g., decreased heart rate, depression) has been reported during combined treatment with CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., quinidine, SSRIs) and timolol.
7.8 Tricyclic Antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressants have been reported to blunt the hypotensive effect of systemic clonidine. It is not known whether the concurrent use of these agents with COMBIGAN® in humans can lead to resulting interference with the IOP-lowering effect. Caution, however, is advised in patients taking tricyclic antidepressants which can affect the metabolism and uptake of circulating amines.
7.9 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors may theoretically interfere with the metabolism of brimonidine and potentially result in an increased systemic side effect such as hypotension. Caution, however, is advised in patients taking MAO inhibitors which can affect the metabolism and uptake of circulating amines.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
COMBIGAN® is contraindicated in children under the age of 2 years [see Contraindications (4.3)]. During post-marketing surveillance, apnea, bradycardia, coma, hypotension, hypothermia, hypotonia, lethargy, pallor, respiratory depression, and somnolence have been reported in infants receiving brimonidine. The safety and effectiveness of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate have not been studied in children below the age of 2 years.
The safety and effectiveness of COMBIGAN® have been established in the age groups 2 – 16 years of age. Use of COMBIGAN® in these age groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of COMBIGAN® in adults with additional data from a study of the concomitant use of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution in pediatric glaucoma patients (ages 2 to 7 years). In this study, brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% was dosed three times a day as adjunctive therapy to beta-blockers. The most commonly observed adverse reactions were somnolence (50%-83% in patients 2 to 6 years) and decreased alertness. In pediatric patients 7 years of age or older (>20 kg), somnolence appears to occur less frequently (25%). Approximately 16% of patients on brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution discontinued from the study due to somnolence.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Patients with bronchial asthma, a history of bronchial asthma, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sinus bradycardia, second or third degree atrioventricular block, or cardiac failure should be advised not to take this product [see Contraindications (4.1, 4.2)].
Patients should be instructed that ocular solutions, if handled improperly or if the tip of the dispensing container contacts the eye or surrounding structures, can become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions or by inadvertent contact with the dropper tip [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. Always replace the cap after using. If solution changes color or becomes cloudy, do not use. Do not use the product after the expiration date marked on the bottle.
Patients also should be advised that if they have ocular surgery or develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection), they should immediately seek their physician's advice concerning the continued use of the present multidose container.
If more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five minutes apart.
Patients should be advised that COMBIGAN® contains benzalkonium chloride which may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Contact lenses should be removed prior to administration of the solution. Lenses may be reinserted 15 minutes following administration of COMBIGAN®.
As with other similar medications, COMBIGAN® may cause fatigue and/or drowsiness in some patients. Patients who engage in hazardous activities should be cautioned of the potential for a decrease in mental alertness.
© 2015 Allergan. All rights reserved.
Irvine, CA 92612, U.S.A.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Patented. See: www.allergan.com/products/patent_notices
Made in the U.S.A.
72060US15
| COMBIGAN
brimonidine tartrate, timolol maleate solution/ drops |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |