Drug Detail:Corifact (Factor xiii [ fak-tor-13 ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous coagulation modifiers
Highlights of Prescribing Information
CORIFACT®, Factor XIII Concentrate (Human)
Lyophilized powder for solution for injection
For intravenous use only.
Initial U.S. Approval: 2011
Indications and Usage for Corifact
CORIFACT is a Factor XIII concentrate indicated for adult and pediatric patients with congenital Factor XIII deficiency for:
- Routine prophylactic treatment
- Peri-operative management of surgical bleeding. (1)
Corifact Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use only.
Dose (2.1)
- 40 International Units (IU) per kg body weight; rate not to exceed 4 mL per min.
- Adjust dose ±5 IU per kg to maintain 5% to 20% trough level of FXIII activity.
Dose Adjustment Using the Berichrom Activity Assay (2.1)
| FXIII Activity Trough Level (%) | Dosage Change |
|---|---|
| One trough level of <5% | Increase by 5 IU per kg |
| Trough level of 5% to 20% | No change |
| Two trough levels of >20% | Decrease by 5 IU per kg |
| One trough level of >25% | Decrease by 5 IU per kg |
Administration (2.2)
- Administer at a rate not exceeding 4 mL per minute
- For routine prophylaxis, administer every 28 days
- For peri-operative management of surgical bleeding, individualize dose based on the patient's FXIII activity level, type of surgery, and clinical response
- Following are dose adjustment examples for peri-operative management in reference to the patient's last prophylactic dose:
Dose Adjustment for Peri-operative Management
| Time Since Last Dose | Dose |
|---|---|
| Within 7 days | Additional dose may not be needed |
| 8 – 21 days | Additional partial or full dose may be needed based on FXIII activity level |
| 21 – 28 days | Full prophylactic dose |
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Each single-dose vial contains 1000-1600 units of lyophilized powder for reconstitution. (3)
Contraindications
Do not use in patients with known anaphylactic or severe systemic reactions to human plasma-derived products. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity reaction may occur. (5.1)
- Inhibitory antibodies have been detected in patients receiving CORIFACT. (5.2)
- Thrombotic events have been reported with CORIFACT. (5.3)
- Because CORIFACT is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) agent. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials (>1%) were joint inflammation, hypersensitivity, rash, pruritus, erythema, hematoma, arthralgia, headache, elevated thrombin-antithrombin levels, and increased blood lactate dehydrogenase. (6)
- Serious adverse reactions reported in clinical trials were hypersensitivity, acute ischemia, and neutralizing antibodies against FXIII. (5.1, 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact the CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance Department at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Pediatric: Shorter half-life and faster clearance compared to adults. Dose adjustment may be needed. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2020
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Corifact
CORIFACT is a Factor XIII Concentrate indicated for routine prophylactic treatment and peri-operative management of surgical bleeding in adult and pediatric patients with congenital FXIII deficiency.
2. Corifact Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dose
- 40 International Units (IU) per kg body weight at a rate not to exceed 4 mL per minute
- Adjust dose ±5 IU per kg to maintain 5% to 20% trough level of FXIII activity as provided in the example below
| FXIII Activity Trough Level (%) | Dosage Change |
|---|---|
| One trough level of <5% | Increase by 5 IU per kg |
| Trough level of 5% to 20% | No change |
| Two trough levels of >20% | Decrease by 5 IU per kg |
| One trough level of >25% | Decrease by 5 IU per kg |
2.2 Administration
- Administer at a rate not exceeding 4 mL per minute
- For routine prophylaxis, administer every 28 days
- For peri-operative management of surgical bleeding:
- Dosing should be individualized based on the patient's FXIII activity level, type of surgery, and clinical response
- Monitor patient's FXIII activity levels during and after surgery
- Following are dose adjustment examples for peri-operative management in reference to the patient's last prophylactic dose:
| Time Since Last Dose | Dose |
|---|---|
| Within 7 days | Additional dose may not be needed |
| 8 – 21 days | Additional partial or full dose may be needed based on FXIII activity level |
| 21 – 28 days | Full prophylactic dose |
The potency expressed in International Units is determined using the Berichrom activity assay, referenced to the current International Standard for Blood Coagulation Factor XIII, Plasma.
2.3 Reconstitution
Perform a visual inspection of the reconstituted solution. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
The procedures below are provided as general guidelines for the preparation and reconstitution of CORIFACT.
Reconstitute CORIFACT at room temperature as follows:
- Ensure that the CORIFACT vial and diluent vial are at room temperature.
- Place the CORIFACT vial, diluent vial, and Mix2Vial® transfer set on a flat surface.
- Remove CORIFACT and diluent vial flip caps. Wipe the stoppers with an alcohol swab and allow the stoppers to dry prior to opening the Mix2Vial transfer set package.
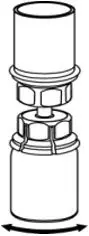
- Open the Mix2Vial transfer set package by peeling away the lid (Fig. 1). Leave the Mix2Vial transfer set in the clear package.
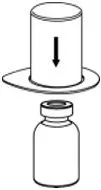
- Place the diluent vial on a flat surface and hold the vial tightly. Grip the Mix2Vial transfer set together with the clear package and push the plastic spike at the blue end of the Mix2Vial transfer set firmly through the center of the stopper of the diluent vial (Fig. 2).
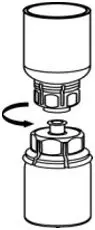
- Carefully remove the clear package from the Mix2Vial transfer set. Make sure that you pull up only the clear package, not the Mix2Vial transfer set (Fig. 3).
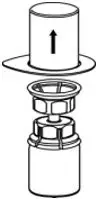
- With the CORIFACT vial placed firmly on a flat surface, invert the diluent vial with the Mix2Vial transfer set attached and push the plastic spike of the transparent adapter firmly through the center of the stopper of the CORIFACT vial (Fig. 4). The diluent will automatically transfer into the CORIFACT vial.
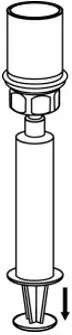
- With the diluent and CORIFACT vial still attached to the Mix2Vial transfer set, gently swirl the CORIFACT vial to ensure that the CORIFACT is fully dissolved (Fig. 5). Do not shake the vial.
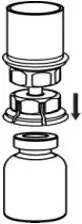
- With one hand, grasp the CORIFACT side of the Mix2Vial transfer set and with the other hand grasp the blue diluent-side of the Mix2Vial transfer set, and unscrew the set into two pieces (Fig. 6).
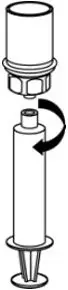
- Draw air into an empty, sterile syringe. While the CORIFACT vial is upright, screw the syringe to the Mix2Vial transfer set. Inject air into the CORIFACT vial. While keeping the syringe plunger pressed, invert the system upside down and draw the concentrate into the syringe by pulling the plunger back slowly (Fig. 7).
- Now that the concentrate has been transferred into the syringe, firmly grasp the barrel of the syringe (keeping the plunger facing down) and unscrew the syringe from the Mix2Vial transfer set (Fig. 8). Attach the syringe to a suitable intravenous administration set.
- If patient requires more than one vial, pool the contents of multiple vials into one syringe. Use a separate unused Mix2Vial transfer set for each product vial.
- CORIFACT is for dose use only. Contains no preservatives. The product must be used within 4 hours after reconstitution. Do not refrigerate or freeze the reconstituted solution. Discard partially used vials.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
CORIFACT is available as lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial containing 1000-1600 units of Factor XIII concentrate for reconstitution. A 20 mL vial of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, is provided for reconstitution.
The actual units of potency of FXIII are stated on each CORIFACT vial label and carton.
4. Contraindications
CORIFACT is contraindicated in patients with known anaphylactic or severe systemic reactions to human plasma-derived products [see Description (11)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity reactions have been observed with CORIFACT. If signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis or hypersensitivity reactions (including urticaria, rash, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension) occur, immediately discontinue administration [see Patient Counseling Information (17)] and institute appropriate treatment.
5.2 Immunogenicity
Development of inhibitory antibodies against FXIII has been detected in patients receiving CORIFACT. Monitor patients for development of inhibitory antibodies. Presence of inhibitory antibodies may manifest as an inadequate response to treatment. If expected plasma FXIII activity levels are not attained, or if breakthrough bleeding occurs while receiving prophylaxis, perform an assay that measures FXIII inhibitory antibody concentrations.
5.3 Thromboembolic Risk
Thromboembolic complications have been reported. Monitor patients with known risk factors for thrombotic events.
5.4 Transmission of Infectious Agents
Because CORIFACT is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. This also applies to unknown or emerging viruses and other pathogens.
All infections thought by a physician to have been possibly transmitted by this product are to be reported by the physician or other healthcare provider to the CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance Department at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
5.5 Monitoring Laboratory Tests
- Monitor patient's trough FXIII activity level during treatment with CORIFACT [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- If breakthrough bleeding occurs, or if expected peak plasma FXIII activity levels are not attained, perform an investigation to determine the presence of FXIII inhibitory antibodies [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials (>1%) are joint inflammation, hypersensitivity, rash, pruritus, erythema, hematoma, arthralgia, headache, elevated thrombin-antithrombin levels, and increased blood lactate dehydrogenase.
The serious adverse reactions, reported (frequency 0.5%), were hypersensitivity, acute ischemia, and neutralizing antibodies against FXIII [see Warnings and Precautions 5)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Twelve clinical studies included a total of 188 subjects, 108 subjects were <16 years of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] and a total of approximately 4314 infusions of CORIFACT were administered in the studies. The most common adverse reactions occurring at a rate of 1-2% are outlined [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
6.2 Immunogenicity
A case of neutralizing antibodies against FXIII was reported in an open enrollment clinical study. The patient received prophylactic treatment with CORIFACT for ten years. Concomitant medications included interferon for hepatitis C infection. This patient presented with bruising, and post-infusion FXIII levels were found to be lower than expected. Over several weeks, FXIII recovery values decreased, so the dose and frequency of treatments were increased. Neutralizing antibodies to FXIII were detected, interferon treatment was discontinued, and the subject underwent plasmapheresis. Within a month, neutralizing antibodies were no longer detectable, FXIII recovery levels improved, and the previous prophylactic regimen was resumed.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Of the 188 subjects in the CORIFACT clinical studies, 108 were subjects <16 years of age at the time of enrollment (see Table 3).
| Age Group | Subjects (n) |
|---|---|
| <1 month | 2 |
| 1 month to <2 years | 16 |
| 2 to 11 years | 60 |
| 12 to <16 years | 30 |
In the pharmacokinetic study [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], 5 of the 14 subjects ranged in age from 2 to <16 years. Subjects less than 16 years had a shorter half-life (5.7 ± 1.00 days) and faster clearance (0.29 ± 0.12 mL/hr/kg) compared to adults (half-life: 7.1 ± 2.74 days, clearance: 0.22 ± 0.07 mL/hr/kg). Dose adjustments may be needed for patients <16 years of age. There were no differences in the safety profile in children as compared to adults.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of CORIFACT did not include subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or another drug therapy.
11. Corifact Description
CORIFACT, Factor XIII Concentrate (Human), is a heat-treated, lyophilized concentrate of coagulation factor XIII for reconstitution for intravenous use. CORIFACT (FXIII) consists of two A-subunits and two B-subunits, and is made from pooled human plasma. Each vial contains 1000-1600 units FXIII, 120 to 200 mg human albumin, 120 to 320 mg total protein, 80 to 120 mg glucose and 140 to 220 mg sodium chloride. Sodium hydroxide may have been used to adjust the pH.
All plasma used in the manufacture of CORIFACT is obtained from US donors and is tested using serological assays for hepatitis B surface antigen and antibodies to HIV-1/2 and HCV. The plasma is tested with Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) for HCV, HIV-1, HAV and HBV and found to be non-reactive (negative), and the plasma is also tested by NAT for Human Parvovirus B19. Only plasma that passed virus screening is used for production, and the limit for Parvovirus B19 in the fractionation pool is set not to exceed 104 International Units of Parvovirus B19 DNA per mL.
CORIFACT is manufactured from cryo-depleted plasma into an ethanol precipitate, which is then purified by the following four steps:
- Precipitation/adsorption
- Ion exchange chromatography
- Heat-treatment (+60°C for 10 hours in an aqueous solution)
- Virus filtration over two 20 nm filters in series
The sterile filtered final bulk solution is filled into vials and lyophilized. These four manufacturing steps were independently validated in a series of in vitro experiments for their capacity to inactivate or remove both enveloped and non-enveloped viruses. Table 4 shows the virus clearance capacity of the CORIFACT manufacturing process, expressed as mean log10 reduction factor.
| Manufacturing Steps | Virus Reduction Factor (log10) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enveloped Viruses | Non-Enveloped Viruses | |||||
| HIV | BVDV | WNV | PRV | HAV | CPV | |
| HIV, Human immunodeficiency virus type 1, model for HIV-1 and HIV-2 BVDV, bovine viral diarrhea virus, model for HCV WNV, West Nile virus PRV, pseudorabies virus, a model for large enveloped DNA viruses HAV, Hepatitis A virus CPV, canine parvovirus, model for B19V B19V, Human parvovirus B19 N/A, not applicable n.d., not done |
||||||
|
||||||
| Al(OH)3 Adsorption / Vitacel® and Defibrination | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 6.9 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Ion Exchange Chromatography | 5.0 | 3.3 | n.d. | ≥8.0 | 3.4 | 3.7 |
| Heat Treatment | ≥7.7 | ≥8.1 | ≥7.4 | N/A* | 4.3 | 1.0† |
| 20 nm / 20 nm Virus Filtration | ≥6.1 | ≥5.0 | ≥7.4 | ≥6.4 | ≥5.6 | 6.1 |
| Cumulative Virus Reduction (log10) | ≥18.8 | ≥16.4 | ≥14.8 | ≥21.3 | ≥13.3 | 10.8 |
12. Corifact - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
CORIFACT (FXIII) is an endogenous plasma glycoprotein consisting of two A-subunits and two B-subunits. FXIIIa promotes cross-linking of fibrin during coagulation and is essential to the physiological protection of the clot against fibrinolysis. FXIIIa is a transglutaminase enzyme that catalyzes the cross-linking of the fibrin α- and γ-chains for fibrin stabilization and renders the fibrin clot more elastic and resistant to fibrinolysis.2,3 FXIIIa also cross-links α2-plasmin inhibitor to the α-chain of fibrin, resulting in protection of the fibrin clot from degradation by plasmin. Cross-linked fibrin is the end result of the coagulation cascade, and provides tensile strength to a primary hemostatic platelet plug.3
The B-subunits in plasma have no enzymatic activity, and function as carrier molecules for the A-subunits. They stabilize the structure of the A-subunits and protect them from proteolysis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Administration of CORIFACT to patients with congenital FXIII deficiency replaces missing or low levels of coagulation Factor XIII, enabling a temporary correction of the factor deficiency and correction of bleeding tendencies. There are no markers that can quantitatively assess the in vivo pharmacodynamics of FXIII. The results of standard coagulation (clot time-based) tests are normal in FXIII deficient patients as it is the quality of the clot that is affected. A qualitative assay of clot suitability is used as an indicator of FXIII deficiency; when performed correctly the test is positive only when the FXIII activity in the sample is close to zero. Thromboelastography can also be affected by FXIII deficiency.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
A 12-week prospective, open-label, multicenter pharmacokinetic and safety study was conducted in 7 females and 7 males with congenital FXIII deficiency, ranging in age from 5 to 42 years (3 children, 2 adolescents, 9 adults). One adult male did not complete the pharmacokinetic study.
Each subject received 40 units per kg CORIFACT intravenously every 28 days for a total of three doses administered at approximately 250 units per minute. Blood samples for doses 1 and 2 were drawn from patients to determine the FXIII activity level at baseline and 30 and 60 minutes after the infusion. Following the infusion of the third dose of CORIFACT, blood samples were drawn at regular intervals up to 28 days to determine the pharmacokinetic parameters. The mean increase in FXIII activity levels was 83% with a range of 48 to 114% over the baseline after the third dose. The pharmacokinetic parameters based on baseline adjusted FXIII activity (Berichrom assay) are shown in Table 5.
| Parameters | Mean ±SD |
|---|---|
| AUC ss, (0-inf) = Area under the plasma concentration curve from time 0 to infinity at steady state Css, max: Peak concentration at steady state Css, min: Trough concentration at steady state Tmax: Time to peak concentration CL: Clearance Vss: Volume of distribution at steady state MRT = Mean residence time SD = Standard deviation |
|
|
|
| AUC ss, 0-inf (units∙hr/mL) | 184.0 ±65.78 |
| Css, max (units/mL)* | 0.9 ±0.20 |
| Css, min (units/mL)* | 0.05 ±0.05 |
| Tmax (hr) | 1.7 ±1.44 |
| Half-life [days] | 6.6 ±2.29 |
| CL [mL/hr/kg] | 0.25 ±0.09 |
| Vss [mL/kg] | 51.1 ±12.61 |
| MRT [days] | 10.0 ±3.45 |
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
CORIFACT was studied in an acute toxicity study in mice and rats at doses up to 3550 units per kg and 1420 units per kg, respectively. Repeat dose toxicity was studied in rats at daily doses up to 350 units per kg for a period of 14 days. No signs of toxicity were observed in the single dose and repeat dose studies.
A local tolerance study in rabbits demonstrated no clinical or histopathological changes at the injection site after intravenous, intra-arterial or para-venous administration of CORIFACT.
A thrombogenicity test was performed in rabbits at doses up to 350 units per kg. CORIFACT showed no thrombogenic potential at the doses tested.
15. References
- Sharief, LAT., Kadir RA.:Congenital factor XIII deficiency in women: a systemic review of literature, Hemophilia. 2013; 19: e349-e357.
- Lauer P, Metzner HJ, Zettlmeissl G, Li M, et al. Targeted Inactivation of the Mouse Locus Encoding Coagulation Factor XIII-A: Hemostatic Abnormalities in Mutant Mice and Characterization of the Coagulation Deficit. Thromb Haemost. 2002;88:967-74.
- Dardik R, Loscalzo J, Inbal A. Factor XIII (FXIII) and Angiogenesis. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:19-25.
- Lusher J, Pipe SW, Alexander S, Nugent D. Prophylactic therapy with Fibrogammin P is associated with a decreased incidence of bleeding episodes: a retrospective study. Haemophilia. 2009;1-6.
16. How is Corifact supplied
| Presentation | Carton NDC Number | Components |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| 1000-1600 units* | 63833-518-02 |
|
17. Patient Counseling Information
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Product Information)
- Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of allergic hypersensitivity reactions, such as urticaria, rash, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension and/or anaphylaxis experienced during or after injection of CORIFACT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of immunogenicity such as breakthrough bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Inform patients of signs and symptoms of thrombosis, such as limb or abdomen swelling and/or pain, chest pain, shortness of breath, loss of sensation or motor power, altered consciousness, vision, or speech [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Inform patients that because CORIFACT is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Description (11)].
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling – Patient Product Information (PPI)
CORIFACT®
Factor XIII Concentrate (Human)
This leaflet summarizes important information about CORIFACT. Please read it carefully before using CORIFACT and each time you get a refill. There may be new information provided. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider, and it does not include all of the important information about CORIFACT. If you have any questions after reading this, ask your healthcare provider.
What is CORIFACT?
CORIFACT is an injectable medicine used for routine prophylactic treatment and peri-operative management of surgical bleeding in adults and pediatric patients with congenital Factor XIII (FXIII) deficiency. CORIFACT is a coagulation FXIII concentrate made from human plasma, and has important functions in hemostasis (stopping of bleeding).
Who should not use CORIFACT?
You should not use CORIFACT if you have experienced hypersensitivity (allergy) reactions, including anaphylactic or severe systemic reactions to human plasma-derived products.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before CORIFACT is given?
Tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including:
- If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It has not been established if CORIFACT can harm your unborn baby. Safety and effectiveness in labor and delivery have not been established.
- Breast feeding: It has not been established if CORIFACT passes into your milk.
Tell your healthcare provider and pharmacist about all of the medicines you take, including all prescription and non-prescription medicines such as over-the-counter medicines, supplements, or herbal remedies.
How is CORIFACT given?
CORIFACT is administered into your vein (intravenous injection). Before infusing, CORIFACT is dissolved using sterile water provided in the package. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the dose that you receive.
What could be the possible side effects of CORIFACT?
Call your healthcare provider or the emergency department right away if you have any of the following symptoms after using CORIFACT:
- shortness of breath
- rash
- pruritus (itching)
- erythema (redness of the skin)
- fainting/dizziness
- chest pain
- signs of a blood clot including pain, swelling, warmth, redness, or a lump in your legs or arms.
Other possible side effects may include:
- chills/rise in temperature
- arthralgia (joint pain)
- headache
- breakthrough bleeding and pain resulting from formation of antibodies against CORIFACT.
Because CORIFACT is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob (CJD) agent.
These are not all the possible side effects of CORIFACT.
Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. You can also report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What else should I know about CORIFACT?
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed here. Do not use CORIFACT for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not share CORIFACT with other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about CORIFACT. If you would like more information, talk to your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about CORIFACT that was written for healthcare professionals.
Talk to your healthcare provider before traveling.
Manufactured by:
CSL Behring GmbH
35041 Marburg Germany
US License No. 1765
Distributed by:
CSL Behring LLC
Kankakee, IL 60901 USA
Mix2Vial® is a registered trademark of West Pharma. Services IL, Ltd., a subsidiary of West Pharmaceuticals Services, Inc.
Revised: Month 2020
| CORIFACT
factor xiii concentrate (human) kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - CSL Behring GmbH (326530474) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSL Behring GmbH | 326530474 | MANUFACTURE(63833-518) | |