Drug Detail:Ddavp (injection) (Desmopressin (injection) [ dez-mo-press-in ])
Drug Class: Antidiuretic hormones
Highlights of Prescribing Information
DDAVP (desmopressin acetate) injection, for intravenous or subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1978
WARNING: HYPONATREMIA
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- DDAVP can cause hyponatremia, which may be life-threatening if severe. (5.1)
- DDAVP is contraindicated in patients at increased risk of severe hyponatremia, such as patients with excessive fluid intake, illnesses that can cause fluid or electrolyte imbalances, and in those using loop diuretics or systemic or inhaled glucocorticoids. (4, 5.1)
- Ensure serum sodium concentration is normal before starting or resuming DDAVP. Measure serum sodium within 1 week and approximately 1 month after starting therapy and periodically during treatment. More frequently monitor serum sodium in patients 65 years of age and older and in patients at increased risk of hyponatremia. (2.1, 5.1)
- If hyponatremia occurs, interrupt or discontinue DDAVP. (5.1)
Indications and Usage for DDAVP
DDAVP Injection is a vasopressin analog used for:
- Central Diabetes Insipidus - as antidiuretic replacement therapy in the management of central (cranial) diabetes insipidus and for the management of the temporary polyuria and polydipsia following head trauma or surgery in the pituitary region. (1.1)
- Hemophilia A- for patients with factor VIII coagulant activity levels greater than 5% to maintain hemostasis during surgical procedures and postoperatively or reduce bleeding with episodes of spontaneous or traumatic injuries such as hemarthroses, intramuscular hematomas, or mucosal bleeding. (1.2)
- von Willebrand's disease (Type I) - for patients with mild to moderate disease with factor VIII levels greater than 5% to maintain hemostasis during surgical procedures or traumatic injuries such as hemarthroses, intramuscular hematomas, or mucosal bleeding. (1.3)
Limitations of Use
- DDAVP is ineffective and not indicated for the treatment of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. (1.3)
- von Willebrand's disease (severe Type I) - not indicated for the treatment of patients with severe Type I von Willebrand's disease and when there is evidence of an abnormal molecular form of factor VIII antigen. (1.3)
DDAVP Dosage and Administration
- Diabetes Insipidus: The daily dose is 2 mcg to 4 mcg administered as one or two divided doses by subcutaneous or intravenous injection. The dosage must be determined for each patient and adjusted according to the pattern of response. (2.1)
- Hemophilia A and von Willebrand's Disease (Type I): 0.3 mcg/kg (to a maximum of 20 mcg) administered by intravenous infusion. Dilute dose as appropriate. (2.1)
- See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on reconstitution, preparation, and administration (2).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
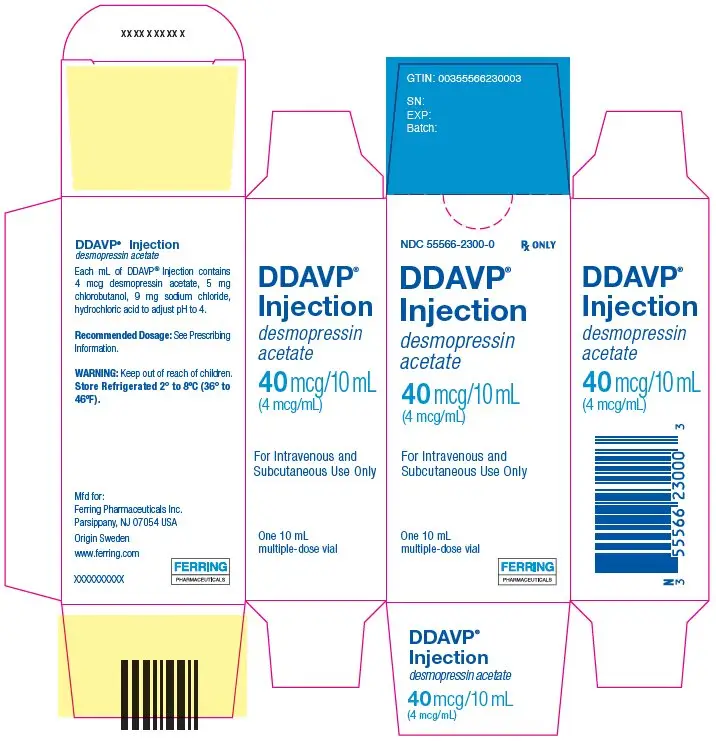
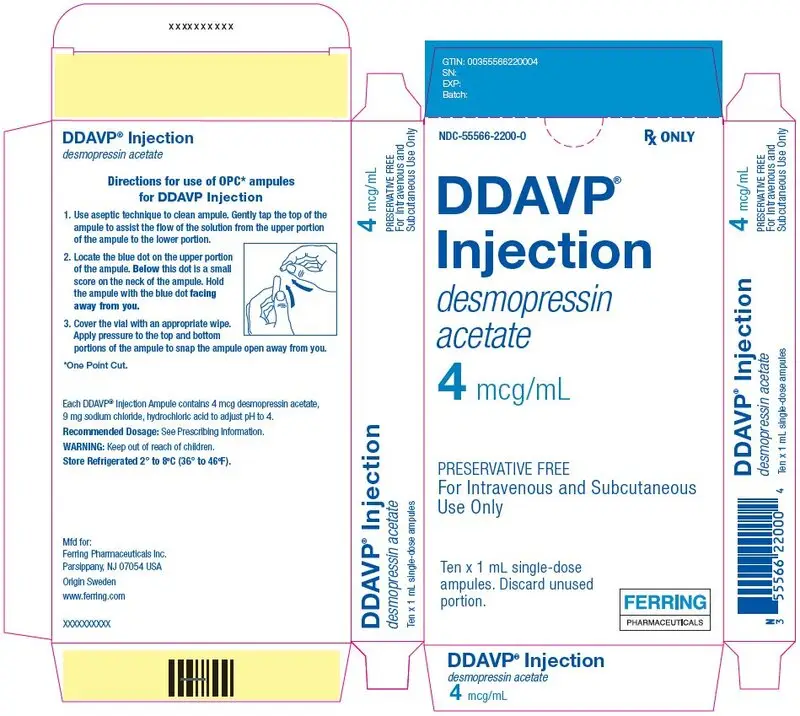
Injection: 4 mcg/mL in 1 mL single-dose ampule and 40 mcg/10 mL (4 mcg/mL) in a multiple-dose vial. (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to desmopressin acetate or to any of the components (4)
- Moderate to severe renal impairment defined as a creatinine clearance below 50 mL/min (4)
- Hyponatremia or a history of hyponatremia (4)
- Known or suspected syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) secretion (4)
- Polydipsia (4)
- Concomitant use with loop diuretics or systemic or inhaled glucocorticoids (4)
- During illnesses that can cause fluid or electrolyte imbalance (4)
- Heart failure or uncontrolled hypertension (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypotension and Hypertension: May cause hypotension with compensatory increase in heart rate or hypertension. Monitor blood pressure during DDAVP administration, especially in patients with heart disease. (5.2)
- Increased Risk of Thrombosis in Patients with von Willebrand's Disease Type IIB: Use of DDAVP in patients with Type IIB von Willebrand's disease may cause thrombosis due to platelet aggregation. (5.3)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Severe reactions have occurred. Monitor for reactions during administration and interrupt if reaction occurs. (5.4)
- Fluid Retention: Fluid retention can worsen underlying conditions that are susceptible to volume status. Not recommended in patients at risk for increased intracranial pressure or with a history of urinary retention. (5.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Common adverse reactions are abdominal cramps, burning pain, erythema, facial flushing, fluid retention, headache, hypersensitivity reactions, hypertension, hyponatremia, hyponatremic seizures, hypotension, nausea, swelling, tachycardia, and thrombotic events. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-888-FERRING (1-888-337-7464) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Drugs that increase risk of hyponatremia: Require more frequent serum sodium monitoring. (7.1)
- Other vasoconstrictors: May require a reduction of the DDAVP dosage. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pediatric Use: Initiate fluid intake restriction to prevent possible hyponatremia and water intoxication. (8.4)
- Geriatric Use: Carefully select dose and monitor renal function more frequently. (8.5)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2022
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: HYPONATREMIA
DDAVP can cause hyponatremia. Severe hyponatremia can be life-threatening, leading to seizures, coma, respiratory arrest, or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
DDAVP is contraindicated in patients at increased risk of severe hyponatremia, such as patients with excessive fluid intake, illnesses that can cause fluid or electrolyte imbalances, and in those using loop diuretics or systemic or inhaled glucocorticoids [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Ensure the serum sodium concentration is normal before starting or resuming DDAVP. Measure serum sodium within 7 days and approximately 1 month after initiating therapy, and periodically during treatment. More frequently monitor serum sodium in patients 65 years of age and older and in patients at increased risk of hyponatremia [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
If hyponatremia occurs, DDAVP may need to be temporarily or permanently discontinued [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for DDAVP
1.1 Central Diabetes Insipidus
DDAVP Injection is indicated as antidiuretic replacement therapy in the management of central (cranial) diabetes insipidus and for the management of the temporary polyuria and polydipsia following head trauma or surgery in the pituitary region.
1.2 Hemophilia A
DDAVP Injection is indicated for patients with hemophilia A with factor VIII coagulant activity levels greater than 5% without factor VIII antibodies to:
- Maintain hemostasis during surgical procedures and postoperatively
- Reduce bleeding with episodes of spontaneous or traumatic injuries such as hemarthroses, intramuscular hematomas, or mucosal bleeding.
1.3 von Willebrand's Disease (Type I)
DDAVP Injection is indicated for patients with mild to moderate von Willebrand's disease (Type I) with factor VIII levels greater than 5% to:
- Maintain hemostasis during surgical procedures and postoperatively
- Reduce bleeding with episodes of spontaneous or traumatic injuries such as hemarthroses, intramuscular hematomas, or mucosal bleeding.
2. DDAVP Dosage and Administration
2.1 Pretreatment Testing and On-Treatment Monitoring
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Initiate fluid restriction during treatment with DDAVP Injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4, 8.5)].
2.3 Preparation and Administration for Patients with Hemophilia A and von Willebrand's Disease (Type I)
Prepare the solution for infusion using aseptic technique. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Withdraw the necessary volume of DDAVP Injection from the vial and dilute by adding to the infusion bag of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP per Table 1. Dilute DDAVP Injection in sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP and infuse slowly over 15 minutes to 30 minutes.
The volume of diluent is weight-based. See Table 1 for volume of diluent to use.
| Patient Weight | Volume of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP for dilution |
|---|---|
| 10 kg or less | 10 mL |
| More than 10 kg | 50 mL |
Monitor blood pressure and pulse during infusion.
2.4 Switching Between Desmopressin Acetate Formulations
DDAVP is also available as nasal spray and tablet dosage forms.
When switching between formulations, the below text is meant as guidance for starting dose. However, dose should always be titrated individually according to the diuresis (antidiuretic response) and electrolyte status (serum sodium) of the patient.
When switching from DDAVP Nasal Spray to DDAVP Injection, the starting dose is one-tenth times the DDAVP Nasal Spray dose.
When switching from DDAVP Tablets to DDAVP Injection, titrate dose individually according to the diuresis (antidiuretic response) and electrolyte status (serum sodium) due to the large variability in both PK and PD. Monitor patients closely during the initial dose titration period.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: DDAVP is a sterile, aqueous, colorless solution available as:
- 4 mcg/mL in single-dose ampule
- 40 mcg/10 mL (4 mcg/mL) in multiple-dose vial
4. Contraindications
DDAVP Injection is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to desmopressin acetate or to any of the components of DDAVP Injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Adverse Reactions (6), Description (11)].
DDAVP Injection is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions due to an increased risk of hyponatremia:
- Moderate to severe renal impairment defined as a creatinine clearance below 50 mL/min [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5, 8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Hyponatremia or a history of hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.1)], Use in Specific Populations (8.4, 8.5)].
- Known or suspected syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) secretion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Polydipsia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Concomitant use with loop diuretics [see Boxed Warning].
- Concomitant use with systemic or inhaled glucocorticoids [see Boxed Warning].
- During illnesses that can cause fluid or electrolyte imbalance, such as gastroenteritis, salt-wasting nephropathies, or systemic infection [see Boxed Warning].
DDAVP Injection is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions because fluid retention increases the risk of worsening the underlying condition:
- Heart failure
- Uncontrolled hypertension
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hyponatremia
DDAVP Injection can cause hyponatremia. Severe hyponatremia can be life-threatening if it is not promptly diagnosed and treated, leading to seizures, coma, respiratory arrest, or death [see Boxed Warning].
DDAVP Injection is contraindicated in patients with hyponatremia (or a history of hyponatremia), with excessive fluid intake (e.g., polydipsia), using loop diuretics or systemic or inhaled glucocorticoids, with known or suspected SIADH, and/or illnesses that can cause fluid or electrolyte imbalances [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7)]. Avoid concomitant treatments that also cause hyponatremia.
Prior to starting or resuming DDAVP Injection, ensure that the serum sodium concentration is normal. Limit fluid intake to a minimum from 1 hour before administration until 8 hours after administration. Use of DDAVP Injection without concomitant reduction of fluid intake may lead to fluid retention and hyponatremia.
Monitor the serum sodium concentration within 1 week and approximately 1 month of initiating DDAVP Injection, and periodically thereafter [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Base the frequency of serum sodium monitoring on the patient's risk of hyponatremia.
Patients with conditions associated with fluid and electrolyte imbalance (i.e., cystic fibrosis, heart failure, and renal disorders), geriatric and pediatric patients, patients receiving concomitant treatments that also cause hyponatremia (i.e., tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chlorpromazine, opiate analgesics, carbamazepine, lamotrigine, thiazide diuretics and chlorpropamide), and patients with habitual or psychogenic polydipsia who may drink excessive amounts of water, may be at increased risk of hyponatremia [see Contraindications (4)].
If hyponatremia occurs, DDAVP Injection may need to be temporarily or permanently discontinued and treatment for the hyponatremia instituted, depending on the clinical circumstances, including the duration and severity of the hyponatremia.
5.2 Hypotension and Hypertension
DDAVP may cause hypotension (with compensatory increase in heart rate) or hypertension. Monitor blood pressure during DDAVP administration, particularly in patients with a history of coronary artery insufficiency and/or hypertensive cardiovascular disease [see Adverse Reactions (6), Drug Interactions (7.2)]
5.3 Increased Risk of Thrombosis in Patients with von Willebrand's Disease Type IIB
Use of DDAVP in patients with Type IIB von Willebrand's disease may result in platelet aggregation, thrombocytopenia, and possibly thrombosis.
5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have been reported with intravenous and intranasal DDAVP, including cases of fatal anaphylaxis with intravenous DDAVP. DDAVP Injection is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to desmopressin acetate or to any of the components of DDAVP Injection [see Contraindications (4)]. It is not known whether antibodies to DDAVP Injection are produced after repeated injections. Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions during administration, interrupt treatment should a reaction occur, and manage medically. Permanently discontinue for serious hypersensitivity reaction [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.5 Fluid Retention
DDAVP Injection can cause fluid retention, which can worsen underlying conditions that are susceptible to volume status. Patients with heart failure or uncontrolled hypertension may be at increased risk. DDAVP Injection is not recommended in patients at risk for increased intracranial pressure or those with a history of urinary retention. Advise patients to limit fluid intake [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hyponatremia [see Contraindications, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypotension and Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Increased risk of thrombosis in patients with von Willebrand's Disease Type IIB [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Fluid retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of DDAVP Injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular: Hypertension, hypotension, tachycardia, thrombotic events, fluid retention
Digestive: Nausea, abdominal cramps
Immune: Hypersensitivity reactions
Integumentary: Erythema, swelling, burning pain, facial flushing
Laboratory: Hyponatremia
Nervous: Headache, hyponatremic seizures
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Other Drugs that may Increase Risk of Hyponatremia
The concomitant administration of DDAVP Injection with other drugs that may increase the risk of water intoxication with hyponatremia, (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors, chlorpromazine, opiate analgesics, thiazide diuretics, NSAIDs, lamotrigine, sulfonylureas, particularly chlorpropamide, oxybutynin and carbamazepine), requires more frequent serum sodium monitoring. Monitor serum sodium more frequently in patients taking DDAVP Injection concomitantly with these drugs and when doses of these drugs are increased [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4, 8.5)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
Data
The breast milk of lactating women was collected over 8 hours following administration of 300 mcg desmopressin nasal spray. The expected area under the plasma concentration time curve (AUC) of desmopressin following 300 mcg nasal spray is 2.4-fold higher to that of 4 mcg DDAVP injection. Based on the measured concentrations of desmopressin following intranasal administration, the amounts of desmopressin that may be transferred to a breastfed infant correspond to 0.0001-0.005% of the dose administered.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of DDAVP have been established in pediatric patients 3 months of age and older with hemophilia A and von Willebrand's disease and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with diabetes insipidus. The safety and effectiveness of DDAVP have not been established in infants less than 3 months of age with hemophilia A or von Willebrand's disease or pediatric patients under 12 years of age with diabetes insipidus. Use in infants and pediatric patients will require careful fluid intake restriction to prevent possible hyponatremia and water intoxication. Fluid restriction should be discussed with the patient and/or guardian [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of DDAVP Injection did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. DDAVP is contraindicated in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (defined as a creatinine clearance below 50 mL/min) [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Use of DDAVP injection in geriatric patients will require careful fluid intake restrictions to prevent possible hyponatremia and water intoxication. Fluid restriction should be discussed with the patient [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Desmopressin acetate is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions may be greater in patients with renal impairment than patients with normal renal function. DDAVP is contraindicated in patients with estimated CLcr by Cockcroft-Gault equation less than 50 mL/min [see Contraindications (4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
Overdosage of DDAVP Injection leads to prolonged duration of action with an increased risk of water retention and hyponatremia. Signs of overdose may include headaches, abdominal cramps, nausea, facial flushing, confusion, drowsiness, problems with passing urine and rapid weight gain due to fluid retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. In case of overdosage, the dosage should be reduced, frequency of administration decreased, or the drug withdrawn according to the severity of the condition, serum sodium assessed, and hyponatremia treated appropriately.
There is no known specific antidote for desmopressin acetate or DDAVP Injection 4 mcg/mL.
11. DDAVP Description
DDAVP Injection (desmopressin acetate) is a synthetic vasopressin analog for intravenous or subcutaneous use. It is chemically defined as follows:
Mol. Wt. 1183.34
Empirical Formula: C46H64N14O12S2∙C2H4O2∙3H2O
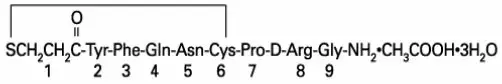
1-(3-mercaptopropionic acid)-8-D-arginine vasopressin monoacetate (salt) trihydrate.
DDAVP solution for injection is a sterile solution in a 1 mL single-dose ampule: Each mL contains 4 mcg of desmopressin acetate which is equivalent to 3.6 mcg of desmopressin free base. The inactive ingredients are sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid and water for injection. Sodium chloride is used to adjust tonicity. Hydrochloric acid is used to adjust pH.
DDAVP solution for injection is a sterile solution in a 10 mL multiple-dose vial: Each mL contains 4 mcg of desmopressin acetate which is equivalent to 3.6 mcg of desmopressin free base. The inactive ingredients are sodium chloride, chlorobutanol (5 mg per mL), hydrochloric acid and water for injection. Sodium chloride is used to adjust tonicity. Hydrochloric acid is used to adjust pH.
12. DDAVP - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Desmopressin acetate increases plasma levels of factor VIII activity in patients with hemophilia and von Willebrand's disease Type I.
The antidiuretic effects of desmopressin acetate are mediated by stimulation of vasopressin 2 (V2) receptors, thereby increasing water re-absorption in the kidney, and hence reducing urine production. Desmopressin acetate is a replacement hormone for antidiuretic hormone in the treatment of central diabetes insipidus. The change in structure of arginine vasopressin to desmopressin acetate resulted in increased duration of action and a decreased vasopressor action and decreased actions on visceral smooth muscle relative to the enhanced antidiuretic activity, so that clinically effective antidiuretic doses were usually below threshold levels for effects on vascular or visceral smooth muscle.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The response to DDAVP of factor VIII activity and plasminogen activator is dose-related, with maximal plasma levels of 300 to 400 percent change from baseline obtained after infusion of 0.4 mcg/kg. The increase of factor VIII is rapid and evident within 30 minutes, reaching a maximum at a point ranging from 90 minutes to two hours. The duration of the hemostatic effect depends on the half-life for VIII:C which is about 8-12 hours. The percentage increase of factor VIII levels in patients with mild hemophilia A and von Willebrand's disease was not significantly different from that observed in normal healthy individuals when treated with 0.3 mcg/kg of DDAVP infused over 10 minutes.
The use of DDAVP Injection in patients with central diabetes insipidus reduces urinary output, increases urine osmolality, and decreases plasma osmolality.
16. How is DDAVP supplied
16.1 How Supplied
DDAVP Injection is available as a sterile solution supplied as 4 mcg/mL in cartons of ten 1 mL single-dose, type 1 glass ampules (NDC 55566-2200-0) and 40 mcg/10 mL (4 mcg/mL) in 10 mL multiple-dose vials, type 1 glass vial with rubber stopper and a flip off seal, (NDC 55566-2300-0), each containing 4 mcg DDAVP per mL.
| DDAVP
desmopressin acetate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| DDAVP
desmopressin acetate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. (103722955) |