Drug Detail:Diphenoxylate (monograph) (Medically reviewed)
Drug Class:
Diphenoxylate and Atropine Description
Each diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate tablet, USP contains:
| Diphenoxylate hydrochloride, USP | 2.5 mg (equivalent to 2.3 mg of diphenoxylate) |
| Atropine sulfate, USP | 0.025 mg (equivalent to 0.01 mg of atropine) |
Diphenoxylate hydrochloride, USP an antidiarrheal, is ethyl 1-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-phenylisonipecotate monohydrochloride and has the following structural formula:
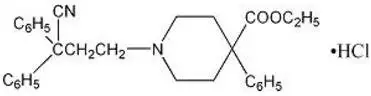
Atropine sulfate, USP an anticholinergic, is endo-(±)-α-(hydroxymethyl) benzeneacetic acid 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1] oct-3-yl ester sulfate (2:1) (salt) monohydrate and has the following structural formula:
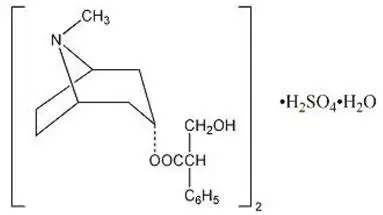
A subtherapeutic amount of atropine sulfate, USP is present to discourage deliberate overdosage.
Diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate tablets, USP contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, microcrystalline stearate, pregelatinized starch and stearic acid.
Diphenoxylate and Atropine - Clinical Pharmacology
Diphenoxylate is rapidly and extensively metabolized in man by ester hydrolysis to diphenoxylic acid (difenoxine), which is biologically active and the major metabolite in the blood. After a 5-mg oral dose of carbon-14 labeled diphenoxylate hydrochloride in ethanolic solution was given to three healthy volunteers, an average of 14% of the drug plus its metabolites was excreted in the urine and 49% in the feces over a four-day period. Urinary excretion of the unmetabolized drug constituted less than 1% of the dose, and diphenoxylic acid plus its glucuronide conjugate constituted about 6% of the dose. In a 16-subject crossover bioavailability study, a linear relationship in the dose range of 2.5 to 10 mg was found between the dose of diphenoxylate hydrochloride (given as diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate liquid) and the peak plasma concentration, the area under the plasma concentration-time curve, and the amount of diphenoxylic acid excreted in the urine. In the same study the bioavailability of the tablet compared with an equal dose of the liquid was approximately 90%. The average peak plasma concentration of diphenoxylic acid following ingestion of four 2.5-mg tablets was 163 ng/ml at about 2 hours, and the elimination half-life of diphenoxylic acid was approximately 12 to 14 hours.
In dogs, diphenoxylate hydrochloride has a direct effect on circular smooth muscle of the bowel that conceivably results in segmentation and prolongation of gastrointestinal transit time. The clinical antidiarrheal action of diphenoxylate hydrochloride may thus be a consequence of enhanced segmentation that allows increased contact of the intraluminal contents with the intestinal mucosa.
Contraindications
Diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate tablets are contraindicated in:
- Pediatric patients less than 6 years of age due to the risks of respiratory and central nervous system (CNS) depression [see WARNINGS].
- Patients with diarrhea associated with pseudomembranous enterocolitis (Clostridium difficile) or other enterotoxin-producing bacteria due to the risk of gastrointestinal (GI) complications, including sepsis [see WARNINGS].
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to diphenoxylate or atropine.
- Patients with obstructive jaundice.
Precautions
Information for Patients
Advise patients:
- Accidental ingestion of diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate in children, especially in those less than 6 years of age, may result in severe respiratory depression or coma. Instruct patients to take steps to store diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate securely and out of reach of children, and to dispose of unused diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate [see WARNINGS].
- To take diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate at the prescribed dosage. Use of a higher than prescribed dosage may include opioid and/or anticholinergic effects [see OVERDOSAGE]. Report to a healthcare facility if they develop anticholinergic symptoms such as hyperthermia, flushing, tachycardia, tachypnea, hypotonia, lethargy, hallucinations, febrile convulsion, dry mouth, mydriasis or opioid symptoms such as progressive CNS and respiratory depression, miosis, seizures, or paralytic ileus.
- Diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate may produce drowsiness or dizziness. Concomitant use of alcohol or other drugs that also cause CNS depression (e.g., barbiturates, benzodiazepines, opioids, buspirone, antihistamines, and muscle relaxants) may increase this effect. Inform patients not to operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery until they are reasonably certain that diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate does not affect them adversely.
- To use fluid and electrolyte therapy, if prescribed along with diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate, as instructed by their healthcare provider.
- Clinical improvement of diarrhea is usually observed within 48 hours. If clinical improvement is not seen within 10 days, discontinue diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate and contact their healthcare provider.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term study in animals has been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential. Diphenoxylate hydrochloride was administered to male and female rats in their diets to provide dose levels of 4 and 20 mg/kg/day throughout a three-litter reproduction study. At 50 times the human dose (20 mg/kg/day), female weight gain was reduced and there was a marked effect on fertility as only 4 of 27 females became pregnant in three test breedings. The relevance of this finding to usage of diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate in humans is unknown.
Pregnancy
Diphenoxylate hydrochloride has been shown to have an effect on fertility in rats when given in doses 50 times the human dose (see above discussion). Other findings in this study include a decrease in maternal weight gain of 30% at 20 mg/kg/day and of 10% at 4 mg/kg/day. At 10 times the human dose (4 mg/kg/day), average litter size was slightly reduced.
Teratology studies were conducted in rats, rabbits, and mice with diphenoxylate hydrochloride at oral doses of 0.4 to 20 mg/kg/day. Due to experimental design and small numbers of litters, embryotoxic, fetotoxic, or teratogenic effects cannot be adequately assessed. However, examination of the available fetuses did not reveal any indication of teratogenicity.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate should be used during pregnancy only if the anticipated benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate is administered to a nursing woman, since the physicochemical characteristics of the major metabolite, diphenoxylic acid, are such that it may be excreted in breast milk and since it is known that atropine is excreted in breast milk.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate have been established in pediatric patients 13 years of age and older as adjunctive therapy in the management of diarrhea. The safety and effectiveness of diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate have not been established in pediatric patients less than 13 years of age.
Diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate is contraindicated in pediatric patients less than 6 years of age due to the risks of severe respiratory depression and coma, possibly resulting in permanent brain damage or death [see CONTRAINDICATIONS].
Diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate has caused atropinism, particularly in pediatric patients with Down's syndrome [see PRECAUTIONS].
In case of accidental ingestion of diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate by pediatric patients, see OVERDOSAGE for recommended treatment.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
- Respiratory and/or CNS depression [see WARNINGS]
- Anticholinergic and opioid-toxicities, including atroponism [see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS]
- Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance [see WARNINGS]
- GI Complications in patients with infectious diarrhea [see WARNINGS]
- Toxic megacolon in patients with acute ulcerative colitis [see WARNINGS]
At therapeutic doses of diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate, the following other adverse reactions have been reported; they are listed in decreasing order of severity, but not of frequency:
Nervous system: numbness of extremities, euphoria, depression, malaise/lethargy, confusion, sedation/drowsiness, dizziness, restlessness, headache, hallucination
Allergic: anaphylaxis, angioneurotic edema, urticaria, swelling of the gums, pruritus
Gastrointestinal system: megacolon, paralytic ileus, pancreatitis, vomiting, nausea, anorexia, abdominal discomfort.
The following adverse reactions related to atropine sulfate are listed in decreasing order of severity, but not of frequency: hyperthermia, tachycardia, urinary retention, flushing, dryness of the skin and mucous membranes.
How is Diphenoxylate and Atropine supplied
Diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate tablets, USP are supplied as white to off-white, round, bi-convex tablets, engraved on one side "U-S" and "90" on the other side. They are supplied as follows:
| Bottles of 90 | (NDC 0832-0590-90) |
| Bottles of 100 | (NDC 0832-0590-11) |
| Bottles of 1000 | (NDC 0832-0590-10) |
| DIPHENOXYLATE HYDROCHLORIDE AND ATROPINE SULFATE
diphenoxylate hydrochloride and atropine sulfate tablet |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Upsher-Smith Laboratories, LLC (047251004) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 005286822 | MANUFACTURE(0832-0590) , ANALYSIS(0832-0590) , LABEL(0832-0590) , PACK(0832-0590) | |





