Drug Detail:Duragesic skin patch (Fentanyl transdermal (skin patch) [ fen-ta-nil-trans-derm-al ])
Drug Class: Opioids (narcotic analgesics)
Highlights of Prescribing Information
DURAGESIC® (fentanyl transdermal system), CII
Initial U.S. Approval: 1968
WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS); LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL EXPOSURE; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME; CYTOCHROME P450 3A4 INTERACTION; RISK OF INCREASED FENTANYL ABSORPTION WITH APPLICATION OF EXTERNAL HEAT; and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE OF BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- DURAGESIC exposes users to risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Assess patient's risk before prescribing, and monitor regularly for these behaviors or conditions. (5.1)
- To ensure that the benefits of opioid analgesics outweigh the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for these products. (5.2)
- Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur. Monitor closely, especially upon initiation or following a dose increase. (5.3)
- Accidental exposure to DURAGESIC, especially in children, can result in fatal overdose of fentanyl. (5.4)
- Prolonged use of DURAGESIC during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated. If opioid use is required for a prolonged period in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available. (5.5)
- Concomitant use with CYP3A4 inhibitors (or discontinuation of CYP3A4 inducers) can result in a fatal overdose of fentanyl. (5.6)
- Exposure of the DURAGESIC application site and surrounding area to direct external heat sources has resulted in fatal overdose of fentanyl. Warn patients to avoid exposing the DURAGESIC application site and surrounding area to direct external heat sources. (5.7)
- Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate; limit dosages and durations to the minimum required; and follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. (5.8, 7)
Indications and Usage for Duragesic
DURAGESIC contains fentanyl, an opioid agonist, and is indicated for the management of pain in opioid-tolerant patients, severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate. (1)
Patients considered opioid-tolerant are those taking, for one week or longer, at least 60 mg oral morphine per day, 25 mcg transdermal fentanyl per hour, 30 mg oral oxycodone per day, 8 mg oral hydromorphone per day, 25 mg oral oxymorphone per day, 60 mg oral hydrocodone per day, or an equianalgesic dose of another opioid. (2.1)
Limitations of use:
- Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses, and because of the greater risks of overdose and death with extended-release opioid formulations, reserve DURAGESIC for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options (e.g., non-opioid analgesics or immediate-release opioids) are ineffective, not tolerated, or would be otherwise inadequate to provide sufficient management of pain. (1)
- DURAGESIC is not indicated as an as-needed (prn) analgesic
Duragesic Dosage and Administration
- To be prescribed only by healthcare providers knowledgeable in use of potent opioids for management of chronic pain. (2.1)
- Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (2.1).
- Individualize dosing based on the severity of pain, patient response, prior analgesic experience, and risk factors for addiction, abuse, and misuse. (2.1)
- Discuss availability of naloxone with the patient and caregiver and assess each patient's need for access to naloxone, both when initiating and renewing treatment with DURAGESIC. Consider prescribing naloxone based on the patient's risk factors for overdose. (2.2, 5.1, 5.3, 5.8)
- Initial dose selection: consult conversion instructions. (2.3)
- Each transdermal system is intended to be worn for 72 hours. (2.3)
- Adhere to instructions concerning administration and disposal of DURAGESIC. (2.7, 2.8)
- Mild to moderate hepatic and renal impairment: Initiate treatment with one half the usual starting dose, titrate slowly, and monitor for signs of respiratory and central nervous system depression. (2.5, 2.6)
- Do not abruptly discontinue DURAGESIC in a physically-dependent patient because rapid discontinuation of opioid analgesics has resulted in serious withdrawal symptoms, uncontrolled pain, and suicide. (2.9)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Transdermal system: 12 mcg/hour, 25 mcg/hour, 37.5 mcg/hour, 50 mcg/hour, 75 mcg/hour, 100 mcg/hour. (3)
Contraindications
- Opioid non-tolerant patients. (4)
- Acute or intermittent pain, postoperative pain, mild pain. (4)
- Significant respiratory depression. (4)
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in absence of resuscitative equipment. (4)
- Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus. (4)
- Known hypersensitivity to fentanyl or any of the components of the transdermal system. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of Increased Fentanyl Absorption with Elevated Body Temperature: Monitor patients with fever closely for sedation and respiratory depression and reduce the dose if necessary. Warn patients to avoid strenuous exertion that may lead to increased body temperature (5.9).
- Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: Monitor closely, particularly during initiation and titration. (5.10)
- Serotonin Syndrome with Concomitant Use of Serotonergic Drugs: Potentially life-threatening condition could result from concomitant serotonergic drug administration. Discontinue DURAGESIC immediately if serotonin syndrome is suspected. (5.11)
- Adrenal Insufficiency: If diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement of corticosteroids, and wean patient off of the opioid. (5.12)
- Severe Hypotension: Monitor during dose initiation and titration. Avoid the use of DURAGESIC in patients with circulatory shock. (5.13)
- Risks of Use in Patients with Increased Intracranial Pressure, Brain Tumors, Head Injury or Impaired Consciousness: Monitor for sedation and respiratory depression. Avoid use of DURAGESIC in patients with impaired consciousness or coma. (5.14)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥5%) are nausea, vomiting, somnolence, dizziness, insomnia, constipation, hyperhidrosis, fatigue, feeling cold, anorexia, headache, and diarrhea. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, call Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc.1-800-526-7736 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Mixed Agonist/Antagonist and Partial Agonist Opioid Analgesics: Avoid use with DURAGESIC because they may reduce analgesic effect of DURAGESIC or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. (5.20, 7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
- Lactation: Not recommended. (8.2)
- Severe Hepatic and Renal Impairment: Use not recommended. (8.6, 8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 4/2022
Related/similar drugs
aspirin, acetaminophen, tramadol, duloxetine, naproxen, oxycodone, TylenolFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS); LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL EXPOSURE; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME; CYTOCHROME P450 3A4 INTERACTION; RISK OF INCREASED FENTANYL ABSORPTION WITH APPLICATION OF EXTERNAL HEAT; and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
1. Indications and Usage for Duragesic
DURAGESIC is indicated for the management of pain in opioid-tolerant patients, severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Patients considered opioid-tolerant are those who are taking, for one week or longer, at least 60 mg morphine per day, 25 mcg transdermal fentanyl per hour, 30 mg oral oxycodone per day, 8 mg oral hydromorphone per day, 25 mg oral oxymorphone per day, 60 mg oral hydrocodone per day, or an equianalgesic dose of another opioid.
2. Duragesic Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
DURAGESIC should be prescribed only by healthcare professionals who are knowledgeable in the use of potent opioids for the management of chronic pain.
Due to the risk of respiratory depression, DURAGESIC is only indicated for use in patients who are already opioid-tolerant. Discontinue or taper all other extended-release opioids when beginning DURAGESIC therapy. As DURAGESIC is only for use in opioid-tolerant patients, do not begin any patient on DURAGESIC as the first opioid [see Indications and Usage (1)].
- Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
- Initiate the dosing regimen for each patient individually, taking into account the patient's severity of pain, patient response, prior analgesic treatment experience, and risk factors for addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24–72 hours of initiating therapy with DURAGESIC when serum concentrations from the initial patch will peak [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2 Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid Overdose
Discuss the availability of naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose with the patient and caregiver and assess the potential need for access to naloxone, both when initiating and renewing treatment with DURAGESIC [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Inform patients and caregivers about the various ways to obtain naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program).
Consider prescribing naloxone, based on the patient's risk factors for overdose, such as concomitant use of CNS depressants, a history of opioid use disorder, or prior opioid overdose. However, the presence of risk factors for overdose should not prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3, 5.8)].
Consider prescribing naloxone if the patient has household members (including children) or other close contacts at risk for accidental exposure or overdose.
2.3 Initial Dosage
Do not initiate treatment with DURAGESIC in opioid nontolerant patients [see Contraindications (4)].
The recommended starting dose when converting from other opioids to DURAGESIC is intended to minimize the potential for overdosing patients with the first dose.
Discontinue all other around-the-clock opioid drugs when DURAGESIC therapy is initiated.
While there are useful tables of opioid equivalents readily available, there is substantial inter-patient variability in the relative potency of different opioid drugs and products. As such, it is preferable to underestimate a patient's 24-hour fentanyl requirements and provide rescue medication (e.g., immediate-release opioid) than to overestimate the 24-hour fentanyl requirements which could result in adverse reactions. In a DURAGESIC clinical trial, patients were converted from their prior opioid to DURAGESIC using Table 1 as a guide for the initial DURAGESIC dose.
Each DURAGESIC transdermal system is worn continuously for up to 72 hours [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].
When converting patients from oral or parenteral opioids to DURAGESIC, use Table 1 (alternatively use Table 2 for adult and pediatric patients taking opioids or doses not listed in Table 1) and consider the following:
- These are not tables of equianalgesic doses.
- The conversion doses in these tables are only for the conversion from one of the listed oral or parenteral opioid analgesics to DURAGESIC.
- The tables cannot be used to convert from DURAGESIC to another opioid because these conversions will result in an overestimation of the dose of the new opioid (these conversions are conservative) and may result in fatal overdosage.
| Current Analgesic | Daily Dosage (mg/day) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Oral morphine | 60–134 | 135–224 | 225–314 | 315–404 |
| Intramuscular or Intravenous morphine | 10–22 | 23–37 | 38–52 | 53–67 |
| Oral oxycodone | 30–67 | 67.5–112 | 112.5–157 | 157.5–202 |
| Oral codeine | 150–447 | |||
| Oral hydromorphone | 8–17 | 17.1–28 | 28.1–39 | 39.1–51 |
| Intravenous hydromorphone | 1.5–3.4 | 3.5–5.6 | 5.7–7.9 | 8–10 |
| Intramuscular meperidine | 75–165 | 166–278 | 279–390 | 391–503 |
| Oral methadone | 20–44 | 45–74 | 75–104 | 105–134 |
| ⇓ | ⇓ | ⇓ | ⇓ | |
| Recommended DURAGESIC Dose | 25 mcg/hour | 50 mcg/hour | 75 mcg/hour | 100 mcg/hour |
Alternatively, for adult and pediatric patients taking opioids or doses not listed in Table 1, use the following methodology when converting patients from oral or parenteral opioids to DURAGESIC:
- Calculate the previous 24-hour analgesic requirement.
- Convert this amount to the equianalgesic oral morphine dose using a reliable reference.
- Refer to Table 2 for the range of 24-hour oral morphine doses that are recommended for conversion to each DURAGESIC dose. Use this table to find the calculated 24-hour morphine dose and the corresponding recommended initial DURAGESIC dose.
- Initiate DURAGESIC treatment using the recommended dose and titrate patients upwards (no more frequently than 3 days after the initial dose and every 6 days thereafter) until analgesic efficacy is attained. A 37.5 mcg/hour dose may also be used. The 37.5 mcg/hour strength is not available as DURAGESIC. It is available as Fentanyl Transdermal System. For patients that require more than 100 mcg/hour, several transdermal systems may be used.
- Do not use Table 2 to convert from DURAGESIC to other therapies because this conversion to DURAGESIC is conservative and will overestimate the dose of the new agent.
| Oral 24-hour Morphine (mg/day) | DURAGESIC Dose (mcg/hour) |
|---|---|
| NOTE: In clinical trials, these ranges of daily oral morphine doses were used as a basis for conversion to DURAGESIC. | |
|
|
| 60–134 | 25 |
| 135–224 | 50 |
| 225–314 | 75 |
| 315–404 | 100 |
| 405–494 | 125 |
| 495–584 | 150 |
| 585–674 | 175 |
| 675–764 | 200 |
| 765–854 | 225 |
| 855–944 | 250 |
| 945–1034 | 275 |
| 1035–1124 | 300 |
An additional intermediate strength 37.5 mcg/hour DURAGESIC transdermal system is available and may be considered during conversion from prior opioids or dose titration. For example, the 37.5 mcg/hour system could be used before converting or titrating to a 50 mcg/hour system.
The additional 37.5 mcg/hour system was not used in the clinical studies.
For delivery rates in excess of 100 mcg/hour, multiple systems may be used.
2.4 Titration and Maintenance of Therapy
Individually titrate DURAGESIC to a dose that provides adequate analgesia and minimizes adverse reactions. Continually reevaluate patients receiving DURAGESIC to assess the maintenance of pain control and the relative incidence of adverse reactions, as well as monitoring for the development of addiction, abuse, or misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Frequent communication is important among the prescriber, other members of the healthcare team, the patient, and the caregiver/family during periods of changing analgesic requirements, including initial titration. During chronic therapy, periodically reassess the continued need for opioid analgesics.
Patients who experience breakthrough pain may require a dosage adjustment of DURAGESIC, or may need rescue medication with an appropriate dose of an immediate-release analgesic. If the level of pain increases after dosage stabilization, attempt to identify the source of increased pain before increasing the DURAGESIC dosage.
The dosing interval for DURAGESIC is 72 hours. Do not increase the DURAGESIC dose for the first time until at least 3 days after the initial application. Titrate the dose based on the daily dose of supplemental opioid analgesics required by the patient on the second or third day of the initial application.
It may take up to 6 days for fentanyl levels to reach equilibrium on a new dose [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, evaluate patients for further titration after no less than two 3-day applications before any further increase in dosage is made.
Base dosage increments on the daily dosage of supplementary opioids, using the ratio of 45 mg/24 hours of oral morphine to a 12 mcg/hour increase in DURAGESIC dose.
If unacceptable opioid-related adverse reactions are observed, consider reducing the dosage. Adjust the dose to obtain an appropriate balance between management of pain and opioid-related adverse reactions.
A small proportion of adult patients may not achieve adequate analgesia using a 72-hour dosing interval and may require systems to be applied at 48 hours rather than at 72 hours, only if adequate pain control cannot be achieved using a 72-hour regimen. An increase in the DURAGESIC dose should be evaluated before changing dosing intervals in order to maintain patients on a 72-hour regimen.
Dosing intervals less than every 72 hours were not studied in children and adolescents and are not recommended.
2.5 Dosage Modifications in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Avoid the use of DURAGESIC in patients with severe hepatic impairment. In patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, start with one half of the usual dosage of DURAGESIC. Closely monitor for signs of respiratory and central nervous system depression, including at each dosage increase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16), Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.6 Dosage Modifications in Patients with Renal Impairment
Avoid the use of DURAGESIC in patients with severe renal impairment. In patients with mild to moderate renal impairment, start with one half of the usual dosage of DURAGESIC. Closely monitor for signs of respiratory and central nervous system depression, including at each dosage increase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.7 Administration of DURAGESIC
DURAGESIC PATCHES ARE FOR TRANSDERMAL USE ONLY.
Proper handling of DURAGESIC is necessary in order to prevent serious adverse outcomes, including death, associated with accidental secondary exposure to DURAGESIC [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
2.8 Disposal Instructions
Failure to properly dispose of DURAGESIC has resulted in accidental exposures and deaths, including deaths of children [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Instruct patients to dispose of used patches immediately upon removal by folding the adhesive side of the patch to itself, then flushing down the toilet.
Instruct patients to remove unused patches from their pouches, remove the release liners, fold the patches so that the adhesive side of the patch adheres to itself, and to immediately flush the patches down the toilet.
Instruct patients to dispose of any patches remaining from a prescription as soon as they are no longer needed.
2.9 Safe Reduction or Discontinuation of DURAGESIC
Do not abruptly discontinue DURAGESIC in patients who may be physically dependent on opioids. Rapid discontinuation of opioid analgesics in patients who are physically dependent on opioids has resulted in serious withdrawal symptoms, uncontrolled pain, and suicide. Rapid discontinuation has also been associated with attempts to find other sources of opioid analgesics, which may be confused with drug-seeking for abuse. Patients may also attempt to treat their pain or withdrawal symptoms with illicit opioids, such as heroin, and other substances.
When a decision has been made to decrease the dose or discontinue therapy in an opioid-dependent patient taking DURAGESIC, there are a variety of factors that should be considered, including the dose of DURAGESIC the patient has been taking, the duration of treatment, the type of pain being treated, and the physical and psychological attributes of the patient. It is important to ensure ongoing care of the patient and to agree on an appropriate tapering schedule and follow-up plan so that patient and provider goals and expectations are clear and realistic. When opioid analgesics are being discontinued due to a suspected substance use disorder, evaluate and treat the patient, or refer for evaluation and treatment of the substance use disorder. Treatment should include evidence-based approaches, such as medication assisted treatment of opioid use disorder. Complex patients with comorbid pain and substance use disorders may benefit from referral to a specialist.
There are no standard opioid tapering schedules that are suitable for all patients. Good clinical practice dictates a patient-specific plan to taper the dose of the opioid gradually. For patients on DURAGESIC who are physically opioid-dependent, initiate the taper by a small enough increment (e.g., no greater than 25% of the total daily dose) to avoid withdrawal symptoms, and proceed with dose-lowering at an interval of every 2 to 4 weeks. Patients who have been taking opioids for briefer periods of time may tolerate a more rapid taper.
It may be necessary to provide the patient with a lower dosage strength to accomplish a successful taper. Reassess the patient frequently to manage pain and withdrawal symptoms, should they emerge. Common withdrawal symptoms include restlessness, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, yawning, perspiration, chills, myalgia, and mydriasis. Other signs and symptoms also may develop, including irritability, anxiety, backache, joint pain, weakness, abdominal cramps, insomnia, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, or increased blood pressure, respiratory rate, or heart rate. If withdrawal symptoms arise, it may be necessary to pause the taper for a period of time or raise the dose of the opioid analgesic to the previous dose, and then proceed with a slower taper. In addition, monitor patients for any changes in mood, emergence of suicidal thoughts, or use of other substances.
When managing patients taking opioid analgesics, particularly those who have been treated for a long duration and/or with high doses for chronic pain, ensure that a multimodal approach to pain management, including mental health support (if needed), is in place prior to initiating an opioid analgesic taper. A multimodal approach to pain management may optimize the treatment of chronic pain, as well as assist with the successful tapering of the opioid analgesic [see Warnings and Precautions (5.20), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Transdermal system:
- DURAGESIC 12 mcg/hour1 (system size 5.5 cm2).
- DURAGESIC 25 mcg/hour (system size 11 cm2).
- DURAGESIC 37.5 mcg/hour (system size 16.5 cm2).
- DURAGESIC 50 mcg/hour (system size 22 cm2).
- DURAGESIC 75 mcg/hour (system size 33 cm2).
- DURAGESIC 100 mcg/hour (system size 44 cm2).
The 12 mcg/hour system has a solid green border and the 25, 37.5, 50, 75 and 100 mcg/hour systems have a green background with translucent diagonal stripes that alternate in direction and increase in number with each sequential increasing dosage strength.
- 1
- This lowest strength is designated as 12 mcg/hour (however, the actual strength is 12.5 mcg/hour) to distinguish it from a possible 125 mcg/hour dosage that could be prescribed by using multiple transdermal systems.
4. Contraindications
DURAGESIC is contraindicated in:
- patients who are not opioid-tolerant.
- the management of acute or intermittent pain, or in patients who require opioid analgesia for a short period of time.
- the management of post-operative pain, including use after out-patient or day surgeries, (e.g., tonsillectomies).
- the management of mild pain.
- patients with significant respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
- in patients with acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
- in patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)].
- in patients with hypersensitivity to fentanyl (e.g., anaphylaxis) or any components of the transdermal system [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
DURAGESIC contains fentanyl, an opioid agonist and a Schedule II controlled substance. As an opioid, DURAGESIC exposes users to the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse. Because modified-release products such as DURAGESIC deliver the opioid over an extended period of time, there is a greater risk for overdose and death due to the larger amount of fentanyl present [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
Although the risk of addiction in any individual is unknown, it can occur in patients appropriately prescribed DURAGESIC. Addiction can occur at recommended doses and if the drug is misused or abused.
Assess each patient's risk for opioid addiction, abuse, or misuse prior to prescribing DURAGESIC, and monitor all patients receiving DURAGESIC for the development of these behaviors and conditions. Risks are increased in patients with a personal or family history of substance abuse (including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction) or mental illness (e.g., major depression). The potential for these risks should not, however, prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient. Patients at increased risk may be prescribed opioids such as DURAGESIC, but use in such patients necessitates intensive counseling about the risks and proper use of DURAGESIC along with intensive monitoring for signs of addiction, abuse, and misuse. Consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Abuse or misuse of DURAGESIC by placing it in the mouth, chewing it, swallowing it, or using it in ways other than indicated may cause choking, overdose, and death [see Overdosage (10)].
Opioids are sought by drug abusers and people with addiction disorders and are subject to criminal diversion. Consider these risks when prescribing or dispensing DURAGESIC. Strategies to reduce these risks include prescribing the drug in the smallest appropriate quantity and advising the patient on the proper disposal of unused drug [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Contact local state professional licensing board or state controlled substances authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion of this product.
5.2 Opioid Analgesic Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS)
To ensure that the benefits of opioid analgesics outweigh the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for these products. Under the requirements of the REMS, drug companies with approved opioid analgesic products must make REMS-compliant education programs available to healthcare providers. Healthcare providers are strongly encouraged to do all of the following:
- Complete a REMS-compliant education program offered by an accredited provider of continuing education (CE) or another education program that includes all the elements of the FDA Education Blueprint for Health Care Providers Involved in the Management or Support of Patients with Pain.
- Discuss the safe use, serious risks, and proper storage and disposal of opioid analgesics with patients and/or their caregivers every time these medicines are prescribed. The Patient Counseling Guide (PCG) can be obtained at this link: www.fda.gov/OpioidAnalgesicREMSPCG.
- Emphasize to patients and their caregivers the importance of reading the Medication Guide that they will receive from their pharmacist every time an opioid analgesic is dispensed to them.
- Consider using other tools to improve patient, household, and community safety, such as patient-prescriber agreements that reinforce patient-prescriber responsibilities.
To obtain further information on the opioid analgesic REMS and for a list of accredited REMS CME/CE, call 1-800-503-0784, or log on to www.opioidanalgesicrems.com. The FDA Blueprint can be found at www.fda.gov/OpioidAnalgesicREMSBlueprint.
5.3 Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression has been reported with the use of opioids, even when used as recommended. Respiratory depression, if not immediately recognized and treated, may lead to respiratory arrest and death. Management of respiratory depression may include close observation, supportive measures, and use of opioid antagonists, depending on the patient's clinical status [see Overdosage (10)]. Carbon dioxide (CO2) retention from opioid-induced respiratory depression can exacerbate the sedating effects of opioids.
DURAGESIC is indicated only in opioid tolerant patients because of the risk for respiratory depression and death. While serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression can occur at any time during the use of DURAGESIC, the risk is greatest during the initiation of therapy or following a dosage increase. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression within the first 24–72 hours of initiating therapy with and following dosage increases of DURAGESIC.
To reduce the risk of respiratory depression, proper dosing and titration of DURAGESIC are essential [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. Overestimating the DURAGESIC dosage when converting patients from another opioid product can result in fatal overdose with the first dose.
Accidental exposure to DURAGESIC, especially in children, can result in respiratory depression and death due to an overdose of fentanyl.
Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize respiratory depression and emphasize the importance of calling 911 or getting emergency medical help right away in the event of a known or suspected overdose [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Opioids can cause sleep-related breathing disorders including central sleep apnea (CSA) and sleep-related hypoxemia. Opioid use increases the risk of CSA in a dose-dependent fashion. In patients who present with CSA, consider decreasing the opioid dosage using best practices for opioid taper [see Dosage and Administration (2.9)].
5.4 Accidental Exposure
A considerable amount of active fentanyl remains in DURAGESIC even after use as directed. Death and other serious medical problems have occurred when children and adults were accidentally exposed to DURAGESIC. Accidental or deliberate application or ingestion by a child or adolescent will cause respiratory depression, and has resulted in deaths. Placing DURAGESIC in the mouth, chewing it, swallowing it, or using it in ways other than indicated may cause choking or overdose that could result in death. Improper disposal of DURAGESIC in the trash has resulted in accidental exposures and deaths.
Advise patients about strict adherence to the recommended handling and disposal instructions in order to prevent accidental exposure to DURAGESIC [see Dosage and Administration (2.7), (2.8)]. Exposure to DURAGESIC patches discarded in the trash by children have been reported and have resulted in deaths.
5.5 Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Prolonged use of DURAGESIC during pregnancy can result in withdrawal in the neonate. Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, unlike opioid withdrawal syndrome in adults, may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. Observe newborns for signs of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly. Advise pregnant women of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.6 Risks of Concomitant Use or Discontinuation of Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitors and Inducers
Concomitant use of DURAGESIC with a CYP3A4 inhibitor, such as macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin), azole-antifungal agents (e.g., ketoconazole), and protease inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir), may increase plasma concentrations of fentanyl and prolong opioid adverse reactions, which may cause potentially fatal respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)], particularly when an inhibitor is added after a stable dose of DURAGESIC is achieved. Similarly, discontinuation of a CYP3A4 inducer, such as rifampin, carbamazepine, and phenytoin, in DURAGESIC-treated patients may increase fentanyl plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions. When using DURAGESIC with CYP3A4 inhibitors or discontinuing CYP3A4 inducers in DURAGESIC-treated patients, monitor patients closely at frequent intervals and consider dosage reduction of DURAGESIC until stable drug effects are achieved [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Drug Interactions (7)].
Concomitant use of DURAGESIC with CYP3A4 inducers or discontinuation of a CYP3A4 inhibitor could decrease DURAGESIC plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy or, possibly, lead to a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who had developed physical dependence to fentanyl. When using DURAGESIC with CYP3A4 inducers or discontinuing CYP3A4 inhibitors, monitor patients closely at frequent intervals and consider increasing the opioid dosage if needed to maintain adequate analgesia or if symptoms of opioid withdrawal occur [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.7 Risk of Increased Fentanyl Absorption with Application of External Heat
Exposure to heat may increase fentanyl absorption and there have been reports of overdose and death as a result of exposure to heat. A clinical pharmacology study conducted in healthy adult subjects has shown that the application of heat over the DURAGESIC system increased fentanyl exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Warn patients to avoid exposing the DURAGESIC application site and surrounding area to direct external heat sources [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].
5.8 Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants
Profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result from the concomitant use of DURAGESIC with benzodiazepines and/or other CNS depressants (e.g., non-benzodiazepine sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, other opioids, alcohol). Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioid analgesics alone. Because of similar pharmacological properties, it is reasonable to expect similar risk with the concomitant use of other CNS depressant drugs with opioid analgesics [see Drug Interactions (7)].
If the decision is made to prescribe a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant concomitantly with an opioid analgesic, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations of concomitant use. In patients already receiving an opioid analgesic, prescribe a lower initial dose of the benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant than indicated in the absence of an opioid, and titrate based on clinical response. If an opioid analgesic is initiated in a patient already taking a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant, prescribe a lower initial dose of the opioid analgesic, and titrate based on clinical response. Follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
If concomitant use is warranted, consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation when DURAGESIC is used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (including alcohol and illicit drugs). Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until the effects of concomitant use of the benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant have been determined. Screen patients for risk of substance use disorders, including opioid abuse and misuse, and warn them of the risk for overdose and death associated with the use of additional CNS depressants including alcohol and illicit drugs [see Drug Interactions (7), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.9 Risk of Increased Fentanyl Absorption with Elevated Body Temperature
Based on a pharmacokinetic model, serum fentanyl concentrations could theoretically increase by approximately one-third for patients with a body temperature of 40°C (104°F) due to temperature-dependent increases in fentanyl released from the system and increased skin permeability. Monitor patients wearing DURAGESIC systems who develop fever closely for sedation and respiratory depression and reduce the DURAGESIC dose, if necessary. Warn patients to avoid strenuous exertion that leads to increased core body temperature while wearing DURAGESIC to avoid the risk of potential overdose and death.
5.10 Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients
The use of DURAGESIC in patients with acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment is contraindicated.
5.11 Serotonin Syndrome with Concomitant Use of Serotonergic Drugs
Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of DURAGESIC with serotonergic drugs. Serotonergic drugs include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), triptans, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system (e.g., mirtazapine, trazodone, tramadol), certain muscle relaxants (i.e., cyclobenzaprine, metaxalone), and drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (including MAO inhibitors, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue) [see Drug Interactions (7)]. This may occur within the recommended dosage range. Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination, rigidity), and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). The onset of symptoms generally occurs within several hours to a few days of concomitant use, but may occur later than that. Discontinue DURAGESIC immediately if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
5.12 Adrenal Insufficiency
Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use. Presentation of adrenal insufficiency may include non-specific symptoms and signs including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. If adrenal insufficiency is suspected, confirm the diagnosis with diagnostic testing as soon as possible. If adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids. Wean the patient off of the opioid to allow adrenal function to recover and continue corticosteroid treatment until adrenal function recovers. Other opioids may be tried as some cases reported use of a different opioid without recurrence of adrenal insufficiency. The information available does not identify any particular opioids as being more likely to be associated with adrenal insufficiency.
5.13 Severe Hypotension
DURAGESIC may cause severe hypotension including orthostatic hypotension and syncope in ambulatory patients. There is an increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administration of certain CNS depressant drugs (e.g., phenothiazines or general anesthetics) [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Monitor these patients for signs of hypotension after initiating or titrating the dosage of DURAGESIC. In patients with circulatory shock, DURAGESIC may cause vasodilation that can further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. Avoid the use of DURAGESIC in patients with circulatory shock.
5.14 Risks of Use in Patients with Increased Intracranial Pressure, Brain Tumors, Head Injury, or Impaired Consciousness
In patients who may be susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention (e.g., those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure or brain tumors), DURAGESIC may reduce respiratory drive, and the resultant CO2 retention can further increase intracranial pressure. Monitor such patients for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy with DURAGESIC.
Opioids may also obscure the clinical course in a patient with a head injury. Avoid the use of DURAGESIC in patients with impaired consciousness or coma.
5.15 Cardiac Disease
DURAGESIC may produce bradycardia. Monitor patients with bradyarrhythmias closely for changes in heart rate, particularly when initiating therapy with DURAGESIC.
5.16 Hepatic Impairment
A clinical pharmacology study with DURAGESIC in patients with cirrhosis has shown that systemic fentanyl exposure increased in these patients. Because of the long half-life of fentanyl when administered as DURAGESIC and hepatic metabolism of fentanyl, avoid use of DURAGESIC in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Insufficient information exists to make precise dosing recommendations regarding the use of DURAGESIC in patients with impaired hepatic function. Therefore, to avoid starting patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment on too high of a dose, start with one half of the usual dosage of DURAGESIC. Closely monitor for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, including at each dosage increase [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.17 Renal Impairment
A clinical pharmacology study with intravenous fentanyl in patients undergoing kidney transplantation has shown that patients with high blood urea nitrogen level had low fentanyl clearance. Because of the long half-life of fentanyl when administered as DURAGESIC, avoid the use of DURAGESIC in patients with severe renal impairment. Insufficient information exists to make precise dosing recommendations regarding the use of DURAGESIC in patients with impaired renal function. Therefore, to avoid starting patients with mild to moderate renal impairment on too high of a dose, start with one half of the usual dosage of DURAGESIC. Closely monitor for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, including at each dosage increase [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.18 Risks of Use in Patients with Gastrointestinal Conditions
DURAGESIC is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus.
The fentanyl in DURAGESIC may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. Opioids may cause increases in serum amylase. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis for worsening symptoms.
5.19 Increased Risk of Seizures in Patients with Seizure Disorders
The fentanyl in DURAGESIC may increase the frequency of seizures in patients with seizure disorders, and may increase the risk of seizures occurring in other clinical settings associated with seizures. Monitor patients with a history of seizure disorders for worsened seizure control during DURAGESIC therapy.
5.20 Withdrawal
Do not abruptly discontinue DURAGESIC in a patient physically dependent on opioids. When discontinuing DURAGESIC in a physically dependent patient, gradually taper the dosage. Rapid tapering of DURAGESIC in a patient physically dependent on opioids may lead to a withdrawal syndrome and return of pain [see Dosage and Administration (2.9), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
Additionally, avoid the use of mixed agonist/antagonist (e.g., pentazocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol) or partial agonist (e.g., buprenorphine) analgesics in patients who are receiving a full opioid agonist analgesic, including DURAGESIC. In these patients, mixed agonist/antagonist and partial agonist analgesics may reduce the analgesic effect and/or may precipitate withdrawal symptoms [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.21 Risks of Driving and Operating Machinery
DURAGESIC may impair the mental or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially dangerous activities, such as driving a car or operating machinery. Warn patients not to drive or operate dangerous machinery unless they are tolerant to the effects of the DURAGESIC and know how they will react to the medication [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Accidental Exposure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Interactions with Benzodiazepines or Other Central Nervous System Depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Adrenal Insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Severe Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.19)]
- Withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.20)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of DURAGESIC was evaluated in 216 patients who took at least one dose of DURAGESIC in a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of DURAGESIC. This trial examined patients over 40 years of age with severe pain induced by osteoarthritis of the hip or knee and who were in need of and waiting for joint replacement.
The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) in a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial in patients with severe pain were nausea, vomiting, somnolence, dizziness, insomnia, constipation, hyperhidrosis, fatigue, feeling cold, and anorexia. Other common adverse reactions (≥5%) reported in clinical trials in patients with chronic malignant or nonmalignant pain were headache and diarrhea. Adverse reactions reported for ≥1% of DURAGESIC-treated patients and with an incidence greater than placebo-treated patients are shown in Table 3.
The most common adverse reactions that were associated with discontinuation in patients with pain (causing discontinuation in ≥1% of patients) were depression, dizziness, somnolence, headache, nausea, vomiting, constipation, hyperhidrosis, and fatigue.
| System/Organ Class Adverse Reaction | DURAGESIC % (N=216) | Placebo % (N=200) |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac disorders | ||
| Palpitations | 4 | 1 |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders | ||
| Vertigo | 2 | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Nausea | 41 | 17 |
| Vomiting | 26 | 3 |
| Constipation | 9 | 1 |
| Abdominal pain upper | 3 | 2 |
| Dry mouth | 2 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue | 6 | 3 |
| Feeling cold | 6 | 2 |
| Malaise | 4 | 1 |
| Asthenia | 2 | 0 |
| Edema peripheral | 1 | 1 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Anorexia | 5 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Muscle spasms | 4 | 2 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Somnolence | 19 | 3 |
| Dizziness | 10 | 4 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||
| Insomnia | 10 | 7 |
| Depression | 1 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Hyperhidrosis | 6 | 1 |
| Pruritus | 3 | 2 |
| Rash | 2 | 1 |
Adverse reactions not reported in Table 3 that were reported by ≥1% of DURAGESIC-treated adult and pediatric patients (N=1854) in 11 controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials of DURAGESIC used for the treatment of chronic malignant or nonmalignant pain are shown in Table 4.
| System/Organ Class Adverse Reaction | DURAGESIC % (N=1854) |
|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal disorders | |
| Diarrhea | 10 |
| Abdominal pain | 3 |
| Immune system disorders | |
| Hypersensitivity | 1 |
| Nervous system disorders | |
| Headache | 12 |
| Tremor | 3 |
| Paresthesia | 2 |
| Psychiatric disorders | |
| Anxiety | 3 |
| Confusional state | 2 |
| Hallucination | 1 |
| Renal and urinary disorders | |
| Urinary retention | 1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | |
| Erythema | 1 |
The following adverse reactions occurred in adult and pediatric patients with an overall frequency of <1% and are listed in descending frequency within each System/Organ Class:
Cardiac disorders: cyanosis
Eye disorders: miosis
Gastrointestinal disorders: subileus
General disorders and administration site conditions: application site reaction, influenza-like illness, application site hypersensitivity, drug withdrawal syndrome, application site dermatitis
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: muscle twitching
Nervous system disorders: hypoesthesia
Psychiatric disorders: disorientation, euphoric mood
Reproductive system and breast disorders: erectile dysfunction, sexual dysfunction
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: respiratory depression
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: eczema, dermatitis allergic, dermatitis contact
Pediatrics
The safety of DURAGESIC was evaluated in three open-label trials in 289 pediatric patients with chronic pain, 2 years of age through 18 years of age. Adverse reactions reported by ≥1% of DURAGESIC-treated pediatric patients are shown in Table 5.
| System/Organ Class Adverse Reaction | DURAGESIC % (N=289) |
|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal disorders | |
| Vomiting | 34 |
| Nausea | 24 |
| Constipation | 13 |
| Diarrhea | 13 |
| Abdominal pain | 9 |
| Abdominal pain upper | 4 |
| Dry mouth | 2 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | |
| Edema peripheral | 5 |
| Fatigue | 2 |
| Application site reaction | 1 |
| Asthenia | 1 |
| Immune system disorders | |
| Hypersensitivity | 3 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | |
| Anorexia | 4 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | |
| Muscle spasms | 2 |
| Nervous system disorders | |
| Headache | 16 |
| Somnolence | 5 |
| Dizziness | 2 |
| Tremor | 2 |
| Hypoesthesia | 1 |
| Psychiatric disorders | |
| Insomnia | 6 |
| Anxiety | 4 |
| Depression | 2 |
| Hallucination | 2 |
| Renal and urinary disorders | |
| Urinary retention | 3 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | |
| Respiratory depression | 1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | |
| Pruritus | 13 |
| Rash | 6 |
| Hyperhidrosis | 3 |
| Erythema | 3 |
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of DURAGESIC. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac Disorders: tachycardia, bradycardia
Eye Disorders: vision blurred
Gastrointestinal Disorders: ileus, dyspepsia
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: pyrexia, application site erosion and application site ulcer
Investigations: weight decreased
Nervous System Disorders: convulsions (including clonic convulsions and grand mal convulsion), amnesia, depressed level of consciousness, loss of consciousness
Psychiatric Disorders: agitation
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: respiratory distress, apnea, bradypnea, hypoventilation, dyspnea
Vascular Disorders: hypotension, hypertension
Serotonin syndrome: Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of opioids with serotonergic drugs.
Adrenal insufficiency: Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use.
Anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis, including anaphylactic shock, has been reported with ingredients contained in DURAGESIC.
Androgen deficiency: Cases of androgen deficiency have occurred with chronic use of opioids [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
7. Drug Interactions
Table 6 includes clinically significant drug interactions with DURAGESIC.
| Inhibitors of CYP3A4 | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of DURAGESIC and CYP3A4 inhibitors can increase the plasma concentration of fentanyl, resulting in increased or prolonged opioid effects particularly when an inhibitor is added after a stable dose of DURAGESIC is achieved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. After stopping a CYP3A4 inhibitor, as the effects of the inhibitor decline, the DURAGESIC plasma concentration will decrease [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], resulting in decreased opioid efficacy or a withdrawal syndrome in patients who had developed physical dependence to fentanyl. |
| Intervention: | If concomitant use is necessary, consider dosage reduction of DURAGESIC until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals. If a CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued, consider increasing the DURAGESIC dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal. |
| Examples | Macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin), azole-antifungal agents (e.g. ketoconazole), protease inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir), grapefruit juice |
| CYP3A4 Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of DURAGESIC and CYP3A4 inducers can decrease the plasma concentration of fentanyl [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], resulting in decreased efficacy or onset of a withdrawal syndrome in patients who have developed physical dependence to fentanyl [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the fentanyl plasma concentration will increase [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic effects and adverse reactions, and may cause serious respiratory depression. |
| Intervention: | If concomitant use is necessary, consider increasing the DURAGESIC dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal. If a CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, consider DURAGESIC dosage reduction and monitor for signs of respiratory depression. |
| Examples: | Rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin |
| Benzodiazepines and Other Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants | |
| Clinical Impact: | Due to additive pharmacologic effect, the concomitant use of benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, can increase the risk of hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death. |
| Intervention: | Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients closely for signs of respiratory depression and sedation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. If concomitant use is warranted, consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3, 5.8)]. |
| Examples: | Benzodiazepines and other sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, other opioids, alcohol. |
| Serotonergic Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of opioids with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system has resulted in serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. |
| Intervention: | If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment. Discontinue DURAGESIC if serotonin syndrome is suspected. |
| Examples: | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), triptans, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, drugs that affect the serotonin neurotransmitter system (e.g., mirtazapine, trazodone, tramadol), certain muscle relaxants (i.e., cyclobenzaprine, metaxalone), monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue). |
| Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) | |
| Clinical Impact: | MAOI interactions with opioids may manifest as serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)] or opioid toxicity (e.g., respiratory depression, coma). |
| Intervention: | The use of DURAGESIC is not recommended for patients taking MAOIs or within 14 days of stopping such treatment. |
| Examples: | phenelzine, tranylcypromine, linezolid |
| Mixed Agonist/Antagonist and Partial Agonist Opioid Analgesics | |
| Clinical Impact: | May reduce the analgesic effect of DURAGESIC and/or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. |
| Intervention: | Avoid concomitant use. |
| Examples: | butorphanol, nalbuphine, pentazocine, buprenorphine |
| Muscle Relaxants | |
| Clinical Impact: | DURAGESIC may enhance the neuromuscular blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produce an increased degree of respiratory depression. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients for signs of respiratory depression that may be greater than otherwise expected and decrease the dosage of DURAGESIC and/or the muscle relaxant as necessary. Due to the risk of respiratory depression with concomitant use of skeletal muscle relaxants and opioids, consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.8)]. |
| Diuretics | |
| Clinical Impact: | Opioids can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing the release of antidiuretic hormone. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients for signs of diminished diuresis and/or effects on blood pressure and increase the dosage of the diuretic as needed. |
| Anticholinergic Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs may increase risk of urinary retention and/or severe constipation, which may lead to paralytic ileus. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients for signs of urinary retention or reduced gastric motility when DURAGESIC is used concomitantly with anticholinergic drugs. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety of DURAGESIC was evaluated in three open-label trials in 289 pediatric patients with chronic pain, 2 years of age through 18 years of age. Starting doses of 25 mcg/h and higher were used by 181 patients who had been on prior daily opioid doses of at least 45 mg/day of oral morphine or an equianalgesic dose of another opioid. Initiation of DURAGESIC therapy in pediatric patients taking less than 60 mg/day of oral morphine or an equianalgesic dose of another opioid has not been evaluated in controlled clinical trials.
The safety and effectiveness of DURAGESIC in children under 2 years of age have not been established.
To guard against excessive exposure to DURAGESIC by young children, advise caregivers to strictly adhere to recommended DURAGESIC application and disposal instructions [see Dosage and Administration (2.7), (2.8) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of DURAGESIC did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, use caution when selecting a dosage for an elderly patient, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Data from intravenous studies with fentanyl suggest that the elderly patients may have reduced clearance and a prolonged half-life. Moreover, elderly patients may be more sensitive to the active substance than younger patients. A study conducted with the DURAGESIC patch in elderly patients demonstrated that fentanyl pharmacokinetics did not differ significantly from young adult subjects, although peak serum concentrations tended to be lower and mean half-life values were prolonged to approximately 34 hours [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Respiratory depression is the chief risk for elderly patients treated with opioids, and has occurred after large initial doses were administered to patients who were not opioid-tolerant or when opioids were co-administered with other agents that depress respiration. Titrate the dosage of DURAGESIC slowly in geriatric patients and monitor closely for signs of central nervous system and respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Fentanyl is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of DURAGESIC has not been fully evaluated. A clinical pharmacology study with DURAGESIC in patients with cirrhosis has shown that systemic fentanyl exposure increased in these patients. Because there is in vitro and in vivo evidence of extensive hepatic contribution to the elimination of DURAGESIC, hepatic impairment would be expected to have significant effects on the pharmacokinetics of DURAGESIC. Avoid use of DURAGESIC in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.16) and Clinical Pharmacology 12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of DURAGESIC has not been fully evaluated. A clinical pharmacology study with intravenous fentanyl in patients undergoing kidney transplantation has shown that patients with high blood urea nitrogen level had low fentanyl clearance. Because there is in-vivo evidence of renal contribution to the elimination of DURAGESIC, renal impairment would be expected to have significant effects on the pharmacokinetics of DURAGESIC. Avoid the use of DURAGESIC in patients with severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Warnings and Precautions (5.17) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.2 Abuse
DURAGESIC contains fentanyl, a substance with a high potential for abuse similar to other opioids including hydrocodone, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone, oxymorphone, and tapentadol. DURAGESIC can be abused and is subject to misuse, addiction, and criminal diversion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The high drug content in long-acting formulations adds to the risk of adverse outcomes from abuse and misuse.
All patients treated with opioids require careful monitoring for signs of abuse and addiction, because use of opioid analgesic products carries the risk of addiction even under appropriate medical use.
Prescription drug abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a prescription drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological or physiological effects.
Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that develop after repeated substance use and includes: a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling its use, persisting in its use despite harmful consequences, a higher priority given to drug use than to other activities and obligations, increased tolerance, and sometimes physical withdrawal.
"Drug seeking" behavior is very common in persons with substance use disorders. Drug-seeking tactics include emergency calls or visits near the end of office hours, refusal to undergo appropriate examination, testing or referral, repeated "loss" of prescriptions, tampering with prescriptions, and reluctance to provide prior medical records or contact information for other treating healthcare providers. "Doctor shopping" (visiting multiple prescribers to obtain additional prescriptions) is common among drug abusers and people suffering from untreated addiction. Preoccupation with achieving adequate pain relief can be appropriate behavior in a patient with poor pain control.
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Healthcare providers should be aware that addiction may be accompanied by concurrent tolerance and symptoms of physical dependence in all addicts. In addition, abuse of opioids can occur in the absence of true addiction.
DURAGESIC, like other opioids, can be diverted for non-medical use into illicit channels of distribution. Careful record-keeping of prescribing information, including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests, as required by state and federal law, is strongly advised.
Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic re-evaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs.
9.3 Dependence
Both tolerance and physical dependence can develop during chronic opioid therapy. Tolerance is the need for increasing doses of opioids to maintain a defined effect such as analgesia (in the absence of disease progression or other external factors). Tolerance may occur to both the desired and undesired effects of drugs, and may develop at different rates for different effects.
Physical dependence is a physiological state in which the body adapts to the drug after a period of regular exposure, resulting in withdrawal symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dosage reduction of a drug. Withdrawal also may be precipitated through the administration of drugs with opioid antagonist activity (e.g., naloxone, nalmefene), mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics (e.g., pentazocine, butorphanol, nalbuphine), or partial agonists (e.g., buprenorphine). Physical dependence may not occur to a clinically significant degree until after several days to weeks of continued opioid usage.
Do not abruptly discontinue DURAGESIC in a patient physically dependent on opioids. Rapid tapering of DURAGESIC in a patient physically dependent on opioids may lead to serious withdrawal symptoms, uncontrolled pain, and suicide. Rapid discontinuation has also been associated with attempts to find other sources of opioid analgesics, which may be confused with drug-seeking for abuse.
When discontinuing DURAGESIC, gradually taper the dosage using a patient-specific plan that considers the following: the dose of DURAGESIC the patient has been taking, the duration of treatment, and the physical and psychological attributes of the patient. To improve the likelihood of a successful taper and minimize withdrawal symptoms, it is important that the opioid tapering schedule is agreed upon by the patient. In patients taking opioids for a long duration at high doses, ensure that a multimodal approach to pain management, including mental health support (if needed), is in place prior to initiating an opioid analgesic taper [see Dosage and Administration (2.9), Warnings and Precautions (5.20)].
Infants born to mothers physically dependent on opioids will also be physically dependent and may exhibit respiratory difficulties and withdrawal symptoms [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
11. Duragesic Description
The system contains fentanyl, an opioid agonist, for transdermal administration. The amount of fentanyl released from each system per hour is proportional to the surface area (25 mcg/hour per 11 cm2). The composition per unit area of all transdermal system sizes is identical.
| Strength (mcg/hour) | Size (cm2) | Fentanyl Content (mg) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| 12* | 5.5 | 1.55 |
| 25† | 11 | 3.1 |
| 37.5† | 16.5 | 4.65 |
| 50† | 22 | 6.2 |
| 75† | 33 | 9.3 |
| 100† | 44 | 12.4 |
The molecular weight of fentanyl base is 336.5, and the empirical formula is C22H28N2O. The n-octanol: water partition coefficient is 860:1. The pKa is 8.4.
The chemical name is N-Phenyl-N-(1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl) propanamide. The structural formula is:
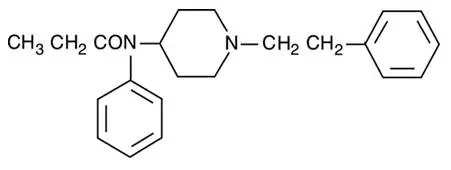
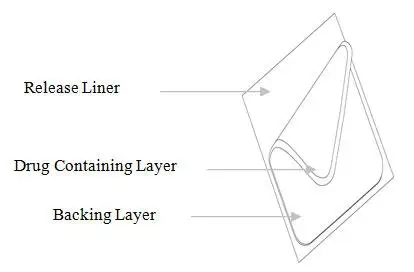
DURAGESIC® is a rectangular translucent system with rounded corners. The product name and dosage strength are printed in green in the center of each system. The 12 mcg/hour system has a solid green border and the 25, 37.5, 50, 75 and 100 mcg/hour systems have a green background with translucent diagonal stripes that alternate in direction and increase in number with each sequential increasing dosage strength.
Each system is comprised of a siliconized polyethylene terephthalate (PET) release liner and two functional layers. Proceeding from the outer surface toward the surface adhering to skin, these functional layers are:
1) a transparent backing layer of ethylene vinyl acetate/polyethylene terephthalate (EVA/PET) film with green print; 2) a drug-in-adhesive layer containing fentanyl, polyacrylate adhesive, and isopropyl myristate. Before use, a siliconized PET release liner covering the drug-in-adhesive layer is removed and discarded.
12. Duragesic - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Fentanyl is an opioid agonist. Fentanyl interacts predominately with the opioid mu-receptor. These mu-binding sites are distributed in the human brain, spinal cord, and other tissues.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
DURAGESIC is a drug-in-adhesive matrix designed formulation. Fentanyl is released from the matrix at a nearly constant amount per unit time. The concentration gradient existing between the matrix and the lower concentration in the skin, drives drug release. Fentanyl moves in the direction of the lower concentration at a rate determined by the matrix and the diffusion of fentanyl through the skin layers. While the actual rate of fentanyl delivery to the skin varies over the 72-hour application period, each system is labeled with a nominal flux which represents the average amount of drug delivered to the systemic circulation per hour across average skin.
While there is variation in dose delivered among patients, the nominal flux of the systems (12.5, 25, 37.5, 50, 75, and 100 mcg of fentanyl per hour) is sufficiently accurate as to allow individual titration of dosage for a given patient.
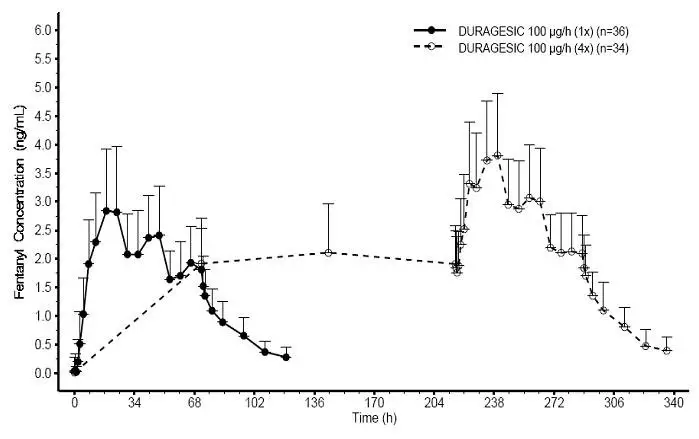
Following DURAGESIC application, the skin under the system absorbs fentanyl, and a depot of fentanyl concentrates in the upper skin layers. Fentanyl then becomes available to the systemic circulation. Serum fentanyl concentrations increase gradually following initial DURAGESIC application, generally leveling off between 12 and 24 hours and remaining relatively constant, with some fluctuation, for the remainder of the 72-hour application period. Peak serum concentrations of fentanyl generally occurred between 20 and 72 hours after initial application (see Table 6). Serum fentanyl concentrations achieved are proportional to the DURAGESIC delivery rate. With continuous use, serum fentanyl concentrations continue to rise for the first two system applications. By the end of the second 72-hour application, a steady-state serum concentration is reached and is maintained during subsequent applications of a patch of the same size (see Figure 1). Patients reach and maintain a steady-state serum concentration that is determined by individual variation in skin permeability and body clearance of fentanyl.
After system removal, serum fentanyl concentrations decline gradually, falling about 50% in approximately 20–27 hours. Continued absorption of fentanyl from the skin accounts for a slower disappearance of the drug from the serum than is seen after an IV infusion, where the apparent half-life is approximately 7 (range 3–12) hours.
A clinical pharmacology study conducted in healthy adult subjects has shown that the application of heat over the DURAGESIC system increased mean overall fentanyl exposure by 120% and average maximum fentanyl level by 61%.
| Mean (SD) Time to Maximal Concentration Tmax (h) | Mean (SD) Maximal Concentration Cmax (ng/mL) |
|
|---|---|---|
| NOTE: After system removal there is continued systemic absorption from residual fentanyl in the skin so that serum concentrations fall 50%, on average, in approximately 20–27 hours. | ||
|
||
| DURAGESIC 12 mcg/hour | 28.8 (13.7) | 0.38 (0.13)* |
| DURAGESIC 25 mcg/hour | 31.7 (16.5) | 0.85 (0.26)† |
| DURAGESIC 50 mcg/hour | 32.8 (15.6) | 1.72 (0.53)† |
| DURAGESIC 75 mcg/hour | 35.8 (14.1) | 2.32 (0.86)† |
| DURAGESIC 100 mcg/hour | 29.9 (13.3) | 3.36 (1.28)† |
 |
| Clearance (L/h) Range [70 kg] | Volume of Distribution VSS (L/kg) Range | Half-Life t1/2 (h) Range |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| NOTE: Information on volume of distribution and half-life not available for renally impaired patients. | |||
|
|||
| Surgical Patients | 27–75 | 3–8 | 3–12 |
| Hepatically Impaired Patients | 3–80* | 0.8–8* | 4–12* |
| Renally Impaired Patients | 30–78 | – | – |
14. Clinical Studies
DURAGESIC as therapy for pain due to cancer has been studied in 153 patients. In this patient population, DURAGESIC has been administered in doses of 25 mcg/h to 600 mcg/h. Individual patients have used DURAGESIC continuously for up to 866 days. At one month after initiation of DURAGESIC therapy, patients generally reported lower pain intensity scores as compared to a pre-study analgesic regimen of oral morphine.
The duration of DURAGESIC use varied in cancer patients; 56% of patients used DURAGESIC for over 30 days, 28% continued treatment for more than 4 months, and 10% used DURAGESIC for more than 1 year.
In the pediatric population, the safety of DURAGESIC has been evaluated in 289 patients with chronic pain 2–18 years of age. The duration of DURAGESIC use varied; 20% of pediatric patients were treated for ≤ 15 days; 46% for 16–30 days; 16% for 31–60 days; and 17% for at least 61 days. Twenty-five patients were treated with DURAGESIC for at least 4 months and 9 patients for more than 9 months.
16. How is Duragesic supplied
DURAGESIC® (fentanyl transdermal system) is supplied in cartons containing 5 individual child-resistant packaged systems. See chart for information regarding individual systems.
| DURAGESIC Strength (mcg/hour) | System Size (cm2) | Fentanyl Content (mg) | NDC Number |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| DURAGESIC-12* | 5.5 | 1.55 | 50458-101-05 |
| DURAGESIC-25 | 11.5 | 3.1 | 50458-102-05 |
| DURAGESIC-37.5† | 16.5 | 4.65 | 50458-103-05 |
| DURAGESIC-50 | 22 | 6.2 | 50458-104-05 |
| DURAGESIC-75 | 33 | 9.3 | 50458-105-05 |
| DURAGESIC-100 | 44 | 12.4 | 50458-106-05 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Instructions for UseDURAGESIC® (Dur-ah-GEE-zik)(Fentanyl Transdermal System) CII
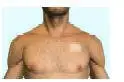
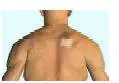
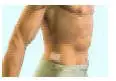
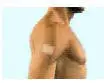
Be sure that you read, understand, and follow these Instructions for Use before you apply DURAGESIC® transdermal system (patch). Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Important information about the DURAGESIC® transdermal system (patch) appearance:
- DURAGESIC® is a rectangular, see-through patch with rounded corners.
- DURAGESIC® comes in 6 different dosage strengths and sizes:
|
|
- The product name, "DURAGESIC®", and dosage strength are printed in green in the center of each patch.
- The 12 mcg/hour patch has a solid green border around it.
- All of the other patches have a green background with see-through diagonal stripes. These stripes change in direction and increase in number as the dosage strength increases.
Parts of the DURAGESIC® patch:

Before applying DURAGESIC®
- Each DURAGESIC® patch is sealed in its own protective pouch. Do not remove a DURAGESIC® patch from the pouch until you are ready to use it.
- Do not use a DURAGESIC® patch if the pouch seal is broken or the patch is cut, damaged or changed in any way.
- DURAGESIC® patches are available in 6 different dosage strengths and patch sizes. Make sure you have the right dose patch or patches that have been prescribed for you.
Applying a DURAGESIC® patch
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Disposing of a DURAGESIC® patch
|
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
ALZA Corporation
Vacaville, CA 95688
Manufactured for:
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Titusville, NJ 08560
Revised:
Bioclusive™ is a trademark of Ethicon, Inc.
Tegaderm™ is a trademark of 3M
©Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2009
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised 04/2022 | |
| Medication Guide DURAGESIC® (Dur-ah-GEE-zik) (fentanyl) Transdermal System, CII |
||
DURAGESIC® is:
|
||
Important information about DURAGESIC®:
|
||
Do not use DURAGESIC® if you have:
|
||
| Before applying DURAGESIC®, tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of: | ||
|
|
|
|
||
Tell your healthcare provider if you:
|
||
When using DURAGESIC®:
|
||
While using DURAGESIC® DO NOT:
|
||
The possible side effects of DURAGESIC® are:
Manufactured for: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Titusville, NJ 08560, USA, www.Duragesic.com or call 1-800-526-7736 |
||
| DURAGESIC
(FENTANYL SYSTEM)
fentanyl patch |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| DURAGESIC
(FENTANYL SYSTEM)
fentanyl patch |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| DURAGESIC
(FENTANYL SYSTEM)
fentanyl patch |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| DURAGESIC
(FENTANYL SYSTEM)
fentanyl patch |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| DURAGESIC
(FENTANYL SYSTEM)
fentanyl patch |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (063137772) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Johnson Matthey Inc. | 808176705 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-101, 50458-102, 50458-104, 50458-105, 50458-106) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| AndersonBrecon, Inc. | 053217022 | PACK(50458-101, 50458-102, 50458-104, 50458-105, 50458-106) | |