Drug Detail:Duzallo (Allopurinol and lesinurad [ al-oh-pure-i-nol-and-le-sin-ure-ad ])
Drug Class: Antihyperuricemic agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
DUZALLO® (lesinurad and allopurinol) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017
WARNING: RISK OF ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
- Acute renal failure has occurred with lesinurad, one of the components of DUZALLO. (5.1, 6.1)
Indications and Usage for Duzallo
DUZALLO, a combination of lesinurad, a URAT1 inhibitor, and allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, is indicated for the treatment of hyperuricemia associated with gout in patients who have not achieved target serum uric acid levels with a medically appropriate daily dose of allopurinol alone. (1)
Limitations of Use:
- DUZALLO is not recommended for the treatment of asymptomatic hyperuricemia. (1.1)
Duzallo Dosage and Administration
- The recommended dose of DUZALLO is one 200 mg lesinurad/300 mg allopurinol tablet per day (or one 200 mg lesinurad/200 mg allopurinol tablet per day for patients with renal impairment (45 - < 60 mL/min eCLcr) on a medically appropriate dose of 200 mg allopurinol (2.2)).
- Use one tablet of DUZALLO in place of an equivalent portion of the total daily allopurinol dose. The total daily dose of allopurinol should be maintained at the time of initiating DUZALLO. (2.1)
- One tablet of DUZALLO contains the maximum daily lesinurad dose (200 mg). (2.1)
- Do not take more than 1 tablet of DUZALLO per day. (2.1)
- Do not combine DUZALLO with ZURAMPIC® (lesinurad). (2.1)
- Use of DUZALLO is not recommended for patients taking daily doses of allopurinol less than 300 mg (or less than 200 mg in patients with moderate renal impairment). (2.1)
- DUZALLO tablets should be taken in the morning with food and water. (2.1)
- Patients should be instructed to stay well hydrated. (2.1)
- Assess renal function before initiating DUZALLO. Do not initiate DUZALLO if eCLcr is below 45 mL/min. (2.2)
- Discontinue DUZALLO if eCLcr persistently falls below 45 mL/min. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets:
- 200 mg lesinurad/200 mg allopurinol (3)
- 200 mg lesinurad/300 mg allopurinol (3)
Contraindications
- Severe renal impairment, end-stage renal disease, kidney transplant recipients, or patients on dialysis (4, 8.6)
- Tumor lysis syndrome or Lesch-Nyhan syndrome (4)
- Known hypersensitivity to allopurinol, including previous occurrence of skin rash (5.2)
Warnings and Precautions
- Renal events: Adverse reactions related to renal function, including acute renal failure, have occurred after initiating lesinurad, one of the components of DUZALLO. A higher incidence has occurred at the 400 mg dose of lesinurad than at the 200 mg dose. Monitor renal function at initiation and during therapy with DUZALLO, particularly in patients with eCLcr below 60 mL/min, and evaluate for signs and symptoms of acute uric acid nephropathy. (5.1)
- Skin Rash and Hypersensitivity: DUZALLO, should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or other signs that may indicate an allergic reaction, as allopurinol has been associated with severe hypersensitivity (some resulting in death). (5.2)
- Hepatotoxicity: Hepatotoxicity has been reported in patients on allopurinol. Inform patients of warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. If symptoms develop, liver function evaluation should be performed. (5.3)
- Cardiovascular events: Major adverse cardiovascular events were observed with lesinurad; a causal relationship has not been established. (5.4)
- Bone Marrow Suppression: Bone marrow depression affecting one or more cell lines has been reported with allopurinol. (5.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Most common adverse reactions in 12-month controlled clinical trials (occurring in greater than or equal to 2% of patients treated with lesinurad in combination with a xanthine oxidase inhibitor and more frequently than on xanthine oxidase inhibitor alone) were headache, influenza, blood creatinine increased, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. (6.1)
- The most frequently reported adverse reaction for allopurinol is skin rash. (6.2)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-844-374-4793 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Mercaptopurine or Azathioprine: Reduce mercaptopurine or azathioprine dose to approximately one-third to one-fourth of the usual dose and closely monitor for therapeutic response and the appearance of toxicity. (5.5, 7.2)
- Coumarin Anticoagulants: Carefully monitor prothrombin time. (5.6, 7.2)
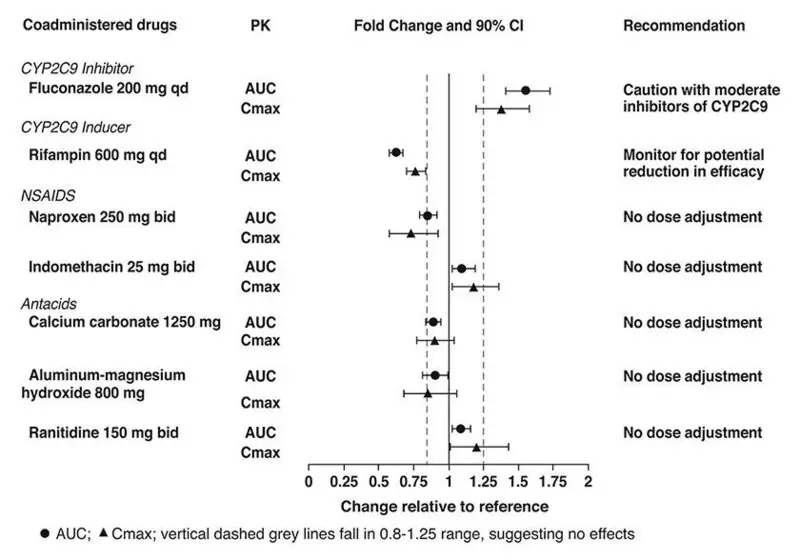
- Moderate Cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) Inhibitors: Use DUZALLO with caution. (7.1)
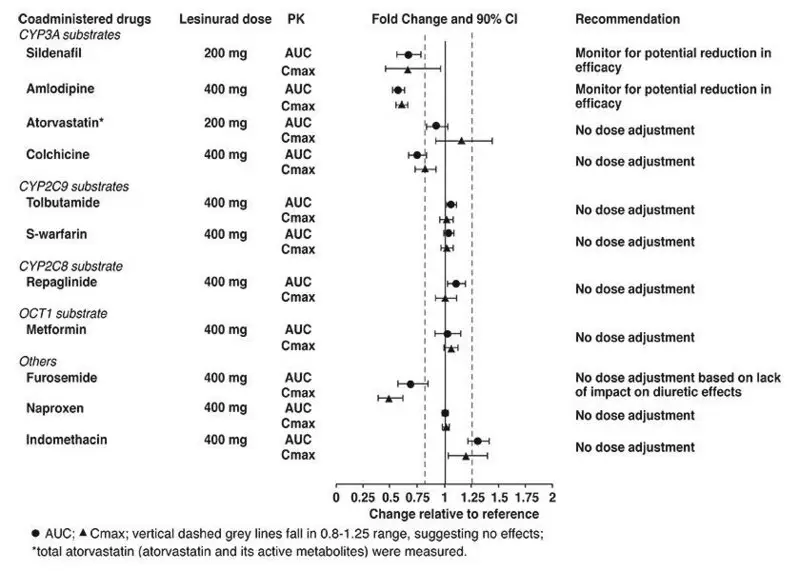
- CYP3A Substrates: Monitor for efficacy of the CYP3A substrate. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
- Renal impairment: Not recommended for patients with eCLcr below 45 mL/min. (2.2, 5.1, 8.6)
- Hepatic impairment: Not recommended for patients with severe hepatic impairment. (8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 11/2017
Related/similar drugs
allopurinol, febuxostat, Zyloprim, Uloric, probenecid, KrystexxaFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISK OF ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
- Acute renal failure has occurred with lesinurad, one of the components of DUZALLO. [see Warning and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
1. Indications and Usage for Duzallo
DUZALLO®, a combination of lesinurad, a uric acid transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitor, and allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, is indicated for the treatment of hyperuricemia associated with gout in patients who have not achieved target serum uric acid levels with a medically appropriate daily dose of allopurinol alone [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Duzallo Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosing
DUZALLO tablets are for oral use. DUZALLO should be taken once daily by mouth, in the morning with food and water. Patients should be instructed to stay well hydrated (e.g., 2 liters of liquid per day).
One tablet of DUZALLO contains the maximum daily lesinurad dose (200 mg). Do not take more than 1 tablet of DUZALLO per day. Do not combine DUZALLO with ZURAMPIC® (lesinurad).
Use of DUZALLO is not recommended for patients taking daily doses of allopurinol less than 300 mg (or less than 200 mg in patients with estimated creatinine clearance [eCLcr] less than 60 mL/min).
Use one tablet of DUZALLO in place of an equivalent portion of the total daily allopurinol dose. The total daily dose of allopurinol should be maintained at the time of initiating DUZALLO.
- For patients who have not achieved target serum uric acid on a medically appropriate dose of allopurinol > 300 mg, DUZALLO may be initiated by using one tablet of DUZALLO in place of an equivalent portion of the total daily allopurinol dose.
- For patients who have not achieved target serum uric acid on a medically appropriate dose of allopurinol of 300 mg, DUZALLO may be initiated by using one tablet of DUZALLO 200 mg lesinurad /300 mg allopurinol daily in place of 300 mg of allopurinol.
- For patients who have not achieved target serum uric acid on a medically appropriate dose of allopurinol of 200 mg, DUZALLO may be initiated by using one tablet of DUZALLO 200 mg lesinurad /200 mg allopurinol daily in place of 200 mg of allopurinol.
For patients currently on ZURAMPIC (lesinurad) in combination with allopurinol, DUZALLO may be initiated by using one tablet of DUZALLO in place of ZURAMPIC (lesinurad) and an equivalent portion of the daily allopurinol dose.
2.2 Patients With Renal Impairment
Patients with decreased renal function require lower doses of allopurinol than those with normal renal function. No dose adjustment is needed for lesinurad in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (eCLcr of 45 mL/min or greater).
Assessment of renal function is recommended prior to initiation of DUZALLO and periodically thereafter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. DUZALLO should not be initiated in patients with an eCLcr less than 45 mL/min. DUZALLO should be discontinued when eCLcr is persistently less than 45 mL/min [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. More frequent renal function monitoring is recommended in patients with an eCLcr below 60 mL/min.
2.3 Gout Flares
Gout flares may occur after initiation of urate-lowering therapy, including DUZALLO, due to changing serum uric acid levels resulting in mobilization of urate from tissue deposits. For patients not currently taking lesinurad, gout flare prophylaxis is recommended when starting DUZALLO, according to practice guidelines.
If a gout flare occurs during DUZALLO treatment, DUZALLO need not be discontinued. The gout flare should be managed concurrently, as appropriate for the individual patient [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
DUZALLO is a combination of lesinurad and allopurinol. DUZALLO capsule-shaped tablets are available in the following dosage forms and strengths:
- 200 mg/200 mg tablets are light orange film-coated tablets debossed with "LES200" above "ALO200".
- 200 mg/300 mg tablets are dark orange film-coated tablets debossed with "LES200" above "ALO300".
4. Contraindications
The use of DUZALLO is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Severe renal impairment (eCLcr less than 30 mL/min), end-stage renal disease, kidney transplant recipients, or patients on dialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
- Tumor lysis syndrome or Lesch-Nyhan syndrome [see Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
- Known hypersensitivity to allopurinol, including previous occurrence of skin rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Renal Events
Adverse reactions related to renal function, including acute renal failure, can occur after initiating DUZALLO. Treatment with lesinurad 200 mg in combination with allopurinol was associated with an increased incidence of serum creatinine elevations, most of which were reversible [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. A higher incidence of serum creatinine elevations and renal-related adverse reactions, including serious adverse reactions of acute renal failure, were observed with lesinurad 400 mg in combination with allopurinol, with the highest incidence when lesinurad was given alone. DUZALLO treatment should be interrupted if serum creatinine is elevated to greater than 2 times the value when lesinurad treatment was initiated. In patients who report symptoms that may indicate acute uric acid nephropathy including flank pain, nausea or vomiting, interrupt treatment and measure serum creatinine promptly. DUZALLO should not be restarted without another explanation for the serum creatinine abnormalities.
DUZALLO should not be initiated in patients with an eCLcr less than 45 mL/min. Renal function should be evaluated prior to initiation of DUZALLO and periodically thereafter, as clinically indicated. More frequent renal function monitoring is recommended in patients with an eCLcr less than 60 mL/min [see Renal Impairment (8.6)] or with serum creatinine elevations 1.5 to 2 times the value when lesinurad treatment was initiated.
Some patients with pre-existing renal disease or poor urate clearance have shown a rise in BUN during administration of allopurinol.
5.2 Skin Rash and Hypersensitivity
Skin rash is a frequently reported adverse event in patients taking allopurinol [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. In some instances, a skin rash may be followed by more severe hypersensitivity reactions associated with exfoliation, fever, lymphadenopathy, arthralgia and/or eosinophilia including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Associated vasculitis and tissue response may be manifested in various ways including hepatitis, renal impairment, seizures, and on rare occasions, death. The HLA-B*5801 allele is a genetic risk marker for severe skin reactions indicative of hypersensitivity to allopurinol.
DUZALLO should be discontinued immediately at the first appearance of skin rash or other signs which may indicate an allergic reaction, and additional medical care should be provided as needed.
Hypersensitivity reactions to allopurinol may be increased in patients with decreased renal function receiving thiazide diuretics and DUZALLO concurrently. For this reason, in this clinical setting, such combinations should be administered with caution and patients should be observed closely.
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
A few cases of reversible clinical hepatotoxicity have been reported in patients taking allopurinol, and in some patients, asymptomatic rises in serum alkaline phosphatase or serum transaminase have been observed. If anorexia, weight loss, or pruritus develops in patients on DUZALLO, evaluation of liver function should be performed. In patients with pre-existing liver disease, periodic liver function tests are recommended.
5.4 Cardiovascular Events
In clinical trials with lesinurad and allopurinol, major adverse cardiovascular events (cardiovascular deaths, non-fatal myocardial infarctions, and non-fatal strokes) were observed [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. A causal relationship has not been established.
5.5 Bone Marrow Depression
Bone marrow depression has been reported in patients receiving allopurinol, most of whom received concomitant drugs with the potential for causing this reaction. This has occurred as early as six weeks to as long as six years after the initiation of allopurinol therapy. Rarely a patient may develop varying degrees of bone marrow depression, affecting one or more cell lines, while receiving allopurinol alone.
Patients taking allopurinol and mercaptopurine or azathioprine require a reduction in dose to approximately one-third to one-fourth of the usual dose of mercaptopurine or azathioprine. Subsequent adjustment of doses of mercaptopurine or azathioprine should be made on the basis of therapeutic response and the appearance of toxic effects. Patients should be closely monitored for therapeutic response and the appearance of toxicity [see Drug Interaction (7.2)].
5.6 Increase in Prothrombin Time
It has been reported that allopurinol prolongs the half-life of dicumarol, a coumarin anticoagulant. The prothrombin time should be reassessed periodically in patients receiving coumarin anticoagulants (dicumarol, warfarin) concomitantly with DUZALLO [see Drug Interaction (7.2)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are also discussed in other sections:
- Renal Events [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Skin Rash and Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Cardiovascular Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Bone Marrow Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Drowsiness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7. Drug Interactions
No drug interactions studies were conducted with DUZALLO. However, as DUZALLO contains lesinurad and allopurinol, any interactions that have been identified with these agents individually may occur with DUZALLO. The following interactions have been noted with the individual components of DUZALLO.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
No dose adjustment is necessary in elderly patients. In a pool of clinical safety and efficacy studies of lesinurad in combination with allopurinol in gout patients, 12% were 65 years and older and 2% were 75 years and older. No overall differences between lesinurad in combination with allopurinol and allopurinol alone in safety and effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. Greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The efficacy and safety of lesinurad in combination with allopurinol were evaluated in studies that included gout patients with mild and moderate renal impairment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14)]. There were no clear differences in safety and effectiveness of lesinurad in combination with allopurinol in patients with mild renal impairment compared to patients with normal renal function. No lesinurad dose adjustment is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), and Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Across all lesinurad and placebo treatment groups, patients with moderate renal impairment had a higher occurrence of renal-related adverse reactions compared to patients with mild renal impairment or normal renal function [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The experience with lesinurad in combination with allopurinol in patients with an eCLcr less than 45 mL/min is limited and there was a trend toward lesser efficacy [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. DUZALLO should not be initiated in patients with an eCLcr less than 45 mL/min. No lesinurad dose adjustment is recommended in patients with an eCLcr 45 to less than 60 mL/min, however, more frequent renal function monitoring is recommended. DUZALLO should be discontinued when eCLcr is persistently less than 45 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The efficacy and safety of DUZALLO have not been evaluated in gout patients with severe renal impairment (eCLcr less than 30 mL/min), with end-stage renal disease, or receiving dialysis. DUZALLO is not expected to be effective in these patient populations [see Contraindications (4)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh classes A and B) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Neither DUZALLO nor its individual components have been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment; DUZALLO is therefore not recommended in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
8.8 Secondary Hyperuricemia
No studies with DUZALLO have been conducted in patients with secondary hyperuricemia (including organ transplant recipients); DUZALLO is contraindicated for use in tumor lysis syndrome or Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, where the rate of uric acid formation is greatly increased [see Contraindications (4)].
11. Duzallo Description
DUZALLO (lesinurad and allopurinol) tablets contain 2 oral medications used in the treatment of hyperuricemia: lesinurad and allopurinol. Lesinurad is a URAT1 inhibitor and allopurinol is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor.
12. Duzallo - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
DUZALLO combines two medications with complementary mechanisms of action for treatment of hyperuricemia associated with gout: lesinurad, a uric acid reabsorption inhibitor, and allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor. DUZALLO lowers serum uric acid levels by increasing excretion and inhibiting production of uric acid.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Drug-Drug Interactions
Pharmacokinetic drug interaction studies with DUZALLO have not been performed; however, such studies have been conducted with the individual components lesinurad and allopurinol.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
Lesinurad in combination with allopurinol has been studied in hyperuricemic gout patients who have not achieved target serum uric acid levels with allopurinol alone.
There have been no phase 3 clinical trials with DUZALLO. Bioequivalence of DUZALLO to co-administered lesinurad and allopurinol was demonstrated, and efficacy of the combination of allopurinol and lesinurad has been demonstrated in two phase 3 studies (Study 1 and 2).
14.1 Lesinurad Add-On to Allopurinol in Inadequate Responders
Both studies were 12-month multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies in adult patients with hyperuricemia and gout. Patients received prophylaxis for gout flares with colchicine or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) during the first 5 months of study treatment. Lesinurad 200 mg and 400 mg once daily in combination with allopurinol were studied. Lesinurad 200 mg is the only recommended lesinurad dose, and is the dose combined with allopurinol in DUZALLO.
Study 1 and Study 2 enrolled patients with gout who were on a stable dose of allopurinol of at least 300 mg (or 200 mg for moderate renal impairment), had a serum uric acid > 6.5 mg/dL, and reported at least 2 gout flares in the prior 12 months. Mean years since gout diagnosis were 12 years. More than half of the patients (61%) had mild or moderate renal impairment and 19% of the patients had tophi. Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to receive lesinurad 200 mg, lesinurad 400 mg, or placebo once daily; all were to continue on their stable allopurinol dose. The majority of patients in these studies received daily allopurinol doses of 200 mg or 300 mg, corresponding to the allopurinol doses contained in DUZALLO. The average dose of allopurinol in the studies was 310 mg (range: 200-900 mg).
As shown in Table 5, lesinurad 200 mg in combination with allopurinol was superior to allopurinol alone in lowering serum uric acid to less than 6 mg/dL at Month 6.
| Study | Timepoint | Patients Achieving Serum Uric Acid Target | Difference of Proportion (95% C.I.) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo + Allopurinol | Lesinurad 200 mg + Allopurinol | |||
|
||||
| Study 1 (N=402*) | Month 6 | 28% | 54% | 0.26 ( 0.17, 0.36) |
| Study 2 (N=410*) | Month 6 | 23% | 55% | 0.32 (0.23, 0.41) |
The estimated effect of lesinurad 200 mg on serum uric acid in the subgroup of patients taking thiazide diuretics at baseline was similar to the estimated effect in the overall population. The estimated effect was also similar in the subgroup of patients taking low-dose aspirin at baseline.
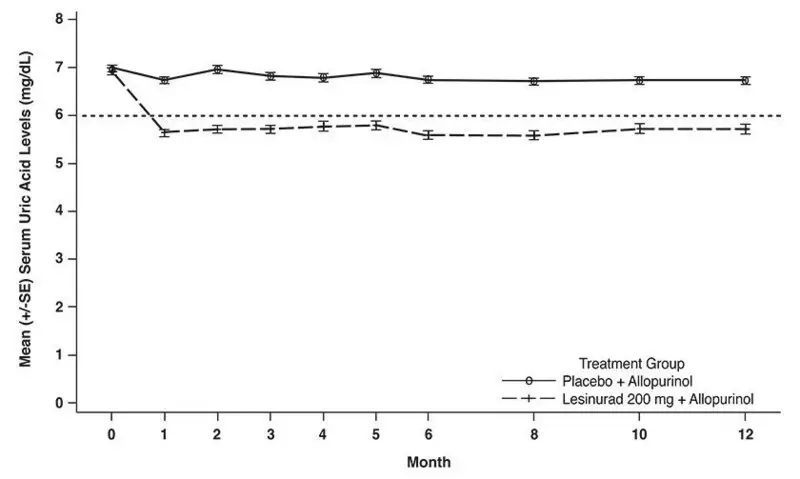
As shown in Figure 3, reduction in average serum uric acid levels to < 6 mg/dL was noted for lesinurad 200 mg in combination with allopurinol at the Month 1 visit and was maintained throughout the 12-month studies.
Figure 3: Mean Serum Uric Acid Levels Over Time in Pooled Clinical Studies With Lesinurad in Combination With Allopurinol (Study 1 and Study 2)
14.2 Gout Flares
In Study 1 and Study 2, the rates of gout flare requiring treatment from the end of Month 6 to the end of Month 12 were not statistically different between lesinurad 200 mg in combination with allopurinol compared with allopurinol alone.
14.3 Use in Patients With Renal Impairment
The estimated differences between lesinurad and placebo in the proportions of patients achieving target serum uric acid levels in the renal impairment subgroups were largely consistent with the results in the overall population in the studies. However, there were limited data in patients with eCLcr less than 45 mL/min and there was a trend toward decreasing magnitude of effect with decreasing renal function. Based on integrated data from Study 1 and Study 2, the estimated difference between lesinurad 200 mg in combination with allopurinol and allopurinol alone in the proportion achieving serum uric acid < 6.0 mg/dL at Month 6 was 10% (95% CI: -17, 37) in those with eCLcr less than 45 mL/min as compared with 27% (95% CI: 9, 45) in the 45 to less than 60 mL/min subgroup and 30% (95% CI: 23, 37) in the 60 mL/min or greater subgroup.
16. How is Duzallo supplied
16.1 How Supplied
DUZALLO tablets have markings on one side, are plain on the reverse side and are available in the strengths and packages listed in Table 6.
| Tablet Strength (Lesinurad/Allopurinol) | Capsule-Shaped, Film-Coated, Tablet | Tablet Markings | Pack Size | NDC Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200/200 mg | Light orange film-coated tablet | Debossed with "LES200" above "ALO200" | Bottle of 5 tablets Bottle of 30 tablets Bottle of 90 tablets | 70785-021-05 70785-021-30 70785-021-90 |
| 200/300 mg | Dark orange film-coated tablet | Debossed with "LES200" above "ALO300" | Bottle of 5 tablets Bottle of 30 tablets Bottle of 90 tablets | 70785-022-05 70785-022-30 70785-022-90 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| MEDICATION GUIDE DUZALLO® (Dew-ZAL-oh) (lesinurad and allopurinol) tablets, for oral use |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Revised: 11/2017 | ||
|
What is the most important information I should know about DUZALLO? DUZALLO can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||
|
|
||
| See "What are the possible side effects of DUZALLO?" for more information about side effects. | |||
|
What is DUZALLO?
It is not known if DUZALLO is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age. |
|||
|
Do not take DUZALLO if you have:
|
|||
|
Before taking DUZALLO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. DUZALLO may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how DUZALLO works. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take any of these medicines. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|||
|
How should I take DUZALLO?
|
|||
|
What should I avoid while taking DUZALLO?
|
|||
|
What are the possible side effects of DUZALLO? DUZALLO may cause serious side effects including:
|
|||
|
|
||
The most common side effects of DUZALLO include: |
|||
|
|
||
| Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you, or that does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of DUZALLO. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |||
|
How should I store DUZALLO?
Keep DUZALLO and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|||
|
General Information about the safe and effective use of DUZALLO. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use DUZALLO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give DUZALLO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about DUZALLO that is written for health professionals. |
|||
|
What are the ingredients in DUZALLO? Active ingredients: lesinurad and allopurinol Inactive ingredients: crospovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. DUZALLO 200/200 mg tablets are coated with Opadry orange and DUZALLO 200/300 mg tablets are coated with Opadry beige. Manufactured for: Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Cambridge, MA 02142 By: AstraZeneca AB, SE-151 85 Sodertalje, Sweden. Ironwood and the three-leaf design are registered trademarks of Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Inc. DUZALLO and ZURAMPIC are registered trademarks of the AstraZeneca group of companies. © AstraZeneca and Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2017 For more information, go to www.DUZALLO.com or call 1-844-374-4793. |
|||
| DUZALLO
lesinurad and allopurinol tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DUZALLO
lesinurad and allopurinol tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (054451401) |