Drug Detail:Edarbyclor (Azilsartan and chlorthalidone [ ay-zil-sar-tan-and-klor-thal-i-done ])
Drug Class: Angiotensin II inhibitors with thiazides
Highlights of Prescribing Information
EDARBYCLOR (azilsartan medoxomil and chlorthalidone) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2011
WARNING: FETAL TOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- When pregnancy is detected, discontinue EDARBYCLOR as soon as possible (5.1, 8.1)
- Drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and death to the developing fetus (5.1, 8.1)
Indications and Usage for Edarbyclor
Edarbyclor is a combination of azilsartan medoxomil, an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) and chlorthalidone, a thiazide-like diuretic combination product indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure:
- In patients not adequately controlled with monotherapy (1)
- As initial therapy in patients likely to need multiple drugs to help achieve blood pressure goals (1)
Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions (1)
Edarbyclor Dosage and Administration
- Starting dose is 40/12.5 mg once daily (2.1)
- Edarbyclor may be used to provide additional blood pressure lowering for patients not adequately controlled on azilsartan medoxomil 80 mg or chlorthalidone 25 mg (2.1)
- Dose may be increased to 40/25 mg after 2 to 4 weeks as needed to achieve blood pressure goals (2.1)
- Maximal dose is 40/25 mg (2.1)
- May be administered with other antihypertensive agents (2.1)
- Edarbyclor may be administered with or without food (2.1)
- Replace volume in volume-depleted patients prior to use (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets (azilsartan/chlorthalidone): 40/12.5 mg and 40/25 mg (3)
Contraindications
- Anuria (4)
- Do not coadminister aliskiren-containing products with Edarbyclor in patients with diabetes (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- In patients with an activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), such as volume- and/or salt-depleted patients, Edarbyclor can cause excessive hypotension. Correct volume or salt depletion prior to administration of Edarbyclor (5.2)
- In patients with renal artery stenosis, Edarbyclor may cause renal failure (5.3)
- Monitor renal function in patients with renal impairment. Consider discontinuing Edarbyclor with progressive renal impairment (5.3)
- Monitor serum electrolytes periodically (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥2%) are dizziness and fatigue (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-461-7449 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Renal clearance of lithium is reduced by diuretics, such as chlorthalidone increasing the risk of lithium toxicity (7)
- NSAIDS increase risk of renal dysfunction and interfere with antihypertensive effect (7)
- Dual inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system: Increased risk of renal impairment, hypotension, and hyperkalemia (7)
- Lithium: Increases in serum lithium concentrations and lithium toxicity (7)
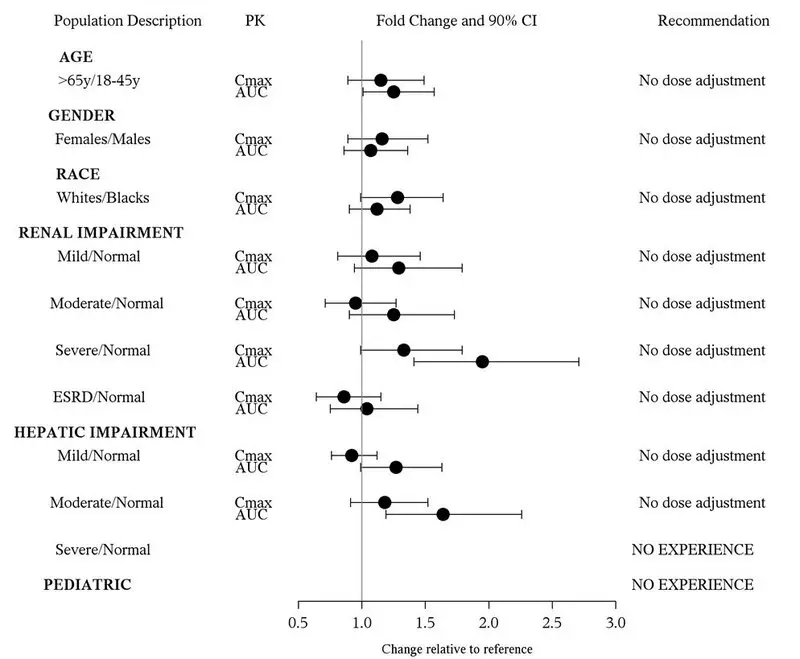
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2023
Related/similar drugs
amlodipine, lisinopril, metoprolol, losartan, furosemide, hydrochlorothiazideFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: FETAL TOXICITY
- When pregnancy is detected, discontinue Edarbyclor as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and death to the developing fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Edarbyclor
Edarbyclor is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure.
Edarbyclor may be used in patients whose blood pressure is not adequately controlled on monotherapy.
Edarbyclor may be used as initial therapy if a patient is likely to need multiple drugs to achieve blood pressure goals.
Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including thiazide-like diuretics such as chlorthalidone and ARBs such as azilsartan medoxomil. There are no controlled trials demonstrating risk reduction with Edarbyclor.
Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management of high blood pressure, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program's Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC).
Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly.
Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal.
Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients; however, the blood pressure effect of Edarbyclor in blacks is similar to that in non-blacks. Many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy.
The choice of Edarbyclor as initial therapy for hypertension should be based on an assessment of potential benefits and risks including whether the patient is likely to tolerate the starting dose of Edarbyclor.
Patients with moderate-to-severe hypertension are at a relatively high risk of cardiovascular events (e.g., stroke, heart attack, and heart failure), kidney failure, and vision problems, so prompt treatment is clinically relevant. Consider the patient's baseline blood pressure, target goal and the incremental likelihood of achieving the goal with a combination product, such as Edarbyclor, versus a monotherapy product when deciding upon initial therapy. Individual blood pressure goals may vary based on the patient's risk.
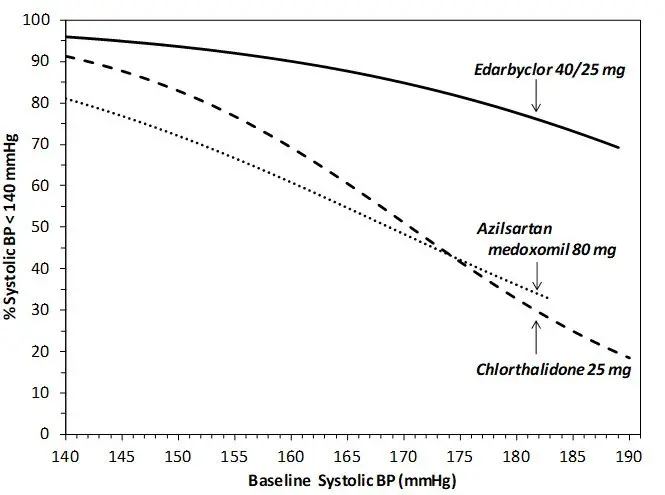
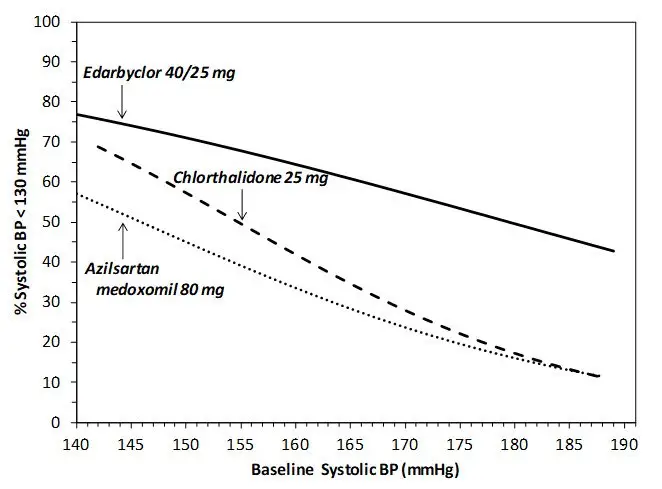
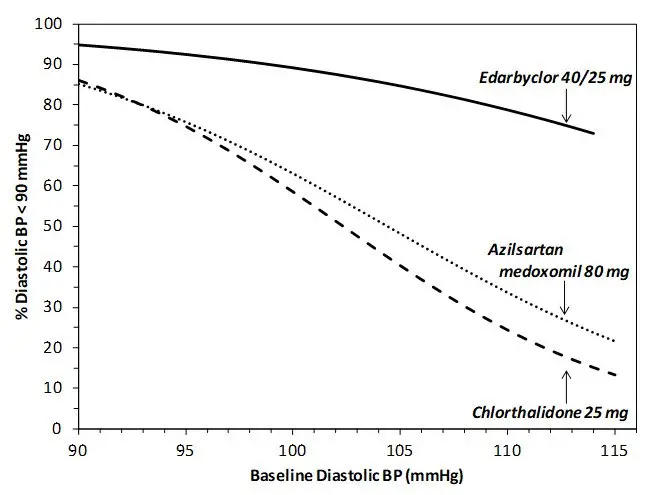
Data from an 8-week, active-controlled, factorial trial provide estimates of the probability of reaching a target blood pressure with Edarbyclor compared with azilsartan medoxomil or chlorthalidone monotherapy [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Figures 1.a-1.d provide estimates of the likelihood of achieving target clinic systolic and diastolic blood pressure control with Edarbyclor 40/25 mg tablets after 8 weeks, based on baseline systolic or diastolic blood pressure. The curve for each treatment group was estimated by logistic regression modeling and is more variable at the tails.
 |
 |
 |
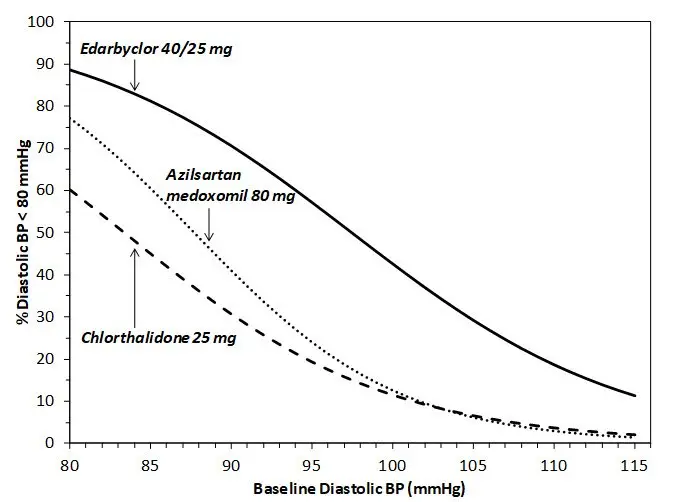 |
For example, a patient with a baseline blood pressure of 170/105 mm Hg has approximately a 48% likelihood of achieving a goal of <140 mm Hg (systolic) and 48% likelihood of achieving <90 mm Hg (diastolic) on azilsartan medoxomil 80 mg. The likelihood of achieving these same goals on chlorthalidone 25 mg is approximately 51% (systolic) and 40% (diastolic). These likelihoods rise to 85% (systolic) and 85% (diastolic) with Edarbyclor 40/25 mg.
2. Edarbyclor Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosing Information
The recommended starting dose of Edarbyclor is 40/12.5 mg taken orally once daily. Most of the antihypertensive effect is apparent within 1 to 2 weeks. The dosage may be increased to 40/25 mg after 2 to 4 weeks as needed to achieve blood pressure goals. Edarbyclor doses above 40/25 mg are probably not useful.
Patients titrated to the individual components (azilsartan medoxomil and chlorthalidone) may instead receive the corresponding dose of Edarbyclor.
Edarbyclor may be administered with other antihypertensive agents as needed.
2.2 Prior to Dosing
Correct any volume depletion prior to administration of Edarbyclor, particularly in patients with impaired renal function or those treated with high doses of diuretics [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Patients who experience dose-limiting adverse reactions on chlorthalidone may be switched to Edarbyclor, initially with a lower dose of chlorthalidone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Edarbyclor is supplied in the following dosage strengths:
- 40/12.5 mg: pale red, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets, approximately 9.7 mm in diameter, with "A/C" and "40/12.5" imprinted on one side. Each tablet contains 40 mg of azilsartan medoxomil and 12.5 mg of chlorthalidone.
- 40/25 mg: light red, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets, approximately 9.7 mm in diameter, with "A/C" and "40/25" imprinted on one side. Each tablet contains 40 mg of azilsartan medoxomil and 25 mg of chlorthalidone.
4. Contraindications
- Edarbyclor is contraindicated in patients with anuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Do not coadminister aliskiren-containing products with Edarbyclor in patients with diabetes [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.2 Hypotension in Volume- or Salt-Depleted Patients
In patients with an activated renin-angiotensin system, such as volume- or salt-depleted patients (e.g., those being treated with high doses of diuretics), symptomatic hypotension may occur after initiation of treatment with Edarbyclor. Such patients are probably not good candidates to start therapy with more than one drug; therefore, correct volume prior to administration of Edarbyclor. If hypotension does occur, the patient should be placed in the supine position and, if necessary, given an intravenous infusion of normal saline. A transient hypotensive response is not a contraindication to further treatment, which usually can be continued without difficulty once the blood pressure has stabilized.
5.4 Serum Electrolyte Imbalances
Thiazide diuretics can cause hyponatremia and hypokalemia. Drugs that inhibit the renin angiotensin system can cause hyperkalemia. Hypokalemia is a dose-dependent adverse reaction that may develop with chlorthalidone. Co-administration of digitalis may exacerbate the adverse effects of hypokalemia. Monitor serum electrolytes periodically.
Edarbyclor attenuates chlorthalidone-associated hypokalemia. In patients with normal potassium levels at baseline, 1.7% of Edarbyclor-treated patients, 0.9% of azilsartan medoxomil-treated patients, and 13.4% of chlorthalidone-treated patients shifted to low potassium values (less than 3.4 mmol/L).
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following potential adverse reactions with Edarbyclor, azilsartan medoxomil, or chlorthalidone and similar agents are included in more detail in the Warnings and Precautions section of the label:
- Fetal toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypotension in Volume- or Salt-Depleted Patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Impaired Renal Function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hyperuricemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Edarbyclor has been evaluated for safety in more than 3900 patients with hypertension; more than 700 patients were treated for at least 6 months and more than 280 for at least 1 year. Adverse reactions have generally been mild and transient in nature.
Common adverse reactions that occurred in the 8-week factorial design trial in at least 2% of Edarbyclor-treated patients and greater than azilsartan medoxomil or chlorthalidone are presented in Table 1.
| Preferred Term | Azilsartan medoxomil 20, 40, 80 mg (N=470) | Chlorthalidone 12.5, 25 mg (N=316) | Edarbyclor 40 / 12.5, 40 / 25 mg (N=302) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dizziness | 1.7% | 1.9% | 8.9% |
| Fatigue | 0.6% | 1.3% | 2.0% |
Hypotension and syncope were reported in 1.7% and 0.3%, respectively, of patients treated with Edarbyclor.
Study discontinuation because of adverse reactions occurred in 8.3% of patients treated with the recommended doses of Edarbyclor compared with 3.2% of patients treated with azilsartan medoxomil and 3.2% of patients treated with chlorthalidone. The most common reasons for discontinuation of therapy with Edarbyclor were serum creatinine increased (3.6%) and dizziness (2.3%).
The adverse reaction profile obtained from 52 weeks of open-label combination therapy with azilsartan medoxomil plus chlorthalidone or Edarbyclor was similar to that observed during the double-blind, active controlled trials.
In 3 double-blind, active controlled, titration studies, in which Edarbyclor was titrated to higher doses in a step-wise manner, adverse reactions and discontinuations for adverse events were less frequent than in the fixed-dose factorial trial.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during the postmarketing use of EDARBYCLOR. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Loss of consciousness
- Pruritus
- Angioedema
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents including Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors (COX-2 Inhibitors)
In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or who have compromised renal function, co-administration of NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors, with angiotensin II receptor antagonists, including azilsartan, may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible. Monitor renal function periodically in patients receiving Edarbyclor and NSAID therapy.
The antihypertensive effect of Edarbyclor may be attenuated by NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors.
7.2 Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS)
Dual blockade of the RAS with angiotensin receptor blockers, ACE inhibitors, or aliskiren is associated with increased risks of hypotension, hyperkalemia, and changes in renal function (including acute renal failure) compared to monotherapy. Most patients receiving the combination of two RAS inhibitors do not obtain any additional benefit compared to monotherapy. In general, avoid combined use of RAS inhibitors. Closely monitor blood pressure, renal function and electrolytes in patients on Edarbyclor and other agents that affect the RAS.
Do not coadminister aliskiren with Edarbyclor in patients with diabetes. Avoid use of aliskiren with Edarbyclor in patients with renal impairment (GFR <60 mL/min).
7.3 Lithium
Increases in serum lithium concentrations and lithium toxicity have been reported during concomitant administration of lithium with angiotensin II receptor agonists. Lithium renal clearance is reduced by diuretics, such as chlorthalidone. Monitor serum lithium levels during concomitant use.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of Edarbyclor in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
11. Edarbyclor Description
Edarbyclor is a combination of azilsartan medoxomil (angiotensin II receptor blocker; as its potassium salt) and chlorthalidone (thiazide-like diuretic).
Azilsartan medoxomil, a prodrug, is hydrolyzed to azilsartan in the gastrointestinal tract during absorption. Azilsartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker. Chlorthalidone is a monosulfamyl thiazide-like diuretic that differs chemically from thiazide diuretics by the lack of a benzothiadiazine structure.
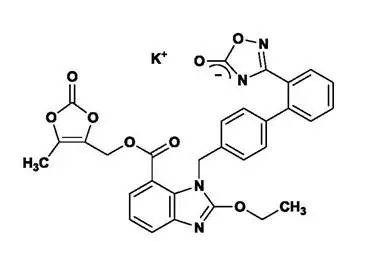
The potassium salt of azilsartan medoxomil, azilsartan kamedoxomil, is chemically described as (5-Methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl 2-ethoxy-1-{[2'-(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylate monopotassium salt. Its empirical formula is C30H23KN4O8.
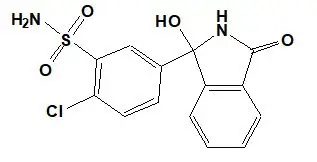
Chlorthalidone is chemically described as 2-chloro-5(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1- isoindolinyl) benzenesulfonamide. Its empirical formula is C14H11ClN2O4S.
The structural formula for azilsartan medoxomil is
The structural formula for chlorthalidone is
Azilsartan kamedoxomil is a white to nearly white powder with a molecular weight of 606.62. It is practically insoluble in water and freely soluble in methanol.
Chlorthalidone is a white to yellowish white powder with a molecular weight of 338.76. Chlorthalidone is practically insoluble in water, in ether, and in chloroform; soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in ethanol.
Edarbyclor is available for oral use as tablets. The tablets have a characteristic odor. Each Edarbyclor tablet contains 42.68 mg of azilsartan kamedoxomil, which is equivalent to containing azilsartan medoxomil 40 mg plus 12.5 or 25 mg of chlorthalidone. Each tablet of Edarbyclor also contains the following inactive ingredients: mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, fumaric acid, sodium hydroxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, hypromellose 2910, talc, titanium dioxide, ferric oxide red, polyethylene glycol 8000, and printing ink gray F1.
12. Edarbyclor - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The active ingredients of Edarbyclor target two separate mechanisms involved in blood pressure regulation.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or fertility studies have been conducted with the combination of azilsartan medoxomil and chlorthalidone or with chlorthalidone alone. However, these studies have been conducted for azilsartan medoxomil, azilsartan and M-II.
14. Clinical Studies
The antihypertensive effects of Edarbyclor have been demonstrated in a total of 5 randomized controlled studies, which included 4 double-blind, active-controlled studies and 1 open-label, long-term active-controlled study. The studies ranged from 8 weeks to 12 months in duration, at doses ranging from 20/12.5 mg to 80/25 mg once daily. A total of 5310 patients (3082 given Edarbyclor and 2228 given active comparator) with moderate or severe hypertension were studied. Overall, randomized patients had a mean age of 57 years, and included 52% males, 72% whites, 21% blacks, 15% with diabetes, 70% with mild or moderate renal impairment, and a mean BMI of 31.6 kg/m2.
An 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, parallel group factorial trial in patients with moderate to severe hypertension compared the effect on blood pressure of Edarbyclor with the respective monotherapies. The trial randomized 1714 patients with baseline systolic blood pressure between 160 and 190 mm Hg (mean 165 mm Hg) and a baseline diastolic blood pressure <119 mm Hg (mean 95 mm Hg) to one of the 11 active treatment arms.
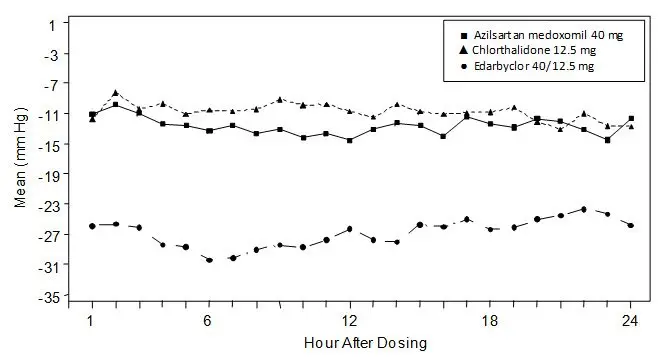
The 6 treatment combinations of azilsartan medoxomil 20, 40, or 80 mg and chlorthalidone 12.5 or 25 mg resulted in statistically significant reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure as determined by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) (Table 2) and clinic measurement (Table 3) at trough compared with the respective individual monotherapies. The clinic blood pressure reductions appear larger than those observed with ABPM, because the former include a placebo effect, which was not directly measured. Most of the antihypertensive effect of Edarbyclor occurs within 1-2 weeks of dosing. The blood pressure lowering effect was maintained throughout the 24-hour period (Figure 3).
| Chlorthalidone, mg | Azilsartan Medoxomil, mg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 80 | |
| 0 | N/A | -12 / -8 | -13 / -7 | -15 / -9 |
| 12.5 | -13 / -7 | -23 / -13 | -24 / -14 | -26 / -17 |
| 25 | -16 / -8 | -26 / -15 | -30 / -17 | -28 / -16 |
| Chlorthalidone, mg | Azilsartan Medoxomil, mg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 40 | 80 | |
| 0 | N/A | -20 / -7 | -23 / -9 | -24 / -10 |
| 12.5 | -21 / -7 | -34 / -14 | -37 / -16 | -37 / -17 |
| 25 | -27 / -9 | -37 / - 16 | -40 / -17 | -40 / -19 |
 |
Edarbyclor was effective in reducing blood pressure regardless of age, gender, or race.
Edarbyclor was effective in treating black patients (usually a low-renin population).
In a 12-week, double-blind forced-titration trial, Edarbyclor 40/25 mg was statistically superior (P<0.001) to olmesartan medoxomil – hydrochlorothiazide (OLM/HCTZ) 40/25 mg in reducing systolic blood pressure in patients with moderate to severe hypertension (Table 4). Similar results were observed in all subgroups, including age, gender, or race of patients.
| Edarbyclor 40/25 mg N=355 | OLM/HCTZ 40/25 mg N=364 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Clinic (Mean Baseline 165/96 mm Hg) | -43 / -19 | -37 / -16 |
| Trough by ABPM (22-24 hours) (Mean Baseline 153/92 mm Hg) | -33 / -20 | -26 / -16 |
Edarbyclor lowered blood pressure more effectively than OLM/HCTZ at each hour of the 24-hour interdosing period as measured by ABPM.
16. How is Edarbyclor supplied
Edarbyclor is supplied as fixed dose combination tablets that are round, biconvex, film-coated, and 9.7 mm in diameter.
| Strength | Color | Imprinting | NDC Number 60631-xxx-xx |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bottle of 30 | |||
| 40 / 12.5 mg | Pale red | A/C 40/12.5 | 412-30 |
| 40 / 25 mg | Light red | A/C 40/25 | 425-30 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Tell patients that if they miss a dose, they should take it later in the same day, but not to double the dose on the following day.
Patient InformationEDARBYCLOR (eh-DAR-bih-clor)(azilsartan medoxomil and chlorthalidone) tablets
Read this Patient Information leaflet before you start taking Edarbyclor and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about Edarbyclor?
- Edarbyclor can cause harm or death to your unborn baby.
- Talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your blood pressure if you plan to become pregnant.
- If you become pregnant while taking Edarbyclor, tell your doctor right away. Your doctor may switch you to a different medicine to treat your high blood pressure.
What Is Edarbyclor?
Edarbyclor is a prescription medicine that contains azilsartan medoxomil, an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) and chlorthalidone, a water pill (diuretic).
Edarbyclor is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension):
- when one medicine to lower your high blood pressure is not enough
- as the first medicine to lower your high blood pressure if your doctor decides you are likely to need more than one medicine.
It is not known if Edarbyclor is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age.
Who should not take Edarbyclor?
Do not take Edarbyclor if you:
- make less urine because of kidney problems
What should I tell my doctor before taking Edarbyclor?
Before you take Edarbyclor, tell your doctor if you:
- have been told that you have abnormal body salt (electrolytes) levels in your blood
- have liver or kidney problems
- have heart problems or stroke
- are vomiting or have diarrhea
- have gout
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. See "What is the most important information I should know about Edarbyclor?"
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Edarbyclor passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take Edarbyclor or breastfeed. You should not do both. Talk with your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take Edarbyclor.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- other medicines used to treat your high blood pressure or heart problem
- water pills (diuretics)
- lithium carbonate (Lithobid), lithium citrate
- digoxin (Lanoxin)
Ask your doctor if you are not sure if you are taking a medicine listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor or pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Edarbyclor?
- Take Edarbyclor exactly as your doctor tells you to.
- Your doctor will tell you how much Edarbyclor to take and when to take it.
- Your doctor may prescribe other medicines for you to take along with Edarbyclor to treat your high blood pressure.
- Edarbyclor can be taken with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take it later in the same day. Do not take more than 1 dose of Edarbyclor in a day.
- If you take too much Edarbyclor and have symptoms of low blood pressure (hypotension) and dizziness, call your doctor for advice. See "What are the possible side effects of Edarbyclor?"
What are the possible side effects of Edarbyclor?
Edarbyclor may cause serious side effects, including:
- See "What is the most important information I should know about Edarbyclor?"
-
Low blood pressure (hypotension) and dizziness is most likely to happen if you also:
- take water pills (diuretics)
- are on a low-salt diet
- take other medicines that affect your blood pressure
- sweat a lot
- get sick with vomiting or diarrhea
- do not drink enough fluids
If you feel faint or dizzy, lie down and call your doctor right away. If you pass out (faint) have someone call your doctor or get medical help. Stop taking Edarbyclor.
- Kidney problems. Kidney problems may become worse in people that already have kidney disease. Some people have changes in blood tests for kidney function and may need a lower dose of Edarbyclor or may need to stop treatment with Edarbyclor. During treatment with Edarbyclor, certain people who have severe heart failure, narrowing of the artery to the kidney, or who lose too much body fluid such as with nausea, vomiting, bleeding, or trauma, may develop sudden kidney failure and in rare instances, death.
-
Fluid and body salt (electrolyte) problems. Tell your doctor if you get any of the following symptoms:
- dry mouth
- thirst
- lack of energy (lethargic)
- weakness
- drowsiness
- confusion
- seizures
- muscle pain or cramps
- restlessness
- muscle tiredness (fatigue)
- passing very little urine or passing large amounts of urine
- fast or abnormal heartbeat
- nausea and vomiting
- constipation
- Increased uric acid levels in the blood. People who have increased levels of uric acid in the blood may develop gout. If you already have gout, tell your doctor about worsening of your gout symptoms.
The most common side effects of Edarbyclor are:
- dizziness, and
- tiredness
These are not all the possible side effects with Edarbyclor. Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Edarbyclor?
- Store Edarbyclor at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store Edarbyclor in the original container that you received from your pharmacist or doctor. Do not put Edarbyclor into a different container.
- Keep the container closed tightly, and keep Edarbyclor out of the light.
Keep Edarbyclor and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about Edarbyclor
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Edarbyclor for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Edarbyclor to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about Edarbyclor. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about Edarbyclor that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.edarbyclor.com or call 1-800-461-7449.
What is high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Blood pressure is the force in your blood vessels when your heart beats and when your heart rests. You have high blood pressure when the force is too great.
High blood pressure makes the heart work harder to pump blood through the body and causes damage to the blood vessels. Edarbyclor tablets can help your blood vessels relax so your blood pressure is lower. Medicines that lower your blood pressure may lower your chance of having a stroke or heart attack.
What are the ingredients in Edarbyclor?
Active ingredients: azilsartan medoxomil and chlorthalidone
Inactive ingredients: mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, fumaric acid, sodium hydroxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, hypromellose 2910, talc, titanium dioxide, ferric oxide red, polyethylene glycol 8000, and printing ink gray F1.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Takeda
Ireland
Manufactured for:
azurity®
pharmaceuticals
Woburn, MA 01801
Patent: https://azurity.com/patents
Revised: April 2023
Edarbyclor is a trademark of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and used under license by Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
EC-PI-09
| EDARBYCLOR
azilsartan kamedoxomil and chlorthalidone tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EDARBYCLOR
azilsartan kamedoxomil and chlorthalidone tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (formerly Arbor Pharmaceuticals) (117505635) |