Drug Detail:Edurant (Rilpivirine [ ril-pi-vir-een ])
Drug Class: NNRTIs
Highlights of Prescribing Information
EDURANT® (rilpivirine) tablets for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2011
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1.2) | 3/2022 |
| Dosage and Administration (2.2) | 3/2022 |
| Warnings and Precautions | |
| Fat Redistribution (5.5) | Removed 10/22 |
Indications and Usage for Edurant
EDURANT is a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) specific, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in treatment-naïve patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 35 kg with HIV-1 RNA less than or equal to 100,000 copies/mL (1.1).
Limitations of Use:
- More EDURANT treated subjects with HIV-1 RNA greater than 100,000 copies/mL at the start of therapy experienced virologic failure (HIV-1 RNA ≥50 copies/mL) compared to EDURANT treated subjects with HIV-1 RNA less than or equal to 100,000 copies/mL. (1.1, 14)
EDURANT is indicated in combination with VOCABRIA (cabotegravir), for short-term treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and adolescents 12 years and older and weighing at least 35 kg who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL) on a stable regimen with no history of treatment failure and with no known or suspected resistance to either cabotegravir or rilpivirine. (1.2)
Edurant Dosage and Administration
- One tablet taken once daily with a meal. (2.1, 2.2)
- See full prescribing information for dosing information when used in combination with cabotegravir (2.2)
- For pregnant patients who are already on a stable EDURANT regimen prior to pregnancy and who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) the recommended dosage is one 25 mg tablet once daily taken orally with a meal. (2.1, 12.3)
- Rifabutin coadministration: Take two 25 mg tablets of rilpivirine once daily with a meal for the duration of the rifabutin coadministration. (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
25 mg tablets (3)
Contraindications
Coadministration of EDURANT is contraindicated with drugs where significant decreases in rilpivirine plasma concentrations may occur, which may result in loss of virologic response and possible resistance and cross-resistance. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Skin and Hypersensitivity Reactions: Severe skin and hypersensitivity reactions have been reported during postmarketing experience, including cases of Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), with rilpivirine-containing regimens. Immediately discontinue treatment if hypersensitivity or rash with systemic symptoms or elevations in hepatic serum biochemistries develop and closely monitor clinical status, including hepatic serum biochemistries. (5.1)
- Hepatotoxicity: Hepatic adverse events have been reported in patients with underlying liver disease, including hepatitis B or C virus co-infection, or in patients with elevated baseline transaminases. A few cases of hepatotoxicity have occurred in patients with no pre-existing hepatic disease. Monitor liver function tests before and during treatment with EDURANT in patients with underlying hepatic disease, such as hepatitis B or C virus co-infection, or marked elevations in transaminase. Also consider monitoring liver functions tests in patients without pre-existing hepatic dysfunction or other risk factors. (5.2)
- Depressive Disorders: Severe depressive disorders have been reported. Immediate medical evaluation is recommended for severe depressive disorders. (5.3)
- Patients may develop immune reconstitution syndrome. (5.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse drug reactions to EDURANT (incidence >2%) of at least moderate to severe intensity (≥ Grade 2) were depressive disorders, headache, insomnia and rash. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Products, LP at 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Consider alternatives to EDURANT when coadministered with drugs with a known risk of torsade de pointes. (5.4)
- EDURANT should not be used in combination with NNRTIs. (4, 7)
- Coadministration of EDURANT with drugs that induce or inhibit CYP3A may affect the plasma concentrations of rilpivirine. (4, 7)
- Coadministration of EDURANT with drugs that increase gastric pH may decrease plasma concentrations of rilpivirine. (4, 7)
- Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for other drugs that should not be coadministered with EDURANT and for other drugs that may require a change in dose or regimen. (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Total rilpivirine exposures were generally lower during pregnancy compared to the postpartum period. (2.1, 8.1, 12.3)
- Lactation: Women infected with HIV should be instructed not to breastfeed due to the potential for HIV transmission. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 10/2022
Related/similar drugs
Biktarvy, Truvada, tenofovir, Atripla, Complera, Stribild, EpzicomFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Edurant
1.1 Treatment of HIV-1 in Treatment-Naïve Patients
EDURANT, in combination with other antiretroviral agents, is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in antiretroviral treatment-naïve patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 35 kg with plasma HIV-1 RNA less than or equal to 100,000 copies/mL at the start of therapy.
1.2 Treatment of HIV-1 in Combination with Cabotegravir
EDURANT is indicated in combination with VOCABRIA (cabotegravir) for short-term treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and adolescents 12 years and older and weighing at least 35 kg who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL) on a stable antiretroviral regimen with no history of treatment failure and with no known or suspected resistance to either cabotegravir or rilpivirine, for use as [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]:
- oral lead-in to assess the tolerability of rilpivirine prior to administration of rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension, a component of CABENUVA (cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension; rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension).
- oral therapy for patients who will miss planned injection dosing with CABENUVA (cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension; rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension).
2. Edurant Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage in Treatment-Naïve Patients
The recommended dosage of EDURANT in patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 35 kg is one 25 mg tablet taken orally once daily with a meal [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
For pregnant patients who are already on a stable EDURANT regimen prior to pregnancy and who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) the recommended dosage is one 25 mg tablet once daily taken orally with a meal. Lower exposures of rilpivirine were observed during pregnancy, therefore viral load should be monitored closely [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Combination with Cabotegravir in Adults and Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at Least 35 kg
Consult the prescribing information for CABENUVA (cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension; rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension) before initiating EDURANT to ensure therapy with CABENUVA is appropriate.
2.3 Recommended Dosage with Rifabutin Coadministration
If EDURANT is coadministered with rifabutin, the EDURANT dose should be increased to 50 mg (two tablets of 25 mg each) once daily, taken with a meal. When rifabutin coadministration is stopped, the EDURANT dose should be decreased to 25 mg once daily, taken with a meal [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Note that use of CABENUVA (cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension; rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension) with rifabutin is contraindicated. Refer to CABENUVA labeling for additional detail.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
25 mg white to off-white, film-coated, round, biconvex, tablet of 6.4 mm, debossed with "TMC" on one side and "25" on the other side. Each tablet contains 27.5 mg of rilpivirine hydrochloride, which is equivalent to 25 mg of rilpivirine.
4. Contraindications
EDURANT is contraindicated for coadministration with the drugs in Table 1 for which significant decreases in rilpivirine plasma concentrations may occur due to CYP3A enzyme induction or gastric pH increase, which may result in loss of virologic response and possible resistance to EDURANT or to the class of NNRTIs [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Drug Class | Contraindicated Drugs in Class | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Anticonvulsants | Carbamazepine Oxcarbazepine Phenobarbital Phenytoin | Potential for significant decreases in rilpivirine plasma concentrations due to CYP3A enzyme induction, which may result in loss of virologic response. |
| Antimycobacterials | Rifampin Rifapentine |
|
| Glucocorticoid (systemic) | Dexamethasone (more than a single-dose treatment) |
|
| Herbal Products | St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) | |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors | e.g., Esomeprazole Lansoprazole Omeprazole Pantoprazole Rabeprazole | Potential for significant decreases in rilpivirine plasma concentrations due to gastric pH increase, which may result in loss of virologic response. |
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Skin and Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe skin and hypersensitivity reactions have been reported during the postmarketing experience, including cases of Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), with rilpivirine-containing regimens. While some skin reactions were accompanied by constitutional symptoms such as fever, other skin reactions were associated with organ dysfunctions, including elevations in hepatic serum biochemistries. During the Phase 3 clinical trials, treatment-related rashes with at least Grade 2 severity were reported in 3% of subjects receiving EDURANT. No Grade 4 rash was reported. Overall, most rashes were Grade 1 or 2 and occurred in the first four to six weeks of therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 and 6.2)]. Discontinue EDURANT immediately if signs or symptoms of severe skin or hypersensitivity reactions develop, including but not limited to, severe rash or rash accompanied by fever, blisters, mucosal involvement, conjunctivitis, facial edema, angioedema, hepatitis or eosinophilia. Clinical status including laboratory parameters should be monitored and appropriate therapy should be initiated.
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatic adverse events have been reported in patients receiving a rilpivirine-containing regimen. Patients with underlying hepatitis B or C virus infection, or marked elevations in transaminases prior to treatment may be at increased risk for worsening or development of transaminase elevations with use of EDURANT. A few cases of hepatic toxicity have been reported in adult patients receiving a rilpivirine-containing regimen who had no pre-existing hepatic disease or other identifiable risk factors. Appropriate laboratory testing prior to initiating therapy and monitoring for hepatotoxicity during therapy with EDURANT is recommended in patients with underlying hepatic disease such as hepatitis B or C virus infection, or in patients with marked elevations in transaminases prior to treatment initiation. Liver enzyme monitoring should also be considered for patients without pre-existing hepatic dysfunction or other risk factors.
5.3 Depressive Disorders
The adverse reaction depressive disorders (depressed mood, depression, dysphoria, major depression, mood altered, negative thoughts, suicide attempt, suicidal ideation) has been reported with EDURANT. Patients with severe depressive symptoms should seek immediate medical evaluation to assess the possibility that the symptoms are related to EDURANT, and if so, to determine whether the risks of continued therapy outweigh the benefits.
During the Phase 3 trials in adults (N=1368) through 96 weeks, the incidence of depressive disorders (regardless of causality, severity) reported among EDURANT (n=686) or efavirenz (n=682) was 9% and 8%, respectively. Most events were mild or moderate in severity. The incidence of Grade 3 and 4 depressive disorders (regardless of causality) was 1% for both EDURANT and efavirenz. The incidence of discontinuation due to depressive disorders among EDURANT or efavirenz was 1% in each arm. Suicidal ideation was reported in 4 subjects in each arm while suicide attempt was reported in 2 subjects in the EDURANT arm.
During the Phase 2 trial in pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age (N=36) receiving EDURANT through 48 weeks, the incidence of depressive disorders (regardless of causality, severity) was 19.4% (7/36). Most events were mild or moderate in severity. The incidence of Grade 3 and 4 depressive disorders (regardless of causality) was 5.6% (2/36). None of the subjects discontinued due to depressive disorders. Suicidal ideation and suicide attempt were reported in 1 subject.
5.4 Risk of Adverse Reactions or Loss of Virologic Response Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of EDURANT and other drugs may result in potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Contraindications (4), and Drug Interactions (7)]:
- Loss of therapeutic effect of EDURANT and possible development of resistance.
In healthy subjects, 75 mg once daily and 300 mg once daily (3 times and 12 times the dose in EDURANT) have been shown to prolong the QTc interval of the electrocardiogram. Consider alternatives to EDURANT when coadministered with a drug that is known to have a risk of torsade de pointes [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
See Table 5 for steps to prevent or manage these possible and known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations. Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during EDURANT therapy and review concomitant medications during EDURANT therapy.
5.5 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including EDURANT. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and autoimmune hepatitis) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed below and in other sections of the labeling:
- Skin and Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Depressive Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing experience in patients receiving a rilpivirine containing regimen. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Renal and Genitourinary Disorders: nephrotic syndrome
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Severe skin and hypersensitivity reactions including DRESS (Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms)
7. Drug Interactions
[see Dosage and Administration (2), Contraindications (4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Rilpivirine is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A, and drugs that induce or inhibit CYP3A may thus affect the clearance of rilpivirine. Coadministration of EDURANT and drugs that induce CYP3A may result in decreased plasma concentrations of rilpivirine and loss of virologic response and possible resistance to rilpivirine or to the class of NNRTIs. Coadministration of EDURANT and drugs that inhibit CYP3A may result in increased plasma concentrations of rilpivirine. Coadministration of EDURANT with drugs that increase gastric pH may result in decreased plasma concentrations of rilpivirine and loss of virologic response and possible resistance to rilpivirine or to the class of NNRTIs.
EDURANT at a dose of 25 mg once daily is not likely to have a clinically relevant effect on the exposure of drugs metabolized by CYP enzymes.
Table 5 shows the established and other potentially significant drug interactions based on which alterations in dose or regimen of EDURANT and/or coadministered drug may be recommended. Drugs that are not recommended for coadministration with EDURANT are also included in Table 5.
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration of Rilpivirine or Concomitant Drug | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| ↑=increase, ↓=decrease, ↔=no change |
||
|
||
| Antacids:
antacids (e.g., aluminum or magnesium hydroxide, calcium carbonate) | ↔ rilpivirine (antacids taken at least 2 hours before or at least 4 hours after rilpivirine) | The combination of EDURANT and antacids should be used with caution as coadministration may cause significant decreases in rilpivirine plasma concentrations (increase in gastric pH). Antacids should only be administered either at least 2 hours before or at least 4 hours after EDURANT. |
| ↓ rilpivirine (concomitant intake) | ||
| Anticonvulsants:
carbamazepine oxcarbazepine phenobarbital phenytoin | ↓Rilpivirine | Coadministration is contraindicated with EDURANT [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Antimycobacterials:
rifampin rifapentine | ↓Rilpivirine | Coadministration is contraindicated with EDURANT [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Antimycobacterials:
rifabutin* | ↓ rilpivirine | Concomitant use of EDURANT with rifabutin may cause a decrease in the plasma concentrations of rilpivirine (induction of CYP3A enzymes). Throughout coadministration of EDURANT with rifabutin, the EDURANT dose should be increased from 25 mg once daily to 50 mg once daily. When rifabutin coadministration is stopped, the EDURANT dose should be decreased to 25 mg once daily. |
| Azole Antifungal Agents:
fluconazole itraconazole ketoconazole*† posaconazole voriconazole | ↑ rilpivirine ↓ ketoconazole | Concomitant use of EDURANT with azole antifungal agents may cause an increase in the plasma concentrations of rilpivirine (inhibition of CYP3A enzymes). No rilpivirine dose adjustment is required when EDURANT is coadministered with azole antifungal agents. Clinically monitor for breakthrough fungal infections when azole antifungals are coadministered with EDURANT. |
| Glucocorticoid (systemic):
dexamethasone (more than a single-dose treatment) | ↓Rilpivirine | Coadministration is contraindicated with EDURANT [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| H2-Receptor Antagonists:
cimetidine famotidine*† nizatidine ranitidine | ↔ rilpivirine (famotidine taken 12 hours before rilpivirine or 4 hours after rilpivirine) | The combination of EDURANT and H2-receptor antagonists should be used with caution as coadministration may cause significant decreases in rilpivirine plasma concentrations (increase in gastric pH). H2-receptor antagonists should only be administered at least 12 hours before or at least 4 hours after EDURANT. |
| ↓ rilpivirine (famotidine taken 2 hours before rilpivirine) | ||
| Herbal Products:
St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) | ↓Rilpivirine | Coadministration is contraindicated with EDURANT [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| HIV-Antiviral Agents: Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs) | ||
| NNRTI (delavirdine) | ↑ rilpivirine ↔ delavirdine | It is not recommended to coadminister EDURANT with delavirdine and other NNRTIs. |
| Other NNRTIs (efavirenz, etravirine, nevirapine) | ↓ rilpivirine ↔ other NNRTIs | |
| HIV-Antiviral Agents: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs) | ||
| didanosine*† | ↔ rilpivirine ↔ didanosine | No dose adjustment is required when EDURANT is coadministered with didanosine. Didanosine is to be administered on an empty stomach and at least two hours before or at least four hours after EDURANT (which should be administered with a meal). |
| HIV-Antiviral Agents: Protease Inhibitors (PIs)-Boosted (i.e., with coadministration of low-dose ritonavir) or Unboosted (i.e., without coadministration of low-dose ritonavir) | ||
| darunavir/ritonavir*† | ↑ rilpivirine ↔ boosted darunavir | Concomitant use of EDURANT with darunavir/ritonavir may cause an increase in the plasma concentrations of rilpivirine (inhibition of CYP3A enzymes). No dose adjustment is required when EDURANT is coadministered with darunavir/ritonavir. |
| lopinavir/ritonavir*† | ↑ rilpivirine ↔ boosted lopinavir | Concomitant use of EDURANT with lopinavir/ritonavir may cause an increase in the plasma concentrations of rilpivirine (inhibition of CYP3A enzymes). No dose adjustment is required when EDURANT is coadministered with lopinavir/ritonavir. |
| other boosted PIs (atazanavir/ritonavir, fosamprenavir/ritonavir, saquinavir/ritonavir, tipranavir/ritonavir) | ↑ rilpivirine ↔ boosted PI | Concomitant use of EDURANT with boosted PIs may cause an increase in the plasma concentrations of rilpivirine (inhibition of CYP3A enzymes). EDURANT is not expected to affect the plasma concentrations of coadministered PIs. |
| unboosted PIs (atazanavir, fosamprenavir, indinavir, nelfinavir) | ↑ rilpivirine ↔ unboosted PI | Concomitant use of EDURANT with unboosted PIs may cause an increase in the plasma concentrations of rilpivirine (inhibition of CYP3A enzymes). EDURANT is not expected to affect the plasma concentrations of coadministered PIs. |
| Macrolide or ketolide antibiotics:
azithromycin clarithromycin erythromycin | ↑ rilpivirine ↔ azithromycin ↔ clarithromycin ↔ erythromycin | Macrolides are expected to increase concentrations of rilpivirine and are associated with a risk of Torsade de Pointes [Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Where possible, consider alternatives, such as azithromycin, which increases rilpivirine concentrations less than other macrolides. |
| Narcotic Analgesics:
methadone* | ↓ R(-) methadone ↓ S(+) methadone | No dose adjustments are required when initiating coadministration of methadone with EDURANT. However, clinical monitoring is recommended as methadone maintenance therapy may need to be adjusted in some patients. |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors:
e.g., esomeprazole lansoprazole omeprazole pantoprazole rabeprazole | ↓Rilpivirine | Coadministration is contraindicated with EDURANT [see Contraindications (4)]. |
In addition to the drugs included in Table 5, the interaction between EDURANT and the following drugs was evaluated in clinical studies and no dose adjustment is needed for either drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]: acetaminophen, atorvastatin, chlorzoxazone, cabotegravir, ethinylestradiol, norethindrone, raltegravir, sildenafil, simeprevir and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Rilpivirine did not have a clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin or metformin. No clinically relevant drug-drug interaction is expected when EDURANT is coadministered with maraviroc, ribavirin or the NRTIs abacavir, emtricitabine, lamivudine, stavudine and zidovudine.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of EDURANT were evaluated in a single arm, open-label, Phase 2 trial that enrolled 36 antiretroviral treatment-naïve, HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 32 kg [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of EDURANT did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, caution should be exercised in the administration and monitoring of EDURANT in elderly patients reflecting the greater frequency of decreased renal and hepatic function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. However, in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease, rilpivirine should be used with caution and with increased monitoring for adverse effects, as rilpivirine concentrations may be increased due to alteration of drug absorption, distribution, and metabolism secondary to renal dysfunction. As rilpivirine is highly bound to plasma proteins, it is unlikely that it will be significantly removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
There is no specific antidote for overdose with EDURANT. Human experience of overdose with EDURANT is limited. Treatment of overdose with EDURANT consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and ECG (QT interval) as well as observation of the clinical status of the patient. It is advisable to contact a poison control center to obtain the latest recommendations for the management of an overdose. Since rilpivirine is highly bound to plasma protein, dialysis is unlikely to result in significant removal of the active substance.
11. Edurant Description
EDURANT® (rilpivirine) is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). EDURANT is available as a white to off-white, film-coated, round, biconvex, 6.4 mm tablet for oral administration. Each tablet contains 27.5 mg of rilpivirine hydrochloride, which is equivalent to 25 mg of rilpivirine.
The chemical name for rilpivirine hydrochloride is 4-[[4-[[4-[(E)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl]amino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]benzonitrile monohydrochloride. Its molecular formula is C22H18N6 ∙ HCl and its molecular weight is 402.88. Rilpivirine hydrochloride has the following structural formula:
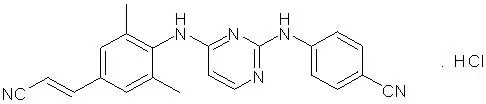
Rilpivirine hydrochloride is a white to almost white powder. Rilpivirine hydrochloride is practically insoluble in water over a wide pH range.
Each EDURANT tablet also contains the inactive ingredients croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polysorbate 20, povidone K30 and silicified microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet coating contains hypromellose 2910 6 mPa.s, lactose monohydrate, PEG 3000, titanium dioxide and triacetin.
12. Edurant - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics in Adults
The pharmacokinetic properties of rilpivirine have been evaluated in adult healthy subjects and in adult antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected subjects. Exposure to rilpivirine was generally lower in HIV-1 infected subjects than in healthy subjects.
| Parameter | Rilpivirine 25 mg once daily N=679 |
|---|---|
| AUC24h (ng∙h/mL) | |
| Mean±Standard Deviation | 2235±851 |
| Median (Range) | 2096 (198 – 7307) |
| C0h (ng/mL) | |
| Mean±Standard Deviation | 79±35 |
| Median (Range) | 73 (2 – 288) |
Special Populations
Pregnancy and Postpartum
The exposure (C0h and AUC24h) to total rilpivirine after intake of rilpivirine 25 mg once daily as part of an antiretroviral regimen was 30 to 40% lower during pregnancy (similar for the second and third trimester), compared with postpartum (see Table 7). However, the exposure during pregnancy was not significantly different from exposures obtained in Phase 3 trials. Based on the exposure-response relationship for rilpivirine, this decrease is not considered clinically relevant in patients who are virollogically suppressed. The protein binding of rilpivirine was similar (>99%) during the second trimester, third trimester, and postpartum.
| Pharmacokinetics of total rilpivirine (mean ± SD, tmax: median [range]) | Postpartum (6–12 Weeks) (n=11) | 2nd Trimester of pregnancy (n=15) | 3rd Trimester of pregnancy (n=13) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0h, ng/mL | 111±69.2 | 65.0±23.9 | 63.5±26.2 |
| Cmin, ng/mL | 84.0±58.8 | 54.3±25.8 | 52.9±24.4 |
| Cmax, ng/mL | 167±101 | 121±45.9 | 123±47.5 |
| tmax, h | 4.00 (2.03–25.08) | 4.00 (1.00–9.00) | 4.00 (2.00–24.93) |
| AUC24h, ng.h/mL | 2714±1535 | 1792±711 | 1762±662 |
Drug Interactions
[see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Rilpivirine is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A, and drugs that induce or inhibit CYP3A may thus affect the clearance of rilpivirine. Coadministration of EDURANT and drugs that induce CYP3A may result in decreased plasma concentrations of rilpivirine and loss of virologic response and possible resistance. Coadministration of EDURANT and drugs that inhibit CYP3A may result in increased plasma concentrations of rilpivirine. Coadministration of EDURANT with drugs that increase gastric pH may result in decreased plasma concentrations of rilpivirine and loss of virologic response and possible resistance to rilpivirine and to the class of NNRTIs.
EDURANT at a dose of 25 mg once daily is not likely to have a clinically relevant effect on the exposure of medicinal products metabolized by CYP enzymes.
Drug interaction studies were performed with EDURANT and other drugs likely to be coadministered or commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interactions. The effects of coadministration of other drugs on the Cmax, AUC, and Cmin values of rilpivirine are summarized in Table 9 (effect of other drugs on EDURANT). The effect of coadministration of EDURANT on the Cmax, AUC, and Cmin values of other drugs are summarized in Table 10 (effect of EDURANT on other drugs). [For information regarding clinical recommendations, see Drug Interactions (7)].
| Coadministered Drug | Dose/Schedule | N | Mean Ratio of Rilpivirine
Pharmacokinetic Parameters With/Without Coadministered Drug (90% CI); No Effect=1.00 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coadministered Drug | Rilpivirine | Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||
| CI=Confidence Interval; N=maximum number of subjects with data; N.A.=not available; ↑=increase; ↓=decrease; ↔=no change; q.d.=once daily; b.i.d.=twice daily | ||||||
|
||||||
| Coadministration With HIV Protease Inhibitors (PIs) | ||||||
| Darunavir/ritonavir | 800/100 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 14 | 1.79 (1.56–2.06) | 2.30 (1.98–2.67) | 2.78 (2.39–3.24) |
| Lopinavir/ritonavir (soft gel capsule) | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 15 | 1.29 (1.18–1.40) | 1.52 (1.36–1.70) | 1.74 (1.46–2.08) |
| Coadministration With HIV Nucleoside or Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs/N[t]RTIs) | ||||||
| Didanosine | 400 mg q.d. delayed release capsules taken 2 hours before rilpivirine | 150 mg q.d.* | 21 | 1.00 (0.90–1.10) | 1.00 (0.95–1.06) | 1.00 (0.92–1.09) |
| Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 300 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 0.96 (0.81–1.13) | 1.01 (0.87–1.18) | 0.99 (0.83–1.16) |
| Coadministration With HIV Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors | ||||||
| Cabotegravir | 30 mg q.d. | 25 mg q.d. | 11 | 0.96 (0.85–1.09) | 0.99 (0.89–1.09) | 0.92 (0.79–1.07) |
| Raltegravir | 400 mg b.i.d. | 25 mg q.d. | 23 | 1.12 (1.04–1.20) | 1.12 (1.05–1.19) | 1.03 (0.96–1.12) |
| Coadministration With other Antivirals | ||||||
| Simeprevir | 150 mg q.d. | 25 mg q.d. | 23 | 1.04 (0.95–1.13) | 1.12 (1.05–1.19) | 1.25 (1.16–1.35) |
| Coadministration With Drugs other than Antiretrovirals | ||||||
| Acetaminophen | 500 mg single dose | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 1.09 (1.01–1.18) | 1.16 (1.10–1.22) | 1.26 (1.16–1.38) |
| Atorvastatin | 40 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 0.91 (0.79–1.06) | 0.90 (0.81–0.99) | 0.90 (0.84–0.96) |
| Chlorzoxazone | 500 mg single dose taken 2 hours after rilpivirine | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 1.17 (1.08–1.27) | 1.25 (1.16–1.35) | 1.18 (1.09–1.28) |
| Ethinylestradiol/Norethindrone | 0.035 mg q.d./ 1 mg q.d. | 25 mg q.d. | 15 | ↔† | ↔† | ↔† |
| Famotidine | 40 mg single dose taken 12 hours before rilpivirine | 150 mg single dose* | 24 | 0.99 (0.84–1.16) | 0.91 (0.78–1.07) | N.A. |
| Famotidine | 40 mg single dose taken 2 hours before rilpivirine | 150 mg single dose* | 23 | 0.15 (0.12–0.19) | 0.24 (0.20–0.28) | N.A. |
| Famotidine | 40 mg single dose taken 4 hours after rilpivirine | 150 mg single dose* | 24 | 1.21 (1.06–1.39) | 1.13 (1.01–1.27) | N.A. |
| Ketoconazole | 400 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 15 | 1.30 (1.13–1.48) | 1.49 (1.31–1.70) | 1.76 (1.57–1.97) |
| Methadone | 60–100 mg q.d., individualized dose | 25 mg q.d. | 12 | ↔† | ↔† | ↔† |
| Omeprazole | 20 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 0.60 (0.48–0.73) | 0.60 (0.51–0.71) | 0.67 (0.58–0.78) |
| Rifabutin | 300 mg q.d. | 25 mg q.d. | 18 | 0.69 (0.62–0.76) | 0.58 (0.52–0.65) | 0.52 (0.46–0.59) |
| Rifabutin | 300 mg q.d. | 50 mg q.d. | 18 | 1.43 (1.30–1.56) | 1.16 (1.06–1.26) | 0.93 (0.85–1.01) |
| (reference arm for comparison was 25 mg q.d. rilpivirine administered alone) | ||||||
| Rifampin | 600 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 0.31 (0.27–0.36) | 0.20 (0.18–0.23) | 0.11 (0.10–0.13) |
| Sildenafil | 50 mg single dose | 75 mg q.d.* | 16 | 0.92 (0.85–0.99) | 0.98 (0.92–1.05) | 1.04 (0.98–1.09) |
| Coadministered Drug | Dose/Schedule | N | Mean Ratio of Coadministered Drug
Pharmacokinetic Parameters With/Without EDURANT (90% CI); No Effect=1.00 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coadministered Drug | Rilpivirine | Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||
| CI=Confidence Interval; N=maximum number of subjects with data; N.A.=not available; ↑=increase; ↓=decrease; ↔=no change; q.d.=once daily; b.i.d.=twice daily | ||||||
|
||||||
| Coadministration With HIV Protease Inhibitors (PIs) | ||||||
| Darunavir/ritonavir | 800/100 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 15 | 0.90 (0.81–1.00) | 0.89 (0.81–0.99) | 0.89 (0.68–1.16) |
| Lopinavir/ritonavir (soft gel capsule) | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 15 | 0.96 (0.88–1.05) | 0.99 (0.89–1.10) | 0.89 (0.73–1.08) |
| Coadministration With HIV Nucleoside or Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs/N[t]RTIs) | ||||||
| Didanosine | 400 mg q.d. delayed release capsules taken 2 hours before rilpivirine | 150 mg q.d.* | 13 | 0.96 (0.80–1.14) | 1.12 (0.99–1.27) | N.A. |
| Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 300 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 1.19 (1.06–1.34) | 1.23 (1.16–1.31) | 1.24 (1.10–1.38) |
| Coadministration With HIV Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors | ||||||
| Cabotegravir | 30 mg q.d. | 25 mg q.d. | 11 | 1.05 (0.96–1.15) | 1.12 (1.05–1.19) | 1.14 (1.04–1.24) |
| Raltegravir | 400 mg b.i.d. | 25 mg q.d. | 23 | 1.10 (0.77–1.58) | 1.09 (0.81–1.47) | 1.27 (1.01–1.60) |
| Coadministration With other Antivirals | ||||||
| Simeprevir | 150 mg q.d. | 25 mg q.d. | 21 | 1.10 (0.97–1.26) | 1.06 (0.94–1.19) | 0.96 (0.83–1.11) |
| Coadministration With Drugs other than Antiretrovirals | ||||||
| Acetaminophen | 500 mg single dose | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 0.97 (0.86–1.10) | 0.91 (0.86–0.97) | N.A. |
| Atorvastatin | 40 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 1.35 (1.08–1.68) | 1.04 (0.97–1.12) | 0.85 (0.69–1.03) |
| 2-hydroxy-atorvastatin | 16 | 1.58 (1.33–1.87) | 1.39 (1.29–1.50) | 1.32 (1.10–1.58) |
||
| 4-hydroxy-atorvastatin | 16 | 1.28 (1.15–1.43) | 1.23 (1.13–1.33) | N.A. | ||
| Chlorzoxazone | 500 mg single dose taken 2 hours after rilpivirine | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 0.98 (0.85–1.13) | 1.03 (0.95–1.13) | N.A. |
| Digoxin | 0.5 mg single dose | 25 mg q.d. | 22 | 1.06 (0.97–1.17) | 0.98 (0.93–1.04)† | N.A. |
| Ethinylestradiol | 0.035 mg q.d. | 25 mg q.d. | 17 | 1.17 (1.06–1.30) | 1.14 (1.10–1.19) | 1.09 (1.03–1.16) |
| Norethindrone | 1 mg q.d. | 17 | 0.94 (0.83–1.06) | 0.89 (0.84–0.94) | 0.99 (0.90–1.08) |
|
| Ketoconazole | 400 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 14 | 0.85 (0.80–0.90) | 0.76 (0.70–0.82) | 0.34 (0.25–0.46) |
| R(-) methadone | 60–100 mg q.d., individualized dose | 25 mg q.d. | 13 | 0.86 (0.78–0.95) | 0.84 (0.74–0.95) | 0.78 (0.67–0.91) |
| S(+) methadone | 13 | 0.87 (0.78–0.97) | 0.84 (0.74–0.96) | 0.79 (0.67–0.92) |
||
| Metformin | 850 mg single dose | 25 mg q.d. | 20 | 1.02 (0.95–1.10) | 0.97 (0.90–1.06)‡ | N.A. |
| Omeprazole | 20 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 15 | 0.86 (0.68–1.09) | 0.86 (0.76–0.97) | N.A. |
| Rifampin | 600 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d.* | 16 | 1.02 (0.93–1.12) | 0.99 (0.92–1.07) | N.A. |
| 25-desacetylrifampin | 16 | 1.00 (0.87–1.15) | 0.91 (0.77–1.07) | N.A. | ||
| Sildenafil | 50 mg single dose | 75 mg q.d.* | 16 | 0.93 (0.80–1.08) | 0.97 (0.87–1.08) | N.A. |
| N-desmethyl-sildenafil | 16 | 0.90 (0.80–1.02) | 0.92 (0.85–0.99)† | N.A. | ||
12.4 Microbiology
Resistance
In Treatment-Naïve Adult Subjects
In the Week 96 pooled resistance analysis of the Phase 3 trials C209 and C215, the emergence of resistance was greater among subjects' viruses in the EDURANT arm compared to the efavirenz arm, and was dependent on baseline viral load. In the pooled resistance analysis, 58% (57/98) of the subjects who qualified for resistance analysis (resistance analysis subjects) in the EDURANT arm had virus with genotypic and/or phenotypic resistance to rilpivirine compared to 45% (25/56) of the resistance analysis subjects in the efavirenz arm who had genotypic and/or phenotypic resistance to efavirenz. Moreover, genotypic and/or phenotypic resistance to a background drug (emtricitabine, lamivudine, tenofovir, abacavir or zidovudine) emerged in viruses from 52% (51/98) of the resistance analysis subjects in the rilpivirine arm compared to 23% (13/56) in the efavirenz arm.
Emerging NNRTI substitutions in the rilpivirine resistance analysis of subjects' viruses included V90I, K101E/P/T, E138K/A/Q/G, V179I/L, Y181C/I, V189I, H221Y, F227C/L and M230L, which were associated with a rilpivirine phenotypic fold change range of 2.6 – 621. The E138K substitution emerged most frequently during rilpivirine treatment commonly in combination with the M184I substitution. The emtricitabine and lamivudine resistance-associated substitutions M184I or V and NRTI resistance-associated substitutions (K65R/N, A62V, D67N/G, K70E, Y115F, T215S/T, or K219E/R) emerged more frequently in rilpivirine resistance analysis subjects compared to efavirenz resistance analysis subjects (see Table 11).
NNRTI- and NRTI-resistance substitutions emerged less frequently in resistance analysis of viruses from subjects with baseline viral load of ≤100,000 copies/mL compared to viruses from subjects with baseline viral load of >100,000 copies/mL: 26% (14/54) compared to 74% (40/54) of NNRTI-resistance substitutions and 22% (11/50) compared to 78% (39/50) of NRTI-resistance substitutions. This difference was also observed for the individual emtricitabine/lamivudine and tenofovir resistance substitutions: 23% (11/47) compared to 77% (36/47) for M184I/V and 0% (0/8) compared to 100% (8/8) for K65R/N. Additionally, NNRTI- and NRTI-resistance substitutions emerged less frequently in the resistance analysis of viruses from subjects with baseline CD4+ cell counts ≥200 cells/mm3 compared to viruses from subjects with baseline CD4+ cell counts <200 cells/mm3: 37% (20/54) compared to 63% (34/54) of NNRTI-resistance substitutions and 28% (14/50) compared to 72% (36/50) of NRTI-resistance substitutions.
| C209 and C215 N=1368 |
||
|---|---|---|
| EDURANT + BR N=686 | Efavirenz + BR N=682 |
|
| BR=background regimen | ||
|
||
| Subjects who Qualified for Resistance Analysis | 15% (98/652) | 9% (56/604) |
| Subjects with Evaluable Post-Baseline Resistance Data | 87 | 43 |
| Emerging NNRTI Substitutions† | ||
| Any | 62% (54/87) | 53% (23/43) |
| V90I | 13% (11/87) | 2% (1/43) |
| K101E/P/T/Q | 20% (17/87) | 9% (4/43) |
| K103N | 1% (1/87) | 40% (17/43) |
| E138K/A/Q/G | 40% (35/87) | 2% (1/43) |
| E138K+ M184I‡ | 25% (22/87) | 0 |
| V179I/L/D | 6% (5/87) | 7% (3/43) |
| Y181C/I/S | 10% (9/87) | 2% (1/43) |
| V189I | 8% (7/87) | 2% (1/43) |
| H221Y | 9% (8/87) | 0 |
| Emerging NRTI Substitutions§ | ||
| Any | 57% (50/87) | 30% (13/43) |
| M184I/V | 54% (47/87) | 26% (11/43) |
| K65R/N | 9% (8/87) | 5% (2/43) |
| A62V, D67N/G, K70E, Y115F, T215S/T or K219E/R¶ | 21% (18/87) | 2% (1/43) |
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Treatment-Naïve Adult Subjects
The evidence of efficacy of EDURANT is based on the analyses of 48- and 96-week data from 2 randomized, double-blinded, active controlled, Phase 3 trials TMC278-C209 (ECHO) and TMC278-C215 (THRIVE) in antiretroviral treatment-naïve adults. Antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected subjects enrolled in the Phase 3 trials had a plasma HIV-1 RNA ≥5000 copies/mL and were screened for susceptibility to N(t)RTIs and for absence of specific NNRTI resistance-associated substitutions (RASs). The Phase 3 trials were identical in design, apart from the background regimen (BR). In TMC278-C209, the BR was fixed to the N(t)RTIs, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate plus emtricitabine. In TMC278-C215, the BR consisted of 2 investigator-selected N(t)RTIs: tenofovir disoproxil fumarate plus emtricitabine or zidovudine plus lamivudine or abacavir plus lamivudine. In both trials, randomization was stratified by screening viral load. In TMC278-C215, randomization was also stratified by N(t)RTI BR.
In the pooled analysis for TMC278-C209 and TMC278-C215, demographics and baseline characteristics were balanced between the EDURANT arm and the efavirenz arm. Table 12 displays selected demographic and baseline disease characteristics of the subjects in the EDURANT and efavirenz arms.
| Pooled Data from the Phase 3 TMC278-C209 and TMC278-C215 Trials | ||
|---|---|---|
| EDURANT + BR N=686 | Efavirenz + BR N=682 |
|
| BR=background regimen | ||
| Demographic Characteristics | ||
| Median Age, years (range) | 36 (18–78) | 36 (19–69) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 76% | 76% |
| Female | 24% | 24% |
| Race | ||
| White | 61% | 60% |
| Black/African American | 24% | 23% |
| Asian | 11% | 14% |
| Other | 2% | 2% |
| Not allowed to ask per local regulations | 1% | 1% |
| Baseline Disease Characteristics | ||
| Median Baseline Plasma HIV-1 RNA (range), log10 copies/mL | 5.0 (2–7) | 5.0 (3–7) |
| Percentage of Patients with Baseline Plasma Viral Load: | ||
| ≤100,000 | 54% | 48% |
| >100,000 to ≤500,000 | 36% | 40% |
| >500,000 | 10% | 12% |
| Median Baseline CD4+ Cell Count (range), cells/mm3 | 249 (1–888) | 260 (1–1137) |
| Percentage of Subjects with: | ||
| Hepatitis B/C Virus Co-infection | 7% | 10% |
| Percentage of Patients with the Following Background Regimens: | ||
| tenofovir disoproxil fumarate plus emtricitabine | 80% | 80% |
| zidovudine plus lamivudine | 15% | 15% |
| abacavir plus lamivudine | 5% | 5% |
Week 96 efficacy outcomes for subjects treated with EDURANT 25 mg once daily from the pooled analysis are shown in Table 13. The incidence of virologic failure was higher in the EDURANT arm than the efavirenz arm at Week 96. Virologic failures and discontinuations due to adverse events mostly occurred in the first 48 weeks of treatment. Regardless of HIV-1 RNA at the start of therapy, more EDURANT treated subjects with CD4+ cell count less than 200 cells/mm3 experienced virologic failure compared to EDURANT treated subjects with CD4+ cell count greater than or equal to 200 cells/mm3.
| EDURANT + BR N=686 | Efavirenz + BR N=682 |
|
|---|---|---|
| N=total number of subjects per treatment group; BR=background regimen. | ||
| Note: Analysis was based on the last observed viral load data within the Week 96 window (Week 90–103), respectively. | ||
|
||
| HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL* | 76% | 77% |
| HIV-1 RNA ≥50 copies/mL† | 16% | 10% |
| No virologic data at Week 96 window
Reasons | ||
| Discontinued study due to adverse event or death‡ | 4% | 8% |
| Discontinued study for other reasons and last available HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL (or missing)§ | 4% | 5% |
| Missing data during window but on study | <1% | <1% |
| HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL by Baseline HIV-1 RNA (copies/mL) | ||
| ≤100,000 | 82% | 78% |
| >100,000 | 70% | 75% |
| HIV-1 RNA ≥50 copies/mL† by Baseline HIV-1 RNA (copies/mL) | ||
| ≤100,000 | 9% | 8% |
| >100,000 | 24% | 11% |
| HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL by CD4+ cell count (cells/mm3) | ||
| <200 | 68% | 74% |
| ≥200 | 81% | 77% |
| HIV-1 RNA ≥50 copies/mL† by CD4+ cell count (cells/mm3) | ||
| <200 | 27% | 10% |
| ≥200 | 10% | 9% |
At Week 96, the mean CD4+ cell count increase from baseline was 228 cells/mm3 for EDURANT-treated subjects and 219 cells/mm3 for efavirenz-treated subjects in the pooled analysis of the TMC278-C209 and TMC278-C215 trials.
Study TMC278-C204 was a randomized, active-controlled, Phase 2b trial in antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected adult subjects consisting of 2 parts: an initial 96 weeks, partially-blinded dose-finding part [EDURANT doses blinded] followed by a long-term, open-label part. After Week 96, subjects randomized to one of the 3 doses of EDURANT were switched to EDURANT 25 mg once daily. Subjects in the control arm received efavirenz 600 mg once daily in addition to a BR in both parts of the study. The BR consisted of 2 investigator-selected N(t)RTIs: zidovudine plus lamivudine or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate plus emtricitabine.
Study TMC278-C204 enrolled 368 HIV-1-infected treatment-naïve adult subjects who had a plasma HIV-1 RNA ≥5000 copies/mL, previously received ≤2 weeks of treatment with an N(t)RTI or protease inhibitor, had no prior use of NNRTIs, and were screened for susceptibility to N(t)RTI and for absence of specific NNRTI RASs.
At 96 weeks, the proportion of subjects with <50 HIV-1 RNA copies/mL receiving EDURANT 25 mg (N=93) compared to subjects receiving efavirenz (N=89) was 76% and 71%, respectively. The mean increase from baseline in CD4+ counts was 146 cells/mm3 in subjects receiving EDURANT 25 mg and 160 cells/mm3 in subjects receiving efavirenz.
At 240 weeks, 60% (56/93) of subjects who originally received 25 mg once daily achieved HIV RNA <50 copies/mL compared to 57% (51/89) of subjects in the control group.
14.2 Virologically-Suppressed Adults Treated in Combination with Cabotegravir
The use of EDURANT in combination with VOCABRIA (cabotegravir) as an oral lead-in and in patients who miss planned injections with CABENUVA (cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension; rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension) was evaluated in two Phase 3 randomized, multicenter, active-controlled, parallel-arm, open-label, non-inferiority trials (Trial 201584: FLAIR [NCT02938520], Trial 201585: ATLAS [NCT2951052]), and one Phase 3b randomized, multicenter, parallel-group, open-label, non-inferiority trial (Trial 207966: ATLAS-2M [NCT03299049]) in subjects who were virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL). See full prescribing information for VOCABRIA and CABENUVA for additional information.
14.3 Treatment-Naïve Pediatric Subjects (12 to less than 18 years of age)
The pharmacokinetics, safety, tolerability and efficacy of EDURANT 25 mg once daily, in combination with an investigator-selected background regimen (BR) containing two NRTIs, was evaluated in trial TMC278-C213, a single-arm, open-label Phase 2 trial in antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 32 kg. Thirty six (36) subjects were enrolled in the trial to complete at least 48 weeks of treatment. The 36 subjects had a median age of 14.5 years (range: 12 to 17 years), and were 55.6% female, 88.9% Black and 11.1% Asian.
In the efficacy analysis, most subjects (75%; 28/36) had baseline HIV RNA <100,000 copies/mL. For these 28 subjects the median baseline plasma HIV-1 RNA was 44,250 (range: 2,060–92,600 copies/mL) and the median baseline CD4+ cell count was 445.5 cells/mm3 (range: 123 to 983 cells/mm3).
Among the subjects who had baseline HIV RNA ≤100,000, the proportion with HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL at Week 48 was 79% (22/28), versus 50.0% (4/8) in those with >100,000 copies/mL. The proportion of virologic failures among subjects with a baseline viral load ≤100,000 copies/mL was 21.4% (6/28), versus 37.5% (3/8) in those with >100,000 copies/mL. At Week 48, the mean increase in CD4+ cell count from baseline was 201.2 cells/mm3.
16. How is Edurant supplied
EDURANT® (rilpivirine) tablets are supplied as white to off-white, film-coated, round, biconvex, 6.4 mm tablets. Each tablet contains 27.5 mg of rilpivirine hydrochloride, which is equivalent to 25 mg of rilpivirine. Each tablet is debossed with "TMC" on one side and "25" on the other side.
EDURANT tablets are packaged in bottles in the following configuration: 25 mg tablets-bottles of 30 (NDC 59676-278-01).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised 10/2022 | |||
| PATIENT INFORMATION EDURANT® (ee' dur ant) (rilpivirine) tablets, for oral use |
||||
| What is EDURANT?
EDURANT is a prescription medicine that is used with
HIV-1 is the virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). If you take EDURANT in combination with oral VOCABRIA (cabotegravir), you should also read the Patient Information that comes with oral VOCABRIA (cabotegravir). It is not known if EDURANT is safe and effective in children less than 12 years of age or who weigh less than 77 lbs (35 kg). |
||||
| Do not take EDURANT if you are taking any of the following medicines: | ||||
|
|
|||
Before taking EDURANT, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | ||||
| Some medicines interact with EDURANT. Keep a list of your medicines to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with EDURANT. Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take EDURANT with other medicines. |
||||
How should I take EDURANT?
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of EDURANT? | ||||
| EDURANT can cause serious side effects including: | ||||
|
||||
|
|
|||
|
||||
|
|
|||
|
||||
| The most common side effects of EDURANT include depression, headache, trouble sleeping (insomnia) and rash. These are not all the possible side effects with EDURANT. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||
How should I store EDURANT?
|
||||
| Keep EDURANT and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of EDURANT. | ||||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use EDURANT for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give EDURANT to other people even if they have the same condition you have. It may harm them. | ||||
| You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about EDURANT that is written for health professionals. | ||||
| What are the ingredients in EDURANT? | ||||
| Active ingredient: rilpivirine. | ||||
| Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polysorbate 20, povidone K30 and silicified microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet coating contains hypromellose 2910 6 mPa.s, lactose monohydrate, PEG 3000, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. | ||||
| Manufactured by: Janssen-Cilag SpA, Latina, Italy Manufactured for: Janssen Therapeutics, Division of Janssen Products, LP, Titusville NJ 08560 EDURANT® is a registered trademark of Johnson & Johnson © 2011 Janssen Products, LP For more information go to www.EDURANT.com or call 1-800-526-7736 |
||||
| EDURANT
rilpivirine hydrochloride tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Products, LP (804684207) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen-Cilag SpA | 542797928 | MANUFACTURE(59676-278) , ANALYSIS(59676-278) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica NV | 400345889 | API MANUFACTURE(59676-278) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutical Sciences Unlimited Company | 985639841 | API MANUFACTURE(59676-278) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| AndersonBrecon Inc | 053217022 | LABEL(59676-278) , PACK(59676-278) | |





