Drug Detail:Emtriva (Emtricitabine [ em-trye-sye-ta-been ])
Drug Class: Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)
Highlights of Prescribing Information
EMTRIVA ® (emtricitabine) capsule, for oral use
EMTRIVA ® (emtricitabine) oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 2003
WARNING: POSTTREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Severe acute exacerbations of Hepatitis B (HBV) have been reported in patients coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV who have discontinued EMTRIVA. Hepatic function should be monitored closely in patients coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV who discontinue EMTRIVA. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted. (5.1)
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration | |
| Testing Prior to Initiation of Treatment with EMTRIVA (2.1) | 12/2018 |
| Warnings and Precautions | |
| Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV (5.1) | 12/2018 |
| Coadministration with Related Products | Removed 12/2018 |
Indications and Usage for Emtriva
EMTRIVA, a nucleoside analog HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor, is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. (1)
Emtriva Dosage and Administration
- Testing: Prior to or when initiating EMTRIVA test for hepatitis B virus infection. (2.1)
- EMTRIVA may be taken without regard to food. (2.2)
- Adult Patients (18 years of age and older) (2.3):
- EMTRIVA capsules: One 200 mg capsule administered once daily orally.
- EMTRIVA oral solution: 240 mg (24 mL) administered once daily orally.
- Pediatric Patients (0–3 months of age) (2.4):
- EMTRIVA oral solution: 3 mg/kg administered once daily orally.
- Pediatric Patients (3 months through 17 years of age) (2.5):
- EMTRIVA capsules: For children weighing more than 33 kg who can swallow an intact capsule, one 200 mg capsule administered once daily orally.
- EMTRIVA oral solution: 6 mg/kg up to a maximum of 240 mg (24 mL) administered once daily orally.
- Dose interval adjustment in adult patients with renal impairment (2.6):
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation | ≥50 mL/min | 30–49 mL/min | 15–29 mL/min | <15 mL/min or on hemodialysis* |
|
||||
| Capsule (200 mg) | 200 mg every 24 hours | 200 mg every 48 hours | 200 mg every 72 hours | 200 mg every 96 hours |
| Oral Solution (10 mg/mL) | 240 mg every 24 hours (24 mL) | 120 mg every 24 hours (12 mL) | 80 mg every 24 hours (8 mL) | 60 mg every 24 hours (6 mL) |
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Capsules: 200 mg (3)
- Oral solution: 10 mg per mL (3)
Contraindications
EMTRIVA is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to any of the components of the products. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Immune reconstitution syndrome: May necessitate further evaluation and treatment. (5.2)
- Lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis: Discontinue treatment in patients who develop symptoms or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity. (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥10%) are headache, diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, dizziness, depression, insomnia, abnormal dreams, rash, abdominal pain, asthenia, increased cough, and rhinitis. Skin hyperpigmentation was very common (≥10%) in pediatric patients. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gilead Sciences, Inc. at 1-800-GILEAD-5 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended. (8.2)
- Pediatrics: Dose adjustment based on age and weight. (2.4, 2.5, 12.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 12/2018
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: POSTTREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B (HBV) have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued EMTRIVA. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and discontinue EMTRIVA. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Emtriva
EMTRIVA® is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection.
2. Emtriva Dosage and Administration
2.1 Testing Prior to Initiation of Treatment with EMTRIVA
Prior to or when initiating EMTRIVA, test patients for hepatitis B virus infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
EMTRIVA is taken by mouth once daily and may be taken without regard to food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Recommended Dosage in Adult Patients (18 years of age and older)
EMTRIVA capsules: One 200 mg capsule administered once daily orally.
EMTRIVA oral solution: 240 mg (24 mL) administered once daily orally.
2.4 Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients (0–3 months of age)
EMTRIVA oral solution: 3 mg per kg administered once daily orally.
2.5 Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients (3 months through 17 years of age)
EMTRIVA oral solution: 6 mg per kg up to a maximum of 240 mg (24 mL) administered once daily orally.
EMTRIVA capsules: For pediatric patients weighing more than 33 kg who can swallow an intact capsule, one 200 mg capsule administered once daily orally.
2.6 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment
Table 1 provides dosage interval adjustment for patients with renal impairment. No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 50–80 mL/min). The safety and effectiveness of dose adjustment recommendations in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance below 50 mL/min) have not been clinically evaluated. Therefore, clinical response to treatment and renal function should be closely monitored in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation | ≥50 mL/min | 30–49 mL/min | 15–29 mL/min | <15 mL/min or on hemodialysis* |
|
||||
| Capsule (200 mg) | 200 mg every 24 hours | 200 mg every 48 hours | 200 mg every 72 hours | 200 mg every 96 hours |
| Oral Solution (10 mg/mL) | 240 mg every 24 hours (24 mL) | 120 mg every 24 hours (12 mL) | 80 mg every 24 hours (8 mL) | 60 mg every 24 hours (6 mL) |
There are insufficient data available to make dosage recommendations in pediatric patients with renal impairment.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
EMTRIVA is available as capsules or as an oral solution.
- 200 mg Capsules: 200 mg of emtricitabine (FTC): size 1 hard gelatin capsules with a blue cap and white body, printed with "200 mg" in black on the cap and with "GILEAD" and the corporate logo in black on the body.
- Oral solution: clear, orange to dark orange liquid containing 10 mg of FTC per mL.
4. Contraindications
EMTRIVA is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to any of the components of the products.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV
All patients should be tested for the presence of chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) before or when initiating EMTRIVA [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B (e.g., liver decompensation and liver failure) have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued EMTRIVA. Patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV who discontinue EMTRIVA should be closely monitored with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months after stopping treatment. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted, especially in patients with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis, since posttreatment exacerbation of hepatitis may lead to hepatic decompensation and liver failure.
5.2 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including EMTRIVA. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia [PCP], or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
5.3 Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including FTC, alone or in combination with other antiretrovirals. Treatment with EMTRIVA should be suspended in any patient who develops clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity (which may include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked transaminase elevations).
5.4 Dose Adjustment in Patients with New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Emtricitabine is principally eliminated by the kidney. Reduction of the dosage of EMTRIVA is recommended for patients with impaired renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Immune Reconstitution Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
7. Drug Interactions
The potential for drug interactions with EMTRIVA has been studied in combination with AZT, indinavir, d4T, famciclovir, and tenofovir DF (TDF). There were no clinically significant drug interactions for any of these drugs. Drug interactions trials are described elsewhere in the labeling [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of FTC in patients between 3 months and 21 years of age is supported by data from three open-label, nonrandomized clinical trials in which FTC was administered to 169 HIV-1 infected treatment-naïve and experienced (defined as virologically suppressed on a 3TC containing regimen for which FTC was substituted for 3TC) subjects [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
The pharmacokinetics of FTC were studied in 20 neonates born to HIV-1 positive mothers [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]. All neonates were HIV-1 negative at the end of the trial; the efficacy of FTC in preventing or treating HIV-1 could not be determined.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of EMTRIVA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for the elderly patient should be cautious, keeping in mind the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
10. Overdosage
If overdose occurs, the patient should be monitored for evidence of toxicity, and standard supportive treatment applied as necessary.
Hemodialysis treatment removes approximately 30% of the FTC dose over a 3-hour dialysis period starting within 1.5 hours of FTC dosing (blood flow rate of 400 mL/min and a dialysate flow rate of 600 mL/min). It is not known whether FTC can be removed by peritoneal dialysis.
11. Emtriva Description
EMTRIVA is the brand name of emtricitabine (FTC), a synthetic nucleoside analog with activity against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase.
The chemical name of FTC is 5-fluoro-1-(2R,5S)-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]cytosine. Emtricitabine is the (-) enantiomer of a thio analog of cytidine, which differs from other cytidine analogs in that it has a fluorine in the 5-position.
It has a molecular formula of C8H10FN3O3S and a molecular weight of 247.24. It has the following structural formula:
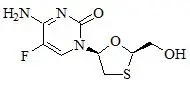
Emtricitabine is a white to off-white powder with a solubility of approximately 112 mg/mL in water at 25 °C. The partition coefficient (log P) for FTC is −0.43 and the pKa is 2.65.
EMTRIVA is available as capsules or as an oral solution.
EMTRIVA capsules are for oral administration. Each capsule contains 200 mg of FTC and the inactive ingredients crospovidone, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, titanium dioxide, gelatin, and FD&C blue No. 2.
EMTRIVA oral solution is for oral administration. One milliliter (1 mL) of EMTRIVA oral solution contains 10 mg of FTC in an aqueous solution with the following inactive ingredients: cotton candy flavor, FD&C yellow No. 6, edetate disodium, methylparaben and propylparaben (added as preservatives), sodium phosphate (monobasic), propylene glycol, water, and xylitol (added as a sweetener). Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid may be used to adjust pH.
12. Emtriva - Clinical Pharmacology
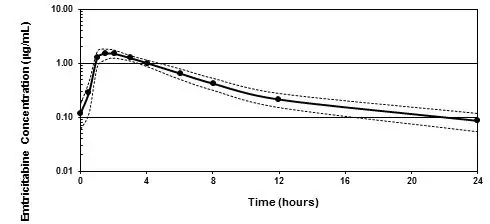
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In long-term oral carcinogenicity studies of FTC, no drug-related increases in tumor incidence were found in mice at doses up to 750 mg/kg/day (26 times the human systemic exposure at the therapeutic dose of 200 mg/day) or in rats at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day (31 times the human systemic exposure at the therapeutic dose).
Emtricitabine was not genotoxic in the reverse mutation bacterial test (Ames test) or mouse lymphoma or mouse micronucleus assays.
Emtricitabine did not affect fertility in male rats at approximately 140-fold or in male and female mice at approximately 60-fold higher exposures (AUC) than in humans given the recommended 200 mg daily dose. Fertility was normal in the offspring of mice exposed daily from before birth (in utero) through sexual maturity at daily exposures (AUC) of approximately 60-fold higher than human exposures at the recommended 200 mg daily dose.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Overview of Clinical Trials
The efficacy and safety of EMTRIVA were evaluated in the trials summarized in Table 10.
| Trial | Population | Trial Arms (N)* | Timepoint (Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Trial 934†
(NCT00112047) | HIV-1 treatment-naïve adults | EMTRIVA+TDF+EFV (227) AZT/3TC+EFV (229) | 144 |
| Trial 301A‡
(NCT00006208) | EMTRIVA+didanosine+EFV (286) d4T+didanosine+EFV (285) | 48 | |
| Trial 303†
(NCT00002416) | HIV-1 treatment-experienced adults | EMTRIVA+AZT/d4T+NNRTI/PI (294) 3TC+AZT/d4T+NNRTI/PI (146) | 48 |
| Trial 202§
(NCT00016718) | HIV-1 treatment-naïve and experienced pediatrics | EMTRIVA+didanosine+EFV (43) | 48 |
| Trial 203§
(NCT00743340) | EMTRIVA+d4T+lopinavir/ritonavir (116) | 48 | |
| Trial 211§
(NCT00642291) | EMTRIVA+didanosine+EFV (16) | 48 | |
14.4 Clinical Trial Results in Pediatrics
In three open-label, nonrandomized clinical trials, FTC was administered to 169 HIV-1 infected treatment-naïve and experienced (defined as virologically suppressed on a 3TC-containing regimen for which FTC was substituted for 3TC) subjects between 3 months and 21 years of age. Subjects received once-daily EMTRIVA oral solution (6 mg/kg to a maximum of 240 mg/day) or EMTRIVA capsules (a single 200 mg capsule once daily) in combination with at least two other antiretroviral agents.
Subjects had a mean age of 7.9 years (range 0.3–21); 49% were male, 15% Caucasian, 61% Black, and 24% Hispanic. Subjects had a median baseline HIV-1 RNA of 4.6 log10 copies/mL (range 1.7–6.4) and a mean baseline CD4+ cell count of 745 cells/mm3 (range 2–2650). Through 48 weeks of therapy, the overall proportion of subjects who achieved and sustained an HIV-1 RNA <400 copies/mL was 86%, and <50 copies/mL was 73%. The mean increase from baseline in CD4+ cell count was 232 cells/mm3 (−945, +1512). The adverse reaction profile observed during these clinical trials was similar to that of adult subjects, with the exception of the occurrence of anemia and higher frequency of hyperpigmentation in children [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The pharmacokinetics of FTC were studied in 20 neonates born to HIV-1 positive mothers. Each mother received prenatal and intrapartum combination antiretroviral therapy. Neonates received up to 6 weeks of AZT prophylactically after birth. The neonates were administered two short courses of FTC oral solution (each 3 mg/kg once daily × 4 days) during the first 3 months of life. FTC exposures in neonates were similar to the exposures achieved in subjects aged 3 months to 17 years [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. During the two short dosing periods on FTC, there were no safety issues identified in the treated neonates. All neonates were HIV-1 negative at the end of the trial; the efficacy of FTC in preventing or treating HIV-1 could not be determined.
16. How is Emtriva supplied
EMTRIVA capsules are available in bottles containing 30 capsules with child-resistant closure as follows:
200 mg of FTC capsules are size 1 hard gelatin capsules with a blue cap and white body and printed with "200 mg" in black on the cap and with "GILEAD" and the corporate logo in black on the body (NDC 61958–0601–1).
- Store EMTRIVA capsules at 25 °C (77 °F); excursions permitted to 15–30 °C (59–86 °F).
- Dispense only in original container. Keep container tightly closed.
EMTRIVA oral solution is a clear, orange to dark orange liquid containing 10 mg/mL of FTC and is available in unit of use plastic, amber bottles containing 170 mL of oral solution closed with a child resistant closure, and packaged with a marked dosing cup (NDC 61958–0602–1).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: December/2018 | |
|
Patient Information |
||
|
What is the most important information I should know about EMTRIVA? EMTRIVA can cause serious side effects, including:
For more information about side effects, see the section "What are the possible side effects of EMTRIVA?" |
||
|
What is EMTRIVA? EMTRIVA is a prescription medicine used in combination with other antiretroviral medicines to treat Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) infection. HIV-1 is the virus that causes Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). |
||
|
Who should not take EMTRIVA? Do not take EMTRIVA if you are allergic to emtricitabine or any of the ingredients in EMTRIVA. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in EMTRIVA. |
||
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking EMTRIVA? Before taking EMTRIVA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines may interact with EMTRIVA. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with EMTRIVA. Do not start a new medicine without telling your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take EMTRIVA with other medicines. |
||
|
How should I take EMTRIVA?
|
||
|
What are the possible side effects of EMTRIVA? EMTRIVA may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
The most common side effects of EMTRIVA include: |
||
|
|
|
|
Skin discoloration in children may also happen with EMTRIVA. These are not all the possible side effects of EMTRIVA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
|
How should I store EMTRIVA?
Keep EMTRIVA and all other medicines out of reach of children. |
||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of EMTRIVA. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use EMTRIVA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give EMTRIVA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about EMTRIVA that is written for health professionals. |
||
|
What are the ingredients of EMTRIVA? Active Ingredient: emtricitabine Inactive Ingredients: EMTRIVA capsules: crospovidone, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, titanium dioxide, gelatin, and FD&C blue No. 2. EMTRIVA oral solution: cotton candy flavor, FD&C yellow No. 6, edetate disodium, methylparaben and propylparaben, sodium phosphate (monobasic), propylene glycol, water, and xylitol. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid may be used to adjust pH. Manufactured for and distributed by: |
||
| EMTRIVA
emtricitabine capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| EMTRIVA
emtricitabine solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Gilead Sciences, Inc. (185049848) |