Drug Detail:Esbriet (Pirfenidone [ pir-fen-i-done ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous uncategorized agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ESBRIET® (pirfenidone) capsules and film-coated tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2014
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration (2.3) | 02/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.3) | 02/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Esbriet
ESBRIET is a pyridone indicated for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). (1)
Esbriet Dosage and Administration
- Take with food.
- Recommended dosage: 801 mg three times daily (2403 mg/day). (2)
- Upon initiation of treatment, titrate to the full dosage of 2403 mg/day over a 14-day period as follows:
| Treatment days | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Days 1 through 7 | 267 mg three times daily (801 mg/day) |
| Days 8 through 14 | 534 mg three times daily (1602 mg/day) |
| Days 15 onward | 801 mg three times daily (2403 mg/day) |
- Consider temporary dosage reduction, treatment interruption, or discontinuation for management of adverse reactions. (2.3, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4)
- Prior to treatment, conduct liver function tests. (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Capsules: 267 mg (3)
- Tablets: 267 mg, 801 mg (3)
Contraindications
None (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Elevated liver enzymes and drug-induced liver injury: ALT, AST, and bilirubin elevations have occurred with ESBRIET including cases of drug-induced liver injury. In the postmarketing setting, non-serious and serious cases of drug-induced liver injury, including severe liver injury with fatal outcomes, have been reported. Monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin before and during treatment. Temporary dosage reductions or discontinuations may be required. (2.1, 5.1)
- Photosensitivity and rash: Photosensitivity and rash have been noted with ESBRIET. Avoid exposure to sunlight and sunlamps. Wear sunscreen and protective clothing daily. Temporary dosage reductions or discontinuations may be required. (5.2)
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCAR): Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and drug reactions with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) have been reported in association with the use of ESBRIET in the postmarketing setting. Interrupt ESBRIET in case of signs or symptoms of SCAR. Permanently discontinue ESBRIET if a SCAR is confirmed. (5.3)
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, gastro-esophageal reflux disease, and abdominal pain have occurred with ESBRIET. Temporary dosage reductions or discontinuations may be required. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) are nausea, rash, abdominal pain, upper respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, fatigue, headache, decreased appetite, dyspepsia, dizziness, vomiting, gastro-esophageal reflux disease, sinusitis, insomnia, weight decreased, and arthralgia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genentech at 1-888-835-2555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Moderate (e.g., ciprofloxacin) and strong inhibitors of CYP1A2 (e.g., fluvoxamine) increase systemic exposure of ESBRIET and may alter the adverse reaction profile of ESBRIET. Discontinue fluvoxamine prior to administration of ESBRIET or reduce to 267 mg three times a day . Consider dosage reduction with use of ciprofloxacin. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
- Hepatic Impairment: Monitor for adverse reactions and consider dosage modification or discontinuation of ESBRIET as needed. ESBRIET is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (8.6, 12.3)
- Renal Impairment: Monitor for adverse reactions and consider dosage modification or discontinuation of ESBRIET as needed. ESBRIET is not recommended for use in patients with end stage renal disease on dialysis. (8.7, 12.3)
- Smokers: Decreased exposure has been noted in smokers which may alter the efficacy profile of ESBRIET. (8.8)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2023
Related/similar drugs
Ofev, nintedanib, pirfenidone, interferon gamma-1b, ActimmuneFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Esbriet
ESBRIET is indicated for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
2. Esbriet Dosage and Administration
2.1 Testing Prior to ESBRIET Administration
Conduct liver function tests prior to initiating treatment with ESBRIET [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended daily maintenance dosage of ESBRIET is 801 mg three times daily for a total of 2403 mg/day. Doses should be taken with food at the same time each day.
Upon initiation of treatment, titrate to the full dosage of 2403 mg/day over a 14-day period as follows:
| Treatment days | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Days 1 through 7 | 267 mg three times daily (801 mg/day) |
| Days 8 through 14 | 534 mg three times daily (1602 mg/day) |
| Days 15 onward | 801 mg three times daily (2403 mg/day) |
Dosages above 2403 mg/day are not recommended for any patient. Patients should not take 2 doses at the same time to make up for a missed dose. Patients should not take more than 3 doses per day.
2.3 Dosage Modifications due to Adverse Reactions
Patients who miss 14 or more days of ESBRIET should re-initiate treatment by undergoing the initial 2-week titration regimen up to the full maintenance dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. For treatment interruption of less than 14 days, the dosage prior to the interruption can be resumed.
If patients experience significant adverse reactions (i.e., gastrointestinal, photosensitivity reaction or rash, severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR)), consider temporary dosage reductions or interruptions of ESBRIET to allow for resolution of symptoms. If a SCAR is confirmed, permanently discontinue ESBRIET [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules: 267 mg, white to off-white, hard gelatin capsules printed with "PFD 267 mg" on the cap of the capsule in brown ink.
Film-coated tablets: oval, biconvex, debossed with "PFD", containing 267 mg (yellow) and 801 mg (brown) pirfenidone
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Elevated Liver Enzymes and Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Cases of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) have been observed with ESBRIET. In the postmarketing period, non-serious and serious cases of DILI, including severe liver injury with fatal outcome, have been reported. Patients treated with Esbriet 2403 mg/day in three Phase 3 trials had a higher incidence of elevations in ALT or AST ≥3× ULN than placebo patients (3.7% vs 0.8%, respectively). Elevations ≥10×ULN in ALT or AST occurred in 0.3% of patients in the Esbriet 2403 mg/day group and in 0.2% of patients in the placebo group. Increases in ALT and AST ≥3× ULN were reversible with dose modification or treatment discontinuation.
Conduct liver function tests (ALT, AST, and bilirubin) prior to the initiation of therapy with ESBRIET, monthly for the first 6 months, every 3 months thereafter, and as clinically indicated. Measure liver function tests promptly in patients who report symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine, or jaundice. Dosage modification or interruption may be necessary for liver enzyme elevations [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3)].
5.2 Photosensitivity Reaction or Rash
Patients treated with ESBRIET 2403 mg/day in the three Phase 3 studies had a higher incidence of photosensitivity reactions (9%) compared with patients treated with placebo (1%). The majority of the photosensitivity reactions occurred during the initial 6 months. Instruct patients to avoid or minimize exposure to sunlight (including sunlamps), to use a sunblock (SPF 50 or higher), and to wear clothing that protects against sun exposure. Additionally, instruct patients to avoid concomitant medications known to cause photosensitivity. Dosage reduction or discontinuation may be necessary in some cases of photosensitivity reaction or rash [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), have been reported in association with the use of ESBRIET in the postmarketing setting. If signs or symptoms of SCAR occur, interrupt ESBRIET treatment until the etiology of the reaction has been determined. Consultation with a dermatologist is recommended. If a SCAR is confirmed, permanently discontinue ESBRIET.
5.4 Gastrointestinal Disorders
In the clinical studies, gastrointestinal events of nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, vomiting, gastro-esophageal reflux disease, and abdominal pain were more frequently reported by patients in the ESBRIET treatment groups than in those taking placebo. Dosage reduction or interruption for gastrointestinal events was required in 18.5% of patients in the 2403 mg/day group, as compared to 5.8% of patients in the placebo group; 2.2% of patients in the ESBRIET 2403 mg/day group discontinued treatment due to a gastrointestinal event, as compared to 1.0% in the placebo group. The most common (>2%) gastrointestinal events that led to dosage reduction or interruption were nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and dyspepsia. The incidence of gastrointestinal events was highest early in the course of treatment (with highest incidence occurring during the initial 3 months) and decreased over time. Dosage modifications may be necessary in some cases of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Liver Enzyme Elevations and Drug-Induced Liver Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Photosensitivity Reaction or Rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Gastrointestinal Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of pirfenidone has been evaluated in more than 1400 subjects with over 170 subjects exposed to pirfenidone for more than 5 years in clinical trials.
ESBRIET was studied in 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Studies 1, 2, and 3) in which a total of 623 patients received 2403 mg/day of ESBRIET and 624 patients received placebo. Subjects ages ranged from 40 to 80 years (mean age of 67 years). Most patients were male (74%) and Caucasian (95%). The mean duration of exposure to ESBRIET was 62 weeks (range: 2 to 118 weeks) in these 3 trials.
At the recommended dosage of 2403 mg/day, 14.6% of patients on ESBRIET compared to 9.6% on placebo permanently discontinued treatment because of an adverse event. The most common (>1%) adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were rash and nausea. The most common (>3%) adverse reactions leading to dosage reduction or interruption were rash, nausea, diarrhea, and photosensitivity reaction.
The most common adverse reactions with an incidence of ≥10% and more frequent in the ESBRIET than placebo treatment group are listed in Table 2.
| Adverse Reaction | % of Patients (0 to 118 Weeks) | |
|---|---|---|
| ESBRIET 2403 mg/day (N = 623) | Placebo (N = 624) |
|
|
||
| Nausea | 36% | 16% |
| Rash | 30% | 10% |
| Abdominal Pain* | 24% | 15% |
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infection | 27% | 25% |
| Diarrhea | 26% | 20% |
| Fatigue | 26% | 19% |
| Headache | 22% | 19% |
| Decreased Appetite | 21% | 8% |
| Dyspepsia | 19% | 7% |
| Dizziness | 18% | 11% |
| Vomiting | 13% | 6% |
| Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease | 11% | 7% |
| Sinusitis | 11% | 10% |
| Insomnia | 10% | 7% |
| Weight Decreased | 10% | 5% |
| Arthralgia | 10% | 7% |
Adverse reactions occurring in ≥5 to <10% of ESBRIET-treated patients and more commonly than placebo are photosensitivity reaction (9% vs. 1%), pruritus (8% vs. 5%), asthenia (6% vs. 4%), dysgeusia (6% vs. 2%), and non-cardiac chest pain (5% vs. 4%).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions identified from clinical trials the following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ESBRIET. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Agranulocytosis
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Drug-induced liver injury
Immune System Disorders: Angioedema
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCAR)
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
Pirfenidone is metabolized primarily (70 to 80%) via CYP1A2 with minor contributions from other CYP isoenzymes including CYP2C9, 2C19, 2D6 and 2E1.
7.2 CYP1A2 Inducers
The concomitant use of ESBRIET and a CYP1A2 inducer may decrease the exposure of ESBRIET and this may lead to loss of efficacy. Therefore, discontinue use of strong CYP1A2 inducers prior to ESBRIET treatment and avoid the concomitant use of ESBRIET and a strong CYP1A2 inducer [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ESBRIET in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in the clinical studies receiving ESBRIET, 714 (67%) were 65 years old and over, while 231 (22%) were 75 years old and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between older and younger patients. No dosage adjustment is required based upon age.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
ESBRIET should be used with caution in patients with mild (Child Pugh Class A) to moderate (Child Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. Monitor for adverse reactions and consider dosage modification or discontinuation of ESBRIET as needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
The safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of ESBRIET have not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment. ESBRIET is not recommended for use in patients with severe (Child Pugh Class C) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
ESBRIET should be used with caution in patients with mild (CLcr 50–80 mL/min), moderate (CLcr 30–50 mL/min), or severe (CLcr less than 30 mL/min) renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Monitor for adverse reactions and consider dosage modification or discontinuation of ESBRIET as needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. The safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of ESBRIET have not been studied in patients with end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis. Use of ESBRIET in patients with end-stage renal diseases requiring dialysis is not recommended.
10. Overdosage
There is limited clinical experience with overdosage. Multiple dosages of ESBRIET up to a maximum tolerated dose of 4005 mg per day were administered as five 267 mg capsules three times daily to healthy adult volunteers over a 12-day dose escalation.
In the event of a suspected overdosage, appropriate supportive medical care should be provided, including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient.
11. Esbriet Description
ESBRIET belongs to the chemical class of pyridone. ESBRIET is available as a white to off-white hard gelatin capsule containing 267 mg of pirfenidone for oral administration, or, as film-coated tablets containing 267 mg (yellow) and 801 mg (brown) pirfenidone.
Pirfenidone has a molecular formula of C12H11NO and a molecular weight of 185.23. Pirfenidone has the following structural formula, which has been referred to as 5-methyl-1-phenyl-2-1(H)-pyridone or 5-methyl-1-phenyl-2-(1H)-pyridone.
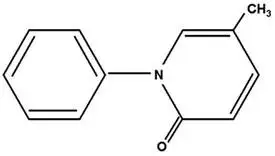
Pirfenidone is a white to pale yellow, non-hygroscopic powder. It is more soluble in methanol, ethyl alcohol, acetone and chloroform than in water and 1.0 N HCl. The melting point is approximately 109°C.
ESBRIET capsule contains pirfenidone and the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, povidone, and magnesium stearate.
In addition, the capsule shell contains gelatin and titanium dioxide. The capsule brown printing ink includes shellac, iron oxide black, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, propylene glycol, ammonium hydroxide.
ESBRIET tablets contain pirfenidone and the following inactive ingredients: Microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal anhydrous silica, povidone, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, macrogol (polyethylene glycol), talc, and iron oxide.
12. Esbriet - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of pirfenidone in the treatment of IPF has not been established.
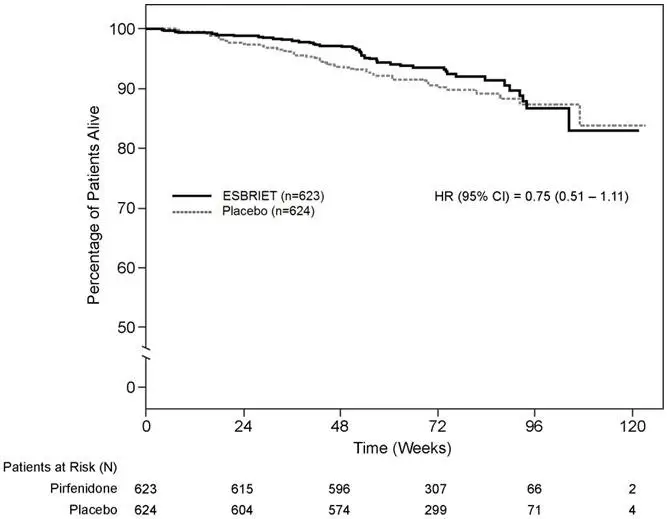
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of ESBRIET was evaluated in patients with IPF in three phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials (Studies 1, 2, and 3).
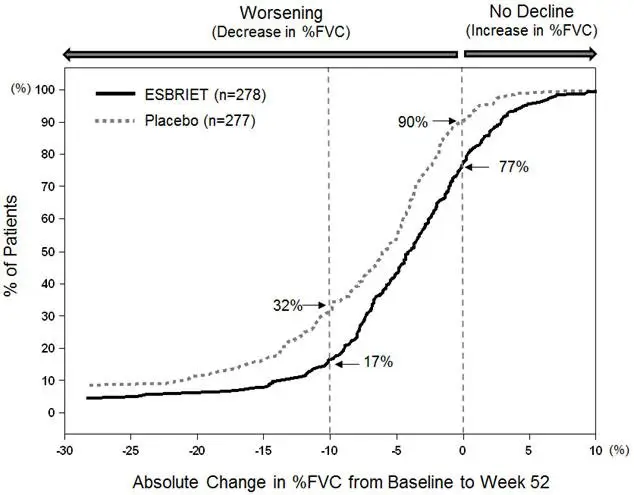
Study 1 was a 52-week trial comparing ESBRIET 2403 mg/day (n=278) versus placebo (n=277) in patients with IPF. Study 2 and Study 3 were nearly identical to each other in design, with few exceptions, including an intermediate dose treatment arm in Study 2. Study 2 compared treatment with either ESBRIET 2403 mg/day (n=174) or ESBRIET 1197 mg/day (n=87) to placebo (n=174), while Study 3 compared ESBRIET 2403 mg/day (n=171) to placebo (n=173). Study drug was administered three times daily with food for a minimum of 72 weeks. Patients continued on treatment until the last patient completed 72 weeks of treatment, which included observations to approximately 120 weeks of study treatment. The primary endpoint was the change in percent predicted forced vital capacity (%FVC) from baseline to study end, measured at 52 weeks in Study 1, and at 72 weeks in Studies 2 and 3.
Studies 1, 2 and 3 enrolled adult patients who had a clinical and radiographic diagnosis of IPF (with or without accompanying surgical lung biopsy), without evidence or suspicion of an alternative diagnosis for interstitial lung disease. Eligible patients were to have %FVC greater than or equal to 50% at baseline and a percent predicted diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (%DLCO) greater than or equal to 30% (Study 1) or 35% (Studies 2 and 3) at baseline. In all three trials, over 80% of patients completed study treatment.
A total of 1247 patients with IPF were randomized to receive ESBRIET 2403 mg/day (n=623) or placebo (n=624) in these three trials. Baseline characteristics were generally balanced across treatment groups. The study population ranged from 40 to 80 years of age (mean age 67 years). Most patients were male (74%), white (95%), and current or former smokers (65%). Approximately 93% of patients met criteria for definite IPF on high resolution computed tomography (HRCT). Baseline mean %FVC and %DLCO were 72% and 46%, respectively. Approximately 15% subjects discontinued from each treatment group.
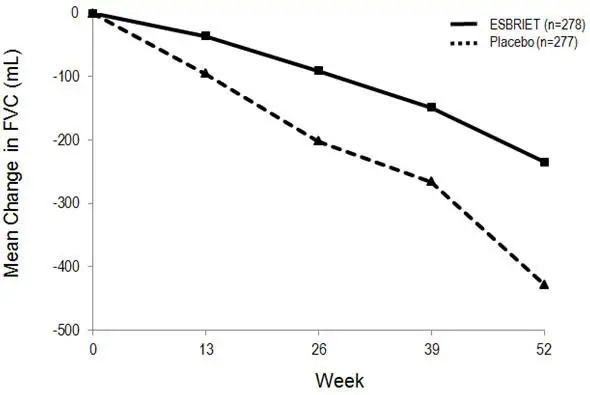
Mean Change from Baseline in FVC (mL)
In Study 1, a reduction in the mean decline in FVC (in mL) was observed in patients receiving ESBRIET 2403 mg/day (-235 mL) compared to placebo (-428 mL) (mean treatment difference 193 mL) at Week 52 (see Figure 2). In Study 2, a reduction in the decline in FVC volume was also observed in patients receiving ESBRIET 2403 mg/day compared with placebo (mean treatment difference 157 mL) at Week 72. There was no statistically significant difference in decline in FVC volume seen in Study 3.
Figure 2. Mean Change from Baseline in Forced Vital Capacity (Study 1)
16. How is Esbriet supplied
ESBRIET white to off-white hard gelatin capsules contain 267 mg of pirfenidone. The cap of the capsule is printed with "PFD 267 mg" in brown ink. The capsule is supplied either in a bottle, a 14-day titration blister pack or a 4-week maintenance blister pack.
ESBRIET film-coated tablets are oval, biconvex, debossed with "PFD", containing 267 mg (yellow) and 801 mg (brown) pirfenidone. The film-coated tablets are supplied in bottles.
ESBRIET capsules:
- NDC 50242-121-01, bottle for a 30-day supply containing 270 capsules and closed with a child-resistant closure
- NDC 50242-121-02, 14-day titration blister pack, carton containing a total of 63 capsules in two blister cards – a Week 1 blister card containing 21 capsules (1 capsule per blister well) and a Week 2 blister card containing 42 capsules (2 capsules per blister well)
- NDC 50242-121-03, 4-week maintenance blister pack, carton containing a total of 252 capsules in four blister cards each with 63 capsules (3 capsules per blister well)
ESBRIET film-coated tablets:
- NDC 50242-122-05, carton containing 3 bottles, each containing ninety 267 mg tablets (270 tablets total) with a child-resistant closure
- NDC 50242-122-06, carton containing 1 bottle containing 270 tablets, 267 mg each, with a child-resistant closure
- NDC 50242-123-01, carton containing 1 bottle containing ninety 801 mg tablets, with a child-resistant closure
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| Patient Information ESBRIET (es-BREE-et) (pirfenidone) capsules and film-coated tablets |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Revised: February 2023 | |||||
What is ESBRIET?
|
||||||
Before you take ESBRIET, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. |
||||||
How should I take ESBRIET?
|
||||||
| Esbriet 267 mg Dosing Schedule | ||||||
| Week | Morning (Breakfast) | Afternoon (Lunch) | Evening (Dinner) | Total Pills Each Day | ||
| Days 1-7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Days 8-14 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | ||
| Days 15 onward | 3 | 3 | 3 | 9 | ||
|
||||||
| Esbriet 801 mg Dosing Schedule | ||||||
| Week | Morning (Breakfast) | Afternoon (Lunch) | Evening (Dinner) | Total Pills Each Day | ||
| Days 15 onward | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||
|
||||||
|
What should I avoid while taking ESBRIET?
|
||||||
| What are the possible side effects of ESBRIET?
ESBRIET may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effects of ESBRIET include feeling tired, insomnia, upper respiratory tract infections, sinusitis, headache, dizziness, decreased weight and decreased or loss of appetite. These are not all the possible side effects of ESBRIET. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||||
How should I store ESBRIET?
Safely throw away any ESBRIET that is out of date or no longer needed. Keep ESBRIET and all medicines out of reach of children. |
||||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of ESBRIET.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ESBRIET for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ESBRIET to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about ESBRIET that is written for health professionals. |
||||||
| What are the ingredients in ESBRIET capsules?
Active ingredient: pirfenidone Inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, povidone, and magnesium stearate Capsule Shell: gelatin and titanium dioxide Capsule Brown Printing Ink: shellac, iron oxide black, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, propylene glycol, ammonium hydroxide What are the ingredients in ESBRIET film-coated tablets? Active ingredient: pirfenidone Inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal anhydrous silica, povidone, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, macrogol (polyethylene glycol), talc, and iron oxide For more information, go to www.ESBRIET.com or call 1-888-835-2555. © 2023 Genentech USA, Inc. |
||||||
Representative sample of labeling (see the HOW SUPPLIED section for complete listing):
| ESBRIET
pirfenidone capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ESBRIET
pirfenidone tablet, coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ESBRIET
pirfenidone tablet, coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG | 482242971 | ANALYSIS(50242-121, 50242-122, 50242-123) | |