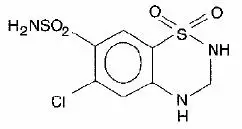
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Adverse reactions are usually reversible upon reduction of dosage or discontinuation of Esidrix. Whenever adverse reactions are moderate or severe, it may be necessary to discontinue the drug.
The following adverse reactions have been observed, but there has not been enough systematic collection of data to support an estimate of their frequency. Consequently the reactions are categorized by organ systems and are listed in decreasing order of severity and not frequency.
Digestive: Pancreatitis, jaundice (intrahepatic cholestatic), sialadenitis, vomiting, diarrhea, cramping, nausea, gastric irritation, constipation, anorexia.
Cardiovascular: Orthostatic hypotension (may be potentiated by alcohol, barbiturates, or narcotics).
Neurologic: Vertigo, dizziness, transient blurred vision, headache, paresthesia, xanthopsia, weakness, restlessness.
Musculoskeletal: Muscle spasm.
Hematologic: Aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Metabolic: Hyperglycemia, glycosuria, hyperuricemia.
Hypersensitive Reactions: Necrotizing angiitis, Stevens- Johnson syndrome, respiratory distress including pneumonitis and pulmonary edema, purpura, urticaria, rash, photosensitivity.