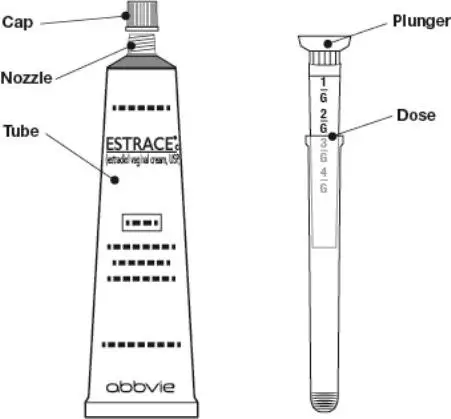
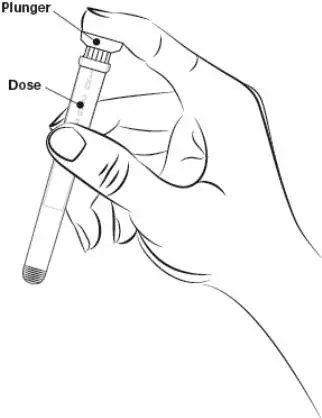
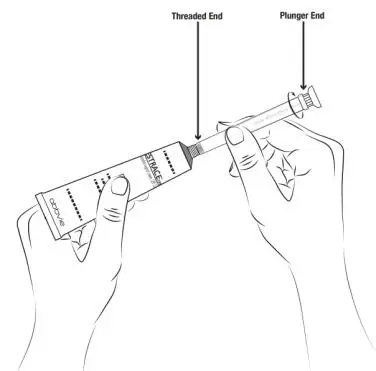
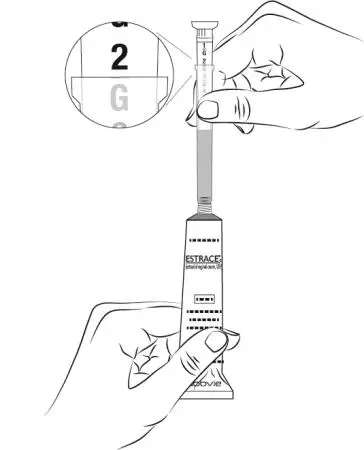
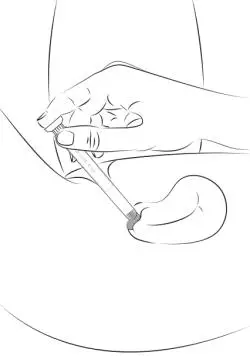
Drug Detail:Estrace vaginal (local) (Estradiol vaginal (local) [ es-tra-dye-ole-va-jin-ul ])
Drug Class: Estrogens Miscellaneous vaginal agents
WARNING: ENDOMETRIAL CANCER, CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS, BREAST CANCER and PROBABLE DEMENTIA
Estrogen-Alone Therapy
Endometrial Cancer
There is an increased risk of endometrial cancer in a woman with a uterus who uses unopposed estrogens. Adding a progestin to estrogen therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer. Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding [see WARNINGS, Malignant Neoplasms, Endometrial Cancer].
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
Estrogen-alone therapy should not be used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Disorders, and Probable Dementia].
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen-alone substudy reported increased risks of stroke and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 7.1 years of treatment with daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE) [0.625 mg]-alone, relative to placebo [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Disorders].
The WHI Memory Study (WHIMS) estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age or older during 5.2 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg) -alone, relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Probable Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use].
In the absence of comparable data, these risks should be assumed to be similar for other doses of CE and other dosage forms of estrogens.
Estrogens with or without progestins should be prescribed at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Estrogen Plus Progestin Therapy
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
Estrogen plus progestin therapy should not be used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Disorders, and Probable Dementia].
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy reported increased risks of DVT, pulmonary embolism (PE), stroke and myocardial infarction (MI) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 5.6 years of treatment with daily oral CE (0.625 mg) combined with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) [2.5 mg], relative to placebo [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Disorders].
The WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study of the WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age or older during 4 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg) combined with MPA (2.5 mg), relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Probable Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use].
Breast Cancer
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy also demonstrated an increased risk of invasive breast cancer [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Malignant Neoplasms, Breast Cancer].
In the absence of comparable data, these risks should be assumed to be similar for other doses of CE and MPA, and other combinations and dosage forms of estrogens and progestins.
Estrogens with or without progestins should be prescribed at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Clinical Studies
Women’s Health Initiative Studies
The WHI enrolled approximately 27,000 predominantly healthy postmenopausal women in two substudies to assess the risks and benefits of daily oral CE (0.625 mg)-alone or in combination with MPA (2.5 mg) compared to placebo in the prevention of certain chronic diseases. The primary endpoint was the incidence of coronary heart disease (CHD) (defined as nonfatal MI, silent MI and CHD death), with invasive breast cancer as the primary adverse outcome. A “global index” included the earliest occurrence of CHD, invasive breast cancer, stroke, PE, endometrial cancer (only in the CE plus MPA substudy), colorectal cancer, hip fracture, or death due to other cause. These substudies did not evaluate the effects of CE or CE plus MPA on menopausal symptoms.
WHI Estrogen-Alone Substudy
The WHI estrogen-alone substudy was stopped early because an increased risk of stroke was observed, and it was deemed that no further information would be obtained regarding the risks and benefits of estrogen-alone in predetermined primary endpoints.
Results of the estrogen-alone substudy, which included 10,739 women (average 63 years of age, range 50 to 79; 75.3 percent White, 15.1 percent Black, 6.1 percent Hispanic, 3.6 percent Other), after an average follow-up of 7.1 years are presented in Table 1.
|
Event | Relative Risk
CE vs. Placebo (95% nCIb) | CE
n = 5,310 | Placebo
n = 5,429 |
| Absolute Risk per 10,000 Women-Years | |||
| CHD eventsc | 0.95 (0.78-1.16) | 54 | 57 |
| Non-fatal MIc | 0.91 (0.73-1.14) | 40 | 43 |
| CHD deathc | 1.01 (0.71-1.43) | 16 | 16 |
| All Strokec | 1.33 (1.15-1.68) | 45 | 33 |
| Ischemic strokec | 1.55 (1.19-2.01) | 38 | 25 |
| Deep vein thrombosisc,d | 1.47 (1.06-2.06) | 23 | 15 |
| Pulmonary embolismc | 1.37 (0.90-2.07) | 14 | 10 |
| Invasive breast cancerc | 0.80 (0.62-1.04) | 28 | 34 |
| Colorectal cancerc | 1.08 (0.75-1.55) | 17 | 16 |
| Hip fracturec | 0.65 (0.45-0.94) | 12 | 19 |
| Vertebral fracturesc,d | 0.64 (0.44-0.93) | 11 | 18 |
| Lower arm/wrist fracturesc,d | 0.58 (0.47-0.72) | 35 | 59 |
| Total fracturesc,d | 0.71 (0.64-0.80) | 144 | 197 |
| Death due to other causese,f | 1.08 (0.88-1.32) | 53 | 50 |
| Overall mortalityc,d | 1.04 (0.88-1.22) | 79 | 75 |
| Global Indexg | 1.02 (0.92-1.13) | 206 | 201 |
a Adapted from numerous WHI publications. WHI publications can be viewed at www.nhlbi.nih.gov/whi.
b Nominal confidence intervals unadjusted for multiple looks and multiple comparisons.
c Results are based on centrally adjudicated data for an average follow-up of 7.1 years.
d Not included in “global index”.
e Results are base on an average follow-up of 6.8 years.
f All deaths, except from beast or colorectal cancer, definite or probable CHD, PE, or cerebrovascular disease.
g A subset of the events was combined in a “global index” defined as the earliest occurrence of CHD events, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism, endometrial cancer, colorectal cancer, hip fracture, or death due to other causes.
For those outcomes included in the WHI “global index” that reached statistical significance, the absolute excess risk per 10,000 women-years in the group treated with CE-alone was 12 more strokes, while the absolute risk reduction per 10,000 women-years was 7 fewer hip fractures1. The absolute excess risk of events included in the “global index” was a non-significant 5 events per 10,000 women-years. There was no difference between the groups in terms of all-cause mortality.
No overall difference for primary CHD events (nonfatal MI, silent MI and CHD death) and invasive breast cancer incidence in women receiving CE-alone compared with placebo was reported in final centrally adjudicated results from the estrogen-alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 7.1 years.
Centrally adjudicated results for stroke events from the estrogen-alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 7.1 years, reported no significant differences in distribution of stroke subtypes or severity, including fatal strokes, in women receiving CE-alone compared to placebo. Estrogen-alone increased the risk for ischemic stroke, and this excess risk was present in all subgroups of women examined2.
Timing of the initiation of estrogen-alone therapy relative to the start of menopause may affect the overall risk benefit profile. The WHI estrogen-alone substudy stratified by age showed in women 50 to 59 years of age a non-significant trend toward reduced risk for CHD [hazard ratio (HR) 0.63 (95 percent CI, 0.36-1.09)] and overall mortality [HR 0.71 (95 percent CI, 0.46-1.11)].
WHI Estrogen Plus Progestin Substudy
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy was also stopped early. According to the predefined stopping rule, after an average follow-up of 5.6 years of treatment, the increased risk of breast cancer and cardiovascular events exceeded the specified benefits included in the “global index.” The absolute excess risk of events included in the “global index” was 19 per 10,000 women-years.
For those outcomes included in the WHI “global index” that reached statistical significance after 5.6 years of follow-up, the absolute excess risks per 10,000 women-years in the group treated with CE plus MPA were 7 more CHD events, 8 more strokes, 10 more PEs, and 8 more invasive breast cancers, while the absolute risk reductions per 10,000 women-years were 6 fewer colorectal cancers and 5 fewer hip fractures.
Results of the CE plus MPA substudy, which included 16,608 women (average 63 years of age, range 50 to 79; 83.9 percent White, 6.8 percent Black, 5.4 percent Hispanic, 3.9 percent Other), are presented in Table 2. These results reflect centrally adjudicated data after an average follow-up of 5.6 years.
TABLE 2 -Relative and Absolute Risk Seen in the Estrogen Plus Progestin Substudy of WHI at an Average of 5.6 Yearsa,b
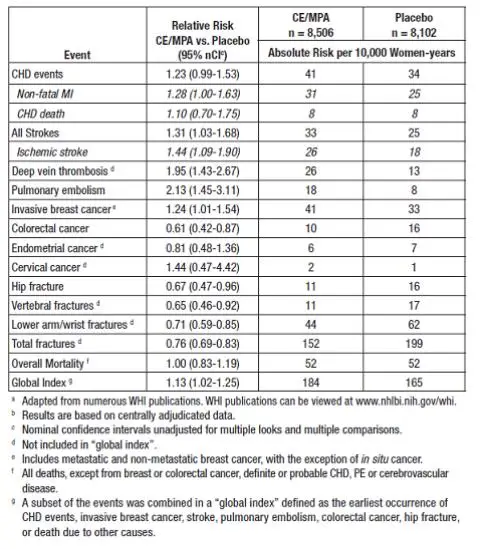
Timing of the initiation of estrogen plus progestin therapy relative to the start of menopause may affect the overall risk benefit profile. The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy stratified by age showed in women 50 to 59 years of age, a non-significant trend toward reduced risk for overall mortality [HR 0.69 (95 percent CI, 0.44-1.07)].
Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study
The WHIMS estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI enrolled 2,947 predominantly healthy hysterectomized postmenopausal women 65 to 79 years of age and older (45 percent were 65 to 69 years of age; 36 percent were 70 to 74 years of age; 19 percent were 75 years of age and older) to evaluate the effects of daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone on the incidence of probable dementia (primary outcome) compared to placebo.
After an average follow-up of 5.2 years, the relative risk of probable dementia for CE-alone versus placebo was 1.49 (95 percent CI, 0.83-2.66). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE-alone versus placebo was 37 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years. Probable dementia as defined in this study included Alzheimer’s disease (AD), vascular dementia (VaD) and mixed types (having features of both AD and VaD). The most common classification of probable dementia in the treatment group and the placebo group was AD. Since the ancillary study was conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women [see BOXED WARNINGS, WARNINGS, Probable Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use].
The WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study of WHI enrolled 4,532 predominantly healthy postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older (47 percent were 65 to 69 years of age; 35 percent were 70 to 74 years; 18 percent were 75 years of age and older) to evaluate the effects of daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) on the incidence of probable dementia (primary outcome) compared to placebo.
After an average follow-up of 4 years, the relative risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 2.05 (95 percent CI, 1.21-3.48). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 45 versus 22 per 10,000 women-years. Probable dementia as defined in this study included AD, VaD and mixed types (having features of both AD and VaD). The most common classification of probable dementia in the treatment group and the placebo group was AD. Since the ancillary study was conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women [see WARNINGS, Probable Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use].
When data from the two populations were pooled as planned in the WHIMS protocol, the reported overall relative risk for probable dementia was 1.76 (95 percent CI, 1.19-2.60). Differences between groups became apparent in the first year of treatment. It is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women [see WARNINGS, Probable Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use].
Contraindications
ESTRACE (estradiol vaginal cream USP 0.01%) should not be used in women with any of the following conditions:
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding.
- Known, suspected, or history of cancer of the breast.
- Known or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia.
- Active DVT, PE or history of these conditions.
- Active arterial thromboembolic disease (for example, stroke, MI) or a history of these conditions.
- Known anaphylactic reaction or angioedema to ESTRACE (estradiol vaginal cream USP 0.01%).
- Known liver dysfunction or disease.
- Known protein C, protein S, or antithrombin deficiency, or other known thrombophilic disorders.
- Known or suspected pregnancy.
Warnings
See BOXED WARNINGS.
Systemic absorption may occur with the use of ESTRACE (estradiol vaginal cream USP 0.01%). The warnings, precautions, and adverse reactions associated with oral estrogen treatment should be taken into account.
1. Cardiovascular Disorders
An increased risk of stroke and DVT has been reported with estrogen-alone therapy. An increased risk of PE, DVT, stroke and MI has been reported with estrogen plus progestin therapy. Should any of these occur or be suspected, estrogen with or without progestin therapy should be discontinued immediately.
Risk factors for arterial vascular disease (e.g., hypertension, diabetes mellitus, tobacco use, hypercholesterolemia, and obesity) and/or venous thromboembolism (VTE) (e.g., personal history or family history of VTE, obesity, and systemic lupus erythematosus) should be managed appropriately.
2. Malignant Neoplasms
a. Endometrial Cancer
An increased risk of endometrial cancer has been reported with the use of unopposed estrogen therapy in a woman with a uterus. The reported endometrial cancer risk among unopposed estrogen users is about 2- to 12-times greater than in non-users, and appears dependent on duration of treatment and on estrogen dose. Most studies show no significant increased risk associated with use of estrogens for less than one year. The greatest risk appears associated with prolonged use, with increased risks of 15- to 24-fold for five to ten years or more and this risk has been shown to persist for at least 8 to 15 years after estrogen therapy is discontinued.
Clinical surveillance of all women using estrogen-alone or estrogen plus progestin therapy is important. Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding.
There is no evidence that the use of natural estrogens results in a different endometrial risk profile than synthetic estrogens of equivalent estrogen dose. Adding a progestin to estrogen therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer.
b. Breast Cancer
The most important randomized clinical trial providing information about breast cancer in estrogen-alone users is the WHI substudy of daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone. In the WHI estrogen-alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 7.1 years, daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone was not associated with an increased risk of invasive breast cancer (relative risk [RR] 0.80) 7 [see CLINICAL STUDIES].
The most important randomized clinical trial providing information about breast cancer in estrogen plus progestin users is the WHI substudy of daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg). After a mean follow-up of 5.6 years, the estrogen plus progestin substudy reported an increased risk of invasive breast cancer in women who took daily CE plus MPA. In this substudy, prior use of estrogen-alone or estrogen plus progestin therapy was reported by 26 percent of the women. The relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.24, and the absolute risk was 41 versus 33 cases per 10,000 women-years, for CE plus MPA compared with placebo. Among women who reported prior use of hormone therapy, the relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.86, and the absolute risk was 46 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years, for CE plus MPA compared with placebo. Among women who reported no prior use of hormone therapy, the relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.09, and the absolute risk was 40 versus 36 cases per 10,000 women-years, for CE plus MPA compared with placebo. In the same substudy, invasive breast cancers were larger, were more likely to be node positive, and were diagnosed at a more advanced stage in the CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) group compared with the placebo group. Metastatic disease was rare with no apparent difference between the two groups. Other prognostic factors such as histologic subtype, grade and hormone receptor status did not differ between the groups8 [see CLINICAL STUDIES].
Consistent with the WHI clinical trial, observational studies have also reported an increased risk of breast cancer for estrogen plus progestin therapy, and a smaller increased risk for estrogen- alone therapy, after several years of use. The risk increased with duration of use, and appeared to return to baseline in about 5 years after stopping treatment (only the observational studies have substantial data on risk after stopping). Observational studies also suggest that the risk of breast cancer was greater, and became apparent earlier, with estrogen plus progestin therapy as compared to estrogen-alone therapy. However, these studies have not generally found significant variation in the risk of breast cancer among different estrogen plus progestin combinations, doses, or routes of administration.
The use of estrogen-alone and estrogen plus progestin therapy has been reported to result in an increase in abnormal mammograms requiring further evaluation.
All women should receive yearly breast examinations by a healthcare provider and perform monthly breast self-examinations. In addition, mammography examinations should be scheduled based on patient age, risk factors, and prior mammogram results.
3. Probable Dementia
In the WHIMS estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI, a population of 2,947 hysterectomized women 65 to 79 years of age was randomized to daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone or placebo.
After an average follow-up of 5.2 years, 28 women in the estrogen-alone group and 19 women in the placebo group were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia for CE-alone versus placebo was 1.49 (95 percent CI, 0.83-2.66). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE-alone versus placebo was 37 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years10 [see CLINICAL STUDIES and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use].
In the WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study, a population of 4,532 postmenopausal women 65 to 79 years of age was randomized to daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) or placebo.
After an average follow-up of 4 years, 40 women in the CE plus MPA group and 21 women in the placebo group were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 2.05 (95 percent CI, 1.21-3.48). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 45 versus 22 cases per 10,000 women-years10 [see CLINICAL STUDIES and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use].
When data from the two populations in the WHIMS estrogen-alone and estrogen plus progestin ancillary studies were pooled as planned in the WHIMS protocol, the reported overall relative risk for probable dementia was 1.76 (95 percent CI, 1.19-2.60). Since both ancillary studies were conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women10 [see PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use].
Precautions
I. Geriatric Use
There have not been sufficient numbers of geriatric patients involved in studies utilizing ESTRACE to determine whether those over 65 years of age differ from younger subjects in their response to ESTRACE.
The Women’s Health Initiative Study
In the WHI estrogen-alone substudy (daily CE [0.625 mg]-alone versus placebo), there was a higher relative risk of stroke in women greater than 65 years of age [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS].
In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy (daily CE [0.625 mg] plus MPA [2.5 mg] versus placebo), there was a higher relative risk of nonfatal stroke and invasive breast cancer in women greater than 65 years of age [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS].
The Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study
In the WHIMS ancillary studies of postmenopausal women 65 to 79 years of age, there was an increased risk of developing probable dementia in women receiving estrogen-alone or estrogen plus progestin when compared to placebo [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS].
Since both ancillary studies were conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women 10 [see CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS].
| ESTRACE
estradiol cream |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspen Oss B.V. | 491017488 | analysis(0430-3754) , api manufacture(0430-3754) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspen Oss B.V. | 491013870 | analysis(0430-3754) , api manufacture(0430-3754) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contract Pharmaceuticals Limited Canada | 248761249 | manufacture(0430-3754) | |