Drug Detail:Ethamolin (Ethanolamine oleate [ eth-a-nole-a-meen-oh-lee-ate ])
Drug Class: Sclerosing agents
Ethamolin Description
ETHAMOLIN® (Ethanolamine Oleate) Injection is a mild sclerosing agent. Chemically it is C17H33COOH•NH2CH2CH2OH. It has the following structure:
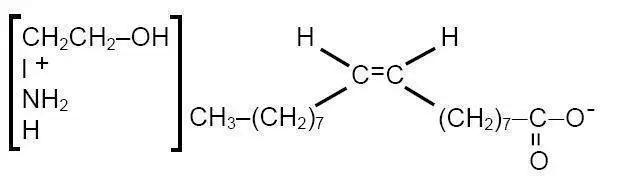
The empirical formula is C20H41NO3, representing a molecular weight of 343.55.
ETHAMOLIN Injection consists of ethanolamine, a basic substance, which when combined with oleic acid, forms a clear pale-yellow to straw-colored, deliquescent oleate. The pH ranges from 8.0 to 9.0.
ETHAMOLIN Injection is a sterile, apyrogenic, aqueous solution containing in each mL approximately 50 mg of ethanolamine oleate with benzyl alcohol 2% by volume as preservative.
Warnings
ETHAMOLlN Injection should be used in pregnant women only when clearly needed (see PRECAUTIONS).
The practice of injecting varicosities of the leg with ETHAMOLlN Injection is not supported by adequately-controlled clinical trials. Therefore, such use is not recommended.
Precautions
Fatal anaphylactic shock was reported following injection of a larger than normal volume of ETHAMOLlN Injection into a male who had a known allergic disposition. Although there are only three known reports of anaphylaxis, the possibility of an anaphylactic reaction should be kept in mind, and the physician should be prepared to treat it appropriately. In extreme emergencies, 0.25 mL of a 1:1,000 intravenous solution of epinephrine (0.25 mg) should be used, and allergic reactions should be controlled with antihistamines.
Acute renal failure with spontaneous recovery followed injection of 15 to 20 mL of ETHAMOLIN Injection into two women.
The physician should bear in mind that severe injection necrosis may result from direct injection of sclerosing agents, especially if excessive volumes are used. At least one fatal case of extensive esophageal necrosis and death has been reported. The drug should be administered by physicians who are familiar with an acceptable injection technique.
Patients in Child Class C are more likely to develop esophageal ulceration than those in Classes Aand B. Complications of ulceration, necrosis, and delayed esophageal perforation appear to occur more frequently when ETHAMOLIN Injection is injected submucosally. This route is not recommended.
In patients with concomitant cardiorespiratory disease, careful monitoring and minimization of the total dose per session is recommended.
Fatal aspiration pneumonia has occurred in elderly patients undergoing esophageal variceal sclerotherapy with ETHAMOLIN Injection. This adverse event appears to be procedure-related, rather than drug-related; but, as aspiration of blood and/or stomach contents is not uncommon in patients with bleeding esophageal varices, special precautions should be taken to prevent its occurrence, especially in elderly and critically-ill subjects.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The reported frequency of complications/adverse events per injection session was 13%. The most common complications were pleural effusion/infiltration (2.1%), esophageal ulcer (2.1 %), pyrexia (1.8%), retrosterual pain (1.6%), esophageal stricture .(1.3%), and pneumonia (1.2%).
Other adverse local esophageal reactions have also been reported at rates of 0.1 to 0.4%, including esophagitis, tearing of the esophagus, sloughing of the mucosa overlying the injected varix, ulceration, stricture, necrosis, periesophageal abscess and perforation (see PRECAUTIONS). These complications appear to be dependent upon the dose and the patient's clinical state.
Bacteremia has been observed in patients following injection of esophageal varices with ETHAMOLlN. Pyrexia and retrosternal pain are not infrequently observed during the post-injection period. Fatal aspiration pneumonia has occurred in patients with esophageal varices who underwent ETHAMOLIN Injection Sclerotherapy (see PRECAUTIONS). Anaphylactic shock and acute renal failure with spontaneous recovery have occurred (see PRECAUTIONS). A case of disseminated intravascular coagulation has been reported.
Spinal cord paralysis due to occlusion of the anterior spinal artery has been reported in one child eight hours after ETHAMOLIN sclerotherapy.
Overdosage
Overdosage of ETHAMOLIN Injection can result in severe intramural necrosis of the esophagus. Complications resulting from such overdosage have resulted in death.
Ethamolin Dosage and Administration
Local ETHAMOLIN Injection sclerotherapy of esophageal varices should be performed by physicians who are famillar with an acceptable technique. The usual intravenous dose is 1.5 to 5.0 mL per varix. The maximum dose per treatment session should not exceed 20 mL. Patients with significant liver dysfunction (Child Class C) or concomitant cardiopulmonary disease should usually receive less than the recommended maximum dose. Submucosal injections are not recommended, as they reportedly are more likely to result in ulceration at the site of injection.
To obliterate the varix, injections may be made at the time of theacute bleeding episode and then after one week, six weeks, three months, and six months, as indicated.
Note: Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration whenever solution and container permit.
| ETHAMOLIN
ethanolamine oleate injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - QOL Medical, LLC. (140026258) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jubilant HollisterStier General Partnership | 246762764 | manufacture(67871-479) | |






