Drug Detail:Evekeo odt (Amphetamine [ am-fet-a-meen ])
Drug Class: CNS stimulants
Highlights of Prescribing Information
EVEKEO ODT (amphetamine sulfate) orally disintegrating tablets, CII
Initial U.S. Approval: 1984
WARNING: ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- CNS stimulants, including EVEKEO ODT, other amphetamine-containing products, and methylphenidate, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. (5.1, 9.3)
- Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy. (9.2, 9.3)
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1) | 9/2022 |
| Dosage and Administration (2.2) | 9/2022 |
Indications and Usage for Evekeo ODT
EVEKEO ODT is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in pediatric patients 3 to 17 years of age. (1)
Evekeo ODT Dosage and Administration
- Administer in the morning with or without food or liquid. (2.2)
- Recommended starting dosage is 5 mg once or twice daily. If necessary, administer an additional dose after 4 to 6 hours. Titrate the dosage in increments of 5 mg at weekly intervals. (2.2)
- Only in rare cases will it be necessary to exceed a total of 40 mg daily. (2.2)
- Place the whole tablet on tongue and allow to disintegrate in saliva, so that it can be swallowed. (2.3)
- Do not substitute for other amphetamine products on a milligram-per-milligram basis because of different amphetamine salt compositions and differing pharmacokinetic profiles. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Orally disintegrating tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, and 20 mg. (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients in EVEKEO ODT. (4)
- Use of monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) or within 14 days of the last MAOI dose. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Serious Cardiovascular Reactions: Sudden death has been reported in association with CNS stimulant treatment at recommended doses in pediatric patients with structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems. In adults, sudden death, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported. Avoid use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart arrhythmia, or coronary artery disease. (5.2)
- Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases: Monitor blood pressure and pulse. Consider benefits and risks before use in patients for whom blood pressure increases may be problematic. (5.3)
- Psychiatric Adverse Reactions: May cause psychotic or manic symptoms in patients with no prior history, or exacerbation of symptoms in patients with pre-existing psychosis. Evaluate for bipolar disorder prior to EVEKEO ODT use. (5.4)
- Long-term Suppression of Growth: Monitor height and weight in pediatric patients during treatment. (5.5)
- Seizures: May lower the convulsive threshold. If a seizure occurs, discontinue EVEKEO ODT. (5.6)
- Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon: Stimulants used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon. Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants. (5.7)
- Serotonin Syndrome: Increased risk when co-administered with serotonergic agents (e.g., SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans), but also during overdosage situations. If it occurs, discontinue EVEKEO ODT and initiate supportive treatment. (5.8)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥4% and at a rate at least twice placebo) in pediatric patients are: decreased appetite and insomnia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Arbor Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-800-461-7449 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Acidifying and Alkalinizing Agents: Agents that alter GI and urinary pH can alter blood levels of amphetamine. Acidifying agents (GI and urinary) can decrease amphetamine blood levels, while alkalinizing agents (GI and urinary) can increase amphetamine blood levels. Adjust EVEKEO ODT dosage accordingly. (2.5, 7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 9/2022
Related/similar drugs
Adderall, Vyvanse, methylphenidate, Strattera, Ritalin, ConcertaFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
CNS stimulants, including EVEKEO ODT, other amphetamine-containing products, and methylphenidate, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
1. Indications and Usage for Evekeo ODT
EVEKEO ODT is indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age.
2. Evekeo ODT Dosage and Administration
2.1 Pre-treatment Screening
Prior to treating patients with EVEKEO ODT, assess for the presence of cardiac disease (i.e., perform a careful history, family history of sudden death or ventricular arrhythmia, and physical exam) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy. Maintain careful prescription records, educate patients about abuse, monitor for signs of abuse and overdose, and periodically re-evaluate the need for EVEKEO ODT use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
2.2 Dosage Information
Administer EVEKEO ODT orally in the morning with or without food or liquid.
The recommended starting dosage for pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age is 5 mg once or twice daily. If necessary, administer an additional dose after 4 to 6 hours. Titrate the dosage in increments of 5 mg at weekly intervals depending on response and tolerability.
Only in rare cases will it be necessary to exceed a total of 40 mg daily.
Where possible, drug administration should be interrupted occasionally to determine if there is a recurrence of behavioral symptoms sufficient to require continued therapy.
Amphetamine should be administered at the lowest effective dosage and dosage should be individually adjusted.
2.3 Administration Instructions
Instruct the patient or caregiver on the following administration instructions:
- Do not remove the tablet from the blister pack until just prior to dosing. Do not store the tablet for future use.
- Use dry hands to open the blister.
- Remove the tablet by pushing it through the back of the foil-lined blister pack.
- As soon as the blister is opened, remove the tablet and place the tablet on the patient's tongue.
- Place the whole tablet on the tongue and allow it to disintegrate without chewing or crushing.
- The tablet will disintegrate in saliva so that it can be swallowed. No liquid is needed to take the tablet. The tablet can be actively moved around between the tongue and the roof of the mouth until it disintegrates.
2.4 Switching from Other Amphetamine Products
Switching from EVEKEO to EVEKEO ODT can be done on a milligram-per-milligram basis.
When switching from other amphetamine products, discontinue treatment and titrate with EVEKEO ODT using the titration schedule above. Do not substitute for other amphetamine products on a milligram-per-milligram basis because of different amphetamine salt compositions and differing pharmacokinetic profiles [see Description (11), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.5 Dosage Modifications Due to Drug Interactions
Agents that alter urinary pH can impact urinary excretion and alter blood levels of amphetamine. Acidifying agents (e.g., ascorbic acid) decrease blood levels, while alkalinizing agents (e.g., sodium bicarbonate) increase blood levels. Adjust EVEKEO ODT dosage accordingly [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
EVEKEO ODT (amphetamine sulfate) orally disintegrating tablets are supplied as follows:
- 5 mg: white to off-white, round, flat-faced radius-edged tablet with "5" on one side and "EVI" on the other.
- 10 mg: white to off-white, round, flat-faced radius-edged tablet with "10" on one side and "EVI" on the other.
- 15 mg: white to off-white, round, flat-faced radius-edged tablet with "15" on one side and "EVI" on the other.
- 20 mg: white to off-white, round, flat-faced radius-edged tablet with "20" on one side and "EVI" on the other.
4. Contraindications
EVEKEO ODT is contraindicated in patients:
- With known hypersensitivity to amphetamine, or other components of EVEKEO ODT. Hypersensitivity reactions such as angioedema and anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients treated with other amphetamine products [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- Receiving concomitant treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days following discontinuation of treatment with an MAOI (including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue), because of an increased risk of hypertensive crisis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Potential for Abuse and Dependence
CNS stimulants, including EVEKEO ODT, other amphetamine-containing products, and methylphenidate, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
5.2 Serious Cardiovascular Reactions
Sudden death, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported in adults with CNS stimulant treatment at recommended doses. Sudden death has been reported in pediatric patients with structural cardiac abnormalities and other serious heart problems taking CNS stimulants at recommended doses for ADHD. Avoid use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart arrhythmia, coronary artery disease, and other serious heart problems. Further evaluate patients who develop exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or arrhythmias during EVEKEO ODT treatment.
5.3 Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases
CNS stimulants cause an increase in blood pressure (mean increase about 2-4 mm Hg) and heart rate (mean increase about 3-6 bpm). Monitor all patients for potential tachycardia and hypertension.
5.5 Long-Term Suppression of Growth
CNS stimulants have been associated with weight loss and slowing of growth rate in pediatric patients. Closely monitor growth (weight and height) in pediatric patients treated with CNS stimulants, including EVEKEO ODT.
Patients who are not growing or gaining height or weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.6 Seizures
There is some clinical evidence that stimulants may lower the convulsive threshold in patients with prior history of seizures, in patients with prior EEG abnormalities in absence of seizures, and, very rarely, in patients without a history of seizures and no prior EEG evidence of seizures. In the presence of seizures, discontinue EVEKEO ODT.
5.7 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon
Stimulants, including EVEKEO ODT, used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon. Signs and symptoms are usually intermittent and mild; however, very rare sequelae include digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown. Effects of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon, were observed in post-marketing reports at different times and at therapeutic doses in all age groups throughout the course of treatment. Signs and symptoms generally improve after reduction in dose or discontinuation of drug. Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for certain patients.
5.8 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening reaction, may occur when amphetamines are used in combination with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems such as MAOIs, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, and St. John's Wort [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. The co-administration with cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) inhibitors may also increase the risk with increased exposure to EVEKEO ODT. In these situations, consider an alternative non-serotonergic drug or an alternative drug that does not inhibit CYP2D6 [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
Concomitant use of EVEKEO ODT with MAOI drugs is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)].
Discontinue treatment with EVEKEO ODT and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if the above symptoms occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of EVEKEO ODT with other serotonergic drugs or CYP2D6 inhibitors is clinically warranted, initiate EVEKEO ODT with lower doses, monitor patients for the emergence of serotonin syndrome during drug initiation or titration, and inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Abuse and Dependence [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2,9.3)]
- Hypersensitivity to amphetamine, or other components of EVEKEO ODT [see Contraindications (4)]
- Hypertensive Crisis When Used Concomitantly with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
- Serious Cardiovascular Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Psychiatric Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Long-Term Suppression of Growth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Study 1 was conducted with EVEKEO tablets (i.e., not the ODT formulation) in children ages 6 to 12 years who met Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition, Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR) criteria for ADHD. This study began with an 8-week, open-label, dose-optimization phase followed by a 2-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, crossover phase. Adverse reactions reported in > 5% of patients (N=105; doses of 10 to 40 mg/day) during the open-label phase included: decreased appetite (28%), infections (22%), abdominal pain (15%), irritability (14%), headache (13%), nausea (6%), vomiting (6%), affect lability (includes mood swings; 9%), tachycardia (9%), insomnia (10%), fatigue (10%),and dry mouth (6%). During the open-label phase, six patients discontinued due to adverse reactions: irritability (n=3), affect lability (n=1), initial insomnia (n=1), and rash (n=1).
Table 1 lists the adverse reactions reported during the double-blind, cross-over phase. No patient discontinued the study for an adverse reaction during the double-blind crossover phase. Because of the trial design (an initial 8-week, open-label, active treatment phase), the adverse reaction rates described in the double-blind phase are lower than expected in clinical practice.
| System Organ Class Preferred Term | EVEKEO (n= 97) | Placebo (n= 97) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Subjects with at least one adverse event | 22% | 14% |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 4% | 0% |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Abdominal pain | 3% | 0% |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Affect Lability† | 3% | 0% |
| Insomnia | 4% | 0% |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | ||
| Injury | 3% | 2% |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been associated during post approval use of amphetamines. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular: Palpitations, tachycardia, elevation of blood pressure, sudden death, myocardial infarction. There have been isolated reports of cardiomyopathy associated with chronic amphetamine use.
Central Nervous System: Psychotic episodes at recommended doses, overstimulation, irritability, restlessness, dizziness, insomnia, euphoria, mood swings, aggression, anger, logorrhea, dermatillomania, dyskinesia, dysphoria, tremor, fatigue, headache, exacerbation of motor and phonic tics and Tourette's syndrome
Gastrointestinal: Dry mouth, unpleasant taste, constipation, nausea, intestinal ischemia, other gastrointestinal disturbances, anorexia, and weight loss.
Allergic: Urticaria, rash, hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema and anaphylaxis. Serious skin rashes, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported.
Endocrine: Impotence, changes in libido, and frequent or prolonged erections.
Skin: Alopecia.
Vascular Disorders: Raynaud's phenomenon.
Musculoskeletal: Rhabdomyolysis.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with Amphetamines
| MAO Inhibitors (MAOI) | |
| Clinical Impact | MAOI antidepressants slow amphetamine metabolism, increasing amphetamines effect on the release of norepinephrine and other monoamines from adrenergic nerve endings causing headaches and other signs of hypertensive crisis. Toxic neurological effects and malignant hyperpyrexia can occur, sometimes with fatal results. |
| Intervention | Do not administer EVEKEO ODT during or within 14 days following the administration of MAOI [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Examples | selegiline, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, tranylcypromine, linezolid, methylene blue |
| Serotonergic Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of EVEKEO ODT and serotonergic drugs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
| Intervention | Initiate with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during EVEKEO ODT initiation or dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue EVEKEO ODT and concomitant serotonergic drug(s) [see Warnings and Precautions 5.8]. |
| Examples | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRI), triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, St. John's Wort |
| Alkalinizing Agents | |
| Clinical Impact | May increase exposure to amphetamine and exacerbate the action of amphetamine. |
| Intervention | Caution should be taken when co-administering EVEKEO ODT and gastrointestinal and urinary alkalinizing agents. |
| Examples | Gastrointestinal alkalinizing agents (e.g., sodium bicarbonate; proton pump inhibitors [e.g. omeprazole]) Urinary alkalinizing agents (e.g. acetazolamide, some thiazides) |
| Acidifying Agents | |
| Clinical Impact | Lower blood levels and efficacy of amphetamines. |
| Intervention | Increase dose of EVEKEO ODT based on clinical response. |
| Examples | Gastrointestinal acidifying agents (e.g., guanethidine, reserpine, glutamic acid HCl, ascorbic acid) Urinary acidifying agents (e.g., ammonium chloride, sodium acid phosphate, methenamine salts) |
| Tricyclic Antidepressants | |
| Clinical Impact | May enhance the activity of tricyclic or sympathomimetic agents causing sustained increases in the concentration of d- amphetamine in the brain; cardiovascular effects can be potentiated. |
| Intervention | Monitor frequently and adjust EVEKEO ODT dose or use alternative therapy based on clinical response. |
| Examples | desipramine, protriptyline |
| CYP2D6 Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of EVEKEO ODT and CYP2D6 inhibitors may increase the exposure of EVEKEO ODT compared to the use of the drug alone and increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
| Intervention | Initiate with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome particularly during EVEKEO ODT initiation and after a dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue EVEKEO ODT and the CYP2D6 inhibitor. Alternatively, consider using a drug that does not inhibit CYP2D6 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Overdosage (10)]. |
| Examples | paroxetine and fluoxetine (also serotonergic drugs), quinidine, ritonavir. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of EVEKEO ODT have been established in pediatric patients 6 years and older. Use of EVEKEO ODT is based on one adequate and well-controlled study with another immediate-release amphetamine sulfate product (EVEKEO) in pediatric patients 6 to 12 years [see Clinical Studies (14)], along with dosing and safety information for other amphetamine products.
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients below the age of 6 years have not been established.
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.2 Abuse
CNS stimulants including EVEKEO ODT, other amphetamine-containing products, and methylphenidates have a high potential for abuse. Abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, to achieve a desired psychological or physiological effect. Abuse is characterized by impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm, and craving. Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that may include a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling drug use (e.g., continuing drug use despite harmful consequences, giving a higher priority to drug use than other activities and obligations), and possible tolerance or physical dependence. Both abuse and misuse may lead to addiction, and some individuals may develop addiction even when taking EVEKEO ODT as prescribed.
Signs and symptoms of amphetamine abuse may include increased heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and/or sweating, dilated pupils, hyperactivity, restlessness, insomnia, decreased appetite, loss of coordination, tremors, flushed skin, vomiting, and/or abdominal pain. Anxiety, psychosis, hostility, aggression, suicidal or homicidal ideation have also been seen. Abusers of amphetamine may use unapproved routes of administration which can result in overdose and death [see Overdosage (10)].
To reduce the abuse of CNS stimulants, including EVEKEO ODT, assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing. After prescribing, keep careful prescription records, educate patients and their families about abuse and on proper storage and disposal of CNS stimulants. Monitor for signs of abuse while on therapy, and re-evaluate the need for EVEKEO ODT use.
10. Overdosage
Consult with a Certified Poison Control Center (1-800-222-1222) for up-to-date guidance and advice for treatment of overdosage. Individual patient response to amphetamines varies widely. Toxic symptoms may occur idiosyncratically at low doses.
Manifestations of amphetamine overdose include restlessness, tremor, hyperreflexia, rapid respiration, confusion, assaultiveness, hallucinations, panic states, hyperpyrexia, and rhabdomyolysis. Fatigue and depression usually follow the central nervous system stimulation. Other reactions include arrhythmias, hypertension or hypotension, circulatory collapse, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Fatal poisoning is usually preceded by convulsions and coma.
D-amphetamine is not dialyzable.
11. Evekeo ODT Description
EVEKEO ODT orally disintegrating tablets contain amphetamine sulfate, a CNS stimulant, as a 1 to 1 ratio of dextroamphetamine sulfate and levoamphetamine sulfate (d- and l-amphetamine sulfate). Amphetamine sulfate is a white, odorless crystalline powder. It has a slightly bitter taste. Its solutions are acid to litmus, having a pH of 5.0 to 6.0. It is freely soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol.
Structural Formula:
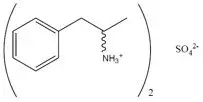
C18H28N2SO4 MW 368.49
EVEKEO ODT tablets are intended for oral use. Each EVEKEO ODT tablet contains 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, or 20 mg of racemic amphetamine sulfate. Each tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: amino methacrylate copolymer, citric acid, crospovidone, ethylcellulose, dibutyl sebacate, magnesium stearate, malic acid, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, and sucralose.
12. Evekeo ODT - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Amphetamines are non-catecholamine sympathomimetic amines with central nervous system (CNS) stimulant activity. The mode of therapeutic action in ADHD is not known.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Amphetamines block the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into the presynaptic neuron and increase the release of these monoamines into the extraneuronal space.
EVEKEO ODT is a 1:1 racemic mixture of d- and l-amphetamine. The l-isomer is more potent than the d-isomer in cardiovascular activity while the d-isomer is more potent than the l-isomer in causing CNS excitatory effects.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Amphetamine demonstrates linear pharmacokinetics over the dose range of 5 to 40 mg.
14. Clinical Studies
The safety and effectiveness of EVEKEO ODT for the treatment of ADHD has been established based on an adequate and well-controlled study of immediate-release amphetamine sulfate (EVEKEO). Below is a description of this study and its results.
Study 1 (NCT01986062) was conducted with EVEKEO tablets in children ages 6 to 12 years who met DSM-IV-TR criteria for ADHD. Following 8 weeks of open-label dose optimization, patients were randomly assigned to continue their optimized dose of EVEKEO (10 to 40 mg/day in divided doses) or placebo for 1 week. After 1 week, patients crossed-over to receive the alternate treatment. At the end of each treatment week, efficacy assessments were conducted at 0.75, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 hours post-dose using the Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham (SKAMP) rating scale. SKAMP is a 13-item teacher-rated scale that assesses manifestations of ADHD in a classroom setting. The SKAMP-Combined score was obtained by summing items 1 through 13. The primary efficacy outcome assessed by the SKAMP-Combined score at 2 hours postdose was statistically significantly better in EVEKEO treatment compared to placebo (Table 3). Key secondary efficacy endpoints were the time-to-onset and duration-of-effect of EVEKEO using SKAMP-Combined scores. SKAMP-Combined scores were statistically significantly better for patients in the EVEKEO treatment group compared to patients in the placebo treatment group beginning at 0.75 hours post-dose and at each assessment through 10 hours post-dose. (Figure 1).
| Study Number | Treatment Group | Primary Efficacy Measure: SKAMP-Combined Score at 2 Hours Post-dose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Pre-Dose Score (SD) | LS Mean (SE) at 2 Hours Post-dose | Placebo-subtracted Difference* (95% CI) | ||
| SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; LS Mean: least-squares mean; CI: confidence interval. | ||||
|
||||
| Study 1 | Evekeo | 18.1 (11.6) | 10.3 (1.09) | -7.9 (-10.1, -5.6) |
| Placebo | 15.3 (11.4) | 18.1 (1.09) | -- | |
Figure 1: LS Mean SKAMP-Combined Scores by Treatment and Timepoint for Pediatric Patients (6 to 12 years) with ADHD after 1 Week of Double Blind Treatment (Study 1)
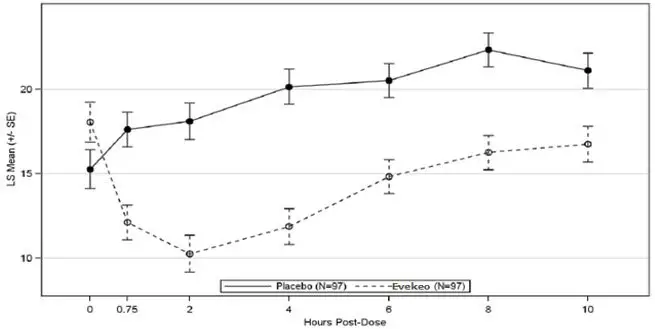
The values at pre-dose hour (zero) are observed means.
16. How is Evekeo ODT supplied
EVEKEO ODT (amphetamine sulfate) orally disintegrating tablets are supplied as follows:
- 5 mg: white to off-white, round, flat-faced radius-edged tablet with "5" on one side and "EVI" on the other
- NDC 24338-031-30: One blister card of 30-count 5 mg strength tablets within a plastic sleeve
- NDC 24338-031-01: Carton containing one plastic sleeve.
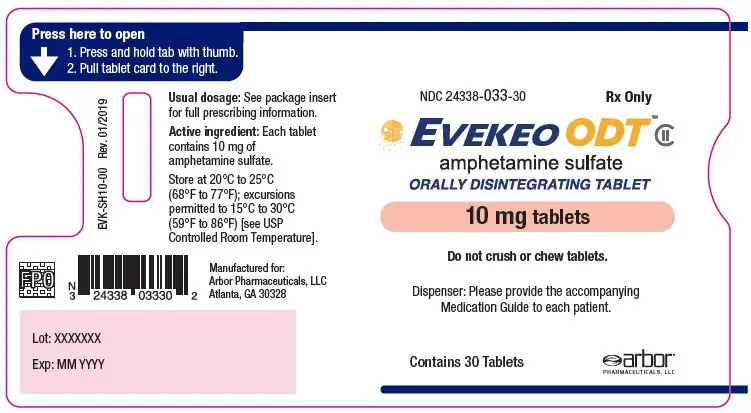
- 10 mg: white to off-white, round, flat-faced radius-edged tablet with "10" on one side and "EVI" on the other
- NDC 24338-033-30: One blister card of 30-count 10 mg strength tablets within a plastic sleeve
- NDC 24338-033-01: Carton containing one plastic sleeve
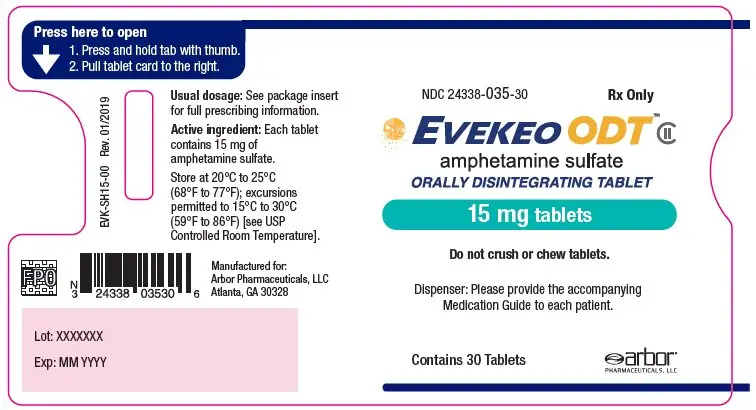
- 15 mg: white to off-white, round, flat-faced radius-edged tablet with "15" on one side and "EVI" on the other
- NDC 24338-035-30: One blister card of 30-count 15 mg strength tablets within a plastic sleeve
- NDC 24338-035-01: Carton containing one plastic sleeve
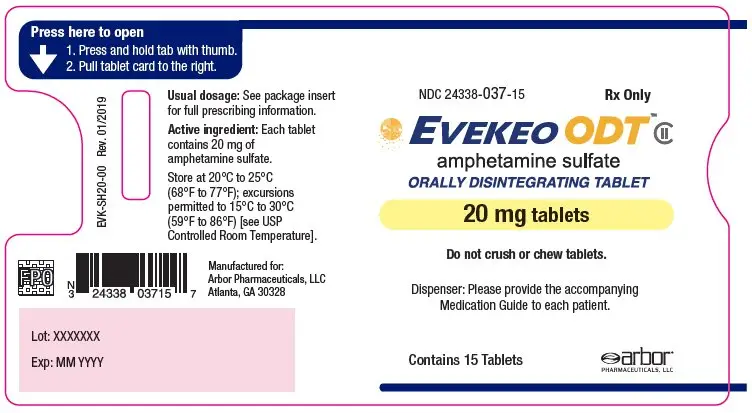
- 20 mg: white to off-white, round, flat-faced radius-edged tablet with "20" on one side and "EVI" on the other
- NDC 24338-037-15: One blister card of 15-count 20 mg strength tablets within a plastic sleeve
- NDC 24338-037-02: Carton containing two 15-count plastic sleeves
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| MEDICATION GUIDE EVEKEO ODT® (ee-VEEK-ee-o) (amphetamine sulfate) orally disintegrating tablets, CII |
||
|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. EVK-MG-03 | Revised: 9/2022 | |
| What is the most important information I should know about EVEKEO ODT? | ||
EVEKEO ODT can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
| What is EVEKEO ODT? | ||
| EVEKEO ODT is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant prescription medicine used for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children 6 to 17 years of age. EVEKEO ODT may help increase attention and decrease impulsiveness and hyperactivity in people with ADHD. | ||
| It is not known if EVEKEO ODT is safe and effective in children under 6 years of age. | ||
| EVEKEO ODT is a federally controlled substance (CII) because it contains amphetamine that can be a target for people who abuse prescription medicines or street drugs. Keep EVEKEO ODT in a safe place to protect it from theft. Never give your EVEKEO ODT to anyone else, because it may cause death or harm them. Selling or giving away EVEKEO ODT may harm others and is against the law. | ||
Do not take EVEKEO ODT if you or your child are:
|
||
Before taking EVEKEO ODT, tell your healthcare provider about all medical conditions, including if you or your child:
|
||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines that you or your child take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | ||
| EVEKEO ODT and some medicines may interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Sometimes the doses of other medicines will need to be changed while taking EVEKEO ODT. | ||
| Especially tell your healthcare provider if you or your child take medicines used to treat depression including MAOIs. | ||
| Know the medicines that you or your child takes. Keep a list of all medicines with you to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | ||
| Your healthcare provider will decide whether EVEKEO ODT can be taken with other medicines. Do not start any new medicine during treatment with EVEKEO ODT without talking to your healthcare provider first. | ||
How should EVEKEO ODT be taken?
|
||
Use the following instructions when taking EVEKEO ODT:
|
||
| If you or your child take too much EVEKEO ODT, call your healthcare provider or poison control center, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away. In case of poisoning call your poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. | ||
| What are possible side effects of EVEKEO ODT? | ||
EVEKEO ODT may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
|
|
|
| The most common side effects of EVEKEO ODT include decreased appetite and trouble sleeping. | ||
| These are not all the possible side effects of EVEKEO ODT. | ||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Arbor Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-800-461-7449 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||
How should I store EVEKEO ODT?
|
||
| Keep EVEKEO ODT and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||
| General information about the safe and effective use of EVEKEO ODT. | ||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use EVEKEO ODT for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give EVEKEO ODT to other people, even if they have the same symptoms. It may harm them and it is against the law. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about EVEKEO ODT that was written for healthcare professionals. | ||
| What are the ingredients in EVEKEO ODT? | ||
| Active ingredient: amphetamine sulfate | ||
| Inactive ingredients: mannitol, silicified microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, ethylcellulose, amino methacrylate copolymer, anhydrous citric acid, magnesium stearate, dibutyl sebacate, malic acid and sucralose | ||
| Distributed by: Arbor® Pharmaceuticals, LLC, Atlanta, GA 30328 | ||
| All rights reserved. | ||
| For more information about EVEKEO ODT, please contact Arbor Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-800-461-7449. | ||
| EVEKEO ODT
amphetamine sulfate tablet, orally disintegrating |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EVEKEO ODT
amphetamine sulfate tablet, orally disintegrating |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EVEKEO ODT
amphetamine sulfate tablet, orally disintegrating |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EVEKEO ODT
amphetamine sulfate tablet, orally disintegrating |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (117505635) |