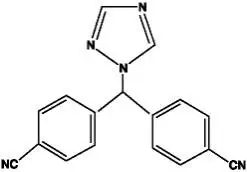
Drug Detail:Femara (Letrozole [ let-roe-zol ])
Drug Class: Aromatase inhibitors Hormones / antineoplastics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
FEMARA (letrozole) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997
Indications and Usage for Femara
Femara is an aromatase inhibitor indicated for:
- Adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor positive early breast cancer. (1.1)
- Extended adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with early breast cancer who have received prior standard adjuvant tamoxifen therapy. (1.2)
- First and second-line treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor positive or unknown advanced breast cancer. (1.3)
Femara Dosage and Administration
Femara tablets are taken orally without regard to meals (2):
- Recommended dose: 2.5.mg once daily. (2.1)
- Patients with cirrhosis or severe hepatic impairment: 2.5 mg every other day. (2.5, 5.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
2.5 mg tablets. (3)
Contraindications
- Pregnancy. (4)
- Known hypersensitivity to the active substance, or to any of the excipients. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Decreases in bone mineral density may occur. Consider bone mineral density monitoring. (5.1)
- Increases in total cholesterol may occur. Consider cholesterol monitoring. (5.2)
- Fatigue, dizziness, and somnolence may occur. Exercise caution when operating machinery. (5.4)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Obtain a pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception. (5.6, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (greater than 20%) were hot flashes, arthralgia; flushing, asthenia, edema, arthralgia, headache, dizziness, hypercholesterolemia, sweating increased, bone pain; and musculoskeletal. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 5/2020
Related/similar drugs
Ibrance, Keytruda, tamoxifen, letrozole, Arimidex, paclitaxel, XelodaFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Femara
1.1 Adjuvant Treatment of Early Breast Cancer
Femara (letrozole) is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor positive early breast cancer.
1.2 Extended Adjuvant Treatment of Early Breast Cancer
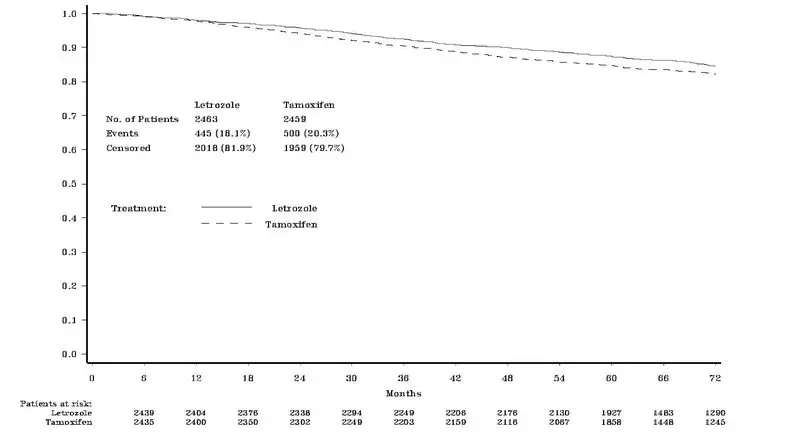
Femara is indicated for the extended adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer in postmenopausal women, who have received 5 years of adjuvant tamoxifen therapy. The effectiveness of Femara in extended adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer is based on an analysis of disease-free survival (DFS) in patients treated with Femara for a median of 60 months [see Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.3)].
1.3 First and Second-Line Treatment of Advanced Breast Cancer
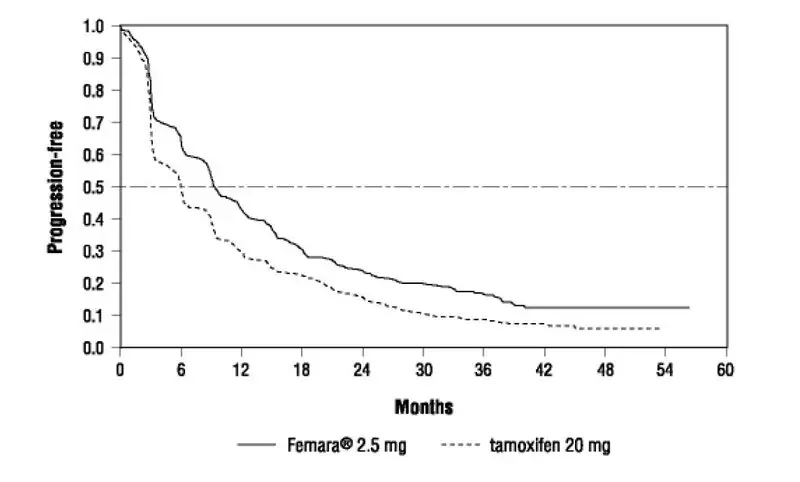
Femara is indicated for first-line treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor positive or unknown, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Femara is also indicated for the treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression following antiestrogen therapy [see Clinical Studies (14.4, 14.5)].
2. Femara Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dose
The recommended dose of Femara is one 2.5 mg tablet administered once a day, without regard to meals.
2.5 Use in Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, although Femara blood concentrations were modestly increased in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment due to cirrhosis. The dose of Femara in patients with cirrhosis and severe hepatic dysfunction should be reduced by 50% [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. The recommended dose of Femara for such patients is 2.5 mg administered every other day. The effect of hepatic impairment on Femara exposure in noncirrhotic cancer patients with elevated bilirubin levels has not been determined.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
2.5 mg tablets: dark yellow, film-coated, round, slightly biconvex, with beveled edges (imprinted with the letters FV on one side and CG on the other side).
4. Contraindications
- Pregnancy: Letrozole can cause fetal harm [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Known hypersensitivity to the active substance, or to any of the excipients [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Bone Effects
Use of Femara may cause decreases in bone mineral density (BMD). Consideration should be given to monitoring BMD. Results of a safety study to evaluate safety in the adjuvant setting comparing the effect on lumbar spine (L2-L4) BMD of adjuvant treatment with letrozole to that with tamoxifen showed at 24 months a median decrease in lumbar spine BMD of 4.1% in the letrozole arm compared to a median increase of 0.3% in the tamoxifen arm (difference = 4.4%) (P < 0.0001) [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Updated results from the BMD substudy (MA-17B) in the extended adjuvant setting demonstrated that at 2 years patients receiving letrozole had a median decrease from baseline of 3.8% in hip BMD compared to a median decrease of 2.0% in the placebo group. The changes from baseline in lumbar spine BMD in letrozole and placebo treated groups were not significantly different [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
In the adjuvant trial (BIG 1-98) the incidence of bone fractures at any time after randomization was 14.7% for letrozole and 11.4% for tamoxifen at a median follow-up of 96 months. The incidence of osteoporosis was 5.1% for letrozole and 2.7% for tamoxifen [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. In the extended adjuvant trial (MA-17), the incidence of bone fractures at any time after randomization was 13.3% for letrozole and 7.8% for placebo at a median follow-up of 62 months. The incidence of new osteoporosis was 14.5% for letrozole and 7.8% for placebo [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.2 Cholesterol
Consideration should be given to monitoring serum cholesterol. In the adjuvant trial (BIG 1-98), hypercholesterolemia was reported in 52.3% of letrozole patients and 28.6% of tamoxifen patients. Grade 3-4 hypercholesterolemia was reported in 0.4% of letrozole patients and 0.1% of tamoxifen patients. Also in the adjuvant setting, an increase of greater than or equal to 1.5 x upper limit of normal (ULN) in total cholesterol (generally nonfasting) was observed in patients on monotherapy who had baseline total serum cholesterol within the normal range (i.e., less than =1.5 x ULN) in 155/1843 (8.4%) patients on letrozole vs 71/1840 (3.9%) patients on tamoxifen Lipid lowering medications were required for 29% of patients on letrozole and 20% on tamoxifen [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.3 Hepatic Impairment
Subjects with cirrhosis and severe hepatic impairment who were dosed with 2.5 mg of Femara experienced approximately twice the exposure to Femara as healthy volunteers with normal liver function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, a dose reduction is recommended for this patient population. The effect of hepatic impairment on Femara exposure in cancer patients with elevated bilirubin levels has not been determined [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.4 Fatigue and Dizziness
Because fatigue, dizziness, and somnolence have been reported with the use of Femara, caution is advised when driving or using machinery until it is known how the patient reacts to Femara use.
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on post-marketing reports, findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action, Femara can cause fetal harm and is contraindicated for use in pregnant women. In post-marketing reports, use of letrozole during pregnancy resulted in cases of spontaneous abortions and congenital birth defects. Letrozole caused embryo-fetal toxicities in rats and rabbits at maternal exposures that were below the maximum recommended human dose (MHRD) on a mg/m2 basis. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during therapy with Femara and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose [see Adverse Reactions (6.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling.
- Bone effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Increases in cholesterol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Fatigue and Dizziness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adjuvant Treatment of Early Breast Cancer
In study, BIG 1-98, the median treatment duration of adjuvant treatment was 60 months and the median duration of follow-up for safety was 96 months for patients receiving Femara and tamoxifen.
Certain adverse reactions were prospectively specified for analysis (see Table 1), based on the known pharmacologic properties and side effect profiles of the two drugs.
Adverse reactions were analyzed irrespective of whether a symptom was present or absent at baseline. Most adverse reactions reported (approximately 75% of patients who reported AEs) were Grade 1 or Grade 2 applying the Common Toxicity Criteria (CTC) Version 2.0/Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), Version 3.0. Table 1 describes adverse reactions (Grades 1-4 and Grades 3-4) irrespective of relationship to study treatment in the adjuvant trial for the monotherapy arms analysis (safety population).
| Grades 1-4 | Grades 3-4 | |||||||
| Femara | Tamoxifen | Femara | Tamoxifen | |||||
| Adverse Reactions | N = 2448 | N = 2447 | N = 2448 | N = 2447 | ||||
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||||
| Patients with any adverse reaction | 2309 | (94.3) | 2212 | (90.4) | 636 | (26.0) | 606 | (24.8) |
| Hypercholesterolemia* | 1280 | (52.3) | 700 | (28.6) | 11 | (0.4) | 6 | (0.2) |
| Hot flashes* | 819 | (33.5) | 929 | (38.0) | - | - | - | - |
| Arthralgia/arthritis* | 621 | (25.4) | 504 | (20.6) | 84 | (3.4) | 50 | (2.0) |
| Bone fractures1 | 361 | (14.7) | 280 | (11.4) | - | - | - | - |
| Night sweats* | 356 | (14.5) | 426 | (17.4) | - | - | - | - |
| Weight increase* | 317 | (12.9) | 378 | (15.4) | 27 | (1.1) | 39 | (1.6) |
| Nausea* | 284 | (11.6) | 277 | (11.3) | 6 | (0.2) | 9 | (0.4) |
| Bone fractures**2 | 249 | (10.2) | 175 | (7.2) | - | - | - | - |
| Fatigue (lethargy, malaise, asthenia)* | 235 | (9.6) | 250 | (10.2) | 6 | (0.2) | 7 | (0.3) |
| Myalgia* | 221 | (9.0) | 212 | (8.7) | 18 | (0.7) | 14 | (0.6) |
| Vaginal bleeding* | 129 | (5.3) | 320 | (13.1) | 1 | (< 0.1) | 8 | (0.3) |
| Edema* | 164 | (6.7) | 160 | (6.5) | 3 | (0.1) | 1 | (< 0.1) |
| Weight decrease | 140 | (5.7) | 129 | (5.3) | 8 | (0.3) | 5 | (0.2) |
| Osteoporosis** | 126 | (5.1) | 67 | (2.7) | 10 | (0.4) | 5 | (0.2) |
| Back pain | 125 | (5.1) | 136 | (5.6) | 7 | (0.3) | 11 | (0.4) |
| Bone pain | 123 | (5.0) | 109 | (4.5) | 6 | (0.2) | 4 | (0.2) |
| Depression | 119 | (4.9) | 114 | (4.7) | 16 | (0.7) | 14 | (0.6) |
| Vaginal irritation* | 112 | (4.6) | 77 | (3.1) | 2 | (< 0.1) | 2 | (< 0.1) |
| Headache* | 105 | (4.3) | 94 | (3.8) | 8 | (0.3) | 4 | (0.2) |
| Pain in extremity | 103 | (4.2) | 79 | (3.2) | 6 | (0.2) | 4 | (0.2) |
| Osteopenia* | 87 | (3.6) | 76 | (3.1) | 0 | - | 3 | (0.1) |
| Dizziness/light-headedness* | 84 | (3.4) | 80 | (3.3) | 1 | (< 0.1) | 6 | (0.2) |
| Alopecia | 83 | (3.4) | 84 | (3.4) | - | - | - | - |
| Vomiting* | 80 | (3.3) | 80 | (3.3) | 3 | (0.1) | 5 | (0.2) |
| Cataract* | 49 | (2.0) | 54 | (2.2) | 16 | (0.7) | 17 | (0.7) |
| Constipation* | 49 | (2.0) | 71 | (2.9) | 3 | (0.1) | 1 | (< 0.1) |
| Myocardial infarction1 | 42 | (1.7) | 28 | (1.1) | - | - | - | - |
| Breast pain* | 37 | (1.5) | 43 | (1.8) | 1 | (< 0.1) | - | - |
| Anorexia* | 20 | (0.8) | 20 | (0.8) | 1 | (< 0.1) | 1 | (< 0.1) |
| Endometrial proliferation disorders* | 14 | (0.6) | 86 | (3.5) | 0 | - | 14 | (0.6) |
| Ovarian cyst* | 11 | (0.4) | 18 | (0.7) | 4 | (0.2) | 4 | (0.2) |
| Endometrial hyperplasia/cancer**1 | 11 | (0.4) | 72 | (2.9) | - | - | - | - |
| Endometrial hyperplasia/cancer**,3 | 6/1909 | (0.3) | 57/1943 | (2.9) | - | - | - | - |
| Other endometrial disorders* | 2 | (< 0.1) | 3 | (0.1) | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Myocardial infarction**2 | 24 | (1.0) | 12 | (0.5) | - | - | - | - |
| Myocardial ischemia | 6 | (0.2) | 9 | (0.4) | - | - | - | - |
| Cerebrovascular accident/TIA**1 | 74 | (3.0) | 68 | (2.8) | - | - | - | - |
| Cerebrovascular accident/TIA**2 | 51 | (2.1) | 47 | (1.9) | - | - | - | - |
| Angina requiring surgery**1 | 35 | (1.4) | 33 | (1.3) | - | - | - | - |
| Angina requiring surgery**2 | 25 | (1.0) | 25 | (1.0) | - | - | - | - |
| Thromboembolic event**1 | 79 | (3.2) | 113 | (4.6) | - | - | - | - |
| Thromboembolic event**2 | 51 | (2.1) | 89 | (3.6) | - | - | - | - |
| Cardiac failure1 | 39 | (1.6) | 34 | (1.4) | - | - | - | - |
| Cardiac failure2 | 27 | (1.1) | 15 | (0.6) | - | - | - | - |
| Hypertension1 | 160 | (6.5) | 175 | (7.2) | - | - | - | - |
| Hypertension2 | 138 | (5.6) | 139 | (5.7) | - | - | - | - |
| Other cardiovascular**1 | 172 | (7.0) | 174 | (7.1) | - | - | - | - |
| Other cardiovascular**2 | 120 | (4.9) | 119 | (4.9) | - | - | - | - |
| Second primary malignancy1 | 129 | (5.3) | 150 | (6.1) | - | - | - | - |
| Second primary malignancy2 | 54 | (2.2) | 79 | (3.2) | - | - | - | - |
| *Target events pre-specified for analysis **Events pre-printed on CRF |
||||||||
| 1At median follow-up of 96 months (i.e., any time after randomization) for Femara (range up to 144 months) and 95 months for tamoxifen (range up to 143 months). 2At median treatment duration of 60 months (i.e. during treatment + 30 days after discontinuation of treatment) for Femara and tamoxifen (range up to 68 months). 3Excluding women who had undergone hysterectomy before study entry. TIA = Transient ischemic attack. Note: Cardiovascular events (including cerebrovascular and thromboembolic events), skeletal and urogenital/endometrial events and second primary malignancies were collected life -long. All of these events were assumed to be of CTC Grade 3 to 5 and were not individually graded. |
||||||||
When considering all grades during study treatment, a higher incidence of events was seen for Femara regarding fractures (10.1% vs 7.1%), myocardial infarctions (1.0% vs 0.5%), and arthralgia (25.2% vs 20.4%) (Femara vs tamoxifen respectively). A higher incidence was seen for tamoxifen regarding thromboembolic events (2.1% vs 3.6%), endometrial hyperplasia/cancer (0.3% vs 2.9%), and endometrial proliferation disorders (0.3% vs 1.8%) (Femara vs tamoxifen respectively).
At a median follow-up of 96 months, a higher incidence of events was seen for Femara (14.7%) than for tamoxifen (11.4%) regarding fractures. A higher incidence was seen for tamoxifen compared to Femara regarding thromboembolic events (4.6% vs 3.2%), and endometrial hyperplasia or cancer (2.9% vs 0.4%) (tamoxifen vs Femara, respectively).
Bone Study: Results of a safety trial in 263 postmenopausal women with resected receptor positive early breast cancer in the adjuvant setting comparing the effect on lumbar spine (L2-L4) BMD of adjuvant treatment with letrozole to that with tamoxifen showed at 24 months a median decrease in lumbar spine BMD of 4.1% in the letrozole arm compared to a median increase of 0.3% in the tamoxifen arm (difference = 4.4%) (P < 0.0001). No patients with a normal BMD at baseline became osteoporotic over the 2 years and only 1 patient with osteopenia at baseline (T score of -1.9) developed osteoporosis during the treatment period (assessment by central review). The results for total hip BMD were similar, although the differences between the two treatments were less pronounced. During the 2 year period, fractures were reported by 4 of 103 patients (4%) in the letrozole arm, and 6 of 97 patients (6%) in the tamoxifen arm.
Lipid Study: In a safety trial in 263 postmenopausal women with resected receptor positive early breast cancer at 24 months comparing the effects on lipid profiles of adjuvant letrozole to tamoxifen, 12% of patients on letrozole had at least one total cholesterol value of a higher CTCAE grade than at baseline compared with 4% of patients on tamoxifen. In another postapproval randomized, multicenter, open label, study of letrozole vs anastrozole in the adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor and node positive breast cancer (FACE, NCT00248170), the median duration of treatment was 60 months for both treatment arms. Table 2 describes adverse reactions (Grades 1-4 and Grades 3-4) irrespective of relationship to study treatment in the adjuvant study (safety population).
|
Adverse Reactions | Letrozole
N = 2049 n (%) | Anastrozole
N = 2062 n (%) |
||
|
| Grade 3/4
n (%) | All Grades
n (%) | Grade 3/4
n (%) | All Grades
n (%) |
| Patients with at least one AR | 628 (30.6) | 2049 (100.0) | 591 (28.7) | 2062 (100.0) |
| Arthralgia | 80 (3.9) | 987 (48.2) | 69 (3.3) | 987 (47.9) |
| Hot flush | 17 (0.8) | 666 (32.5) | 9 (0.4) | 666 (32.3) |
| Fatigue | 8 (0.4) | 345 (16.8) | 10 (0.5) | 343 (16.6) |
| Osteoporosis | 5 (0.2) | 223 (10.9) | 11 (0.5) | 225 (10.9) |
| Myalgia | 16 (0.8) | 233 (11.4) | 15 (0.7) | 212 (10.3) |
| Back pain | 11 (0.5) | 212 (10.3) | 17 (0.8) | 193 (9.4) |
| Osteopenia | 4 (0.2) | 203 (9.9) | 1 (0.0) | 173 (8.4) |
| Pain in extremity | 9 (0.4) | 168 (8.2) | 3 (0.1) | 174 (8.4) |
| Lymphoedema | 5 (0.2) | 159 (7.8) | 2 (0.1) | 179 (8.7) |
| Insomnia | 7 (0.3) | 160 (7.8) | 3 (0.1) | 149 (7.2) |
| Hypercholesterolaemia | 2 (0.1) | 155 (7.6) | 1 (0.0) | 151 (7.3) |
| Hypertension | 25 (1.2) | 156 (7.6) | 20 (1.0) | 149 (7.2) |
| Depression | 16 (0.8) | 147 (7.2) | 13 (0.6) | 137 (6.6) |
| Bone pain | 10 (0.5) | 138 (6.7) | 9 (0.4) | 122 (5.9) |
| Nausea | 6 (0.3) | 137 (6.7) | 5 (0.2) | 152 (7.4) |
| Headache | 3 (0.1) | 130 (6.3) | 5 (0.2) | 168 (8.1) |
| Alopecia | 2 (0.1) | 127 (6.2) | 0 (0.0) | 134 (6.5) |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 6 (0.3) | 123 (6.0) | 9 (0.4) | 147 (7.1) |
| Radiation skin injury | 11 (0.5) | 120 (5.9) | 6 (0.3) | 88 (4.3) |
| Dyspnea | 16 (0.8) | 118 (5.8) | 10 (0.5) | 96 (4.7) |
| Cough | 1 (0.0) | 106 (5.2) | 1 (0.0) | 120 (5.8) |
| Musculoskeletal stiffness | 2 (0.1) | 102 (5.0) | 2 (0.1) | 84 (4.1) |
| Dizziness | 2 (0.2) | 94 (4.6) | 7 (0.3) | 109 (5.3) |
The following adverse reactions were also identified in less than 5% of the 2049 patients treated with letrozole and not included in the table: fall, vertigo, hyperbilirubinemia, jaundice, and chest pain.
Extended Adjuvant Treatment of Early Breast Cancer, Median Treatment Duration of 24 Months
In study MA-17, the median duration of extended adjuvant treatment was 24 months and the median duration of follow-up for safety was 28 months for patients receiving Femara and placebo.
Table 3 describes the adverse reactions occurring at a frequency of at least 5% in any treatment group during treatment. Most adverse reactions reported were Grade 1 and Grade 2 based on the CTC Version 2.0. In the extended adjuvant setting, the reported drug-related adverse reactions that were significantly different from placebo were hot flashes, arthralgia/arthritis, and myalgia.
| Number (%) of Patients with Grade 1-4 Adverse Reactions | Number (%) of Patients with Grade 3-4 Adverse Reactions | |||
| Femara | Placebo | Femara | Placebo | |
| N = 2563 | N = 2573 | N = 2563 | N = 2573 | |
| Any Adverse Reactions | 2232 (87.1) | 2174 (84.5) | 419 (16.3) | 389 (15.1) |
| Vascular Disorders | 1375 (53.6) | 1230 (47.8) | 59 (2.3) | 74 (2.9) |
| Flushing | 1273 (49.7) | 1114 (43.3) | 3 (0.1) | 0 |
| General Disorders | 1154 (45) | 1090 (42.4) | 30 (1.2) | 28 (1.1) |
| Asthenia | 862 (33.6) | 826 (32.1) | 16 (0.6) | 7 (0.3) |
| Edema NOS | 471 (18.4) | 416 (16.2) | 4 (0.2) | 3 (0.1) |
| Musculoskeletal Disorders | 978 (38.2) | 836 (32.5) | 71 (2.8) | 50 (1.9) |
| Arthralgia | 565 (22) | 465 (18.1) | 25 (1) | 20 (0.8) |
| Arthritis NOS | 173 (6.7) | 124 (4.8) | 10 (0.4) | 5 (0.2) |
| Myalgia | 171 (6.7) | 122 (4.7) | 8 (0.3) | 6 (0.2) |
| Back Pain | 129 (5) | 112 (4.4) | 8 (0.3) | 7 (0.3) |
| Nervous System Disorders | 863 (33.7) | 819 (31.8) | 65 (2.5) | 58 (2.3) |
| Headache | 516 (20.1) | 508 (19.7) | 18 (0.7) | 17 (0.7) |
| Dizziness | 363 (14.2) | 342 (13.3) | 9 (0.4) | 6 (0.2) |
| Skin Disorders | 830 (32.4) | 787 (30.6) | 17 (0.7) | 16 (0.6) |
| Sweating Increased | 619 (24.2) | 577 (22.4) | 1 (< 0.1) | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | 725 (28.3) | 731 (28.4) | 43 (1.7) | 42 (1.6) |
| Constipation | 290 (11.3) | 304 (11.8) | 6 (0.2) | 2 (< 0.1) |
| Nausea | 221 (8.6) | 212 (8.2) | 3 (0.1) | 10 (0.4) |
| Diarrhea NOS | 128 (5) | 143 (5.6) | 12 (0.5) | 8 (0.3) |
| Metabolic Disorders | 551 (21.5) | 537 (20.9) | 24 (0.9) | 32 (1.2) |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 401 (15.6) | 398 (15.5) | 2 (< 0.1) | 5 (0.2) |
| Reproductive Disorders | 303 (11.8) | 357 (13.9) | 9 (0.4) | 8 (0.3) |
| Vaginal Hemorrhage | 123 (4.8) | 171 (6.6) | 2 (< 0.1) | 5 (0.2) |
| Vulvovaginal Dryness | 137 (5.3) | 127 (4.9) | 0 | 0 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | 320 (12.5) | 276 (10.7) | 21 (0.8) | 16 (0.6) |
| Insomnia | 149 (5.8) | 120 (4.7) | 2 (< 0.1) | 2 (< 0.1) |
| Respiratory Disorders | 279 (10.9) | 260 (10.1) | 30 (1.2) | 28 (1.1) |
| Dyspnea | 140 (5.5) | 137 (5.3) | 21 (0.8) | 18 (0.7) |
| Investigations | 184 (7.2) | 147 (5.7) | 13 (0.5) | 13 (0.5) |
| Infections and Infestations | 166 (6.5) | 163 (6.3) | 40 (1.6) | 33 (1.3) |
| Renal Disorders | 130 (5.1) | 100 (3.9) | 12 (0.5) | 6 (0.2) |
Based on a median follow-up of patients for 28 months, the incidence of clinical fractures from the core randomized study in patients who received Femara was 5.9% (152) and placebo was 5.5% (142). The incidence of self-reported osteoporosis was higher in patients who received Femara 6.9% (176) than in patients who received placebo 5.5% (141). Bisphosphonates were administered to 21.1% of the patients who received Femara and 18.7% of the patients who received placebo.
The incidence of cardiovascular ischemic events from the core randomized study was comparable between patients who received Femara 6.8% (175) and placebo 6.5% (167).
A patient-reported measure that captures treatment impact on important symptoms associated with estrogen deficiency demonstrated a difference in favor of placebo for vasomotor and sexual symptom domains.
Bone Substudy: [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Lipid Substudy: In the extended adjuvant setting, based on a median duration of follow-up of 62 months, there was no significant difference between Femara and placebo in total cholesterol or in any lipid fraction at any time over 5 years. Use of lipid lowering drugs or dietary management of elevated lipids was allowed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Updated Analysis, Extended Adjuvant Treatment of Early Breast Cancer, Median Treatment Duration of 60 Months
The extended adjuvant treatment trial (MA-17) was unblinded early [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. At the updated (final analysis), overall the side effects seen were consistent to those seen at a median treatment duration of 24 months.
During treatment or within 30 days of stopping treatment (median duration of treatment 60 months) a higher rate of fractures was observed for Femara (10.4%) compared to placebo (5.8%), as also a higher rate of osteoporosis (Femara 12.2% vs placebo 6.4%).
Based on 62 months median duration of follow-up in the randomized letrozole arm in the safety population the incidence of new fractures at any time after randomization was 13.3% for letrozole and 7.8% for placebo. The incidence of new osteoporosis was 14.5% for letrozole and 7.8% for placebo.
During treatment or within 30 days of stopping treatment (median duration of treatment 60 months), the incidence of cardiovascular events was 9.8% for Femara and 7.0% for placebo.
Based on 62 months median duration of follow-up in the randomized letrozole arm in the safety population the incidence of cardiovascular disease at any time after randomization was 14.4% for letrozole and 9.8% for placebo.
Lipid Substudy: In the extended adjuvant setting (MA-17), based on a median duration of follow-up of 62 months, there was no significant difference between Femara and placebo in total cholesterol or in any lipid fraction over 5 years. Use of lipid lowering drugs or dietary management of elevated lipids was allowed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
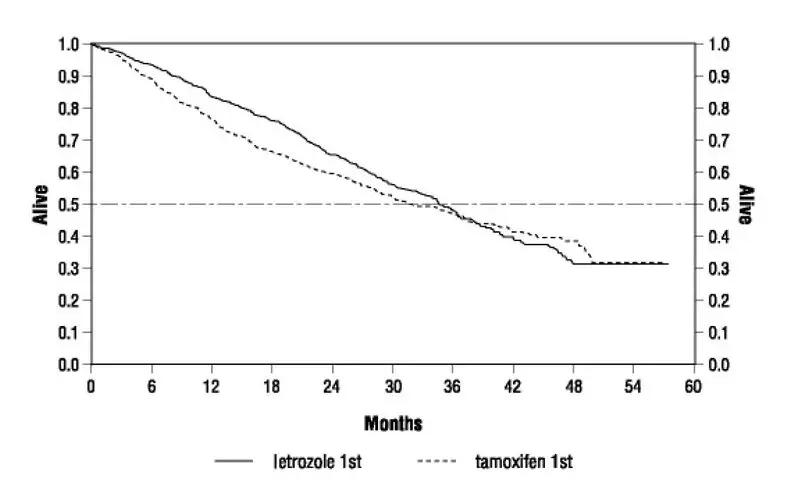
First-Line Treatment of Advanced Breast Cancer
In study P025 a total of 455 patients were treated for a median time of exposure of 11 months in the Femara arm (median 6 months in the tamoxifen arm). The incidence of adverse reactions was similar for Femara and tamoxifen. The most frequently reported adverse reactions were bone pain, hot flushes, back pain, nausea, arthralgia, and dyspnea. Discontinuations for adverse reactions other than progression of tumor occurred in 10/455 (2%) of patients on Femara and in 15/455 (3%) of patients on tamoxifen.
Adverse reactions that were reported in at least 5% of the patients treated with Femara 2.5 mg or tamoxifen 20 mg in the first-line treatment study are shown in Table 4.
| Adverse | Femara | Tamoxifen |
| Reactions | 2.5 mg | 20 mg |
| (N = 455) | (N = 455) | |
| % | % | |
| General Disorders | ||
| Fatigue | 13 | 13 |
| Chest Pain | 8 | 9 |
| Edema Peripheral | 5 | 6 |
| Pain NOS | 5 | 7 |
| Weakness | 6 | 4 |
| Investigations | ||
| Weight Decreased | 7 | 5 |
| Vascular Disorders | ||
| Hot Flushes | 19 | 16 |
| Hypertension | 8 | 4 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Nausea | 17 | 17 |
| Constipation | 10 | 11 |
| Diarrhea | 8 | 4 |
| Vomiting | 7 | 8 |
| Infections/Infestations | ||
| Influenza | 6 | 4 |
| Urinary Tract Infection NOS | 6 | 3 |
| Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications | ||
| Post-Mastectomy Lymphedema | 7 | 7 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||
| Anorexia | 4 | 6 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
| Bone Pain | 22 | 21 |
| Back Pain | 18 | 19 |
| Arthralgia | 16 | 15 |
| Pain in Limb | 10 | 8 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Headache NOS | 8 | 7 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Insomnia | 7 | 4 |
| Reproductive System and Breast Disorders | ||
| Breast Pain | 7 | 7 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||
| Dyspnea | 18 | 17 |
| Cough | 13 | 13 |
| Chest Wall Pain | 6 | 6 |
Other less frequent (less than or equal to 2%) adverse reactions considered consequential for both treatment groups, included peripheral thromboembolic events, cardiovascular events, and cerebrovascular events. Peripheral thromboembolic events included venous thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, portal vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Cardiovascular events included angina, myocardial infarction, myocardial ischemia, and coronary heart disease. Cerebrovascular events included transient ischemic attacks, thrombotic or hemorrhagic strokes, and development of hemiparesis.
Second-Line Treatment of Advanced Breast Cancer
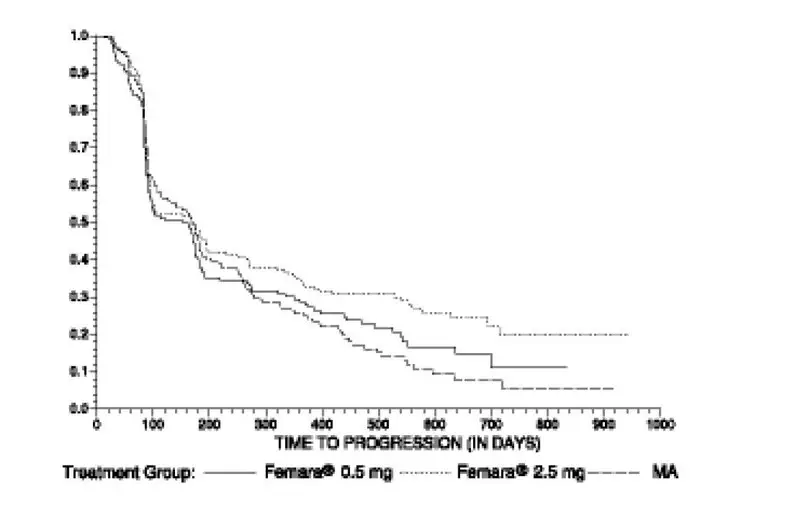
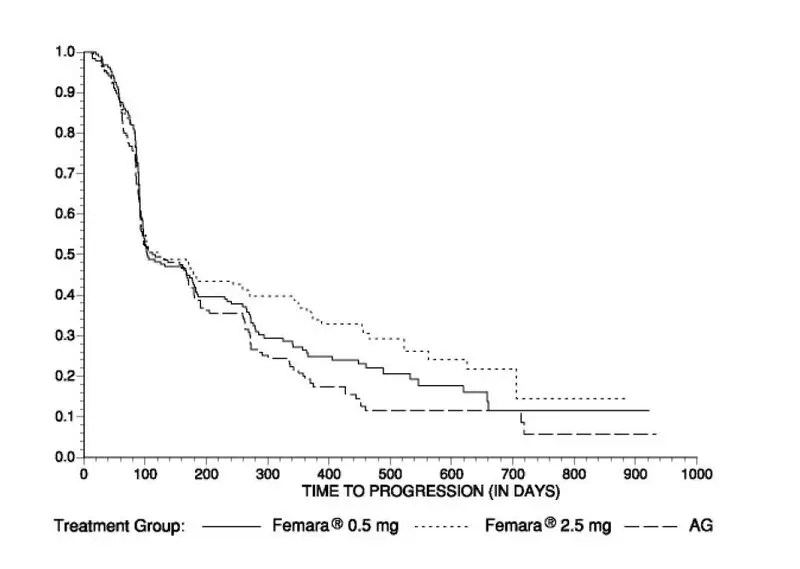
Study discontinuations in the megestrol acetate comparison study (AR/BC2) for adverse reactions other than progression of tumor were 5/188 (2.7%) on Femara 0.5 mg, in 4/174 (2.3%) on Femara 2.5 mg, and in 15/190 (7.9%) on megestrol acetate. There were fewer thromboembolic events at both Femara doses than on the megestrol acetate arm (0.6% vs 4.7%). There was also less vaginal bleeding (0.3% vs 3.2%) on Femara than on megestrol acetate. In the aminoglutethimide comparison study (AR/BC3), discontinuations for reasons other than progression occurred in 6/193 (3.1%) on 0.5 mg Femara, 7/185 (3.8%) on 2.5 mg Femara, and 7/178 (3.9%) of patients on aminoglutethimide.
Comparisons of the incidence of adverse reactions revealed no significant differences between the high and low dose Femara groups in either study. Most of the adverse reactions observed in all treatment groups were mild to moderate in severity and it was generally not possible to distinguish adverse reactions due to treatment from the consequences of the patient’s metastatic breast cancer, the effects of estrogen deprivation, or intercurrent illness.
Adverse reactions that were reported in at least 5% of the patients treated with Femara 0.5 mg, Femara 2.5 mg, megestrol acetate, or aminoglutethimide in the two controlled trials AR/BC2 and AR/BC3 are shown in Table 5.
| 1Includes peripheral edema, leg edema, dependent edema, edema. 2Includes musculoskeletal pain, skeletal pain, back pain, arm pain, leg pain. 3Includes rash, erythematous rash, maculopapular rash, psoriasiform rash, vesicular rash. |
||||
| Adverse | Pooled | Pooled | Megestrol | |
| Reactions | Femara | Femara | Acetate | Aminoglutethimide |
| 2.5 mg | 0.5 mg | 160 mg | 500 mg | |
| (N = 359) | (N = 380) | (N = 189) | (N = 178) | |
| % | % | % | % | |
| Body as a Whole | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chest Pain | 6 | 3 | 7 | 3 |
| Peripheral Edema1 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 3 |
| Asthenia | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 |
| Weight Increase | 2 | 2 | 9 | 3 |
| Cardiovascular | ||||
| Hypertension | 5 | 7 | 5 | 6 |
| Digestive System | ||||
| Nausea | 13 | 15 | 9 | 14 |
| Vomiting | 7 | 7 | 5 | 9 |
| Constipation | 6 | 7 | 9 | 7 |
| Diarrhea | 6 | 5 | 3 | 4 |
| Pain-Abdominal | 6 | 5 | 9 | 8 |
| Anorexia | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Dyspepsia | 3 | 4 | 6 | 5 |
| Infections/Infestations | ||||
| Viral Infection | 6 | 5 | 6 | 3 |
| Lab Abnormality | ||||
| Hypercholesterolemia | 3 | 3 | 0 | 6 |
| Musculoskeletal System | ||||
| Musculoskeletal2 | 21 | 22 | 30 | 14 |
| Arthralgia | 8 | 8 | 8 | 3 |
| Nervous System | ||||
| Headache | 9 | 12 | 9 | 7 |
| Somnolence | 3 | 2 | 2 | 9 |
| Dizziness | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3 |
| Respiratory System | ||||
| Dyspnea | 7 | 9 | 16 | 5 |
| Coughing | 6 | 5 | 7 | 5 |
| Skin and Appendages | ||||
| Hot Flushes | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Rash3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| Pruritus | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
Other less frequent (less than 5%) adverse reactions considered consequential and reported in at least 3 patients treated with Femara, included hypercalcemia, fracture, depression, anxiety, pleural effusion, alopecia, increased sweating, and vertigo.
First and Second-Line Treatment of Advanced Breast Cancer
In the combined analysis of the first- and second-line metastatic trials and postmarketing experiences other adverse reactions that were reported were cataract, eye irritation, palpitations, cardiac failure, tachycardia, dysesthesia (including hypesthesia/paresthesia), arterial thrombosis, memory impairment, irritability, nervousness, urticaria, increased urinary frequency, leukopenia, stomatitis cancer pain, pyrexia, vaginal discharge, appetite increase, dryness of skin and mucosa (including dry mouth), and disturbances of taste and thirst.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on postmarketing reports, findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action, Femara can cause fetal harm and is contraindicated for use in pregnant women. In post-marketing reports, use of letrozole during pregnancy resulted in cases of spontaneous abortions and congenital birth defects; however, the data are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.2), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
In animal reproduction studies, administration of letrozole to pregnant animals during organogenesis resulted in increased post-implantation pregnancy loss and resorption, fewer live fetuses, and fetal malformation affecting the renal and skeletal systems in rats and rabbits at doses approximately 0.1 times the daily maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m2 basis (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. However, the background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2%-4% and of miscarriage is 15%-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
In a fertility and early embryonic development toxicity study in female rats, oral administration of letrozole starting 2 weeks before mating until pregnancy day 6 resulted in an increase in pre-implantation loss at doses ≥ 0.003 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.01 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis).
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study in rats, daily administration of oral letrozole during the period of organogenesis at doses ≥ 0.003 mg/kg (approximately 0.01 time the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis) resulted in embryo-fetal toxicity including intrauterine mortality, increased resorptions and postimplantation loss, decreased numbers of live fetuses and fetal anomalies, including absence and shortening of renal papilla, dilation of ureter, edema, and incomplete ossification of frontal skull and metatarsals. Letrozole was teratogenic to rats at a dose of 0.03 mg/kg (approximately 0.01 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis) and caused fetal domed head and cervical/centrum vertebral fusion.
In the embryo-fetal development toxicity study in rabbits, daily administration of oral letrozole during the period of organogenesis at doses ≥ 0.002 mg/kg (approximately 0.01 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis) resulted in embryo-fetal toxicity, including intrauterine mortality, increased resorption, increased postimplantation loss and decreased numbers of live fetuses. Fetal anomalies included incomplete ossification of the skull, sternebrae, and fore- and hind legs.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known if letrozole is present in human milk. There are no data on the effects of letrozole on the breastfed infant or milk production. Exposure of lactating rats to letrozole was associated with impaired reproductive performance of the male offspring (see Data). Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from Femara, advise lactating women not to breastfeed while taking Femara and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose.
Data
Animal Data
In a postnatal developmental toxicity study in lactating rats, letrozole was administered orally at doses of 1, 0.003, 0.03, or 0.3 mg/kg/day on Day 0 through Day 20 of lactation. The reproductive performance of the male offspring was impaired at letrozole dose as low as 0.003 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.01 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis), as reflected by decreased mating and pregnancy ratios. There were no effects on the reproductive performance of female offspring.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Based on animal studies, Femara can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Females of reproductive potential should have a pregnancy test prior to starting treatment with Femara.
Contraception
Females
Based on animal studies, Femara can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Femara and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Females
Based on studies in female animals, Femara may impair fertility in females of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Males
Based on studies in male animals, Femara may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
| FEMARA
letrozole tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |