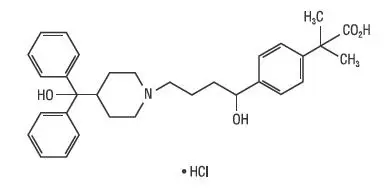
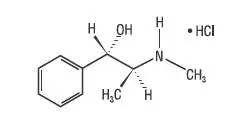
Drug Class: Upper respiratory combinations
Related/similar drugs
prednisone, fluticasone nasal, cetirizine, loratadine, promethazine, ZyrtecFexofenadine and Pseudoephedrine - Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine hydrochloride in subjects with seasonal allergic rhinitis were similar to those in healthy volunteers.
Contraindications
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients.
Due to its pseudoephedrine component, Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma or urinary retention, and in patients receiving monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor therapy or within fourteen (14) days of stopping such treatment (see Drug Interactions section). It is also contraindicated in patients with severe hypertension, or severe coronary artery disease, and in those who have shown idiosyncrasy to its components, to adrenergic agents, or to other drugs of similar chemical structures. Manifestations of patient idiosyncrasy to adrenergic agents include: insomnia, dizziness, weakness, tremor, or arrhythmias.
Warnings
Sympathomimetic amines should be used with caution in patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischemic heart disease, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, renal impairment, or prostatic hypertrophy (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). Sympathomimetic amines may produce central nervous system stimulation with convulsions or cardiovascular collapse with accompanying hypotension.
Precautions
Information for Patients
Patients taking Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets should receive the following information: Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets are prescribed for the relief of symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis. Patients should be instructed to take Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets only as prescribed. Do not exceed the recommended dose. If nervousness, dizziness, or sleeplessness occur, discontinue use and consult the doctor. Patients should also be advised against the concurrent use of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets with over-the-counter antihistamines and decongestants.
The product should not be used by patients who are hypersensitive to it or to any of its ingredients. Due to its pseudoephedrine component, this product should not be used by patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, urinary retention, or by patients receiving a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor or within 14 days of stopping use of MAO inhibitor. It also should not be used by patients with severe hypertension or severe coronary artery disease.
Patients should be told that this product should be used in pregnancy or lactation only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus or nursing infant. Patients should be advised to take the tablet on an empty stomach with water. Patients should be directed to swallow the tablet whole. Patients should be cautioned not to break or chew the tablet. Patients should also be instructed to store the medication in a tightly closed container in a cool, dry place, away from children.
Patients should be told that the inactive ingredients may occasionally be eliminated in the feces in a form that may resemble the original tablet (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Drug Interactions
Fexofenadine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride do not influence the pharmacokinetics of each other when administered concomitantly.
Fexofenadine has been shown to exhibit minimal (ca. 5%) metabolism. However, co-administration of fexofenadine hydrochloride with either ketoconazole or erythromycin led to increased plasma concentrations of fexofenadine. Fexofenadine had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of either erythromycin or ketoconazole. In 2 separate studies, fexofenadine hydrochloride 120 mg twice daily (twice the recommended dose) was co-administered with erythromycin 500 mg every 8 hours or ketoconazole 400 mg once daily under steady-state conditions to healthy volunteers (n=24, each study). No differences in adverse events or QTc interval were observed when subjects were administered fexofenadine hydrochloride alone or in combination with either erythromycin or ketoconazole. The findings of these studies are summarized in the following table.
| Concomitant Drug | Cmax SS
(Peak plasma concentration) | AUCSS(0–12h) (Extent of systemic exposure) |
|---|---|---|
| Erythromycin (500 mg every 8 hrs) | +82% | +109% |
| Ketoconazole (400 mg once daily) | +135% | +164% |
The changes in plasma levels were within the range of plasma levels achieved in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
The mechanism of these interactions has been evaluated in in vitro, in situ, and in vivo animal models. These studies indicate that ketoconazole or erythromycin co-administration enhances fexofenadine gastrointestinal absorption. This observed increase in the bioavailability of fexofenadine may be due to transport-related effects, such as p-glycoprotein. In vivo animal studies also suggest that in addition to enhancing absorption, ketoconazole decreases fexofenadine gastrointestinal secretion, while erythromycin may also decrease biliary excretion.
Due to the pseudoephedrine component, Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors and for 14 days after stopping use of an MAO inhibitor. Concomitant use with antihypertensive drugs which interfere with sympathetic activity (e.g., methyldopa, mecamylamine, and reserpine) may reduce their antihypertensive effects. Increased ectopic pacemaker activity can occur when pseudoephedrine is used concomitantly with digitalis. Care should be taken in the administration of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets concomitantly with other sympathomimetic amines because combined effects on the cardiovascular system may be harmful to the patient (see WARNINGS).
Fexofenadine and Pseudoephedrine Dosage and Administration
The recommended dose of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets is one tablet twice daily administered on an empty stomach with water for adults and children 12 years of age and older. It is recommended that the administration of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets with food should be avoided. A dose of one tablet once daily is recommended as the starting dose in patients with decreased renal function. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and PRECAUTIONS.)
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets must be swallowed whole and never crushed or chewed. Occasionally, the inactive ingredients of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets may be eliminated in the feces in a form that may resemble the original tablet. (See PRECAUTIONS, Information for Patients.)
| FEXOFENADINE HYDROCHLORIDE AND PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE
fexofenadine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride tablet, film coated, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA INC (118234421) |
| Registrant - Sanofi-Aventis U.S. LLC (824676584) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanofi-Aventis U.S. LLC | 783243835 | MANUFACTURE, ANALYSIS, LABEL, PACK | |