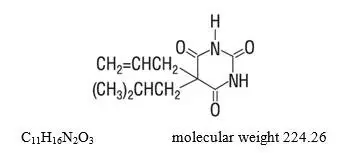
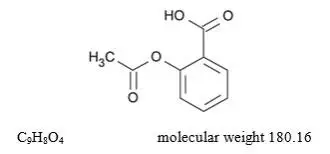
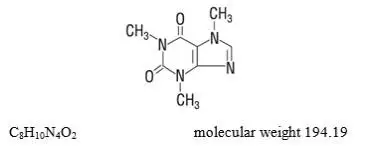
Drug Detail:Fiorinal (Aspirin, butalbital, and caffeine [ as-pir-in, bue-tal-bi-tal, kaf-een ])
Drug Class: Analgesic combinations
Overdosage
The toxic effects of acute overdosage of FIORINAL are attributable mainly to its barbiturate component, and, to a lesser extent, aspirin. Because toxic effects of caffeine occur in very high dosages only, the possibility of significant caffeine toxicity from FIORINAL overdosage is unlikely.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms attributable to acute barbiturate poisoning include drowsiness, confusion, and coma; respiratory depression; hypotension; hypovolemic shock. Symptoms attributable to acute aspirin poisoning include hyperpnea; acid-base disturbances with development of metabolic acidosis; vomiting and abdominal pain; tinnitus; hyperthermia; hypoprothrombinemia; restlessness; delirium; convulsions. Acute caffeine poisoning may cause insomnia, restlessness, tremor, and delirium; tachycardia and extrasystoles.
Treatment
Treatment consists primarily of management of barbiturate intoxication and the correction of the acid-base imbalance due to salicylism. Vomiting should be induced mechanically or with emetics in the conscious patient. Gastric lavage may be used if the pharyngeal and laryngeal reflexes are present and if less than 4 hours have elapsed since ingestion. A cuffed endotracheal tube should be inserted before gastric lavage of the unconscious patient and when necessary to provide assisted respiration. Diuresis, alkalinization of the urine, and correction of electrolyte disturbances should be accomplished through administration of intravenous fluids such as 1% sodium bicarbonate in 5% dextrose in water. Meticulous attention should be given to maintaining adequate pulmonary ventilation. The value of vasopressor agents such as Norepinephrine or Phenylephrine Hydrochloride in treating hypotension is questionable since they increase vasoconstriction and decrease blood flow. However, if prolonged support of blood pressure is required, Norepinephrine Bitartrate (Levophed®) may be given I.V. with the usual precautions and serial blood pressure monitoring. In severe cases of intoxication, peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, or exchange transfusion may be lifesaving. Hypoprothrombinemia should be treated with Vitamin K, intravenously.
Up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose can often be obtained from a Certified Regional Poison Control Center. Telephone numbers of Certified Regional Poison Control Centers are listed in the Physicians’ Desk Reference®.
Toxic and Lethal Doses (for adults)
Butalbital: toxic dose 1 g (20 capsules)
Aspirin: toxic blood level greater than 30 mg/100 mL; lethal dose 10-30 g
Caffeine: toxic dose 1 g (25 capsules)
| FIORINAL
butalbital, aspirin, and caffeine capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |