Drug Detail:Gatifloxacin (eent) (monograph) (Zymar)
Drug Class:
Highlights of Prescribing Information
GATIFLOXACIN ophthalmic solution 0.05%, for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1999
Indications and Usage for Gatifloxacin Eye Drops
Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5% is a quinolone antimicrobial indicated for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis caused by susceptible strains of the following organisms: (1)
Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus mitis group , Streptococcus oralis, Streptococcus pneumoniae (1)
Gatifloxacin Eye Drops Dosage and Administration
Day 1: Instill one drop every two hours in the affected eye(s) while awake, up to 8 times on Day 1. (2)
Days 2 through 7: Instill one drop two to four times daily in the affected eye(s) while awake on Days 2 through 7. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
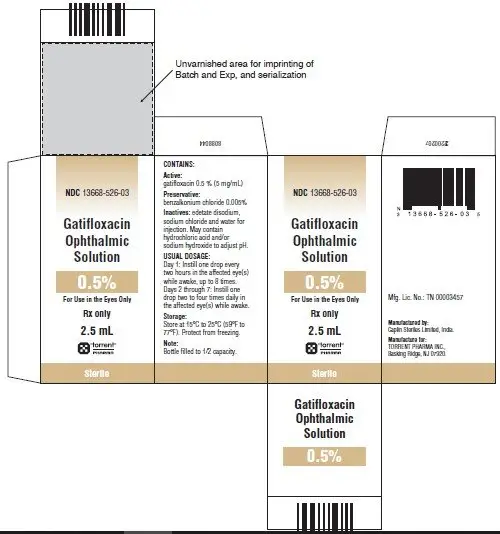
Ophthalmic solution: 0.5% gatifloxacin (5 mg/mL) (3)
Contraindications
Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5% is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to gatifloxacin, to other quinolones, or to any of the components in this medication. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
Hypersensitivity ( 5.1)
Growth of Resistant Organisms with Prolonged Use ( 5.2)
Corneal Endothelial Cell Injury ( 5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients included worsening of conjunctivitis, eye irritation, dysgeusia, and eye pain. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Torrent Pharma Inc. at 1-800-912-9561 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2022
Related/similar drugs
ciprofloxacin ophthalmic, diclofenac ophthalmic, azithromycin ophthalmic, dexamethasone ophthalmic, triamcinolone, levofloxacin ophthalmic, ceftriaxoneFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Gatifloxacin Eye Drops
• Aerobic gram-positive bacteria:
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus mitis group *
Streptococcus oralis*
Streptococcus pneumoniae
• Aerobic gram-negative bacteria:
Haemophilus influenzae
*Efficacy for these organisms were studied in fewer than 10 infections.
2. Gatifloxacin Eye Drops Dosage and Administration
- Day 1: Instill one drop every two hours in the affected eye(s) while awake, up to 8 times.
- Day 2 through Day 7: Instill one drop two to four times daily in the affected eye(s) while awake.
5. Warnings and Precautions
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity [ see Contraindications ( 4) and Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1) ]
- Growth of Resistant Organisms With Prolonged Use [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) ]
- Corneal Endothelial Cell Injury [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3) ]
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
In clinical studies of patients with bacterial conjunctivitis treated with gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5% (N=717), the most frequently reported adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients were: worsening of the conjunctivitis, eye irritation, dysgeusia, and eye pain.
Additional adverse reactions reported with other formulations of gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution in other clinical studies included chemosis, conjunctival hemorrhage, dry eye, eye discharge, eyelid edema, headache, increased lacrimation, keratitis, red eye, papillary conjunctivitis, and reduced visual acuity.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
There are no available data on the use of gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5% in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. Administration of oral gatifloxacin to pregnant rats and rabbits throughout organogenesis did not produce adverse development outcomes at clinically relevant doses. Administration of gatifloxacin to rats during late gestation through lactation did not produce adverse maternal, fetal or neonatal effects at clinically relevant doses.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of gatifloxacin to pregnant rats throughout organogenesis produced teratogenic effects in rat fetuses, including skeletal/craniofacial malformations, delayed ossification, atrial enlargement, and reduced fetal weight, at doses greater than or equal to 150 mg/kg/day (approximately 600-fold higher than the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose [MRHOD] for gatifloxacin of 0.04 mg/kg/day, on a mg/m 2 basis). No teratogenic effects were observed in rat or rabbit fetuses at doses of gatifloxacin up to 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 200-and 400-fold higher than the MRHOD, respectively, on a mg/m 2 basis).
In a perinatal/postnatal study in rats, oral administration of gatifloxacin during late gestation through lactation produced an increase in late gestation fetal loss and neonatal/perinatal mortality at 200 mg/kg/day (approximately 800-fold higher than the MRHOD on a mg/m 2 basis).
8.2 Lactation
There is no information regarding the presence of gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5% in human milk, the effect of gatifloxacin on breastfed infants, or the effect of gatifloxacin on milk production. Gatifloxacin was found in the breast milk of rats following oral administration of gatifloxacin during lactation. However, systemic levels of gatifloxacin following topical ocular administration are low [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)], and it is not known whether gatifloxacin would be present in maternal milk at measurable levels following topical ocular administration. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5% and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5%.
11. Gatifloxacin Eye Drops Description
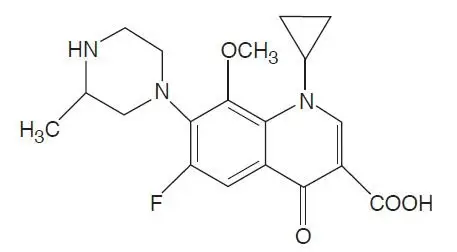
Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5% contains the active ingredient gatifloxacin 0.5% (5 mg/mL) and the inactive ingredients benzalkonium chloride 0.005%, edetate disodium, sodium chloride and water for injection. Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5 %may contain hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust pH.
12. Gatifloxacin Eye Drops - Clinical Pharmacology
12.4 Microbiology
Resistance to gatifloxacin in vitro develops via multiple-step mutations. Resistance to gatifloxacin in vitro occurs at a general frequency of 1 x 10 -7 to 10 -10.
Gatifloxacin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following organisms both microbiologically and clinically, in conjunctival infections:
• Aerobic gram-positive bacteria:
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus mitis group*
Streptococcus oralis*
Streptococcus pneumonia
• Aerobic gram-negative bacteria:
Haemophilus influenzae
* Efficacy for these organisms were studied in fewer than 10 infections.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
There was no increase in neoplasms among B6C3F1 mice given gatifloxacin in the diet for 18 months at doses averaging 81 mg/kg/day in males and 90 mg/kg/day in females. These doses are approximately 175-fold higher than the maximum recommended ophthalmic dose (MRHOD) of 0.04 mg/kg/day gatifloxacin in a 60 kg human (on a mg/m 2 basis).
A statistically significant increase in the incidence of large granular lymphocyte (LGL) leukemia was seen in male rats treated with 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 405-fold higher than the MRHOD, on a mg/m 2 basis). Fischer 344 rats have a high spontaneous background rate of LGL leukemia and the incidence in high-dose males only slightly exceeded the historical control range established for this strain. There was no increase in neoplasms among Fischer 344 rats given gatifloxacin in the diet for 2 years at doses averaging 47 mg/kg/day in males and 139 mg/kg/day in females (approximately 190 - and 560-fold higher than the MRHOD, respectively), on a mg/m 2 basis.
Mutagenesis
In genetic toxicity tests, gatifloxacin was positive in 1 of 5 strains used in bacterial reverse mutation assays: Salmonella strain TA102. Gatifloxacin was positive in in vitro mammalian cell mutation and chromosome aberration assays. Gatifloxacin was positive in in vitro unscheduled DNA synthesis in rat hepatocytes but not human leukocytes. Gatifloxacin was negative in in vivo micronucleus tests in mice, cytogenetics test in rats, and DNA repair test in rats. The genotoxic findings are similar to findings obtained with other quinolones and may be due to the pharmacologic inhibitory effects of high concentrations of gatifloxacin on eukaryotic type II DNA topoisomerase.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral administration of gatifloxacin produced no adverse effects on fertility or reproduction in rats at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day (approximately 800-fold higher than the MRHOD, on a mg/m 2 basis).
16. How is Gatifloxacin Eye Drops supplied
2.5 mL in 5 mL bottle: NDC 13668-526-03
Storage: Store at 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F). Protect from freezing.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Avoiding Contamination of the Product
Instruct patients to avoid contaminating the applicator tip with material from the eye, fingers, or other source.
Potential for Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients to discontinue use immediately and contact the physician at the first sign of a rash or hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1) and Contraindication ( 4)].

Caplin Steriles Limited, India.
TN/DRUGS/TN00003457
Manufactured for
TORRENT PHARMA INC. Basking Ridge, NJ 07920
8087280 Revised June 2022
22200206
| GATIFLOXACIN
gatifloxacin solution/ drops |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Torrent Pharmaceuticals Limited (916488547) |
| Registrant - Torrent Pharma, Inc. (790033935) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caplin Steriles Limited | 650744670 | analysis(13668-526) , manufacture(13668-526) , pack(13668-526) | |