Drug Class: Antiviral combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
GENVOYA® (elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2015
WARNING: POST TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued products containing emtricitabine and/or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), and may occur with discontinuation of GENVOYA. Hepatic function should be monitored closely in these patients. If appropriate, anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted. (5.1)
Recent Major Changes
| Warnings and Precautions, New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment (5.4) | 03/2021 |
Indications and Usage for Genvoya
GENVOYA is a four-drug combination of elvitegravir (EVG), an HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI), cobicistat (COBI), a CYP3A inhibitor, and emtricitabine (FTC) and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF), both HIV-1 nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), and is indicated as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 25 kg who have no antiretroviral treatment history or to replace the current antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically-suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) on a stable antiretroviral regimen for at least 6 months with no history of treatment failure and no known substitutions associated with resistance to the individual components of GENVOYA. (1)
Genvoya Dosage and Administration
- Testing: Prior to or when initiating GENVOYA test for hepatitis B virus infection. Prior to or when initiating GENVOYA, and during treatment on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus. (2.1)
- Recommended dosage in adult and pediatric patients weighing at least 25 kg: One tablet taken orally once daily with food in patients with body weight at least 25 kg and a creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL per minute, or in adult patients with creatinine clearance less than 15 mL per minute who are receiving chronic hemodialysis. On days of hemodialysis, administer GENVOYA after hemodialysis. (2.2)
- Renal impairment: GENVOYA is not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute, or below 15 mL per minute who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis. (2.3)
- Hepatic impairment: GENVOYA is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 150 mg of elvitegravir, 150 mg of cobicistat, 200 mg of emtricitabine, and 10 mg of tenofovir alafenamide. (3)
Contraindications
Coadministration of GENVOYA is contraindicated with drugs that:
- Are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious adverse events. (4)
- Strongly induce CYP3A, which may lead to lower exposure of one or more components and loss of efficacy of GENVOYA and possible resistance. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of adverse reactions or loss of virologic response due to drug interactions: The concomitant use of GENVOYA and other drugs may result in known or potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to loss of therapeutic effect of GENVOYA and possible development of resistance; clinically significant adverse reactions from greater exposures of concomitant drugs; or loss of therapeutic effect of concomitant drugs. (5.2)
- Immune reconstitution syndrome: May necessitate further evaluation and treatment. (5.3)
- New onset or worsening renal impairment: Assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose and urine protein when initiating GENVOYA and during therapy on a clinically appropriate schedule in all patients. Also assess serum phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease. (5.4)
- Lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis: Discontinue treatment in patients who develop symptoms or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity. (5.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reaction (incidence greater than or equal to 10%, all grades) is nausea. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gilead Sciences, Inc. at 1-800-GILEAD-5 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- GENVOYA should not be administered with other antiretroviral medications for treatment of HIV-1 infection. (7.1)
- GENVOYA can alter the concentration of drugs metabolized by CYP3A or CYP2D6. Drugs that induce CYP3A can alter the concentrations of one or more components of GENVOYA. Consult the full prescribing information prior to and during treatment for potential drug-drug interactions. (4, 7.2, 7.3, 12.3)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Not recommended for use during pregnancy because of substantially lower exposures of cobicistat and elvitegravir during pregnancy. GENVOYA should not be initiated in pregnant individuals. (2.5, 8.1)
- Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended due to the potential for HIV transmission. (8.2)
- Pediatrics: Not recommended for patients weighing less than 25 kg. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 1/2022
Related/similar drugs
Biktarvy, Triumeq, Stribild, Descovy, Truvada, tenofovir, AtriplaFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: POST TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued products containing emtricitabine and/or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), and may occur with discontinuation of GENVOYA. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and discontinue GENVOYA. If appropriate, anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Genvoya
GENVOYA is indicated as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 25 kg who have no antiretroviral treatment history or to replace the current antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically-suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) on a stable antiretroviral regimen for at least 6 months with no history of treatment failure and no known substitutions associated with resistance to the individual components of GENVOYA [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Genvoya Dosage and Administration
2.1 Testing When Initiating and During Treatment with GENVOYA
Prior to or when initiating GENVOYA, test patients for hepatitis B virus infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Prior to or when initiating GENVOYA, and during treatment with GENVOYA on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Adults and Pediatric Patients Weighing at Least 25 kg
GENVOYA is a four-drug fixed dose combination product containing elvitegravir (EVG), cobicistat (COBI), emtricitabine (FTC), and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF). The recommended dosage of GENVOYA is one tablet containing 150 mg EVG,150 mg COBI, 200 mg FTC, and 10 mg TAF taken orally once daily with food in:
- adults and pediatric patients with body weight at least 25 kg and creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL per minute; or
- adults with creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute who are receiving chronic hemodialysis. On days of hemodialysis, administer GENVOYA after completion of hemodialysis treatment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Not Recommended in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
GENVOYA is not recommended in patients with:
- severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute); or
- end stage renal disease (ESRD; estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute) who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
2.4 Not Recommended in Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
GENVOYA is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.5 Not Recommended During Pregnancy
GENVOYA is not recommended for use during pregnancy because of substantially lower exposures of cobicistat and elvitegravir during the second and third trimesters [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
GENVOYA should not be initiated in pregnant individuals. An alternative regimen is recommended for individuals who become pregnant during therapy with GENVOYA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Each GENVOYA tablet contains 150 mg of elvitegravir (EVG), 150 mg of cobicistat (COBI), 200 mg of emtricitabine (FTC), and 10 mg of tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) (equivalent to 11.2 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate).
The tablets are green, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with "GSI" on one side of the tablet and the number "510" on the other side of the tablet.
4. Contraindications
Coadministration of GENVOYA is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events. These drugs and other contraindicated drugs (which may lead to reduced efficacy of GENVOYA and possible resistance) are listed below [see Drug Interactions (7.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonist: alfuzosin
- Anticonvulsants: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin
- Antimycobacterial: rifampin
- Antipsychotics: lurasidone, pimozide
- Ergot Derivatives: dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine
- Herbal Products: St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- Lipid-modifying Agents: lomitapide, lovastatin, simvastatin
- Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) Inhibitor: sildenafil when administered as REVATIO® for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Sedative/hypnotics: triazolam, orally administered midazolam
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV
Patients with HIV-1 should be tested for the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) before or when initiating antiretroviral therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B (e.g., liver decompensation and liver failure) have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued products containing emtricitabine and/or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), and may occur with discontinuation of GENVOYA. Patients coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV who discontinue GENVOYA should be closely monitored with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months after stopping treatment. If appropriate, anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted, especially in patients with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis, since post-treatment exacerbation of hepatitis may lead to hepatic decompensation and liver failure.
5.2 Risk of Adverse Reactions or Loss of Virologic Response Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of GENVOYA and other drugs may result in known or potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.5)]:
- Loss of therapeutic effect of GENVOYA and possible development of resistance.
- Clinically significant adverse reactions, potentially leading to severe, life-threatening, or fatal events, from greater exposures of concomitant drugs metabolized by CYP3A.
- Loss of therapeutic effect of concomitant drugs that utilize CYP3A to form active metabolites.
See Table 5 for steps to prevent or manage these possible and known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during GENVOYA therapy; review concomitant medications during GENVOYA therapy; and monitor for the adverse reactions associated with the concomitant drugs.
5.3 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including emtricitabine, a component of GENVOYA. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections [such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP), or tuberculosis], which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and autoimmune hepatitis) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution, however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
5.4 New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Postmarketing cases of renal impairment, including acute renal failure, proximal renal tubulopathy (PRT), and Fanconi syndrome have been reported with TAF-containing products; while most of these cases were characterized by potential confounders that may have contributed to the reported renal events, it is also possible these factors may have predisposed patients to tenofovir-related adverse events [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. GENVOYA is not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute, or in patients with estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis.
Patients taking tenofovir prodrugs who have impaired renal function and those taking nephrotoxic agents including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are at increased risk of developing renal-related adverse reactions.
Prior to or when initiating GENVOYA, and during treatment with GENVOYA on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus. Discontinue GENVOYA in patients who develop clinically significant decreases in renal function or evidence of Fanconi syndrome.
Cobicistat, a component of GENVOYA, produces elevations of serum creatinine due to inhibition of tubular secretion of creatinine without affecting glomerular filtration [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The elevation is typically seen within 2 weeks of starting therapy and is reversible after discontinuation. Patients who experience a confirmed increase in serum creatinine of greater than 0.4 mg per dL from baseline should be closely monitored for renal safety.
5.5 Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including emtricitabine, a component of GENVOYA, and tenofovir DF, another prodrug of tenofovir, alone or in combination with other antiretrovirals. Treatment with GENVOYA should be suspended in any patient who develops clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity (which may include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked transaminase elevations).
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse drug reactions are discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Severe Acute Exacerbations of Hepatitis B [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Immune Reconstitution Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Clinical Trials in Pediatric Subjects:
Safety in Pediatric Patients
The safety of GENVOYA in HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects was evaluated in treatment-naïve subjects between the ages of 12 to less than 18 years and weighing at least 35 kg (N=50) through Week 48 (cohort 1), and in virologically-suppressed subjects between the ages of 6 to less than 12 years and weighing at least 25 kg (N=52) through Week 48 (cohort 2) in an open-label clinical trial (Study 106) [see Clinical Studies (14.5)]. With the exception of a decrease in the mean CD4+ cell count observed in cohort 2 of Study 106, the safety profile in pediatric subjects who received treatment with GENVOYA was similar to that in adults. One 13-year-old female subject developed unexplained uveitis while receiving GENVOYA that resolved and did not require discontinuation of GENVOYA.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following events have been identified during post approval use of products containing TAF, including GENVOYA. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Not Recommended with Other Antiretroviral Medications
GENVOYA is a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection; therefore, coadministration of GENVOYA with other antiretroviral medications for treatment of HIV-1 infection should be avoided. Complete information regarding potential drug-drug interactions with other antiretroviral medications is not provided [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Potential for GENVOYA to Affect Other Drugs
Cobicistat, a component of GENVOYA, is an inhibitor of CYP3A and CYP2D6 and an inhibitor of the following transporters: P-glycoprotein (P-gp), BCRP, OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. Thus, coadministration of GENVOYA with drugs that are primarily metabolized by CYP3A or CYP2D6, or are substrates of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1 or OATP1B3 may result in increased plasma concentrations of such drugs . Coadministration of GENVOYA with drugs that have active metabolite(s) formed by CYP3A may result in reduced plasma concentration of these active metabolite(s) (see Table 5). Elvitegravir is a modest inducer of CYP2C9 and may decrease the plasma concentrations of CYP2C9 substrates. TAF is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or UGT1A1. TAF is a weak inhibitor of CYP3A in vitro. TAF is not an inhibitor or inducer of CYP3A in vivo.
7.3 Potential for Other Drugs to Affect One or More Components of GENVOYA
Elvitegravir and cobicistat, components of GENVOYA, are metabolized by CYP3A. Cobicistat is also metabolized, to a minor extent, by CYP2D6.
Drugs that induce CYP3A activity are expected to increase the clearance of elvitegravir and cobicistat, resulting in decreased plasma concentration of cobicistat, elvitegravir, and TAF, which may lead to loss of therapeutic effect of GENVOYA and development of resistance (see Table 5).
Coadministration of GENVOYA with other drugs that inhibit CYP3A may decrease the clearance and increase the plasma concentration of cobicistat. (see Table 5). TAF, a component of GENVOYA, is a substrate of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. Drugs that inhibit P-gp and/or BCRP, such as cobicistat, may increase the absorption of TAF (see Table 13). However, when TAF is administered as a component of GENVOYA, its availability is increased by cobicistat and a further increase of TAF concentrations is not expected upon coadministration of an additional P-gp and/or BCRP inhibitor. Drugs that induce P-gp activity are expected to decrease the absorption of TAF, resulting in decreased plasma concentration of TAF.
7.4 Drugs Affecting Renal Function
Because emtricitabine and tenofovir are primarily excreted by the kidneys by a combination of glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion, coadministration of GENVOYA with drugs that reduce renal function or compete for active tubular secretion may increase concentrations of emtricitabine, tenofovir, and other renally eliminated drugs and this may increase the risk of adverse reactions. Some examples of drugs that are eliminated by active tubular secretion include, but are not limited to, acyclovir, cidofovir, ganciclovir, valacyclovir, valganciclovir, aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin), and high-dose or multiple NSAIDs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
7.5 Established and Other Potentially Significant Interactions
Table 5 provides a listing of established or potentially clinically significant drug interactions [see Contraindications (4)]. The drug interactions described are based on studies conducted with either GENVOYA, the components of GENVOYA (elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide) as individual agents and/or in combination, or are predicted drug interactions that may occur with GENVOYA [for magnitude of interaction, see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The table includes potentially significant interactions but is not all inclusive.
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration† | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonist:
alfuzosin | ↑ alfuzosin | Coadministration with alfuzosin is contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as hypotension. |
| Antiarrhythmics:
e.g., amiodarone bepridil digoxin‡ disopyramide flecainide systemic lidocaine mexiletine propafenone quinidine | ↑ antiarrhythmics ↑ digoxin | Caution is warranted and therapeutic concentration monitoring, if available, is recommended for antiarrhythmics when coadministered with GENVOYA. |
| Antibacterials:
clarithromycin telithromycin | ↑ clarithromycin ↑ telithromycin ↑ cobicistat | Patients with CLcr greater than or equal to 60 mL/minute:
No dosage adjustment of clarithromycin is required. Patients with CLcr between 50 mL/minute and 60 mL/minute: The dosage of clarithromycin should be reduced by 50%. |
| Anticoagulants:
Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) apixaban rivaroxaban betrixaban dabigatran edoxaban | ↑ apixaban | Due to potentially increased bleeding risk, dosing recommendations for coadministration with GENVOYA depends on the apixaban dose. Refer to apixaban dosing instructions for coadministration with strong CYP3A and P-gp inhibitors in apixaban prescribing information. |
| ↑ rivaroxaban ↑ betrixaban ↑ dabigatran ↑ edoxaban | Coadministration of rivaroxaban with GENVOYA is not recommended because it may lead to an increased bleeding risk. Due to potentially increased bleeding risk, dosing recommendations for coadministration of betrixaban, dabigatran, or edoxaban with a P-gp inhibitor such as GENVOYA depends on DOAC indication and renal function. Refer to DOAC dosing instructions for coadministration with P-gp inhibitors in DOAC prescribing information. |
|
| warfarin | Effect on warfarin unknown | Monitor the international normalized ratio (INR) upon coadministration of warfarin with GENVOYA. |
| Anticonvulsants:
carbamazepine‡ phenobarbital phenytoin | ↓ elvitegravir ↓ cobicistat ↓ TAF | Coadministration with carbamazepine, phenobarbital, or phenytoin is contraindicated due to potential for loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance. |
| oxcarbazepine | Alternative anticonvulsants should be considered when GENVOYA is administered with oxcarbazepine. | |
| ethosuximide | ↑ ethosuximide | Clinical monitoring is recommended upon coadministration of ethosuximide with GENVOYA. |
| Antidepressants:
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) e.g., paroxetine Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) e.g., amitriptyline desipramine‡ imipramine nortriptyline bupropion trazodone | ↑ SSRIs (except sertraline) ↑ TCAs ↑ trazodone | Careful dosage titration of the antidepressant and monitoring for antidepressant response are recommended when coadministered with GENVOYA. |
| Antifungals:
itraconazole ketoconazole‡ voriconazole | ↑ elvitegravir ↑ cobicistat ↑ itraconazole ↑ ketoconazole ↑ voriconazole | When administering with GENVOYA, the maximum daily dosage of ketoconazole or itraconazole should not exceed 200 mg per day. An assessment of benefit/risk ratio is recommended to justify use of voriconazole with GENVOYA. |
| Anti-gout:
colchicine | ↑ colchicine | GENVOYA is not recommended to be coadministered with colchicine to patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Treatment of gout-flares – coadministration of colchicine in patients receiving GENVOYA: 0.6 mg (1 tablet) × 1 dose, followed by 0.3 mg (half tablet) 1 hour later. Treatment course to be repeated no earlier than 3 days. Prophylaxis of gout-flares – coadministration of colchicine in patients receiving GENVOYA: If the original regimen was 0.6 mg twice a day, the regimen should be adjusted to 0.3 mg once a day. If the original regimen was 0.6 mg once a day, the regimen should be adjusted to 0.3 mg once every other day. Treatment of familial Mediterranean fever – coadministration of colchicine in patients receiving GENVOYA: Maximum daily dosage of 0.6 mg (may be given as 0.3 mg twice a day). |
| Antimycobacterial:
rifampin | ↓ elvitegravir ↓ cobicistat ↓ TAF | Coadministration with rifampin is contraindicated due to potential for loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance. |
| rifabutin‡
rifapentine | Coadministration of GENVOYA with rifabutin or rifapentine is not recommended. | |
| Antiplatelets: | ||
| ticagrelor | ↑ ticagrelor | Coadminstration with ticagrelor is not recommended. |
| clopidogrel | ↓ clopidogrel active metabolite | Coadministration with clopidogrel is not recommended due to protential reduction of the antiplatelet activity of clopidogrel. |
| Antipsychotics: | ||
| lurasidone | ↑ lurasidone | Coadministration with lurasidone is contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions. |
| pimozide | ↑ pimozide | Coadministration with pimozide is contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias. |
| quetiapine | ↑ quetiapine | Initiation of GENVOYA in patients taking quetiapine:
Consider alternative antiretroviral therapy to avoid increases in quetiapine exposure. If coadministration is necessary, reduce the quetiapine dose to 1/6 of the current dose and monitor for quetiapine-associated adverse reactions. Refer to the quetiapine prescribing information for recommendations on adverse reaction monitoring. Initiation of quetiapine in patients taking GENVOYA: Refer to the quetiapine prescribing information for initial dosing and titration of quetiapine. |
| Other antipsychotics e.g., perphenazine risperidone thioridazine | ↑ antipsychotic | A decrease in dose of the antipsychotics that are metabolized by CYP3A or CYP2D6 may be needed when coadministered with GENVOYA. |
| Beta-Blockers:
e.g., metoprolol timolol | ↑ beta-blockers | Clinical monitoring is recommended and a dosage decrease of the beta blocker may be necessary when these agents are coadministered with GENVOYA. |
| Calcium Channel Blockers:
e.g., amlodipine diltiazem felodipine nicardipine nifedipine verapamil | ↑ calcium channel blockers | Caution is warranted and clinical monitoring is recommended upon coadministration of calcium channel blockers with GENVOYA. |
| Corticosteroids:
e.g., betamethasone budesonide ciclesonide dexamethasone fluticasone methylprednisolone mometasone prednisone triamcinolone | ↓ elvitegravir ↓ cobicistat ↑ corticosteroids | Coadministration with oral dexamethasone or other systemic corticosteroids that induce CYP3A may result in loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance to elvitegravir. Consider alternative corticosteroids. Coadministration with corticosteroids (all routes of administration) whose exposures are significantly increased by strong CYP3A inhibitors can increase the risk for Cushing's syndrome and adrenal suppression. Alternative corticosteroids including beclomethasone and prednisolone (whose PK and/or PD are less affected by strong CYP3A inhibitors relative to other studied steroids) should be considered, particularly for long-term use. |
| Endothelin Receptor Antagonists:
bosentan | ↑ bosentan | Coadministration of bosentan in patients on GENVOYA:
In patients who have been receiving GENVOYA for at least 10 days, start bosentan at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability. Coadministration of GENVOYA in patients on bosentan: Discontinue use of bosentan at least 36 hours prior to initiation of GENVOYA. After at least 10 days following the initiation of GENVOYA, resume bosentan at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability. |
| Ergot Derivatives:
dihydroergotamine ergotamine methylergonovine | ↑ ergot derivatives | Coadministration is contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as acute ergot toxicity characterized by peripheral vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities and other tissues [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Herbal Products:
St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) | ↓ elvitegravir ↓ cobicistat ↓ TAF | Coadministration is contraindicated due to potential for loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance. |
| Hormonal Contraceptives:
drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol‡ levonorgestrel norgestimate/ethinyl estradiol | ↑ drospirenone ↑ norgestimate ↑ levonorgestrel ↓ ethinyl estradiol | Additional or alternative non-hormonal forms of contraception should be considered when estrogen based contraceptives are coadministered with GENVOYA. Plasma concentrations of drospirenone may be increased when coadministered with cobicistat-containing products. Clinical monitoring is recommended due to the potential for hyperkalemia. The effects of increases in the concentration of the progestational component norgestimate are not fully known and can include increased risk of insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, acne, and venous thrombosis. The potential risks and benefits associated with coadministration of norgestimate/ethinyl estradiol with GENVOYA should be considered, particularly in patients who have risk factors for these events. The effect of GENVOYA on other hormonal contraceptives (e.g., contraceptive patch, contraceptive vaginal ring, or injectable contraceptives) or oral contraceptives containing progestogens other than drospirenone, levonorgestrel, or norgestimate has not been studied; therefore, alternative (non-hormonal) methods of contraception can be considered. |
| Immuno-suppressants:
e.g., cyclosporine (CsA) sirolimus tacrolimus | ↑ immuno-suppressants ↑ elvitegravir (with CsA) ↑ cobicistat (with CsA) | Therapeutic monitoring of the immunosuppressive agents is recommended upon coadministration with GENVOYA. Monitor for adverse events associated with GENVOYA when coadministered with cyclosporine. |
| Lipid-modifying Agents: | ||
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors:
lovastatin simvastatin | ↑ lovastatin ↑ simvastatin | Coadministration with lovastatin or simvastatin is contraindicated due to potential for serious reactions such as myopathy including rhabdomyolysis. |
| atorvastatin | ↑ atorvastatin | Initiate atorvastatin with the lowest starting dose of atorvastatin and titrate carefully while monitoring for safety (e.g., myopathy). Do not exceed a dosage of atorvastatin 20 mg daily. |
| Other Lipid-modifying Agents:
lomitapide | ↑ lomitapide | Coadministration with lomitapide is contraindicated due to potential for markedly increased transaminases. |
| Narcotic Analgesics:
buprenorphine/ naloxone‡ | ↑ buprenorphine ↑ norbuprenorphine ↓ naloxone | No dosage adjustment of buprenorphine/naloxone is required upon coadministration with GENVOYA. Patients should be closely monitored for sedation and cognitive effects. |
| fentanyl | ↑ fentanyl | Careful monitoring of therapeutic and adverse effects of fentanyl (including potentially fatal respiratory depression) is recommended with coadministration. |
| tramadol | ↑ tramadol | A dose decrease may be needed for tramadol with concomitant use. |
| Inhaled Beta Agonist:
salmeterol | ↑ salmeterol | Coadministration of salmeterol and GENVOYA is not recommended. Coadministration of salmeterol with GENVOYA may result in increased risk of cardiovascular adverse events associated with salmeterol, including QT prolongation, palpitations, and sinus tachycardia. |
| Medications or Oral Supplements Containing Polyvalent Cations (e.g., Mg, Al, Ca, Fe, Zn):
calcium or iron supplements, including multivitamins cation-containing antacids‡ or laxatives sucralfate buffered medications | ↓ elvitegravir | Separate GENVOYA and administration of medications, antacids, or oral supplements containing polyvalent cations by at least 2 hours. |
| Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) Inhibitors:
sildenafil tadalafil vardenafil | ↑ PDE5 inhibitors | Use of PDE-5 inhibitors for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH):
Coadministration of sildenafil with GENVOYA is contraindicated when used for treatment of PAH, due to potential for PDE-5 inhibitor associated adverse reactions, including hypotension, syncope, visual disturbances, and priapism. The following dose adjustments are recommended for the use of tadalafil with GENVOYA: Coadministration of tadalafil in patients on GENVOYA: In patients receiving GENVOYA for at least 1 week, start tadalafil at 20 mg once daily. Increase tadalafil dose to 40 mg once daily based upon individual tolerability. Coadministration of GENVOYA in patients on tadalafil: Avoid use of tadalafil during the initiation of GENVOYA. Stop tadalafil at least 24 hours prior to starting GENVOYA. After at least one week following initiation of GENVOYA, resume tadalafil at 20 mg once daily. Increase tadalafil dose to 40 mg once daily based upon individual tolerability. Use of PDE-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction: Sildenafil at a single dose not exceeding 25 mg in 48 hours, vardenafil at a single dose not exceeding 2.5 mg in 72 hours, or tadalafil at a single dose not exceeding 10 mg in 72 hours can be used with increased monitoring for PDE-5 inhibitor associated with adverse events. |
| Sedative/hypnotic:
midazolam (oral) triazolam | ↑ midazolam ↑ triazolam | Coadministration with triazolam or orally administered midazolam is contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as prolonged or increased sedation or respiratory depression. |
| Other benzodiazepines: e.g., parenterally administered midazolam clorazepate diazepam estazolam flurazepam | ↑ sedatives/hypnotics | Triazolam and orally administered midazolam are extensively metabolized by CYP3A. Coadministration of triazolam or orally administered midazolam with GENVOYA may cause large increases in the concentrations of these benzodiazepines. Coadministration of parenteral midazolam with GENVOYA should be done in a setting that ensures close clinical monitoring and appropriate medical management in case of respiratory depression and/or prolonged sedation. Dosage reduction for midazolam should be considered, especially if more than a single dose of midazolam is administered. |
| buspirone zolpidem | With other sedative/hypnotics, dose reduction may be necessary and clinical monitoring is recommended. | |
7.6 Drugs without Clinically Significant Interactions with GENVOYA
Based on drug interaction studies conducted with the components of GENVOYA, no clinically significant drug interactions have been observed or are expected when GENVOYA is combined with the following drugs: famciclovir, famotidine, ledipasvir, methadone, omeprazole, prasugrel (active metabolite), sertraline, sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and voxilaprevir.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Data
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of GENVOYA for the treatment of HIV-1 infection was established in pediatric patients with body weight greater than or equal to 25 kg [see Indications and Usage (1) and Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Use of GENVOYA in pediatric patients less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 25 kg is supported by studies in adults and by an open-label study in antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects aged 12 to less than 18 years and weighing at least 35 kg (cohort 1 of Study 106, N=50) and in virologically-suppressed pediatric subjects aged 6 to less than 12 years and weighing at least 25 kg (cohort 2 of Study 106, N=52). The safety and efficacy of GENVOYA in adolescent subjects was similar to that in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.5)].
The safety and efficacy of GENVOYA in subjects 6 to 12 years of age weighing at least 25 kg was similar to that in antiretroviral treatment-naïve adults and adolescents with the exception of a decrease from baseline CD4+ cell count [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.5)].
A pharmacokinetic evaluation of a reduced strength GENVOYA formulation containing 90 mg of EVG, 90 mg of COBI, 120 mg of FTC, and 6 mg TAF was performed in 27 virologically-suppressed pediatric patients at least 2 years of age and weighing at least 14 to less than 25 kg (cohort 3 of Study 106). Virologic, immunologic, and safety outcomes were similar to those observed in cohort 2 of Study 106. No clinically meaningful differences in drug exposures except EVG were identified between pediatric patients in cohort 3 receiving the reduced strength formulation and adults receiving the GENVOYA tablet containing 150 mg of EVG,150 mg of COBI, 200 mg of FTC, and 10 mg TAF. The median observed EVG Ctrough values in subjects in cohort 3 were significantly lower than the values correlated with efficacy in adults. Therefore, efficacy cannot be extrapolated from adults to pediatric patients weighing 14 to 25 kg.
Safety and effectiveness of GENVOYA in pediatric patients weighing less than 25 kg have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of GENVOYA included 97 subjects (80 receiving GENVOYA) aged 65 years and over. No differences in safety or efficacy have been observed between elderly subjects and adults between 18 and less than 65 years of age.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics, safety, and virologic and immunologic responses of GENVOYA in HIV-1 infected adult subjects with renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance between 30 and 69 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method) were evaluated in 248 subjects in an open-label trial, Study 112.
The pharmacokinetics, safety, virologic and immunologic responses of GENVOYA in HIV-1 infected adult subjects with ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance of less than 15 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method) receiving chronic hemodialysis were evaluated in 55 subjects in an open-label trial, Study 1825 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.4)].
No dosage adjustment of GENVOYA is recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL per minute, or in adult patients with ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute) who are receiving chronic hemodialysis. On days of hemodialysis, administer GENVOYA after completion of hemodialysis treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
GENVOYA is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute), or in patients with ESRD who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis, as the safety of GENVOYA has not been established in these populations [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of GENVOYA is required in patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. GENVOYA has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). Therefore, GENVOYA is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
No data are available on overdose of GENVOYA in patients. If overdose occurs, monitor the patient for evidence of toxicity. Treatment of overdose with GENVOYA consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs as well as observation of the clinical status of the patient.
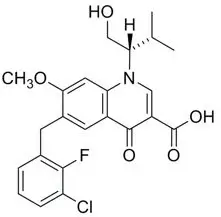
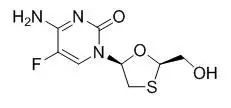
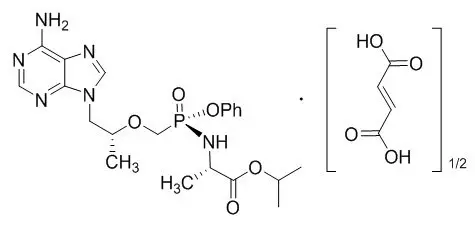
11. Genvoya Description
GENVOYA (elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide) is a fixed-dose combination tablet containing elvitegravir (EVG), cobicistat (COBI), emtricitabine (FTC), and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) for oral administration.
- EVG is an HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitor.
- COBI is a mechanism-based inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes of the CYP3A family.
- FTC, a synthetic nucleoside analog of cytidine, is an HIV nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor (HIV NRTI).
- TAF, an HIV NRTI, is converted in vivo to tenofovir, an acyclic nucleoside phosphonate (nucleotide) analog of adenosine 5'-monophosphate.
Each tablet contains 150 mg of EVG, 150 mg of COBI, 200 mg of FTC, and 10 mg of TAF (equivalent to 11.2 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate). The tablets include the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, silicon dioxide, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing FD&C Blue No. 2/indigo carmine aluminum lake, iron oxide yellow, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12. Genvoya - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
GENVOYA is a fixed-dose combination of antiretroviral drugs elvitegravir (plus the CYP3A inhibitor cobicistat), emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Special Populations
Drug Interaction Studies
[see also Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7)]
The drug-drug interaction studies described in Tables 11–14 were conducted with GENVOYA, elvitegravir (coadministered with cobicistat or ritonavir), cobicistat administered alone, or TAF (administered alone or coadministered with emtricitabine).
As GENVOYA should not be administered with other antiretroviral medications, information regarding drug-drug interactions with other antiretrovirals agents is not provided.
The effects of coadministered drugs on the exposure of elvitegravir, emtricitabine, and TAF are shown in Table 11, Table 12, and Table 13 respectively. The effects of GENVOYA or its components on the exposure of coadministered drugs are shown in Table 14. For information regarding clinical recommendations, see Drug Interactions (7).
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug (mg) | Elvitegravir Dose (mg) | CYP3A Inhibitor Cobicistat or Ritonavir Dose (mg) | N | Mean Ratio of Elvitegravir Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI); No effect = 1.00 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | |||||
|
|||||||
| Maximum strength antacid† | 20 mL single dose given 4 hours before elvitegravir | 50 single dose | Ritonavir 100 single dose | 8 | 0.95 (0.84,1.07) | 0.96 (0.88,1.04) | 1.04 (0.93,1.17) |
| 20 mL single dose given 4 hours after elvitegravir | 10 | 0.98 (0.88,1.10) | 0.98 (0.91,1.06) | 1.00 (0.90,1.11) |
|||
| 20 mL single dose given 2 hours before elvitegravir | 11 | 0.82 (0.74,0.91) | 0.85 (0.79,0.91) | 0.90 (0.82,0.99) |
|||
| 20 mL single dose given 2 hours after elvitegravir | 10 | 0.79 (0.71,0.88) | 0.80 (0.75,0.86) | 0.80 (0.73,0.89) |
|||
| Atorvastatin | 10 single dose | 150 once daily‡ | Cobicistat 150 once daily‡ | 16 | 0.91 (0.85,0.98) | 0.92 (0.87,0.98) | 0.88 (0.81,0.96) |
| Carbamazepine | 200 twice daily | 150 once daily | Cobicistat 150 once daily | 12 | 0.55 (0.49,0.61) | 0.31 (0.28,0.33) | 0.03 (0.02,0.40) |
| Famotidine | 40 once daily given 12 hours after elvitegravir | 150 once daily | Cobicistat 150 once daily | 10 | 1.02 (0.89,1.17) | 1.03 (0.95,1.13) | 1.18 (1.05,1.32) |
| 40 once daily given simultaneously with elvitegravir | 16 | 1.00 (0.92,1.10) | 1.03 (0.98,1.08) | 1.07 (0.98,1.17) |
|||
| Ketoconazole | 200 twice daily | 150 once daily | Ritonavir 100 once daily | 18 | 1.17 (1.04,1.33) | 1.48 (1.36,1.62) | 1.67 (1.48,1.88) |
| Ledipasvir/ Sofosbuvir | 90/400 once daily | 150 once daily‡ | Cobicistat 150 once daily‡ | 30 | 0.98 (0.90,1.07) | 1.11 (1.02,1.20) | 1.46 (1.28,1.66) |
| Omeprazole | 40 once daily given 2 hours before elvitegravir | 50 once daily | Ritonavir 100 once daily | 9 | 0.93 (0.83,1.04) | 0.99 (0.91,1.07) | 0.94 (0.85,1.04) |
| 20 once daily given 2 hours before elvitegravir | 150 once daily | Cobicistat 150 once daily | 11 | 1.16 (1.04,1.30) | 1.10 (1.02,1.19) | 1.13 (0.96,1.34) |
|
| 20 once daily given 12 hours after elvitegravir | 11 | 1.03 (0.92,1.15) | 1.05 (0.93,1.18) | 1.10 (0.92,1.32) |
|||
| Rifabutin | 150 once every other day | 150 once daily | Cobicistat 150 once daily | 12 | 0.91 (0.84,0.99) | 0.79 (0.74,0.85) | 0.33 (0.27,0.40) |
| Rosuvastatin | 10 single dose | 150 once daily | Cobicistat 150 once daily | 10 | 0.94 (0.83,1.07) | 1.02 (0.91,1.14) | 0.98 (0.83,1.16) |
| Sertraline | 50 single dose | 150 once daily‡ | Cobicistat 150 once daily‡ | 19 | 0.88 (0.82,0.93) | 0.94 (0.89,0.98) | 0.99 (0.93,1.05) |
| Sofosbuvir/ Velpatasvir | 400/100 once daily | 150 once daily‡ | Cobicistat 150 once daily‡ | 24 | 0.87 (0.80,0.94) | 0.94 (0.88,1.00) | 1.08 (0.97,1.20) |
| Sofosbuvir/ Velpatasvir/ Voxilaprevir | 400/100/100 + 100 Voxilaprevir§ once daily | 150 once daily‡ | Cobicistat 150 once daily‡ | 29 | 0.79 (0.75,0.85) | 0.94 (0.88,1.00) | 1.32 (1.17,1.49) |
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug (mg) | Emtricitabine Dose (mg) | N | Mean Ratio of Emtricitabine Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI); No effect = 1.00 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
|
||||||
| Famciclovir | 500 single dose | 200 single dose | 12 | 0.90 (0.80,1.01) | 0.93 (0.87,0.99) | NC |
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug (mg) | TAF Dose (mg) | N | Mean Ratio of TAF Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI); No effect = 1.00 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| NC = Not Calculated | ||||||
|
||||||
| Cobicistat | 150 once daily | 8 once daily | 12 | 2.83 (2.20,3.65) | 2.65 (2.29,3.07) | NC |
| Ledipasvir/ Sofosbuvir | 90/400 once daily | 10 once daily† | 30 | 0.90 (0.73,1.11) | 0.86 (0.78,0.95) | NC |
| Sertraline | 50 single dose | 10 once daily† | 19 | 1.00 (0.86,1.16) | 0.96 (0.89,1.03) | NC |
| Sofosbuvir/ Velpatasvir | 400/100 once daily | 10 once daily† | 24 | 0.80 (0.68,0.94) | 0.87 (0.81,0.94) | NC |
| Sofosbuvir/ Velpatasvir/ Voxilaprevir | 400/100/100 + 100 Voxilaprevir‡ once daily | 10 once daily† | 29 | 0.79 (0.68,0.92) | 0.93 (0.85,1.01) | NC |
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug (mg) | Elvitegravir Dose (mg) | CYP3A Inhibitor Cobicistat Dose (mg) | FTC Dose (mg) | TAF Dose (mg) | N | Mean Ratio of Coadministered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI); No effect = 1.00 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | |||||||
| FTC = emtricitabine; TAF = tenofovir alafenamide | |||||||||
| N/A = Not Applicable; NC = Not Calculated | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Atorvastatin | 10 single dose | 150 once daily† | 150 once daily† | 200 once daily† | 10 once daily† | 16 | 2.32 (1.91,2.82) | 2.60 (2.31,2.93) | NC |
| Buprenorphine | 16 – 24 once daily | 150 once daily | 150 once daily | N/A | N/A | 17 | 1.12 (0.98,1.27) | 1.35 (1.18,1.55) | 1.66 (1.43,1.93) |
| Norbuprenorphine | 1.24 (1.03,1.49) | 1.42 (1.22,1.67) | 1.57 (1.31,1.88) |
||||||
| Carbamazepine | 200 twice daily | 150 once daily | 150 once daily | N/A | N/A | 12 | 1.40 (1.32,1.49) | 1.43 (1.36,1.52) | 1.51 (1.41,1.62) |
| Carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide | 0.73 (0.70,0.78) | 0.65 (0.63,0.66) | 0.59 (0.57,0.61) |
||||||
| Desipramine | 50 single dose | N/A | 150 once daily | N/A | N/A | 8 | 1.24 (1.08,1.44) | 1.65 (1.36,2.02) | NC |
| Digoxin | 0.5 single dose | N/A | 150 once daily | N/A | N/A | 22 | 1.41 (1.29,1.55) | 1.08 (1.00,1.17) | NC |
| Famciclovir | 500 single dose | N/A | N/A | 200 single dose | N/A | 12 | 0.93 (0.78,1.11) | 0.91 (0.84,0.99) | N/A |
| Ledipasvir | 90 once daily | 150 once daily† | 150 once daily† | 200 once daily† | 10 once daily† | 30 | 1.65 (1.53,1.78) | 1.79 (1.64,1.96) | 1.93 (1.74,2.15) |
| Sofosbuvir | 400 once daily | 1.28 (1.13,1.47) | 1.47 (1.35,1.59) | N/A | |||||
| GS-331007‡ | 1.29 (1.24,1.35) | 1.48 (1.44,1.53) | 1.66 (1.60,1.73) |
||||||
| Naloxone | 4–6 once daily | 150 once daily | 150 once daily | N/A | N/A | 17 | 0.72 (0.61,0.85) | 0.72 (0.59,0.87) | N/A |
| Norgestimate/ ethinyl estradiol§ | 0.180/0.215/ 0.250 norgestimate once daily | 150 once daily§ | 150 once daily§ | 200 once daily§ | N/A | 13 | 2.08 (2.00,2.17) | 2.26 (2.15,2.37) | 2.67 (2.43,2.92) |
| 0.025 ethinyl estradiol once daily | 0.94 (0.86,1.04) | 0.75 (0.69,0.81) | 0.56 (0.52,0.61) |
||||||
| Norgestromin | 0.180/0.215/ 0.250 norgestimate once daily / 0.025 ethinyl estradiol once daily | N/A | N/A | 200 once daily¶ | 25 once daily¶ | 15 | 1.17 (1.07,1.26) | 1.12 (1.07,1.17) | 1.16 (1.08,1.24) |
| Norgestrel | 1.10 (1.02,1.18) | 1.09 (1.01,1.18) | 1.11 (1.03,1.20) |
||||||
| Ethinyl estradiol | 1.22 (1.15,1.29) | 1.11 (1.07,1.16) | 1.02 (0.92,1.12) |
||||||
| R-Methadone | 80–120 daily | 150 once daily | 150 once daily | N/A | N/A | 11 | 1.01 (0.91,1.13) | 1.07 (0.96,1.19) | 1.10 (0.95,1.28) |
| S-Methadone | 0.96 (0.87,1.06) | 1.00 (0.89,1.12) | 1.02 (0.89,1.17) |
||||||
| Sertraline | 50 single dose | 150 once daily† | 150 once daily† | 200 once daily† | 10 once daily† | 19 | 1.14 (0.94,1.38) | 0.93 (0.77,1.13) | N/A |
| Rifabutin | 150 once every other day | 150 once daily | 150 once daily | N/A | N/A | 12 | 1.09 (0.98,1.20)# | 0.92 (0.83,1.03)# | 0.94 (0.85,1.04)# |
| 25-O-desacetyl-rifabutin | 12 | 4.84 (4.09,5.74)# | 6.25 (5.08,7.69)# | 4.94 (4.04,6.04)# |
|||||
| Rosuvastatin | 10 single dose | 150 once daily | 150 once daily | N/A | N/A | 10 | 1.89 (1.48,2.42) | 1.38 (1.14,1.67) | NC |
| Sofosbuvir | 400 once daily | 150 once daily† | 150 once daily† | 200 once daily† | 10 once daily† | 24 | 1.23 (1.07,1.42) | 1.37 (1.24,1.52) | N/A |
| GS-331007‡ | 1.29 (1.25,1.33) | 1.48 (1.43,1.53) | 1.58 (1.52,1.65) |
||||||
| Velpatasvir | 100 once daily | 1.30 (1.17,1.45) | 1.50 (1.35,1.66) | 1.60 (1.44,1.78) | |||||
| Sofosbuvir | 400 once daily | 150 once daily† | 150 once daily† | 200 once daily† | 10 once daily† | 29 | 1.27 (1.09,1.48) | 1.22 (1.12,1.32) | NC |
| GS-331007‡ | 1.28 (1.25,1.32) | 1.43 (1.39,1.47) | NC | ||||||
| Velpatasvir | 100 once daily | 0.96 (0.89,1.04) | 1.16 (1.06,1.27) | 1.46 (1.30,1.64) |
|||||
| Voxilaprevir | 100 + 100Þ once daily | 1.92 (1.63,2.26) | 2.71 (2.30,3.19) | 4.50 (3.68,5.50) |
|||||
12.4 Microbiology
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Minimal to slight infiltration of mononuclear cells in the posterior uvea was observed in dogs with similar severity after three and nine month administration of TAF; reversibility was seen after a three month recovery period. At the NOAEL for eye toxicity, the systemic exposure in dogs was 5 (TAF) and 15 (tenofovir) times the exposure seen in humans at the recommended daily GENVOYA dosage.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Description of Clinical Trials
The efficacy and safety of GENVOYA were evaluated in the studies summarized in Table 15.
| Trial | Population | Study Arms (N) | Timepoint (Week) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Study 104*
Study 111* | Treatment-naïve adults | GENVOYA (866) STRIBILD (867) | 144 |
| Study 109† | Virologically-suppressed‡ adults | GENVOYA (959) ATRIPLA® or TRUVADA®+atazanavir+cobicistat or ritonavir or STRIBILD (477) | 96 |
| Study 112§ | Virologically-suppressed‡ adults with renal impairment¶ | GENVOYA (242) | 144 |
| Study 1825§ | Virologically-suppressed‡ adults with ESRD# receiving chronic hemodialysis | GENVOYA (55) | 48 |
| Study 106 (cohort 1)§ | Treatment-naïve adolescents between the ages of 12 to less than 18 years (at least 35 kg) | GENVOYA (50) | 48 |
| Study 106 (cohort 2)§ | Virologically-suppressed‡ children between the ages of 6 to less than 12 years (at least 25 kg) | GENVOYA (52) | 48 |
14.2 Clinical Trial Results in HIV-1 Treatment-Naïve Subjects
In both Study 104 and Study 111, subjects were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either GENVOYA (N=866) once daily or STRIBILD (elvitegravir 150 mg, cobicistat 150 mg, emtricitabine 200 mg, TDF 300 mg) (N=867) once daily. The mean age was 36 years (range 18–76), 85% were male, 57% were White, 25% were Black, and 10% were Asian. Nineteen percent of subjects identified as Hispanic/Latino. The mean baseline plasma HIV-1 RNA was 4.5 log10 copies per mL (range 1.3–7.0) and 23% of subjects had baseline viral loads greater than 100,000 copies per mL. The mean baseline CD4+ cell count was 427 cells per mm3 (range 0–1360) and 13% had CD4+ cell counts less than 200 cells per mm3.
Pooled treatment outcomes of Studies 104 and 111 through Week 144 are presented in Table 16.
| GENVOYA (N=866) | STRIBILD (N=867) |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL† | 84% | 80% |
| HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 copies/mL‡ | 5% | 4% |
| No Virologic Data at Week 144 Window | 11% | 16% |
| Discontinued Study Drug Due to AE or Death§ | 2% | 3% |
| Discontinued Study Drug Due to Other Reasons and Last Available HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL¶ | 9% | 11% |
| Missing Data During Window but on Study Drug | 1% | 1% |
Treatment outcomes were similar across subgroups by age, sex, race, baseline viral load, and baseline CD4+ cell count.
In Studies 104 and 111, the mean increase from baseline in CD4+ cell count at Week 144 was 326 cells per mm3 in GENVOYA-treated subjects and 305 cells per mm3 in STRIBILD-treated subjects.
14.3 Clinical Trial Results in HIV-1 Virologically-Suppressed Adults Who Switched to GENVOYA
In Study 109, the efficacy and safety of switching from ATRIPLA, TRUVADA plus atazanavir (given with either cobicistat or ritonavir), or STRIBILD to GENVOYA once daily were evaluated in a randomized, open-label trial of virologically-suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) HIV-1 infected adults (N=1436). Subjects must have been suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) on their baseline regimen for at least 6 months and had no known resistance-associated substitutions to any of the components of GENVOYA prior to study entry. Subjects were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to either switch to GENVOYA at baseline (N=959), or stay on their baseline antiretroviral regimen (N=477). Subjects had a mean age of 41 years (range 21–77), 89% were male, 67% were White, and 19% were Black. The mean baseline CD4+ cell count was 697 cells per mm3 (range 79–1951).
Subjects were stratified by prior treatment regimen. At screening, 42% of subjects were receiving TRUVADA plus atazanavir (given with either cobicistat or ritonavir), 32% were receiving STRIBILD, and 26% were receiving ATRIPLA.
Treatment outcomes of Study 109 through 96 weeks are presented in Table 17.
| GENVOYA (N=959) | ATRIPLA or TRUVADA+atazanavir +cobicistat or ritonavir or STRIBILD (N=477) |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL | 93% | 89% |
| HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 copies/mL† | 2% | 2% |
| No Virologic Data at Week 48 Window | 5% | 9% |
| Discontinued Study Drug Due to AE or Death‡ | 1% | 3% |
| Discontinued Study Drug Due to Other Reasons and Last Available HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL§ | 3% | 6% |
| Missing Data During Window but on Study Drug | 1% | <1% |
Treatment outcomes were similar across subgroups receiving ATRIPLA, TRUVADA plus atazanavir (given with either cobicistat or ritonavir), or STRIBILD prior to randomization. In Study 109, the mean increase from baseline in CD4+ cell count at Week 96 was 60 cells per mm3 in GENVOYA-treated subjects and 42 cells per mm3 in subjects who stayed on their baseline regimen.
14.5 Clinical Trial Results in HIV-1 Infected Pediatric Subjects Between the Ages of 6 to Less than 18 Years
In Study 106, an open-label, single arm trial the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of GENVOYA in HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects were evaluated in treatment-naïve adolescents between the ages of 12 to less than 18 years weighing at least 35 kg (N=50) and in virologically-suppressed children between the ages of 6 to less than 12 years weighing at least 25 kg (N=52).
16. How is Genvoya supplied
GENVOYA tablets are available in bottles containing 30 tablets with a silica gel desiccant, polyester coil, and child-resistant closure as follows:
- GENVOYA tablets each contain 150 mg of elvitegravir (EVG), 150 mg of cobicistat (COBI), 200 mg of emtricitabine (FTC), and 10 mg of tenofovir alafenamide (TAF). These tablets are green, capsule-shaped, film-coated, debossed with "GSI" on one side of the tablet and the number "510" on the other side (NDC 61958-1901-1).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Revised: 01/2022 |
| Patient Information | |
| GENVOYA® (jen-VOY-uh) (elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide) tablets |
|
|
Important: Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about medicines that should not be taken with GENVOYA. For more information, see the section "What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking GENVOYA?" |
|
|
What is the most important information I should know about GENVOYA? GENVOYA can cause serious side effects, including:
For more information about side effects, see "What are the possible side effects of GENVOYA?" |
|
|
What is GENVOYA? GENVOYA is a prescription medicine that is used without other human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) medicines to treat HIV-1 infection in adults and children who weigh at least 55 pounds (25 kg):
HIV-1 is the virus that causes Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). GENVOYA contains the prescription medicines elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide. It is not known if GENVOYA is safe and effective in children who weigh less than 55 pounds (25 kg). |
|
| Do not take GENVOYA if you also take a medicine that contains: | |
|
|
|
|
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking GENVOYA? Before taking GENVOYA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines may interact with GENVOYA. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
|
|
|
How should I take GENVOYA?
|
|
|
What are the possible side effects of GENVOYA? GENVOYA may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effect of GENVOYA is nausea. These are not all the possible side effects of GENVOYA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
|
How should I store GENVOYA?
Keep GENVOYA and all medicines out of reach of children. |
|
|
General information about the safe and effective use of GENVOYA. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use GENVOYA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give GENVOYA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about GENVOYA that is written for health professionals. |
|
|
What are the ingredients in GENVOYA? Active ingredients: elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, silicon dioxide, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing FD&C Blue No. 2/indigo carmine aluminum lake, iron oxide yellow, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide. Manufactured and distributed by: Gilead Sciences, Inc. Foster City, CA 94404 GENVOYA is a trademark of Gilead Sciences, Inc., or its related companies. © 2022 Gilead Sciences, Inc. All rights reserved. 207561-GS--017 For more information, call 1-800-445-3235 or go to www.GENVOYA.com. |
|
| GENVOYA
elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Gilead Sciences, Inc. (185049848) |