Drug Detail:Glyxambi (Empagliflozin and linagliptin [ em-pa-gli-floe-zin-and-lin-a-glip-tin ])
Drug Class: Antidiabetic combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
GLYXAMBI® (empagliflozin and linagliptin tablets), for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2015
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1) | 3/2020 |
| Warnings and Precautions | |
| Pancreatitis (5.1) | 7/2019 |
| Ketoacidosis (5.4) | 1/2020 |
| Increased Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) – Removed | 3/2020 |
| Bullous Pemphigoid (5.12) | 7/2019 |
| Macrovascular Outcomes – Removed | 7/2019 |
Indications and Usage for Glyxambi
GLYXAMBI is a combination of empagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor and linagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Empagliflozin is indicated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease. (1)
Limitations of Use
- Not recommended for patients with type 1 diabetes or for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis (1)
- Has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis (1)
Glyxambi Dosage and Administration
- The recommended dose of GLYXAMBI is 10 mg empagliflozin/5 mg linagliptin once daily, taken in the morning, with or without food (2.1)
- Dose may be increased to 25 mg empagliflozin/5 mg linagliptin once daily (2.1)
- Assess renal function before initiating GLYXAMBI. Do not initiate GLYXAMBI if eGFR is below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 (2.2)
- Discontinue GLYXAMBI if eGFR falls persistently below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets:
10 mg empagliflozin/5 mg linagliptin
25 mg empagliflozin/5 mg linagliptin (3)
Contraindications
- Severe renal impairment, end-stage renal disease, or dialysis (4)
- Hypersensitivity to empagliflozin, linagliptin, or any of the excipients in GLYXAMBI (4, 5.10)
Warnings and Precautions
- Pancreatitis: There have been reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue GLYXAMBI. (5.1)
- Heart Failure: Heart failure has been observed with two other members of the DPP-4 inhibitor class. Consider risks and benefits of GLYXAMBI in patients who have known risk factors for heart failure. Monitor for signs and symptoms. (5.2)
- Hypotension: Before initiating GLYXAMBI assess and correct volume status in patients with renal impairment, the elderly, in patients with low systolic blood pressure, and in patients on diuretics. Monitor for signs and symptoms during therapy. (5.3)
- Ketoacidosis: Assess patients who present with signs and symptoms of metabolic acidosis for ketoacidosis, regardless of blood glucose level. If suspected, discontinue GLYXAMBI, evaluate and treat promptly. Before initiating GLYXAMBI, consider risk factors for ketoacidosis. Patients on GLYXAMBI may require monitoring and temporary discontinuation of therapy in clinical situations known to predispose to ketoacidosis. (5.4)
- Acute Kidney Injury: Consider temporarily discontinuing in settings of reduced oral intake or fluid losses. If acute kidney injury occurs, discontinue and promptly treat. Monitor renal function during therapy. (5.5)
- Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis: Evaluate patients for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections and treat promptly, if indicated (5.6)
- Hypoglycemia: Consider lowering the dose of insulin secretagogue or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when initiating GLYXAMBI (5.7)
- Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene): Serious, life-threatening cases have occurred in both females and males. Assess patients presenting with pain or tenderness, erythema, or swelling in the genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise. If suspected, institute prompt treatment. (5.8)
- Genital Mycotic Infections: Monitor and treat as appropriate (5.9)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions) have occurred with empagliflozin and linagliptin. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue GLYXAMBI, treat promptly, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. (5.10)
- Arthralgia: Severe and disabling arthralgia has been reported in patients taking DPP-4 inhibitors. Consider as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate. (5.11)
- Bullous Pemphigoid: There have been reports of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, discontinue GLYXAMBI. (5.12)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- The most common adverse reactions associated with GLYXAMBI (a 5% or greater incidence) were urinary tract infections, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infections (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257 or 1-800-459-9906 TTY, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Advise females of the potential risk to a fetus especially during the second and third trimesters (8.1)
- Lactation: GLYXAMBI is not recommended when breastfeeding (8.2)
- Pediatric Patients: Safety and effectiveness of GLYXAMBI in pediatric patients have not been established (8.4)
- Geriatric Patients: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to volume depletion and reduced renal function (5.3, 5.5, 8.5)
- Renal Impairment: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to reduced renal function (2.2, 5.5, 8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 3/2020
Related/similar drugs
metformin, Trulicity, Lantus, Victoza, Tresiba, LevemirFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Glyxambi
GLYXAMBI is a combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Empagliflozin is indicated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
2. Glyxambi Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of GLYXAMBI is 10 mg empagliflozin/5 mg linagliptin once daily in the morning, taken with or without food. In patients tolerating GLYXAMBI, the dose may be increased to 25 mg empagliflozin/5 mg linagliptin once daily.
In patients with volume depletion, correcting this condition prior to initiation of GLYXAMBI is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.5) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
No studies have been performed specifically examining the safety and efficacy of GLYXAMBI in patients previously treated with other oral antihyperglycemic agents and switched to GLYXAMBI. Any change in therapy of type 2 diabetes should be undertaken with care and appropriate monitoring as changes in glycemic control can occur.
2.2 Patients with Renal Impairment
Assessment of renal function is recommended prior to initiation of GLYXAMBI and periodically thereafter.
GLYXAMBI should not be initiated in patients with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m2.
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with an eGFR greater than or equal to 45 mL/min/1.73 m2.
GLYXAMBI should be discontinued if eGFR is persistently less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
GLYXAMBI is a combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin. GLYXAMBI is available in the following dosage forms and strengths:
- 10 mg empagliflozin/5 mg linagliptin tablets are pale yellow, arc triangular, flat-faced, bevel-edged, film-coated tablets. One side is debossed with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol; the other side is debossed with "10/5".
- 25 mg empagliflozin/5 mg linagliptin tablets are pale pink, arc triangular, flat-faced, bevel-edged, film-coated tablets. One side is debossed with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol; the other side is debossed with "25/5".
4. Contraindications
GLYXAMBI is contraindicated in patients with:
- Severe renal impairment, end-stage renal disease, or dialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
- Hypersensitivity to empagliflozin, linagliptin, or any of the excipients in GLYXAMBI, reactions such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, exfoliative skin conditions, urticaria, or bronchial hyperreactivity have occurred [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, has been reported in patients treated with linagliptin. In the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14.3)], acute pancreatitis was reported in 9 (0.3%) patients treated with linagliptin and in 5 (0.1%) patients treated with placebo. Two patients treated with linagliptin in the CARMELINA trial had acute pancreatitis with a fatal outcome. There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, in patients treated with linagliptin.
Take careful notice of potential signs and symptoms of pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue GLYXAMBI and initiate appropriate management. It is unknown whether patients with a history of pancreatitis are at increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using GLYXAMBI.
5.2 Heart Failure
An association between DPP-4 inhibitor treatment and heart failure has been observed in cardiovascular outcomes trials for two other members of the DPP-4 inhibitor class. These trials evaluated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Consider the risks and benefits of GLYXAMBI prior to initiating treatment in patients at risk for heart failure, such as those with a prior history of heart failure and a history of renal impairment, and observe these patients for signs and symptoms of heart failure during therapy. Advise patients of the characteristic symptoms of heart failure and to immediately report such symptoms. If heart failure develops, evaluate and manage according to current standards of care and consider discontinuation of GLYXAMBI.
5.3 Hypotension
Empagliflozin causes intravascular volume contraction. Symptomatic hypotension may occur after initiating empagliflozin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] particularly in patients with renal impairment, the elderly, in patients with low systolic blood pressure, and in patients on diuretics. Before initiating GLYXAMBI, assess for volume contraction and correct volume status if indicated. Monitor for signs and symptoms of hypotension after initiating therapy and increase monitoring in clinical situations where volume contraction is expected [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
5.4 Ketoacidosis
Reports of ketoacidosis, a serious life-threatening condition requiring urgent hospitalization have been identified in postmarketing surveillance in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving sodium glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, including empagliflozin. Fatal cases of ketoacidosis have been reported in patients taking empagliflozin. GLYXAMBI is not indicated for the treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus [see Indications and Usage (1)].
Patients treated with GLYXAMBI who present with signs and symptoms consistent with severe metabolic acidosis should be assessed for ketoacidosis regardless of presenting blood glucose levels, as ketoacidosis associated with GLYXAMBI may be present even if blood glucose levels are less than 250 mg/dL. If ketoacidosis is suspected, GLYXAMBI should be discontinued, patient should be evaluated, and prompt treatment should be instituted. Treatment of ketoacidosis may require insulin, fluid and carbohydrate replacement.
In many of the postmarketing reports, and particularly in patients with type 1 diabetes, the presence of ketoacidosis was not immediately recognized and institution of treatment was delayed because presenting blood glucose levels were below those typically expected for diabetic ketoacidosis (often less than 250 mg/dL). Signs and symptoms at presentation were consistent with dehydration and severe metabolic acidosis and included nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, generalized malaise, and shortness of breath. In some but not all cases, factors predisposing to ketoacidosis such as insulin dose reduction, acute febrile illness, reduced caloric intake, surgery, pancreatic disorders suggesting insulin deficiency (e.g., type 1 diabetes, history of pancreatitis or pancreatic surgery), and alcohol abuse were identified.
Before initiating GLYXAMBI, consider factors in the patient history that may predispose to ketoacidosis including pancreatic insulin deficiency from any cause, caloric restriction, and alcohol abuse.
For patients who undergo scheduled surgery, consider temporarily discontinuing GLYXAMBI for at least 3 days prior to surgery [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2, 12.3)].
Consider monitoring for ketoacidosis and temporarily discontinuing GLYXAMBI in other clinical situations known to predispose to ketoacidosis (e.g., prolonged fasting due to acute illness or post-surgery). Ensure risk factors for ketoacidosis are resolved prior to restarting GLYXAMBI.
Educate patients on the signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis and instruct patients to discontinue GLYXAMBI and seek medical attention immediately if signs and symptoms occur.
5.5 Acute Kidney Injury
Empagliflozin causes intravascular volume contraction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] and can cause renal impairment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. There have been postmarketing reports of acute kidney injury, some requiring hospitalization and dialysis, in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including empagliflozin; some reports involved patients younger than 65 years of age.
Before initiating GLYXAMBI, consider factors that may predispose patients to acute kidney injury including hypovolemia, chronic renal impairment, heart failure and concomitant medications (diuretics, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, NSAIDs). Consider temporarily discontinuing GLYXAMBI in any setting of reduced oral intake (such as acute illness or fasting) or fluid losses (such as gastrointestinal illness or excessive heat exposure); monitor patients for signs and symptoms of acute kidney injury. If acute kidney injury occurs, discontinue GLYXAMBI promptly and institute treatment.
Empagliflozin increases serum creatinine and decreases eGFR. Patients with hypovolemia may be more susceptible to these changes. Renal function abnormalities can occur after initiating GLYXAMBI [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Renal function should be evaluated prior to initiation of GLYXAMBI and monitored periodically thereafter. More frequent renal function monitoring is recommended in patients with an eGFR below 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Use of GLYXAMBI is not recommended when eGFR is persistently less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 and is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Contraindications (4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.6 Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis
There have been postmarketing reports of serious urinary tract infections including urosepsis and pyelonephritis requiring hospitalization in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including empagliflozin. Treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors increases the risk for urinary tract infections. Evaluate patients for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections and treat promptly, if indicated [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.7 Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin and Insulin Secretagogues
Insulin and insulin secretagogues are known to cause hypoglycemia. The use of empagliflozin or linagliptin in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin was associated with a higher rate of hypoglycemia compared with placebo in a clinical trial. Therefore, a lower dose of the insulin secretagogue or insulin may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with GLYXAMBI.
5.8 Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene)
Reports of necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier's gangrene), a rare but serious and life-threatening necrotizing infection requiring urgent surgical intervention, have been identified in postmarketing surveillance in patients with diabetes mellitus receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including empagliflozin. Cases have been reported in both females and males. Serious outcomes have included hospitalization, multiple surgeries, and death.
Patients treated with GLYXAMBI presenting with pain or tenderness, erythema, or swelling in the genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise, should be assessed for necrotizing fasciitis. If suspected, start treatment immediately with broad-spectrum antibiotics and, if necessary, surgical debridement. Discontinue GLYXAMBI, closely monitor blood glucose levels, and provide appropriate alternative therapy for glycemic control.
5.9 Genital Mycotic Infections
Empagliflozin increases the risk for genital mycotic infections [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Patients with a history of chronic or recurrent genital mycotic infections were more likely to develop genital mycotic infections. Monitor and treat as appropriate.
5.10 Hypersensitivity Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with linagliptin (one of the components of GLYXAMBI). These reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions. Onset of these reactions occurred predominantly within the first 3 months after initiation of treatment with linagliptin, with some reports occurring after the first dose.
Angioedema has also been reported with other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Use caution in a patient with a history of angioedema to another DPP-4 inhibitor because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to angioedema with GLYXAMBI.
There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions, (e.g., angioedema) in patients treated with empaglifozin (one of the components of GLYXAMBI).
If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue GLYXAMBI, treat promptly per standard of care, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. GLYXAMBI is contraindicated in patients with a previous serious hypersensitivity reaction to linagliptin or empagliflozin [see Contraindications (4)].
5.11 Severe and Disabling Arthralgia
There have been postmarketing reports of severe and disabling arthralgia in patients taking DPP-4 inhibitors. The time to onset of symptoms following initiation of drug therapy varied from one day to years. Patients experienced relief of symptoms upon discontinuation of the medication. A subset of patients experienced a recurrence of symptoms when restarting the same drug or a different DPP-4 inhibitor. Consider as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate.
5.12 Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid was reported in 7 (0.2%) patients treated with linagliptin compared to none in patients treated with placebo in the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14.3)], and 3 of these patients were hospitalized due to bullous pemphigoid. Postmarketing cases of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization have been reported with DPP-4 inhibitor use. In reported cases, patients typically recovered with topical or systemic immunosuppressive treatment and discontinuation of the DPP-4 inhibitor. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions while receiving GLYXAMBI. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, GLYXAMBI should be discontinued and referral to a dermatologist should be considered for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following important adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Acute Kidney Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin and Insulin Secretagogues [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Genital Mycotic Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Severe and Disabling Arthralgia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Bullous Pemphigoid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of linagliptin and empagliflozin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Acute Pancreatitis, including Fatal Pancreatitis [see Indications and Usage (1)]
- Ketoacidosis
- Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis
- Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's gangrene)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions including Anaphylaxis, Angioedema, and Exfoliative Skin Conditions
- Severe and Disabling Arthralgia
- Bullous Pemphigoid
- Skin Reactions (e.g., rash, urticaria)
- Mouth Ulceration, Stomatitis
- Rhabdomyolysis
7. Drug Interactions
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Data
8.2 Lactation
Data
Empagliflozin was present at a low level in rat fetal tissues after a single oral dose to the dams at gestation day 18. In rat milk, the mean milk to plasma ratio ranged from 0.634 to 5, and was greater than one from 2 to 24 hours post-dose. The mean maximal milk to plasma ratio of 5 occurred at 8 hours post-dose, suggesting accumulation of empagliflozin in the milk. Juvenile rats directly exposed to empagliflozin showed a risk to the developing kidney (renal pelvic and tubular dilatations) during maturation.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of GLYXAMBI in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
10. Overdosage
In the event of an overdose with GLYXAMBI, contact the Poison Control Center. Removal of empagliflozin by hemodialysis has not been studied, and removal of linagliptin by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is unlikely.
11. Glyxambi Description
GLYXAMBI tablets contain two oral antihyperglycemic drugs used in the management of type 2 diabetes: empagliflozin and linagliptin.
12. Glyxambi - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Specific Populations
Drug Interactions
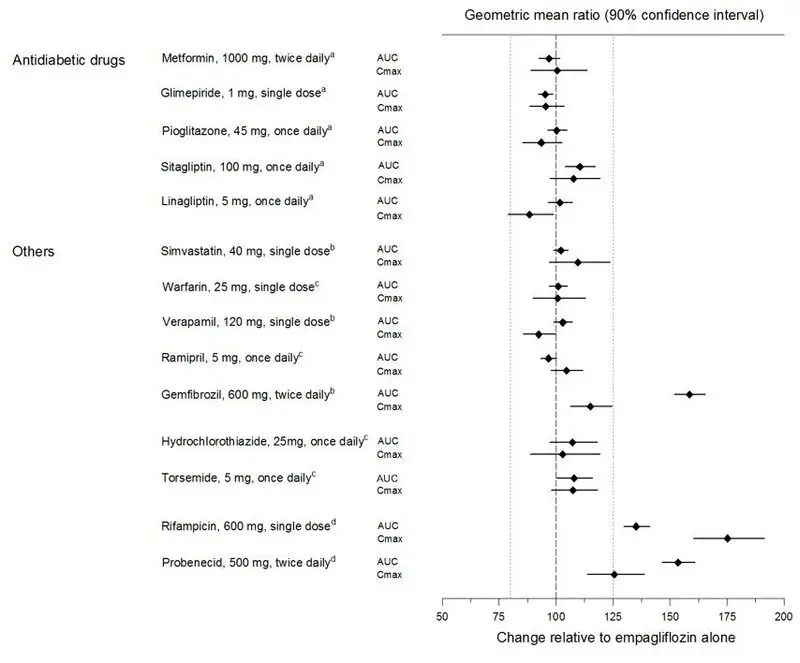
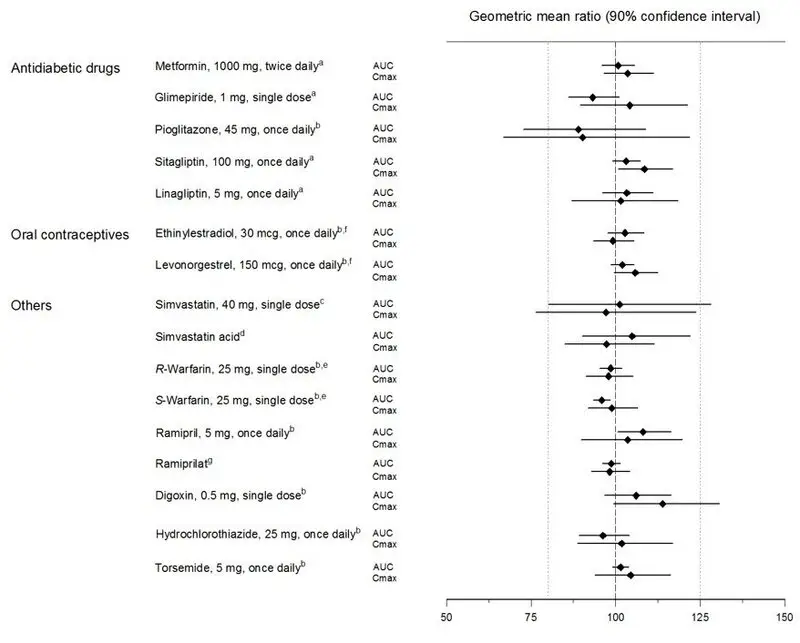
Pharmacokinetic drug interaction studies with GLYXAMBI have not been performed; however, such studies have been conducted with the individual components of GLYXAMBI (empagliflozin and linagliptin).
Empagliflozin
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 GLYXAMBI Glycemic Control Studies
Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin
A total of 686 patients with type 2 diabetes participated in a double-blind, active-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg in combination with linagliptin 5 mg compared to the individual components.
Patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on at least 1500 mg of metformin per day entered a single-blind placebo run-in period for 2 weeks. At the end of the run-in period, patients who remained inadequately controlled and had an HbA1c between 7% and 10.5% were randomized 1:1:1:1:1 to one of 5 active-treatment arms of empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg, linagliptin 5 mg, or linagliptin 5 mg in combination with 10 mg or 25 mg empagliflozin as a fixed dose combination tablet.
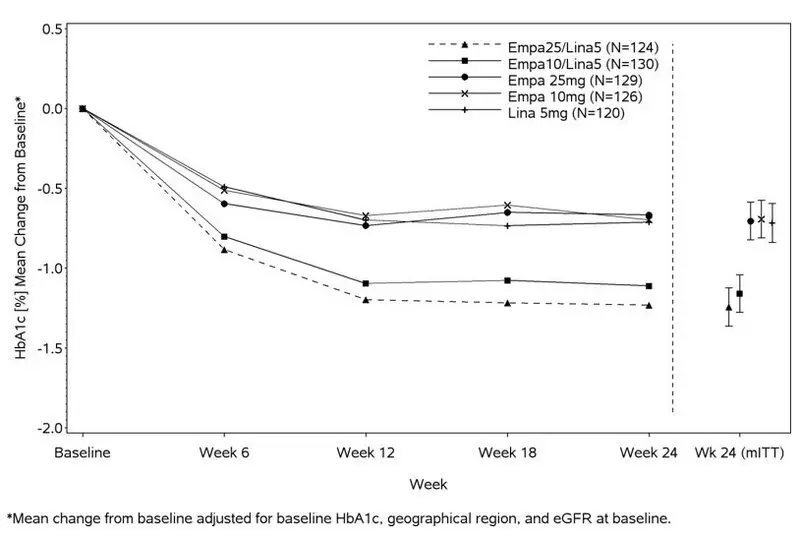
At Week 24, empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg used in combination with linagliptin 5 mg provided statistically significant improvement in HbA1c (p-value <0.0001) and FPG (p-value <0.001) compared to the individual components in patients who had been inadequately controlled on metformin (see Table 5, Figure 3). Treatment with GLYXAMBI 25 mg/5 mg or GLYXAMBI 10 mg/5 mg daily also resulted in a statistically significant reduction in body weight compared to linagliptin 5 mg (p-value <0.0001). There was no statistically significant difference compared to empagliflozin alone.
| GLYXAMBI 10 mg/5 mg | GLYXAMBI 25 mg/5 mg | Empagliflozin 10 mg | Empagliflozin 25 mg | Linagliptin 5 mg |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aFull analysis population (observed case) using MMRM. MMRM model included treatment, renal function, region, visit, visit by treatment interaction, and baseline HbA1c. | |||||
| bPatients with HbA1c above 7% at baseline: GLYXAMBI 25 mg/5 mg, n=123; GLYXAMBI 10 mg/5 mg, n=128; empagliflozin 25 mg, n=132; empagliflozin 10 mg, n=125; linagliptin 5 mg, n=119. Non-completers were considered failures (NCF). | |||||
| cFull analysis population using last observation carried forward. ANCOVA model included treatment, renal function, region, baseline weight, and baseline HbA1c. | |||||
| dp<0.001 for FPG; p<0.0001 for HbA1c and body weight | |||||
| HbA1c (%) | |||||
| Number of patients | n=135 | n=133 | n=137 | n=139 | n=128 |
| Baseline (mean) | 8.0 | 7.9 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -1.1 | -1.2 | -0.7 | -0.6 | -0.7 |
| Comparison vs empagliflozin 25 mg or 10 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI)a | -0.4 (-0.6, -0.2)d | -0.6 (-0.7, -0.4)d | -- | -- | -- |
| Comparison vs linagliptin 5 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI)a | -0.4 (-0.6, -0.2)d | -0.5 (-0.7, -0.3)d | -- | -- | -- |
| Patients [n (%)] achieving HbA1c <7%b | 74 (58) | 76 (62) | 35 (28) | 43 (33) | 43 (36) |
| FPG (mg/dL) | |||||
| Number of patients | n=133 | n=131 | n=136 | n=137 | n=125 |
| Baseline (mean) | 157 | 155 | 162 | 160 | 156 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -33 | -36 | -21 | -21 | -13 |
| Comparison vs empagliflozin 25 mg or 10 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI)a | -12 (-18, -5)d | -15 (-22, -9)d | -- | -- | -- |
| Comparison vs linagliptin 5 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI)a | -20 (-27, -13)d | -23 (-29, -16)d | -- | -- | -- |
| Body Weight | |||||
| Number of patients | n=135 | n=134 | n=137 | n=140 | n=128 |
| Baseline (mean) in kg | 87 | 85 | 86 | 88 | 85 |
| % change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -3.1 | -3.4 | -3.0 | -3.5 | -0.7 |
| Comparison vs empagliflozin 25 mg or 10 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI)c | 0.0 (-0.9, 0.8) | 0.1 (-0.8, 0.9) | -- | -- | -- |
| Comparison vs linagliptin 5 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI)c | -2.4 (-3.3, -1.5)d | -2.7 (-3.6, -1.8)d | -- | -- | -- |
Figure 3 Adjusted Mean HbA1c Change at Each Time Point (Completers) and at Week 24 (mITT population)
14.2 Empagliflozin Cardiovascular Outcome Study in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Empagliflozin is indicated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease. The effect of empagliflozin on cardiovascular risk in adult patients with type 2 diabetes and established, stable, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is presented below.
The EMPA-REG OUTCOME study, a multicenter, multi-national, randomized, double-blind parallel group trial compared the risk of experiencing a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) between empagliflozin and placebo when these were added to and used concomitantly with standard of care treatments for diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Coadministered antidiabetic medications were to be kept stable for the first 12 weeks of the trial. Thereafter, antidiabetic and atherosclerotic therapies could be adjusted, at the discretion of investigators, to ensure participants were treated according to the standard care for these diseases.
A total of 7020 patients were treated (empagliflozin 10 mg = 2345; empagliflozin 25 mg = 2342; placebo = 2333) and followed for a median of 3.1 years. Approximately 72% of the study population was Caucasian, 22% was Asian, and 5% was Black. The mean age was 63 years and approximately 72% were male.
All patients in the study had inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus at baseline (HbA1c greater than or equal to 7%). The mean HbA1c at baseline was 8.1% and 57% of participants had diabetes for more than 10 years. Approximately 31%, 22% and 20% reported a past history of neuropathy, retinopathy and nephropathy to investigators respectively and the mean eGFR was 74 mL/min/1.73 m2. At baseline, patients were treated with one (~30%) or more (~70%) antidiabetic medications including metformin (74%), insulin (48%), sulfonylurea (43%) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (11%).
All patients had established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease at baseline including one (82%) or more (18%) of the following: a documented history of coronary artery disease (76%), stroke (23%) or peripheral artery disease (21%). At baseline, the mean systolic blood pressure was 136 mmHg, the mean diastolic blood pressure was 76 mmHg, the mean LDL was 86 mg/dL, the mean HDL was 44 mg/dL, and the mean urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) was 175 mg/g. At baseline, approximately 81% of patients were treated with renin angiotensin system inhibitors, 65% with beta-blockers, 43% with diuretics, 77% with statins, and 86% with antiplatelet agents (mostly aspirin).
The primary endpoint in EMPA-REG OUTCOME was the time to first occurrence of a Major Adverse Cardiac Event (MACE). A major adverse cardiac event was defined as occurrence of either a cardiovascular death or a non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) or a non-fatal stroke. The statistical analysis plan had pre-specified that the 10 and 25 mg doses would be combined. A Cox proportional hazards model was used to test for non-inferiority against the pre-specified risk margin of 1.3 for the hazard ratio of MACE and superiority on MACE if non-inferiority was demonstrated. Type-1 error was controlled across multiples tests using a hierarchical testing strategy.
Empagliflozin significantly reduced the risk of first occurrence of primary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke (HR: 0.86; 95% CI 0.74, 0.99). The treatment effect was due to a significant reduction in the risk of cardiovascular death in subjects randomized to empagliflozin (HR: 0.62; 95% CI 0.49, 0.77), with no change in the risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction or non-fatal stroke (see Table 6 and Figures 4 and 5). Results for the 10 mg and 25 mg empagliflozin doses were consistent with results for the combined dose groups.
| Placebo N=2333 | Empagliflozin N=4687 | Hazard ratio vs placebo (95% CI) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| aTreated set (patients who had received at least one dose of study drug) | |||
| bp–value for superiority (2–sided) 0.04 | |||
| cTotal number of events | |||
| Composite of cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke (time to first occurrence)b | 282 (12.1%) | 490 (10.5%) | 0.86 (0.74, 0.99) |
| Non-fatal myocardial infarctionc | 121 (5.2%) | 213 (4.5%) | 0.87 (0.70, 1.09) |
| Non-fatal strokec | 60 (2.6%) | 150 (3.2%) | 1.24 (0.92, 1.67) |
| Cardiovascular deathc | 137 (5.9%) | 172 (3.7%) | 0.62 (0.49, 0.77) |
Figure 4 Estimated Cumulative Incidence of First MACE
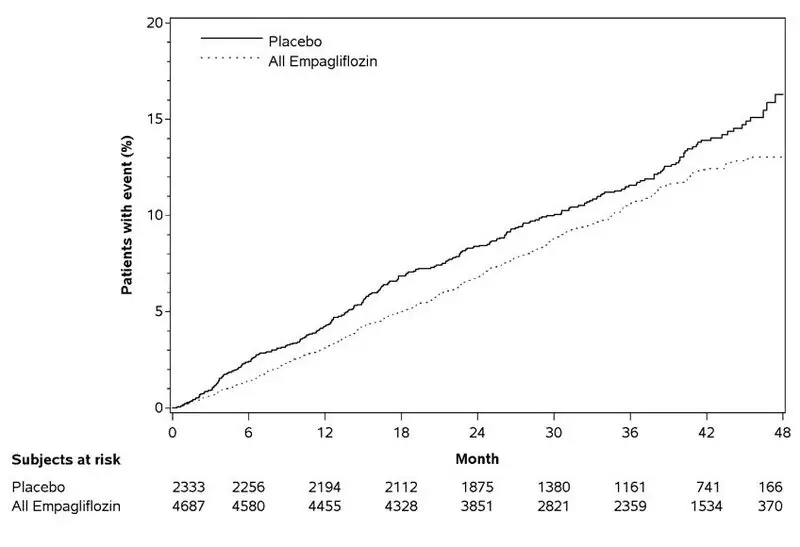
Figure 5 Estimated Cumulative Incidence of Cardiovascular Death
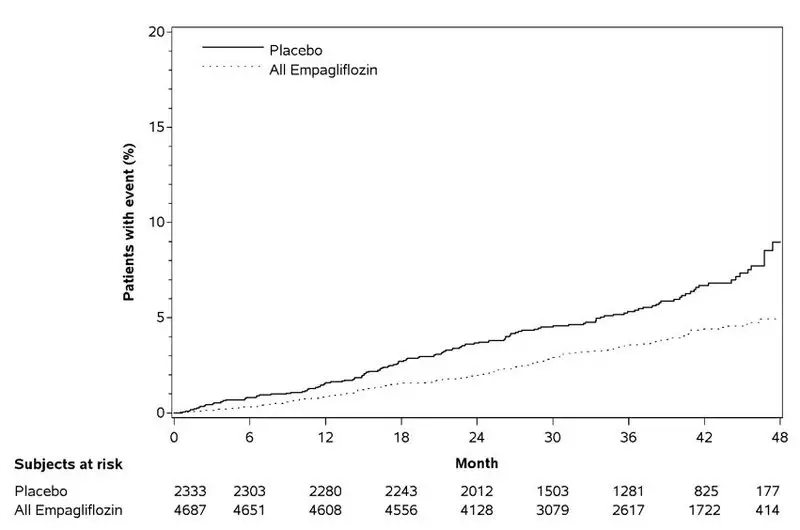
The efficacy of empagliflozin on cardiovascular death was generally consistent across major demographic and disease subgroups.
Vital status was obtained for 99.2% of subjects in the trial. A total of 463 deaths were recorded during the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Most of these deaths were categorized as cardiovascular deaths. The non-cardiovascular deaths were only a small proportion of deaths, and were balanced between the treatment groups (2.1% in patients treated with empagliflozin, and 2.4% of patients treated with placebo).
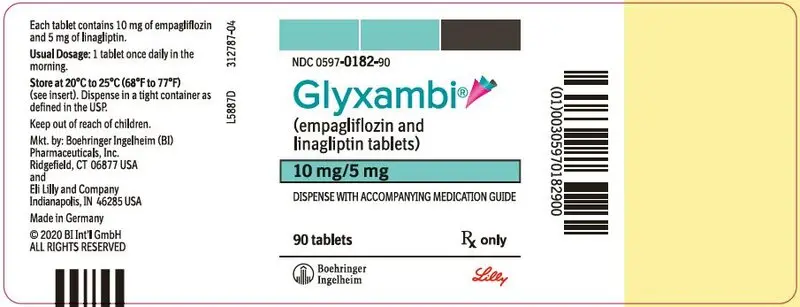
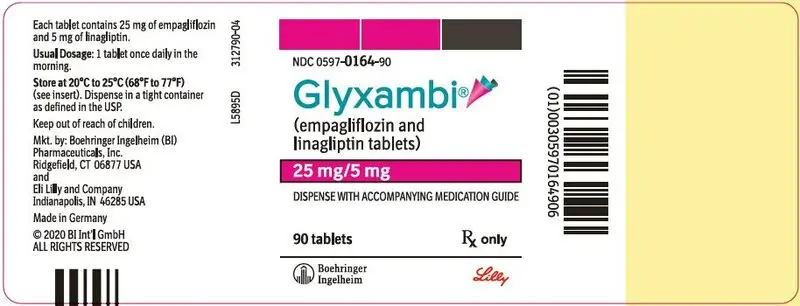
16. How is Glyxambi supplied
GLYXAMBI (empagliflozin and linagliptin) tablets are available in 10 mg/5 mg and 25 mg/5 mg strengths as follows:
10 mg/5 mg tablets: pale yellow, arc triangular, flat-faced, bevel-edged, film-coated tablets. One side is debossed with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol; the other side is debossed with "10/5".
Bottles of 30 (NDC 0597-0182-30)
Bottles of 90 (NDC 0597-0182-90)
Cartons containing 3 blister cards of 10 tablets each (3 × 10) (NDC 0597-0182-39), institutional pack.
25 mg/5 mg tablets: pale pink, arc triangular, flat-faced, bevel-edged, film-coated tablets. One side is debossed with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol; the other side is debossed with "25/5".
Bottles of 30 (NDC 0597-0164-30)
Bottles of 90 (NDC 0597-0164-90)
Cartons containing 3 blister cards of 10 tablets each (3 × 10) (NDC 0597-0164-39), institutional pack.
If repackaging is required, dispense in a tight container as defined in USP.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| MEDICATION GUIDE GLYXAMBI® (glik-SAM-bee) (empagliflozin and linagliptin tablets) for oral use |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: March 2020 | |||||
| What is the most important information I should know about GLYXAMBI? | ||||||
| GLYXAMBI can cause serious side effects, including: | ||||||
|
||||||
|
|
|||||
| Stop taking GLYXAMBI and call your doctor right away if you have pain in your stomach area (abdomen) that is severe and will not go away. The pain may be felt going from your abdomen to your back. The pain may happen with or without vomiting. These may be symptoms of pancreatitis. | ||||||
|
||||||
| You may be at higher risk of dehydration if you: | ||||||
|
|
|||||
| Talk to your doctor about what you can do to prevent dehydration including how much fluid you should drink on a daily basis. | ||||||
| What is GLYXAMBI? | ||||||
|
||||||
| Who should not take GLYXAMBI? | ||||||
| Do not take GLYXAMBI if you: | ||||||
|
||||||
| If you have any of these symptoms, stop taking GLYXAMBI and call your doctor right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room. | ||||||
| What should I tell my doctor before taking GLYXAMBI? | ||||||
| Before taking GLYXAMBI, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | ||||||
|
||||||
| Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | ||||||
| GLYXAMBI may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how GLYXAMBI works. | ||||||
| Especially tell your doctor if you take: | ||||||
|
||||||
| Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | ||||||
| How should I take GLYXAMBI? | ||||||
|
||||||
| What are the possible side effects of GLYXAMBI? | ||||||
| GLYXAMBI may cause serious side effects, including: | ||||||
|
||||||
|
|
|||||
| If you get any of these symptoms during treatment with GLYXAMBI, if possible, check for ketones in your urine, even if your blood sugar is less than 250 mg/dL. | ||||||
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||
|
||||||
|
|
|||||
|
||||||
|
|
|||||
| Talk to your doctor about what to do if you get symptoms of a yeast infection of the vagina or penis. Your doctor may tell you to use an over-the-counter antifungal medicine. Talk to your doctor right away if you use an over-the-counter antifungal medicine and your symptoms do not go away. | ||||||
|
||||||
| If you have any of these symptoms, stop taking GLYXAMBI and call your doctor right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room. | ||||||
|
||||||
| The most common side effects of GLYXAMBI include: | ||||||
|
|
|||||
| Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. | ||||||
| These are not all the possible side effects of GLYXAMBI. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. | ||||||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||||||
| How should I store GLYXAMBI? | ||||||
|
||||||
| Keep GLYXAMBI and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of GLYXAMBI. | ||||||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use GLYXAMBI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give GLYXAMBI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. | ||||||
| You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about GLYXAMBI that is written for health professionals. | ||||||
| What are the ingredients in GLYXAMBI? | ||||||
| Active ingredients: empagliflozin and linagliptin | ||||||
| Inactive ingredients: mannitol, pregelatinized starch, corn starch, copovidone, crospovidone, talc and magnesium stearate. The film coating contains the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, mannitol, talc, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol. | ||||||
| 10 mg/5 mg tablets also contain yellow ferric oxide. 25 mg/5 mg tablets also contain red ferric oxide. |
||||||
| Distributed by: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA | ||||||
| Marketed by: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA and Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN 46285 USA Licensed from: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Ingelheim, Germany |
||||||
| GLYXAMBI is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. | ||||||
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. either owns or uses the Glyxambi®, Jardiance®, Tradjenta®, EMPA-REG OUTCOME®, CARMELINA®, and CAROLINA® trademarks under license. | ||||||
| The other brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | ||||||
| Copyright © 2020 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH ALL RIGHTS RESERVED |
||||||
| IT5885SC312020 | ||||||
| For more information about GLYXAMBI including current prescribing information and Medication Guide, go to www.glyxambi.com, or scan the code below, or call Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257 or (TTY) 1-800-459-9906. | ||||||
|
|
||||||
| GLYXAMBI
empagliflozin and linagliptin tablet, film coated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GLYXAMBI
empagliflozin and linagliptin tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Registrant - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH and Co. KG | 551147440 | MANUFACTURE(0597-0164, 0597-0182) , API MANUFACTURE(0597-0164, 0597-0182) , PACK(0597-0164, 0597-0182) , LABEL(0597-0164, 0597-0182) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sixarp, LLC | 016329513 | PACK(0597-0164, 0597-0182) , LABEL(0597-0164, 0597-0182) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| West-Ward Columbus Inc. | 058839929 | PACK(0597-0164, 0597-0182) , LABEL(0597-0164, 0597-0182) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rottendorf Pharma GmbH | 315974691 | MANUFACTURE(0597-0164, 0597-0182) , PACK(0597-0164, 0597-0182) , LABEL(0597-0164, 0597-0182) | |