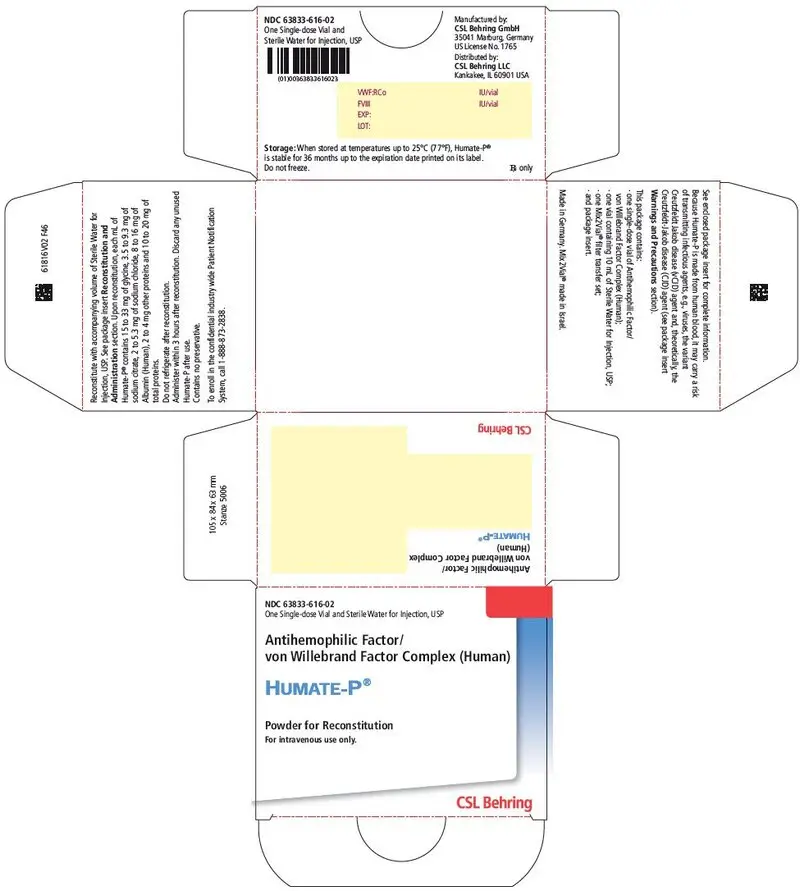
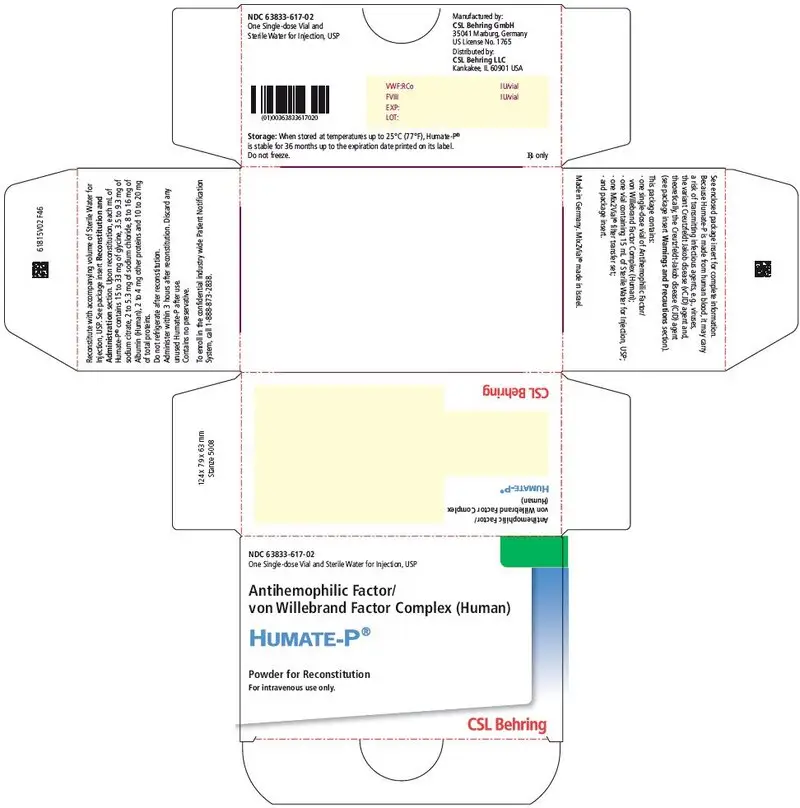
Drug Class: Miscellaneous coagulation modifiers
Highlights of Prescribing Information
HUMATE-P safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for HUMATE-P.
HUMATE-P [Antihemophilic Factor/von Willebrand Factor Complex (Human)]
Lyophilized Powder for Reconstitution for Intravenous Use Only.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1986
Indications and Usage for Humate-P
HUMATE-P is an Antihemophilic Factor/von Willebrand Factor (VWF) Complex (Human) indicated for:
- Hemophilia A – Treatment and prevention of bleeding in adults. (1.1)
- Von Willebrand disease (VWD) – in adults and pediatric patients in the (1) Treatment of spontaneous and trauma-induced bleeding episodes, and (2) Prevention of excessive bleeding during and after surgery. This applies to patients with severe VWD as well as patients with mild to moderate VWD where the use of desmopressin is known or suspected to be inadequate. (1.2) HUMATE-P is not indicated for the prophylaxis of spontaneous bleeding episodes in VWD.
Humate-P Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use only.
Hemophilia A
- One International Unit (IU) of factor VIII (FVIII) activity per kg body weight increases the circulating FVIII level by approximately 2.0 IU/dL. Individualize dosage based on the patient's weight, type and severity of hemorrhage, FVIII level, and presence of inhibitors. (2.1)
VWD
- Treatment of bleeding episodes – 40-80 IU VWF:Ristocetin Cofactor (RCo) per kg body weight (BW) every 8-12 hours. (2.2)
- Prevention of excessive bleeding during and after surgery for all types of VWD. (2.3)
| Type of Surgery (see Table 3 for complete surgical dosing) | Calculation of Loading Dose Initial maintenance dose should be half the loading dose (see Table 4 for monitoring recommendations). |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Major Surgery (2.3) | Δ* VWF:RCo × BW (kg)
IVR† | = IU VWF:RCo required |
| Minor/Oral Surgery‡ (2.3) | Δ* VWF:RCo × BW (kg)
IVR | = IU VWF:RCo required |
| Emergency Surgery (2.3) | Administer a dose of 50-60 IU VWF:RCo/kg BW | |
Dosage Forms and Strengths
HUMATE-P is available as a lyophilized powder in single-dose vials that contain the labeled amount of VWF:RCo and FVIII activity expressed in IU. The average ratio of VWF:RCo to FVIII is 2.4:1. Approximate potencies are shown below: (3)
| VWF:RCo/vial | FVIII/vial | Diluent |
|---|---|---|
| 600 IU | 250 IU | 5 mL |
| 1200 IU | 500 IU | 10 mL |
| 2400 IU | 1000 IU | 15 mL |
Contraindications
Anaphylactic or severe systemic reaction to antihemophilic factor or VWF preparations. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- VWD patients receiving HUMATE-P may be at risk of developing thromboembolic events. (5.1)
- Monitor for intravascular hemolysis and decreasing hematocrit values in patients with A, B, and AB blood groups who are receiving large or frequent doses. (5.2)
- Monitor VWF:RCo and FVIII levels in VWD patients, especially those undergoing surgery. (5.3)
- Products made from human blood may contain infectious agents (e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions observed by >5% of subjects after receiving HUMATE-P are allergic-anaphylactic reactions (e.g., urticaria, chest tightness, rash, pruritus, edema) and, in patients undergoing surgery, postoperative wound and injection-site bleeding, and epistaxis. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: No human or animal data. Use only if clearly needed. (8.1)
- The hemostatic efficacy of HUMATE-P has been studied in 34 pediatric subjects with VWD. (8.4) Based on the data from a subset of these subjects, age had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of VWF:RCo. (12.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2020
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Humate-P
1.1 Hemophilia A
HUMATE-P, Antihemophilic Factor/von Willebrand Factor Complex (Human), is indicated for treatment and prevention of bleeding in adults with hemophilia A (classical hemophilia).
1.2 Von Willebrand Disease (VWD)
HUMATE-P is also indicated in adult and pediatric patients with von Willebrand disease (VWD) for:
- (1)
- treatment of spontaneous and trauma-induced bleeding episodes, and
- (2)
- prevention of excessive bleeding during and after surgery. This applies to patients with severe VWD as well as patients with mild to moderate VWD where use of desmopressin (DDAVP) is known or suspected to be inadequate.
Controlled clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of prophylactic dosing with HUMATE-P to prevent spontaneous bleeding have not been conducted in VWD subjects [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Humate-P Dosage and Administration
2.1 Therapy for Hemophilia A
One International Unit (IU) of Factor VIII (FVIII) activity per kg body weight will increase the circulating FVIII level by approximately 2.0 International Units (IU)/dL. Dosage must be individualized based on the patient's weight, type and severity of hemorrhage, FVIII level, and presence of inhibitors. Judge the adequacy of treatment by clinical effects and, in all cases, adjust doses as needed based on clinical judgment and on frequent monitoring of the patient's FVIII level. Table 1 provides dosing recommendations for the treatment of hemophilia A in adults.
| Hemorrhagic Event | Dosage (IU FVIII:C/kg Body Weight) |
|---|---|
| IU = International Units. | |
Minor hemorrhage:
| Loading dose 15 IU FVIII:C/kg to achieve a FVIII:C plasma level of approximately 30% of normal; one infusion may be sufficient. If needed, half of the loading dose may be given once or twice daily for 1-2 days. |
Moderate hemorrhage:
| Loading dose 25 IU FVIII:C/kg to achieve a FVIII:C plasma level of approximately 50% of normal, followed by 15 IU FVIII:C/kg every 8-12 hours for the first 1-2 days to maintain the FVIII:C plasma level at 30% of normal. Continue the same dose once or twice daily for up to 7 days or until adequate wound healing is achieved. |
Life-threatening hemorrhage:
| Initially 40-50 IU FVIII:C/kg, followed by 20-25 IU FVIII:C/kg every 8 hours to maintain the FVIII:C plasma level at 80-100% of normal for 7 days. Continue the same dose once or twice daily for another 7 days to maintain the FVIII:C level at 30-50% of normal. |
2.2 Treatment of Bleeding Episodes in VWD
Administer 40 to 80 International Units (IU) VWF:RCo (corresponding to 17 to 33 International Units (IU) FVIII in HUMATE-P) per kg body weight every 8 to 12 hours. Adjust the dosage based on the extent and location of bleeding. Administer repeat doses as long as needed based on monitoring of appropriate clinical and laboratory measures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]. Expected levels of VWF:RCo are based on an expected in vivo recovery (IVR) of 2.0 International Units (IU)/dL rise per International Unit (IU)/kg VWF:RCo administered. The administration of 1 International Unit (IU) of FVIII per kg body weight can be expected to lead to a rise in circulating VWF:RCo of approximately 5 International Units (IU)/dL. Table 2 provides dosing recommendations for adult and pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].2
| VWD Type | Severity of Hemorrhage | Dosage (IU* VWF:RCo/kg Body Weight) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Type 1 VWD – Mild (baseline VWF:RCo activity typically >30%) | Minor (e.g., epistaxis, oral bleeding, menorrhagia) | Typically treatable with desmopressin. |
| Minor (when desmopressin is known or suspected to be inadequate) Major† (e.g., severe or refractory epistaxis, GI bleeding, CNS trauma, traumatic hemorrhage) | Loading dose 40-60 IU/kg. Then 40-50 IU/kg every 8-12 hours for 3 days to keep the trough level of VWF:RCo >50%. Then 40-50 IU/kg daily for up to 7 days. |
|
| Type 1 VWD – Moderate or severe (baseline VWF:RCo typically <30%) | Minor (e.g., epistaxis, oral bleeding, menorrhagia) | 40-50 IU/kg (1 or 2 doses). |
| Major (e.g., severe or refractory epistaxis, GI bleeding, CNS trauma, hemarthrosis, traumatic hemorrhage) | Loading dose 50-75 IU/kg. Then 40-60 IU/kg every 8-12 hours for 3 days to keep the trough level of VWF:RCo >50%. Then 40-60 IU/kg daily for up to 7 days. |
|
| Type 2 VWD (all variants) and Type 3 VWD | Minor (clinical indications above) | 40-50 IU/kg (1 or 2 doses). |
| Major (clinical indications above) | Loading dose 60-80 IU/kg. Then 40-60 IU/kg every 8-12 hours for 3 days to keep the trough level of VWF:RCo >50%. Then 40-60 IU/kg daily for up to 7 days. |
|
2.3 Prevention of Excessive Bleeding During and After Surgery in VWD
The following information provides guidelines for calculating loading and maintenance doses of HUMATE-P for patients undergoing surgery. However in the case of emergency surgery, administer a loading dose of 50 to 60 International Units (IU) VWF:RCo/kg body weight and, subsequently, closely monitor the patient's trough coagulation factor levels.
Measure incremental IVR and assess plasma VWF:RCo and FVIII:C levels in all patients prior to surgery when possible.
To determine IVR:
- Measure the baseline plasma VWF:RCo level.
- Infuse a calculated dose [International Units (IU)/kg] of VWF:RCo product intravenously at "time 0".
- At "time+30 minutes", measure the plasma VWF:RCo level.
Use the following formula to calculate IVR:
IVR = (Plasma VWF:RCotime+30 min – Plasma VWF:RCobaseline International Units (IU)/dL)
Calculated dose (International Units (IU)/kg)
For example, assuming a baseline VWF:RCo of 30 International Units (IU)/dL at "time 0", a calculated dose of 60 International Units (IU)/kg, and a VWF:RCo of 120 International Units (IU)/dL at "time+30 minutes", the IVR would be 1.5 International Units (IU)/dL per International Units (IU)/kg of VWF:RCo administered.
Loading Dose
Table 3 provides guidelines for calculating the loading dose for adult and pediatric patients based on the target peak plasma VWF:RCo level, the baseline VWF:RCo level, body weight in kilograms, and IVR. When individual recovery values are not available, a standardized loading dose can be used based on an assumed VWF:RCo IVR of 2.0 International Units (IU)/dL per International Unit (IU)/kg of VWF:RCo administered.
| Type of Surgery | VWF:RCo Target Peak Plasma Level | FVIII:C Target Peak Plasma Level | Calculation of Loading Dose (to be administered 1 to 2 hours before surgery) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IU = International Units. BW = body weight. |
||||
|
||||
| Major | 100 IU/dL | 80-100 IU/dL | Δ* VWF:RCo × BW (kg)
IVR† | = IU VWF:RCo required |
| If the IVR is not available, assume an IVR of 2.0 IU/dL per IU/kg and calculate the loading dose as follows: (100 – baseline plasma VWF:RCo) × BW (kg)/2.0 |
||||
| Minor/Oral‡ | 50-60 IU/dL | 40-50 IU/dL | Δ* VWF:RCo × BW (kg)
IVR | = IU VWF:RCo required |
| Emergency | 100 IU/dL | 80-100 IU/dL | Administer a dose of 50-60 IU VWF:RCo/kg body weight. | |
For example, the loading dose of HUMATE-P required assuming a target VWF:RCo level of 100 International Units (IU)/dL, a baseline VWF:RCo level of 20 International Units (IU)/dL, an IVR of 2.0 International Units (IU)/dL per International Units (IU)/kg, and a body weight of 70 kg would be 2,800 International Units (IU) VWF:RCo, calculated as follows:
| IU = International Units. | |
| (100 IU/dL – 20 IU/dL) × 70 kg | = 2,800 IU VWF:RCo required |
| 2.0 (IU/dL)/(IU/kg) | |
Attaining a target peak FVIII:C plasma level of 80 to 100 International Units (IU) FVIII:C/dL for major surgery and 40 to 50 International Units (IU) FVIII:C/dL for minor surgery or oral surgery might require additional dosing with HUMATE-P. Because the ratio of VWF:RCo to FVIII:C activity in HUMATE-P is 2.4:1, any additional dosing will increase VWF:RCo proportionally more than FVIII:C. Assuming an incremental IVR of 2.0 International Units (IU) VWF:RCo/dL per International Units (IU)/kg infused, additional dosing to increase FVIII:C in plasma will also increase plasma VWF:RCo by approximately 5 International Units (IU)/dL for each International Unit (IU)/kg of FVIII administered.
Maintenance Doses
The initial maintenance dose of HUMATE-P for the prevention of excessive bleeding during and after surgery should be half of the loading dose, irrespective of additional dosing required to meet FVIII:C targets. Subsequent maintenance doses should be based on the patient's VWF:RCo and FVIII levels. Table 4 provides recommendations for target trough plasma levels (based on type of surgery and number of days following surgery) and minimum duration of treatment for subsequent maintenance doses. These recommendations apply to both adult and pediatric patients.
| Type of Surgery | VWF:RCo Target Trough Plasma Level* | FVIII:C Target Trough Plasma Level* | Minimum Duration of Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up to 3 days following surgery | After Day 3 | Up to 3 days following surgery | After Day 3 | ||
| IU = International Units. | |||||
|
|||||
| Major | >50 IU/dL | >30 IU/dL | >50 IU/dL | >30 IU/dL | 72 hours |
| Minor | ≥30 IU/dL | – | – | >30 IU/dL | 48 hours |
| Oral† | ≥30 IU/dL | – | – | >30 IU/dL | 8-12 hours‡ |
Based on individual pharmacokinetic-derived half-lives, the frequency of maintenance doses is generally every 8 or 12 hours; patients with shorter half-lives may require dosing every 6 hours. In the absence of pharmacokinetic data, it is recommended that HUMATE-P be administered initially every 8 hours with further adjustments determined by monitoring trough coagulation factor levels. When hemostatic levels are judged insufficient or trough levels are outside the recommended range, consider modifying the administration interval and/or the dose.
It is advisable to monitor trough VWF:RCo and FVIII:C levels at least once a day in order to adjust HUMATE-P dosing as needed to avoid excessive accumulation of coagulation factors. The duration of treatment generally depends on the type of surgery performed, but must be assessed for individual patients based on their hemostatic response [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
2.4 Reconstitution
- Prepare and administer using aseptic techniques.
- Use either the Mix2Vial® filter transfer set provided with HUMATE-P [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)] or a commercially available double-ended needle and vented filter spike.
- Use plastic disposable syringes with HUMATE-P. Protein solutions of this type tend to adhere to the ground glass surface of all-glass syringes.
- Reconstitute HUMATE-P at room temperature as follows:
- Ensure that the HUMATE-P vial and diluent vial are at room temperature.
- Place the HUMATE-P vial, diluent vial and Mix2Vial transfer set on a flat surface.
- Remove the HUMATE-P and diluent vial flip caps. Wipe the stoppers with an alcohol swab and allow the stoppers to dry prior to opening the Mix2Vial transfer set package.
- Open the Mix2Vial transfer set package by peeling away the lid (Fig. 1). Leave the Mix2Vial transfer set in the clear package.
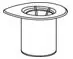
Fig. 1 - Place the diluent vial on a flat surface and hold the vial tightly. Grip the Mix2Vial transfer set together with the clear package and push the plastic spike at the blue end of the Mix2Vial transfer set firmly through the center of the stopper of the diluent vial (Fig. 2).
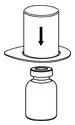
Fig. 2 - Carefully remove the clear package from the Mix2Vial transfer set. Make sure that you pull up only the clear package, not the Mix2Vial transfer set (Fig. 3).
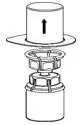
Fig. 3 - With the HUMATE-P vial placed firmly on a flat surface, invert the diluent vial with the Mix2Vial transfer set attached and push the plastic spike of the transparent adapter firmly through the center of the stopper of the HUMATE-P vial (Fig. 4). The diluent will automatically transfer into the HUMATE-P vial.
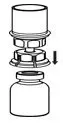
Fig. 4 - With the diluent and Humate-P vial still attached to the Mix2Vial transfer set, gently swirl the HUMATE-P vial to ensure that the HUMATE-P is fully dissolved (Fig. 5). Do not shake the vial.
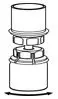
Fig. 5 - With one hand grasp the HUMATE-P side of the Mix2Vial transfer set and with the other hand grasp the blue diluent-side of the Mix2Vial transfer set, and unscrew the set into two pieces (Fig. 6).
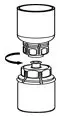
Fig. 6 - Draw air into an empty, sterile syringe. While the HUMATE-P vial is upright, screw the syringe to the Mix2Vial transfer set. Inject air into the HUMATE-P vial. While keeping the syringe plunger pressed, invert the system upside down and draw the concentrate into the syringe by pulling the plunger back slowly (Fig. 7).
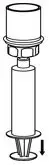
Fig. 7 - Now that the concentrate has been transferred into the syringe, firmly grasp the barrel of the syringe (keeping the syringe plunger facing down) and unscrew the syringe from the Mix2Vial transfer set (Fig. 8). Attach the syringe to a suitable intravenous administration set.
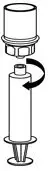
Fig. 8 - If patient requires more than one vial, pool the contents of multiple vials into one syringe. Use a separate unused Mix2Vial for each product vial.
2.5 Administration
HUMATE-P is for intravenous use only.
- The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent. After filtering/withdrawal, the reconstituted product should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Even if the directions for use for the reconstitution procedure are precisely followed, it is not uncommon for a few flakes or particles to remain. The filter included in the Mix2Vial device removes those particles completely. Filtration does not influence dosage calculations. Do not use visibly cloudy solutions or solutions still containing flakes or particles after filtration.
- Do not refrigerate HUMATE-P after reconstitution. Administer within 3 hours after reconstitution.
- Slowly infuse the solution (maximally 4 mL/minute) with a suitable intravenous administration set.
- Discard the administration equipment and any unused HUMATE-P after use.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
HUMATE-P is available as a sterile, lyophilized powder for intravenous administration following reconstitution. Each single-dose vial of HUMATE-P contains the labeled amount of VWF:RCo and FVIII activity expressed in International Units (IU). The average ratio of VWF:RCo to FVIII is 2.4:1.
Approximate potencies are shown below; check each carton/vial for the actual potency prior to reconstitution:
| VWF:RCo/vial | FVIII/vial | Diluent |
|---|---|---|
| IU = International Units. | ||
| 600 IU | 250 IU | 5 mL |
| 1200 IU | 500 IU | 10 mL |
| 2400 IU | 1000 IU | 15 mL |
4. Contraindications
HUMATE-P is contraindicated in individuals who have had an anaphylactic or severe systemic reaction to antihemophilic factor or von Willebrand factor preparations.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Thromboembolic Events (VWD Patients)
Thromboembolic events have been reported in VWD patients receiving Antihemophilic Factor/von Willebrand Factor Complex replacement therapy, especially in the setting of known risk factors for thrombosis.3,4 Early reports indicate a higher incidence may occur in females. Endogenous high levels of FVIII have also been associated with thrombosis, but no causal relationship has been established. Exercise caution and consider antithrombotic measures in all at-risk VWD patients who are receiving coagulation factor replacement therapy.
5.2 Monitoring for Intravascular Hemolysis
HUMATE-P contains blood group isoagglutinins (anti-A and anti-B). When doses are very large or need to be repeated frequently (for example, when inhibitors are present or when pre- and post-surgical care is involved), monitor patients of blood groups A, B, and AB for signs of intravascular hemolysis and decreasing hematocrit values and treat appropriately.
5.3 Monitoring VWF:RCo and FVIII Levels
Monitor the VWF:RCo and FVIII levels of VWD patients receiving HUMATE-P using standard coagulation tests, especially in cases of surgery. It is advisable to monitor trough VWF:RCo and FVIII:C levels at least once a day in order to adjust the dosage of HUMATE-P as needed to avoid excessive accumulation of coagulation factors [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)].
5.4 Transmission of Infectious Agents
Because HUMATE-P is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent [see Description (11) and Patient Counseling Information (17)]. The risk that such products will transmit an infectious agent has been reduced by screening plasma donors for prior exposure to certain viruses, by testing for the presence of certain current virus infections, and by inactivating and/or removing certain viruses during manufacturing [see Description (11)].
Despite these measures, such products can still potentially transmit disease. There is also the possibility that unknown infectious agents may be present in such products. Thus the risk of transmission of infectious agents cannot be eliminated completely. Report all infections thought by a physician possibly to have been transmitted by this product to CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Some viruses, such as Parvovirus B19 virus (B19V) or hepatitis A (HAV), are particularly difficult to remove or inactivate. B19V may most seriously affect pregnant women and immune-compromised individuals.
Although the overwhelming number of B19V and HAV cases are community acquired, reports of these infections have been associated with the use of some plasma-derived products. Therefore, physicians should be alert to the potential symptoms of B19V and HAV infections [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Symptoms of B19V may include low-grade fever, rash, arthralgia, and transient symmetric, nondestructive arthritis. Diagnosis is often established by measuring B19V-specific IgM and IgG antibodies. Symptoms of HAV include low-grade fever, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and jaundice. A diagnosis may be established by measuring specific IgM antibodies.
Physicians should strongly consider administration of hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines to individuals receiving plasma derivatives. Potential risks and benefits of vaccination should be weighed by the physician and discussed with the patient.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most serious adverse reaction observed in patients receiving HUMATE-P is anaphylaxis. Thromboembolic events have also been observed in patients receiving HUMATE-P for the treatment of VWD [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Reports of thromboembolic events in VWD patients with other thrombotic risk factors receiving coagulation factor replacement therapy have been obtained from spontaneous reports, published literature, and a European clinical study. In some cases, inhibitors to coagulation factors may occur. However, no inhibitor formation was observed in any of the clinical studies.
In patients receiving HUMATE-P in clinical studies for treatment of VWD, the most commonly reported adverse reactions observed by >5% of subjects are allergic-anaphylactic reactions (including urticaria, chest tightness, rash, pruritus, and edema). For patients undergoing surgery, the most common adverse reactions are postoperative wound and injection-site bleeding, and epistaxis.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical trials and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of HUMATE-P. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to HUMATE-P exposure.
Adverse reactions reported in patients receiving HUMATE-P for treatment of VWD or hemophilia A are allergic-anaphylactic reactions (including urticaria, chest tightness, rash, pruritus, edema, and shock), development of inhibitors to FVIII, and hemolysis. Additional adverse reactions reported for VWD are thromboembolic complications, chills and fever, and hypervolemia.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with HUMATE-P. It is also not known whether HUMATE-P can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. HUMATE-P should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
It is not known whether HUMATE-P can cause harm to the mother or the fetus when administered during labor and delivery. HUMATE-P should be given during labor and delivery only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when HUMATE-P is administered to a nursing woman.
11. Humate-P Description
HUMATE-P, Antihemophilic Factor/von Willebrand Factor Complex (Human), is a purified, sterile, lyophilized concentrate of Factor VIII (FVIII) and von Willebrand Factor (VWF) (Human) for intravenous administration in the treatment of patients with classical hemophilia (hemophilia A) and VWD [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
HUMATE-P is purified from the cold insoluble fraction of pooled human plasma. The pooled human plasma used to produce HUMATE-P is collected from licensed facilities in the United States (US). All source plasma used in the manufacture of HUMATE-P is tested by FDA-licensed Nucleic Acid Tests (NAT) for hepatitis C virus (HCV), human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1), hepatitis A virus (HAV), and hepatitis B virus (HBV) and found to be nonreactive (negative).
Each vial of HUMATE-P contains the labeled amount of von Willebrand Factor:Ristocetin Cofactor (VWF:RCo) and FVIII activity expressed in International Units (IU) [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3)], as defined by the current international standard established by the World Health Organization. One International Unit (IU) of VWF:RCo or FVIII is approximately equal to the amount of VWF:RCo or FVIII in 1.0 mL of fresh-pooled human plasma. The average ratio of VWF:RCo to FVIII is 2.4:1. Fibrinogen content in HUMATE-P is less than or equal to 0.2 mg/mL. HUMATE-P contains anti-A and anti-B blood group isoagglutinins [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
When reconstituted with the volume of Sterile Water for Injection, USP provided, each mL of HUMATE-P contains 72 to 224 International Units (IU) VWF:RCo activity1, 40 to 80 International Units (IU) FVIII activity, 15 to 33 mg of glycine, 3.5 to 9.3 mg of sodium citrate, 2 to 5.3 mg of sodium chloride, 8 to 16 mg of Albumin (Human), 2 to 4 mg of other proteins, and 10 to 20 mg of total proteins. HUMATE-P contains no preservative.
The manufacturing procedure for HUMATE-P includes multiple processing steps that reduce the risk of virus transmission. The virus inactivation/removal capacity consists of four steps:
- Cryoprecipitation
- Al(OH)3 adsorption, glycine precipitation, and NaCl precipitation, studied in combination
- Heat treatment at 60°C for 10 hours in aqueous solution
- Lyophilization
The total cumulative virus reductions range from 6.0 to ≥11.7 log10 as shown in Table 8.
| Manufacturing Step | Virus Reduction Factor (log10) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enveloped Viruses | Non-Enveloped Viruses | ||||||
| HIV-1 | BVDV | PRV | WNV | HAV | CPV | B19V | |
| HIV-1, human immunodeficiency virus type 1, model for HIV-1 and HIV-2 BVDV, bovine viral diarrhea virus, model for HCV PRV, pseudorabies virus, model for large enveloped DNA viruses WNV, West Nile virus HAV, hepatitis A virus CPV, canine parvovirus, model for B19V B19V, human parvovirus B19 ND, not determined NA, not applicable |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Cryoprecipitation | ND | ND | 1.6 | ND | ND | 1.9 | ND |
| Al(OH)3 Adsorption/Glycine Precipitation/NaCl Precipitation | 3.8 | 2.8 | 3.9 | ND | 2.3 | 3.0 | ND |
| Heat Treatment* | ≥6.4 | ≥8.9 | 4.7 | ≥7.8 | 4.2 | 1.1 | ≥3.9† |
| Lyophilization | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1.3 | ND | ND |
| Cumulative Virus Reduction [log10] | ≥10.2 | ≥11.7 | 10.2 | NA | 7.8 | 6.0 | NA |
- 1
- This correlates to a VWF:RCo to FVIII activity average ratio of 2.4:1, which is used to calculate the nominal values of VWF:RCo activity and is the average VWF:RCo activity.
12. Humate-P - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The active components of HUMATE-P consist of two different noncovalently bound proteins (FVIII and VWF). FVIII is an essential cofactor in activation of factor X, leading ultimately to the formation of thrombin and, subsequently, fibrin. VWF promotes platelet aggregation and platelet adhesion on damaged vascular endothelium; activated platelets interact with clotting proteins to form a clot. VWF also serves as a stabilizing carrier protein for the procoagulant protein FVIII.5,6 The activity of VWF is measured as VWF:RCo.
14. Clinical Studies
Controlled clinical studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of prophylactic dosing with HUMATE-P to prevent spontaneous bleeding have not been conducted in VWD subjects. Adequate data are not presently available on which to evaluate or to base dosing recommendations in this setting.
14.1 Treatment of Bleeding Episodes in VWD
Clinical efficacy of HUMATE-P in the control of bleeding in subjects with VWD was determined by a retrospective review of clinical safety and efficacy data obtained from 97 Canadian VWD subjects who received product under an Emergency Drug Release Program. The dosage schedule and duration of therapy were determined by the medical practitioner.
There were 514 requests for product use for surgery, bleeding, or prophylaxis in the 97 subjects. Of these, HUMATE-P was not used in 151 cases, and follow-up safety and/or efficacy information was available for 303 (83%) of the remaining 363 requests. In many cases, HUMATE-P from a single request was used for several treatment courses in one subject. Therefore, there are more reported treatment courses than requests.
HUMATE-P was administered to 97 subjects in 530 treatment courses: 73 for surgery, 344 for treatment of bleeding, and 20 for prophylaxis of bleeding. The majority of the 93 "other" uses involved dental procedures, diagnostic procedures, prophylaxis prior to a procedure, or test doses.
Table 10 summarizes the dosing information (all subjects) for bleeding episodes.
| Type/Location of Bleeding Episode | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digestive System | Nose+Mouth +Pharynx | Integument System | Female Genital System | Musculo-skeletal | ||
| SD, standard deviation. | ||||||
|
||||||
| No. of Subjects | 14 | 29 | 11 | 4 | 22 | |
| Loading Dose | Mean Dose (SD)* | 62.1 (31.1) | 66.9 (24.3) | 73.4 (37.7) | 88.5 (28.3) | 50.2 (24.9) |
| No. of Infusions† | 37 | 127 | 22 | 7 | 107 | |
| Maintenance Dose | Mean Dose (SD)* | 61.5 (38.0) | 67.5 (22.4) | 56.5 (63.3) | 74.5 (17.7) | 63.8 (28.8) |
| No. of Infusions† | 250 | 55 | 4 | 15 | 121 | |
| No. of Treatment Days per Bleeding Episode | Mean (SD) No. of Events | 4.6 (3.6) 49 | 1.4 (1.2) 130 | 1.1 (0.4) 22 | 2.8 (2.9) 9 | 2.0 (1.9) 108 |
| No. of Infusions by Treatment Day | ||||||
| No. of Subjects | 14 | 29 | 11 | 4 | 22 | |
| Day 1‡ | Mean (SD) No. of Events | 1.2 (0.4) 49 | 1.1 (0.2) 130 | 1.0 (0.2) 22 | 1.0 (0.0) 9 | 1.0 (0.1) 108 |
| No. of Subjects | 13 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 15 | |
| Day 2 | Mean (SD) No. of Events | 1.2 (0.6) 41 | 1.3 (0.5) 12 | 1.0 (0.0) 3 | 1.0 (-) 1 | 1.2 (0.5) 26 |
| No. of Subjects | 12 | 6 | - | 2 | 10 | |
| Day 3 | Mean (SD) No. of Events | 1.5 (0.8) 25 | 1.4 (0.7) 9 | - - | 1.0 (0.0) 3 | 1.2 (0.4) 18 |
14.2 Prevention of Excessive Bleeding During and After Surgery in VWD
Two prospective, open-label, non-controlled, multicenter clinical studies, one in the US and one in Europe, investigated the safety and hemostatic efficacy of HUMATE-P in subjects with VWD undergoing surgery.
14.3 Virus Transmission Studies
Clinical evidence of the absence of virus transmission in HUMATE-P was obtained in additional studies.
In one study, none of the evaluable subjects (31 of 67) who received HUMATE-P developed HBV infection or showed clinical signs of non-A, non-B (NANB) hepatitis infection.
In another study, 32 lots of HUMATE-P were administered to 26 subjects with hemophilia or VWD who had not previously received any blood products. No subject developed any signs of an infectious disease, and the 10 subjects not previously vaccinated remained seronegative for markers of infection with HBV, HAV, cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus, and HIV.
In a retrospective study, 155 subjects evaluated remained negative for the presence of HIV-1 antibodies for time periods ranging from 4 months to 9 years from the initial administration of HUMATE-P. All 67 of the subjects tested for HIV-2 antibodies remained seronegative.
15. References
- Levine PH, Brettler DB. Clinical aspects and therapy for hemophilia A. In: Hoffman R, Benz JB, Shattil SJ, Furie B, Cohen HJ, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. New York: Churchill Livingstone Inc.; 1991:1296-1297.
- Scott JP, Montgomery RT. Therapy of von Willebrand disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1993;19:37-47.
- Mannucci, PM. Venous Thromboembolism in Von Willebrand Disease. Thromb Haemostas. 2002;88:378-379.
- Markis M, Colvin B, Gupta V, Shields ML, Smith MP. Venous thrombosis following the use of intermediate purity FVIII concentrate to treat patients with von Willebrand's disease. Thromb Haemostas. 2002;88:387-388.
- Hoyer LW. The factor VIII complex: structure and function. Blood. 1981;58:1-13.
- Meyer D, Girma J-P. von Willebrand factor: structure and function. Thromb Haemostas. 1993;70:99-104.
- Berntorp E, Nilsson IM. Biochemical and in vivo properties of commercial virus-inactivated factor VIII concentrates. Eur J Haematol. 1988;40:205-214.
- Berntorp E. Plasma product treatment in various types of von Willebrand's disease. Haemostasis. 1994;24:289-297.
16. How is Humate-P supplied
- HUMATE-P is supplied in a single-dose vial containing the labeled amount of VWF:RCo and FVIII activity expressed in International Units (IU).
- Components are not made with natural rubber latex.
- When stored at temperatures up to 25°C (77°F), HUMATE-P is stable for 36 months up to the expiration date printed on its label. Do not freeze.
- HUMATE-P does not contain a preservative and should be used within 3 hours after reconstitution.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Inform patients that HUMATE-P is made from human plasma (part of the blood) and may contain infectious agents that can cause disease (e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob (CJD) agent). Explain that the risk that HUMATE-P may transmit an infectious agent has been reduced by screening plasma donors, by testing the donated plasma for certain virus infections, and by inactivating and/or removing certain viruses during manufacturing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Inform patients that some viruses, such as B19V and HAV, may be particularly difficult to remove or inactivate. Advise patients, especially pregnant women and immune-compromised individuals, to report low-grade fever, rash, joint pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and jaundice [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
| HUMATE-P
antihemophilic factor/von willebrand factor complex (human) kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| HUMATE-P
antihemophilic factor/von willebrand factor complex (human) kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| HUMATE-P
antihemophilic factor/von willebrand factor complex (human) kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - CSL Behring GmbH (326530474) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSL Behring GmbH | 326530474 | MANUFACTURE | |