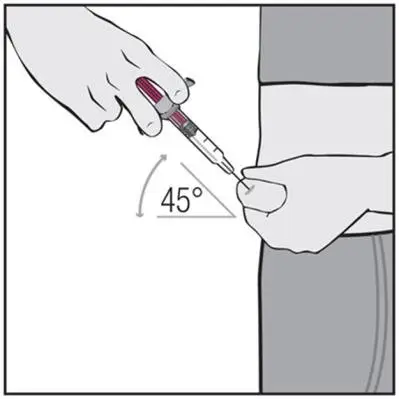
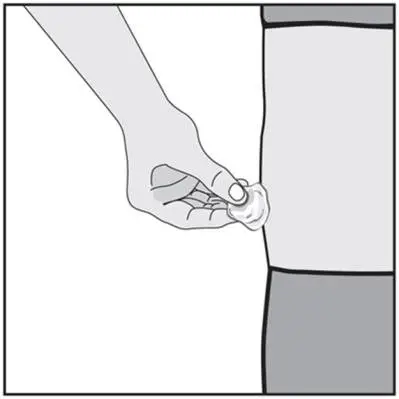
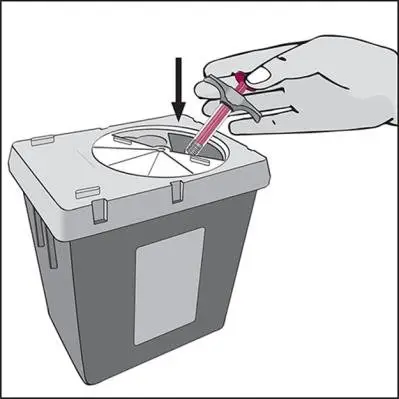
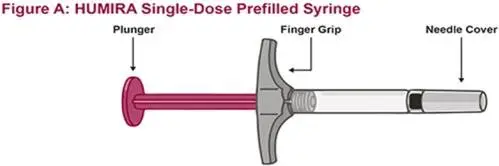
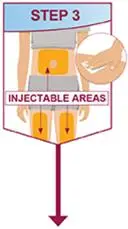
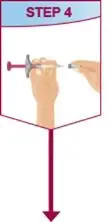
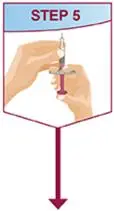
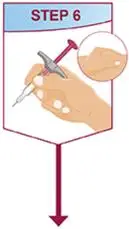
Drug Detail:Humira (Adalimumab [ ay-da-lim-ue-mab ])
Drug Class: Antirheumatics TNF alfa inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
HUMIRA® (adalimumab) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2002
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS AND MALIGNANCY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
SERIOUS INFECTIONS (5.1, 6.1):
-
Increased risk of serious infections leading to hospitalization or death, including tuberculosis (TB), bacterial sepsis, invasive fungal infections (such as histoplasmosis), and infections due to other opportunistic pathogens.
-
Discontinue HUMIRA if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis during treatment.
-
Perform test for latent TB; if positive, start treatment for TB prior to starting HUMIRA.
- Monitor all patients for active TB during treatment, even if initial latent TB test is negative.
MALIGNANCY (5.2):
-
Lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children and adolescent patients treated with TNF blockers including HUMIRA.
- Post-marketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL), a rare type of T-cell lymphoma, have occurred in adolescent and young adults with inflammatory bowel disease treated with TNF blockers including HUMIRA.
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage, Ulcerative Colitis (1.6) | 2/2021 |
| Dosage and Administration, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis (2.1) | 12/2020 |
| Dosage and Administration, Ulcerative Colitis (2.4) | 2/2021 |
| Dosage and Administration, Hidradenitis Suppurativa (2.6) | 12/2020 |
Indications and Usage for Humira
HUMIRA is a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker indicated for:
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (1.1): reducing signs and symptoms, inducing major clinical response, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with moderately to severely active RA.
-
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) (1.2): reducing signs and symptoms of moderately to severely active polyarticular JIA in patients 2 years of age and older.
-
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) (1.3): reducing signs and symptoms, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with active PsA.
-
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) (1.4): reducing signs and symptoms in adult patients with active AS.
-
Crohn’s Disease (CD) (1.5): treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
-
Ulcerative Colitis (UC) (1.6): treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults and pediatric patients 5 years of age and older.
Limitations of Use: Effectiveness has not been established in patients who have lost response to or were intolerant to TNF blockers.
-
Plaque Psoriasis (Ps) (1.7): treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy, and when other systemic therapies are medically less appropriate.
-
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) (1.8): treatment of moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa in patients 12 years of age and older.
- Uveitis (UV) (1.9): treatment of non-infectious intermediate, posterior, and panuveitis in adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older.
Humira Dosage and Administration
- Administer by subcutaneous injection (2)
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis (2.1):
-
Adults: 40 mg every other week.
● Some patients with RA not receiving methotrexate may benefit from increasing the dosage to 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week.
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis or Pediatric Uveitis (2.2):
| Pediatric Weight
2 Years of Age and Older | Recommended Dosage |
| 10 kg (22 lbs) to less than 15 kg (33 lbs) | 10 mg every other week |
| 15 kg (33 lbs) to less than 30 kg (66 lbs) | 20 mg every other week |
| 30 kg (66 lbs) and greater | 40 mg every other week |
Crohn's Disease (2.3):
-
Adults: 160 mg on Day 1 (given in one day or split over two consecutive days); 80 mg on Day 15; and 40 mg every other week starting on Day 29.
- Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older:
| Pediatric Weight
| Recommended Dosage | |
| Days 1 and 15 | Starting on Day 29 | |
| 17 kg (37 lbs) to less than 40 kg (88 lbs) | Day 1: 80 mg Day 15: 40 mg | 20 mg every other week |
| 40 kg (88 lbs) and greater | Day 1: 160 mg (single dose or split over two consecutive days) Day 15: 80 mg | 40 mg every other week |
Ulcerative Colitis (2.4):
-
Adults: 160 mg on Day 1 (given in one day or split over two consecutive days), 80 mg on Day 15 and 40 mg every other week starting on Day 29. Discontinue in patients without evidence of clinical remission by eight weeks (Day 57).
- Pediatric Patients 5 Years of Age and Older:
| Pediatric Weight
| Recommended Dosage | |
| Days 1 through 15 | Starting on Day 29* | |
| 20 kg (44 lbs) to less than 40 kg (88 lbs) | Day 1: 80 mg Day 8: 40 mg Day 15: 40 mg | 40 mg every other week or 20 mg every week |
| 40 kg (88 lbs) and greater | Day 1: 160 mg (single dose or split over two consecutive days) Day 8: 80 mg Day 15: 80 mg | 80 mg every other week or 40 mg every week |
| * Continue the recommended pediatric dosage in patients who turn 18 years of age and who are well-controlled on their HUMIRA regimen. | ||
Plaque Psoriasis or Adult Uveitis (2.5):
- Adults: 80 mg initial dose, followed by 40 mg every other week starting one week after initial dose.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (2.6):
-
Adults:
○ Day 1: 160 mg (given in one day or split over two consecutive days)
○ Day 15: 80 mg
○ Day 29 and subsequent doses: 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week
- Adolescents 12 years of age and older:
| Adolescent
Weight | Recommended Dosage |
| 30 kg (66 lbs) to less than 60 kg (132 lbs) | Day 1: 80 mg Day 8 and subsequent doses: 40 mg every other week |
| 60 kg (132 lbs) and greater | Day 1: 160 mg (given in one day or split over two consecutive days) Day 15: 80 mg Day 29 and subsequent doses: 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week |
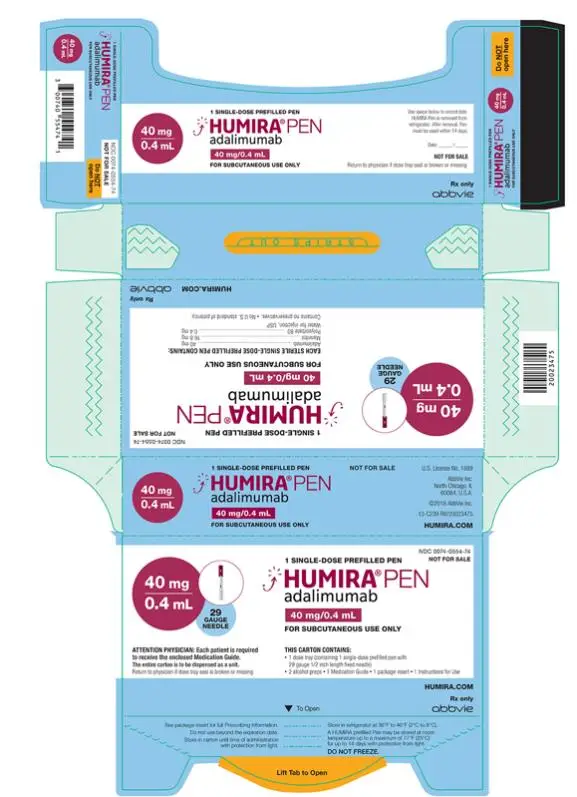
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection:
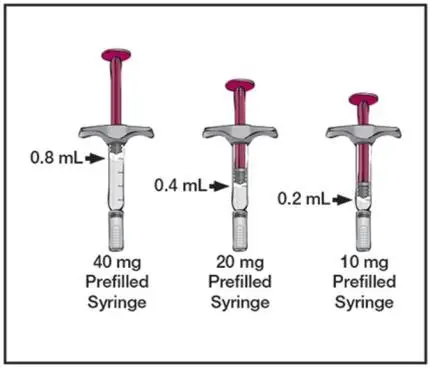
- Single-dose prefilled pen (HUMIRA Pen): 80 mg/0.8 mL, 40 mg/0.8 mL, and 40 mg/0.4 mL (3)
- Single-dose prefilled glass syringe: 80 mg/0.8 mL, 40 mg/0.8 mL, 40 mg/0.4 mL, 20 mg/0.4 mL, 20 mg/0.2 mL, 10 mg/0.2 mL, 10 mg/0.1 mL (3)
- Single-dose glass vial for institutional use only: 40 mg/0.8 mL (3)
Contraindications
None (4)
Warnings and Precautions
-
Serious infections: Do not start HUMIRA during an active infection. If an infection develops, monitor carefully, and stop HUMIRA if infection becomes serious. (5.1)
-
Invasive fungal infections: For patients who develop a systemic illness on HUMIRA, consider empiric antifungal therapy for those who reside or travel to regions where mycoses are endemic. (5.1)
-
Malignancies: Incidence of malignancies was greater in HUMIRA-treated patients than in controls (5.2)
-
Anaphylaxis or serious hypersensitivity reactions may occur (5.3)
-
Hepatitis B virus reactivation: Monitor HBV carriers during and several months after therapy. If reactivation occurs, stop HUMIRA and begin anti-viral therapy. (5.4)
-
Demyelinating disease: Exacerbation or new onset, may occur. (5.5)
-
Cytopenias, pancytopenia: Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms develop, and consider stopping HUMIRA. (5.6)
-
Heart failure: Worsening or new onset, may occur. (5.8)
- Lupus-like syndrome: Stop HUMIRA if syndrome develops. (5.9)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (>10%) are: infections (e.g. upper respiratory, sinusitis), injection site reactions, headache and rash. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie Inc. at 1-800-633-9110 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
-
Abatacept: Increased risk of serious infection. (5.1, 5.11, 7.2)
-
Anakinra: Increased risk of serious infection. (5.1, 5.7, 7.2)
- Live vaccines: Avoid use with HUMIRA. (5.10, 7.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 2/2021
Related/similar drugs
Orencia, Trexall, Ilumya, Entyvio, Otezla, Sotyktu, prednisoneFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Humira
1.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis
HUMIRA is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms, inducing major clinical response, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis. HUMIRA can be used alone or in combination with methotrexate or other non-biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
1.2 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
HUMIRA is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms of moderately to severely active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older. HUMIRA can be used alone or in combination with methotrexate.
1.3 Psoriatic Arthritis
HUMIRA is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis. HUMIRA can be used alone or in combination with non-biologic DMARDs.
1.4 Ankylosing Spondylitis
HUMIRA is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms in adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis.
1.5 Crohn’s Disease
HUMIRA is indicated for the treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
1.6 Ulcerative Colitis
HUMIRA is indicated for the treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults and pediatric patients 5 years of age and older.
Limitations of Use
The effectiveness of HUMIRA has not been established in patients who have lost response to or were intolerant to TNF blockers [see Clinical Studies (14.7, 14.8)].
1.7 Plaque Psoriasis
HUMIRA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy, and when other systemic therapies are medically less appropriate. HUMIRA should only be administered to patients who will be closely monitored and have regular follow-up visits with a physician [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
2. Humira Dosage and Administration
2.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HUMIRA for adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), or ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is 40 mg administered every other week. Methotrexate (MTX), other non-biologic DMARDS, glucocorticoids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and/or analgesics may be continued during treatment with HUMIRA. In the treatment of RA, some patients not taking concomitant MTX may derive additional benefit from increasing the dosage of HUMIRA to 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week.
2.2 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis or Pediatric Uveitis
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HUMIRA for patients 2 years of age and older with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) or pediatric uveitis is based on weight as shown below. MTX, glucocorticoids, NSAIDs, and/or analgesics may be continued during treatment with HUMIRA.
| Pediatric Weight
(2 Years of Age and older) | Recommended Dosage |
| 10 kg (22 lbs) to less than 15 kg (33 lbs) | 10 mg every other week |
| 15 kg (33 lbs) to less than 30 kg (66 lbs) | 20 mg every other week |
| 30 kg (66 lbs) and greater | 40 mg every other week |
HUMIRA has not been studied in patients with polyarticular JIA or pediatric uveitis less than 2 years of age or in patients with a weight below 10 kg.
2.3 Crohn’s Disease
Adults
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HUMIRA for adult patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) is 160 mg initially on Day 1 (given in one day or split over two consecutive days), followed by 80 mg two weeks later (Day 15). Two weeks later (Day 29) begin a dosage of 40 mg every other week. Aminosalicylates and/or corticosteroids may be continued during treatment with HUMIRA. Azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] or MTX may be continued during treatment with HUMIRA if necessary.
Pediatrics
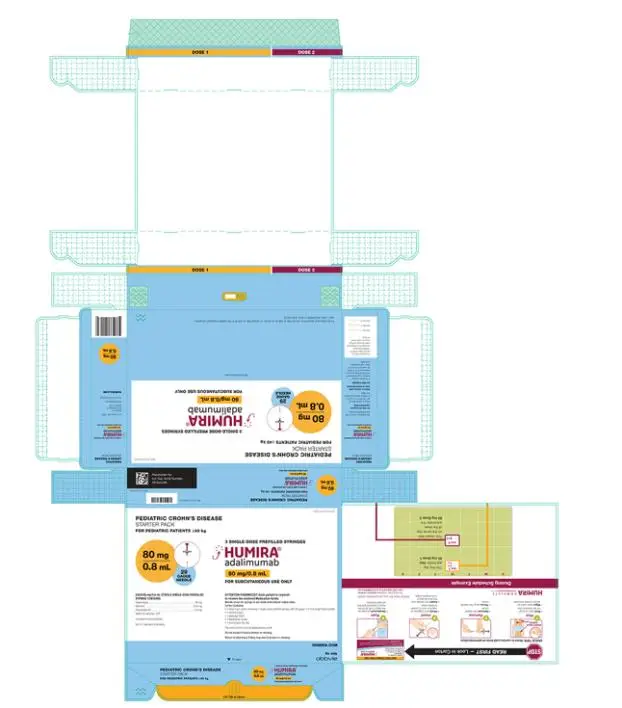
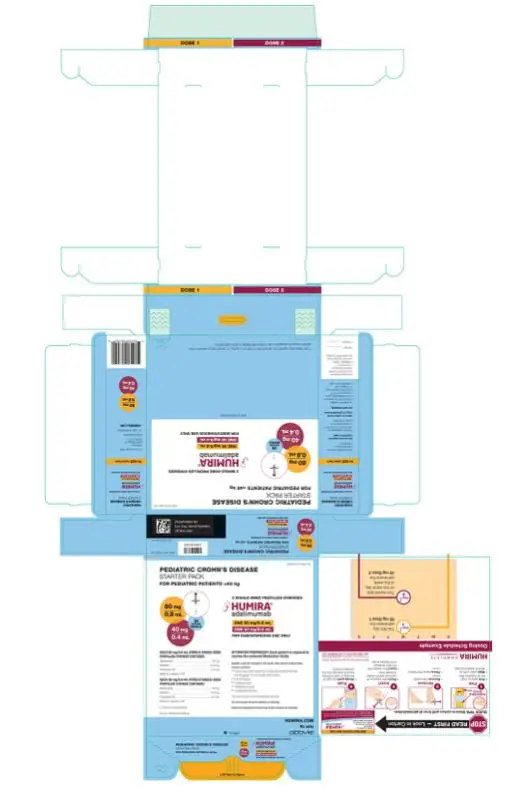
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HUMIRA for pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with Crohn’s disease (CD) is based on body weight as shown below:
| Pediatric Weight
| Recommended Dosage | |
| Days 1 through 15 | Starting on Day 29 | |
| 17 kg (37 lbs) to less than 40 kg (88 lbs) | Day 1: 80 mg Day 15: 40 mg | 20 mg every other week |
| 40 kg (88 lbs) and greater | Day 1: 160 mg (single dose or split over two consecutive days) Day 15: 80 mg | 40 mg every other week |
2.4 Ulcerative Colitis
Adults
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HUMIRA for adult patients with ulcerative colitis is 160 mg initially on Day 1 (given in one day or split over two consecutive days), followed by 80 mg two weeks later (Day 15). Two weeks later (Day 29) continue with a dosage of 40 mg every other week.
Discontinue HUMIRA in adult patients without evidence of clinical remission by eight weeks (Day 57) of therapy. Aminosalicylates and/or corticosteroids may be continued during treatment with HUMIRA. Azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] may be continued during treatment with HUMIRA if necessary.
Pediatrics
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HUMIRA for pediatric patients 5 years of age and older with ulcerative colitis is based on body weight as shown below:
| Pediatric Weight | Recommended Dosage | |
| Days 1 through 15 | Starting on Day 29* | |
| 20 kg (44 lbs) to less than 40 kg (88 lbs) | Day 1: 80 mg Day 8: 40 mg Day 15: 40 mg | 40 mg every other week or 20 mg every week |
| 40 kg (88 lbs) and greater | Day 1: 160 mg (single dose or split over two consecutive days) Day 8: 80 mg Day 15: 80 mg | 80 mg every other week or 40 mg every week |
| * Continue the recommended pediatric dosage in patients who turn 18 years of age and who are well-controlled on their HUMIRA regimen. | ||
2.5 Plaque Psoriasis or Adult Uveitis
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HUMIRA for adult patients with plaque psoriasis (Ps) or Uveitis (UV) is an initial dose of 80 mg, followed by 40 mg given every other week starting one week after the initial dose. The use of HUMIRA in moderate to severe chronic Ps beyond one year has not been evaluated in controlled clinical studies.
2.6 Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Adults
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HUMIRA for adult patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is an initial dose of 160 mg (given in one day or split over two consecutive days), followed by 80 mg two weeks later (Day 15). Begin 40 mg weekly or 80 mg every other week dosing two weeks later (Day 29).
Adolescents
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HUMIRA for adolescent patients 12 years of age and older weighing at least 30 kg with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is based on body weight as shown below [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]:
| Body Weight of Adolescent
Patients (12 years of age and older) | Recommended Dosage |
| 30 kg (66 lbs) to less than 60 kg (132 lbs) |
|
| 60 kg (132 lbs) and greater |
|
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
HUMIRA is a clear and colorless solution available as:
-
Pen (HUMIRA Pen)
Injection: 80 mg/0.8 mL in a single-dose pen.
Injection: 40 mg/0.8 mL in a single-dose pen.
Injection: 40 mg/0.4 mL in a single-dose pen.
-
Prefilled Syringe
Injection: 80 mg/0.8 mL in a single-dose prefilled glass syringe.
Injection: 40 mg/0.8 mL in a single-dose prefilled glass syringe.
Injection: 40 mg/0.4 mL in a single-dose prefilled glass syringe.
Injection: 20 mg/0.4 mL in a single-dose prefilled glass syringe.
Injection: 20 mg/0.2 mL in a single-dose prefilled glass syringe.
Injection: 10 mg/0.2 mL in a single-dose prefilled glass syringe.
Injection: 10 mg/0.1 mL in a single-dose prefilled glass syringe.
-
Single-Dose Institutional Use Vial
Injection: 40 mg/0.8 mL in a single-dose, glass vial for institutional use only.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Serious Infections
Patients treated with HUMIRA are at increased risk for developing serious infections involving various organ systems and sites that may lead to hospitalization or death. Opportunistic infections due to bacterial, mycobacterial, invasive fungal, viral, parasitic, or other opportunistic pathogens including aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, legionellosis, listeriosis, pneumocystosis and tuberculosis have been reported with TNF blockers. Patients have frequently presented with disseminated rather than localized disease.
The concomitant use of a TNF blocker and abatacept or anakinra was associated with a higher risk of serious infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA); therefore, the concomitant use of HUMIRA and these biologic products is not recommended in the treatment of patients with RA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.11) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Treatment with HUMIRA should not be initiated in patients with an active infection, including localized infections. Patients 65 years of age and older, patients with co-morbid conditions and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressants (such as corticosteroids or methotrexate), may be at greater risk of infection. Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating therapy in patients:
- with chronic or recurrent infection;
- who have been exposed to tuberculosis;
- with a history of an opportunistic infection;
- who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses, such as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, or blastomycosis; or
- with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection.
Tuberculosis
Cases of reactivation of tuberculosis and new onset tuberculosis infections have been reported in patients receiving HUMIRA, including patients who have previously received treatment for latent or active tuberculosis. Reports included cases of pulmonary and extrapulmonary (i.e., disseminated) tuberculosis. Evaluate patients for tuberculosis risk factors and test for latent infection prior to initiating HUMIRA and periodically during therapy.
Treatment of latent tuberculosis infection prior to therapy with TNF blocking agents has been shown to reduce the risk of tuberculosis reactivation during therapy. Prior to initiating HUMIRA, assess if treatment for latent tuberculosis is needed; and consider an induration of ≥ 5 mm a positive tuberculin skin test result, even for patients previously vaccinated with Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG).
Consider anti-tuberculosis therapy prior to initiation of HUMIRA in patients with a past history of latent or active tuberculosis in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed, and for patients with a negative test for latent tuberculosis but having risk factors for tuberculosis infection. Despite prophylactic treatment for tuberculosis, cases of reactivated tuberculosis have occurred in patients treated with HUMIRA. Consultation with a physician with expertise in the treatment of tuberculosis is recommended to aid in the decision whether initiating anti-tuberculosis therapy is appropriate for an individual patient.
Strongly consider tuberculosis in the differential diagnosis in patients who develop a new infection during HUMIRA treatment, especially in patients who have previously or recently traveled to countries with a high prevalence of tuberculosis, or who have had close contact with a person with active tuberculosis.
Monitoring
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with HUMIRA, including the development of tuberculosis in patients who tested negative for latent tuberculosis infection prior to initiating therapy. Tests for latent tuberculosis infection may also be falsely negative while on therapy with HUMIRA.
Discontinue HUMIRA if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis. For a patient who develops a new infection during treatment with HUMIRA, closely monitor them, perform a prompt and complete diagnostic workup appropriate for an immunocompromised patient, and initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Invasive Fungal Infections
If patients develop a serious systemic illness and they reside or travel in regions where mycoses are endemic, consider invasive fungal infection in the differential diagnosis. Antigen and antibody testing for histoplasmosis may be negative in some patients with active infection. Consider appropriate empiric antifungal therapy, taking into account both the risk for severe fungal infection and the risks of antifungal therapy, while a diagnostic workup is being performed. To aid in the management of such patients, consider consultation with a physician with expertise in the diagnosis and treatment of invasive fungal infections.
5.2 Malignancies
Consider the risks and benefits of TNF-blocker treatment including HUMIRA prior to initiating therapy in patients with a known malignancy other than a successfully treated non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) or when considering continuing a TNF blocker in patients who develop a malignancy.
Malignancies in Adults
In the controlled portions of clinical trials of some TNF-blockers, including HUMIRA, more cases of malignancies have been observed among TNF-blocker-treated adult patients compared to control-treated adult patients. During the controlled portions of 39 global HUMIRA clinical trials in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), Crohn’s disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC), plaque psoriasis (Ps), hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and uveitis (UV), malignancies, other than non-melanoma (basal cell and squamous cell) skin cancer, were observed at a rate (95% confidence interval) of 0.7 (0.48, 1.03) per 100 patient-years among 7973 HUMIRA-treated patients versus a rate of 0.7 (0.41, 1.17) per 100 patient-years among 4848 control-treated patients (median duration of treatment of 4 months for HUMIRA-treated patients and 4 months for control-treated patients). In 52 global controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials of HUMIRA in adult patients with RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV, the most frequently observed malignancies, other than lymphoma and NMSC, were breast, colon, prostate, lung, and melanoma. The malignancies in HUMIRA-treated patients in the controlled and uncontrolled portions of the studies were similar in type and number to what would be expected in the general U.S. population according to the SEER database (adjusted for age, gender, and race).1
In controlled trials of other TNF blockers in adult patients at higher risk for malignancies (i.e., patients with COPD with a significant smoking history and cyclophosphamide-treated patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis), a greater portion of malignancies occurred in the TNF blocker group compared to the control group.
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
During the controlled portions of 39 global HUMIRA clinical trials in adult patients with RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV, the rate (95% confidence interval) of NMSC was 0.8 (0.52, 1.09) per 100 patient-years among HUMIRA-treated patients and 0.2 (0.10, 0.59) per 100 patient-years among control-treated patients. Examine all patients, and in particular patients with a medical history of prior prolonged immunosuppressant therapy or psoriasis patients with a history of PUVA treatment for the presence of NMSC prior to and during treatment with HUMIRA.
Lymphoma and Leukemia
In the controlled portions of clinical trials of all the TNF-blockers in adults, more cases of lymphoma have been observed among TNF-blocker-treated patients compared to control-treated patients. In the controlled portions of 39 global HUMIRA clinical trials in adult patients with RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV, 2 lymphomas occurred among 7973 HUMIRA-treated patients versus 1 among 4848 control-treated patients. In 52 global controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials of HUMIRA in adult patients with RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV with a median duration of approximately 0.7 years, including 24,605 patients and over 40,215 patient-years of HUMIRA, the observed rate of lymphomas was approximately 0.11 per 100 patient-years. This is approximately 3-fold higher than expected in the general U.S. population according to the SEER database (adjusted for age, gender, and race).1 Rates of lymphoma in clinical trials of HUMIRA cannot be compared to rates of lymphoma in clinical trials of other TNF blockers and may not predict the rates observed in a broader patient population. Patients with RA and other chronic inflammatory diseases, particularly those with highly active disease and/or chronic exposure to immunosuppressant therapies, may be at a higher risk (up to several fold) than the general population for the development of lymphoma, even in the absence of TNF blockers. Post-marketing cases of acute and chronic leukemia have been reported in association with TNF-blocker use in RA and other indications. Even in the absence of TNF-blocker therapy, patients with RA may be at a higher risk (approximately 2-fold) than the general population for the development of leukemia.
Malignancies in Pediatric Patients and Young Adults
Malignancies, some fatal, have been reported among children, adolescents, and young adults who received treatment with TNF-blockers (initiation of therapy ≤ 18 years of age), of which HUMIRA is a member. Approximately half the cases were lymphomas, including Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The other cases represented a variety of different malignancies and included rare malignancies usually associated with immunosuppression and malignancies that are not usually observed in children and adolescents. The malignancies occurred after a median of 30 months of therapy (range 1 to 84 months). Most of the patients were receiving concomitant immunosuppressants. These cases were reported post-marketing and are derived from a variety of sources including registries and spontaneous postmarketing reports.
Postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL), a rare type of T-cell lymphoma, have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers including HUMIRA. These cases have had a very aggressive disease course and have been fatal. The majority of reported TNF blocker cases have occurred in patients with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis and the majority were in adolescent and young adult males. Almost all of these patients had received treatment with the immunosuppressants azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine (6–MP) concomitantly with a TNF blocker at or prior to diagnosis. It is uncertain whether the occurrence of HSTCL is related to use of a TNF blocker or a TNF blocker in combination with these other immunosuppressants. The potential risk with the combination of azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine and HUMIRA should be carefully considered.
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylaxis and angioneurotic edema have been reported following HUMIRA administration. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, immediately discontinue administration of HUMIRA and institute appropriate therapy. In clinical trials of HUMIRA, hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., rash, anaphylactoid reaction, fixed drug reaction, non-specified drug reaction, urticaria) have been observed.
5.4 Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation
Use of TNF blockers, including HUMIRA, may increase the risk of reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in patients who are chronic carriers of this virus. In some instances, HBV reactivation occurring in conjunction with TNF blocker therapy has been fatal. The majority of these reports have occurred in patients concomitantly receiving other medications that suppress the immune system, which may also contribute to HBV reactivation. Evaluate patients at risk for HBV infection for prior evidence of HBV infection before initiating TNF blocker therapy. Exercise caution in prescribing TNF blockers for patients identified as carriers of HBV. Adequate data are not available on the safety or efficacy of treating patients who are carriers of HBV with anti-viral therapy in conjunction with TNF blocker therapy to prevent HBV reactivation. For patients who are carriers of HBV and require treatment with TNF blockers, closely monitor such patients for clinical and laboratory signs of active HBV infection throughout therapy and for several months following termination of therapy. In patients who develop HBV reactivation, stop HUMIRA and initiate effective anti-viral therapy with appropriate supportive treatment. The safety of resuming TNF blocker therapy after HBV reactivation is controlled is not known. Therefore, exercise caution when considering resumption of HUMIRA therapy in this situation and monitor patients closely.
5.5 Neurologic Reactions
Use of TNF blocking agents, including HUMIRA, has been associated with rare cases of new onset or exacerbation of clinical symptoms and/or radiographic evidence of central nervous system demyelinating disease, including multiple sclerosis (MS) and optic neuritis, and peripheral demyelinating disease, including Guillain-Barré syndrome. Exercise caution in considering the use of HUMIRA in patients with preexisting or recent-onset central or peripheral nervous system demyelinating disorders; discontinuation of HUMIRA should be considered if any of these disorders develop. There is a known association between intermediate uveitis and central demyelinating disorders.
5.6 Hematological Reactions
Rare reports of pancytopenia including aplastic anemia have been reported with TNF blocking agents. Adverse reactions of the hematologic system, including medically significant cytopenia (e.g., thrombocytopenia, leukopenia) have been infrequently reported with HUMIRA. The causal relationship of these reports to HUMIRA remains unclear. Advise all patients to seek immediate medical attention if they develop signs and symptoms suggestive of blood dyscrasias or infection (e.g., persistent fever, bruising, bleeding, pallor) while on HUMIRA. Consider discontinuation of HUMIRA therapy in patients with confirmed significant hematologic abnormalities.
5.7 Increased Risk of Infection When Used with Anakinra
Concurrent use of anakinra (an interleukin-1 antagonist) and another TNF-blocker, was associated with a greater proportion of serious infections and neutropenia and no added benefit compared with the TNF-blocker alone in patients with RA. Therefore, the combination of HUMIRA and anakinra is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.8 Heart Failure
Cases of worsening congestive heart failure (CHF) and new onset CHF have been reported with TNF blockers. Cases of worsening CHF have also been observed with HUMIRA. HUMIRA has not been formally studied in patients with CHF; however, in clinical trials of another TNF blocker, a higher rate of serious CHF-related adverse reactions was observed. Exercise caution when using HUMIRA in patients who have heart failure and monitor them carefully.
5.9 Autoimmunity
Treatment with HUMIRA may result in the formation of autoantibodies and, rarely, in the development of a lupus-like syndrome. If a patient develops symptoms suggestive of a lupus-like syndrome following treatment with HUMIRA, discontinue treatment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.10 Immunizations
In a placebo-controlled clinical trial of patients with RA, no difference was detected in anti-pneumococcal antibody response between HUMIRA and placebo treatment groups when the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine and influenza vaccine were administered concurrently with HUMIRA. Similar proportions of patients developed protective levels of anti-influenza antibodies between HUMIRA and placebo treatment groups; however, titers in aggregate to influenza antigens were moderately lower in patients receiving HUMIRA. The clinical significance of this is unknown. Patients on HUMIRA may receive concurrent vaccinations, except for live vaccines. No data are available on the secondary transmission of infection by live vaccines in patients receiving HUMIRA.
It is recommended that pediatric patients, if possible, be brought up to date with all immunizations in agreement with current immunization guidelines prior to initiating HUMIRA therapy. Patients on HUMIRA may receive concurrent vaccinations, except for live vaccines.
The safety of administering live or live-attenuated vaccines in infants exposed to HUMIRA in utero is unknown. Risks and benefits should be considered prior to vaccinating (live or live-attenuated) exposed infants [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.4)].
5.11 Increased risk of Infection When Used with Abatacept
In controlled trials, the concurrent administration of TNF-blockers and abatacept was associated with a greater proportion of serious infections than the use of a TNF-blocker alone; the combination therapy, compared to the use of a TNF-blocker alone, has not demonstrated improved clinical benefit in the treatment of RA. Therefore, the combination of abatacept with TNF-blockers including HUMIRA is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Neurologic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hematological Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Autoimmunity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most common adverse reaction with HUMIRA was injection site reactions. In placebo-controlled trials, 20% of patients treated with HUMIRA developed injection site reactions (erythema and/or itching, hemorrhage, pain or swelling), compared to 14% of patients receiving placebo. Most injection site reactions were described as mild and generally did not necessitate drug discontinuation.
The proportion of patients who discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions during the double-blind, placebo-controlled portion of studies in patients with RA (i.e., Studies RA-I, RA-II, RA-III and RA-IV) was 7% for patients taking HUMIRA and 4% for placebo-treated patients. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of HUMIRA in these RA studies were clinical flare reaction (0.7%), rash (0.3%) and pneumonia (0.3%).
Infections
In the controlled portions of the 39 global HUMIRA clinical trials in adult patients with RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV, the rate of serious infections was 4.3 per 100 patient-years in 7973 HUMIRA-treated patients versus a rate of 2.9 per 100 patient-years in 4848 control-treated patients. Serious infections observed included pneumonia, septic arthritis, prosthetic and post-surgical infections, erysipelas, cellulitis, diverticulitis, and pyelonephritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Tuberculosis and Opportunistic Infections
In 52 global controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials in RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV that included 24,605 HUMIRA-treated patients, the rate of reported active tuberculosis was 0.20 per 100 patient-years and the rate of positive PPD conversion was 0.09 per 100 patient-years. In a subgroup of 10,113 U.S. and Canadian HUMIRA-treated patients, the rate of reported active TB was 0.05 per 100 patient-years and the rate of positive PPD conversion was 0.07 per 100 patient-years. These trials included reports of miliary, lymphatic, peritoneal, and pulmonary TB. Most of the TB cases occurred within the first eight months after initiation of therapy and may reflect recrudescence of latent disease. In these global clinical trials, cases of serious opportunistic infections have been reported at an overall rate of 0.05 per 100 patient-years. Some cases of serious opportunistic infections and TB have been fatal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Autoantibodies
In the rheumatoid arthritis controlled trials, 12% of patients treated with HUMIRA and 7% of placebo-treated patients that had negative baseline ANA titers developed positive titers at week 24. Two patients out of 3046 treated with HUMIRA developed clinical signs suggestive of new-onset lupus-like syndrome. The patients improved following discontinuation of therapy. No patients developed lupus nephritis or central nervous system symptoms. The impact of long-term treatment with HUMIRA on the development of autoimmune diseases is unknown.
Liver Enzyme Elevations
There have been reports of severe hepatic reactions including acute liver failure in patients receiving TNF-blockers. In controlled Phase 3 trials of HUMIRA (40 mg SC every other week) in patients with RA, PsA, and AS with control period duration ranging from 4 to 104 weeks, ALT elevations ≥ 3 x ULN occurred in 3.5% of HUMIRA-treated patients and 1.5% of control-treated patients. Since many of these patients in these trials were also taking medications that cause liver enzyme elevations (e.g., NSAIDS, MTX), the relationship between HUMIRA and the liver enzyme elevations is not clear. In a controlled Phase 3 trial of HUMIRA in patients with polyarticular JIA who were 4 to 17 years, ALT elevations ≥ 3 x ULN occurred in 4.4% of HUMIRA-treated patients and 1.5% of control-treated patients (ALT more common than AST); liver enzyme test elevations were more frequent among those treated with the combination of HUMIRA and MTX than those treated with HUMIRA alone. In general, these elevations did not lead to discontinuation of HUMIRA treatment. No ALT elevations ≥ 3 x ULN occurred in the open-label study of HUMIRA in patients with polyarticular JIA who were 2 to <4 years.
In controlled Phase 3 trials of HUMIRA (initial doses of 160 mg and 80 mg, or 80 mg and 40 mg on Days 1 and 15, respectively, followed by 40 mg every other week) in adult patients with Crohn’s Disease with a control period duration ranging from 4 to 52 weeks, ALT elevations ≥ 3 x ULN occurred in 0.9% of HUMIRA-treated patients and 0.9% of control-treated patients. In the Phase 3 trial of HUMIRA in pediatric patients with Crohn’s disease which evaluated efficacy and safety of two body weight based maintenance dose regimens following body weight based induction therapy up to 52 weeks of treatment, ALT elevations ≥ 3 x ULN occurred in 2.6% (5/192) of patients, of whom 4 were receiving concomitant immunosuppressants at baseline; none of these patients discontinued due to abnormalities in ALT tests. In controlled Phase 3 trials of HUMIRA (initial doses of 160 mg and 80 mg on Days 1 and 15 respectively, followed by 40 mg every other week) in adult patients with UC with control period duration ranging from 1 to 52 weeks, ALT elevations ≥3 x ULN occurred in 1.5% of HUMIRA-treated patients and 1.0% of control-treated patients. In the controlled Phase 3 trial of HUMIRA in patients with pediatric ulcerative colitis (N=93), which evaluated efficacy and safety of a maintenance dose of 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) every other week (N=31) and a maintenance dose of 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) every week (N=32), following body weight based induction doses of 2.4 mg/kg (maximum of 160 mg) at Week 0 and Week 1, and 1.2 mg/kg (maximum of 80 mg) at Week 2 (N=63), or an induction dose of 2.4 mg/kg (maximum of 160 mg) at Week 0, placebo at Week 1, and 1.2 mg/kg (maximum of 80 mg) at Week 2 (N=30), ALT elevations ≥ 3 X ULN occurred in 1.1% (1/93) of patients. In controlled Phase 3 trials of HUMIRA (initial dose of 80 mg then 40 mg every other week) in patients with Ps with control period duration ranging from 12 to 24 weeks, ALT elevations ≥ 3 x ULN occurred in 1.8% of HUMIRA-treated patients and 1.8% of control-treated patients. In controlled trials of HUMIRA (initial doses of 160 mg at Week 0 and 80 mg at Week 2, followed by 40 mg every week starting at Week 4), in subjects with HS with a control period duration ranging from 12 to 16 weeks, ALT elevations ≥ 3 x ULN occurred in 0.3% of HUMIRA-treated subjects and 0.6% of control-treated subjects. In controlled trials of HUMIRA (initial doses of 80 mg at Week 0 followed by 40 mg every other week starting at Week 1) in adult patients with uveitis with an exposure of 165.4 PYs and 119.8 PYs in HUMIRA-treated and control-treated patients, respectively, ALT elevations ≥ 3 x ULN occurred in 2.4% of HUMIRA-treated patients and 2.4% of control-treated patients.
Other Adverse Reactions
Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Studies
The data described below reflect exposure to HUMIRA in 2468 patients, including 2073 exposed for 6 months, 1497 exposed for greater than one year and 1380 in adequate and well-controlled studies (Studies RA-I, RA-II, RA-III, and RA-IV). HUMIRA was studied primarily in placebo-controlled trials and in long-term follow up studies for up to 36 months duration. The population had a mean age of 54 years, 77% were female, 91% were Caucasian and had moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis. Most patients received 40 mg HUMIRA every other week [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Table 1 summarizes reactions reported at a rate of at least 5% in patients treated with HUMIRA 40 mg every other week compared to placebo and with an incidence higher than placebo. In Study RA-III, the types and frequencies of adverse reactions in the second year open-label extension were similar to those observed in the one-year double-blind portion.
| HUMIRA 40 mg subcutaneous Every Other Week | Placebo | |
| (N=705) | (N=690) | |
| Adverse Reaction (Preferred Term) | ||
| Respiratory | ||
| Upper respiratory infection | 17% | 13% |
| Sinusitis | 11% | 9% |
| Flu syndrome | 7% | 6% |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Nausea | 9% | 8% |
| Abdominal pain | 7% | 4% |
| Laboratory Tests* | ||
| Laboratory test abnormal | 8% | 7% |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 6% | 4% |
| Hyperlipidemia | 7% | 5% |
| Hematuria | 5% | 4% |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 5% | 3% |
| Other | ||
| Headache | 12% | 8% |
| Rash | 12% | 6% |
| Accidental injury | 10% | 8% |
| Injection site reaction ** | 8% | 1% |
| Back pain | 6% | 4% |
| Urinary tract infection | 8% | 5% |
| Hypertension | 5% | 3% |
| * Laboratory test abnormalities were reported as adverse reactions in European trials ** Does not include injection site erythema, itching, hemorrhage, pain or swelling |
||
Less Common Adverse Reactions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Studies
Other infrequent serious adverse reactions that do not appear in the Warnings and Precautions or Adverse Reaction sections that occurred at an incidence of less than 5% in HUMIRA-treated patients in RA studies were:
Body As A Whole: Pain in extremity, pelvic pain, surgery, thorax pain
Cardiovascular System: Arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, chest pain, coronary artery disorder, heart arrest, hypertensive encephalopathy, myocardial infarct, palpitation, pericardial effusion, pericarditis, syncope, tachycardia
Digestive System: Cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, esophagitis, gastroenteritis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hepatic necrosis, vomiting
Endocrine System: Parathyroid disorder
Hemic And Lymphatic System: Agranulocytosis, polycythemia
Metabolic And Nutritional Disorders: Dehydration, healing abnormal, ketosis, paraproteinemia, peripheral edema
Musculo-Skeletal System: Arthritis, bone disorder, bone fracture (not spontaneous), bone necrosis, joint disorder, muscle cramps, myasthenia, pyogenic arthritis, synovitis, tendon disorder
Neoplasia: Adenoma
Nervous System: Confusion, paresthesia, subdural hematoma, tremor
Respiratory System: Asthma, bronchospasm, dyspnea, lung function decreased, pleural effusion
Special Senses: Cataract
Thrombosis: Thrombosis leg
Urogenital System: Cystitis, kidney calculus, menstrual disorder
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Clinical Studies
In general, the adverse reactions in the HUMIRA-treated patients in the polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) trials (Studies JIA-I and JIA-II) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] were similar in frequency and type to those seen in adult patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5), Adverse Reactions (6)]. Important findings and differences from adults are discussed in the following paragraphs.
In Study JIA-I, HUMIRA was studied in 171 patients who were 4 to 17 years of age, with polyarticular JIA. Severe adverse reactions reported in the study included neutropenia, streptococcal pharyngitis, increased aminotransferases, herpes zoster, myositis, metrorrhagia, and appendicitis. Serious infections were observed in 4% of patients within approximately 2 years of initiation of treatment with HUMIRA and included cases of herpes simplex, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, pharyngitis, and herpes zoster.
In Study JIA-I, 45% of patients experienced an infection while receiving HUMIRA with or without concomitant MTX in the first 16 weeks of treatment. The types of infections reported in HUMIRA-treated patients were generally similar to those commonly seen in polyarticular JIA patients who are not treated with TNF blockers. Upon initiation of treatment, the most common adverse reactions occurring in this patient population treated with HUMIRA were injection site pain and injection site reaction (19% and 16%, respectively). A less commonly reported adverse event in patients receiving HUMIRA was granuloma annulare which did not lead to discontinuation of HUMIRA treatment.
In the first 48 weeks of treatment in Study JIA-I, non-serious hypersensitivity reactions were seen in approximately 6% of patients and included primarily localized allergic hypersensitivity reactions and allergic rash.
In Study JIA-I, 10% of patients treated with HUMIRA who had negative baseline anti-dsDNA antibodies developed positive titers after 48 weeks of treatment. No patient developed clinical signs of autoimmunity during the clinical trial.
Approximately 15% of patients treated with HUMIRA developed mild-to-moderate elevations of creatine phosphokinase (CPK) in Study JIA-I. Elevations exceeding 5 times the upper limit of normal were observed in several patients. CPK concentrations decreased or returned to normal in all patients. Most patients were able to continue HUMIRA without interruption.
In Study JIA-II, HUMIRA was studied in 32 patients who were 2 to <4 years of age or 4 years of age and older weighing <15 kg with polyarticular JIA. The safety profile for this patient population was similar to the safety profile seen in patients 4 to 17 years of age with polyarticular JIA.
In Study JIA-II, 78% of patients experienced an infection while receiving HUMIRA. These included nasopharyngitis, bronchitis, upper respiratory tract infection, otitis media, and were mostly mild to moderate in severity. Serious infections were observed in 9% of patients receiving HUMIRA in the study and included dental caries, rotavirus gastroenteritis, and varicella.
In Study JIA-II, non-serious allergic reactions were observed in 6% of patients and included intermittent urticaria and rash, which were all mild in severity.
Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Studies
HUMIRA has been studied in 395 patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in two placebo-controlled trials and in an open label study and in 393 patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) in two placebo-controlled studies [see Clinical Studies (14.3, 14.4)]. The safety profile for patients with PsA and AS treated with HUMIRA 40 mg every other week was similar to the safety profile seen in patients with RA, HUMIRA Studies RA-I through IV.
Crohn’s Disease Clinical Studies
Adults: The safety profile of HUMIRA in 1478 adult patients with Crohn’s disease from four placebo-controlled and two open-label extension studies [see Clinical Studies (14.5)] was similar to the safety profile seen in patients with RA.
Pediatric Patients 6 Years to 17 Years: The safety profile of HUMIRA in 192 pediatric patients from one double-blind study (Study PCD-I) and one open-label extension study [see Clinical Studies (14.6)] was similar to the safety profile seen in adult patients with Crohn’s disease.
During the 4-week open label induction phase of Study PCD-I, the most common adverse reactions occurring in the pediatric population treated with HUMIRA were injection site pain and injection site reaction (6% and 5%, respectively).
A total of 67% of children experienced an infection while receiving HUMIRA in Study PCD-I. These included upper respiratory tract infection and nasopharyngitis.
A total of 5% of children experienced a serious infection while receiving HUMIRA in Study PCD-I. These included viral infection, device related sepsis (catheter), gastroenteritis, H1N1 influenza, and disseminated histoplasmosis.
In Study PCD-I, allergic reactions were observed in 5% of children which were all non-serious and were primarily localized reactions.
Ulcerative Colitis Clinical Studies
Adults: The safety profile of HUMIRA in 1010 adult patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) from two placebo-controlled studies and one open-label extension study [see Clinical Studies (14.7)] was similar to the safety profile seen in patients with RA.
Pediatric Patients 5 Years to 17 Years: The safety profile of HUMIRA in 93 pediatric patients with ulcerative colitis from one double-blind study and one open-label extension study [see Clinical Studies (14.8)] was similar to the safety profile seen in adult patients with ulcerative colitis.
Plaque Psoriasis Clinical Studies
HUMIRA has been studied in 1696 subjects with plaque psoriasis (Ps) in placebo-controlled and open-label extension studies [see Clinical Studies (14.9)]. The safety profile for subjects with Ps treated with HUMIRA was similar to the safety profile seen in subjects with RA with the following exceptions. In the placebo-controlled portions of the clinical trials in Ps subjects, HUMIRA-treated subjects had a higher incidence of arthralgia when compared to controls (3% vs. 1%).
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Studies
HUMIRA has been studied in 727 subjects with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) in three placebo-controlled studies and one open-label extension study [see Clinical Studies (14.10)]. The safety profile for subjects with HS treated with HUMIRA weekly was consistent with the known safety profile of HUMIRA.
Flare of HS, defined as ≥25% increase from baseline in abscesses and inflammatory nodule counts and with a minimum of 2 additional lesions, was documented in 22 (22%) of the 100 subjects who were withdrawn from HUMIRA treatment following the primary efficacy timepoint in two studies.
Uveitis Clinical Studies
HUMIRA has been studied in 464 adult patients with uveitis (UV) in placebo-controlled and open-label extension studies and in 90 pediatric patients with uveitis (Study PUV-I) [see Clinical Studies (14.11, 14.12)] . The safety profile for patients with UV treated with HUMIRA was similar to the safety profile seen in patients with RA.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Methotrexate
HUMIRA has been studied in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients taking concomitant methotrexate (MTX). Although MTX reduced the apparent adalimumab clearance, the data do not suggest the need for dose adjustment of either HUMIRA or MTX [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Biological Products
In clinical studies in patients with RA, an increased risk of serious infections has been observed with the combination of TNF blockers with anakinra or abatacept, with no added benefit; therefore, use of HUMIRA with abatacept or anakinra is not recommended in patients with RA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.11)]. A higher rate of serious infections has also been observed in patients with RA treated with rituximab who received subsequent treatment with a TNF blocker. There is insufficient information regarding the concomitant use of HUMIRA and other biologic products for the treatment of RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV. Concomitant administration of HUMIRA with other biologic DMARDS (e.g., anakinra and abatacept) or other TNF blockers is not recommended based upon the possible increased risk for infections and other potential pharmacological interactions.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available studies with use of adalimumab during pregnancy do not reliably establish an association between adalimumab and major birth defects. Clinical data are available from the Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS)/MotherToBaby HUMIRA Pregnancy Registry in pregnant women with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or Crohn’s disease (CD). Registry results showed a rate of 10% for major birth defects with first trimester use of adalimumab in pregnant women with RA or CD and a rate of 7.5% for major birth defects in the disease-matched comparison cohort. The lack of pattern of major birth defects is reassuring and differences between exposure groups may have impacted the occurrence of birth defects (see Data).
Adalimumab is actively transferred across the placenta during the third trimester of pregnancy and may affect immune response in the in-utero exposed infant (see Clinical Considerations). In an embryo-fetal perinatal development study conducted in cynomolgus monkeys, no fetal harm or malformations were observed with intravenous administration of adalimumab during organogenesis and later in gestation, at doses that produced exposures up to approximately 373 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 40 mg subcutaneous without methotrexate (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and embryo/fetal risk
Published data suggest that the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with RA or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with increased disease activity. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include preterm delivery (before 37 weeks of gestation), low birth weight (less than 2500 g) infants, and small for gestational age at birth.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Monoclonal antibodies are increasingly transported across the placenta as pregnancy progresses, with the largest amount transferred during the third trimester (see Data). Risks and benefits should be considered prior to administering live or live-attenuated vaccines to infants exposed to HUMIRA in utero [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Data
Human Data
A prospective cohort pregnancy exposure registry conducted by OTIS/MotherToBaby in the U.S. and Canada between 2004 and 2016 compared the risk of major birth defects in live-born infants of 221 women (69 RA, 152 CD) treated with adalimumab during the first trimester and 106 women (74 RA, 32 CD) not treated with adalimumab.
The proportion of major birth defects among live-born infants in the adalimumab-treated and untreated cohorts was 10% (8.7% RA, 10.5% CD) and 7.5% (6.8% RA, 9.4% CD), respectively. The lack of pattern of major birth defects is reassuring and differences between exposure groups may have impacted the occurrence of birth defects. This study cannot reliably establish whether there is an association between adalimumab and major birth defects because of methodological limitations of the registry, including small sample size, the voluntary nature of the study, and the non-randomized design.
In an independent clinical study conducted in ten pregnant women with IBD treated with HUMIRA, adalimumab concentrations were measured in maternal serum as well as in cord blood (n=10) and infant serum (n=8) on the day of birth. The last dose of HUMIRA was given between 1 and 56 days prior to delivery. Adalimumab concentrations were 0.16-19.7 µg/mL in cord blood, 4.28-17.7 µg/mL in infant serum, and 0-16.1 µg/mL in maternal serum. In all but one case, the cord blood concentration of adalimumab was higher than the maternal serum concentration, suggesting adalimumab actively crosses the placenta. In addition, one infant had serum concentrations at each of the following: 6 weeks (1.94 µg/mL), 7 weeks (1.31 µg/mL), 8 weeks (0.93 µg/mL), and 11 weeks (0.53 µg/mL), suggesting adalimumab can be detected in the serum of infants exposed in utero for at least 3 months from birth.
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal perinatal development study, pregnant cynomolgus monkeys received adalimumab from gestation days 20 to 97 at doses that produced exposures up to 373 times that achieved with the MRHD without methotrexate (on an AUC basis with maternal IV doses up to 100 mg/kg/week). Adalimumab did not elicit harm to the fetuses or malformations.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of HUMIRA have been established for:
- reducing signs and symptoms of moderately to severely active polyarticular JIA in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older.
- the treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
- the treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in pediatric patients 5 years of age and older.
- the treatment of moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa in patients 12 years of age and older.
- the treatment of non-infectious intermediate, posterior, and panuveitis in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older.
Due to its inhibition of TNFα, HUMIRA administered during pregnancy could affect immune response in the in utero-exposed newborn and infant. Data from eight infants exposed to HUMIRA in utero suggest adalimumab crosses the placenta [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. The clinical significance of elevated adalimumab concentrations in infants is unknown. The safety of administering live or live-attenuated vaccines in exposed infants is unknown. Risks and benefits should be considered prior to vaccinating (live or live-attenuated) exposed infants.
Post-marketing cases of lymphoma, including hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported among children, adolescents, and young adults who received treatment with TNF-blockers including HUMIRA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
In Study JIA-I, HUMIRA was shown to reduce signs and symptoms of active polyarticular JIA in patients 4 to 17 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. In Study JIA-II, the safety profile for patients 2 to <4 years of age was similar to the safety profile for patients 4 to 17 years of age with polyarticular JIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. HUMIRA has not been studied in patients with polyarticular JIA less than 2 years of age or in patients with a weight below 10 kg.
The safety of HUMIRA in patients in the polyarticular JIA trials was generally similar to that observed in adults with certain exceptions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of HUMIRA have not been established in pediatric patients with JIA less than 2 years of age.
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease
The safety and effectiveness of HUMIRA for the treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease have been established in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Use of HUMIRA for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with additional data from a randomized, double-blind, 52-week clinical study of two dose concentrations of HUMIRA in 192 pediatric patients (6 years to 17 years of age) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2, 12.3), Clinical Studies (14.6)]. The adverse reaction profile in patients 6 years to 17 years of age was similar to adults.
The safety and effectiveness of HUMIRA have not been established in pediatric patients with Crohn’s disease less than 6 years of age.
Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis
The safety and effectiveness of HUMIRA for the treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis have been established in pediatric patients 5 years of age and older. Use of HUMIRA for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with additional data from a randomized, double-blind, 52-week clinical study of two dose concentrations of HUMIRA in 93 pediatric patients (5 years to 17 years of age) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14.8)]. The adverse reaction profile in patients 5 years to 17 years of age was similar to adults.
The effectiveness of HUMIRA has not been established in patients who have lost response or were intolerant to TNF blockers.
The safety and effectiveness of HUMIRA have not been established in pediatric patients with ulcerative colitis less than 5 years of age.
Pediatric Uveitis
The safety and effectiveness of HUMIRA for the treatment of non-infectious uveitis have been established in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older. The use of HUMIRA is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of HUMIRA in adults and a 2:1 randomized, controlled clinical study in 90 pediatric patients [see Clinical Studies (14.12)]. The safety and effectiveness of HUMIRA have not been established in pediatric patients with uveitis less than 2 years of age.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Use of HUMIRA in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older for HS is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of HUMIRA in adult HS patients. Additional population pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation predicted that weight-based dosing of HUMIRA in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older can provide generally similar exposure to adult HS patients. The course of HS is sufficiently similar in adult and adolescent patients to allow extrapolation of data from adult to adolescent patients. The recommended dosage in pediatric patients 12 years of age or older is based on body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.10)].
The safety and effectiveness of HUMIRA have not been established in patients less than 12 years of age with HS.
12. Humira - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
After treatment with HUMIRA, a decrease in concentrations of acute phase reactants of inflammation (C-reactive protein [CRP] and erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR]) and serum cytokines (IL-6) was observed compared to baseline in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A decrease in CRP concentrations was also observed in patients with Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and hidradenitis suppurativa. Serum concentrations of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1 and MMP-3) that produce tissue remodeling responsible for cartilage destruction were also decreased after HUMIRA administration.
For pediatric patients 5 years to 17 years with ulcerative colitis, the recommended dosage of HUMIRA is based on modeled dose/exposure-efficacy relationships and pharmacokinetic data. There are no anticipated clinically relevant differences in efficacy between the studied higher dosage administered in the clinical trial (Weeks 0 to 52 in Study PUC-I) [see Clinical Studies (14.8)] and the recommended dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of adalimumab were linear over the dose range of 0.5 to 10 mg/kg following administration of a single intravenous dose (HUMIRA is not approved for intravenous use). Following 20, 40, and 80 mg every other week and every week subcutaneous administration, adalimumab mean serum trough concentrations at steady state increased approximately proportionally with dose in RA patients. The mean terminal half-life was approximately 2 weeks, ranging from 10 to 20 days across studies. Healthy subjects and patients with RA displayed similar adalimumab pharmacokinetics.
Adalimumab exposure in patients treated with 80 mg every other week is estimated to be comparable with that in patients treated with 40 mg every week.
Absorption
The average absolute bioavailability of adalimumab following a single 40 mg subcutaneous dose was 64%. The mean time to reach the maximum concentration was 5.5 days (131 ± 56 hours) and the maximum serum concentration was 4.7 ± 1.6 mcg/mL in healthy subjects following a single 40 mg subcutaneous administration of HUMIRA.
Distribution
The distribution volume (Vss) ranged from 4.7 to 6.0 L following intravenous administration of doses ranging from 0.25 to 10 mg/kg in RA patients.
Elimination
The single dose pharmacokinetics of adalimumab in RA patients were determined in several studies with intravenous doses ranging from 0.25 to 10 mg/kg. The systemic clearance of adalimumab is approximately 12 mL/hr. In long-term studies with dosing more than two years, there was no evidence of changes in clearance over time in RA patients.
Patient Population
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis: In patients receiving 40 mg HUMIRA every other week, adalimumab mean steady-state trough concentrations were approximately 5 mcg/mL and 8 to 9 mcg/mL, without and with MTX concomitant treatment, respectively. Adalimumab concentrations in the synovial fluid from five rheumatoid arthritis patients ranged from 31 to 96% of those in serum. The pharmacokinetics of adalimumab in patients with AS were similar to those in patients with RA.
Psoriatic Arthritis: In patients receiving 40 mg every other week, adalimumab mean steady-state trough concentrations were 6 to 10 mcg/mL and 8.5 to 12 mcg/mL, without and with MTX concomitant treatment, respectively.
Plaque Psoriasis: Adalimumab mean steady-state trough concentration was approximately 5 to 6 mcg/mL during HUMIRA 40 mg every other week treatment.
Adult Uveitis: Adalimumab mean steady concentration was approximately 8 to 10 mcg/mL during HUMIRA 40 mg every other week treatment.
Adult Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Adalimumab trough concentrations were approximately 7 to 8 mcg/mL at Week 2 and Week 4, respectively, after receiving 160 mg on Week 0 followed by 80 mg on Week 2. Mean steady-state trough concentrations at Week 12 through Week 36 were approximately 7 to 11 mcg/mL during HUMIRA 40 mg every week treatment.
Adult Crohn’s Disease: Adalimumab mean trough concentrations were approximately 12 mcg/mL at Week 2 and Week 4 after receiving 160 mg on Week 0 followed by 80 mg on Week 2. Mean steady-state trough concentrations were 7 mcg/mL at Week 24 and Week 56 during HUMIRA 40 mg every other week treatment.
Adult Ulcerative Colitis: Adalimumab mean trough concentrations were approximately 12 mcg/mL at Week 2 and Week 4 after receiving 160 mg on Week 0 followed by 80 mg on Week 2. Mean steady-state trough concentrations were approximately 8 mcg/mL and 15 mcg/mL at Week 52 after receiving a dose of HUMIRA 40 mg every other week and 40 mg every week, respectively.
Anti-Drug Antibody Effects on Pharmacokinetics
Rheumatoid Arthritis: A trend toward higher apparent clearance of adalimumab in the presence of anti-adalimumab antibodies was identified.
Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis: Antibodies to adalimumab by ECL assay were associated with reduced serum adalimumab concentrations in pediatric patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa: In subjects with moderate to severe HS, antibodies to adalimumab were associated with reduced serum adalimumab concentrations. In general, the extent of reduction in serum adalimumab concentrations is greater with increasing titers of antibodies to adalimumab.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients: A lower clearance with increasing age was observed in patients with RA aged 40 to >75 years.
Pediatric Patients:
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis:
-
4 years to 17 years of age: The adalimumab mean steady-state trough concentrations were 6.8 mcg/mL and 10.9 mcg/mL in patients weighing <30 kg receiving 20 mg HUMIRA subcutaneously every other week as monotherapy or with concomitant MTX, respectively. The adalimumab mean steady-state trough concentrations were 6.6 mcg/mL and 8.1 mcg/mL in patients weighing ≥30 kg receiving 40 mg HUMIRA subcutaneously every other week as monotherapy or with MTX concomitant treatment, respectively.
- 2 years to <4 years of age or 4 years of age and older weighing <15 kg: The adalimumab mean steady-state trough adalimumab concentrations were 6.0 mcg/mL and 7.9 mcg/mL in patients receiving HUMIRA subcutaneously every other week as monotherapy or with MTX concomitant treatment, respectively.
Pediatric Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Adalimumab concentrations in adolescent patients with HS receiving the recommended dosage regimens are predicted to be similar to those observed in adult subjects with HS based on population pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation.
Pediatric Crohn's Disease: Adalimumab mean ± SD concentrations were 15.7±6.5 mcg/mL at Week 4 following 160 mg at Week 0 and 80 mg at Week 2, and 10.5±6.0 mcg/mL at Week 52 following 40 mg every other week dosing in patients weighing ≥ 40 kg. Adalimumab mean ± SD concentrations were 10.6±6.1 mcg/mL at Week 4 following dosing 80 mg at Week 0 and 40 mg at Week 2, and 6.9±3.6 mcg/mL at Week 52 following 20 mg every other week dosing in patients weighing < 40 kg.
Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis: The adalimumab mean steady-state trough concentration was 5.0±3.3 mcg/mL at Week 52 following subcutaneous administration of 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) every other week in pediatric UC patients 5 years to 17 years of age. In patients who received 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) every week, the mean steady-state trough concentration was 15.7±5.6 mcg/mL at Week 52 in pediatric UC patients 5 years to 17 years of age.
Male and Female Patients: No gender-related pharmacokinetic differences were observed after correction for a patient’s body weight. Healthy subjects and patients with rheumatoid arthritis displayed similar adalimumab pharmacokinetics.
Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment: No pharmacokinetic data are available in patients with hepatic or renal impairment.
Rheumatoid factor or CRP concentrations: Minor increases in apparent clearance were predicted in RA patients receiving doses lower than the recommended dose and in RA patients with high rheumatoid factor or CRP concentrations. These increases are not likely to be clinically important.
Drug Interaction Studies:
Methotrexate: MTX reduced adalimumab apparent clearance after single and multiple dosing by 29% and 44% respectively, in patients with RA [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis
The efficacy and safety of HUMIRA were assessed in five randomized, double-blind studies in patients ≥18 years of age with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) diagnosed according to American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria. Patients had at least 6 swollen and 9 tender joints. HUMIRA was administered subcutaneously in combination with methotrexate (MTX) (12.5 to 25 mg, Studies RA-I, RA-III and RA-V) or as monotherapy (Studies RA-II and RA-V) or with other disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) (Study RA-IV).
Study RA-I evaluated 271 patients who had failed therapy with at least one but no more than four DMARDs and had inadequate response to MTX. Doses of 20, 40 or 80 mg of HUMIRA or placebo were given every other week for 24 weeks.
Study RA-II evaluated 544 patients who had failed therapy with at least one DMARD. Doses of placebo, 20 or 40 mg of HUMIRA were given as monotherapy every other week or weekly for 26 weeks.
Study RA-III evaluated 619 patients who had an inadequate response to MTX. Patients received placebo, 40 mg of HUMIRA every other week with placebo injections on alternate weeks, or 20 mg of HUMIRA weekly for up to 52 weeks. Study RA-III had an additional primary endpoint at 52 weeks of inhibition of disease progression (as detected by X-ray results). Upon completion of the first 52 weeks, 457 patients enrolled in an open-label extension phase in which 40 mg of HUMIRA was administered every other week for up to 5 years.
Study RA-IV assessed safety in 636 patients who were either DMARD-naive or were permitted to remain on their pre-existing rheumatologic therapy provided that therapy was stable for a minimum of 28 days. Patients were randomized to 40 mg of HUMIRA or placebo every other week for 24 weeks.
Study RA-V evaluated 799 patients with moderately to severely active RA of less than 3 years duration who were ≥18 years old and MTX naïve. Patients were randomized to receive either MTX (optimized to 20 mg/week by week 8), HUMIRA 40 mg every other week or HUMIRA/MTX combination therapy for 104 weeks. Patients were evaluated for signs and symptoms, and for radiographic progression of joint damage. The median disease duration among patients enrolled in the study was 5 months. The median MTX dose achieved was 20 mg.
Clinical Response
The percent of HUMIRA treated patients achieving ACR 20, 50 and 70 responses in Studies RA-II and III are shown in Table 3.
| Study RA-II
Monotherapy (26 weeks) | Study RA-III
Methotrexate Combination (24 and 52 weeks) |
||||
| Response | Placebo | HUMIRA | HUMIRA | Placebo/MTX | HUMIRA/MTX |
| 40 mg every | 40 mg weekly | 40 mg every | |||
| other week | other week | ||||
| N=110 | N=113 | N=103 | N=200 | N=207 | |
| ACR20 | |||||
| Month 6 | 19% | 46%* | 53%* | 30% | 63%* |
| Month 12 | NA | NA | NA | 24% | 59%* |
| ACR50 | |||||
| Month 6 | 8% | 22%* | 35%* | 10% | 39%* |
| Month 12 | NA | NA | NA | 10% | 42%* |
| ACR70 | |||||
| Month 6 | 2% | 12%* | 18%* | 3% | 21%* |
| Month 12 | NA | NA | NA | 5% | 23%* |
| * p<0.01, HUMIRA vs. placebo | |||||
The results of Study RA-I were similar to Study RA-III; patients receiving HUMIRA 40 mg every other week in Study RA-I also achieved ACR 20, 50 and 70 response rates of 65%, 52% and 24%, respectively, compared to placebo responses of 13%, 7% and 3% respectively, at 6 months (p<0.01).
The results of the components of the ACR response criteria for Studies RA-II and RA-III are shown in Table 4. ACR response rates and improvement in all components of ACR response were maintained to week 104. Over the 2 years in Study RA-III, 20% of HUMIRA patients receiving 40 mg every other week achieved a major clinical response, defined as maintenance of an ACR 70 response over a 6-month period. ACR responses were maintained in similar proportions of patients for up to 5 years with continuous HUMIRA treatment in the open-label portion of Study RA-III.
| Study RA-II | Study RA-III | |||||||
| Parameter (median) | Placebo
N=110 | HUMIRAa
N=113 | Placebo/MTX
N=200 | HUMIRAa/MTX
N=207 |
||||
| Baseline | Wk 26 | Baseline | Wk 26 | Baseline | Wk 24 | Baseline | Wk 24 | |
| Number of tender joints (0-68) | 35 | 26 | 31 | 16* | 26 | 15 | 24 | 8* |
| Number of swollen joints (0-66) | 19 | 16 | 18 | 10* | 17 | 11 | 18 | 5* |
| Physician global assessmentb | 7.0 | 6.1 | 6.6 | 3.7* | 6.3 | 3.5 | 6.5 | 2.0* |
| Patient global assessmentb | 7.5 | 6.3 | 7.5 | 4.5* | 5.4 | 3.9 | 5.2 | 2.0* |
| Painb | 7.3 | 6.1 | 7.3 | 4.1* | 6.0 | 3.8 | 5.8 | 2.1* |
| Disability index (HAQ)c | 2.0 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.5* | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 0.8* |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 3.9 | 4.3 | 4.6 | 1.8* | 1.0 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.4* |
| a 40 mg HUMIRA administered every other week b Visual analogue scale; 0 = best, 10 = worst c Disability Index of the Health Assessment Questionnaire; 0 = best, 3 = worst, measures the patient’s ability to perform the following: dress/groom, arise, eat, walk, reach, grip, maintain hygiene, and maintain daily activity * p<0.001, HUMIRA vs. placebo, based on mean change from baseline |
||||||||
The time course of ACR 20 response for Study RA-III is shown in Figure 1.
In Study RA-III, 85% of patients with ACR 20 responses at week 24 maintained the response at 52 weeks. The time course of ACR 20 response for Study RA-I and Study RA-II were similar.
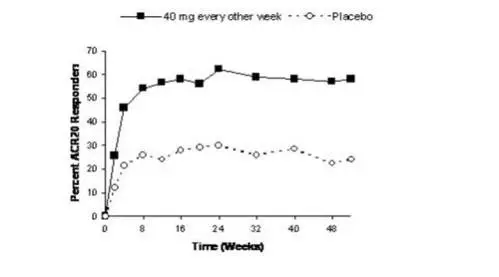
Figure 1. Study RA-III ACR 20 Responses over 52 Weeks
In Study RA-IV, 53% of patients treated with HUMIRA 40 mg every other week plus standard of care had an ACR 20 response at week 24 compared to 35% on placebo plus standard of care (p<0.001). No unique adverse reactions related to the combination of HUMIRA (adalimumab) and other DMARDs were observed.
In Study RA-V with MTX naïve patients with recent onset RA, the combination treatment with HUMIRA plus MTX led to greater percentages of patients achieving ACR responses than either MTX monotherapy or HUMIRA monotherapy at Week 52 and responses were sustained at Week 104 (see Table 5).
| Response | MTXb
N=257 | HUMIRAc
N=274 | HUMIRA/MTX
N=268 |
| ACR20
Week 52 Week 104 |
63% 56% |
54% 49% |
73% 69% |
| ACR50
Week 52 Week 104 |
46% 43% |
41% 37% |
62% 59% |
| ACR70
Week 52 Week 104 |
27% 28% |
26% 28% |
46% 47% |
| Major Clinical Response a | 28% | 25% | 49% |
| a Major clinical response is defined as achieving an ACR70 response for a continuous six month period b p<0.05, HUMIRA/MTX vs. MTX for ACR 20 p<0.001, HUMIRA/MTX vs. MTX for ACR 50 and 70, and Major Clinical Response c p<0.001, HUMIRA/MTX vs. HUMIRA |
|||
At Week 52, all individual components of the ACR response criteria for Study RA-V improved in the HUMIRA/MTX group and improvements were maintained to Week 104.
Radiographic Response
In Study RA-III, structural joint damage was assessed radiographically and expressed as change in Total Sharp Score (TSS) and its components, the erosion score and Joint Space Narrowing (JSN) score, at month 12 compared to baseline. At baseline, the median TSS was approximately 55 in the placebo and 40 mg every other week groups. The results are shown in Table 6. HUMIRA/MTX treated patients demonstrated less radiographic progression than patients receiving MTX alone at 52 weeks.
| Placebo/MTX | HUMIRA/MTX 40 mg every other week | Placebo/MTX- HUMIRA/MTX (95% Confidence Interval*) | P-value** | |
| Total Sharp score | 2.7 | 0.1 | 2.6 (1.4, 3.8) | <0.001 |
| Erosion score | 1.6 | 0.0 | 1.6 (0.9, 2.2) | <0.001 |
| JSN score | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.9 (0.3, 1.4) | 0.002 |
| *95% confidence intervals for the differences in change scores between MTX and HUMIRA. **Based on rank analysis |
||||
In the open-label extension of Study RA-III, 77% of the original patients treated with any dose of HUMIRA were evaluated radiographically at 2 years. Patients maintained inhibition of structural damage, as measured by the TSS. Fifty-four percent had no progression of structural damage as defined by a change in the TSS of zero or less. Fifty-five percent (55%) of patients originally treated with 40 mg HUMIRA every other week have been evaluated radiographically at 5 years. Patients had continued inhibition of structural damage with 50% showing no progression of structural damage defined by a change in the TSS of zero or less.
In Study RA-V, structural joint damage was assessed as in Study RA-III. Greater inhibition of radiographic progression, as assessed by changes in TSS, erosion score and JSN was observed in the HUMIRA/MTX combination group as compared to either the MTX or HUMIRA monotherapy group at Week 52 as well as at Week 104 (see Table 7).
| MTXa
N=257 | HUMIRAa,b
N=274 | HUMIRA/MTX
N=268 |
||
| 52 Weeks | Total Sharp score | 5.7 (4.2, 7.3) | 3.0 (1.7, 4.3) | 1.3 (0.5, 2.1) |
| Erosion score | 3.7 (2.7, 4.8) | 1.7 (1.0, 2.4) | 0.8 (0.4, 1.2) | |
| JSN score | 2.0 (1.2, 2.8) | 1.3 (0.5, 2.1) | 0.5 (0.0, 1.0) | |
| 104 Weeks | Total Sharp score | 10.4 (7.7, 13.2) | 5.5 (3.6, 7.4) | 1.9 (0.9, 2.9) |
| Erosion score | 6.4 (4.6, 8.2) | 3.0 (2.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (0.4, 1.6) | |
| JSN score | 4.1 (2.7, 5.4) | 2.6 (1.5, 3.7) | 0.9 (0.3, 1.5) | |
| * mean (95% confidence interval) a p<0.001, HUMIRA/MTX vs. MTX at 52 and 104 weeks and for HUMIRA/MTX vs. HUMIRA at 104 weeks b p<0.01, for HUMIRA/MTX vs. HUMIRA at 52 weeks |
||||
Physical Function Response
In studies RA-I through IV, HUMIRA showed significantly greater improvement than placebo in the disability index of Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ-DI) from baseline to the end of study, and significantly greater improvement than placebo in the health-outcomes as assessed by The Short Form Health Survey (SF 36). Improvement was seen in both the Physical Component Summary (PCS) and the Mental Component Summary (MCS).
In Study RA-III, the mean (95% CI) improvement in HAQ-DI from baseline at week 52 was 0.60 (0.55, 0.65) for the HUMIRA patients and 0.25 (0.17, 0.33) for placebo/MTX (p<0.001) patients. Sixty-three percent of HUMIRA-treated patients achieved a 0.5 or greater improvement in HAQ-DI at week 52 in the double-blind portion of the study. Eighty-two percent of these patients maintained that improvement through week 104 and a similar proportion of patients maintained this response through week 260 (5 years) of open-label treatment. Mean improvement in the SF-36 was maintained through the end of measurement at week 156 (3 years).
In Study RA-V, the HAQ-DI and the physical component of the SF-36 showed greater improvement (p<0.001) for the HUMIRA/MTX combination therapy group versus either the MTX monotherapy or the HUMIRA monotherapy group at Week 52, which was maintained through Week 104.
14.2 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
The safety and efficacy of HUMIRA was assessed in two studies (Studies JIA-I and JIA-II) in patients with active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Study JIA-I
The safety and efficacy of HUMIRA were assessed in a multicenter, randomized, withdrawal, double-blind, parallel-group study in 171 patients who were 4 to 17 years of age with polyarticular JIA. In the study, the patients were stratified into two groups: MTX-treated or non-MTX-treated. All patients had to show signs of active moderate or severe disease despite previous treatment with NSAIDs, analgesics, corticosteroids, or DMARDS. Patients who received prior treatment with any biologic DMARDS were excluded from the study.
The study included four phases: an open-label lead in phase (OL-LI; 16 weeks), a double-blind randomized withdrawal phase (DB; 32 weeks), an open-label extension phase (OLE-BSA; up to 136 weeks), and an open-label fixed dose phase (OLE-FD; 16 weeks). In the first three phases of the study, HUMIRA was administered based on body surface area at a dose of 24 mg/m2 up to a maximum total body dose of 40 mg subcutaneously (SC) every other week. In the OLE-FD phase, the patients were treated with 20 mg of HUMIRA SC every other week if their weight was less than 30 kg and with 40 mg of HUMIRA SC every other week if their weight was 30 kg or greater. Patients remained on stable doses of NSAIDs and or prednisone (≤0.2 mg/kg/day or 10 mg/day maximum).
Patients demonstrating a Pediatric ACR 30 response at the end of OL-LI phase were randomized into the double blind (DB) phase of the study and received either HUMIRA or placebo every other week for 32 weeks or until disease flare. Disease flare was defined as a worsening of ≥30% from baseline in ≥3 of 6 Pediatric ACR core criteria, ≥2 active joints, and improvement of >30% in no more than 1 of the 6 criteria. After 32 weeks or at the time of disease flare during the DB phase, patients were treated in the open-label extension phase based on the BSA regimen (OLE-BSA), before converting to a fixed dose regimen based on body weight (OLE-FD phase).
Study JIA-I Clinical Response
At the end of the 16-week OL-LI phase, 94% of the patients in the MTX stratum and 74% of the patients in the non-MTX stratum were Pediatric ACR 30 responders. In the DB phase significantly fewer patients who received HUMIRA experienced disease flare compared to placebo, both without MTX (43% vs. 71%) and with MTX (37% vs. 65%). More patients treated with HUMIRA continued to show pediatric ACR 30/50/70 responses at Week 48 compared to patients treated with placebo. Pediatric ACR responses were maintained for up to two years in the OLE phase in patients who received HUMIRA throughout the study.
Study JIA-II
HUMIRA was assessed in an open-label, multicenter study in 32 patients who were 2 to <4 years of age or 4 years of age and older weighing <15 kg with moderately to severely active polyarticular JIA. Most patients (97%) received at least 24 weeks of HUMIRA treatment dosed 24 mg/m2 up to a maximum of 20 mg every other week as a single SC injection up to a maximum of 120 weeks duration. During the study, most patients used concomitant MTX, with fewer reporting use of corticosteroids or NSAIDs. The primary objective of the study was evaluation of safety [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
14.3 Psoriatic Arthritis
The safety and efficacy of HUMIRA was assessed in two randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled studies in 413 patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Upon completion of both studies, 383 patients enrolled in an open-label extension study, in which 40 mg HUMIRA was administered every other week.
Study PsA-I enrolled 313 adult patients with moderately to severely active PsA (>3 swollen and >3 tender joints) who had an inadequate response to NSAID therapy in one of the following forms: (1) distal interphalangeal (DIP) involvement (N=23); (2) polyarticular arthritis (absence of rheumatoid nodules and presence of plaque psoriasis) (N=210); (3) arthritis mutilans (N=1); (4) asymmetric PsA (N=77); or (5) AS-like (N=2). Patients on MTX therapy (158 of 313 patients) at enrollment (stable dose of ≤30 mg/week for >1 month) could continue MTX at the same dose. Doses of HUMIRA 40 mg or placebo every other week were administered during the 24-week double-blind period of the study.
Compared to placebo, treatment with HUMIRA resulted in improvements in the measures of disease activity (see Tables 8 and 9). Among patients with PsA who received HUMIRA, the clinical responses were apparent in some patients at the time of the first visit (two weeks) and were maintained up to 88 weeks in the ongoing open-label study. Similar responses were seen in patients with each of the subtypes of psoriatic arthritis, although few patients were enrolled with the arthritis mutilans and ankylosing spondylitis-like subtypes. Responses were similar in patients who were or were not receiving concomitant MTX therapy at baseline.
Patients with psoriatic involvement of at least three percent body surface area (BSA) were evaluated for Psoriatic Area and Severity Index (PASI) responses. At 24 weeks, the proportions of patients achieving a 75% or 90% improvement in the PASI were 59% and 42% respectively, in the HUMIRA group (N=69), compared to 1% and 0% respectively, in the placebo group (N=69) (p<0.001). PASI responses were apparent in some patients at the time of the first visit (two weeks). Responses were similar in patients who were or were not receiving concomitant MTX therapy at baseline.
| Placebo N=162 | HUMIRA*
N=151 |
|
| ACR20
Week 12 Week 24 |
14% 15% |
58% 57% |
| ACR50
Week 12 Week 24 |
4% 6% |
36% 39% |
| ACR70
Week 12 Week 24 |
1% 1% |
20% 23% |
| * p<0.001 for all comparisons between HUMIRA and placebo | ||
| Placebo N=162 | HUMIRA*
N=151 |
|||
| Parameter: median | Baseline | 24 weeks | Baseline | 24 weeks |
| Number of tender jointsa | 23.0 | 17.0 | 20.0 | 5.0 |
| Number of swollen jointsb | 11.0 | 9.0 | 11.0 | 3.0 |
| Physician global assessmentc | 53.0 | 49.0 | 55.0 | 16.0 |
| Patient global assessmentc | 49.5 | 49.0 | 48.0 | 20.0 |
| Painc | 49.0 | 49.0 | 54.0 | 20.0 |
| Disability index (HAQ) d | 1.0 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| CRP (mg/dL)e | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| * p<0.001 for HUMIRA vs. placebo comparisons based on median changes a Scale 0-78 b Scale 0-76 c Visual analog scale; 0=best, 100=worst d Disability Index of the Health Assessment Questionnaire; 0=best, 3=worst; measures the patient’s ability to perform the following: dress/groom, arise, eat, walk, reach, grip, maintain hygiene, and maintain daily activity. e Normal range: 0-0.287 mg/dL |
||||
Similar results were seen in an additional, 12-week study in 100 patients with moderate to severe psoriatic arthritis who had suboptimal response to DMARD therapy as manifested by ≥3 tender joints and ≥3 swollen joints at enrollment.
Radiographic Response
Radiographic changes were assessed in the PsA studies. Radiographs of hands, wrists, and feet were obtained at baseline and Week 24 during the double-blind period when patients were on HUMIRA or placebo and at Week 48 when all patients were on open-label HUMIRA. A modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS), which included distal interphalangeal joints (i.e., not identical to the TSS used for rheumatoid arthritis), was used by readers blinded to treatment group to assess the radiographs.
HUMIRA-treated patients demonstrated greater inhibition of radiographic progression compared to placebo-treated patients and this effect was maintained at 48 weeks (see Table 10).
| Placebo
N=141 | HUMIRA
N=133 |
||
| Week 24 | Week 24 | Week 48 | |
| Baseline mean | 22.1 | 23.4 | 23.4 |
| Mean Change ± SD | 0.9 ± 3.1 | -0.1 ± 1.7 | -0.2 ± 4.9* |
| * <0.001 for the difference between HUMIRA, Week 48 and Placebo, Week 24 (primary analysis) | |||
Physical Function Response
In Study PsA-I, physical function and disability were assessed using the HAQ Disability Index (HAQ-DI) and the SF-36 Health Survey. Patients treated with 40 mg of HUMIRA every other week showed greater improvement from baseline in the HAQ-DI score (mean decreases of 47% and 49% at Weeks 12 and 24 respectively) in comparison to placebo (mean decreases of 1% and 3% at Weeks 12 and 24 respectively). At Weeks 12 and 24, patients treated with HUMIRA showed greater improvement from baseline in the SF-36 Physical Component Summary score compared to patients treated with placebo, and no worsening in the SF-36 Mental Component Summary score. Improvement in physical function based on the HAQ-DI was maintained for up to 84 weeks through the open-label portion of the study.
14.4 Ankylosing Spondylitis
The safety and efficacy of HUMIRA 40 mg every other week was assessed in 315 adult patients in a randomized, 24 week double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) who had an inadequate response to glucocorticoids, NSAIDs, analgesics, methotrexate or sulfasalazine. Active AS was defined as patients who fulfilled at least two of the following three criteria: (1) a Bath AS disease activity index (BASDAI) score ≥4 cm, (2) a visual analog score (VAS) for total back pain ≥ 40 mm, and (3) morning stiffness ≥ 1 hour. The blinded period was followed by an open-label period during which patients received HUMIRA 40 mg every other week subcutaneously for up to an additional 28 weeks.
Improvement in measures of disease activity was first observed at Week 2 and maintained through 24 weeks as shown in Figure 2 and Table 11.
Responses of patients with total spinal ankylosis (n=11) were similar to those without total ankylosis.
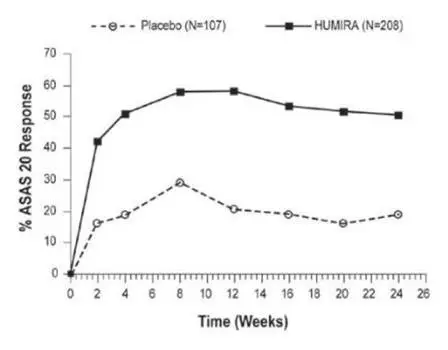
Figure 2. ASAS 20 Response By Visit, Study AS-I
At 12 weeks, the ASAS 20/50/70 responses were achieved by 58%, 38%, and 23%, respectively, of patients receiving HUMIRA, compared to 21%, 10%, and 5% respectively, of patients receiving placebo (p <0.001). Similar responses were seen at Week 24 and were sustained in patients receiving open-label HUMIRA for up to 52 weeks.
A greater proportion of patients treated with HUMIRA (22%) achieved a low level of disease activity at 24 weeks (defined as a value <20 [on a scale of 0 to 100 mm] in each of the four ASAS response parameters) compared to patients treated with placebo (6%).
| Placebo N=107 | HUMIRA N=208 |
|||
| Baseline mean | Week 24 mean | Baseline mean | Week 24 mean | |
| ASAS 20 Response Criteria* | ||||
| Patient’s Global Assessment of Disease Activitya* | 65 | 60 | 63 | 38 |
| Total back pain* | 67 | 58 | 65 | 37 |
| Inflammationb* | 6.7 | 5.6 | 6.7 | 3.6 |
| BASFIc* | 56 | 51 | 52 | 34 |
| BASDAId score* | 6.3 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 3.7 |
| BASMIe score* | 4.2 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 3.3 |
| Tragus to wall (cm) | 15.9 | 15.8 | 15.8 | 15.4 |
| Lumbar flexion (cm) | 4.1 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 4.4 |
| Cervical rotation (degrees) | 42.2 | 42.1 | 48.4 | 51.6 |
| Lumbar side flexion (cm) | 8.9 | 9.0 | 9.7 | 11.7 |
| Intermalleolar distance (cm) | 92.9 | 94.0 | 93.5 | 100.8 |
| CRPf* | 2.2 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 0.6 |
| a Percent of subjects with at least a 20% and 10-unit improvement measured on a Visual Analog Scale (VAS) with 0 = “none” and 100 = “severe” b mean of questions 5 and 6 of BASDAI (defined in ‘d’) c Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index d Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index e Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index f C-Reactive Protein (mg/dL) * statistically significant for comparisons between HUMIRA and placebo at Week 24 |
||||
A second randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 82 patients with ankylosing spondylitis showed similar results.
Patients treated with HUMIRA achieved improvement from baseline in the Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life Questionnaire (ASQoL) score (-3.6 vs. -1.1) and in the Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) Physical Component Summary (PCS) score (7.4 vs. 1.9) compared to placebo-treated patients at Week 24.
14.5 Adult Crohn’s Disease
The safety and efficacy of multiple doses of HUMIRA were assessed in adult patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease, CD, (Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (CDAI) ≥ 220 and ≤ 450) in randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies. Concomitant stable doses of aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, and/or immunomodulatory agents were permitted, and 79% of patients continued to receive at least one of these medications.
Induction of clinical remission (defined as CDAI < 150) was evaluated in two studies. In Study CD-I, 299 TNF-blocker naïve patients were randomized to one of four treatment groups: the placebo group received placebo at Weeks 0 and 2, the 160/80 group received 160 mg HUMIRA at Week 0 and 80 mg at Week 2, the 80/40 group received 80 mg at Week 0 and 40 mg at Week 2, and the 40/20 group received 40 mg at Week 0 and 20 mg at Week 2. Clinical results were assessed at Week 4.
In the second induction study, Study CD-II, 325 patients who had lost response to, or were intolerant to, previous infliximab therapy were randomized to receive either 160 mg HUMIRA at Week 0 and 80 mg at Week 2, or placebo at Weeks 0 and 2. Clinical results were assessed at Week 4.
Maintenance of clinical remission was evaluated in Study CD-III. In this study, 854 patients with active disease received open-label HUMIRA, 80 mg at week 0 and 40 mg at Week 2. Patients were then randomized at Week 4 to 40 mg HUMIRA every other week, 40 mg HUMIRA every week, or placebo. The total study duration was 56 weeks. Patients in clinical response (decrease in CDAI ≥70) at Week 4 were stratified and analyzed separately from those not in clinical response at Week 4.
Induction of Clinical Remission
A greater percentage of the patients treated with 160/80 mg HUMIRA achieved induction of clinical remission versus placebo at Week 4 regardless of whether the patients were TNF blocker naïve (CD-I), or had lost response to or were intolerant to infliximab (CD-II) (see Table 12).
| CD-I | CD-II | |||
| Placebo
N=74 | HUMIRA 160/80 mg
N=76 | Placebo
N=166 | HUMIRA 160/80 mg
N=159 |
|
| Week 4 | ||||
| Clinical remission | 12% | 36%* | 7% | 21%* |
| Clinical response | 34% | 58%** | 34% | 52%** |
| Clinical remission is CDAI score < 150; clinical response is decrease in CDAI of at least 70 points. * p<0.001 for HUMIRA vs. placebo pairwise comparison of proportions ** p<0.01 for HUMIRA vs. placebo pairwise comparison of proportions |
||||
Maintenance of Clinical Remission
In Study CD-III at Week 4, 58% (499/854) of patients were in clinical response and were assessed in the primary analysis. At Weeks 26 and 56, greater proportions of patients who were in clinical response at Week 4 achieved clinical remission in the HUMIRA 40 mg every other week maintenance group compared to patients in the placebo maintenance group (see Table 13). The group that received HUMIRA therapy every week did not demonstrate significantly higher remission rates compared to the group that received HUMIRA every other week.
| Placebo | 40 mg HUMIRA
every other week |
|
| N=170 | N=172 | |
| Week 26 | ||
| Clinical remission | 17% | 40%* |
| Clinical response | 28% | 54%* |
| Week 56 | ||
| Clinical remission | 12% | 36%* |
| Clinical response | 18% | 43%* |
| Clinical remission is CDAI score < 150; clinical response is decrease in CDAI of at least 70 points. *p<0.001 for HUMIRA vs. placebo pairwise comparisons of proportions |
||
Of those in response at Week 4 who attained remission during the study, patients in the HUMIRA every other week group maintained remission for a longer time than patients in the placebo maintenance group. Among patients who were not in response by Week 12, therapy continued beyond 12 weeks did not result in significantly more responses.
14.6 Pediatric Crohn’s Disease
A randomized, double-blind, 52-week clinical study of 2 dose concentrations of HUMIRA (Study PCD-I) was conducted in 192 pediatric patients (6 to 17 years of age) with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease (defined as Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (PCDAI) score > 30). Enrolled patients had over the previous two year period an inadequate response to corticosteroids or an immunomodulator (i.e., azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, or methotrexate). Patients who had previously received a TNF blocker were allowed to enroll if they had previously had loss of response or intolerance to that TNF blocker.
Patients received open-label induction therapy at a dose based on their body weight (≥40 kg and <40 kg). Patients weighing ≥40 kg received 160 mg (at Week 0) and 80 mg (at Week 2). Patients weighing <40 kg received 80 mg (at Week 0) and 40 mg (at Week 2). At Week 4, patients within each body weight category (≥40 kg and <40 kg) were randomized 1:1 to one of two maintenance dose regimens (high dose and low dose). The high dose was 40 mg every other week for patients weighing ≥40 kg and 20 mg every other week for patients weighing <40 kg. The low dose was 20 mg every other week for patients weighing ≥40 kg and 10 mg every other week for patients weighing <40 kg.
Concomitant stable dosages of corticosteroids (prednisone dosage ≤40 mg/day or equivalent) and immunomodulators (azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, or methotrexate) were permitted throughout the study.
At Week 12, patients who experienced a disease flare (increase in PCDAI of ≥ 15 from Week 4 and absolute PCDAI > 30) or who were non-responders (did not achieve a decrease in the PCDAI of ≥ 15 from baseline for 2 consecutive visits at least 2 weeks apart) were allowed to dose-escalate (i.e., switch from blinded every other week dosing to blinded every week dosing); patients who dose-escalated were considered treatment failures.
At baseline, 38% of patients were receiving corticosteroids, and 62% of patients were receiving an immunomodulator. Forty-four percent (44%) of patients had previously lost response or were intolerant to a TNF blocker. The median baseline PCDAI score was 40.
Of the 192 patients total, 188 patients completed the 4 week induction period, 152 patients completed 26 weeks of treatment, and 124 patients completed 52 weeks of treatment. Fifty-one percent (51%) (48/95) of patients in the low maintenance dose group dose-escalated, and 38% (35/93) of patients in the high maintenance dose group dose-escalated.
At Week 4, 28% (52/188) of patients were in clinical remission (defined as PCDAI ≤ 10).
The proportions of patients in clinical remission (defined as PCDAI ≤ 10) and clinical response (defined as reduction in PCDAI of at least 15 points from baseline) were assessed at Weeks 26 and 52.
At both Weeks 26 and 52, the proportion of patients in clinical remission and clinical response was numerically higher in the high dose group compared to the low dose group (Table 14). The recommended maintenance regimen is 20 mg every other week for patients weighing < 40 kg and 40 mg every other week for patients weighing ≥ 40 kg. Every week dosing is not the recommended maintenance dosing regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
| Low Maintenance Dose†
(20 or 10 mg every other week) N = 95 | High Maintenance Dose#
(40 or 20 mg every other week) N = 93 |
|
| Week 26 | ||
| Clinical Remission‡ | 28% | 39% |
| Clinical Response§ | 48% | 59% |
| Week 52 | ||
| Clinical Remission‡ | 23% | 33% |
| Clinical Response§ | 28% | 42% |
| †The low maintenance dose was 20 mg every other week for patients weighing ≥ 40 kg and 10 mg every other week for patients weighing < 40 kg. #The high maintenance dose was 40 mg every other week for patients weighing ≥ 40 kg and 20 mg every other week for patients weighing < 40 kg. ‡Clinical remission defined as PCDAI ≤ 10. §Clinical response defined as reduction in PCDAI of at least 15 points from baseline. |
||
14.7 Adult Ulcerative Colitis
The safety and efficacy of HUMIRA were assessed in adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (Mayo score 6 to 12 on a 12 point scale, with an endoscopy subscore of 2 to 3 on a scale of 0 to 3) despite concurrent or prior treatment with immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids, azathioprine, or 6-MP in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies (Studies UC-I and UC-II). Both studies enrolled TNF-blocker naïve patients, but Study UC-II also allowed entry of patients who lost response to or were intolerant to TNF-blockers. Forty percent (40%) of patients enrolled in Study UC-II had previously used another TNF-blocker.
Concomitant stable doses of aminosalicylates and immunosuppressants were permitted. In Studies UC-I and II, patients were receiving aminosalicylates (69%), corticosteroids (59%) and/or azathioprine or 6-MP (37%) at baseline. In both studies, 92% of patients received at least one of these medications.
Induction of clinical remission (defined as Mayo score ≤ 2 with no individual subscores > 1) at Week 8 was evaluated in both studies. Clinical remission at Week 52 and sustained clinical remission (defined as clinical remission at both Weeks 8 and 52) were evaluated in Study UC-II.
In Study UC-I, 390 TNF-blocker naïve patients were randomized to one of three treatment groups for the primary efficacy analysis. The placebo group received placebo at Weeks 0, 2, 4 and 6. The 160/80 group received 160 mg HUMIRA at Week 0 and 80 mg at Week 2, and the 80/40 group received 80 mg HUMIRA at Week 0 and 40 mg at Week 2. After Week 2, patients in both HUMIRA treatment groups received 40 mg every other week.
In Study UC-II, 518 patients were randomized to receive either HUMIRA 160 mg at Week 0, 80 mg at Week 2, and 40 mg every other week starting at Week 4 through Week 50, or placebo starting at Week 0 and every other week through Week 50. Corticosteroid taper was permitted starting at Week 8.
In both Studies UC-I and UC-II, a greater percentage of the patients treated with 160/80 mg of HUMIRA compared to patients treated with placebo achieved induction of clinical remission. In Study UC-II, a greater percentage of the patients treated with 160/80 mg of HUMIRA compared to patients treated with placebo achieved sustained clinical remission (clinical remission at both Weeks 8 and 52) (Table 15).
| Study UC-I | Study UC-II | |||||
| Placebo
N=130 | HUMIRA 160/80 mg N=130 | Treatment Difference
(95% CI) | Placebo
N=246 | HUMIRA
160/80 mg N=248 | Treatment Difference
(95% CI) |
|
| Induction of Clinical Remission (Clinical Remission at Week 8) | 9.2% | 18.5% | 9.3%* (0.9%, 17.6%) | 9.3% | 16.5% | 7.2%* (1.2%, 12.9%) |
| Sustained Clinical Remission (Clinical Remission at both Weeks 8 and 52) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 4.1% | 8.5% | 4.4%* (0.1%, 8.6%) |
| Clinical remission is defined as Mayo score ≤ 2 with no individual subscores > 1. CI=Confidence interval * p<0.05 for HUMIRA vs. placebo pairwise comparison of proportions |
||||||
In Study UC-I, there was no statistically significant difference in clinical remission observed between the HUMIRA 80/40 mg group and the placebo group at Week 8.
In Study UC-II, 17.3% (43/248) in the HUMIRA group were in clinical remission at Week 52 compared to 8.5% (21/246) in the placebo group (treatment difference: 8.8%; 95% confidence interval (CI): [2.8%, 14.5%]; p<0.05).
In the subgroup of patients in Study UC-II with prior TNF-blocker use, the treatment difference for induction of clinical remission appeared to be lower than that seen in the whole study population, and the treatment differences for sustained clinical remission and clinical remission at Week 52 appeared to be similar to those seen in the whole study population. The subgroup of patients with prior TNF-blocker use achieved induction of clinical remission at 9% (9/98) in the HUMIRA group versus 7% (7/101) in the placebo group, and sustained clinical remission at 5% (5/98) in the HUMIRA group versus 1% (1/101) in the placebo group. In the subgroup of patients with prior TNF-blocker use, 10% (10/98) were in clinical remission at Week 52 in the HUMIRA group versus 3% (3/101) in the placebo group.
14.8 Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis
The safety and efficacy of HUMIRA were assessed in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial (Study PUC-I, NCT02065557) in 93 pediatric patients 5 years to 17 years of age with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (Mayo score 6 to 12 with endoscopy subscore of 2 to 3 points, confirmed by centrally read endoscopy) who had an inadequate response or intolerance to therapy with corticosteroids and/or an immunomodulator (i.e., azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, or methotrexate). Fifteen out of 93 patients (16%) in the study had prior experience with a TNF blocker. Patients who received corticosteroids at enrollment were allowed to taper their corticosteroid therapy after Week 4.
Seventy-seven patients were initially randomized 3:2 to receive double-blind treatment with one of two dosages of HUMIRA. Patients in both dosage groups received 2.4 mg/kg (maximum of 160 mg) at Week 0, 1.2 mg/kg (maximum of 80 mg) at Week 2, and 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) at Weeks 4 and 6. The higher dosage group also received an additional dosage of 2.4 mg/kg (maximum of 160 mg) at Week 1. Following an amendment to the study design, 16 additional patients were enrolled and received open-label treatment with HUMIRA at the higher dosage.
At Week 8, 62 patients who demonstrated clinical response per Partial Mayo Score (PMS; a subset of the Mayo score with no endoscopic component and defined as a decrease in PMS ≥ 2 points and ≥ 30% from baseline) were randomized equally to receive double-blind treatment with HUMIRA 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) every other week (lower dosage group), or 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) every week (higher dosage group). Prior to an amendment to the study design, 12 additional patients who demonstrated clinical response per PMS were randomized to receive placebo.
There are no anticipated clinically relevant differences in efficacy between the studied higher dosage administered during the 52-week PUC-I trial and the recommended dosage of HUMIRA [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Patients who met criteria for disease flare at or after Week 12 were randomized to receive a re-induction dose of 2.4 mg/kg (maximum of 160 mg) or a dose of 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) and then continued the dose to which they were randomized at Week 8.
The co-primary endpoints of the study were clinical remission per PMS (defined as PMS ≤ 2 and no individual subscore > 1) at Week 8, and clinical remission per the Mayo Score (defined as Mayo Score ≤ 2 and no individual subscore > 1) at Week 52 in patients who achieved clinical response per PMS at Week 8. Secondary endpoints included Mayo Score response (defined as a decrease in Mayo Score of ≥ 3 points and ≥ 30% from baseline) at Week 52 in Week 8 PMS responders, endoscopic improvement (defined as a Mayo endoscopy subscore ≤ 1) at Week 52 in Week 8 PMS responders, and Mayo Score remission at Week 52 in Week 8 PMS remitters.
Week 8 Results
At Week 8, PMS remission was achieved by 60% [28/47; 95% confidence interval (CI): (44%, 74%)] of patients in the higher dosage group (not including the 16 patients receiving open-label higher dosage) and 43% [13/30; 95% CI: (25%, 63%)] of patients in the lower dosage group. Results from the higher dosage group are representative of the results expected with the recommended dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Week 52 Results
At Week 52, endpoints were assessed in the population of patients who received double-blind placebo, HUMIRA 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) every other week, or HUMIRA 0.6 mg/kg (maximum of 40 mg) every week between Week 8 and Week 52 (Table 16).
|
| Placeboa
n/N (%), 95% CI | HUMIRA
Maximum of 40 mg (0.6 mg/kg) every other weekb n/N (%), 95% CI | HUMIRA
Maximum of 40 mg (0.6 mg/kg) every weekc n/N (%), 95% CI |
| Clinical remission in Week 8 PMS responders | 4/12 (33%) (10%, 65%) | 9/31 (29%) (14%, 48%) | 14/31 (45%) (27%, 64%) |
| Clinical response in Week 8 PMS responders | 4/12 (33%) (10%, 65%) | 19/31 (61%) (42%, 78%) | 21/31 (68%) (49%, 83%) |
| Endoscopic improvement in Week 8 PMS responders | 4/12 (33%) (10%, 65%) | 12/31 (39%) (22%, 58%) | 16/31 (52%) (33%, 70%) |
| Clinical remission in Week 8 PMS remitters | 3/8 (38%) (9%, 76%) | 9/21 (43%) (22%, 66%) | 10/22 (45%) (24%, 68%) |
| CI=Confidence interval a Twelve patients who demonstrated clinical response per PMS at Week 8 were randomized to receive placebo. There are limitations to the interpretability of the placebo data due to the small sample size. b The every other week dosage studied during the 52-week PUC-I trial is a lower dosage than the recommended dosage of HUMIRA [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. c There are no anticipated clinically relevant differences in efficacy between the studied higher dosage administered during the 52-week PUC-I trial and the recommended dosage of HUMIRA. Note: Patients with missing values at Week 52 or who were randomized to receive re-induction or maintenance treatment due to disease flare were considered non-responders for Week 52 endpoints. |
|||
14.9 Plaque Psoriasis
The safety and efficacy of HUMIRA were assessed in randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in 1696 adult subjects with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis (Ps) who were candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
Study Ps-I evaluated 1212 subjects with chronic Ps with ≥10% body surface area (BSA) involvement, Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) of at least moderate disease severity, and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) ≥12 within three treatment periods. In period A, subjects received placebo or HUMIRA at an initial dose of 80 mg at Week 0 followed by a dose of 40 mg every other week starting at Week 1. After 16 weeks of therapy, subjects who achieved at least a PASI 75 response at Week 16, defined as a PASI score improvement of at least 75% relative to baseline, entered period B and received open-label 40 mg HUMIRA every other week. After 17 weeks of open label therapy, subjects who maintained at least a PASI 75 response at Week 33 and were originally randomized to active therapy in period A were re-randomized in period C to receive 40 mg HUMIRA every other week or placebo for an additional 19 weeks. Across all treatment groups the mean baseline PASI score was 19 and the baseline Physician’s Global Assessment score ranged from “moderate” (53%) to “severe” (41%) to “very severe” (6%).
Study Ps-II evaluated 99 subjects randomized to HUMIRA and 48 subjects randomized to placebo with chronic plaque psoriasis with ≥10% BSA involvement and PASI ≥12. Subjects received placebo, or an initial dose of 80 mg HUMIRA at Week 0 followed by 40 mg every other week starting at Week 1 for 16 weeks. Across all treatment groups the mean baseline PASI score was 21 and the baseline PGA score ranged from “moderate” (41%) to “severe” (51%) to “very severe” (8%).
Studies Ps-I and II evaluated the proportion of subjects who achieved “clear” or “minimal” disease on the 6-point PGA scale and the proportion of subjects who achieved a reduction in PASI score of at least 75% (PASI 75) from baseline at Week 16 (see Table 17 and 18).
Additionally, Study Ps-I evaluated the proportion of subjects who maintained a PGA of “clear” or “minimal” disease or a PASI 75 response after Week 33 and on or before Week 52.
| HUMIRA 40 mg every other week | Placebo | |
| N = 814 | N = 398 | |
| PGA: Clear or minimal* | 506 (62%) | 17 (4%) |
| PASI 75 | 578 (71%) | 26 (7%) |
| * Clear = no plaque elevation, no scale, plus or minus hyperpigmentation or diffuse pink or red coloration Minimal = possible but difficult to ascertain whether there is slight elevation of plaque above normal skin, plus or minus surface dryness with some white coloration, plus or minus up to red coloration |
||
| HUMIRA 40 mg every other week | Placebo | |
| N = 99 | N = 48 | |
| PGA: Clear or minimal* | 70 (71%) | 5 (10%) |
| PASI 75 | 77 (78%) | 9 (19%) |
| * Clear = no plaque elevation, no scale, plus or minus hyperpigmentation or diffuse pink or red coloration Minimal = possible but difficult to ascertain whether there is slight elevation of plaque above normal skin, plus or minus surface dryness with some white coloration, plus or minus up to red coloration |
||
Additionally, in Study Ps-I, subjects on HUMIRA who maintained a PASI 75 were re-randomized to HUMIRA (N = 250) or placebo (N = 240) at Week 33. After 52 weeks of treatment with HUMIRA, more subjects on HUMIRA maintained efficacy when compared to subjects who were re-randomized to placebo based on maintenance of PGA of “clear” or “minimal” disease (68% vs. 28%) or a PASI 75 (79% vs. 43%).
A total of 347 stable responders participated in a withdrawal and retreatment evaluation in an open-label extension study. Median time to relapse (decline to PGA “moderate” or worse) was approximately 5 months. During the withdrawal period, no subject experienced transformation to either pustular or erythrodermic psoriasis. A total of 178 subjects who relapsed re-initiated treatment with 80 mg of HUMIRA, then 40 mg every other week beginning at week 1. At week 16, 69% (123/178) of subjects had a response of PGA “clear” or “minimal”.
A randomized, double-blind study (Study Ps-III) compared the efficacy and safety of HUMIRA versus placebo in 217 adult subjects. Subjects in the study had to have chronic plaque psoriasis of at least moderate severity on the PGA scale, fingernail involvement of at least moderate severity on a 5-point Physician’s Global Assessment of Fingernail Psoriasis (PGA-F) scale, a Modified Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (mNAPSI) score for the target-fingernail of ≥ 8, and either a BSA involvement of at least 10% or a BSA involvement of at least 5% with a total mNAPSI score for all fingernails of ≥ 20. Subjects received an initial dose of 80 mg HUMIRA followed by 40 mg every other week (starting one week after the initial dose) or placebo for 26 weeks followed by open-label HUMIRA treatment for an additional 26 weeks. This study evaluated the proportion of subjects who achieved “clear” or “minimal” assessment with at least a 2-grade improvement on the PGA-F scale and the proportion of subjects who achieved at least a 75% improvement from baseline in the mNAPSI score (mNAPSI 75) at Week 26.
At Week 26, a higher proportion of subjects in the HUMIRA group than in the placebo group achieved the PGA-F endpoint. Furthermore, a higher proportion of subjects in the HUMIRA group than in the placebo group achieved mNAPSI 75 at Week 26 (see Table 19).
| Endpoint | HUMIRA 40 mg every other week* N=109 | Placebo N=108 |
| PGA-F: ≥2-grade improvement and clear or minimal | 49% | 7% |
| mNAPSI 75 | 47% | 3% |
| *Subjects received 80 mg of HUMIRA at Week 0, followed by 40 mg every other week starting at Week 1. | ||
Nail pain was also evaluated and improvement in nail pain was observed in Study Ps-III.
14.10 Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (Studies HS-I and II) evaluated the safety and efficacy of HUMIRA in a total of 633 adult subjects with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) with Hurley Stage II or III disease and with at least 3 abscesses or inflammatory nodules. In both studies, subjects received placebo or HUMIRA at an initial dose of 160 mg at Week 0, 80 mg at Week 2, and 40 mg every week starting at Week 4 and continued through Week 11. Subjects used topical antiseptic wash daily. Concomitant oral antibiotic use was allowed in Study HS-II.
Both studies evaluated Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) at Week 12. HiSCR was defined as at least a 50% reduction in total abscess and inflammatory nodule count with no increase in abscess count and no increase in draining fistula count relative to baseline (see Table 18). Reduction in HS-related skin pain was assessed using a Numeric Rating Scale in patients who entered the study with an initial baseline score of 3 or greater on a 11 point scale.
In both studies, a higher proportion of HUMIRA- than placebo-treated subjects achieved HiSCR (see Table 20).
| HS Study I | HS Study II* | |||
| Placebo | Humira 40 mg Weekly | Placebo | Humira 40 mg Weekly | |
| Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) | N = 154 40 (26%) | N = 153 64 (42%) | N=163 45 (28%) | N=163 96 (59%) |
| *19.3% of subjects in Study HS-II continued baseline oral antibiotic therapy during the study. | ||||
In both studies, from Week 12 to Week 35 (Period B), subjects who had received HUMIRA were re-randomized to 1 of 3 treatment groups (HUMIRA 40 mg every week, HUMIRA 40 mg every other week, or placebo). Subjects who had been randomized to placebo were assigned to receive HUMIRA 40 mg every week (Study HS-I) or placebo (Study HS-II).
During Period B, flare of HS, defined as ≥25% increase from baseline in abscesses and inflammatory nodule counts and with a minimum of 2 additional lesions, was documented in 22 (22%) of the 100 subjects who were withdrawn from HUMIRA treatment following the primary efficacy timepoint in two studies.
14.11 Adult Uveitis
The safety and efficacy of HUMIRA were assessed in adult patients with non-infectious intermediate, posterior and panuveitis excluding patients with isolated anterior uveitis, in two randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled studies (UV I and II). Patients received placebo or HUMIRA at an initial dose of 80 mg followed by 40 mg every other week starting one week after the initial dose. The primary efficacy endpoint in both studies was ´time to treatment failure´.
Treatment failure was a multi-component outcome defined as the development of new inflammatory chorioretinal and/or inflammatory retinal vascular lesions, an increase in anterior chamber (AC) cell grade or vitreous haze (VH) grade or a decrease in best corrected visual acuity (BCVA).
Study UV I evaluated 217 patients with active uveitis while being treated with corticosteroids (oral prednisone at a dose of 10 to 60 mg/day). All patients received a standardized dose of prednisone 60 mg/day at study entry followed by a mandatory taper schedule, with complete corticosteroid discontinuation by Week 15.
Study UV II evaluated 226 patients with inactive uveitis while being treated with corticosteroids (oral prednisone 10 to 35 mg/day) at baseline to control their disease. Patients subsequently underwent a mandatory taper schedule, with complete corticosteroid discontinuation by Week 19.
Clinical Response
Results from both studies demonstrated statistically significant reduction of the risk of treatment failure in patients treated with HUMIRA versus patients receiving placebo. In both studies, all components of the primary endpoint contributed cumulatively to the overall difference between HUMIRA and placebo groups (Table 21).
| UV I | UV II | |||||
| Placebo (N = 107) | HUMIRA (N = 110) | HR [95% CI]a | Placebo (N = 111) | HUMIRA (N = 115) | HR [95% CI]a |
|
| Failureb n (%) | 84 (78.5) | 60 (54.5) | 0.50 [0.36, 0.70] | 61 (55.0) | 45 (39.1) | 0.57 [0.39, 0.84] |
| Median Time to Failure (Months) [95% CI] | 3.0 [2.7, 3.7] | 5.6 [3.9, 9.2] | N/A | 8.3 [4.8, 12.0] | NEc | N/A |
| ª HR of HUMIRA versus placebo from proportional hazards regression with treatment as factor. b Treatment failure at or after Week 6 in Study UV I, or at or after Week 2 in Study UV II, was counted as event. Subjects who discontinued the study were censored at the time of dropping out. c NE = not estimable. Fewer than half of at-risk subjects had an event. |
||||||
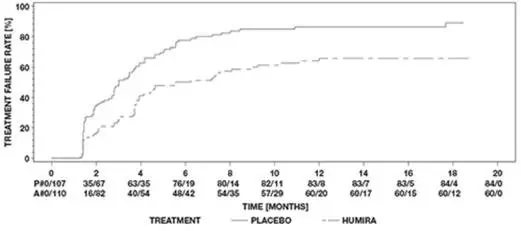
Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier Curves Summarizing Time to Treatment Failure on or after Week 6 (Study UV I) or Week 2 (Study UV II)
Study UV I
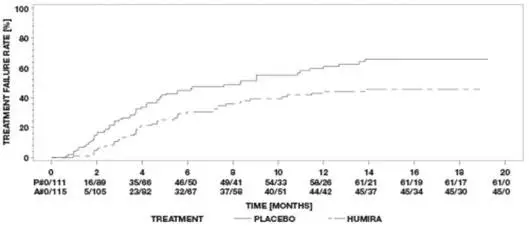
Study UV II
Note: P# = Placebo (Number of Events/Number at Risk); A# = HUMIRA (Number of Events/Number at Risk).
14.12 Pediatric Uveitis
The safety and efficacy of HUMIRA were assessed in a randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled study of 90 pediatric patients from 2 to < 18 years of age with active JIA-associated non-infectious uveitis (PUV-I). Patients received either placebo or 20 mg adalimumab (if < 30 kg) or 40 mg adalimumab (if ≥ 30 kg) every other week in combination with a dose of methotrexate. Concomitant dosages of corticosteroids were permitted at study entry followed by a mandatory reduction in topical corticosteroids within 3 months.
The primary endpoint was ‘time to treatment failure’. The criteria determining treatment failure were worsening or sustained non-improvement in ocular inflammation, or worsening of ocular co-morbidities.
Clinical Response
HUMIRA significantly decreased the risk of treatment failure by 75% relative to placebo (HR = 0.25 [95% CI: 0.12, 0.49]) (Table 22).
| Placebo
(N=30) | HUMIRA
(N=60) | HR (95% CI)ª | |
| Failure (n[%]) | 18 (60%) | 16 (26.7%) | 0.25 (0.12, 0.49) |
| Median Time to
Failure (Weeks) (95% CI)ᵇ | 24.1 (12.4, 81.0) | NEᶜ | |
| a HR of adalimumab versus placebo from proportional hazards regression with treatment as factor. b Estimated based on Kaplan-Meier curve. c NE = not estimable. Fewer than half of at-risk subjects had an event. |
|||
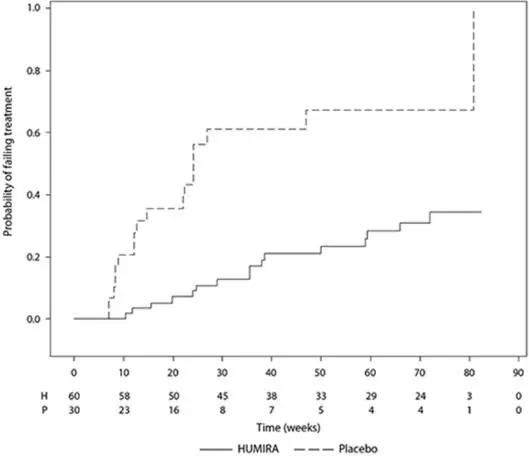
Figure 4: Kaplan-Meier Curves Summarizing Time to Treatment Failure (Study PUV-I)
Study PUV-I
Note: P = Placebo (Number at Risk); H = HUMIRA (Number at Risk).
16. How is Humira supplied
HUMIRA® (adalimumab) is supplied as a preservative-free, sterile, clear and colorless solution for subcutaneous administration. The following packaging configurations are available.
-
HUMIRA Pen Carton - 40 mg/0.8 mL
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing two alcohol preps and two dose trays. Each dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The needle cover may contain natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-4339-02.
-
HUMIRA Pen Carton - 40 mg/0.4 mL
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing two alcohol preps and two dose trays. Each dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.4 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0554-02.
-
HUMIRA Pen Carton – 80 mg/0.8 mL
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing two alcohol preps and two dose trays. Each dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 80 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0124-02.
-
HUMIRA Pen 40 mg/0.8 mL - Starter Package for Crohn's Disease, Ulcerative Colitis or Hidradenitis Suppurativa
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 6 alcohol preps and 6 dose trays (Starter Package for Crohn’s Disease, Ulcerative Colitis or Hidradenitis Suppurativa). Each dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The needle cover may contain natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-4339-06.
-
HUMIRA Pen 40 mg/0.4 mL - Starter Package for Crohn's Disease, Ulcerative Colitis or Hidradenitis Suppurativa
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 6 alcohol preps and 6 dose trays (Starter Package for Crohn’s Disease, Ulcerative Colitis or Hidradenitis Suppurativa). Each dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.4 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0554-06.
-
HUMIRA Pen 80 mg/0.8 mL - Starter Package for Crohn's Disease, Ulcerative Colitis or Hidradenitis Suppurativa
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 4 alcohol preps and 3 dose trays (Starter Package for Crohn’s Disease, Ulcerative Colitis or Hidradenitis Suppurativa). Each dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 80 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0124-03.
-
HUMIRA Pen 40 mg/0.8 mL - Psoriasis, Uveitis or Adolescent Hidradenitis Suppurativa Starter Package
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 4 alcohol preps and 4 dose trays (Psoriasis, Uveitis or Adolescent Hidradenitis Suppurativa Starter Package). Each dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The needle cover may contain natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-4339-07.
-
HUMIRA Pen 40 mg/0.4 mL - Psoriasis, Uveitis or Adolescent Hidradenitis Suppurativa Starter Package
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 4 alcohol preps and 4 dose trays (Psoriasis, Uveitis or Adolescent Hidradenitis Suppurativa Starter Package). Each dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.4 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0554-04.
-
HUMIRA Pen 80 mg/0.8 mL and 40 mg/0.4 mL - Psoriasis, Uveitis or Adolescent Hidradenitis Suppurativa Starter Package
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 4 alcohol preps and 3 dose trays (Psoriasis, Uveitis or Adolescent Hidradenitis Suppurativa Starter Package). One dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 80 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The other two dose trays each consist of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.4 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-1539-03.
-
HUMIRA Pen 80 mg/0.8 mL – Starter Package for Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis (4 count)
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 4 alcohol preps and 4 dose trays (Starter Package for Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis). Each dose tray consists of a single-dose pen, containing a 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 80 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0124-04.
-
Prefilled Syringe Carton - 40 mg/0.8 mL
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing two alcohol preps and two dose trays. Each dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The needle cover may contain natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-3799-02.
-
Prefilled Syringe Carton - 40 mg/0.4 mL
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing two alcohol preps and two dose trays. Each dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.4 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0243-02.
-
Prefilled Syringe Carton - 20 mg/0.4 mL
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing two alcohol preps and two dose trays. Each dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed ½ inch needle, providing 20 mg/0.4 mL of HUMIRA. The needle cover may contain natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-9374-02.
-
Prefilled Syringe Carton - 20 mg/0.2 mL
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing two alcohol preps and two dose trays. Each dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 20 mg/0.2 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0616-02.
-
Prefilled Syringe Carton - 10 mg/0.2 mL
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing two alcohol preps and two dose trays. Each dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed ½ inch needle, providing 10 mg/0.2 mL of HUMIRA. The needle cover may contain natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-6347-02.
-
Prefilled Syringe Carton - 10 mg/0.1 mL
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing two alcohol preps and two dose trays. Each dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 10 mg/0.1 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0817-02.
-
HUMIRA Prefilled Syringe 40 mg/0.8 mL - Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Starter Package (6 count)
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 6 alcohol preps and 6 dose trays (Pediatric Starter Package). Each dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The needle cover may contain natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-3799-06.
-
HUMIRA Prefilled Syringe 80 mg/0.8 mL - Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Starter Package (3 count)
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 4 alcohol preps and 3 dose trays (Pediatric Starter Package). Each dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 80 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-2540-03.
-
HUMIRA Prefilled Syringe 40 mg/0.8 mL - Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Starter Package (3 count)
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 4 alcohol preps and 3 dose trays (Pediatric Starter Package). Each dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The needle cover may contain natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-3799-03.
-
HUMIRA Prefilled Syringe 80 mg/0.8 mL and 40 mg/0.4 mL - Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Starter Package (2 count)
HUMIRA is supplied in a carton containing 2 alcohol preps and 2 dose trays (Pediatric Starter Package). One dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 80 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The other dose tray consists of a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe with a fixed thin wall, ½ inch needle, providing 40 mg/0.4 mL of HUMIRA. The black needle cover is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-0067-02.
-
Single-Dose Institutional Use Vial Carton - 40 mg/0.8 mL
HUMIRA is supplied for institutional use only in a carton containing a single-dose, glass vial, providing 40 mg/0.8 mL of HUMIRA. The vial stopper is not made with natural rubber latex. The NDC number is 0074-3797-01.
Storage and Stability
Do not use beyond the expiration date on the container. HUMIRA must be refrigerated at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). DO NOT FREEZE. Do not use if frozen even if it has been thawed.
Store in original carton until time of administration to protect from light.
If needed, for example when traveling, HUMIRA may be stored at room temperature up to a maximum of 77°F (25°C) for a period of up to 14 days, with protection from light. HUMIRA should be discarded if not used within the 14-day period. Record the date when HUMIRA is first removed from the refrigerator in the spaces provided on the carton and dose tray.
Do not store HUMIRA in extreme heat or cold.
Medication Guide
| MEDICATION GUIDE
HUMIRA® (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) injection, for subcutaneous use |
||
| Read the Medication Guide that comes with HUMIRA before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or treatment. | ||
| What is the most important information I should know about HUMIRA?
HUMIRA is a medicine that affects your immune system. HUMIRA can lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections. Serious infections have happened in people taking HUMIRA. These serious infections include tuberculosis (TB) and infections caused by viruses, fungi or bacteria that have spread throughout the body. Some people have died from these infections.
Before starting HUMIRA, tell your doctor if you:
|
||
|
|
|
HUMIRA can make you more likely to get infections or make any infection that you may have worse. |
||
Cancer
|
||
| What is HUMIRA?
HUMIRA is a medicine called a Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) blocker. HUMIRA is used:
|
||
| What should I tell my doctor before taking HUMIRA?
HUMIRA may not be right for you. Before starting HUMIRA, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Especially tell your doctor if you use:
|
||
How should I take HUMIRA?
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of HUMIRA?
HUMIRA can cause serious side effects, including: See “What is the most important information I should know about HUMIRA?” |
||
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
| Call your doctor or get medical care right away if you develop any of the above symptoms. Your treatment with HUMIRA may be stopped.
The most common side effects of HUMIRA include:
|
||
| These are not all the possible side effects with HUMIRA. Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
How should I store HUMIRA?
|
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of HUMIRA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use HUMIRA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give HUMIRA to other people, even if they have the same condition. It may harm them. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about HUMIRA. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about HUMIRA that is written for health professionals. |
||
| What are the ingredients in HUMIRA?
Active ingredient: adalimumab HUMIRA Pen 40 mg/0.8 mL, HUMIRA 40 mg/0.8 mL prefilled syringe, HUMIRA 20 mg/0.4 mL prefilled syringe, HUMIRA 10 mg/0.2 mL prefilled syringe, and HUMIRA 40 mg/0.8 mL institutional use vial: Inactive ingredients: citric acid monohydrate, dibasic sodium phosphate dihydrate, mannitol, monobasic sodium phosphate dihydrate, polysorbate 80, sodium chloride, sodium citrate and Water for Injection. Sodium hydroxide is added as necessary to adjust pH. HUMIRA Pen 80 mg/0.8 mL, HUMIRA 80 mg/0.8 mL prefilled syringe, HUMIRA Pen 40 mg/0.4 mL, HUMIRA 40 mg/0.4 mL prefilled syringe, HUMIRA 20 mg/0.2 mL prefilled syringe and HUMIRA 10 mg/0.1 mL prefilled syringe: Inactive ingredients: mannitol, polysorbate 80, and Water for Injection. Manufactured by: AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL 60064, U.S.A. For more information go to www.HUMIRA.com or you can enroll in a patient support program by calling 1-800-4HUMIRA (1-800-448-6472). US License Number 1889 |
||
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 20066566 | Revised: 02/2021 | |
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
HUMIRA® (Hu-MARE-ah)
(adalimumab)
40 MG/0.8 ML
SINGLE-DOSE PEN
Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand this Instructions for Use. If your doctor decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your injections of HUMIRA at home, you should receive training on the right way to prepare and inject HUMIRA. It is important that you read, understand, and follow these instructions so that you inject HUMIRA the right way. It is also important to talk to your doctor to be sure you understand your HUMIRA dosing instructions. To help you remember when to inject HUMIRA, you can mark your calendar ahead of time. Call your healthcare provider if you or your caregiver have any questions about the right way to inject HUMIRA.
IMPORTANT:
- Do not use HUMIRA if frozen, even if it has been thawed.
- The HUMIRA Pen contains glass. Do not drop or crush the Pen because the glass inside may break.
- Each HUMIRA Pen has 2 caps on it. Do not remove the gray cap (Cap #1) or the plum-colored cap (Cap #2) until right before your injection.
- When the plum-colored button on the HUMIRA Pen is pressed to give your dose of HUMIRA, you will hear a loud “click” sound.
● You must practice injecting HUMIRA with your doctor or nurse so that you are not startled by this click when you start giving yourself the injections at home.
● The loud click sound means the start of the injection.
● You will know that the injection has finished when the yellow indicator appears fully in the window view and stops moving.
See the section below called “Preparing the HUMIRA Pen”.
Gather the Supplies for Your Injection
- You will need the following supplies for each injection of HUMIRA.
Find a clean, flat surface to place the supplies on.
● 1 alcohol swab
● 1 cotton ball or gauze pad (not included in your HUMIRA carton)
● 1 HUMIRA Pen (See Figure A)
● Puncture-resistant sharps disposal container for HUMIRA Pen disposal (not included in your HUMIRA carton). See the “How should I throw away (dispose of) the used HUMIRA Pen?” section at the end of this Instructions for Use.
If more comfortable, take your HUMIRA Pen out of the refrigerator 15 to 30 minutes before injecting to allow the liquid to reach room temperature. Do not remove the gray cap (Cap #1) or the plum-colored cap (Cap #2) while allowing it to reach room temperature. Do not warm HUMIRA in any other way (for example, do not warm it in a microwave or in hot water).
If you do not have all the supplies you need to give yourself an injection, go to a pharmacy or call your pharmacist. The figure below shows what the HUMIRA Pen looks like. See Figure A.
Figure A
Check the carton, dose tray, and HUMIRA Pen.
1. Make sure the name HUMIRA appears on the carton, dose tray, and HUMIRA Pen label.
2. Do not use and do call your doctor or pharmacist if:
- you drop or crush your HUMIRA Pen.
- the seals on the top or bottom of the carton are broken or missing.
- the expiration date on the carton, dose tray, and Pen has passed.
- the HUMIRA Pen has been frozen or left in direct sunlight.
- HUMIRA has been kept at room temperature for longer than 14 days or HUMIRA has been stored above 77°F (25°C).
See the “How should I store HUMIRA?” section at the end of this Instructions for Use.
3. Hold the Pen with the gray cap (Cap # 1) pointed down.
4. Make sure the amount of liquid in the Pen is at the fill line or close to the fill line seen through the window. This is the full dose of HUMIRA that you will inject. See Figure B.
5. If the Pen does not have the full amount of liquid, do not use that Pen. Call your pharmacist.
Figure B
6. Turn the Pen over and hold the Pen with the gray cap (Cap # 1) pointed up. See Figure C.
7. Check the solution through the windows on the side of the Pen to make sure the liquid is clear and colorless. Do not use your HUMIRA Pen if the liquid is cloudy, discolored, or if it has flakes or particles in it. Call your pharmacist. It is normal to see one or more bubbles in the window.
Figure C
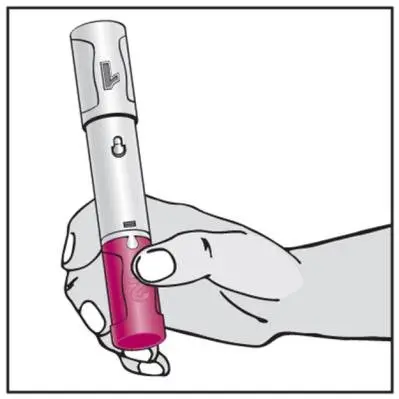
Choose the Injection Site
8. Wash and dry your hands well.
9. Choose an injection site on:
- the front of your thighs or
- your lower abdomen (belly). If you choose your abdomen, do not use the area 2 inches around your belly button (navel). See Figure D.
Figure D
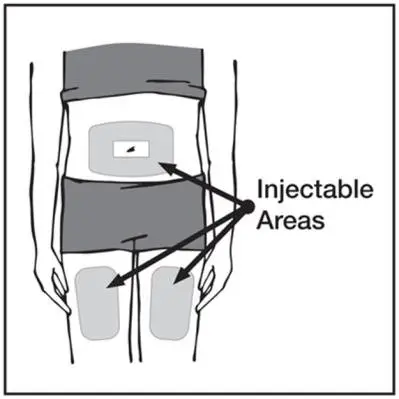
- Choose a different site each time you give yourself an injection. Each new injection should be given at least one inch from a site you used before.
-
Do not inject HUMIRA into skin that is:
● sore (tender)
● bruised
● red
● hard
● scarred or where you have stretch marks
- If you have psoriasis, do not inject directly into any raised, thick, red or scaly skin patches or lesions on your skin.
- Do not inject through your clothes.
Prepare the Injection Site
10. Wipe the injection site with an alcohol prep (swab) using a circular motion.
- Do not touch this area again before giving the injection. Allow the skin to dry before injecting. Do not fan or blow on the clean area.
Preparing the HUMIRA Pen
11. Do not remove the gray cap (Cap # 1) or the plum-colored cap (Cap # 2) until right before your injection.
12. Hold the middle of the Pen (gray body) with one hand so that you are not touching the gray cap (Cap # 1) or the plum-colored cap (Cap # 2). Turn the Pen so that the gray cap (Cap # 1) is pointing up. See Figure E.
Figure E
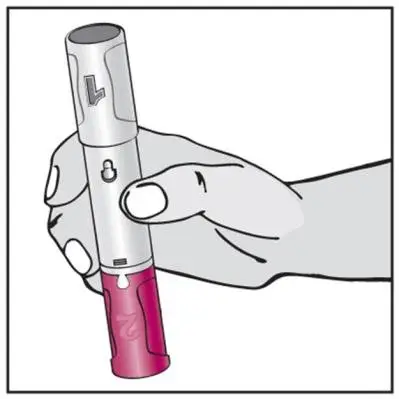
13. With your other hand, pull the gray cap (Cap # 1) straight off (do not twist the cap). Make sure the small needle cover of the syringe has come off with the gray cap (Cap # 1). See Figure F.
14. Throw away the gray cap (Cap # 1).
Figure F
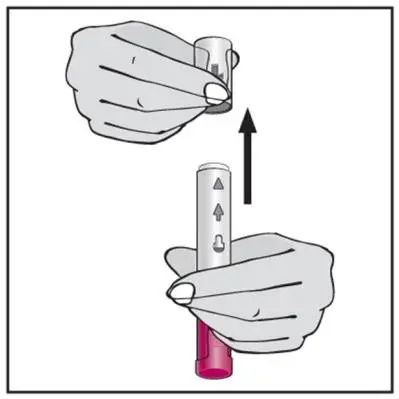
-
Do not put the gray cap (Cap # 1) back on the Pen. Putting the gray cap (Cap # 1) back on may damage the needle.
- The white needle sleeve, which covers the needle, can now be seen.
-
Do not touch the needle with your fingers or let the needle touch anything.
- You may see a few drops of liquid come out of the needle. This is normal.
15. Remove the plum-colored cap (Cap # 2) from the bottom of the Pen by pulling it straight off (do not twist the cap). The Pen is now activated. Throw away the plum-colored cap (Cap # 2).
- Do not put the plum-colored cap (Cap # 2) back on the Pen because it could cause medicine to come out of the syringe.
The plum-colored activator button:
- Turn the Pen so the plum-colored activator button is pointed up. See Figure G.
Figure G
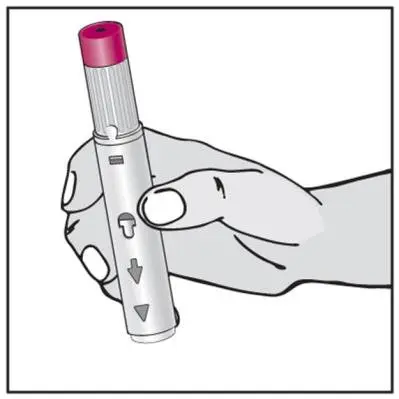
-
Do not press the plum-colored activator button until you are ready to inject HUMIRA. Pressing the plum-colored activator button will release the medicine from the Pen.
- Hold the Pen so that you can see the window. See Figure H. It is normal to see one or more bubbles in the window.
Figure H

Position the Pen and Inject HUMIRA
16. Position the Pen:
- Squeeze the area of the cleaned skin and hold it firmly until the injection is complete. See Figure I. You will inject into this raised area of skin.
Figure I
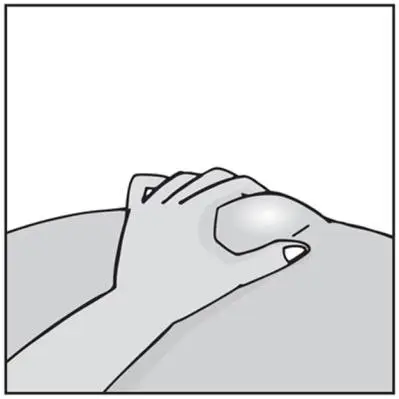
17. Place the white end of the Pen straight (at a 90º angle) and flat against the raised area of your skin that you are squeezing. Place the Pen so that it will not inject the needle into your fingers that are holding the raised skin. See Figure J.
Figure J
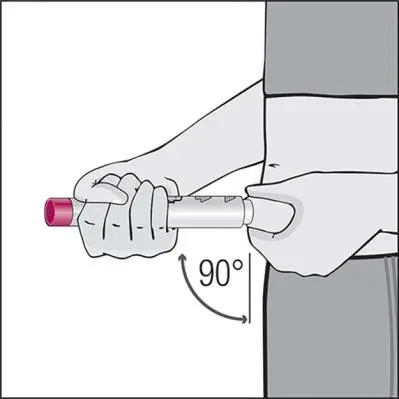
18. Inject HUMIRA
-
It is important that you firmly push the Pen down all the way against the injection site before starting the injection.
-
Keep pushing down to prevent the Pen from moving away from the skin during the injection.
- Press the plum-colored activator button with your thumb to begin the injection. Try not to cover the window. See Figure K.
Figure K
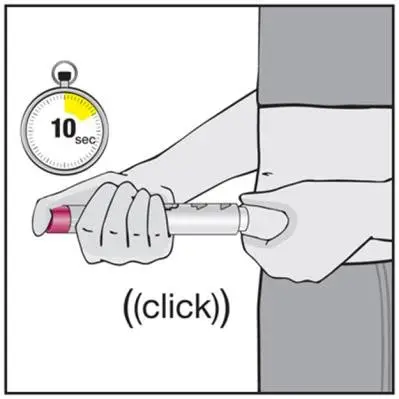
- You will hear a loud ‘click’ when you press the plum-colored activator button. The loud click means the start of the injection.
- Keep pressing the plum-colored activator button and continue to push the Pen against your squeezed, raised skin until all the medicine is injected. This can take up to 10 seconds, so count slowly to ten. Keep pushing the Pen against the squeezed, raised skin of your injection site for the whole time so you get the full dose of medicine.
- You will know that the injection has finished when the yellow indicator fully appears in the window view and stops moving. See Figure L.
Figure L
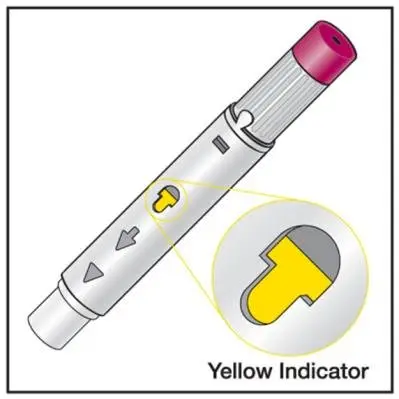
19. When the injection is finished, slowly pull the Pen from your skin. The white needle sleeve will move to cover the needle tip. See Figure M.
- Do not touch the needle. The white needle sleeve is there to prevent you from touching the needle.
Figure M
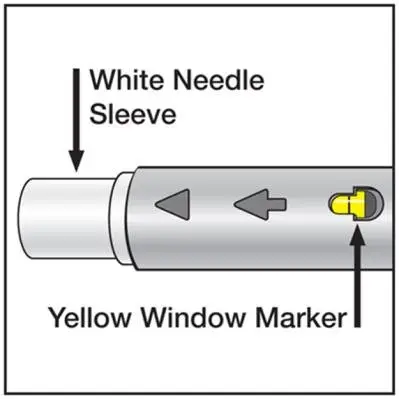
- There may be a small amount of liquid on the injection site. This is normal.
- Press a cotton ball or gauze pad over the injection site and hold it for 10 seconds. Do not rub the injection site. You may have slight bleeding. This is normal.
20. Throw away (dispose of) your used HUMIRA Pen in a sharps disposal container right away after use. See the section “How should I dispose of the used HUMIRA Pen?”
21. Keep a record of the dates and location of your injection sites. To help you remember when to take HUMIRA, you can mark your calendar ahead of time.
How should I throw away (dispose of) the used HUMIRA Pen?
- Put your Pen in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. See Figure N. Do not throw away the Pen in your household trash.
- Do not try to touch the needle. The white needle sleeve is there to prevent you from touching the needle.
Figure N
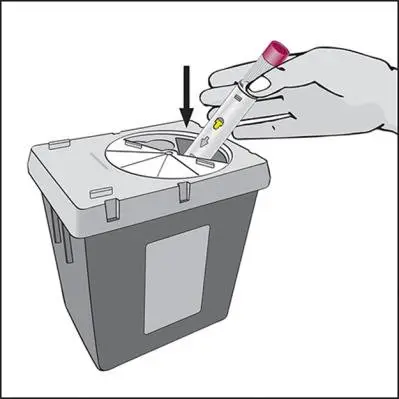
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
○ made of a heavy-duty plastic,
○ can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
○ upright and stable during use,
○ leak-resistant, and
○ properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- For the safety and health of you and others, never re-use your HUMIRA Pens.
- The used alcohol pads, cotton balls, dose trays and packaging may be placed in your household trash.
-
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
- Always keep the sharps container out of the reach of children.
How should I store HUMIRA?
- Store HUMIRA in the refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC). Store HUMIRA in the original carton until use to protect it from light.
-
Do not freeze HUMIRA. Do not use HUMIRA if frozen, even if it has been thawed.
- Refrigerated HUMIRA may be used until the expiration date printed on the HUMIRA carton, dose tray or Pen. Do not use HUMIRA after the expiration date.
- If needed, for example when you are traveling, you may also store HUMIRA at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) for up to 14 days. Store HUMIRA in the original carton until use to protect it from light.
- Throw away HUMIRA if it has been kept at room temperature and not been used within 14 days.
- Record the date you first remove HUMIRA from the refrigerator in the spaces provided on the carton and dose tray.
- Do not store HUMIRA in extreme heat or cold.
- Do not use a Pen if the liquid is cloudy, discolored, or has flakes or particles in it.
- Do not drop or crush HUMIRA.
- Keep HUMIRA, injection supplies, and all other medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, IL 60064, U.S.A.
US License Number 1889
20066944
Revised: 02/2021
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| HUMIRA
adalimumab injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - AbbVie Inc. (078458370) |