Drug Detail:Tussicaps (Chlorpheniramine and hydrocodone [ klor-fen-ir-a-meen-and-hye-droe-koe-done ])
Drug Class: Upper respiratory combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
HYDROCODONE BITARTRATE AND CHLORPHENIRMINE MALEATE Oral Solution for oral administration CII.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1987
WARNING: RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death
[see Warnings and Precautions (
5.1), Drug Interactions (
7.1)]
. Avoid use of opioid cough medications in patients taking benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol.
Recent Major Changes
| Boxed Warning | 1/2017 | |
| Warnings and Precautions ( 5) | 1/2017 | |
Indications and Usage for Hydrocodone and Chlorpheniramine Solution
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is a combination of hydrocodone bitartrate, an antitussive, and chlorpheniramine maleate, a histamine-1 (H
1) receptor antagonist, indicated for relief of cough and symptoms associated with upper respiratory allergies or a common cold (
1.1)
Limitations of Use:
Not indicated for pediatric patients under 18 years of age ( 1.1)
Hydrocodone and Chlorpheniramine Solution Dosage and Administration
- For Oral Use Only ( 2)
- Adults 18 years of age and older: 5 mL every 4 to 6 hours as needed, not to exceed 4 doses (20 mL) in 24 hours ( 2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Each 5 mL of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution contains: hydrocodone bitartrate, USP, 5 mg and chlorpheniramine maleate, USP, 4 mg ( 3)
Contraindications
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to hydrocodone bitartrate, chlorpheniramine, or any of the inactive ingredients of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution ( 4)
- Patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) therapy or within 14 days of stopping such therapy ( 4)
- Patients with narrow angle glaucoma, urinary retention, severe hypertension or severe coronary artery disease ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or other CNS Depressants: Use with caution ( 5.1)
- Drug Dependence: Prescribe with caution that is appropriate to the use of other opioids ( 5.3)
- Head injury and increased intracranial pressure: Avoid in patients with head injury, intracranial lesions, or increased intracranial pressure ( 5.4)
- Avoid engaging in hazardous tasks requiring complete mental alertness such as driving or operating machinery ( 5.5)
- Avoid concurrent use of alcohol or other central nervous system depressants ( 5.5)
- Acute abdominal conditions: Use with caution in patients with acute abdominal conditions ( 5.6)
- Coexisting Conditions: Use with caution in patients with thyroid disease, Addison’s disease, prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture, or asthma ( 5.10)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions were sedation, somnolence, mental clouding, lethargy, impairment of mental and physical performance, anxiety, fear, dysphoria, dizziness, nausea, psychic dependence, mood changes; blurred, double, or other visual disturbances; confusion, headache, euphoria, facial dyskinesia, feeling faint, lightheadedness, agitation, irritability, tremor (
6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Acella Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-800-541-4802 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Benzodiazepines, opioids, antihistamines, antipsychotics, anti-anxiety agents, or other CNS depressants: Avoid use with hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution; may cause additive CNS depression ( 7.1)
- MAOIs or tricyclic antidepressants: Do not use. May increase the effect of either the antidepressant or hydrocodone ( 7.2)
- Anticholinergic drugs: Use with caution. Additive adverse effects resulting from cholinergic blockade (e.g., xerostomia, blurred vision, or constipation) may occur ( 7.3)
Use In Specific Populations
- Renal Impairment: Use with caution ( 8.6)
- Hepatic Impairment: Use with caution ( 8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 6/2017
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1), Drug Interactions ( 7.1)] . Avoid use of opioid cough medications in patients taking benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol.
1. Indications and Usage for Hydrocodone and Chlorpheniramine Solution
1.1 Cough and Upper Respiratory Allergy Symptoms
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is indicated for relief of cough and symptoms associated with upper respiratory allergies or a common cold in adults 18 years of age and older.
Important Limitations of Use
Not indicated for pediatric patients under 18 years of age [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4)] .
2. Hydrocodone and Chlorpheniramine Solution Dosage and Administration
Administer Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution by the oral route only. Measure hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution with an accurate milliliter measuring device. Do not use a household teaspoon to measure the dose [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9)] .
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is a clear, colorless to light yellow, grape-flavored liquid.
5 mL of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution contains: hydrocodone bitartrate, USP, 5 mg and chlorpheniramine maleate, USP, 4 mg [see Description ( 11)] .
4. Contraindications
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is contraindicated in:
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to hydrocodone bitartrate, chlorpheniramine maleate or any of the inactive ingredients of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution.
- Patients receiving MAOI therapy or within 14 days of stopping such therapy.
- Patients with narrow angle glaucoma, urinary retention, severe hypertension, or severe coronary artery disease.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or other CNS Depressants
Concomitant use of opioids, including hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution, with benzodiazepines, or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Because of these risks, avoid use of opioid cough medications in patients taking benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol [see Drug Interactions ( 7.1)] . Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioids alone. Because of similar pharmacologic properties, it is reasonable to expect similar risk with concomitant use of opioid cough medications and benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol. Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation if hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is used with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other CNS depressants [see Patient Counseling Information ( 17.3)] .
5.2 Respiratory Depression
Hydrocodone bitartrate, one of the active ingredients in hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution, produces dose-related respiratory depression by directly acting on brain stem respiratory centers. Overdose of hydrocodone bitartrate in adults has been associated with fatal respiratory depression, and the use of hydrocodone bitartrate in children less than 6 years of age has been associated with fatal respiratory depression. Exercise caution when administering hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution because of the potential for respiratory depression. If respiratory depression occurs, discontinue hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution and use naloxone hydrochloride when indicated to antagonize the effect and other supportive measures as necessary [see Overdosage ( 10)].
5.3 Drug Dependence
Hydrocodone can produce drug dependence of the morphine type and therefore, has the potential for being abused. Psychic dependence, physical dependence, and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution. Prescribe and administer hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution with the same degree of caution appropriate to the use of other opioid drugs [see Drug Abuse and Dependence ( 9.2, 9.3)] .
5.4 Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure
The respiratory depression effects of opioids and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intracranial lesions, or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Furthermore, opioids produce adverse reactions which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries. The use of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution should be avoided in these patients.
5.5 Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate, the active ingredients in Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Chlorpheniramine Maleate Oral Solution, may produce marked drowsiness and impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. Advise patients to avoid engaging in hazardous tasks requiring mental alertness and motor coordination after ingestion of Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Chlorpheniramine Maleate Oral Solution. Concurrent use of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
5.6 Acute Abdominal Conditions
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution should be used with caution in patients with acute abdominal conditions since the administration of hydrocodone may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions. The concurrent use of other anticholinergics with hydrocodone may produce paralytic ileus [see Drug Interactions ( 7.3)] .
5.7 Co-administration with Anticholinergics
The concurrent use of anticholinergics with hydrocodone may produce paralytic ileus. Exercise caution when using hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution in patients taking anticholinergic medications [see Drug Interactions ( 7.3)] .
5.8 Co-administration with MAOIs or Tricyclic Antidepressants
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate Oral Solution should not be used in patients receiving MAOI therapy or within 14 days of stopping such therapy. The use of MAOIs or tricyclic antidepressants with hydrocodone bitartrate, one of the active ingredients in Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Chlorpheniramine Maleate Oral Solution, may increase the effect of either the antidepressant or hydrocodone [see Contraindications ( 4) and Drug Interactions ( 7.2)] .
5.9 Dosing
Patients should be advised to measure hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution with an accurate milliliter measuring device. Patients should be informed that a household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage, which can result in serious adverse reactions [see Overdosage ( 10)] . Patients should be advised to ask their pharmacist to recommend an appropriate measuring device and for instructions for measuring the correct dose.
5.10 Coexisting Conditions
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution should be used with caution in patients with thyroid disease, Addison’s disease, prostatic hypertrophy, urethral stricture, or asthma.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Use of hydrocodone bitartrate, a semisynthetic opioid, may result in the following:
- Respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) and Overdosage ( 10)]
- Drug dependence [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)]
- Increased intracranial pressure [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4) and Overdosage ( 10)]
- Decreased mental alertness with impaired mental and/or physical abilities [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)]
- Paralytic ileus [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6)]
Use of chlorpheniramine, an antihistamine, may result in:
- Decreased mental alertness with impaired mental and/or physical abilities [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)]
The following adverse reactions have been identified either during clinical trials of hydrocodone bitartrate and/or chlorpheniramine maleate or during their use post-approval. Because these reactions may be reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The most common adverse reactions of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution include: Sedation, somnolence, mental clouding, lethargy, impairment of mental and physical performance, anxiety, fear, dysphoria, dizziness, nausea, psychic dependence, mood changes; blurred, double, or other visual disturbances; confusion, headache, euphoria, facial dyskinesia, feeling faint, lightheadedness, agitation, irritability, tremor.
Other adverse reactions include:
Respiratory: Dryness of the pharynx and respiratory passages, occasional tightness of the chest, laryngismus, wheezing, or troubled breathing.
Gastrointestinal System: Nausea and vomiting (more frequent in ambulatory than in recumbent patients), constipation, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, acute pancreatitis, dry mouth, dyspepsia, epigastric distress, and/or loss of appetite.
Genitourinary System: Ureteral spasm, spasm of vesicle sphincters, urinary retention, dysuria, urinary frequency, urinary hesitancy.
Dermatological System: Skin rash, pruritus, erythema, urticaria, excessive perspiration.
7. Drug Interactions
No specific interaction studies have been conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution.
7.1 Benzodiazepines, Opioids, Antihistamines, Antipsychotics, Anti-anxiety Agents, or Other CNS Depressants (Including Alcohol)
The use of benzodiazepines, opioids, antihistamines, antipsychotics, anti-anxiety agents, or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution may cause an additive CNS depressant effect and should be avoided [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)] .
7.2 MAOIs and Tricyclic Antidepressants
Do not prescribe hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution if the patient is taking a prescription MAOI (i.e., certain drugs used for depression, psychiatric or emotional conditions, or Parkinson’s disease), or for 2 weeks after stopping a MAOI drug. The use of MAOIs or tricyclic antidepressants with hydrocodone preparations may increase the effect of either the antidepressant or hydrocodone [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.8)] .
7.3 Anticholinergic Drugs
Hydrocodone and chlorpheniramine should be administered cautiously to persons receiving other anticholinergic drugs in order to avoid paralytic ileus and excessive anticholinergic effects.
Additive adverse effects resulting from cholinergic blockade (e.g., xerostomia, blurred vision, or constipation) may occur when anticholinergic drugs are administered with chlorpheniramine [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7)] .
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution in pregnant women. Reproductive toxicity studies have not been conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution; however, studies are available with individual active ingredients or related active ingredients. Hydrocodone was teratogenic in hamsters. Codeine, an opiate related to hydrocodone, increased resorptions and decreased fetal weight in rats. A single retrospective study reported that chlorpheniramine was teratogenic in humans; however, the significance of these findings was not known. Developmental toxicity was also evident with chlorpheniramine in mice and rats. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution should be used during pregnancy only if the benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Hydrocodone:
Hydrocodone has been shown to be teratogenic in hamsters when given in a dose approximately 35 times the maximum recommended human daily dose (MRHDD) (on a mg/m 2 basis at a single subcutaneous dose of 102 mg/kg on gestation day 8). Reproductive toxicology studies were also conducted with codeine, an opiate related to hydrocodone. In a study in which pregnant rats were dosed throughout organogenesis, a dose of codeine approximately 50 times the MRHDD of hydrocodone (on a mg/m 2 basis at an oral dose of 120 mg/kg/day of codeine) increased resorptions and decreased fetal weight; however, these effects occurred in the presence of maternal toxicity. In studies in which rabbits and mice were dosed throughout organogenesis, doses of codeine up to approximately 25 and 120 times, respectively, the MRHDD of hydrocodone (on a mg/m 2 basis at oral doses of 30 and 600 mg/kg/day, respectively), produced no adverse developmental effects.
Chlorpheniramine:
A retrospective study found a small, but statistically significant, association between maternal use of chlorpheniramine and inguinal hernia and eye or ear anomalies in children. Other retrospective studies have found that the frequency of congenital anomalies, in general, was not increased among offspring of women who took chlorpheniramine during pregnancy. The significance of these findings to the therapeutic use of chlorpheniramine in human pregnancy is not known.
In studies with chlorpheniramine in which pregnant rats and rabbits were dosed throughout organogenesis, oral doses up to approximately 20 and 25 times the MRHDD on a mg/m 2 basis, respectively, produced no adverse developmental effects. However, when mice were dosed throughout pregnancy, a dose approximately 5 times the MRHDD (on a mg/m 2 basis at an oral dose of 20 mg/kg/day) was embryolethal, and postnatal survival was decreased when dosing was continued after parturition. Embryolethality was also observed when male and female rats were dosed with approximately 5 times the MRHDD (on a mg/m 2 basis at an oral dose of 10 mg/kg/day) prior to mating.
Nonteratogenic Effects: Babies born to mothers who have been taking opioids regularly prior to delivery will be physically dependent. The withdrawal signs include irritability and excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, increased respiratory rate, increased stools, sneezing, yawning, vomiting, and fever. The intensity of the syndrome does not always correlate with the duration of maternal opioid use or dose.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
As with all opioids, administration of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution to the mother shortly before delivery may result in some degree of respiratory depression in the newborn, especially if higher doses are used.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is administered to nursing mothers. Hydrocodone and chlorpheniramine are excreted in human milk. The clinical significance is unknown; however, the anticholinergic action of chlorpheniramine may suppress lactation if taken prior to nursing. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established. The use of hydrocodone in children less than 6 years of age has been associated with fatal respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies have not been conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution. Other reported clinical experience with the individual active ingredients of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and patients younger than 65 years of age. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be made with caution, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is a Schedule II controlled prescription containing hydrocodone bitartrate and should be prescribed and administered with caution.
9.2 Abuse
Hydrocodone can produce drug dependence of the morphine type and therefore, has the potential for being abused. Psychic dependence, physical dependence, and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution, and it should be prescribed and administered with the same degree of caution appropriate to the use of other opioid drugs.
9.3 Dependence
Psychic dependence, physical dependence, and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of opioids; therefore, hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution Solution should be prescribed and administered with caution.
Physical dependence, the condition in which continued administration of the drug is required to prevent the appearance of a withdrawal syndrome, assumes clinically significant proportions only after several weeks of continued oral opioid use, although some mild degree of physical dependence may develop after a few days of opioid therapy.
10. Overdosage
No human overdosage data are available for hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution.
Hydrocodone:
Overdosage with hydrocodone is characterized by respiratory depression (a decrease in respiratory rate and/or tidal volume, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, cyanosis), extreme somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, and sometimes bradycardia and hypotension. In severe overdosage, apnea, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest, and death may occur.
Chlorpheniramine:
Manifestations of chlorpheniramine overdosage may vary from central nervous system depression to stimulation. Central toxic effects are characterized by agitation, anxiety, delirium, disorientation, hallucinations, hyperactivity, sedation, and seizures. Severe overdosage may produce coma, medullary paralysis, and death. Peripheral toxicity includes hypertension, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, vasodilation, hyperpyrexia, mydriasis, urinary retention, and diminished gastrointestinal motility. Dry mouth, pharynx, bronchi, and nasal passages may be observed.
Impaired secretion from sweat glands following toxic doses of drugs with anticholinergic side effects may predispose to hyperthermia.
An adult ingested 400 mg chlorpheniramine with no reported serious adverse effects. Toxic psychosis, a possible class effect from overdose of sedating antihistamines, has been reported with accidental overdose of chlorpheniramine.
Treatment of overdosage consists of discontinuation of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution together with institution of appropriate therapy. Primary attention should be given to the reestablishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent airway and the institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. The opioid antagonist naloxone hydrochloride is a specific antidote for respiratory depression which may result from overdosage or unusual sensitivity to opioids including hydrocodone. Therefore, an appropriate dose of naloxone hydrochloride should be administered, preferably by the intravenous route, simultaneously with efforts at respiratory resuscitation. For further information, see full prescribing information for naloxone hydrochloride. An antagonist should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory depression. Oxygen, intravenous fluids, vasopressors, and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated. Gastric emptying may be useful in removing unabsorbed drug.
Hemodialysis is not routinely used to enhance the elimination of chlorpheniramine from the body. Urinary excretion of chlorpheniramine is increased when the pH of the urine is acidic; however, acid diuresis is NOT recommended to enhance elimination in overdose, as the risks of acidemia and acute tubular necrosis in patients with rhabdomyolysis far outweigh any potential benefit.
11. Hydrocodone and Chlorpheniramine Solution Description
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution contains hydrocodone bitartrate (a semisynthetic centrally-acting opioid antitussive) and chlorpheniramine maleate (an antihistamine).
Each 5 mL dose of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution contains: hydrocodone bitartrate, USP, 5 mg and chlorpheniramine maleate, USP, 4 mg.
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution also contains: citric acid anhydrous, glycerin, grape flavor, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium citrate, sodium saccharin, and sucrose.
Hydrocodone bitartrate is morphinan-6-one, 4,5-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methyl-, (5α)-, [ R-( R*, R*)]-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate (1:1), hydrate (2:5); also known as 4,5α-Epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-one tartrate (1:1) hydrate (2:5); a fine white crystal or crystalline powder, which is derived from the opium alkaloid, thebaine; and may be represented by the following structural formula:
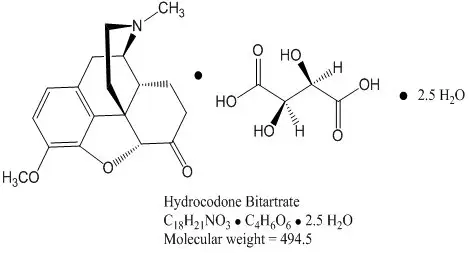
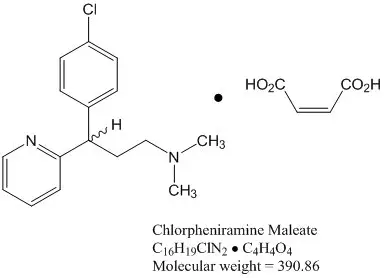
Chlorpheniramine maleate is 2-pyridinepropanamine, γ-(4-chlorophenyl)- N, N-dimethyl-, ( Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) and has the following chemical structure:
12. Hydrocodone and Chlorpheniramine Solution - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Hydrocodone is a semisynthetic narcotic antitussive and analgesic with multiple actions qualitatively similar to those of codeine. The precise mechanism of action of hydrocodone and other opiates is not known; however, hydrocodone is believed to act directly on the cough center. In excessive doses, hydrocodone will depress respiration. Hydrocodone can produce miosis, euphoria, and physical and physiological dependence.
Chlorpheniramine is an antihistamine drug (H 1 receptor antagonist) that also possesses anticholinergic and sedative activity. It prevents released histamine from dilating capillaries and causing edema of the respiratory mucosa.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Systemic exposure (in terms of peak plasma concentrations and area under plasma concentration versus time curve) of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate after single dose administration of 5 mL hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution are equivalent to respective reference solutions of 5 mL hydrocodone bitartrate (5 mg/5 mL), and 5 mL chlorpheniramine maleate (4 mg/5 mL).
Hydrocodone had mean (SD) peak plasma concentration of 10.6 (2.63) ng/mL at 1.4 (0.55) hours. The mean plasma half-life of hydrocodone is approximately 4.9 hours. Chlorpheniramine had a mean (SD) plasma peak concentration of 7.20 (1.98) ng/mL at 3.5 (1.6) hours. The mean plasma half-life of chlorpheniramine is approximately 24 hours.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, and reproductive studies have not been conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution; however, published information is available for the individual active ingredients or related active ingredients.
Hydrocodone:
Carcinogenicity studies were conducted with codeine, an opiate related to hydrocodone. In 2 year studies in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice, codeine showed no evidence of tumorigenicity at dietary doses up to 70 and 400 mg/kg/day, respectively (approximately 30 and 80 times, respectively, the MRHDD of hydrocodone on a mg/m 2 basis).
Chlorpheniramine:
In 2 year studies in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice, chlorpheniramine maleate showed no evidence of tumorigenicity when administered 5 days/week at oral doses up to 30 and 50 mg/kg/day, respectively (approximately 15 times the MRHDD on a mg/m 2 basis).
Chlorpheniramine maleate was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay or the in vitro mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay. Chlorpheniramine maleate was clastogenic in the in vitro CHO cell chromosomal aberration assay.
Chlorpheniramine maleate had no effects on fertility in rats and rabbits at oral doses approximately 20 and 25 times the MRHDD on a mg/m 2 basis, respectively.
14. Clinical Studies
Efficacy studies were not conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution. Efficacy of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is based on demonstration of bioequivalence to the individual reference products [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)] .
16. How is Hydrocodone and Chlorpheniramine Solution supplied
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is supplied as a clear, colorless to light yellow, grape-flavored solution containing 5 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 4 mg chlorpheniramine maleate in each 5 mL. It is available in:
White HDPE bottles of one pint (480 mL): NDC 42192-612-16
Store solution at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container, as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure.
17. Patient Counseling Information
17.1 Overdosage
Patients should be advised not to increase the dose or dosing frequency of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution because serious adverse events such as respiratory depression may occur with overdosage [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2); Overdosage ( 10)].
17.2 Dosing
Patients should be advised to measure hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution with an accurate milliliter measuring device. Patients should be informed that a household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage, especially when half a teaspoon is measured. Patients should be advised to ask their pharmacist to recommend an appropriate measuring device and for instructions for measuring the correct dose [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9)] .
17.3 Interactions with Benzodiazepines and Other Central Nervous System Depressants
Inform patients and caregivers that potentially fatal additive effects may occur if hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol. Because of this risk, patients should avoid concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1), Drug Interactions ( 7.1)] .
17.4 Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
Patients should be advised to avoid engaging in hazardous tasks that require mental alertness and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle as hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution may produce marked drowsiness [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)] .
17.5 Drug Dependence
Patients should be cautioned that hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution contains hydrocodone bitartrate and can produce drug dependence [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)] .
17.6 MAOIs
Patients should be informed that they should not use hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution with a MAOI or within 14 days of stopping use of an MAOI [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.8)] .
Distributed by:

Alpharetta, GA 30005
1-800-541-4802
500458-05
L-0035 Rev 0919-01
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - BOTTLE LABEL

Bottle Label - 16 fl oz
NDC 42192-612-16
Hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution CII
5 mg /4 mg per 5 mL
Contains:
Hydrocodone
bitartrate.....5 mg/5 mL
WARNING: May be habit forming.
Chlorpheniramine
Maleate.....4 mg/5 mL
Rx Only
Acella
Pharmaceuticals, LLC
16 fl oz (480 mL)
USUAL DOSAGE: See Package Insert for Complete Dosage Recommendations.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure.
WARNING: KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room
Temperature].
Tamper evident by foil seal under cap. Do not use if foil seal is
broken or missing.
Distributed by:

Alpharetta, GA 30022
1-800-541-4802
400829-08
Rev. 07/2017
| HYDROCODONE BITARTRATE AND CHLORPHENIRAMINE MALEATE
hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine maleate solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Acella Pharmaceuticals, LLC (825380939) |




