Drug Detail:Ilevro (Nepafenac ophthalmic [ ne-pa-fan-ak-off-thal-mik ])
Drug Class:
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ILEVRO* (nepafenac ophthalmic suspension) 0.3%, topical ophthalmic
Initial U.S. Approval: 2005
Indications and Usage for Ilevro
ILEVRO* 0.3% is a nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory prodrug indicated for the treatment of pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery (1).
Ilevro Dosage and Administration
One drop of ILEVRO* 0.3% should be applied to the affected eye one-time-daily beginning 1 day prior to cataract surgery, continued on the day of surgery and through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period. An additional drop should be administered 30 to 120 minutes prior to surgery. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Sterile ophthalmic suspension 0.3%: 1.7 mL in a 4 mL bottle and 3 mL in a 4 mL bottle. (3)
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the formula or to other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS). (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation (5.1)
- Delayed healing (5.2)
- Corneal effects including keratitis (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (5% to 10%) are capsular opacity, decreased visual acuity, foreign body sensation, increased intraocular pressure, and sticky sensation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alcon Laboratories, Inc. at 1-800-757-9195 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 1/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Ilevro
ILEVRO* 0.3% is indicated for the treatment of pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery.
2. Ilevro Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosing
One drop of ILEVRO* 0.3% should be applied to the affected eye one time daily beginning 1 day prior to cataract surgery, continued on the day of surgery and through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period. An additional drop should be administered 30 to 120 minutes prior to surgery.
2.2 Use with Other Topical Ophthalmic Medications
ILEVRO* 0.3% may be administered in conjunction with other topical ophthalmic medications such as beta-blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, alpha-agonists, cycloplegics, and mydriatics.
If more than one topical ophthalmic medication is being used, the medicines must be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Sterile ophthalmic suspension 0.3%: 1.7 mL in a 4 mL bottle and 3 mL in a 4 mL bottle.
4. Contraindications
ILEVRO* 0.3% is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the formula or to other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Increased Bleeding Time
With some NSAIDS including ILEVRO* 0.3%, there exists the potential for increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues (including hyphema) in conjunction with ocular surgery.
It is recommended that ILEVRO* 0.3% be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies or who are receiving other medications which may prolong bleeding time.
5.2 Delayed Healing
Topical NSAIDs including ILEVRO* 0.3%, may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems.
5.3 Corneal Effects
Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration, or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs including ILEVRO* 0.3% and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs suggests that patients with complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface diseases (e.g., dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period of time may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events, which may become sight threatening. Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in these patients.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggests that use more than 1 day prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days post-surgery may increase patient risk and severity of corneal adverse events.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Serious and Otherwise Important Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of labeling.
- Increased Bleeding Time [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Delayed Healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Corneal Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.2 Ocular Adverse Reactions
The most frequently reported ocular adverse reactions following cataract surgery were capsular opacity, decreased visual acuity, foreign body sensation, increased intraocular pressure (IOP), and sticky sensation. These reactions occurred in approximately 5% to 10% of patients.
Other ocular adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of approximately 1% to 5% included conjunctival edema, corneal edema, dry eye, lid margin crusting, ocular discomfort, ocular hyperemia, ocular pain, ocular pruritus, photophobia, tearing, and vitreous detachment.
Some of these reactions may be the consequence of the cataract surgical procedure.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects.
Pregnancy Category C: Reproduction studies performed with nepafenac in rabbits and rats at oral doses up to 10 mg/kg/day have revealed no evidence of teratogenicity due to nepafenac, despite the induction of maternal toxicity. At this dose, the animal plasma exposure to nepafenac and amfenac was approximately 70 and 630 times human plasma exposure at the recommended human topical ophthalmic dose for rats and 20 and 180 times human plasma exposure for rabbits, respectively. In rats, maternally toxic doses greater than or equal to 10 mg/kg were associated with dystocia, increased postimplantation loss, reduced fetal weights and growth, and reduced fetal survival.
Nepafenac has been shown to cross the placental barrier in rats. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, ILEVRO* 0.3% should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Non-teratogenic Effects
Because of the known effects of prostaglandin biosynthesis inhibiting drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of the ductus arteriosus), the use of ILEVRO* 0.3% during late pregnancy should be avoided.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Nepafenac is excreted in the milk of lactating rats. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ILEVRO* 0.3% is administered to a nursing woman.
11. Ilevro Description
ILEVRO* 0.3% is a sterile, topical, NSAID prodrug for ophthalmic use. Each mL of ILEVRO* 0.3% contains 3 mg of nepafenac. Nepafenac is designated chemically as 2-amino-3-benzoylbenzeneacetamide with an empirical formula of C15H14N2O2. The structural formula of nepafenac is:
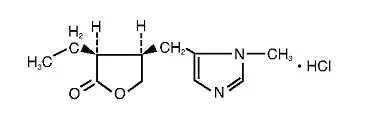
Nepafenac is a yellow crystalline powder. The molecular weight of nepafenac is 254.28 g/mol. ILEVRO* 0.3% is supplied as a sterile, aqueous suspension with a pH approximately of 6.8.
The osmolality of ILEVRO* 0.3% is approximately 300 mOsm/kg.
Each mL of ILEVRO* 0.3% contains: Active: nepafenac 0.3%. Inactives: boric acid, propylene glycol, carbomer 974P, sodium chloride, guar gum, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, edetate disodium, benzalkonium chloride 0.005% (preservative), sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid to adjust pH and purified water, USP.
12. Ilevro - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
After topical ocular dosing, nepafenac penetrates the cornea and is converted by ocular tissue hydrolases to amfenac, a NSAID. Nepafenac and amfenac are thought to inhibit the action of prostaglandin H synthase (cyclooxygenase), an enzyme required for prostaglandin production.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following bilateral topical ocular once-daily dosing of ILEVRO* 0.3%, the concentrations of nepafenac and amfenac peaked at a median time of 0.5 hour and 0.75 hour, respectively on both Day 1 and Day 4. The mean steady-state Cmax for nepafenac and for amfenac were 0.847 ± 0.269 ng/mL and 1.13 ± 0.491 ng/mL, respectively.
Nepafenac at concentrations up to 3000 ng/mL and amfenac at concentrations up to 1000 ng/mL did not inhibit the in vitro metabolism of six specific marker substrates of cytochrome P450 (CYP) isozymes (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4). Therefore, drug-drug interactions involving CYP mediated metabolism of concomitantly administered drugs are unlikely.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Nepafenac has not been evaluated in long-term carcinogenicity studies. Increased chromosomal aberrations were observed in Chinese hamster ovary cells exposed in vitro to nepafenac suspension. Nepafenac was not mutagenic in the Ames assay or in the mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay. Oral doses up to 5000 mg/kg did not result in an increase in the formation of micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes in vivo in the mouse micronucleus assay in the bone marrow of mice.
Nepafenac did not impair fertility when administered orally to male and female rats at 3 mg/kg.
14. Clinical Studies
In two double masked, randomized clinical trials in which patients were dosed daily beginning one day prior to cataract surgery, continued on the day of surgery and for the first two weeks of the postoperative period, ILEVRO* 0.3% demonstrated superior clinical efficacy compared to its vehicle in treating postoperative pain and inflammation.
Treatment effect over vehicle for resolution of ocular pain occurred as early as Day 1 postsurgery. Treatment effect over vehicle for resolution of inflammation was significantly better than vehicle in both studies at Day 7 and Day 14 post-surgery.
| Study | Treatment | Inflammation Resolution at Postop Day 14 | Ocular Pain Resolution at Postop Day 14 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | Nepafenac ophthalmic suspension, 0.3% (n/N)(1) | 552/851 (65%) | 734/851 (86%) |
| NEVANAC (n/N)(1) | 568/845 (67%) | 737/845 (87%) | |
| Vehicle (n/N)(1) | 67/211 (32%) | 98/211 (46%) | |
| Difference (95% CI)(2) | 33% (26%, 40%) | 40% (32%, 47%) | |
| Study 2 | Nepafenac ophthalmic suspension, 0.3% (n/N)(1) | 331/540 (61%) | 456/540 (84%) |
| Vehicle (n/N)(1) | 63/268 (24%) | 101/268 (38%) | |
| Difference (95% CI)(2) | 38% (31%, 45%) | 47% (40%, 54%) |
Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval.
(1)n/N is the ratio of those with complete resolution of anterior chamber cell and flare by the postoperative Day 14 visit over all randomized subjects.
(2)Difference is Nepafenac ophthalmic suspension, 0.3% (n/N) – vehicle. The 95% CI is derived using asymptotic approximation.
16. How is Ilevro supplied
ILEVRO* 0.3% is supplied in a white, oval, low density polyethylene DROP-TAINER® dispenser with a natural low density polyethylene dispensing plug and gray polypropylene cap. The 1.7 mL fill is presented in an overwrap, which provides tamper evidence to the package. Tamper evidence for the 3 mL fill is provided with a shrink band around the closure and neck area of the package.
1.7 mL in 4 mL bottle NDC 0065-1750-07
3 mL in 4 mL bottle NDC 0065-1750-14
Storage: Store at 2°C-25°C (36°F-77°F).
Protect from light.
| ILEVRO
nepafenac suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Alcon Laboratories, Inc. (008018525) |





