Drug Detail:Intuniv (Guanfacine [ gwahn-fa-seen ])
Drug Class: Antiadrenergic agents, centrally acting
Highlights of Prescribing Information
INTUNIV® (guanfacine) extended-release tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1986
Indications and Usage for Intuniv
INTUNIV® is a central alpha2A-adrenergic receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) as monotherapy and as adjunctive therapy to stimulant medications (1,14).
Intuniv Dosage and Administration
- Recommended dose: 1 mg to 7 mg (0.05-0.12 mg/kg target weight based dose range) once daily in the morning or evening based on clinical response and tolerability (2.2).
- Begin at a dose of 1 mg once daily and adjust in increments of no more than 1 mg/week (2.2).
- Do not crush, chew or break tablets before swallowing (2.1).
- Do not administer with high-fat meals, because of increased exposure (2.1).
- Do not substitute for immediate-release guanfacine tablets on a mg-per-mg basis, because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles (2.3).
- If switching from immediate-release guanfacine, discontinue that treatment and titrate with INTUNIV® as directed (2.3).
- When discontinuing, taper the dose in decrements of no more than 1 mg every 3 to 7 days to avoid rebound hypertension (2.5).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Extended-release tablets: 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg (3)
Contraindications
History of hypersensitivity to INTUNIV®, its inactive ingredients, or other products containing guanfacine (4).
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypotension, bradycardia, syncope: Titrate slowly and monitor vital signs frequently in patients at risk for hypotension, heart block, bradycardia, syncope, cardiovascular disease, vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease or chronic renal failure. Measure heart rate and blood pressure prior to initiation of therapy, following dose increases, and periodically while on therapy. Avoid concomitant use of drugs with additive effects unless clinically indicated. Advise patients to avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated (5.1).
- Sedation and somnolence: Occur commonly with INTUNIV®. Consider the potential for additive sedative effects with CNS depressant drugs. Caution patients against operating heavy equipment or driving until they know how they respond to INTUNIV® (5.2).
- Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities: May worsen sinus node dysfunction and atrioventricular (AV) block, especially in patients taking other sympatholytic drugs. Titrate slowly and monitor vital signs frequently (5.3).
- Rebound Hypertension: Abrupt discontinuation of INTUNIV® can lead to clinically significant and persistent rebound hypertension. Subsequent hypertensive encephalopathy was also reported. To minimize the risk of rebound hypertension upon discontinuation, the total daily dose of INTUNIV® should be tapered in decrements of no more than 1 mg every 3 to 7 days (5.4).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥5% and at least twice placebo rate) in fixed-dose monotherapy ADHD trials in children and adolescents (6 to 17 years): hypotension, somnolence, fatigue, nausea, and lethargy (6.1)
Flexible dose-optimization ADHD trials in children (6 to 12 years) and adolescents (13 to 17 years): somnolence, hypotension, abdominal pain, insomnia, fatigue, dizziness, dry mouth, irritability, nausea, vomiting, and bradycardia (6.1).
Adjunctive treatment to psychostimulant ADHD trial in children and adolescents (6 to 17 years): somnolence, fatigue, insomnia, dizziness, and abdominal pain (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Takeda Pharmaceuticals at 1-800-828-2088 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors increase guanfacine exposure. Decrease INTUNIV® to 50% of target dosage when coadministered with strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (2.7).
- Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inducers decrease guanfacine exposure. Based on patient response, consider titrating INTUNIV dosage up to double the target dosage over 1 to 2 weeks (2.7).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2020
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Intuniv
INTUNIV® is indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) as monotherapy and as adjunctive therapy to stimulant medications [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Intuniv Dosage and Administration
2.1 General Instruction for Use
Swallow tablets whole. Do not crush, chew, or break tablets because this will increase the rate of guanfacine release. Do not administer with high fat meals, due to increased exposure.
2.2 Dose Selection
Take INTUNIV orally once daily, either in the morning or evening, at approximately the same time each day. Begin at a dose of 1 mg/day, and adjust in increments of no more than 1 mg/week.
In monotherapy clinical trials, there was dose- and exposure-related clinical improvement as well as risks for several clinically significant adverse reactions (hypotension, bradycardia, sedative events). To balance the exposure-related potential benefits and risks, the recommended target dose range depending on clinical response and tolerability for INTUNIV® is 0.05-0.12 mg/kg/day (total daily dose between 1-7 mg) (See Table 1).
| Weight | Target dose range (0.05 - 0.12 mg/kg/day) |
|---|---|
| Doses above 4 mg/day have not been evaluated in children (ages 6-12 years) and doses above 7 mg/day have not been evaluated in adolescents (ages 13-17 years) | |
| 25-33.9 kg | 2-3 mg/day |
| 34-41.4 kg | 2-4 mg/day |
| 41.5-49.4 kg | 3-5 mg/day |
| 49.5-58.4 kg | 3-6 mg/day |
| 58.5-91 kg | 4-7 mg/day |
| >91 kg | 5-7 mg/day |
In the adjunctive trial which evaluated INTUNIV® treatment with psychostimulants, the majority of patients reached optimal doses in the 0.05-0.12 mg/kg/day range. Doses above 4 mg/day have not been studied in adjunctive trials.
2.3 Switching from Immediate-Release Guanfacine to INTUNIV®
If switching from immediate-release guanfacine, discontinue that treatment, and titrate with INTUNIV® following above recommended schedule.
Do not substitute for immediate-release guanfacine tablets on a milligram-per-milligram basis, because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles. INTUNIV® has significantly reduced Cmax (60% lower), bioavailability (43% lower), and a delayed Tmax (3 hours later) compared to those of the same dose of immediate-release guanfacine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Maintenance Treatment
Pharmacological treatment of ADHD may be needed for extended periods. Healthcare providers should periodically re-evaluate the long-term use of INTUNIV®, and adjust weight-based dosage as needed. The majority of children and adolescents reach optimal doses in the 0.05-0.12 mg/kg/day range. Doses above 4 mg/day have not been evaluated in children (ages 6-12 years) and above 7 mg/day have not been evaluated in adolescents (ages 13-17 years) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2.5 Discontinuation of Treatment
Following discontinuation of INTUNIV®, patients may experience increases in blood pressure and heart rate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6)]. Patients/caregivers should be instructed not to discontinue INTUNIV® without consulting their health care provider. Monitor blood pressure and pulse when reducing the dose or discontinuing the drug. Taper the daily dose in decrements of no more than 1 mg every 3 to 7 days to minimize the risk of rebound hypertension.
2.6 Missed Doses
When reinitiating patients to the previous maintenance dose after two or more missed consecutive doses, consider titration based on patient tolerability.
2.7 Dosage Adjustment with Concomitant Use of Strong and Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Inducers
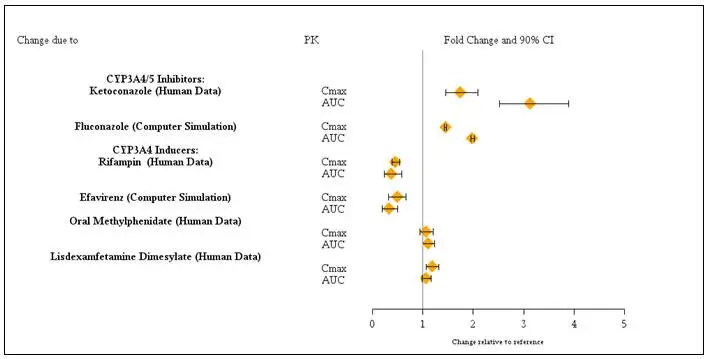
Dosage adjustments for INTUNIV® are recommended with concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) or CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine) (Table 2) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
| Clinical Scenarios | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Starting INTUNIV® while currently on a CYP3A4 modulator | Continuing INTUNIV® while adding a CYP3A4 modulator | Continuing INTUNIV® while stopping a CYP3A4 modulator | |
| CYP3A4 Strong and moderate Inhibitors | Decrease INTUNIV® dosage to half the recommended level. (see Table 1) | Decrease INTUNIV® dosage to half the recommended level. (see Table 1) | Increase INTUNIV® dosage to recommended level. (see Table 1) |
| CYP3A4 Strong and moderate Inducers | Consider increasing INTUNIV® dosage up to double the recommended level. (see Table 1) | Consider increasing INTUNIV® dosage up to double the recommended level over 1 to 2 weeks. (see Table 1) | Decrease INTUNIV® dosage to recommended level over 1 to 2 weeks. (see Table 1) |
4. Contraindications
INTUNIV is contraindicated in patients with a history of a hypersensitivity reaction to INTUNIV or its inactive ingredients, or other products containing guanfacine. Rash and pruritus have been reported.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypotension, Bradycardia, and Syncope
Treatment with INTUNIV® can cause dose-dependent decreases in blood pressure and heart rate. Decreases were less pronounced over time of treatment. Orthostatic hypotension and syncope have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Measure heart rate and blood pressure prior to initiation of therapy, following dose increases, and periodically while on therapy. Titrate INTUNIV slowly in patients with a history of hypotension, and those with underlying conditions that may be worsened by hypotension and bradycardia; e.g., heart block, bradycardia, cardiovascular disease, vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, or chronic renal failure. In patients who have a history of syncope or may have a condition that predisposes them to syncope, such as hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, or dehydration, advise patients to avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate, and adjust dosages accordingly in patients treated concomitantly with antihypertensives or other drugs that can reduce blood pressure or heart rate or increase the risk of syncope.
5.2 Sedation and Somnolence
Somnolence and sedation were commonly reported adverse reactions in clinical studies [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Before using INTUNIV® with other centrally active depressants, consider the potential for additive sedative effects. Caution patients against operating heavy equipment or driving until they know how they respond to treatment with INTUNIV®. Advise patients to avoid use with alcohol.
5.3 Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities
The sympatholytic action of INTUNIV® may worsen sinus node dysfunction and atrioventricular (AV) block, especially in patients taking other sympatholytic drugs. Titrate INTUNIV slowly and monitor vital signs frequently in patients with cardiac conduction abnormalities or patients concomitantly treated with other sympatholytic drugs.
5.4 Rebound Hypertension
In post marketing experience, abrupt discontinuation of INTUNIV® has resulted in clinically significant and persistent rebound hypertension above baseline levels and increases in heart rate. Hypertensive encephalopathy has also been reported in association with rebound hypertension with both INTUNIV® and immediate release guanfacine [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. In these cases, high-dosage guanfacine was discontinued; concomitant stimulant use was also reported, which may potentially increase hypertensive response upon abrupt discontinuation of guanfacine. Children commonly have gastrointestinal illnesses that lead to vomiting, and a resulting inability to take medications, so they may be especially at risk for rebound hypertension.
To minimize the risk of rebound hypertension upon discontinuation, the total daily dose of INTUNIV® should be tapered in decrements of no more than 1 mg every 3 to 7 days [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Blood pressure and heart rate should be monitored when reducing the dose or discontinuing INTUNIV®. If abrupt discontinuation occurs (especially with concomitant stimulant use), patients should be closely followed for rebound hypertension.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypotension, bradycardia, and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Sedation and somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiac conduction abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Rebound Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect clinical trial exposure to INTUNIV® in 2,825 patients. This includes 2,330 patients from completed studies in children and adolescents, ages 6 to 17 years and 495 patients in completed studies in adult healthy volunteers.
The mean duration of exposure of 446 patients that previously participated in two 2-year, open-label long-term studies was approximately 10 months.
Fixed Dose Trials
| INTUNIV® (mg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo (N=149) | 1mg*
(N=61) | 2mg (N=150) | 3mg (N=151) | 4mg (N=151) | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=513) |
|
||||||
| Somnolence† | 11% | 28% | 30% | 38% | 51% | 38% |
| Fatigue | 3% | 10% | 13% | 17% | 15% | 14% |
| Hypotension‡ | 3% | 8% | 5% | 7% | 8% | 7% |
| Dizziness | 4% | 5% | 3% | 7% | 10% | 6% |
| Lethargy | 3% | 2% | 3% | 8% | 7% | 6% |
| Nausea | 2% | 7% | 5% | 5% | 6% | 6% |
| Dry mouth | 1% | 0% | 1% | 6% | 7% | 4% |
| INTUNIV® (mg) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo (N=149) | 1mg*
(N=61) | 2mg (N=150) | 3mg (N=151) | 4mg (N=151) | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=513) | ||||||
| n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | |
| Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation in ≥2% in any dose group but did not meet this criteria in all doses combined: hypotension (hypotension, diastolic hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, blood pressure decreased, blood pressure diastolic decreased, blood pressure systolic decreased), headache, and dizziness. | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Total patients | 4 | (3%) | 2 | (3%) | 10 | (7%) | 15 | (10%) | 27 | (18%) | 54 | (11%) |
| Somnolence† | 1 | (1%) | 2 | (3%) | 5 | (3%) | 6 | (4%) | 17 | (11%) | 30 | (6%) |
| Fatigue | 0 | (0%) | 0 | (0%) | 2 | (1%) | 2 | (1%) | 4 | (3%) | 8 | (2%) |
| INTUNIV® (mg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo (N=149) | 1mg*
(N=61) | 2mg (N=150) | 3mg (N=151) | 4mg (N=151) | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=513) |
| Adverse reactions ≥2% for all doses of INTUNIV and >rate in placebo in any dose group but did not meet this criteria in all doses combined: insomnia (insomnia, initial insomnia, middle insomnia, terminal insomnia, sleep disorder), vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal/stomach discomfort (abdominal discomfort, epigastric discomfort, stomach discomfort), rash (rash, rash generalized, rash papular), dyspepsia, increased weight, bradycardia (bradycardia, sinus bradycardia), asthma (asthma, bronchospasm, wheezing), agitation, anxiety (anxiety, nervousness), sinus arrhythmia, blood pressure increased (blood pressure increased, blood pressure diastolic increased), and first degree atrioventricular block. | ||||||
|
||||||
| Headache | 19% | 26% | 25% | 16% | 28% | 23% |
| Abdominal Pain† | 9% | 10% | 7% | 11% | 15% | 11% |
| Decreased Appetite | 4% | 5% | 4% | 9% | 6% | 6% |
| Irritability | 4% | 5% | 8% | 3% | 7% | 6% |
| Constipation | 1% | 2% | 2% | 3% | 4% | 3% |
| Nightmare‡ | 0% | 0% | 0% | 3% | 4% | 2% |
| Enuresis§ | 1% | 0% | 1% | 3% | 2% | 2% |
| Affect Lability¶ | 1% | 2% | 1% | 3% | 1% | 2% |
Monotherapy Flexible Dose Trials
| INTUNIV® | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo (N=112) | AM (N=107) | PM (N=114) | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=221) |
|
||||
| Somnolence* | 15% | 57% | 54% | 56% |
| Abdominal Pain† | 7% | 8% | 19% | 14% |
| Fatigue | 3% | 10% | 11% | 11% |
| Irritability | 3% | 7% | 7% | 7% |
| Nausea | 1% | 6% | 5% | 5% |
| Dizziness | 3% | 6% | 4% | 5% |
| Vomiting | 2% | 7% | 4% | 5% |
| Hypotension‡ | 0% | 6% | 4% | 5% |
| Decreased Appetite | 3% | 6% | 3% | 4% |
| Enuresis§ | 1% | 2% | 5% | 4% |
| INTUNIV® | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo (N=112) | AM (N=107) | PM (N=114) | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=221) | ||||
| n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | |
| Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation in ≥2% in any dose group but did not meet this criteria in all doses combined: fatigue | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Total patients | 0 | (0%) | 8 | (7%) | 7 | (6%) | 15 | (7%) |
| Somnolence* | 0 | (0%) | 4 | (4%) | 3 | (3%) | 7 | (3%) |
| INTUNIV® | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo (N=112) | AM (N=107) | PM (N=114) | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=221) |
| Adverse reactions ≥2% for all doses of INTUNIV and >rate in placebo in any dose group but did not meet this criteria in all doses combined: affect lability (affect lability, mood swings), increased weight, syncope/loss of consciousness (loss of consciousness, presyncope, syncope), dyspepsia, tachycardia (tachycardia, sinus tachycardia), and bradycardia (bradycardia, sinus bradycardia). | ||||
|
||||
| Headache | 11% | 18% | 16% | 17% |
| Insomnia* | 6% | 8% | 6% | 7% |
| Diarrhea | 4% | 4% | 6% | 5% |
| Lethargy | 0% | 4% | 3% | 3% |
| Constipation | 2% | 2% | 4% | 3% |
| Dry Mouth | 1% | 3% | 3% | 3% |
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo (N=155) | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=157) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Somnolence* | 23% | 54% |
| Insomnia† | 6% | 13% |
| Hypotension‡ | 3% | 9% |
| Dry Mouth | 0% | 8% |
| Postural Dizziness | 2% | 5% |
| Bradycardia§ | 0% | 5% |
There were no specific adverse reactions ≥2% in any treatment group that led to discontinuation in the monotherapy flexible dose study (Study 5).
| INTUNIV® | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo (N=155) | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=157) |
| Adverse reactions ≥2% for all doses of INTUNIV and >rate in placebo in any dose group but did not meet this criteria in all doses combined: nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and depression (depressed mood, depression, depressive symptom). | ||
|
||
| Headache | 18% | 27% |
| Fatigue | 12% | 22% |
| Dizziness | 10% | 16% |
| Decreased Appetite | 14% | 15% |
| Abdominal Pain* | 8% | 12% |
| Irritability | 4% | 7% |
| Anxiety† | 3% | 5% |
| Rash‡ | 1% | 3% |
| Constipation | 0% | 3% |
| Increased Weight | 2% | 3% |
| Abdominal/Stomach Discomfort§ | 1% | 2% |
| Pruritus | 1% | 2% |
Adjunctive Trial
| INTUNIV® + stimulant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo+ stimulant (N=153) | AM (N=150) | PM (N=152) | All Doses (N=302) |
|
||||
| Somnolence* | 7% | 18% | 18% | 18% |
| Insomnia† | 6% | 10% | 14% | 12% |
| Abdominal Pain‡ | 3% | 8% | 12% | 10% |
| Fatigue | 3% | 12% | 7% | 10% |
| Dizziness | 4% | 10% | 5% | 8% |
| Decreased Appetite | 4% | 7% | 8% | 7% |
| Nausea | 3% | 3% | 7% | 5% |
There were no specific adverse reactions ≥2% in any treatment group that led to discontinuation in the short-term adjunctive study (Study 3).
| INTUNIV® + stimulant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | Placebo (N=153) | AM (N=150) | PM (N=152) | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=302) |
| Adverse reactions ≥2% for all doses of INTUNIV and >rate in placebo in any dose group but did not meet this criteria in all doses combined: irritability, vomiting, asthma (asthma, bronchospasm, wheezing), and enuresis (enuresis, nocturia, urinary incontinence). | ||||
|
||||
| Headache | 13% | 21% | 21% | 21% |
| Diarrhea | 1% | 4% | 3% | 4% |
| Hypotension* | 0% | 4% | 2% | 3% |
| Constipation | 0% | 2% | 3% | 2% |
| Affect Lability† | 1% | 3% | 2% | 2% |
| Dry Mouth | 0% | 1% | 3% | 2% |
| Bradycardia‡ | 0% | 1% | 3% | 2% |
| Postural Dizziness | 0% | 1% | 3% | 2% |
| Rash§ | 1% | 1% | 2% | 2% |
| Nightmare¶ | 1% | 2% | 1% | 2% |
| Tachycardia# | 1% | 2% | 1% | 2% |
Other Adverse Reactions Observed in Clinical Studies
Table 13 includes additional adverse reactions observed in short-term, placebo-controlled and long-term, open-label clinical studies not included elsewhere in section 6.1, listed by organ system.
| Body System | Adverse Reaction |
|---|---|
| Cardiac | Atrioventricular block |
| General | Asthenia, chest pain |
| Immune System Disorders | Hypersensitivity |
| Investigations | Increased alanine amino transferase |
| Nervous system | Convulsion |
| Renal | Increased urinary frequency |
| Vascular | Hypertension, pallor |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of guanfacine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Less frequent, possibly guanfacine-related events observed in the post-marketing study and/or reported spontaneously, not included in section 6.1, include:
General: edema, malaise, tremor
Cardiovascular: palpitations, tachycardia, rebound hypertension, hypertensive encephalopathy
Central Nervous System: paresthesias, vertigo
Eye Disorders: blurred vision
Musculo-Skeletal System: arthralgia, leg cramps, leg pain, myalgia
Psychiatric: confusion, hallucinations
Reproductive System, Male: erectile dysfunction
Respiratory System: dyspnea
Skin and Appendages: alopecia, dermatitis, exfoliative dermatitis, pruritus, rash
Special Senses: alterations in taste
7. Drug Interactions
Table 14 contains clinically important drug interactions with INTUNIV® [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Concomitant Drug Name or Drug Class | Clinical Rationale and Magnitude of Drug Interaction | Clinical Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors, e.g., ketoconazole, fluconazole | Guanfacine is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and its plasma concentrations can be significantly affected resulting in an increase in exposure | Consider dose reduction [see Dosage and administration (2.7)] |
| Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inducers, e.g., rifampin, efavirenz | Guanfacine is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and its plasma concentrations can be significantly affected resulting in a decrease in exposure | Consider dose increase [see Dosage and administration (2.7)] |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to ADHD medications, including INTUNIV, during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the National Pregnancy Registry for ADHD Medications at 1-866-961-2388.
8.2 Lactation
Clinical Considerations
Monitor breastfeeding infants exposed to guanfacine through breastmilk for sedation, lethargy, and poor feeding.
Data
Guanfacine was excreted in breast milk of lactating rats at a concentration comparable to that observed in blood, but slightly less than the concentration in plasma when administered following a single oral dose of 5 mg/kg. The concentration of drug in animal milk does not necessarily predict the concentration of drug in human milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of INTUNIV® in pediatric patients less than 6 years of age have not been established. The efficacy of INTUNIV® was studied for the treatment of ADHD in five controlled monotherapy clinical trials (up to 15 weeks in duration), one randomized withdrawal study and one controlled adjunctive trial with psychostimulants (8 weeks in duration) in children and adolescents ages 6-17 who met DSM-IV® criteria for ADHD [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Studies (14)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
The safety and efficacy of INTUNIV® in geriatric patients have not been established.
11. Intuniv Description
INTUNIV® is a once-daily, extended-release formulation of guanfacine hydrochloride (HCl) in a matrix tablet formulation for oral administration only. The chemical designation is N-amidino-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl) acetamide monohydrochloride. The molecular formula is C9H9Cl2 N3O∙HCl corresponding to a molecular weight of 282.55. The chemical structure is:
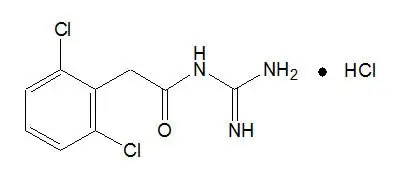
Guanfacine HCl is a white to off-white crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water (approximately 1 mg/mL) and alcohol and slightly soluble in acetone. The only organic solvent in which it has relatively high solubility is methanol (>30 mg/mL). Each tablet contains guanfacine HCl equivalent to 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, or 4 mg of guanfacine base. The tablets also contain hypromellose, methacrylic acid copolymer, lactose, povidone, crospovidone, microcrystalline cellulose, fumaric acid, and glyceryl behenate. In addition, the 3-mg and 4-mg tablets also contain green pigment blend PB-1763.
12. Intuniv - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Guanfacine is a central alpha2A-adrenergic receptor agonist. Guanfacine is not a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. The mechanism of action of guanfacine in ADHD is not known.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Guanfacine is a selective central alpha2A-adrenergic receptor agonist in that it has a 15-20 times higher affinity for this receptor subtype than for the alpha2B or alpha2C subtypes.
Guanfacine is a known antihypertensive agent. By stimulating central alpha2A-adrenergic receptors, guanfacine reduces sympathetic nerve impulses from the vasomotor center to the heart and blood vessels. This results in a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance and a reduction in heart rate.
In a thorough QT study, the administration of two dose levels of immediate-release guanfacine (4 mg and 8 mg) produced concentrations approximately 2 to 4 times the concentrations observed with the maximum recommended dose of INTUNIV® of 0.12 mg/kg. Guanfacine was not shown to prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Distribution
Guanfacine is readily absorbed and approximately 70% bound to plasma proteins independent of drug concentration. After oral administration of INTUNIV® the time to peak plasma concentration is approximately 5 hours in children and adolescents with ADHD.
Immediate-release guanfacine and INTUNIV® have different pharmacokinetic characteristics; dose substitution on a milligram per milligram basis will result in differences in exposure.
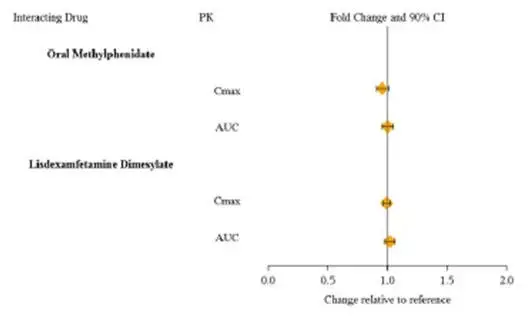
A comparison across studies suggests that the Cmax is 60% lower and AUC0-∞ 43% lower, respectively, for INTUNIV® compared to immediate-release guanfacine. Therefore, the relative bioavailability of INTUNIV® to immediate-release guanfacine is 58%. The mean pharmacokinetic parameters in adults following the administration of INTUNIV® 1 mg once daily and immediate-release guanfacine 1mg once daily are summarized in Table 15.
| Parameter | INTUNIV® 1 mg once daily (n=52) | Immediate-release guanfacine 1 mg once daily (n=12) |
|---|---|---|
| Note: Values are mean +/- SD, except for tmax which is median (range) | ||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 0.6 |
| AUC0-∞ (ng∙h/mL) | 32 ± 9 | 56 ± 15 |
| tmax (h) | 6.0 (4.0 – 8.0) | 3.0 (1.5-4.0) |
| t½ (h) | 18 ± 4 | 16 ± 3 |
Figure 1: Comparison of Pharmacokinetics: INTUNIV® vs. Immediate-release guanfacine in Adults
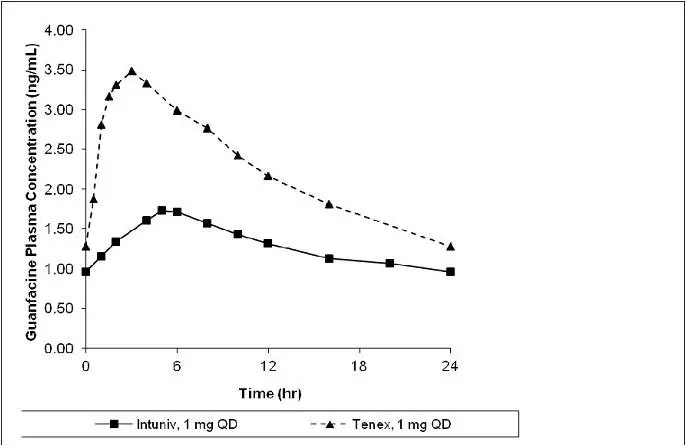
Exposure to guanfacine was higher in children (ages 6-12) compared to adolescents (ages 13-17) and adults. After oral administration of multiple doses of INTUNIV® 4 mg, the Cmax was 10 ng/mL compared to 7 ng/mL and the AUC was 162 ng∙h/mL compared to 116 ng∙h/mL in children (ages 6-12) and adolescents (ages 13-17), respectively. These differences are probably attributable to the lower body weight of children compared to adolescents and adults.
The pharmacokinetics were affected by intake of food when a single dose of INTUNIV® 4 mg was administered with a high-fat breakfast. The mean exposure increased (Cmax ~75% and AUC ~40%) compared to dosing in a fasted state.
14. Clinical Studies
Efficacy of INTUNIV® in the treatment of ADHD was established in children and adolescents (6 to 17 years) in:
- Five short-term, placebo-controlled monotherapy trials (Studies 1, 2, 4, 5, and 6).
- One short-term, placebo-controlled adjunctive trial with psychostimulants (Study 3).
- One long-term, placebo-controlled monotherapy maintenance trial (Study 7).
Studies 1 and 2: Fixed-dose INTUNIV® Monotherapy
Study 1 (301 study) was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, fixed-dose study, in which efficacy of once daily dosing with INTUNIV® (2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg) was evaluated for 5 weeks (n=345) in children and adolescents aged 6-17 years. Study 2 (304 study) was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, fixed-dose study, in which efficacy of once daily dosing with INTUNIV® (1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg) was evaluated for 6 weeks (n=324) in children and adolescents aged 6-17 years. In both studies, randomized patients in 2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg dose groups were titrated to their target fixed dose, and continued on the same dose until a dose tapering phase started. The lowest dose of 1 mg used in Study 2 was not randomized to patients weighing more than 50 kg. Patients who weighed less than 25 kg were not included in either study.
Signs and symptoms of ADHD were evaluated on a once weekly basis using the clinician administered and scored ADHD Rating Scale (ADHD-RS-IV), which includes both hyperactive/impulsive and inattentive subscales. The primary efficacy outcome was the change from baseline to endpoint in ADHD-RS-IV total scores. Endpoint was defined as the last post-randomization treatment week for which a valid score was obtained prior to dose tapering (up to Week 5 in Study 1 and up to Week 6 in Study 2).
The mean reductions in ADHD-RS-IV total scores at endpoint were statistically significantly greater for INTUNIV® compared to placebo for Studies 1 and 2. Placebo-adjusted changes from baseline were statistically significant for each of the 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg INTUNIV® randomized treatment groups in both studies, as well as the 1 mg INTUNIV® treatment group that was included only in Study 2 (see Table 16).
Dose-responsive efficacy was evident, particularly when data were examined on a weight-adjusted (mg/kg) basis. When evaluated over the dose range of 0.01-0.17 mg/kg/day, clinically relevant improvements were observed beginning at doses in the range 0.05-0.08 mg/kg/day. Doses up to 0.12 mg/kg/day were shown to provide additional benefit.
In the monotherapy trials (Studies 1 and 2), subgroup analyses were performed to identify any differences in response based on gender or age (6-12 vs. 13-17). Analyses of the primary outcome did not suggest any differential responsiveness on the basis of gender. Analyses by age revealed a statistically significant treatment effect only in the 6-12 age subgroup. Due to the relatively small proportion of adolescent patients (ages 13-17) enrolled into these studies (approximately 25%), these data may not have been sufficient to demonstrate efficacy in the adolescent patients. In these studies, patients were randomized to a fixed dose of INTUNIV® rather than optimized by body weight. Therefore, some adolescent patients were randomized to a dose that might have resulted in relatively lower plasma guanfacine concentrations compared to the younger patients. Over half (55%) of the adolescent patients received doses of 0.01-0.04 mg/kg. In studies in which systematic pharmacokinetic data were obtained, there was a strong inverse correlation between body weight and plasma guanfacine concentrations.
| Study Number (Age Range) | Treatment Group | Primary Efficacy Measure: ADHD-RS-IV Total Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Baseline Score (SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline (SE) | Placebo-subtracted Difference* (95% CI) | ||
| SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; LS Mean: least-squares mean; CI: unadjusted confidence interval. | ||||
|
||||
| Study 1 (6—17 years) | INTUNIV® 2 mg† | 36.1 (9.99) | -15.9 (1.37) | -7.4 (-11.3, -3.5) |
| INTUNIV® 3 mg† | 36.8 (8.72) | -16.0 (1.38) | -7.5 (-11.4, -3.6) | |
| INTUNIV® 4 mg† | 38.4 (9.21) | -18.5 (1.39) | -10.0 (-13.9, -6.1) | |
| Placebo | 38.1 (9.34) | -8.5 (1.42) | -- | |
| Study 2 (6—17 years) | INTUNIV® 1 mg†‡ | 41.7 (7.81) | -19.4 (1.69) | -6.8 (-11.3, -2.2) |
| INTUNIV® 2 mg† | 39.9 (8.74) | -18.1 (1.60) | -5.4 (-9.9, -0.9) | |
| INTUNIV® 3 mg† | 39.1 (9.22) | -20.0 (1.64) | -7.3 (-11.8, -2.8) | |
| INTUNIV® 4 mg† | 40.6 (8.57) | -20.6 (1.60) | -7.9 (-12.3, -3.4) | |
| Placebo | 39.3 (8.85) | -12.7 (1.60) | -- | |
Studies 4, 5 and 6: Flexible-dose INTUNIV® Monotherapy
Study 4 (314 study) was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-optimization study, in which efficacy of once daily dosing (morning or evening) with INTUNIV® (1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg) was evaluated for 8 weeks in children aged 6-12 years (n=340).
Signs and symptoms of ADHD were evaluated on a once weekly basis using the clinician administered and scored ADHD Rating Scale (ADHD-RS-IV), which includes both hyperactive/impulsive and inattentive subscales. The primary efficacy outcome was the change from baseline score at endpoint on the ADHD-RS-IV total scores. Endpoint was defined as the last post-randomization treatment week for which a valid score was obtained prior to dose tapering (up to Week 8).
Mean reductions in ADHD-RS-IV total scores at endpoint were statistically significantly greater for INTUNIV® compared to placebo in both AM and PM dosing groups of INTUNIV® (see Table 17).
Study 5 (312 study) was a 15-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-optimization study conducted in adolescents aged 13-17 years (n=314) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of INTUNIV® (1-7 mg/day; optimized dose range of 0.05-0.12 mg/kg/day) in the treatment of ADHD as measured by the ADHD Rating Scale-IV (ADHD-RS-IV). Patients receiving INTUNIV® showed statistically significantly greater improvement on the ADHD-RS-IV total score compared with patients receiving placebo (see Table 17).
Study 6 (316 study) was a 12-week (for children aged 6-12) or 15-week (for adolescents aged 13-17), randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo- and active-reference, dose-optimization study conducted in pediatric patients (children and adolescents aged 6-17 years old inclusive) (n=337) to assess the efficacy and safety of once-daily dosing (children: 1-4 mg/day, adolescents: 1-7 mg/day; optimized dose range of 0.05 to 0.12 mg/kg/day) in the treatment of ADHD. INTUNIV® was statistically superior to placebo on symptoms of ADHD in patients 6-17 years as measured by change from baseline in ADHD-RS-IV total scores (see Table 17).
| Study Number (Age Range) | Treatment Group | Primary Efficacy Measure: ADHD-RS-IV Total Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Baseline Score (SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline (SE) | Placebo-subtracted Difference* (95% CI) | ||
| SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; LS Mean: least-squares mean; CI: unadjusted confidence interval. | ||||
|
||||
| Study 3†
(6—17 years) | INTUNIV® 1—4 mg AM‡ | 37.6 (8.13) | -20.3 (0.97) | -4.5 (-7.5, -1.4) |
| INTUNIV® 1—4 mg PM‡ | 37.0 (7.65) | -21.2 (0.97) | -5.3 (-8.3, -2.3) | |
| Placebo | 37.7 (7.75) | -15.9 (0.96) | -- | |
| Study 4 (6—12 years) | INTUNIV® 1—4 mg AM‡ | 41.7 (6.39) | -20.0 (1.23) | -9.4 (-12.8, -6.0) |
| INTUNIV® 1—4 mg PM‡ | 41.6 (6.66) | -20.4 (1.19) | -9.8 (-13.1, -6.4) | |
| Placebo | 42.9 (6.29) | -10.6 (1.20) | --- | |
| Study 5 (13—17 years) | INTUNIV® 1—7 mg‡ | 39.9 (5.57) | -24.6 (1.06) | -6.03 (-8.87, -3.19) |
| Placebo | 40.0 (6.11) | -18.5 (1.08) | -- | |
| Study 6 (6—17 years) | INTUNIV® 1—7 mg‡ | 43.1 (5.47) | -23.89 (1.15) | -8.88 (-11.94, -5.81) |
| Placebo | 43.2 (5.60) | -15.01 (1.16) | -- | |
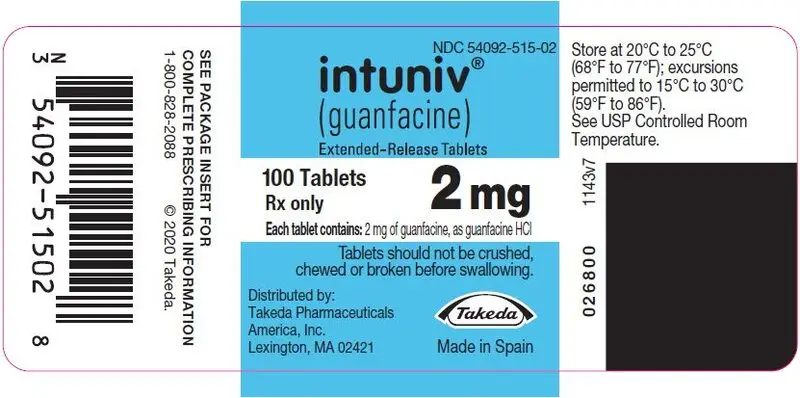
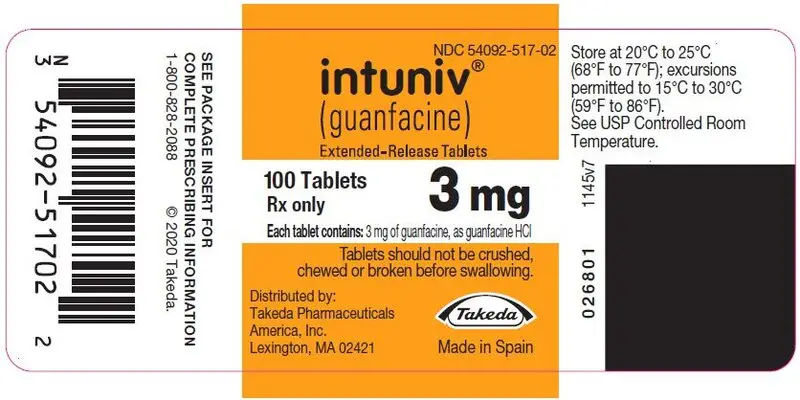
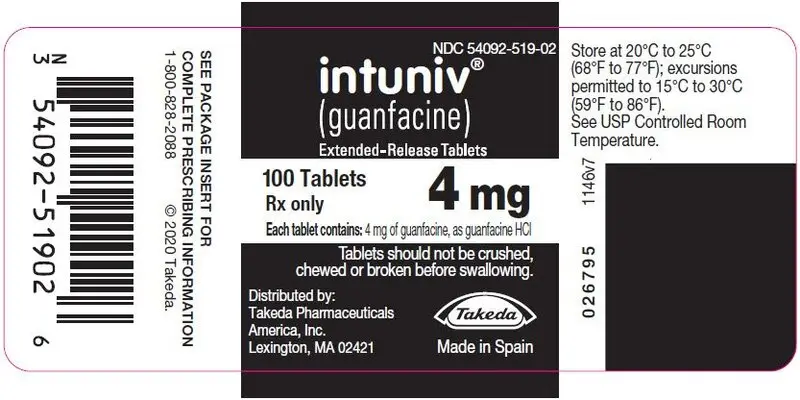
16. How is Intuniv supplied
INTUNIV® is supplied in 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg strength extended-release tablets in 100 count bottles.
| 1 mg | 2 mg | 3 mg | 4 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | White/off-white | White/off-white | Green | Green |
| Shape | Round | Caplet | Round | Caplet |
| Debossment (top/bottom) | 503 / 1 mg | 503 / 2 mg | 503 / 3 mg | 503 / 4 mg |
| NDC number | 54092-513-02 | 54092-515-02 | 54092-517-02 | 54092-519-02 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Patient Information
INTUNIV® (in-TOO-niv)
(guanfacine)
Extended-Release Tablets
Read the Patient Information that comes with INTUNIV® before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is INTUNIV®?
INTUNIV® is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). INTUNIV may be used alone or with ADHD stimulant medicines.
INTUNIV® is not a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant.
It is not known if INTUNIV is safe and effective in children younger than 6 years of age.
Who should not take INTUNIV®?
Do not take INTUNIV if you are allergic to guanfacine or any of the ingredients in INTUNIV. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in INTUNIV.
What should I tell my doctor before taking INTUNIV®?
Before you take INTUNIV®, tell your doctor if you:
- have heart problems or a low heart rate
- have fainted
- have low or high blood pressure
- have liver or kidney problems
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if INTUNIV® will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- There is a pregnancy registry for females who are exposed to ADHD medications, including INTUNIV, during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of females exposed to INTUNIV and their baby. If you or your child becomes pregnant during treatment with INTUNIV, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the National Pregnancy Registry of ADHD medications at 1-866-961-2388.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if INTUNIV® passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby while taking INTUNIV®.
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
INTUNIV® may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how INTUNIV® works.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- ketoconazole
- medicines that can affect enzyme metabolism
- high blood pressure medicine
- sedatives
- benzodiazepines
- barbiturates
- antipsychotics
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take INTUNIV®?
- Take INTUNIV® exactly as your doctor tells you.
- Your doctor may change your dose. Do not change your dose of INTUNIV® without talking to your doctor.
- Do not stop taking INTUNIV® without talking to your doctor.
- Try not to miss your dose of INTUNIV®. If you miss a dose of INTUNIV®, take the next dose at your regular time. If you miss 2 or more doses, talk to your doctor, as you may need to restart INTUNIV® with a lower dose.
- Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
- INTUNIV® should be taken 1 time a day in the morning or in the evening, either alone or in combination with an ADHD stimulant medicine that your doctor may prescribe. Your doctor will tell you when to take INTUNIV® and when to take your ADHD stimulant medication.
- INTUNIV® should be swallowed whole with a small amount of water, milk, or other liquid.
- Do not crush, chew, or break INTUNIV®. Tell your doctor if you cannot swallow INTUNIV® whole.
- Do not take INTUNIV® with a high-fat meal.
- Your doctor will check your blood pressure and heart rate while you take INTUNIV®.
- If you take too much INTUNIV®, call your local Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking INTUNIV®?
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how INTUNIV® affects you. INTUNIV® can slow your thinking and motor skills.
- Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking INTUNIV® until you talk with your doctor. INTUNIV® taken with alcohol or medicines that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
- Do not become dehydrated or overheated. This may increase your chance of having low blood pressure or fainting while taking INTUNIV.
- Do not suddenly stop INTUNIV. Tell your healthcare provider if you have been vomiting and cannot take INTUNIV, you may be at risk for rebound hypertension.
What are the possible side effects of INTUNIV®?
INTUNIV® may cause serious side effects including:
- low blood pressure
- low heart rate
- fainting
- sleepiness
- increased blood pressure and heart rate after suddenly stopping INTUNIV (rebound hypertension). Suddenly stopping INTUNIV can cause increased blood pressure and heart rate and other withdrawal symptoms such as headache, confusion, nervousness, agitation, and tremors. If these symptoms continue to get worse and are left untreated, it could lead to a very serious condition including very high blood pressure, feeling very sleepy or tired, severe headache, vomiting, vision problems, seizures.
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of INTUNIV® include:
- sleepiness
- tiredness
- trouble sleeping
- low blood pressure
- nausea
- stomach pain
- dizziness
- dry mouth
- irritability
- vomiting
- slow heart rate
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of INTUNIV®. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store INTUNIV®?
- Store INTUNIV® between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C)
Keep INTUNIV® and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about the safe and effective use INTUNIV®
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information Leaflet. Do not use INTUNIV® for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give INTUNIV® to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about INTUNIV®. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about INTUNIV® that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.INTUNIV.com or call 1-800-828-2088.
What are the ingredients in INTUNIV®?
Active ingredient: guanfacine hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: hypromellose, methacrylic acid copolymer, lactose, povidone, crospovidone, microcrystalline cellulose, fumaric acid, and glycerol behenate. In addition, the 3 mg and 4 mg tablets also contain green pigment blend PB-1763.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Lexington, MA 02421
INTUNIV® is a registered trademark of Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
© 2020 Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. All rights reserved.
Patented: see www.takeda.com/en-us/patents.
Revised: 08/2020
| INTUNIV
guanfacine tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INTUNIV
guanfacine tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INTUNIV
guanfacine tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INTUNIV
guanfacine tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INTUNIV
guanfacine kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc. (039997266) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industriale Chimica SRL | 436796809 | API MANUFACTURE(54092-513, 54092-515, 54092-517, 54092-519) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalent Pharma Solutions, LLC | 014167995 | ANALYSIS(54092-513, 54092-515, 54092-517, 54092-519) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mayne Pharma International Pty Ltd. | 756003745 | ANALYSIS(54092-513, 54092-515, 54092-517, 54092-519) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Manufacturing Services LLC | 079415560 | ANALYSIS(54092-513, 54092-515, 54092-517, 54092-519) , LABEL(54092-513, 54092-515, 54092-517, 54092-519) , MANUFACTURE(54092-513, 54092-515, 54092-517, 54092-519, 54092-520) , PACK(54092-513, 54092-515, 54092-517, 54092-519) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quimica Sintetica S.A. | 460054141 | API MANUFACTURE(54092-513, 54092-515, 54092-517, 54092-519) | |