Drug Detail:Inveltys (ophthalmic) (Loteprednol (ophthalmic) [ lo-te-pred-nol-off-thal-mik ])
Drug Class: Ophthalmic steroids
Highlights of Prescribing Information
INVELTYS (loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension) 1%, for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1998
Indications and Usage for Inveltys
INVELTYS is a corticosteroid indicated for the treatment of post-operative inflammation and pain following ocular surgery. (1)
Inveltys Dosage and Administration
- Shake for one to two seconds before using. (2)
- Instill one to two drops of INVELTYS into the affected eye twice daily beginning the day after surgery and continuing throughout the first 2 weeks of the post-operative period. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Ophthalmic suspension containing 10 mg/mL of loteprednol etabonate. (3)
Contraindications
INVELTYS is contraindicated in most viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, and varicella, and also in mycobacterial infection of the eye and fungal diseases of ocular structures. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Increase: Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision. If this product is used for 10 days or longer, IOP should be monitored. (5.1)
- Cataracts: Use of corticosteroids may result in posterior subcapsular cataract formation. (5.2)
- Delayed Healing: Use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation. In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations have been known to occur with the use of topical steroids. The initial prescription and renewal of the medication order should be made by a physician only after examination of the patient with the aid of magnification such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining. (5.3)
- Bacterial Infections: Prolonged use of corticosteroids may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections. In acute purulent conditions, steroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection. (5.4)
- Viral Infections: Use of a corticosteroid medication in the treatment of patients with a history of herpes simplex requires great caution. Use of ocular steroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex). (5.5)
-
Fungal Infections: Fungal infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term local steroid application. Fungus invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where a steroid has been used or is in use. (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse drug reactions were eye pain (1%) and posterior capsular opacification (1%). These reactions may have been the consequence of the surgical procedure. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Kala Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-833-287-KALA (1-833-287-5252) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2022
Related/similar drugs
diclofenac ophthalmic, dexamethasone ophthalmic, ketorolac ophthalmic, prednisolone ophthalmic, Lotemax, DurezolFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Inveltys
INVELTYS is a corticosteroid indicated for the treatment of post-operative inflammation and pain following ocular surgery.
2. Inveltys Dosage and Administration
4. Contraindications
INVELTYS is contraindicated in most viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, and varicella, and also in mycobacterial infection of the eye and fungal diseases of ocular structures.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Increase
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, as well as defects in visual acuity and fields of vision. Steroids should be used with caution in the presence of glaucoma. If this product is used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure should be monitored.
5.3 Delayed Healing
Use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation. In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations have been known to occur with the use of topical steroids. The initial prescription and renewal of the medication order should be made by a physician only after examination of the patient with the aid of magnification such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining.
5.4 Bacterial Infections
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections. In acute purulent conditions of the eye, steroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection.
5.5 Viral Infections
Use of corticosteroid medication in the treatment of patients with a history of herpes simplex requires great caution. Use of ocular steroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex).
5.6 Fungal Infections
Fungal infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term local steroid application. Fungus invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where a steroid has been used or is in use. Fungal cultures should be taken when appropriate.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Adverse reactions associated with ophthalmic steroids include elevated intraocular pressure, which may be associated with infrequent optic nerve damage, visual acuity and field defects, posterior subcapsular cataract formation, delayed wound healing and secondary ocular infection from pathogens including herpes simplex, and perforation of the globe where there is thinning of the cornea or sclera.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most common adverse drug reactions in the clinical trials with INVELTYS were eye pain and posterior capsular opacification, both reported in 1% of patients. These reactions may have been the consequence of the surgical procedure.
11. Inveltys Description
Loteprednol etabonate is a corticosteroid. Its chemical name is chloromethyl 17α-[(ethoxycarbonyl)oxy]-11β-hydroxy-3-oxoandrosta-1,4-diene-17β-carboxylate. Its molecular formula is C24H31ClO7 and its chemical structure is:
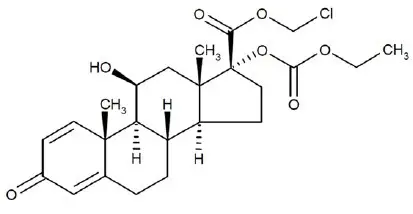
C24H31ClO7
Mol. Wt. 467.0
INVELTYS (loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension) 1% contains a sterile, topical anti-inflammatory corticosteroid for ophthalmic use. Each mL contains:
- ACTIVE: loteprednol etabonate 10 mg (1%)
- INACTIVES: glycerin, sodium citrate dihydrate, Poloxamer 407, sodium chloride, edetate disodium dihydrate, citric acid, and water for injection
- PRESERVATIVE: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%
12. Inveltys - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Corticosteroids inhibit the inflammatory response to a variety of inciting agents and probably delay or slow healing. They inhibit the edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilation, leukocyte migration, capillary proliferation, fibroblast proliferation, deposition of collagen, and scar formation associated with inflammation. While glucocorticoids are known to bind to and activate the glucocorticoid receptor, the molecular mechanisms involved in glucocorticoid/glucocorticoid receptor-dependent modulation of inflammation are not clearly established. However, corticosteroids are thought to inhibit prostaglandin production through several independent mechanisms.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Loteprednol etabonate is lipid soluble and can penetrate into cells. Loteprednol etabonate is synthesized through structural modifications of prednisolone-related compounds so that it will undergo a predictable transformation to an inactive metabolite. Based upon in vivo and in vitro preclinical metabolism studies, loteprednol etabonate undergoes extensive metabolism to inactive carboxylic acid metabolites, PJ-91 and PJ-90.
Following twice-daily unilateral topical ocular dosing of INVELTYS for 14 days in healthy subjects, the plasma concentrations of loteprednol etabonate were below the limit of quantitation (1 ng/mL) at all timepoints.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of loteprednol etabonate. Loteprednol etabonate was not genotoxic in vitro in the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma thymidine kinase (tk) assay, or in a chromosome aberration test in human lymphocytes, or in vivo in the single dose mouse micronucleus assay.
14. Clinical Studies
Clinical efficacy was evaluated in 2 multi-centered, randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled trials in which patients with an anterior cell grade greater than or equal to "2" (a cell count of 6 or higher using a slit-lamp biomicroscope) after cataract surgery were assigned to INVELTYS or placebo (vehicle) following surgery (NCT # 02163824 and NCT # 02793817). One to two drops of INVELTYS or vehicle was self-administered twice a day for 14 days, beginning the day after surgery. Complete resolution of inflammation (a cell count of 0 maintained through day 15 without rescue medication) and complete resolution of pain (a patient-reported pain grade of 0 maintained through day 15 without rescue medication) was assessed 4, 8, and 15 days post-surgery. In the intent-to-treat analysis of both studies, a significant benefit was seen in the INVELTYS-treated group for complete resolution of ocular inflammation at Days 8 and 15, and complete resolution of pain at Days 4, 8, and 15, when compared with placebo. The consolidated clinical trial results are provided below.
Figure 1 Consolidated Clinical Trial Data: Percent of Patients with Complete Resolution of Anterior Chamber Cells (Cell Count = 0) at Days 8 and 15
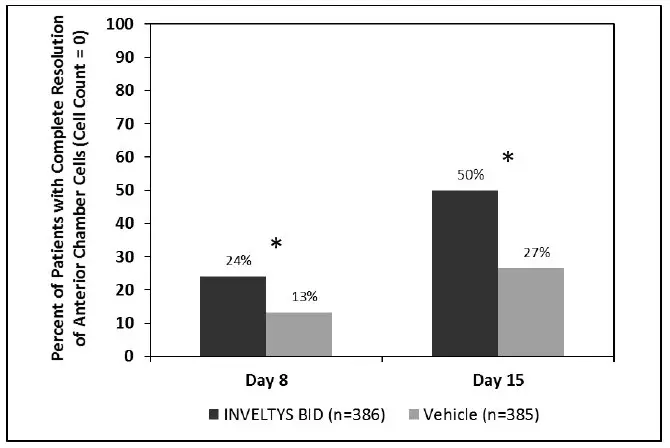
* p-values < 0.01 for treatment comparisons
Figure 2 Consolidated Clinical Trial Data: Percent of Patients Who Were Pain Free at Days 4, 8, and 15
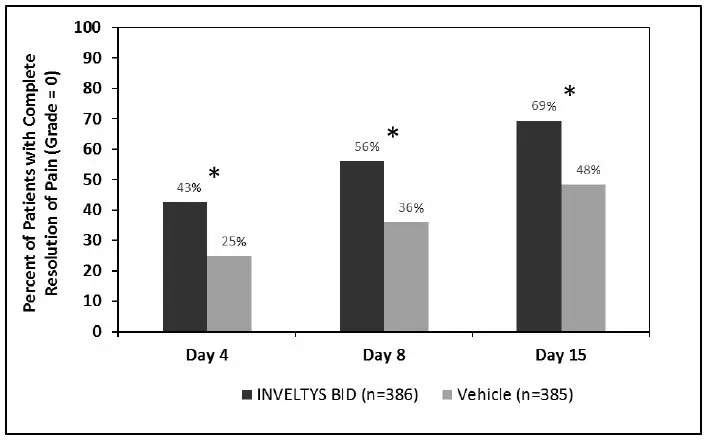
* p-values < 0.01 for treatment comparisons
16. How is Inveltys supplied
INVELTYS (loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension) 1% is a sterile ophthalmic suspension. It is supplied in a white low-density polyethylene plastic dropper bottle with a controlled-drop linear low-density polyethylene tip, a pink high-density polyethylene cap, and a white low-density polyethylene tamper-evident overcap in the following size:
2.8 mL in a 5 mL bottle (NDC 71571-121-28)
|
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
INVELTYS [in-vel-tis] |
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to properly administer INVELTYS.
Important Information You Need to Know Before Using INVELTYS
- INVELTYS is for use in the eye only.
- Wash your hands before using INVELTYS.
- Do not use if the tamper-evident seal is not intact.
- Do not let the INVELTYS dropper tip touch your eye, fingers, or any other surfaces to avoid contamination or injury to your eye.
- Use INVELTYS exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to.
- If you are using INVELTYS with other eye (ophthalmic) medicines, you should wait at least 5 minutes between using INVELTYS and the other medicine.
- If you wear contact lenses, remove them before using INVELTYS.
- Put the pink cap back on INVELTYS after each use.
Before you use INVELTYS for the first time:
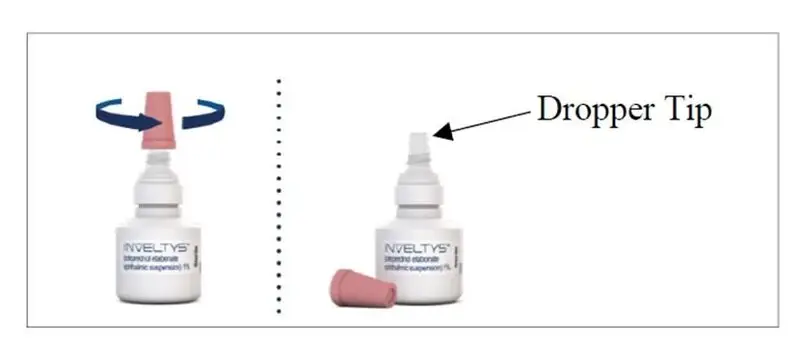
There are two caps on your bottle of INVELTYS. Hold the bottle firmly by its neck. Remove the white cap by twisting it clockwise (See Figure A). Throw away the white cap. INVELTYS is now ready to use.
Follow Steps 1 to 6 each time you use INVELTYS.
| Step 1. | Wash your hands well. |
| Step 2. | Shake the INVELTYS bottle for 1 to 2 seconds (See Figure B). |
| Figure B | |
| Step 3: | Remove the pink cap from the top of the INVELTYS dropper by turning it counterclockwise (See Figure C). Keep the pink cap. Do not let the INVELTYS dropper tip touch your eye, fingers, or any other surface. |
| Figure C | |
| Step 4: | Turn the INVELTYS bottle upside down (See Figure D). |
| Figure D | |
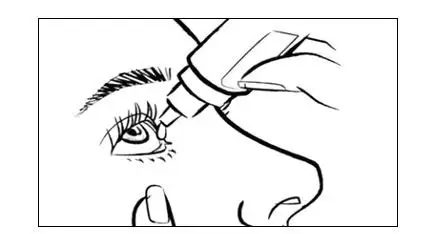
| Step 5: | Tilt your head back. Hold the bottle directly above your affected eye. Squeeze the middle of the INVELTYS bottle gently to put 1 to 2 drops (follow your doctor's recommendation) into the affected eye (See Figure E). |
| Figure E | |
| Step 6: | Place the pink cap back onto the INVELTYS bottle and tighten by turning clockwise (See Figure F). |
| Figure F |
If you use contact lenses, wait for 15 minutes before placing them back in.
How should I store INVELTYS?
- Store INVELTYS upright at 59ºF to 77ºF (15ºC to 25ºC).
- Do not freeze.
Keep INVELTYS and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
Kala Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Arlington, MA 02476
Approved: 3/2022
| INVELTYS
loteprednol etabonate suspension |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - ALCON LABORATORIES, INC. (008018525) |