Drug Detail:Invokamet xr (Canagliflozin and metformin [ kan-a-gli-floe-zin-and-met-for-min ])
Drug Class: Antidiabetic combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
INVOKAMET XR (canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride extended-release) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval – 2016
WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS and LOWER LIMB AMPUTATION
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Lactic Acidosis
- Postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias. Symptoms included malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, somnolence, and abdominal pain. Laboratory abnormalities included elevated blood lactate levels, anion gap acidosis, increased lactate/pyruvate ratio; and metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL. (5.1)
- Risk factors include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs, age >65 years old, radiological studies with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states, excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment. Steps to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis in these high risk groups are provided in the Full Prescribing Information. (5.1)
- If lactic acidosis is suspected, discontinue INVOKAMET XR and institute general supportive measures in a hospital setting. Prompt hemodialysis is recommended. (5.1)
Risk of Lower Limb Amputation
- In patients with type 2 diabetes who have established cardiovascular disease (CVD) or at risk for CVD, canagliflozin, a component of INVOKAMET XR, has been associated with lower limb amputations, most frequently of the toe and midfoot; some also involved the leg. (5.2)
- Before initiating, consider factors that may increase the risk of amputation. Monitor patients receiving INVOKAMET XR for infections or ulcers of the lower limbs, and discontinue if these occur. (5.2)
Recent Major Changes
| Boxed Warning | 07/2017 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.1) | 08/2017 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.2) | 07/2017 |
Indications and Usage for Invokamet XR
INVOKAMET XR is a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor and biguanide combination product indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus when treatment with both canagliflozin and metformin is appropriate (1)
Limitation of use:
Not for treatment of type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis (1)
Invokamet XR Dosage and Administration
- Individualize based on the patient's current regimen (2.1)
- Take two tablets once daily with the morning meal (2.1)
- In patients currently not treated with either canagliflozin or metformin, initiate therapy with two INVOKAMET XR tablets, each tablet containing canagliflozin 50 mg and metformin 500 mg (2.1)
- In patients already treated with canagliflozin and metformin, switch to two INVOKAMET XR tablets containing the same total daily dose of canagliflozin and the same, or nearest appropriate, total daily dose of metformin (2.1)
- In patients that require additional glycemic control that are taking a total daily dose of canagliflozin 100 mg, the INVOKAMET XR dose can be increased to canagliflozin 300 mg once daily. Do not exceed a total daily canagliflozin dose of 300 mg (2.1)
- Gradually escalate metformin dose to reduce the gastrointestinal side effects while not exceeding a total daily dose of 2000 mg (2.1)
- Assess renal function before initiating and periodically thereafter (2.2)
- INVOKAMET XR is contraindicated in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 (2.2)
- Limit the dose of canagliflozin component to two tablets, each tablet containing 50 mg, daily in patients with an eGFR of 45 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (2.2)
- INVOKAMET XR may need to be discontinued at time of, or prior to, iodinated contrast imaging procedures (2.4)
- Swallow whole. Never crush, cut, or chew (2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Film-coated tablets:
- Canagliflozin 50 mg and metformin hydrochloride 500 mg extended-release
- Canagliflozin 50 mg and metformin hydrochloride 1,000 mg extended-release
- Canagliflozin 150 mg and metformin hydrochloride 500 mg extended-release
- Canagliflozin 150 mg and metformin hydrochloride 1,000 mg extended-release (3)
Contraindications
- Moderate to severe renal impairment (eGFR below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2), end stage renal disease or dialysis (4, 5.1, 5.5)
- Metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis (1, 4, 5.1)
- History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to canagliflozin or metformin (4, 5.10)
Warnings and Precautions
- Lactic acidosis: See boxed warning (5.1)
- Lower limb amputation: See boxed warning (5.2)
- Hypotension: Before initiating INVOKAMET XR, assess volume status and correct hypovolemia in patients with renal impairment, the elderly, in patients with low systolic blood pressure, or on diuretics, ACEi, or ARB. Monitor for signs and symptoms during therapy (5.3)
- Ketoacidosis: Assess patients who present with signs and symptoms of metabolic acidosis for ketoacidosis, regardless of blood glucose level. If suspected, discontinue INVOKAMET XR, evaluate and treat promptly. Before initiating INVOKAMET XR, consider risk factors for ketoacidosis. Patients on INVOKAMET XR may require monitoring and temporary discontinuation of therapy in clinical situations known to predispose to ketoacidosis (5.4)
- Acute kidney injury and impairment in renal function: Consider temporarily discontinuing in settings of reduced oral intake or fluid losses. If acute kidney injury occurs, discontinue and promptly treat. Monitor renal function during therapy (5.5)
- Hyperkalemia: Monitor potassium levels in patients with impaired renal function and in patients predisposed to hyperkalemia (2.2, 5.6, 6.1, 8.6)
- Urosepsis and pyelonephritis: Evaluate patients for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections and treat promptly, if indicated (5.7)
- Hypoglycemia: Consider a lower dose of insulin or the insulin secretagogue to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with INVOKAMET XR (5.8)
- Genital mycotic infections: Monitor and treat if indicated (5.9)
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Discontinue INVOKAMET XR and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve (5.10)
- Bone fracture: Consider factors that contribute to fracture risk before initiating INVOKAMET XR (5.11)
- Vitamin B12 deficiency: Metformin may lower vitamin B12 levels. Monitor hematologic parameters annually (5.12)
- Increased LDL-C: Monitor LDL-C and treat if appropriate (5.13)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Most common adverse reactions associated with canagliflozin (5% or greater incidence): female genital mycotic infections, urinary tract infection, and increased urination (6.1)
- Most common adverse reactions associated with metformin (5% or greater incidence) are diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, asthenia, indigestion, abdominal discomfort, and headache (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-526-7736 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may increase risk of lactic acidosis. Consider more frequent monitoring (7.1)
- Drugs that reduce metformin clearance (such as ranolazine, vandetanib, dolutegravir, and cimetidine) may increase the accumulation of metformin. Consider the benefits and risks of concomitant use (7.1)
- Alcohol can potentiate the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake (7.1)
- UGT inducers (e.g., rifampin): Canagliflozin exposure is reduced. Consider increasing canagliflozin from a total daily dose of 100 mg to a total daily dose of 300 mg once daily (2.3, 7.2)
- Digoxin: Monitor digoxin levels (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Advise females of the potential risk to a fetus especially during the second and third trimesters (8.1)
- Lactation: INVOKAMET XR is not recommended when breastfeeding (8.2)
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Advise premenopausal females of the potential for an unintended pregnancy (8.3).
- Geriatrics: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to reduced intravascular volume. Assess renal function more frequently (5.3, 6.1, 8.5)
- Renal impairment: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to reduced intravascular volume and renal function (2.2, 5.5, 8.6)
- Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use in patients with hepatic impairment (8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 1/2018
Related/similar drugs
Repatha, Mounjaro, metformin, Ozempic, Xarelto, simvastatin, TrulicityFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Invokamet XR
INVOKAMET XR (canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride extended release) is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus when treatment with both canagliflozin and metformin is appropriate.
2. Invokamet XR Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
- Individualize the starting dose of INVOKAMET XR (canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride extended-release), taken once-daily with the morning meal, based on the effectiveness and tolerability of the patient's current regimen:
- –
- In patients currently not treated with either canagliflozin or metformin, initiate therapy with two INVOKAMET XR tablets, each tablet containing canagliflozin 50 mg and metformin 500 mg [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
- –
- In patients on metformin, switch to two INVOKAMET XR tablets, where two tablets equal a starting dose of canagliflozin 100 mg daily and the patient's current total daily dose (or nearest appropriate) of metformin.
- –
- In patients on canagliflozin, switch to two INVOKAMET XR tablets, where two tablets equal the patient's current total daily dose of canagliflozin and a starting dose of metformin 1000 mg daily.
- –
- In patients already treated with canagliflozin and metformin, switch to two INVOKAMET XR tablets containing the same total daily dose of canagliflozin and the same, or nearest appropriate, total daily dose of metformin.
- In patients that require additional glycemic control that are taking a total daily dose of canagliflozin 100 mg, the INVOKAMET XR dose can be increased to canagliflozin 300 mg once daily [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3) and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
- The dose of metformin should be gradually escalated to reduce the gastrointestinal side effects due to metformin [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3) and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
- Patients taking an evening dose of metformin XR should skip their last dose before starting INVOKAMET XR the following morning.
- In patients with volume depletion not previously treated with canagliflozin, correct this condition before initiating INVOKAMET XR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.5, 8.6), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
- Adjust dosing based on effectiveness and tolerability while not exceeding the maximum recommended daily dose of metformin 2000 mg and canagliflozin 300 mg in patients with an eGFR of 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or greater [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Patients with Renal Impairment
- Assess renal function before initiating INVOKAMET XR and periodically thereafter.
- INVOKAMET XR is contraindicated in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.4)].
- Limit the dose of INVOKAMET XR to two tablets, each tablet containing canagliflozin 50 mg, in patients with moderate renal impairment with an eGFR of 45 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
2.3 Concomitant Use with UDP-Glucuronosyl Transferase (UGT) Enzyme Inducers
If an inducer of UGTs (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, ritonavir) is co-administered with INVOKAMET XR, consider increasing the dose of canagliflozin to a total daily dose of 300 mg once daily in patients currently tolerating INVOKAMET XR with 100 mg canagliflozin once daily who have an eGFR of 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or greater and require additional glycemic control [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Consider another antihyperglycemic agent in patients with an eGFR of 45 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 receiving concurrent therapy with a UGT inducer.
2.4 Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
Discontinue INVOKAMET XR at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR between 45 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m2; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure; restart INVOKAMET XR if renal function is stable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
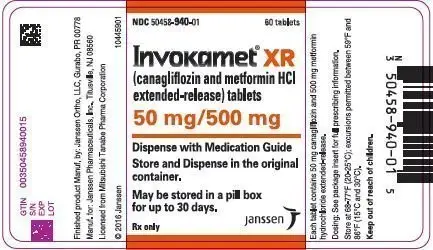
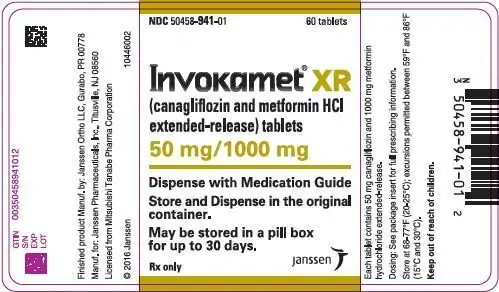
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
INVOKAMET XR (canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride extended-release) film-coated tablets for oral administration are available in the following strengths:
- Canagliflozin 50 mg and metformin hydrochloride 500 mg extended-release tablets are oblong, biconvex, almost white to light orange film-coated tablets with "CM1" on one side. A thin line on the tablet side may be visible.
- Canagliflozin 50 mg and metformin hydrochloride 1,000 mg extended-release tablets are oblong, biconvex, pink, film-coated tablets with "CM3" on one side. A thin line on the tablet side may be visible.
- Canagliflozin 150 mg and metformin hydrochloride 500 mg tablets extended-release are oblong, biconvex, orange, film-coated tablets with "CM2" on one side. A thin line on the tablet side may be visible.
- Canagliflozin 150 mg and metformin hydrochloride 1,000 mg extended-release tablets are oblong, biconvex, reddish brown, film-coated tablets with "CM4" on one side. A thin line on the tablet side may be visible.
4. Contraindications
INVOKAMET XR is contraindicated in patients with:
- Moderate to severe renal impairment (eGFR below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2), end stage renal disease (ESRD) or patients on dialysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
- Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- History of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to canagliflozin or metformin, such as anaphylaxis or angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Lactic Acidosis
There have been post-marketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis, including fatal cases. These cases had a subtle onset and were accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, abdominal pain, respiratory distress, or increased somnolence; however, hypothermia, hypotension and resistant bradyarrhythmias have occurred with severe acidosis. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate concentrations (>5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), and an increased lactate:pyruvate ratio; metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL. Metformin decreases liver uptake of lactate increasing lactate blood levels which may increase the risk of lactic acidosis, especially in patients at risk.
If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, general supportive measures should be instituted promptly in a hospital setting, along with immediate discontinuation of INVOKAMET XR. In INVOKAMET XR-treated patients with a diagnosis or strong suspicion of lactic acidosis, prompt hemodialysis is recommended to correct the acidosis and remove accumulated metformin (metformin hydrochloride is dialyzable, with a clearance of up to 170 mL/minute under good hemodynamic conditions). Hemodialysis has often resulted in reversal of symptoms and recovery.
Educate patients and their families about the symptoms of lactic acidosis and if these symptoms occur instruct them to discontinue INVOKAMET XR and report these symptoms to their healthcare provider.
For each of the known and possible risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis, recommendations to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis are provided below:
5.2 Lower Limb Amputation
An approximately 2-fold increased risk of lower limb amputations associated with canagliflozin, a component of INVOKAMET XR, was observed in CANVAS and CANVAS-R, two large, randomized, placebo-controlled trials evaluating patients with type 2 diabetes who had either established cardiovascular disease or were at risk for cardiovascular disease. In CANVAS, canagliflozin-treated patients and placebo-treated patients had 5.9 and 2.8 amputations per 1000 patients per year, respectively. In CANVAS-R, canagliflozin-treated patients and placebo-treated patients had 7.5 and 4.2 amputations per 1000 patients per year, respectively. The risk of lower limb amputations was observed at both the 100 mg and 300 mg once daily dosage regimens. The amputation data for CANVAS and CANVAS-R are shown in Tables 2 and 3, respectively [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Amputations of the toe and midfoot (99 out of 140 patients with amputations receiving canagliflozin in the two trials) were the most frequent; however, amputations involving the leg, below and above the knee, were also observed (41 out of 140 patients with amputations receiving canagliflozin in the two trials). Some patients had multiple amputations, some involving both lower limbs.
Lower limb infections, gangrene, and diabetic foot ulcers were the most common precipitating medical events leading to the need for an amputation. The risk of amputation was highest in patients with a baseline history of prior amputation, peripheral vascular disease, and neuropathy.
Before initiating INVOKAMET XR, consider factors in the patient history that may predispose to the need for amputations, such as a history of prior amputation, peripheral vascular disease, neuropathy and diabetic foot ulcers. Counsel patients about the importance of routine preventative foot care. Monitor patients receiving INVOKAMET XR for signs and symptoms of infection (including osteomyelitis), new pain or tenderness, sores or ulcers involving the lower limbs, and discontinue INVOKAMET XR if these complications occur.
5.3 Hypotension
Canagliflozin causes intravascular volume contraction. Symptomatic hypotension can occur after initiating INVOKAMET XR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] particularly in patients with eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, elderly patients, patients on either diuretics or medications that interfere with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (e.g., angiotensin-converting-enzyme [ACE] inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs]), or patients with low systolic blood pressure. Before initiating INVOKAMET XR in patients with one or more of these characteristics who were not already on canagliflozin, volume status should be assessed and corrected. Monitor for signs and symptoms after initiating therapy.
5.4 Ketoacidosis
Reports of ketoacidosis, a serious life-threatening condition requiring urgent hospitalization have been identified in postmarketing surveillance in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving sodium glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, including canagliflozin. Fatal cases of ketoacidosis have been reported in patients taking canagliflozin. INVOKAMET XR is not indicated for the treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus [see Indications and Usage (1)].
Patients treated with INVOKAMET XR who present with signs and symptoms consistent with severe metabolic acidosis should be assessed for ketoacidosis regardless of presenting blood glucose levels, as ketoacidosis associated with INVOKAMET XR may be present even if blood glucose levels are less than 250 mg/dL. If ketoacidosis is suspected, INVOKAMET XR should be discontinued, patient should be evaluated, and prompt treatment should be instituted. Treatment of ketoacidosis may require insulin, fluid and carbohydrate replacement.
In many of the postmarketing reports, and particularly in patients with type 1 diabetes, the presence of ketoacidosis was not immediately recognized and institution of treatment was delayed because presenting blood glucose levels were below those typically expected for diabetic ketoacidosis (often less than 250 mg/dL). Signs and symptoms at presentation were consistent with dehydration and severe metabolic acidosis and included nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, generalized malaise, and shortness of breath. In some but not all cases, factors predisposing to ketoacidosis such as insulin dose reduction, acute febrile illness, reduced caloric intake due to illness or surgery, pancreatic disorders suggesting insulin deficiency (e.g., type 1 diabetes, history of pancreatitis or pancreatic surgery), and alcohol abuse were identified.
Before initiating INVOKAMET XR consider factors in the patient history that may predispose to ketoacidosis including pancreatic insulin deficiency from any cause, caloric restriction, and alcohol abuse. In patients treated with INVOKAMET XR consider monitoring for ketoacidosis and temporarily discontinuing INVOKAMET XR in clinical situations known to predispose to ketoacidosis (e.g., prolonged fasting due to acute illness or surgery).
5.5 Acute Kidney Injury and Impairment in Renal Function
Canagliflozin causes intravascular volume contraction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] and can cause renal impairment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. There have been postmarketing reports of acute kidney injury, some requiring hospitalization and dialysis, in patients receiving canagliflozin; some reports involved patients younger than 65 years of age.
Before initiating INVOKAMET XR, consider factors that may predispose patients to acute kidney injury including hypovolemia, chronic renal insufficiency, congestive heart failure, and concomitant medications (diuretics, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, NSAIDs). Consider temporarily discontinuing INVOKAMET XR in any setting of reduced oral intake (such as acute illness or fasting) or fluid losses (such as gastrointestinal illness or excessive heat exposure); monitor patients for signs and symptoms of acute kidney injury. If acute kidney injury occurs, discontinue INVOKAMET XR promptly and institute treatment.
Canagliflozin increases serum creatinine and decreases eGFR. Patients with hypovolemia may be more susceptible to these changes. Renal function abnormalities can occur after initiating INVOKAMET XR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Renal function should be evaluated prior to initiation of INVOKAMET XR and monitored periodically thereafter. Dosage adjustment and more frequent renal function monitoring are recommended in patients with an eGFR below 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. INVOKAMET XR is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.6 Hyperkalemia
Canagliflozin can lead to hyperkalemia. Patients with moderate renal impairment who are taking medications that interfere with potassium excretion, such as potassium-sparing diuretics, or medications that interfere with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system are at an increased risk of developing hyperkalemia [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor serum potassium levels periodically after initiating INVOKAMET XR in patients with impaired renal function and in patients predisposed to hyperkalemia due to medications or other medical conditions.
5.7 Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis
There have been postmarketing reports of serious urinary tract infections including urosepsis and pyelonephritis requiring hospitalization in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including canagliflozin. Treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors increases the risk for urinary tract infections. Evaluate patients for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections and treat promptly, if indicated [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.9 Genital Mycotic Infections
Canagliflozin increases the risk of genital mycotic infections. Patients with a history of genital mycotic infections and uncircumcised males were more likely to develop genital mycotic infections [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Monitor and treat appropriately.
5.10 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema and anaphylaxis, have been reported with canagliflozin. These reactions generally occurred within hours to days after initiating canagliflozin. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue use of INVOKAMET XR; treat and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve [see Contraindications (4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)].
5.11 Bone Fracture
An increased risk of bone fracture, occurring as early as 12 weeks after treatment initiation, was observed in patients using canagliflozin. Consider factors that contribute to fracture risk prior to initiating INVOKAMET XR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.12 Vitamin B12 Levels
In controlled, 29-week clinical trials of metformin, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum vitamin B12 levels, without clinical manifestations, was observed in approximately 7% of metformin-treated patients. Such decreases, possibly due to interference with B12 absorption from the B12-intrinsic factor complex, is, however, very rarely associated with anemia or neurologic manifestations due to the short duration (less than 1 year) of the clinical trials. This risk may be more relevant to patients receiving long-term treatment with metformin and adverse hematologic and neurologic reactions have been reported postmarketing. The decrease in vitamin B12 levels appears to be rapidly reversible with discontinuation of metformin or vitamin B12 supplementation. Measure hematologic parameters on an annual basis in patients on INVOKAMET XR and investigate and treat if abnormalities occur. Patients with inadequate vitamin B12 or calcium intake or absorption may be predisposed to developing subnormal vitamin B12 levels, and routine serum vitamin B12 measurement at 2- to 3-year intervals is recommended in these patients.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are also discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Lactic Acidosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.5)]
- Lower Limb Amputation [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Acute Kidney Injury and Impairment in Renal Function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use of Sulfonylurea or Insulin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Genital Mycotic Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Bone Fracture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Increases in Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Pool of Placebo-Controlled Trials
Canagliflozin
The data in Table 1 is derived from four 26-week placebo-controlled trials. In one trial canagliflozin was used as monotherapy and in three trials canagliflozin was used as add-on therapy with metformin (with or without other agents) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. These data reflect exposure of 1667 patients to canagliflozin and a mean duration of exposure to canagliflozin of 24 weeks with 1275 patients exposed to a combination of canagliflozin and metformin. Patients received canagliflozin 100 mg (N=833), canagliflozin 300 mg (N=834) or placebo (N=646) once daily. The mean daily dose of metformin was 2138 mg (SD 337.3) for the 1275 patients in the three placebo-controlled metformin add-on studies. The mean age of the population was 56 years and 2% were older than 75 years of age. Fifty percent (50%) of the population was male and 72% were Caucasian, 12% were Asian, and 5% were Black or African American. At baseline the population had diabetes for an average of 7.3 years, had a mean HbA1C of 8.0% and 20% had established microvascular complications of diabetes. Baseline renal function was normal or mildly impaired (mean eGFR 88 mL/min/1.73 m2).
Table 1 shows common adverse reactions associated with the use of canagliflozin. These adverse reactions were not present at baseline, occurred more commonly on canagliflozin than on placebo, and occurred in at least 2% of patients treated with either canagliflozin 100 mg or canagliflozin 300 mg.
| Adverse Reaction | Placebo N=646 | Canagliflozin 100 mg N=833 | Canagliflozin 300 mg N=834 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Note: Percentages were weighted by studies. Study weights were proportional to the harmonic mean of the three treatment sample sizes. | |||
|
|||
| Urinary tract infections† | 3.8% | 5.9% | 4.4% |
| Increased urination‡ | 0.7% | 5.1% | 4.6% |
| Thirst§ | 0.1% | 2.8% | 2.4% |
| Constipation | 0.9% | 1.8% | 2.4% |
| Nausea | 1.6% | 2.1% | 2.3% |
| N=312 | N=425 | N=430 | |
| Female genital mycotic infections¶ | 2.8% | 10.6% | 11.6% |
| Vulvovaginal pruritus | 0.0% | 1.6% | 3.2% |
| N=334 | N=408 | N=404 | |
| Male genital mycotic infections# | 0.7% | 4.2% | 3.8% |
Abdominal pain was also more commonly reported in patients taking canagliflozin 100 mg (1.8%), 300 mg (1.7%) than in patients taking placebo (0.8%).
Pool of Placebo- and Active-Controlled Trials - Canagliflozin
The occurrence of adverse reactions for canagliflozin was evaluated in a larger pool of patients participating in placebo- and active-controlled trials.
The data combined eight clinical trials and reflect exposure of 6177 patients to canagliflozin. The mean duration of exposure to canagliflozin was 38 weeks with 1832 individuals exposed to canagliflozin for greater than 50 weeks. Patients received canagliflozin 100 mg (N=3092), canagliflozin 300 mg (N=3085) or comparator (N=3262) once daily. The mean age of the population was 60 years and 5% were older than 75 years of age. Fifty-eight percent (58%) of the population was male and 73% were Caucasian, 16% were Asian, and 4% were Black or African American. At baseline, the population had diabetes for an average of 11 years, had a mean HbA1C of 8.0% and 33% had established microvascular complications of diabetes. Baseline renal function was normal or mildly impaired (mean eGFR 81 mL/min/1.73 m2).
The types and frequency of common adverse reactions observed in the pool of eight clinical trials were consistent with those listed in Table 1. Percentages were weighted by studies. Study weights were proportional to the harmonic mean of the three treatment sample sizes. In this pool, canagliflozin was also associated with the adverse reactions of fatigue (1.8% with comparator, 2.2% with canagliflozin 100 mg, and 2.0% with canagliflozin 300 mg) and loss of strength or energy (i.e., asthenia) (0.6% with comparator, 0.7% with canagliflozin 100 mg, and 1.1% with canagliflozin 300 mg).
In the pool of eight clinical trials, the incidence rate of pancreatitis (acute or chronic) was 0.1%, 0.2%, and 0.1% receiving comparator, canagliflozin 100 mg, and canagliflozin 300 mg, respectively.
In the pool of eight clinical trials, hypersensitivity-related adverse reactions (including erythema, rash, pruritus, urticaria, and angioedema) occurred in 3.0%, 3.8%, and 4.2% of patients receiving comparator, canagliflozin 100 mg, and canagliflozin 300 mg, respectively. Five patients experienced serious adverse reactions of hypersensitivity with canagliflozin, which included 4 patients with urticaria and 1 patient with a diffuse rash and urticaria occurring within hours of exposure to canagliflozin. Among these patients, 2 patients discontinued canagliflozin. One patient with urticaria had recurrence when canagliflozin was re-initiated.
Photosensitivity-related adverse reactions (including photosensitivity reaction, polymorphic light eruption, and sunburn) occurred in 0.1%, 0.2%, and 0.2% of patients receiving comparator, canagliflozin 100 mg, and canagliflozin 300 mg, respectively.
Other adverse reactions occurring more frequently on canagliflozin than on comparator were:
Lower Limb Amputation
An approximately 2-fold increased risk of lower limb amputations associated with canagliflozin, a component of INVOKAMET XR, was observed in CANVAS and CANVAS-R, two large, randomized, placebo-controlled trials evaluating patients with type 2 diabetes who had either established cardiovascular disease or were at risk for cardiovascular disease. Patients in CANVAS and CANVAS-R were followed for an average of 5.7 and 2.1 years, respectively. The amputation data for CANVAS and CANVAS-R are shown in Tables 2 and 3, respectively [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
| Placebo N=1441 | Canagliflozin 100 mg N=1445 | Canagliflozin 300 mg N=1441 | Canagliflozin (Pooled) N=2886 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note: Incidence is based on the number of patients with at least one amputation, and not the total number of amputation events. A patient's follow-up is calculated from Day 1 to the first amputation event date. Some patients had more than one amputation. | ||||
| Patients with an amputation, n (%) | 22 (1.5) | 50 (3.5) | 45 (3.1) | 95 (3.3) |
| Total amputations | 33 | 83 | 79 | 162 |
| Amputation incidence rate (per 1000 patient-years) | 2.8 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 5.9 |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | -- | 2.24 (1.36, 3.69) | 2.01 (1.20, 3.34) | 2.12 (1.34, 3.38) |
| Placebo N=2903 | Canagliflozin 100 mg (with up-titration to 300 mg) N=2904 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Note: Incidence is based on the number of patients with at least one amputation, and not the total number of amputation events. A patient's follow-up is calculated from Day 1 to the first amputation event date. Some patients had more than one amputation. | ||
| Patients with an amputation, n (%) | 25 (0.9) | 45 (1.5) |
| Total amputations | 36 | 59 |
| Amputation incidence rate (per 1000 patient-years) | 4.2 | 7.5 |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | -- | 1.80 (1.10, 2.93) |
Volume Depletion-Related Adverse Reactions
Canagliflozin results in an osmotic diuresis, which may lead to reductions in intravascular volume. In clinical studies, treatment with canagliflozin was associated with a dose-dependent increase in the incidence of volume depletion-related adverse reactions (e.g., hypotension, postural dizziness, orthostatic hypotension, syncope, and dehydration). An increased incidence was observed in patients on the 300 mg dose. The three factors associated with the largest increase in volume depletion-related adverse reactions were the use of loop diuretics, moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), and age 75 years and older (Table 4) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), and Use in Specific Populations (8.5, 8.6)].
| Baseline Characteristic | Comparator Group*
% | Canagliflozin 100 mg % | Canagliflozin 300 mg % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Overall population | 1.5% | 2.3% | 3.4% |
| 75 years of age and older† | 2.6% | 4.9% | 8.7% |
| eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2† | 2.5% | 4.7% | 8.1% |
| Use of loop diuretic† | 4.7% | 3.2% | 8.8% |
Falls
In a pool of nine clinical trials with mean duration of exposure to canagliflozin of 85 weeks, the proportion of patients who experienced falls was 1.3%, 1.5%, and 2.1% with comparator, canagliflozin 100 mg, and canagliflozin 300 mg, respectively. The higher risk of falls for patients treated with canagliflozin was observed within the first few weeks of treatment.
Impairment in Renal Function
Canagliflozin is associated with a dose-dependent increase in serum creatinine and a concomitant fall in estimated GFR (Table 5). Patients with moderate renal impairment at baseline had larger mean changes.
|
|||||
| Placebo N=646 | Canagliflozin 100 mg N=833 | Canagliflozin 300 mg N=834 |
|||
| Pool of Four Placebo-Controlled Trials | Baseline | Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.82 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 87.0 | 88.3 | 88.8 | ||
| Week 6 Change | Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | -1.6 | -3.8 | -5.0 | ||
| End of Treatment Change* | Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | -1.6 | -2.3 | -3.4 | ||
| Placebo N=90 | Canagliflozin 100 mg N=90 | Canagliflozin 300 mg N=89 |
|||
| Moderate Renal Impairment Trial | Baseline | Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.61 | 1.62 | 1.63 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 40.1 | 39.7 | 38.5 | ||
| Week 3 Change | Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.28 | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | -0.7 | -4.6 | -6.2 | ||
| End of Treatment Change* | Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.18 | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | -1.5 | -3.6 | -4.0 | ||
In the pool of four placebo-controlled trials where patients had normal or mildly impaired baseline renal function, the proportion of patients who experienced at least one event of significant renal function decline, defined as an eGFR below 80 mL/min/1.73 m2 and 30% lower than baseline, was 2.1% with placebo, 2.0% with canagliflozin 100 mg, and 4.1% with canagliflozin 300 mg. At the end of treatment, 0.5% with placebo, 0.7% with canagliflozin 100 mg, and 1.4% with canagliflozin 300 mg had a significant renal function decline.
In a trial carried out in patients with moderate renal impairment with a baseline eGFR of 30 to less than 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 (mean baseline eGFR 39 mL/min/1.73 m2), the proportion of patients who experienced at least one event of significant renal function decline, defined as an eGFR 30% lower than baseline, was 6.9% with placebo, 18% with canagliflozin 100 mg, and 22.5% with canagliflozin 300 mg. At the end of treatment, 4.6% with placebo, 3.4% with canagliflozin 100 mg, and 2.2% with canagliflozin 300 mg had a significant renal function decline.
In a pooled population of patients with moderate renal impairment (N=1085) with baseline eGFR of 30 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (mean baseline eGFR 48 mL/min/1.73 m2), the overall incidence of these events was lower than in the dedicated trial but a dose-dependent increase in incident episodes of significant renal function decline compared to placebo was still observed. Use of canagliflozin has been associated with an increased incidence of renal-related adverse reactions (e.g., increased blood creatinine, decreased glomerular filtration rate, renal impairment, and acute renal failure), particularly in patients with moderate renal impairment.
In the pooled analysis of patients with moderate renal impairment, the incidence of renal-related adverse reactions was 3.7% with placebo, 8.9% with canagliflozin 100 mg, and 9.3% with canagliflozin 300 mg. Discontinuations due to renal-related adverse events occurred in 1.0% with placebo, 1.2% with canagliflozin 100 mg, and 1.6% with canagliflozin 300 mg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Hypoglycemia
In canagliflozin clinical trials, hypoglycemia was defined as any event regardless of symptoms, where biochemical hypoglycemia was documented (any glucose value below or equal to 70 mg/dL). Severe hypoglycemia was defined as an event consistent with hypoglycemia where the patient required the assistance of another person to recover, lost consciousness, or experienced a seizure (regardless of whether biochemical documentation of a low glucose value was obtained). In individual clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14.8)], episodes of hypoglycemia occurred at a higher rate when canagliflozin was co-administered with insulin or sulfonylureas (Table 6) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
|
|||
| Monotherapy (26 weeks) | Placebo (N=192) | Canagliflozin 100 mg (N=195) | Canagliflozin 300 mg (N=197) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 5 (2.6) | 7 (3.6) | 6 (3.0) |
| In Combination with Metformin (26 weeks) | Placebo + Metformin (N=183) | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Metformin (N=368) | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin (N=367) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 3 (1.6) | 16 (4.3) | 17 (4.6) |
| Severe [N (%)]† | 0 (0) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) |
| In Combination with Metformin (18 weeks)‡ | Placebo (N=93) | Canagliflozin 100 mg (N=93) | Canagliflozin 300 mg (N=93) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 3 (3.2) | 4 (4.3) | 3 (3.2) |
| In Combination with Metformin + Sulfonylurea (26 weeks) | Placebo + Metformin + Sulfonylurea (N=156) | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Metformin + Sulfonylurea (N=157) | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin + Sulfonylurea (N=156) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 24 (15.4) | 43 (27.4) | 47 (30.1) |
| Severe [N (%)]† | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.6) | 0 |
| In Combination with Metformin + Pioglitazone (26 weeks) | Placebo + Metformin + Pioglitazone (N=115) | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Metformin + Pioglitazone (N=113) | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin + Pioglitazone (N=114) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 3 (2.6) | 3 (2.7) | 6 (5.3) |
| In Combination with Insulin (18 weeks) | Placebo (N=565) | Canagliflozin 100 mg (N=566) | Canagliflozin 300 mg (N=587) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 208 (36.8) | 279 (49.3) | 285 (48.6) |
| Severe [N (%)]† | 14 (2.5) | 10 (1.8) | 16 (2.7) |
| In Combination with Insulin and Metformin (18 weeks)§ | Placebo (N=145) | Canagliflozin 100 mg (N=139) | Canagliflozin 300 mg (N=148) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 66 (45.5) | 58 (41.7) | 70 (47.3) |
| Severe [N (%)]† | 4 (2.8) | 1 (0.7) | 3 (2.0) |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of canagliflozin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7. Drug Interactions
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discuss the potential for unintended pregnancy with premenopausal women as therapy with metformin may result in ovulation in some anovulatory women.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of INVOKAMET XR in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
10. Overdosage
In the event of an overdose with INVOKAMET XR, contact the Poison Control Center. Employ the usual supportive measures (e.g., remove unabsorbed material from the gastrointestinal tract, employ clinical monitoring, and institute supportive treatment) as dictated by the patient's clinical status. Canagliflozin was negligibly removed during a 4-hour hemodialysis session. Canagliflozin is not expected to be dialyzable by peritoneal dialysis. Metformin is dialyzable with a clearance of up to 170 mL/min under good hemodynamic conditions. Therefore, hemodialysis may be useful partly for removal of accumulated metformin from patients in whom INVOKAMET XR overdosage is suspected.
11. Invokamet XR Description
INVOKAMET XR (canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride extended-release) tablets contain two oral antihyperglycemic drugs used in the management of type 2 diabetes: canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride.
12. Invokamet XR - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Specific Populations
Studies characterizing the pharmacokinetics of canagliflozin and metformin after administration of INVOKAMET XR were not conducted in patients with renal and hepatic impairment. Descriptions of the individual components in this patient population are described below.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Canagliflozin
In Vivo Assessment of Drug Interactions
| Co-Administered Drug | Dose of Co-Administered Drug* | Dose of Canagliflozin* | Geometric Mean Ratio (Ratio With/Without Co-Administered Drug) No Effect = 1.0 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC†
(90% CI) | Cmax
(90% CI) |
|||
| QD = once daily; BID = twice daily | ||||
|
||||
| See Drug Interactions (7.2) for the clinical relevance of the following: | ||||
| Rifampin | 600 mg QD for 8 days | 300 mg | 0.49 (0.44, 0.54) | 0.72 (0.61, 0.84) |
| No dose adjustments of canagliflozin required for the following: | ||||
| Cyclosporine | 400 mg | 300 mg QD for 8 days | 1.23 (1.19, 1.27) | 1.01 (0.91, 1.11) |
| Ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel | 0.03 mg ethinyl estradiol and 0.15 mg levonorgestrel | 200 mg QD for 6 days | 0.91 (0.88, 0.94) | 0.92 (0.84, 0.99) |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | 25 mg QD for 35 days | 300 mg QD for 7 days | 1.12 (1.08, 1.17) | 1.15 (1.06, 1.25) |
| Metformin | 2,000 mg | 300 mg QD for 8 days | 1.10 (1.05, 1.15) | 1.05 (0.96, 1.16) |
| Probenecid | 500 mg BID for 3 days | 300 mg QD for 17 days | 1.21 (1.16, 1.25) | 1.13 (1.00, 1.28) |
| Co-Administered Drug | Dose of Co-Administered Drug* | Dose of Canagliflozin* | Geometric Mean Ratio (Ratio With/Without Co-Administered Drug) No Effect = 1.0 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC†
(90% CI) | Cmax
(90% CI) |
||||
| QD = once daily; BID = twice daily; INR = International Normalized Ratio | |||||
|
|||||
| See Drug Interactions (7.2) for the clinical relevance of the following: | |||||
| Digoxin | 0.5 mg QD first day followed by 0.25 mg QD for 6 days | 300 mg QD for 7 days | digoxin | 1.20 (1.12, 1.28) | 1.36 (1.21, 1.53) |
| No dose adjustments of co-administered drug required for the following: | |||||
| Acetaminophen | 1,000 mg | 300 mg BID for 25 days | acetaminophen | 1.06‡
(0.98, 1.14) | 1.00 (0.92, 1.09) |
| Ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel | 0.03 mg ethinyl estradiol and 0.15 mg levonorgestrel | 200 mg QD for 6 days | ethinyl estradiol | 1.07 (0.99, 1.15) | 1.22 (1.10, 1.35) |
| levonorgestrel | 1.06 (1.00, 1.13) | 1.22 (1.11, 1.35) |
|||
| Glyburide | 1.25 mg | 200 mg QD for 6 days | glyburide | 1.02 (0.98, 1.07) | 0.93 (0.85, 1.01) |
| 3-cis-hydroxy-glyburide | 1.01 (0.96, 1.07) | 0.99 (0.91, 1.08) |
|||
| 4-trans-hydroxy-glyburide | 1.03 (0.97, 1.09) | 0.96 (0.88, 1.04) |
|||
| Hydrochlorothiazide | 25 mg QD for 35 days | 300 mg QD for 7 days | Hydrochlorothiazide | 0.99 (0.95, 1.04) | 0.94 (0.87, 1.01) |
| Metformin | 2,000 mg | 300 mg QD for 8 days | metformin | 1.20 (1.08, 1.34) | 1.06 (0.93, 1.20) |
| Simvastatin | 40 mg | 300 mg QD for 7 days | simvastatin | 1.12 (0.94, 1.33) | 1.09 (0.91, 1.31) |
| simvastatin acid | 1.18 (1.03, 1.35) | 1.26 (1.10, 1.45) |
|||
| Warfarin | 30 mg | 300 mg QD for 12 days | (R)-warfarin | 1.01 (0.96, 1.06) | 1.03 (0.94, 1.13) |
| (S)-warfarin | 1.06 (1.00, 1.12) | 1.01 (0.90, 1.13) |
|||
| INR | 1.00 (0.98, 1.03) | 1.05 (0.99, 1.12) |
|||
Metformin
| Co-Administered Drug | Dose of Co-Administered Drug* | Dose of Metformin* | Geometric Mean Ratio (Ratio With/Without Co-Administered Drug) No Effect = 1.00 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC† | Cmax | |||
|
||||
| No dose adjustments required for the following: | ||||
| Glyburide | 5 mg | 500 mg‡ | 0.98§ | 0.99§ |
| Furosemide | 40 mg | 850 mg | 1.09§ | 1.22§ |
| Nifedipine | 10 mg | 850 mg | 1.16 | 1.21 |
| Propranolol | 40 mg | 850 mg | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| Ibuprofen | 400 mg | 850 mg | 1.05§ | 1.07§ |
| Drugs that are eliminated by renal tubular secretion increase the accumulation of metformin [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Drug Interactions (7)] | ||||
| Cimetidine | 400 mg | 850 mg | 1.40 | 1.61 |
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may cause metabolic acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Drug Interactions (7)] | ||||
| Topiramate¶ | 100 mg | 500 mg | 1.25# | 1.18 |
| Co-Administered Drug | Dose of Co-Administered Drug* | Dose of Metformin* | Geometric Mean Ratio (Ratio With/Without Co-Administered Drug) No Effect = 1.00 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC† | Cmax | |||
|
||||
| No dose adjustments required for the following: | ||||
| Glyburide | 5 mg | 500 mg‡ | 0.78§ | 0.63§ |
| Furosemide | 40 mg | 850 mg | 0.87§ | 0.69§ |
| Nifedipine | 10 mg | 850 mg | 1.10‡ | 1.08 |
| Propranolol | 40 mg | 850 mg | 1.01§ | 0.94 |
| Ibuprofen | 400 mg | 850 mg | 0.97¶ | 1.01¶ |
| Cimetidine | 400 mg | 850 mg | 0.95‡ | 1.01 |
Metformin is negligibly bound to plasma proteins and is, therefore, less likely to interact with highly protein-bound drugs such as salicylates, sulfonamides, chloramphenicol, and probenecid.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
Canagliflozin has been studied in combination with metformin alone, metformin and sulfonylurea, metformin and sitagliptin, metformin and a thiazolidinedione (i.e. pioglitazone), and metformin and insulin (with or without other anti-hyperglycemic agents). The efficacy of canagliflozin was compared to a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor (sitagliptin), both as add-on combination therapy with metformin and sulfonylurea, and a sulfonylurea (glimepiride), both as add-on combination therapy with metformin.
There have been no clinical efficacy studies conducted with INVOKAMET XR; however, bioequivalence of INVOKAMET XR to canagliflozin and metformin co-administered as individual tablets was demonstrated in healthy subjects.
In patients with type 2 diabetes, treatment with canagliflozin and metformin produced clinically and statistically significant improvements in HbA1C compared to placebo. Reductions in HbA1C were observed across subgroups including age, gender, race, and baseline body mass index (BMI).
14.1 Canagliflozin as Initial Combination Therapy with Metformin
A total of 1186 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with diet and exercise participated in a 26-week double-blind, active-controlled, parallel-group, 5-arm, multicenter study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of initial therapy with canagliflozin in combination with metformin XR. The median age was 56 years, 48% of patients were men, and the mean baseline eGFR was 87.6 mL/min/1.73 m2. The median duration of diabetes was 1.6 years, and 72% of patients were treatment naïve. After completing a 2-week single-blind placebo run-in period, patients were randomly assigned for a double-blind treatment period of 26 weeks to 1 of 5 treatment groups (Table 11). The metformin XR dose was initiated at 500 mg/day for the first week of treatment and then increased to 1000 mg/day. Metformin XR or matching placebo was up-titrated every 2–3 weeks during the next 8 weeks of treatment to a maximum daily dose of 1500 to 2000 mg/day, as tolerated; about 90% of patients reached 2000 mg/day.
At the end of treatment, canagliflozin 100 mg and canagliflozin 300 mg in combination with metformin XR resulted in a statistically significant greater improvement in HbA1C compared to their respective canagliflozin doses (100 mg and 300 mg) alone or metformin XR alone.
| Efficacy Parameter | Metformin XR (N=237) | Canagliflozin 100 mg (N=237) | Canagliflozin 300 mg (N=238) | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Metformin XR (N=237) | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin XR (N=237) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1C (%) | |||||
|
|||||
| Baseline (mean) | 8.81 | 8.78 | 8.77 | 8.83 | 8.90 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean)† | -1.30 | -1.37 | -1.42 | -1.77 | -1.78 |
| Difference from canagliflozin 100 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI) ‡ | -0.40§
(-0.59, -0.21) | ||||
| Difference from canagliflozin 300 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI) ‡ | -0.36§
(-0.56, -0.17) |
||||
| Difference from metformin XR (adjusted mean) (95% CI) ‡ | -0.46§
(-0.66, -0.27) | -0.48§
(-0.67, -0.28) |
|||
| Percent of patients achieving HbA1C < 7% | 38 | 34 | 39 | 47¶ | 51¶ |
14.2 Canagliflozin as Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin
A total of 1284 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy (greater than or equal to 2,000 mg/day or at least 1,500 mg/day if higher dose not tolerated) participated in a 26-week, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in combination with metformin. The mean age was 55 years, 47% of patients were men, and the mean baseline eGFR was 89 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients already on the required metformin dose (N=1009) were randomized after completing a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in period. Patients taking less than the required metformin dose or patients on metformin in combination with another antihyperglycemic agent (N=275) were switched to metformin monotherapy (at doses described above) for at least 8 weeks before entering the 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in. After the placebo run-in period, patients were randomized to canagliflozin 100 mg, canagliflozin 300 mg, sitagliptin 100 mg, or placebo, administered once daily as add-on therapy to metformin.
At the end of treatment, canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg once daily resulted in a statistically significant improvement in HbA1C (p<0.001 for both doses) compared to placebo when added to metformin. Canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg once daily also resulted in a greater proportion of patients achieving an HbA1C less than 7%, in significant reduction in fasting plasma glucose (FPG), in improved postprandial glucose (PPG), and in percent body weight reduction compared to placebo when added to metformin (see Table 12). Statistically significant (p<0.001 for both doses) mean changes from baseline in systolic blood pressure relative to placebo were -5.4 mmHg and -6.6 mmHg with canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg, respectively.
| Efficacy Parameter | Placebo + Metformin (N=183) | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Metformin (N=368) | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin (N=367) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| HbA1C (%) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 7.96 | 7.94 | 7.95 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -0.17 | -0.79 | -0.94 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -0.62‡
(-0.76, -0.48) | -0.77‡
(-0.91, -0.64) |
|
| Percent of patients achieving HbA1C < 7% | 30 | 46‡ | 58‡ |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 164 | 169 | 173 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | 2 | -27 | -38 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)‡ | -30‡
(-36, -24) | -40‡
(-46, -34) |
|
| 2-hour Postprandial Glucose (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 249 | 258 | 262 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -10 | -48 | -57 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -38‡
(-49, -27) | -47‡
(-58, -36) |
|
| Body Weight | |||
| Baseline (mean) in kg | 86.7 | 88.7 | 85.4 |
| % change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -1.2 | -3.7 | -4.2 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -2.5‡
(-3.1, -1.9) | -2.9‡
(-3.5, -2.3) |
|
14.3 Canagliflozin Compared to Glimepiride, Both as Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin
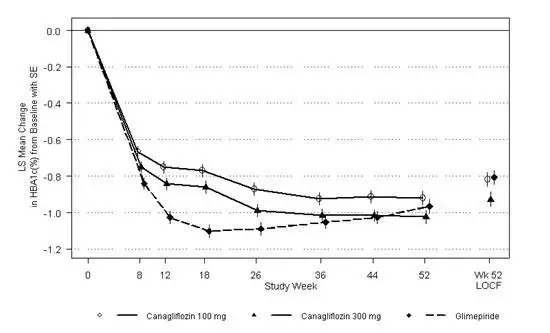
A total of 1450 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy (greater than or equal to 2,000 mg/day or at least 1,500 mg/day if higher dose not tolerated) participated in a 52-week, double-blind, active-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in combination with metformin.
The mean age was 56 years, 52% of patients were men, and the mean baseline eGFR was 90 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients tolerating maximally required metformin dose (N=928) were randomized after completing a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in period. Other patients (N=522) were switched to metformin monotherapy (at doses described above) for at least 10 weeks, then completed a 2-week single-blind run-in period. After the 2-week run-in period, patients were randomized to canagliflozin 100 mg, canagliflozin 300 mg, or glimepiride (titration allowed throughout the 52-week study to 6 or 8 mg), administered once daily as add-on therapy to metformin.
As shown in Table 13 and Figure 1, at the end of treatment, canagliflozin 100 mg provided similar reductions in HbA1C from baseline compared to glimepiride when added to metformin therapy. Canagliflozin 300 mg provided a greater reduction from baseline in HbA1C compared to glimepiride, and the relative treatment difference was -0.12% (95% CI: −0.22; −0.02). As shown in Table 13, treatment with canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg daily provided greater improvements in percent body weight change, relative to glimepiride.
| Efficacy Parameter | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Metformin (N=483) | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin (N=485) | Glimepiride (titrated) + Metformin (N=482) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| HbA1C (%) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 7.78 | 7.79 | 7.83 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -0.82 | -0.93 | -0.81 |
| Difference from glimepiride (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -0.01‡
(-0.11, 0.09) | -0.12‡
(-0.22, -0.02) | |
| Percent of patients achieving HbA1C < 7% | 54 | 60 | 56 |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 165 | 164 | 166 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -24 | -28 | -18 |
| Difference from glimepiride (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -6 (-10, -2) | -9 (-13, -5) | |
| Body Weight | |||
| Baseline (mean) in kg | 86.8 | 86.6 | 86.6 |
| % change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -4.2 | -4.7 | 1.0 |
| Difference from glimepiride (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -5.2§
(-5.7, -4.7) | -5.7§
(-6.2, -5.1) | |
Figure 1: Mean HbA1C Change at Each Time Point (Completers) and at Week 52 Using Last Observation Carried Forward (mITT Population)
14.4 Canagliflozin as Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin and Sitagliptin
A total of 217 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on the combination of metformin (greater than or equal to 1,500 mg/day) and sitagliptin 100 mg/day (or equivalent fixed-dose combination) participated in a 26-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in combination with metformin and sitagliptin. The mean age was 57 years, 58% of patients were men, 73% of patients were Caucasian, 15% were Asian, and 12% were Black or African-American. The mean baseline eGFR was 90 mL/min/1.73 m2 and the mean baseline BMI was 32 kg/m2. The mean duration of diabetes was 10 years. Eligible patients entered a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in period and were subsequently randomized to canagliflozin 100 mg or placebo, administered once daily as add-on to metformin and sitagliptin. Patients with a baseline eGFR of 70 mL/min/1.73 m2 or greater who were tolerating canagliflozin 100 mg and who required additional glycemic control (fasting finger stick 100 mg/dL or greater at least twice within 2 weeks) were up-titrated to canagliflozin 300 mg. While up-titration occurred as early as Week 4, most (90%) patients randomized to canagliflozin were up-titrated to canagliflozin 300 mg by 6 to 8 weeks.
At the end of 26 weeks, canagliflozin once daily resulted in a statistically significant improvement in HbA1C (p<0.001) compared to placebo when added to metformin and sitagliptin.
| Efficacy Parameter | Placebo + Metformin and Sitagliptin (N=108*) | Canagliflozin + Metformin and Sitagliptin (N=109*) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| HbA1C (%) | ||
| Baseline (mean) | 8.40 | 8.50 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -0.03 | -0.83 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)†‡ | -0.81§
(-1.11; -0.51) |
|
| Percent of patients achieving HbA1C < 7%¶ | 9 | 28 |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL)# | ||
| Baseline (mean) | 180 | 185 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -3 | -28 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI) | -25§
(-39; -11) |
|
14.5 Canagliflozin as Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin and Sulfonylurea
A total of 469 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on the combination of metformin (greater than or equal to 2,000 mg/day or at least 1,500 mg/day if higher dose not tolerated) and sulfonylurea (maximal or near-maximal effective dose) participated in a 26-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in combination with metformin and sulfonylurea. The mean age was 57 years, 51% of patients were men, and the mean baseline eGFR was 89 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients already on the protocol-specified doses of metformin and sulfonylurea (N=372) entered a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in period. Other patients (N=97) were required to be on a stable protocol-specified dose of metformin and sulfonylurea for at least 8 weeks before entering the 2-week run-in period. Following the run-in period, patients were randomized to canagliflozin 100 mg, canagliflozin 300 mg, or placebo administered once daily as add-on to metformin and sulfonylurea.
At the end of treatment, canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg once daily resulted in a statistically significant improvement in HbA1C (p<0.001 for both doses) compared to placebo when added to metformin and sulfonylurea. Canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg once daily also resulted in a greater proportion of patients achieving an HbA1C less than 7.0%, in a significant reduction in fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and in percent body weight reduction compared to placebo when added to metformin and sulfonylurea (see Table 15).
| Efficacy Parameter | Placebo + Metformin and Sulfonylurea (N=156) | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Metformin and Sulfonylurea (N=157) | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin and Sulfonylurea (N=156) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| HbA1C (%) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 8.12 | 8.13 | 8.13 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -0.13 | -0.85 | -1.06 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -0.71‡
(-0.90, -0.52) | -0.92‡
(-1.11, -0.73) |
|
| Percent of patients achieving HbA1C < 7% | 18 | 43‡ | 57‡ |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 170 | 173 | 168 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | 4 | -18 | -31 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -22‡
(-31, -13) | -35‡
(-44, -25) |
|
| Body Weight | |||
| Baseline (mean) in kg | 90.8 | 93.5 | 93.5 |
| % change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -0.7 | -2.1 | -2.6 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -1.4‡
(-2.1, -0.7) | -2.0‡
(-2.7, -1.3) |
|
14.6 Canagliflozin Compared to Sitagliptin, Both as Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin and Sulfonylurea
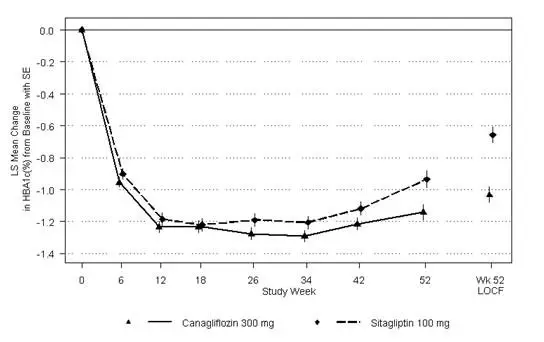
A total of 755 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on the combination of metformin (greater than or equal to 2,000 mg/day or at least 1,500 mg/day if higher dose not tolerated) and sulfonylurea (near-maximal or maximal effective dose) participated in a 52 week, double-blind, active-controlled study to compare the efficacy and safety of canagliflozin 300 mg versus sitagliptin 100 mg in combination with metformin and sulfonylurea. The mean age was 57 years, 56% of patients were men, and the mean baseline eGFR was 88 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients already on protocol-specified doses of metformin and sulfonylurea (N=716) entered a 2-week single-blind, placebo run-in period. Other patients (N=39) were required to be on a stable protocol-specified dose of metformin and sulfonylurea for at least 8 weeks before entering the 2-week run-in period. Following the run-in period, patients were randomized to canagliflozin 300 mg or sitagliptin 100 mg as add-on to metformin and sulfonylurea.
As shown in Table 16 and Figure 2, at the end of treatment, canagliflozin 300 mg provided greater HbA1C reduction compared to sitagliptin 100 mg when added to metformin and sulfonylurea (p<0.05). Canagliflozin 300 mg resulted in a mean percent change in body weight from baseline of -2.5% compared to +0.3% with sitagliptin 100 mg. A mean change in systolic blood pressure from baseline of -5.06 mmHg was observed with canagliflozin 300 mg compared to +0.85 mmHg with sitagliptin 100 mg.
| Efficacy Parameter | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin and Sulfonylurea (N=377) | Sitagliptin 100 mg + Metformin and Sulfonylurea (N=378) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| HbA1C (%) | ||
| Baseline (mean) | 8.12 | 8.13 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -1.03 | -0.66 |
| Difference from sitagliptin (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -0.37‡
(-0.50, -0.25) | |
| Percent of patients achieving HbA1C < 7% | 48 | 35 |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | ||
| Baseline (mean) | 170 | 164 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -30 | -6 |
| Difference from sitagliptin (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -24 (-30, -18) | |
| Body Weight | ||
| Baseline (mean) in kg | 87.6 | 89.6 |
| % change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -2.5 | 0.3 |
| Difference from sitagliptin (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -2.8§
(-3.3, -2.2) | |
Figure 2: Mean HbA1C Change at Each Time Point (Completers) and at Week 52 Using Last Observation Carried Forward (mITT Population)
14.7 Canagliflozin as Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin and Pioglitazone
A total of 342 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on the combination of metformin (greater than or equal to 2,000 mg/day or at least 1,500 mg/day if higher dose not tolerated) and pioglitazone (30 or 45 mg/day) participated in a 26-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in combination with metformin and pioglitazone. The mean age was 57 years, 63% of patients were men, and the mean baseline eGFR was 86 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients already on protocol-specified doses of metformin and pioglitazone (N=163) entered a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in period. Other patients (N=181) were required to be on stable protocol-specified doses of metformin and pioglitazone for at least 8 weeks before entering the 2-week run-in period. Following the run-in period, patients were randomized to canagliflozin 100 mg, canagliflozin 300 mg, or placebo, administered once daily as add-on to metformin and pioglitazone.
At the of end of treatment, canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg once daily resulted in a statistically significant improvement in HbA1C (p<0.001 for both doses) compared to placebo when added to metformin and pioglitazone. Canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg once daily also resulted in a greater proportion of patients achieving an HbA1C less than 7%, in significant reduction in fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and in percent body weight reduction compared to placebo when added to metformin and pioglitazone (see Table 17). Statistically significant (p<0.05 for both doses) mean changes from baseline in systolic blood pressure relative to placebo were -4.1 mmHg and -3.5 mmHg with canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg, respectively.
| Efficacy Parameter | Placebo + Metformin and Pioglitazone (N=115) | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Metformin and Pioglitazone (N=113) | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin and Pioglitazone (N=114) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| HbA1C (%) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 8.00 | 7.99 | 7.84 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -0.26 | -0.89 | -1.03 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -0.62‡
(-0.81, -0.44) | -0.76‡
(-0.95, -0.58) |
|
| Percent of patients achieving HbA1C < 7% | 33 | 47‡ | 64‡ |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 164 | 169 | 164 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | 3 | -27 | -33 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -29‡
(-37, -22) | -36‡
(-43, -28) |
|
| Body Weight | |||
| Baseline (mean) in kg | 94.0 | 94.2 | 94.4 |
| % change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -0.1 | -2.8 | -3.8 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -2.7‡
(-3.6, -1.8) | -3.7‡
(-4.6, -2.8) |
|
14.8 Canagliflozin as Add-on Combination Therapy with Insulin (With or Without Other Anti-Hyperglycemic Agents, Including Metformin)
A total of 1718 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on insulin greater than or equal to 30 units/day or insulin in combination with other antihyperglycemic agents participated in an 18-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled substudy of a cardiovascular study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in combination with insulin. Of these patients, a subgroup of 432 patients with inadequate glycemic control received canagliflozin or placebo plus metformin and ≥ 30 units/day of insulin over 18 weeks.
In this subgroup, the mean age was 61 years, 67% of patients were men, and the mean baseline eGFR was 81 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients on metformin in combination with basal, bolus, or basal/bolus insulin for at least 10 weeks entered a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in period. Approximately 74% of these patients were on a background of metformin and basal/bolus insulin regimen. After the run-in period, patients were randomized to canagliflozin 100 mg, canagliflozin 300 mg, or placebo, administered once daily as add-on to metformin and insulin. The mean daily insulin dose at baseline was 93 units, which was similar across treatment groups.
At the of end of treatment, canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg once daily resulted in a statistically significant improvement in HbA1C (p<0.001 for both doses) compared to placebo when added to metformin and insulin. Canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg once daily also resulted in a greater proportion of patients achieving an HbA1C less than 7%, in significant reductions in fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and in percent body weight reductions compared to placebo (see Table 18). Statistically significant (p=0.023 for the 100 mg and p<0.001 for the 300 mg dose) mean change from baseline in systolic blood pressure relative to placebo was –3.5 mmHg and –6 mmHg with canagliflozin 100 mg and 300 mg, respectively. Fewer patients on canagliflozin in combination with metformin and insulin required glycemic rescue therapy: 3.6% of patients receiving canagliflozin 100 mg, 2.7% of patients receiving canagliflozin 300 mg, and 6.2% of patients receiving placebo. An increased incidence of hypoglycemia was observed in this study, which is consistent with the expected increase of hypoglycemia when an agent not associated with hypoglycemia is added to insulin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
| Efficacy Parameter | Placebo + Metformin + Insulin (N=145) | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Metformin + Insulin (N=139) | Canagliflozin 300 mg + Metformin + Insulin (N=148) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| HbA1C (%) | |||
| Baseline (mean) | 8.15 | 8.20 | 8.22 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | 0.03 | -0.64 | -0.79 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (95% CI)† | -0.66‡
(-0.81, -0.51) | -0.82‡
(-0.96, -0.67) |
|
| Percent of patients achieving HbA1C < 7% | 9 | 19§ | 29‡ |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 163 | 168 | 167 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | 1 | -16 | -24 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (97.5% CI)† | -16‡
(-28, -5) | -25‡
(-36, -14) |
|
| Body Weight | |||
| Baseline (mean) in kg | 102.3 | 99.7 | 101.1 |
| % change from baseline (adjusted mean) | 0.0 | -1.7 | -2.7 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) (97.5% CI)† | -1.7‡
(-2.4, -1.0) | -2.7‡
(-3.4, -2.0) |
|
16. How is Invokamet XR supplied
INVOKAMET XR (canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride extended-release) tablets are available in the strengths and packages listed below:
Canagliflozin 50 mg and metformin hydrochloride 500 mg extended-release tablets are oblong, biconvex, almost white to light orange film-coated tablets with "CM1" on one side. A thin line on the tablet side may be visible.
- NDC 50458-940-01 Bottle of 60
Canagliflozin 50 mg and metformin hydrochloride 1,000 mg extended-release tablets are oblong, biconvex, pink film-coated tablets with "CM3" on one side. A thin line on the tablet side may be visible.
- NDC 50458-941-01 Bottle of 60
Canagliflozin 150 mg and metformin hydrochloride 500 mg extended-release tablets are oblong, biconvex, orange, film-coated tablets with "CM2" on one side. A thin line on the tablet side may be visible.
- NDC 50458-942-01 Bottle of 60
Canagliflozin 150 mg and metformin hydrochloride 1,000 mg extended-release tablets are oblong, biconvex, reddish brown, film-coated tablets with "CM4" on one side. A thin line on the tablet side may be visible.
- NDC 50458-943-01 Bottle of 60
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Medication Guide).
- Lactic Acidosis: Explain the risks of lactic acidosis, its symptoms, and conditions that predispose to its development, as noted in Warnings and Precautions (5.1). Advise patients to discontinue INVOKAMET XR immediately and to promptly notify their healthcare provider if unexplained hyperventilation, myalgias, malaise, unusual somnolence or other nonspecific symptoms occur. Once a patient is stabilized on INVOKAMET XR, gastrointestinal symptoms, which are common during initiation of metformin, are unlikely to recur. Later occurrence of gastrointestinal symptoms could be due to lactic acidosis or other serious disease.
- Instruct patients to keep INVOKAMET XR in the original bottle to protect from moisture. Advise patients that storage in a pill box or pill organizer is allowed for up to 30 days.
- Counsel patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving INVOKAMET XR.
- Inform patients about importance of regular testing of renal function and hematological parameters while receiving INVOKAMET XR.
- Instruct patients to inform their doctor that they are taking INVOKAMET XR prior to any surgical or radiological procedure, as temporary discontinuation of INVOKAMET XR may be required until renal function has been confirmed to be normal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Advise patients to seek medical advice promptly during periods of stress such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, as medication requirements may change.
- Instruct patients that INVOKAMET XR must be swallowed whole and never crushed, cut, or chewed, and that the inactive ingredients may occasionally be eliminated in the feces as a soft mass that may resemble the original tablet.
- Instruct patients to take INVOKAMET XR only as prescribed once daily with the morning meal. If a dose is missed, advise patients to take it as soon as it is remembered unless it is almost time for the next dose, in which case patients should skip the missed dose and take the medicine at the next regularly scheduled time. Advise patients not to take more than two tablets of INVOKAMET XR at the same time.
- Lower Limb Amputation: Inform patients that INVOKAMET XR is associated with an increased risk of amputations. Counsel patients about the importance of routine preventative foot care. Instruct patients to monitor for new pain or tenderness, sores or ulcers, or infections involving the leg or foot and to seek medical advice immediately if such signs or symptoms develop [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Hypotension: Inform patients that symptomatic hypotension may occur with INVOKAMET XR and advise them to contact their doctor if they experience such symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Inform patients that dehydration may increase the risk for hypotension and to have adequate fluid intake.
- Ketoacidosis: Inform patients that ketoacidosis is a serious life-threatening condition. Cases of ketoacidosis have been reported during use of canagliflozin. Instruct patients to check ketones (when possible) if symptoms consistent with ketoacidosis occur even if blood glucose is not elevated. If symptoms of ketoacidosis (including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, tiredness, and labored breathing) occur, instruct patients to discontinue INVOKAMET XR and seek medical advice immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Acute Kidney Injury: Inform patients that acute kidney injury has been reported during use of canagliflozin. Advise patients to seek medical advice immediately if they have reduced oral intake (such as due to acute illness or fasting), or increased fluid losses (such as due to vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive heat exposure), as it may be appropriate to temporarily discontinue INVOKAMET XR use in those settings [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Serious Urinary Tract Infections: Inform patients of the potential for urinary tract infections, which may be serious. Provide them with information on the symptoms of urinary tract infections. Advise them to seek medical advice if such symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- Genital Mycotic Infections in Females: Inform female patients that vaginal yeast infection (e.g., vulvovaginitis) may occur and provide them with information on the signs and symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection. Advise them of treatment options and when to seek medical advice [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
- Genital Mycotic Infections in Males: Inform male patients that yeast infection of penis (e.g., balanitis or balanoposthitis) may occur, especially in uncircumcised males and patients with prior history. Provide them with information on the signs and symptoms of balanitis and balanoposthitis (rash or redness of the glans or foreskin of the penis). Advise them of treatment options and when to seek medical advice [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Inform patients that serious hypersensitivity reactions, such as urticaria, rash, anaphylaxis, and angioedema, have been reported with canagliflozin. Advise patients to report immediately any signs or symptoms suggesting allergic reaction and to discontinue drug until they have consulted prescribing physicians [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
- Bone Fracture: Inform patients that bone fractures have been reported in patients taking canagliflozin. Provide them with information on factors that may contribute to fracture risk.
- Laboratory Tests: Inform patients that they will test positive for glucose in their urine while on INVOKAMET XR [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
- Pregnancy: Advise pregnant women, and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus with treatment with INVOKAMET XR [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Instruct females of reproductive potential to report pregnancies to their physicians as soon as possible.
- Lactation: Advise women that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with INVOKAMET XR [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
- Inform females that treatment with INVOKAMET XR may result in ovulation in some premenopausal anovulatory women which may lead to unintended pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Inform patients that the most common adverse reactions associated with canagliflozin are genital mycotic infection, urinary tract infection, and increased urination. Most common adverse reactions associated with metformin are diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, asthenia, indigestion, abdominal discomfort, and headache.
| Medication Guide INVOKAMET® (in vok' a met) XR (canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride extended-release) Tablets |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised 07/2017 | ||||
| What is the most important information I should know about INVOKAMET XR?
INVOKAMET XR can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
|
||||
| Most people who have had lactic acidosis had other conditions that, in combination with metformin use, led to the lactic acidosis. Tell your doctor if you have any of the following, because you have a higher chance for getting lactic acidosis with INVOKAMET XR if you: | |||||
|
|||||
The best way to keep from having a problem with lactic acidosis from metformin is to tell your doctor if you have any of the problems in the list above. Your doctor will decide to stop your INVOKAMET XR for a while if you have any of these things.
Talk to your doctor about proper foot care. INVOKAMET XR can have other serious side effects. See "What are the possible side effects of INVOKAMET XR?" |
|||||
What is INVOKAMET XR?
|
|||||
| Who should not take INVOKAMET XR?
Do not take INVOKAMET XR if you:
|
|||||
| What should I tell my doctor before taking INVOKAMET XR?
Before you take INVOKAMET XR, tell your doctor if you:
INVOKAMET XR may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect how INVOKAMET XR works. Especially tell your doctor if you take: |
|||||
|
|
||||
| Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure if your medicine is listed above. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|||||
How should I take INVOKAMET XR?
|
|||||
What should I avoid while taking INVOKAMET XR?
|
|||||
| What are the possible side effects of INVOKAMET XR?
INVOKAMET XR may cause serious side effects including:
|
|||||
|
|||||
Talk to your doctor about what you can do to prevent dehydration including how much fluid you should drink on a daily basis.
|
|||||
|
|
||||
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
||||
Talk to your doctor about what to do if you get symptoms of a yeast infection of the vagina or penis. Your doctor may suggest you use an over-the-counter antifungal medicine. Talk to your doctor right away if you use an over-the-counter antifungal medication and your symptoms do not go away.
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||
| Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of INVOKAMET XR. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-526-7736. |
|||||
How should I store INVOKAMET XR?
|
|||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of INVOKAMET XR.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Medication Guide. Do not use INVOKAMET XR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give INVOKAMET XR to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about INVOKAMET XR. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about INVOKAMET XR that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information about INVOKAMET XR, call 1-800-526-7736 or visit our website at www.invokametxr.com. |
|||||
| What are the ingredients of INVOKAMET XR?
Active ingredients: canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride Inactive ingredients: The tablet core contains croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate (vegetable-sourced), microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene oxide, and silicified microcrystalline cellulose (50 mg/500 mg and 50 mg/1,000 mg tablets only). In addition, the tablet coating contains macrogol/PEG3350, polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolyzed), talc, titanium dioxide, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, and iron oxide black (50 mg/1,000 mg and 150 mg/1,000 mg tablets only). |
|||||
|
*The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Manufactured for: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Titusville, NJ 08560. Manufactured by: Janssen Ortho LLC, Gurabo, PR 00778. Licensed from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation. © 2016 Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies |
|||||
| INVOKAMET XR
canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INVOKAMET XR
canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INVOKAMET XR
canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INVOKAMET XR
canagliflozin and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (063137772) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Ortho LLC (Gurabo) | 805887986 | MANUFACTURE(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) , ANALYSIS(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) , PACK(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) , LABEL(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica NV (Geel) | 374747970 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) , ANALYSIS(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rolabo Outsourcing S.L. (Spain) | 513603225 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica NV (Beerse) | 370005019 | ANALYSIS(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc. | 063137772 | ANALYSIS(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmhispania S.A. (Spain) | 462038145 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) , ANALYSIS(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Johnson & Johnson Private Limited (Mumbai) | 677603030 | ANALYSIS(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Puerto Rico, Inc. (Manati) | 143814544 | MANUFACTURE(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) , API MANUFACTURE(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHAST Gesellschaft für Pharmazeutische Qualitätsstandards mbH | 331156161 | ANALYSIS(50458-940, 50458-941, 50458-942, 50458-943) | |