Drug Detail:Iopidine (Apraclonidine ophthalmic [ a-pra-klon-i-deen-off-thal-mik ])
Drug Class: Ophthalmic glaucoma agents
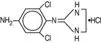
IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution contains apraclonidine hydrochloride, an alpha adrenergic agonist, in a sterile isotonic solution
for topical application to the eye. Apraclonidine hydrochloride is a white to off‑white powder and is highly soluble in water. Its chemical name is 2-[(4‑amino-2,6 dichlorophenyl)imino] imidazolidine monohydrochloride with an empirical formula of C
9H
11Cl
3N
4 and a molecular weight of 281.6. The chemical structure of apraclonidine hydrochloride is:
Each mL of IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution contains:
Actives: apraclonidine hydrochloride 11.5 mg equivalent to apraclonidine base
10 mg.
Inactives: sodium chloride, sodium acetate, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (pH 4.4‑7.8), purified water and benzalkonium
chloride 0.01% (preservative). Osmolality is 260‑320 mOsm.
Apraclonidine is a relatively selective, alpha adrenergic agonist and does not have significant membrane stabilizing (local anesthetic) activity. When instilled into the eye, IOPIDINE 1% (apraclonidine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution) has the action of reducing intraocular pressure (IOP). Ophthalmic apraclonidine has minimal effect on cardiovascular parameters.
Optic nerve head damage and visual field loss may result from an acute elevation in IOP that can occur after argon or Nd:YAG laser surgical procedures. Elevated IOP, whether acute or chronic in duration, is a major risk factor in the pathogenesis of visual field loss. The higher the peak or spike of IOP, the greater the likelihood of visual field loss and optic nerve damage especially in patients with previously compromised optic nerves. The onset of action with IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution can usually be noted within one hour and the maximum IOP reduction usually occurs three to five hours after application of a single dose. The precise mechanism of the ocular hypotensive action of IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution is not completely established at this time. Aqueous fluorophotometry studies in man suggest that its predominant action may be related to a reduction of aqueous formation. Controlled clinical studies of patients requiring argon laser trabeculoplasty, argon laser iridotomy or Nd:YAG posterior capsulotomy showed that IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution controlled or prevented the post-surgical IOP rise typically observed in patients after undergoing those procedures. After surgery, the mean IOP was 1.2 to 4 mmHg below the corresponding pre-surgical baseline pressure before IOPIDINE Ophthalmic Solution treatment. With placebo treatment, post-surgical pressures were 2.5 to 8.4 mmHg higher than their corresponding pre-surgical baselines. Overall, only 2% of patients treated with IOPIDINE* 1% Ophthalmic Solution had severe IOP elevations (spike greater than or equal to 10 mmHg) during the first three hours after laser surgery, whereas 23% of placebo-treated patients responded with severe pressure spikes (Table 1). Of the patients that experienced a pressure spike after surgery, the peak IOP was above 30 mmHg in most patients (Table 2) and was above 50 mmHg in seven placebo-treated patients and one IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution-treated patient.
Table 1: Incidence of IOP Spikes Greater Than or Equal to 10 mmHg
|
Study |
Laser Procedure |
Treatment |
||||
|
Apraclonidine |
Placebo |
|||||
|
P‑Value |
aN |
(%) |
aN |
(%) |
||
|
1 |
Trabeculoplasty |
<0.05 |
0/40 |
(0%) |
6/35 |
(17%) |
|
2 |
Trabeculoplasty |
=0.06 |
2/41 |
(5%) |
8/42 |
(19%) |
|
1 |
Iridotomy |
<0.05 |
0/11 |
(0%) |
4/10 |
(40%) |
|
2 |
Iridotomy |
=0.05 |
0/17 |
(0%) |
4/19 |
(21%) |
|
1 |
Nd:YAG Capsulotomy |
<0.05 |
3/80 |
(4%) |
19/83 |
(23%) |
|
2 |
Nd:YAG Capsulotomy |
<0.05 |
0/83 |
(0%) |
22/81 |
(27%) |
aN = Number Spikes/Number Eyes.
Table 2: Magnitude of Post-surgical IOP in Trabeculoplasty, Iridotomy and Nd:YAG Capsulotomy Patients With Severe Pressure Spikes Greater than or Equal to 10 mmHg
Maximum Postsurgical IOP (mmHg)
|
Treatment |
TotalSpikes |
20-29mmHg |
30-39mmHg |
40-49 mmHg |
> 50 mmHg |
|
IOPIDINE |
8 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
|
Placebo |
78 |
16 |
47 |
8 |
7 |
IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution is indicated to control or prevent
post-surgical elevations in IOP that occur in patients after argon laser
trabeculoplasty, argon laser iridotomy or Nd:YAG posterior capsulotomy.
IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution is contraindicated for patients
receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy and for patients with
hypersensitivity to any component of this medication or to clonidine.
Since IOPIDINE* 1% Ophthalmic Solution is a potent depressor of IOP,
patients who develop exaggerated reductions in IOP should be closely
monitored. Although the acute administration of two drops of IOPIDINE
1% Ophthalmic Solution has minimal effect on heart rate or blood
pressure in clinical studies evaluating patients undergoing anterior
segment laser surgery, the preclinical pharmacologic profile of this drug
suggests that caution should be observed in treating patients with severe
cardiovascular disease including hypertension. IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic
Solution should also be used with caution in patients with severe
coronary insufficiency, recent myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular
disease, chronic renal failure, Raynaud’s disease or thromboangiitis
obliterans.
The possibility of a vasovagal attack occurring during laser surgery
should be considered and caution used in patients with history of such
episodes.
Topical ocular administration of two drops of 0.5%, 1%, and 1.5%
IOPIDINE Ophthalmic Solution to New Zealand Albino rabbits three times
daily for one month resulted in sporadic and transient instances of
minimal corneal cloudiness in the 1.5% group only. No histopathological changes were noted in those eyes. No adverse ocular effects were
observed in cynomolgus monkeys treated with two drops of 1.5%
IOPIDINE Ophthalmic Solution applied three times daily for three months.
No corneal changes were observed in 320 humans given at least one
dose of IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution.
Apraclonidine can cause dizziness and somnolence. Patients who engage
in hazardous activities requiring mental alertness should be warned of the
potential for a decrease in mental alertness on the day of surgery.
No significant change in tumor incidence or type was observed
following two years of oral administration of apraclonidine HCl to rats
and mice at dosages of 1 and 0.6 mg/kg/day, up to 50 and 30 times,
respectively, the maximum dose recommended for human topical
ocular use. Apraclonidine HCl was not mutagenic in a series of in vitro
mutagenicity tests, including the Ames test, a mouse lymphoma forward
mutation assay, a chromosome aberration assay in cultured Chinese
hamster ovary (CHO) cells, a sister chromatid exchange assay in CHO
cells, and a cell transformation assay. An in vivo mouse micronucleus
assay conducted with apraclonidine HCl also provided no evidence of
mutagenicity. Reproduction and fertility studies in rats showed no adverse
effect on male or female fertility at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day (25 times the
maximum recommended human dose).
Apraclonidine HCl has been shown to have an embryocidal effect in
rabbits when given in an oral dose of 3 mg/kg/day (150 times the
maximum recommended human dose). Dose related maternal toxicity
was observed in pregnant rats at 0.3 mg/kg/day (15 times the maximum
recommended human dose). There are no adequate and well controlled
studies in pregnant women. IOPIDINE* 1% Ophthalmic Solution should be
used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential
risk to the fetus.
The following adverse events, occurring in less than 2% of patients, were
reported in association with the use of IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution
in laser surgery: ocular injection, upper lid elevation, irregular heart rate,
nasal decongestion, ocular inflammation, conjunctival blanching, and
mydriasis.
The following adverse events were observed in investigational studies
dosing IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution once or twice daily for up to
28 days in non‑laser studies:
Ocular
Conjunctival blanching, upper lid elevation, mydriasis, burning, discomfort,
foreign body sensation, dryness, itching, hypotony, blurred or dimmed
vision, allergic response, conjunctival microhemorrhage.
Gastrointestinal
Abdominal pain, diarrhea, stomach discomfort, emesis
Cardiovascular
Bradycardia, vasovagal attack, palpitations, orthostatic
episode
Central Nervous System
Insomnia, dream disturbances, irritability, decreased libido.
Other
Taste abnormalities, dry mouth, nasal burning or dryness,
headache, head cold sensation, chest heaviness or burning,
clammy or sweaty palms, body heat sensation, shortness
of breath, increased pharyngeal secretion, extremity pain
or numbness, fatigue, paresthesia, pruritus not associated
with rash.
Clinical Practice
The following events have been identified during postmarketing use
of IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution in clinical practice. Because they
are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates
of frequency cannot be made. The events, which have been chosen for
inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible
causal connection to IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution, or a combination
of these factors, include hypersensitivity.
Ingestion of IOPIDINE* 0.5% Ophthalmic Solution has been reported to
cause bradycardia, drowsiness, and hypothermia. Accidental or intentional
ingestion of oral clonidine has been reported to cause apnea, arrhythmias,
asthenia, bradycardia, conduction defects, diminished or absent reflexes,
dryness of the mouth, hypotension, hypothermia, hypoventilation,
irritability, lethargy, miosis, pallor, respiratory depression, sedation
or coma, seizure, somnolence, transient hypertension, and vomiting.
Treatment of an oral overdose includes supportive and symptomatic
therapy; a patent airway should be maintained. Hemodialysis is of limited
value since a maximum of 5% of circulating drug is removed.
One drop of IOPIDINE* 1% Ophthalmic Solution should be instilled in the
scheduled operative eye one hour before initiating anterior segment
laser surgery and a second drop should be instilled to the same eye
immediately upon completion of the laser surgical procedure. Use
a separate container for each single‑drop dose and discard each
container after use.
IOPIDINE 1% Ophthalmic Solution as base is a sterile, isotonic, aqueous
solution containing apraclonidine hydrochloride.
Supplied as follows: 0.1 mL in plastic ophthalmic dispensers, packaged
two per pouch. These dispensers are enclosed in a foil overwrap as an
added barrier to evaporation.
0.1 mL (packaged two per pouch) NDC 82667‑200-01
Storage: Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F‑77°F).
Protect from light.
Manufactured for:
Harrow Eye, LLC™
Nashville, TN 37205 USA
Revised: February 2023
| IOPIDINE 1%
apraclonidine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution solution/ drops |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Harrow Eye, LLC (118526951) |





