Drug Detail:Isentress (Raltegravir [ ral-teg-ra-veer ])
Drug Class: Integrase strand transfer inhibitor
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ISENTRESS ® (raltegravir) film-coated tablets, for oral use
ISENTRESS ® HD (raltegravir) film-coated tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2007
Indications and Usage for Isentress
Adult Patients:
ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD are human immunodeficiency virus integrase strand transfer inhibitors (HIV-1 INSTI) indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adult patients ( 1).
Pediatric Patients:
ISENTRESS is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in pediatric patients weighing at least 2 kg ( 1).
ISENTRESS HD is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in pediatric patients weighing at least 40 kg ( 1).
Isentress Dosage and Administration
ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD can be administered with or without food ( 2.1).
Do not substitute ISENTRESS chewable tablets or ISENTRESS for oral suspension for the ISENTRESS 400 mg or 600 mg film-coated tablet.
See specific dosing guidance for chewable tablets and the formulation for oral suspension ( 2.1).
Adults
- Treatment-naïve patients or patients who are virologically suppressed on an initial regimen of ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily:
- 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) film-coated tablet orally, once daily or
- 400 mg film-coated tablet orally, twice daily ( 2.2).
- Treatment-experienced patients:
- 400 mg film-coated tablet orally, twice daily ( 2.2).
- During coadministration with rifampin in adults, 800 mg (2 × 400 mg) twice daily ( 2.2).
Pediatrics
- If weighing at least 40 kg, and either
- treatment-naïve patients or
- patients who are virologically suppressed on an initial regimen of ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily:
- 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) film-coated tablet orally, once daily or
- 400 mg film-coated tablet orally, twice daily or
- 300 mg (3 × 100 mg) chewable tablets, twice daily ( 2.3).
- If weighing at least 25 kg: One 400 mg film-coated tablet orally, twice daily. If unable to swallow a tablet, consider the chewable tablet, as specified in Table 2 ( 2.3).
- If weighing at least 3 kg to less than 25 kg: Weight-based dosing using the chewable tablet or oral suspension, as specified in Table 4 ( 2.3).
- For neonates (birth to 4 weeks [28 days] of age): Weight-based dosing of the oral suspension as specified in Table 5 ( 2.3).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Film-Coated Tablets: 400 mg ( 3).
Contraindications
None ( 4).
Warnings and Precautions
- Severe, potentially life-threatening and fatal skin reactions have been reported. This includes cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, hypersensitivity reaction and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Immediately discontinue treatment with ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD and other suspect agents if severe hypersensitivity, severe rash, or rash with systemic symptoms or liver aminotransferase elevations develops and monitor clinical status, including liver aminotransferases closely ( 5.1).
- Monitor for Immune Reconstitution Syndrome ( 5.2).
- Inform patients with phenylketonuria that the 100 mg and 25 mg chewable tablets contain phenylalanine ( 5.3).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- The most common adverse reactions of moderate to severe intensity (≥2%) are insomnia, headache, dizziness, nausea and fatigue ( 6.1).
- Creatine kinase elevations were observed in subjects who received ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD. Myopathy and rhabdomyolysis have been reported. Use with caution in patients at increased risk of myopathy or rhabdomyolysis, such as patients receiving concomitant medications known to cause these conditions and patients with a history of rhabdomyolysis, myopathy or increased serum creatine kinase ( 6.2).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Coadministration of ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD and other drugs may alter the plasma concentration of raltegravir. The potential for drug-drug interactions must be considered prior to and during therapy ( 7).
- Coadministration of ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD with drugs that are strong inducers of UGT1A1, such as rifampin, may result in reduced plasma concentrations of raltegravir ( 2.1, 7.1).
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Women infected with HIV should be instructed not to breastfeed due to the potential for HIV transmission ( 8.2).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2023
Full Prescribing Information
2. Isentress Dosage and Administration
2.1 General Dosing Recommendations
- Because the formulations have different pharmacokinetic profiles, do not substitute ISENTRESS chewable tablets or ISENTRESS for oral suspension for the ISENTRESS 400 mg film-coated tablet or the ISENTRESS HD 600 mg film-coated tablet. See specific dosing guidance for chewable tablets and the formulation for oral suspension.
- Because the extent to which ISENTRESS may be dialyzable is unknown, dosing before a dialysis session should be avoided [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
- ISENTRESS film-coated tablets must be swallowed whole.
- ISENTRESS chewable tablets may be chewed or swallowed whole. Maximum daily dose is 300 mg taken by mouth twice daily.
- For children who have difficulty chewing the 25 mg chewable tablet, the tablet may be crushed.
- Preparation of the crushed 25 mg chewable tablet:
- Place the tablet(s) in a small, clean cup. For each tablet, add a teaspoonful (~5 mL) of liquid (for example, water, juice, or breast milk).
- Within 2 minutes, the tablet(s) will absorb the liquid and fall apart.
- Using a spoon, crush any remaining pieces of the tablet(s). Immediately administer the entire dose orally.
- If any portion of the dose is left in the cup, add another teaspoonful (~5 mL) of liquid, swirl and administer immediately.
- Preparation of the crushed 25 mg chewable tablet:
- ISENTRESS for oral suspension:
- See Instructions for Use for details on preparation and administration of ISENTRESS for oral suspension.
- Using the provided mixing cup, combine 10 mL of water and the entire contents of one packet of ISENTRESS for oral suspension and mix. Each single-use packet for oral suspension contains 100 mg of raltegravir which is suspended in 10 mL of water giving a final concentration of 10 mg per mL. Maximum daily dose is 100 mg taken by mouth twice daily.
- Gently swirl the mixing cup for 45 seconds in a circular motion to mix the powder into a uniform suspension. Do not shake.
- Once mixed, measure the prescribed dose volume of suspension with a syringe and administer the dose orally. The dose should be administered orally within 30 minutes of mixing.
- Discard any remaining suspension into the trash.
2.2 Adults
The recommended adult dosage of ISENTRESS film-coated tablets is displayed in Table 1. ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD should be taken by mouth and may be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
| Population | Recommended Dose |
|---|---|
| Treatment-naïve patients or patients who are virologically suppressed on an initial regimen of ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily | 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) once daily
or 400 mg twice daily |
| Treatment-experienced | 400 mg twice daily |
| Treatment-naïve or treatment-experienced when coadministered with rifampin [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] | 800 mg (2 × 400 mg) twice daily |
2.3 Pediatrics
The recommended pediatric dosage of ISENTRESS is displayed in Table 2. ISENTRESS film-coated tablets, chewable tablets and for oral suspension should be taken by mouth and may be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
| Recommended Pediatric Dosage and Formulation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population/Weight | Film-Coated Tablets 400 mg | Film-Coated Tablets 600 mg | Chewable Tablets 100 mg and 25 mg | For Oral Suspension 100 mg |
|
||||
If at least 40 kg and either:
| 400 mg twice daily | 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) once daily | 300 mg twice daily (see Table 3) | NA |
| If at least 25 kg | 400 mg twice daily * | NA | Weight-based dosing twice daily (see Table 3) | NA |
| If at least 4 weeks of age and weighing 3 kg to less than 25 kg | NA | NA | Weight-based dosing twice daily (see Table 4) | Weight-based dosing twice daily up to 20 kg (see Table 4) |
| From birth to 4 weeks (28 days) weighing at least 2 kg | NA | NA | NA | Weight-based dosing once daily or twice daily (see Table 5) |
| Body Weight
(kg) | Dose | Number of 100 mg Chewable Tablets |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| 25 to less than 28 | 150 mg twice daily | 1.5 × 100 mg † twice daily |
| 28 to less than 40 | 200 mg twice daily | 2 × 100 mg twice daily |
| At least 40 | 300 mg twice daily | 3 × 100 mg twice daily |
| Body Weight
(kg) | Volume (Dose) of Suspension to be Administered | Number of Chewable Tablets † |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| 3 to less than 4 | 2.5 mL (25 mg) twice daily | 1 × 25 mg twice daily ‡ |
| 4 to less than 6 | 3 mL (30 mg) twice daily | |
| 6 to less than 8 | 4 mL (40 mg) twice daily | 2 × 25 mg twice daily ‡ |
| 8 to less than 10 | 6 mL (60 mg) twice daily | |
| 10 to less than 14 | 8 mL (80 mg) twice daily | 3 × 25 mg twice daily ‡ |
| 14 to less than 20 | 10 mL (100 mg) twice daily | 1 × 100 mg twice daily |
| 20 to less than 25 | Not applicable | 1.5 × 100 mg § twice daily |
- For full-term neonates (birth to 4 weeks [28 days] of age): Weight-based dosing of the oral suspension as specified in Table 5.
- No data are available in pre-term neonates. The use of ISENTRESS is not recommended in pre-term neonates.
| Body Weight
(kg) | Volume (Dose) of Suspension to be Administered |
|---|---|
| Note: If the mother has taken ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD 2-24 hours before delivery, the neonate's first dose should be given between 24-48 hours after birth. | |
|
|
| Birth to 1 Week - Once daily dosing * | |
| 2 to less than 3 | 0.4 mL (4 mg) once daily |
| 3 to less than 4 | 0.5 mL (5 mg) once daily |
| 4 to less than 5 | 0.7 mL (7 mg) once daily |
| 1 to 4 Weeks - Twice daily dosing † | |
| 2 to less than 3 | 0.8 mL (8 mg) twice daily |
| 3 to less than 4 | 1 mL (10 mg) twice daily |
| 4 to less than 5 | 1.5 mL (15 mg) twice daily |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Film-coated Tablets
- 400 mg pink, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets with "227" on one side (ISENTRESS).
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Severe Skin and Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe, potentially life-threatening, and fatal skin reactions have been reported. These include cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Hypersensitivity reactions have also been reported and were characterized by rash, constitutional findings, and sometimes, organ dysfunction, including hepatic failure. Discontinue ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD and other suspect agents immediately if signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions or hypersensitivity reactions develop (including, but not limited to, severe rash or rash accompanied by fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, facial edema, hepatitis, eosinophilia, angioedema). Clinical status including liver aminotransferases should be monitored and appropriate therapy initiated. Delay in stopping ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD treatment or other suspect agents after the onset of severe rash may result in a life-threatening reaction.
5.2 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including ISENTRESS. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune systems respond may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
5.3 Phenylketonurics
ISENTRESS Chewable Tablets contain phenylalanine, a component of aspartame. Each 25 mg ISENTRESS Chewable Tablet contains approximately 0.05 mg phenylalanine. Each 100 mg ISENTRESS Chewable Tablet contains approximately 0.10 mg phenylalanine. Phenylalanine can be harmful to patients with phenylketonuria.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Treatment-Naïve Adults
The safety of ISENTRESS was evaluated in HIV-infected treatment-naïve subjects in 2 Phase III studies: STARTMRK evaluated ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily versus efavirenz, both in combination with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), and ONCEMRK evaluated ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) once daily versus ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily, both in combination with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Safety data from these two studies are presented side-by-side in Tables 6 and 7 to simplify presentation; direct comparisons across trials should not be made due to differing duration of follow-up and study design.
ONCEMRK (ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg [2 × 600 mg] once daily)
In ONCEMRK, subjects received ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg once daily (n=531) or ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily (n=266) both in combination with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. During double-blind treatment, the total follow-up for subjects with ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg once daily was 913 patient-years and for ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily was 450 patient-years.
In ONCEMRK, the rate of discontinuation of therapy due to adverse events through Week 96 was 1% in subjects receiving ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) once daily and 2% in subjects receiving ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily.
Clinical adverse reactions of moderate to severe intensity occurring in ≥2% of treatment-naïve subjects treated with ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily or efavirenz in STARTMRK through Week 240 or ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg once daily or ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily in ONCEMRK through Week 96 are presented in Table 6.
In STARTMRK, clinical adverse reactions of all intensities (mild, moderate and severe) occurring in ≥2% of subjects on ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily through Week 240 also include diarrhea, flatulence, asthenia, decreased appetite, abnormal dreams, depression and nightmare. In ONCEMRK, clinical adverse reactions of all intensities (mild, moderate and severe) occurring in ≥2% of subjects on ISENTRESS HD or ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily through Week 96 also include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and decreased appetite.
| System Organ Class, Preferred Term | STARTMRK
Week 240 | ONCEMRK
Week 96 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily
(N= 281) | Efavirenz 600 mg At Bedtime
(N= 282) | ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg Once Daily
(N=531) | ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily
(N=266) |
|
| Note: ISENTRESS BID, ISENTRESS HD and efavirenz were administered with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | ||||
| N= total number of subjects per treatment group | ||||
|
||||
| Headache | 4% | 5% | 1% | <1% |
| Insomnia | 4% | 4% | <1% | <1% |
| Nausea | 3% | 4% | 1% | 0% |
| Dizziness | 2% | 6% | <1% | 0% |
| Fatigue | 2% | 3% | 0% | 0% |
Laboratory Abnormalities
The percentages of adult subjects with selected Grade 2 to 4 laboratory abnormalities (that represent a worsening Grade from baseline) who were treated with ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily or efavirenz in STARTMRK or ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg once daily or ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily in ONCEMRK are presented in Table 7.
| STARTMRK
Week 240 | ONCEMRK
Week 96 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term (Unit) | Limit | ISENTRESS
400 mg Twice Daily (N = 281) | Efavirenz
600 mg At Bedtime (N = 282) | ISENTRESS HD
1200 mg Once Daily (N=531) | ISENTRESS
400 mg Twice Daily (N=266) |
| ULN = Upper limit of normal range | |||||
| Notes: ISENTRESS BID, ISENTRESS HD and Efavirenz were administered with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | |||||
|
|||||
| Hematology | |||||
| Absolute neutrophil count (10 3/µL) | |||||
| Grade 2 | 0.75 - 0.999 | 3% | 5% | 2% | 1% |
| Grade 3 | 0.50 - 0.749 | 3% | 1% | 1% | 1% |
| Grade 4 | <0.50 | 1% | 1% | <1% | 0% |
| Hemoglobin (gm/dL) | |||||
| Grade 2 | 7.5 - 8.4 | 1% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Grade 3 | 6.5 - 7.4 | 1% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Grade 4 | <6.5 | <1% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Platelet count (10 3/µL) | |||||
| Grade 2 | 50 - 99.999 | 1% | 0% | 1% | <1% |
| Grade 3 | 25 - 49.999 | <1% | <1% | 0% | 0% |
| Grade 4 | <25 | 0% | 0% | 0% | <1% |
| Blood chemistry | |||||
| Fasting (non-random) serum glucose test (mg/dL) * | |||||
| Grade 2 | 126 - 250 | 7% | 6% | - | - |
| Grade 3 | 251 - 500 | 2% | 1% | - | - |
| Grade 4 | >500 | 0% | 0% | - | - |
| Total serum bilirubin | |||||
| Grade 2 | 1.6 - 2.5 × ULN | 5% | <1% | 3% | 2% |
| Grade 3 | 2.6 - 5.0 × ULN | 1% | 0% | 1% | <1% |
| Grade 4 | >5.0 × ULN | <1% | 0% | <1% | 0% |
| Creatinine | |||||
| Grade 2 | 1.4-1.8 × ULN | 1% | 1% | 0% | <1% |
| Grade 3 | 1.9-3.4 × ULN | 0% | <1% | 0% | 0% |
| Grade 4 | ≥3.5 × ULN | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Serum aspartate aminotransferase | |||||
| Grade 2 | 2.6 - 5.0 × ULN | 8% | 10% | 5% | 3% |
| Grade 3 | 5.1 - 10.0 × ULN | 5% | 3% | 2% | <1% |
| Grade 4 | >10.0 × ULN | 1% | <1% | 1% | <1% |
| Serum alanine aminotransferase | |||||
| Grade 2 | 2.6 - 5.0 × ULN | 11% | 12% | 4% | 2% |
| Grade 3 | 5.1 - 10.0 × ULN | 2% | 2% | 1% | <1% |
| Grade 4 | >10.0 × ULN | 2% | 1% | 1% | <1% |
| Serum alkaline phosphatase | |||||
| Grade 2 | 2.6 - 5.0 × ULN | 1% | 3% | 1% | 0% |
| Grade 3 | 5.1 - 10.0 × ULN | 0% | 1% | <1% | 0% |
| Grade 4 | >10.0 × ULN | <1% | <1% | 0% | 0% |
| Lipase † | |||||
| Grade 2 | 1.6-3.0 x ULN | - | - | 7% | 5% |
| Grade 3 | 3.1-5.0 × ULN | - | - | 2% | 1% |
| Grade 4 | >5.0 × ULN | - | - | 2% | 1% |
| Creatine kinase † | |||||
| Grade 2 | 6.0-9.9 × ULN | - | - | 4% | 5% |
| Grade 3 | 10.0-19.9 × ULN | - | - | 3% | 3% |
| Grade 4 | ≥20.0 × ULN | - | - | 3% | 2% |
Lipids, Change from Baseline
Changes from baseline in fasting lipids are shown in Table 8.
| Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term | ISENTRESS 400 mg
Twice Daily + Emtricitabine (+) Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate N = 207 | Efavirenz 600 mg
At Bedtime + Emtricitabine (+) Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate N = 187 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change from Baseline at
Week 240 | Change from Baseline at
Week 240 |
|||||
| Baseline
Mean | Week 240
Mean | Mean Change | Baseline
Mean | Week 240
Mean | Mean Change | |
| (mg/dL) | (mg/dL) | (mg/dL) | (mg/dL) | (mg/dL) | (mg/dL) | |
| Notes:
N = total number of subjects per treatment group with at least one lipid test result available. The analysis is based on all available data. If subjects initiated or increased serum lipid-reducing agents, the last available lipid values prior to the change in therapy were used in the analysis. If the missing data was due to other reasons, subjects were censored thereafter for the analysis. At baseline, serum lipid-reducing agents were used in 5% of subjects in the group receiving ISENTRESS and 3% in the efavirenz group. Through Week 240, serum lipid-reducing agents were used in 9% of subjects in the group receiving ISENTRESS and 15% in the efavirenz group. |
||||||
|
||||||
| LDL-Cholesterol * | 96 | 106 | 10 | 93 | 118 | 25 |
| HDL-Cholesterol * | 38 | 44 | 6 | 38 | 51 | 13 |
| Total Cholesterol * | 159 | 175 | 16 | 157 | 201 | 44 |
| Triglyceride * | 128 | 130 | 2 | 141 | 178 | 37 |
Treatment-Experienced Adults
The safety assessment of ISENTRESS in treatment-experienced subjects is based on the pooled safety data from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials, BENCHMRK 1 and BENCHMRK 2 in antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1 infected adult subjects. A total of 462 subjects received the recommended dose of ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily in combination with optimized background therapy (OBT) compared to 237 subjects taking placebo in combination with OBT. The median duration of therapy in these trials was 96 weeks for subjects receiving ISENTRESS and 38 weeks for subjects receiving placebo. The total exposure to ISENTRESS was 708 patient-years versus 244 patient-years on placebo. The rates of discontinuation due to adverse events were 4% in subjects receiving ISENTRESS and 5% in subjects receiving placebo.
Clinical ADRs were considered by investigators to be causally related to ISENTRESS + OBT or placebo + OBT. Clinical ADRs of moderate to severe intensity occurring in ≥2% of subjects treated with ISENTRESS and occurring at a higher rate compared to placebo are presented in Table 9.
| System Organ Class, Adverse Reactions | Randomized Studies BENCHMRK 1 and BENCHMRK 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily + OBT
(n = 462) | Placebo + OBT
(n = 237) |
|
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| n=total number of subjects per treatment group. | ||
|
||
| Headache | 2% | <1% |
Laboratory Abnormalities
The percentages of adult subjects treated with ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily or placebo in Studies BENCHMRK 1 and BENCHMRK 2 with selected Grade 2 to 4 laboratory abnormalities representing a worsening Grade from baseline are presented in Table 10.
| Randomized Studies BENCHMRK 1 and BENCHMRK 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term
(Unit) | Limit | ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily + OBT
(N = 462) | Placebo + OBT
(N = 237) |
| ULN = Upper limit of normal range | |||
| Hematology | |||
| Absolute neutrophil count (10 3/µL) | |||
| Grade 2 | 0.75 - 0.999 | 4% | 5% |
| Grade 3 | 0.50 - 0.749 | 3% | 3% |
| Grade 4 | <0.50 | 1% | <1% |
| Hemoglobin (gm/dL) | |||
| Grade 2 | 7.5 - 8.4 | 1% | 3% |
| Grade 3 | 6.5 - 7.4 | 1% | 1% |
| Grade 4 | <6.5 | <1% | 0% |
| Platelet count (10 3/µL) | |||
| Grade 2 | 50 - 99.999 | 3% | 5% |
| Grade 3 | 25 - 49.999 | 1% | <1% |
| Grade 4 | <25 | 1% | <1% |
| Blood chemistry | |||
| Fasting (non-random) serum glucose test (mg/dL) | |||
| Grade 2 | 126 - 250 | 10% | 7% |
| Grade 3 | 251 - 500 | 3% | 1% |
| Grade 4 | >500 | 0% | 0% |
| Total serum bilirubin | |||
| Grade 2 | 1.6 - 2.5 × ULN | 6% | 3% |
| Grade 3 | 2.6 - 5.0 × ULN | 3% | 3% |
| Grade 4 | >5.0 × ULN | 1% | 0% |
| Serum aspartate aminotransferase | |||
| Grade 2 | 2.6 - 5.0 × ULN | 9% | 7% |
| Grade 3 | 5.1 - 10.0 × ULN | 4% | 3% |
| Grade 4 | >10.0 × ULN | 1% | 1% |
| Serum alanine aminotransferase | |||
| Grade 2 | 2.6 - 5.0 × ULN | 9% | 9% |
| Grade 3 | 5.1 - 10.0 × ULN | 4% | 2% |
| Grade 4 | >10.0 × ULN | 1% | 2% |
| Serum alkaline phosphatase | |||
| Grade 2 | 2.6 - 5.0 × ULN | 2% | <1% |
| Grade 3 | 5.1 - 10.0 × ULN | <1% | 1% |
| Grade 4 | >10.0 × ULN | 1% | <1% |
| Serum pancreatic amylase test | |||
| Grade 2 | 1.6 - 2.0 × ULN | 2% | 1% |
| Grade 3 | 2.1 - 5.0 × ULN | 4% | 3% |
| Grade 4 | >5.0 × ULN | <1% | <1% |
| Serum lipase test | |||
| Grade 2 | 1.6 - 3.0 × ULN | 5% | 4% |
| Grade 3 | 3.1 - 5.0 × ULN | 2% | 1% |
| Grade 4 | >5.0 × ULN | 0% | 0% |
| Serum creatine kinase | |||
| Grade 2 | 6.0 - 9.9 × ULN | 2% | 2% |
| Grade 3 | 10.0 - 19.9 × ULN | 4% | 3% |
| Grade 4 | ≥20.0 × ULN | 3% | 1% |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of ISENTRESS. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: thrombocytopenia
Gastrointestinal Disorders: diarrhea
Hepatobiliary Disorders: hepatic failure (with and without associated hypersensitivity) in patients with underlying liver disease and/or concomitant medications
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: rhabdomyolysis
Nervous System Disorders: cerebellar ataxia
Psychiatric Disorders: anxiety, paranoia
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of Other Agents on the Pharmacokinetics of Raltegravir
Raltegravir is not a substrate of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. Based on in vivo and in vitro studies, raltegravir is eliminated mainly by metabolism via a UGT1A1-mediated glucuronidation pathway. Coadministration of ISENTRESS with drugs that inhibit UGT1A1 may increase plasma levels of raltegravir and coadministration of ISENTRESS with drugs that induce UGT1A1, such as rifampin, may reduce plasma levels of raltegravir (see Table 11).
Selected drug interactions are presented in Table 11 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . In some cases, recommendations differ for ISENTRESS versus ISENTRESS HD.
| Concomitant Drug Class:
Drug Name | Effect on Concentration of Raltegravir | Clinical Comment for ISENTRESS | Clinical Comment for ISENTRESS HD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal-Containing Antacids | |||
| Aluminum and/or magnesium-containing antacids | ↓ | Coadministration or staggered administration is not recommended. | |
| Calcium carbonate antacid | ↓ | No dose adjustment | Co-administration is not recommended |
| Other Agents | |||
| Rifampin | ↓ | The recommended dosage is 800 mg twice daily during coadministration with rifampin. There are no data to guide co-administration of ISENTRESS with rifampin in patients below 18 years of age [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. | Coadministration is not recommended. |
| Tipranavir/ritonavir | No dose adjustment | Coadministration is not recommended | |
| Etravirine | ↓ | No dose adjustment | Coadministration is not recommended. |
| Strong inducers of drug metabolizing enzymes not mentioned above e.g., Carbamazepine
Phenobarbital Phenytoin | ↓↔ | The impact of other strong inducers of drug metabolizing enzymes on raltegravir is unknown. Coadministration is not recommended. | |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ISENTRESS/ISENTRESS HD did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of ISENTRESS is necessary for patients with mild to moderate (Child-Pugh A and B) hepatic impairment. No hepatic impairment study has been conducted with ISENTRESS HD and therefore administration in subjects with hepatic impairment is not recommended. The effect of severe hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of raltegravir has not been studied [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
8.7 Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD is necessary in patients with any degree of renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The extent to which ISENTRESS may be dialyzable is unknown; therefore, dosing before a dialysis session should be avoided.
10. Overdosage
In the event of an overdose, it is reasonable to employ the standard supportive measures, e.g., remove unabsorbed material from the gastrointestinal tract, employ clinical monitoring (including obtaining an electrocardiogram), and institute supportive therapy if required. The extent to which ISENTRESS may be dialyzable is unknown.
11. Isentress Description
ISENTRESS contains raltegravir potassium, a human immunodeficiency virus integrase strand transfer inhibitor. The chemical name for raltegravir potassium is N-[(4-Fluorophenyl) methyl]-1,6-dihydro-5-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-[1-methyl-1-[[(5-methyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)carbonyl]amino]ethyl]-6-oxo-4-pyrimidinecarboxamide monopotassium salt.
The empirical formula is C 20H 20FKN 6O 5 and the molecular weight is 482.51. The structural formula is:
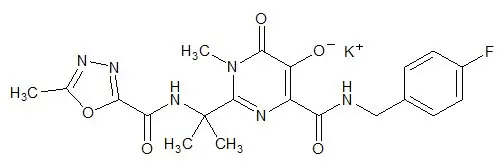
Raltegravir potassium is a white to off-white powder. It is soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, very slightly soluble in ethanol and acetonitrile and insoluble in isopropanol.
Each 400 mg film-coated tablet of ISENTRESS for oral administration contains 434.4 mg of raltegravir (as potassium salt), equivalent to 400 mg of raltegravir free phenol and the following inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate dibasic anhydrous, hypromellose 2208, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, poloxamer 407 (contains 0.01% butylated hydroxytoluene as antioxidant), sodium stearyl fumarate. In addition, the film coating contains the following inactive ingredients: black iron oxide, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol, red iron oxide, talc and titanium dioxide.
12. Isentress - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In a monotherapy study raltegravir (400 mg twice daily) demonstrated rapid antiviral activity with mean viral load reduction of 1.66 log 10 copies/mL by day 10.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Adults
Effect of Food on Oral Absorption
The food effect of various formulations are presented in Table 12.
| PK parameter ratio (fed/fasted) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation | Meal Type | AUC Ratio
(90% CI) | C
max Ratio
(90% CI) | C
min Ratio
(90% CI) |
| Low fat meal: 300 Kcal, 2.5 g fat | ||||
| Moderate fat meal: 600 Kcal, 21 g fat | ||||
| High fat meal: 825 Kcal, 52 g fat | ||||
| 400 mg twice daily | Low Fat | 0.54 (0.41-0.71) | 0.48 (0.35-0.67) | 0.86 (0.54-1.36) |
| Moderate Fat | 1.13 (0.85-1.49) | 1.05 (0.75-1.46) | 1.66 (1.04-2.64) | |
| High Fat | 2.11 (1.60-2.80) | 1.96 (1.41-2.73) | 4.13 (2.60-6.57) | |
| 1200 mg once daily | Low Fat | 0.58 (0.46-0.74) | 0.48 (0.37-0.62) | 0.84 (0.63-1.10) |
| High Fat | 1.02 (0.86-1.21) | 0.72 (0.58-0.90) | 0.88 (0.66-1.18) | |
| Chewable tablet | High Fat | 0.94 (0.78-1.14) | 0.38 (0.28-0.52) | 2.88 (2.21-3.75) |
| Oral suspension | The effect of food on oral suspension was not studied. | |||
Metabolism and Excretion
The apparent terminal half-life of raltegravir is approximately 9 hours, with a shorter α-phase half-life (~1 hour) accounting for much of the AUC. Following administration of an oral dose of radiolabeled raltegravir, approximately 51 and 32% of the dose was excreted in feces and urine, respectively. In feces, only raltegravir was present, most of which is likely derived from hydrolysis of raltegravir-glucuronide secreted in bile as observed in preclinical species. Two components, namely raltegravir and raltegravir-glucuronide, were detected in urine and accounted for approximately 9 and 23% of the dose, respectively. The major circulating entity was raltegravir and represented approximately 70% of the total radioactivity; the remaining radioactivity in plasma was accounted for by raltegravir-glucuronide. The major mechanism of clearance of raltegravir in humans is UGT1A1-mediated glucuronidation.
| Parameter | 400 mg BID
Geometric Mean (%CV) N=6 | 1200 mg QD
Geometric Mean (%CV) N=524 |
|---|---|---|
| AUC (µM∙hr) | AUC 0-12hr= 14.3 (88.6) | AUC 0-24hr = 55.3 (41.5) |
| C max (µM) | 4.5 (128) | 15.7 (45.8) |
| C min (nM) | C 12hr = 142 (63.8) | C 24hr = 107 (97.5) |
Special Populations
Pediatric
ISENTRESS
Two pediatric formulations were evaluated in healthy adult volunteers, where the chewable tablet and oral suspension were compared to the 400 mg tablet. The chewable tablet and oral suspension demonstrated higher oral bioavailability, thus higher AUC, compared to the 400 mg tablet. In the same study, the oral suspension resulted in higher oral bioavailability compared to the chewable tablet. These observations resulted in proposed pediatric doses targeting 6 mg/kg/dose for the chewable tablets and oral suspension. As displayed in Table 14, the doses recommended for HIV-infected infants, children and adolescents 4 weeks to 18 years of age [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] resulted in a pharmacokinetic profile of raltegravir similar to that observed in adults receiving 400 mg twice daily.
Overall, dosing in pediatric patients achieved exposures (C trough) above 45 nM in the majority of subjects, but some differences in exposures between formulations were observed. Pediatric patients above 25 kg administered the chewable tablets had lower trough concentrations (113 nM) compared to pediatric patients above 25 kg administered the 400 mg tablet formulation (233 nM) [see Clinical Studies (14.4)] . As a result, the 400 mg film-coated tablet is the recommended dose in patients weighing at least 25 kg; however, the chewable tablet offers an alternative regimen in patients weighing at least 25 kg who are unable to swallow the film-coated tablet [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] . In addition, pediatric patients weighing 11 to 25 kg who were administered the chewable tablets had the lowest trough concentrations (82 nM) compared to all other pediatric subgroups.
| Body Weight | Formulation | Dose | N * | Geometric Mean
(%CV †) AUC 0-12hr (µM∙hr) | Geometric Mean
(%CV †) C 12hr (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| ≥25 kg | Film-coated tablet | 400 mg twice daily | 18 | 14.1 (121%) | 233 (157%) |
| ≥25 kg | Chewable tablet | Weight-based dosing, see Table 3 | 9 | 22.1 (36%) | 113 (80%) |
| 11 to less than 25 kg | Chewable tablet | Weight-based dosing, see Table 4 | 13 | 18.6 (68%) | 82 (123%) |
| 3 to less than 20 kg | Oral suspension | Weight-based dosing, see Table 4 | 19 | 24.5 (43%) | 113 (69%) |
Elimination of raltegravir in vivo in human is primarily through the UGT1A1-mediated glucuronidation pathway. UGT1A1 catalytic activity is negligible at birth and matures after birth. The dose recommended for neonates less than 4 weeks of age takes into consideration the rapidly increasing UGT1A1 activity and drug clearance from birth to 4 weeks of age. Table 15 displays pharmacokinetic parameters for neonates receiving the granules for oral suspension at the recommended dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
| Age (hours/days) at PK Sampling | Dose (See Table 5) | N * | Geometric Mean
(%CV †) AUC (μM∙hr ) | Geometric Mean
(%CV †) C trough (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Birth – 48 hours | 1.5 mg/kg once daily | 25 | 85.9 (38.4%) ‡ | 2132.9 (64.2%) ‡ |
| 15 to 18 days | 3.0 mg/kg twice daily | 23 | 32.2 (43.3%) § | 1255.5 (83.7%) § |
Drug Interactions
In vitro, raltegravir does not inhibit (IC 50>100 µM) CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 or CYP3A. In vivo, raltegravir does not inhibit CYP3A4. Moreover, in vitro, raltegravir did not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6 or CYP3A4. Similarly, raltegravir is not an inhibitor (IC 50>50 µM) of UGT1A1 or UGT2B7, and raltegravir does not inhibit P-glycoprotein-mediated transport.
Raltegravir drug interaction study results are shown in Tables 16 and 17. For information regarding clinical recommendations [see Drug Interactions (7)] .
| Coadministered Drug | Coadministered Drug Dose/Schedule | Raltegravir
Dose/Schedule | Ratio (90% Confidence Interval) of Raltegravir Pharmacokinetic Parameters with/without Coadministered Drug;
No Effect = 1.00 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | C max | AUC | C min | |||
|
||||||
| aluminum and magnesium hydroxide antacid * | 20 mL single dose given with raltegravir | 400 mg twice daily | 25 | 0.56
(0.42, 0.73) | 0.51
(0.40, 0.65) | 0.37
(0.29, 0.48) |
| 20 mL single dose given 2 hours before raltegravir | 23 | 0.49
(0.33, 0.71) | 0.49
(0.35, 0.67) | 0.44
(0.34, 0.55) |
||
| 20 mL single dose given 2 hours after raltegravir | 23 | 0.78
(0.53, 1.13) | 0.70
(0.50, 0.96) | 0.43
(0.34, 0.55) |
||
| 20 mL single dose given 4 hours before raltegravir | 17 | 0.78
(0.55, 1.10) | 0.81
(0.63, 1.05) | 0.40
(0.31, 0.52) |
||
| 20 mL single dose given 4 hours after raltegravir | 18 | 0.70
(0.48, 1.04) | 0.68
(0.50, 0.92) | 0.38
(0.30, 0.49) |
||
| 20 mL single dose given 6 hours before raltegravir | 16 | 0.90
(0.58, 1.40) | 0.87
(0.64, 1.18) | 0.50
(0.39, 0.65) |
||
| 20 mL single dose given 6 hours after raltegravir | 16 | 0.90
(0.58, 1.41) | 0.89
(0.64, 1.22) | 0.51
(0.40, 0.64) |
||
| aluminum and magnesium hydroxide antacid * | 20 mL single dose given 12 hours after raltegravir | 1200 mg single dose | 19 | 0.86
(0.65, 1.15) | 0.86
(0.73, 1.03) | 0.42
(0.34, 0.52) |
| atazanavir | 400 mg daily | 100 mg single dose | 10 | 1.53 (1.11, 2.12) | 1.72 (1.47, 2.02) | 1.95 (1.30, 2.92) |
| atazanavir | 400 mg daily | 1200 mg single dose | 14 | 1.16 (1.01, 1.33) | 1.67 (1.34, 2.10) | 1.26 (1.08, 1.46) |
| atazanavir/ritonavir | 300 mg/100 mg daily | 400 mg twice daily | 10 | 1.24 (0.87, 1.77) | 1.41 (1.12, 1.78) | 1.77 (1.39, 2.25) |
| boceprevir | 800 mg three times daily | 400 mg single dose | 22 | 1.11
(0.91, 1.36) | 1.04
(0.88, 1.22) | 0.75
(0.45, 1.23) |
| calcium carbonate antacid * | 3000 mg single dose given with raltegravir | 400 mg twice daily | 24 | 0.48
(0.36, 0.63) | 0.45
(0.35, 0.57) | 0.68
(0.53, 0.87) |
| calcium carbonate antacid * | 3000 mg single dose given with raltegravir | 1200 mg single dose | 19 | 0.26
(0.21, 0.32) | 0.28
(0.24, 0.32) | 0.52
(0.45, 0.61) |
| 3000 mg single dose given 12 hours after raltegravir | 0.98
(0.81, 1.17) | 0.90
(0.80, 1.03) | 0.43
(0.36, 0.51) |
|||
| efavirenz | 600 mg daily | 400 mg single dose | 9 | 0.64
(0.41, 0.98) | 0.64
(0.52, 0.80) | 0.79
(0.49, 1.28) |
| efavirenz | 600 mg daily | 1200 mg single dose | 21 | 0.91
(0.70, 1.17) | 0.86
(0.73, 1.01) | 0.94
(0.76, 1.17) |
| etravirine | 200 mg twice daily | 400 mg twice daily | 19 | 0.89
(0.68, 1.15) | 0.90
(0.68, 1.18) | 0.66
(0.34, 1.26) |
| omeprazole * | 20 mg daily | 400 mg twice daily | 18 | 1.51
(0.98, 2.35) | 1.37
(0.99, 1.89) | 1.24
(0.95, 1.62) |
| rifampin | 600 mg daily | 400 mg single dose | 9 | 0.62
(0.37, 1.04) | 0.60
(0.39, 0.91) | 0.39
(0.30, 0.51) |
| rifampin | 600 mg daily | 400 mg twice daily when administered alone; 800 mg twice daily when administered with rifampin | 14 | 1.62
(1.12, 2.33) | 1.27
(0.94, 1.71) | 0.47
(0.36, 0.61) |
| ritonavir | 100 mg twice daily | 400 mg single dose | 10 | 0.76 (0.55, 1.04) | 0.84 (0.70, 1.01) | 0.99 (0.70, 1.40) |
| tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 300 mg daily | 400 mg twice daily | 9 | 1.64
(1.16, 2.32) | 1.49
(1.15, 1.94) | 1.03
(0.73, 1.45) |
| tipranavir/ritonavir | 500 mg/200 mg twice daily | 400 mg twice daily | 15
(14 for C min) | 0.82
(0.46, 1.46) | 0.76
(0.49, 1.19) | 0.45
(0.31, 0.66) |
| Substrate Drug | Raltegravir
Dose/Schedule | Ratio (90% Confidence Interval) of Substrate Pharmacokinetic Parameters with/without Coadministered Drug;
No Effect = 1.00 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | C max | AUC | C min | ||
| Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate 300 mg | 400 mg | 9 | 0.77 (0.69, 0.85) | 0.90 (0.82, 0.99) | C
24hr
0.87 (0.74, 1.02) |
| Etravirine 200 mg | 400 mg | 19 | 1.04 (0.97, 1.12) | 1.10 (1.03, 1.16) | 1.17 (1.10, 1.26) |
In drug interaction studies, there was no effect of raltegravir on the PK of ethinyl estradiol, methadone, midazolam or boceprevir.
12.4 Microbiology
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies of raltegravir in mice did not show any carcinogenic potential. At the highest dose levels, 400 mg/kg/day in females and 250 mg/kg/day in males, systemic exposure was 1.8-fold (females) or 1.2-fold (males) greater than the AUC (54 µM∙hr) at the 400-mg twice daily human dose. Treatment-related squamous cell carcinoma of nose/nasopharynx was observed in female rats dosed with 600 mg/kg/day raltegravir for 104 weeks. These tumors were possibly the result of local irritation and inflammation due to local deposition and/or aspiration of drug in the mucosa of the nose/nasopharynx during dosing. No tumors of the nose/nasopharynx were observed in rats dosed with 150 mg/kg/day (males) and 50 mg/kg/day (females) and the systemic exposure in rats was 1.7-fold (males) to 1.4-fold (females) greater than the AUC (54 µM∙hr) at the 400-mg twice daily human dose.
No evidence of mutagenicity or genotoxicity was observed in in vitro microbial mutagenesis (Ames) tests, in vitro alkaline elution assays for DNA breakage, and in vitro and in vivo chromosomal aberration studies.
No effect on fertility was seen in male and female rats at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day which resulted in a 3-fold exposure above the exposure at the recommended human dose.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Description of Clinical Studies
The evidence of durable efficacy of ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily is based on the analyses of 240-week data from a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial, STARTMRK evaluating ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily in antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected adult subjects, the analysis of 96-week data from a randomized, double-blind, active-control trial, ONCEMRK evaluating ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) once daily in treatment-naïve adult subjects, and 96-week data from 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, BENCHMRK 1 and BENCHMRK 2, evaluating ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily in antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1 infected adult subjects. See Table 18.
| Trial | Study Type | Population | Study Arms (N) | Dose/Formulation | Timepoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STARTMRK | Randomized, double-blind, active-controlled | Treatment-Naïve Adults | ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily (281)
Efavirenz 600 mg At Bedtime (282) Both in combination with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 400 mg film-coated tablet | Week 240 |
| ONCEMRK | Randomized, double-blind, active-controlled | Treatment-Naïve Adults | ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg Once Daily (531) | 600 mg film-coated tablet | Week 96 |
| ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily (266)
Both in combination with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 400 mg film-coated tablet | ||||
| BENCHMRK 1 | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | Treatment-Experienced Adults | ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily (232)
Placebo (118) Both in combination with optimized background therapy | 400 mg film-coated tablet | Week 240 (Week 156 on double-blind plus Week 84 on open-label) |
| BENCHMRK 2 | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | Treatment-Experienced Adults | ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily (230)
Placebo (119) Both in combination with optimized background therapy | 400 mg film-coated tablet | Week 240 (Week 156 on double-blind plus Week 84 on open-label) |
| IMPAACT P1066 | Open-label, non-comparative | Pediatric Patients – 4 weeks to 18 years of age
(Treatment-Experienced or Failed Prior PMTCT) | ISENTRESS 400 mg tablet Twice Daily – 12 to 18 years or 6 to <12 years and ≥25 kg (87)
ISENTRESS chewable tablet- Weight-Based Dose to Approximate 6 mg/kg Twice Daily – 2 to <12 years (39) ISENTRESS for oral suspension- Weight-Based Dose to Approximate 6 mg/kg Twice Daily – 4 weeks to <2 years (26) In combination with optimized background therapy | 400 mg film-coated tablet
25 mg and 100 mg chewable tablet 100 mg sachet for oral suspension | Week 240 |
14.2 Treatment-Naïve Adult Subjects
ONCEMRK (ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg [2 × 600 mg] once daily)
ONCEMRK is a Phase 3 randomized, international, double-blind, active-controlled trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) once daily versus ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily, both in combination with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, in treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected subjects with HIV-1 RNA ≥1000 copies/mL. Randomization was stratified by screening HIV-1 RNA level (≤100,000 or >100,000 copies/mL) and by hepatitis B and C infection status.
In ONCEMRK, 797 subjects were randomized and received at least 1 dose of either raltegravir 1200 mg once daily or raltegravir 400 mg twice daily, both in combination with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. There were 797 subjects included in the efficacy and safety analyses. At baseline, the median age of subjects was 34 years (range: 18-84), 15% female, 41% non-white, 3% had hepatitis B and/or C virus co-infection, 13% were CDC Class C (AIDS), 28% had HIV-1 RNA greater than 100,000 copies per mL, and 13% had CD4+ cell count less than 200 cells per mm 3; the frequencies of these baseline characteristics were similar between treatment groups.
Table 19 shows the virologic outcomes in both studies. Side-by-side tabulation is to simplify presentation; direct comparisons across trials should not be made due to differing duration of follow-up.
| STARTMRK
Week 240 | ONCEMRK
Week 96 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISENTRESS
400 mg Twice Daily (N=281) | Efavirenz
600 mg At Bedtime (N=282) | ISENTRESS HD
1200 mg Once Daily (N=531) | ISENTRESS
400 mg Twice Daily (N=266) |
|
| Notes: ISENTRESS BID, ISENTRESS HD and Efavirenz were administered with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | ||||
|
||||
| HIV RNA < Lower Limit of Quantitation * | 66% | 60% | 82% | 80% |
| Treatment Difference | 6.6% (95% CI: -1.4%, 14.5%) | 1.4% (95% CI: -4.4%, 7.3%) | ||
| HIV RNA ≥ Lower Limit of Quantitation | 8% | 15% | 9% | 8% |
| No Virologic Data at Analysis Timepoint | 26% | 26% | 9% | 12% |
| Reasons | ||||
| Discontinued trial due to AE or Death † | 5% | 10% | 1% | 3% |
| Discontinued trial for Other Reasons ‡ | 15% | 14% | 7% | 8% |
| On trial but missing data at timepoint | 6% | 2% | 1% | 2% |
In the ONCEMRK trial, ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) once daily demonstrated consistent virologic and immunologic efficacy relative to ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily, both in combination with emtricitabine (+) tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, across demographic and baseline prognostic factors, including: baseline HIV RNA levels >100,000 copies/mL and demographic groups (including age, gender, race, ethnicity and region), concomitant proton pump inhibitors/H2 blockers use and viral subtypes (comparing non-clade B as a group to clade B).
Consistent efficacy in subjects receiving ISENTRESS HD 1200 mg (2 × 600 mg) once daily was observed across HIV subtypes with 80.6% (270/335) and 83.5% (162/194) of subjects with B and non-B subtypes respectively, achieving HIV RNA <40 copies/mL at week 96 (Snapshot approach).
14.3 Treatment-Experienced Adult Subjects
BENCHMRK 1 and BENCHMRK 2 are Phase 3 studies to evaluate the safety and antiretroviral activity of ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily in combination with an optimized background therapy (OBT), versus OBT alone, in HIV-1-infected subjects, 16 years or older, with documented resistance to at least 1 drug in each of 3 classes (NNRTIs, NRTIs, PIs) of antiretroviral therapies. Randomization was stratified by degree of resistance to PI (1PI vs. >1PI) and the use of enfuvirtide in the OBT. Prior to randomization, OBT was selected by the investigator based on genotypic/phenotypic resistance testing and prior ART history.
Table 20 shows the demographic characteristics of subjects in the group receiving ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily and subjects in the placebo group.
| Randomized Studies
BENCHMRK 1 and BENCHMRK 2 | ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily + OBT
(N = 462) | Placebo + OBT
(N = 237) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Gender | ||
| Male | 88% | 89% |
| Female | 12% | 11% |
| Race | ||
| White | 65% | 73% |
| Black | 14% | 11% |
| Asian | 3% | 3% |
| Hispanic | 11% | 8% |
| Others | 6% | 5% |
| Age (years) | ||
| Median (min, max) | 45 (16 to 74) | 45 (17 to 70) |
| CD4+ Cell Count | ||
| Median (min, max), cells/mm 3 | 119 (1 to 792) | 123 (0 to 759) |
| ≤50 cells/mm 3 | 32% | 33% |
| >50 and ≤200 cells/mm 3 | 37% | 36% |
| Plasma HIV-1 RNA | ||
| Median (min, max), log 10 copies/mL | 4.8 (2 to 6) | 4.7 (2 to 6) |
| >100,000 copies/mL | 36% | 33% |
| History of AIDS | ||
| Yes | 92% | 91% |
| Prior Use of ART, Median (1 st Quartile, 3 rd Quartile) | ||
| Years of ART Use | 10 (7 to 12) | 10 (8 to 12) |
| Number of ART | 12 (9 to 15) | 12 (9 to 14) |
| Hepatitis Co-infection * | ||
| No Hepatitis B or C virus | 83% | 84% |
| Hepatitis B virus only | 8% | 3% |
| Hepatitis C virus only | 8% | 12% |
| Co-infection of Hepatitis B and C virus | 1% | 1% |
| Stratum | ||
| Enfuvirtide in OBT | 38% | 38% |
| Resistant to ≥2 PI | 97% | 95% |
Table 21 compares the characteristics of optimized background therapy at baseline in the group receiving ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily and subjects in the control group.
| Randomized Studies
BENCHMRK 1 and BENCHMRK 2 | ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily + OBT
(N = 462) | Placebo + OBT
(N = 237) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Number of ARTs in OBT | ||
| Median (min, max) | 4 (1 to 7) | 4 (2 to 7) |
| Number of Active PI in OBT by Phenotypic Resistance Test * | ||
| 0 | 36% | 41% |
| 1 or more | 60% | 58% |
| Phenotypic Sensitivity Score (PSS) † | ||
| 0 | 15% | 18% |
| 1 | 31% | 30% |
| 2 | 31% | 28% |
| 3 or more | 18% | 20% |
| Genotypic Sensitivity Score (GSS) † | ||
| 0 | 25% | 27% |
| 1 | 38% | 40% |
| 2 | 24% | 21% |
| 3 or more | 11% | 10% |
Week 96 outcomes for the 699 subjects randomized and treated with the recommended dose of ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily or placebo in the pooled BENCHMRK 1 and 2 studies are shown in Table 22.
| ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily + OBT
(N = 462) | Placebo + OBT
(N = 237) |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Subjects with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL | 55% | 27% |
| Virologic Failure * | 35% | 66% |
| No virologic data at Week 96 Window | ||
| Reasons | ||
| Discontinued study due to AE or death † | 3% | 3% |
| Discontinued study for other reasons ‡ | 4% | 4% |
| Missing data during window but on study | 4% | <1% |
The mean changes in CD4 count from baseline were 118 cells/mm 3 in the group receiving ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily and 47 cells/mm 3 for the control group.
Treatment-emergent CDC Category C events occurred in 4% of the group receiving ISENTRESS 400 mg twice daily and 5% of the control group.
Virologic responses at Week 96 by baseline genotypic and phenotypic sensitivity score are shown in Table 23.
| Percent with HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL At Week 96 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | ISENTRESS 400 mg Twice Daily + OBT
(N = 462) | n | Placebo + OBT
(N = 237) |
|
|
||||
| Phenotypic Sensitivity Score (PSS) * | ||||
| 0 | 67 | 43 | 43 | 5 |
| 1 | 144 | 58 | 71 | 23 |
| 2 | 142 | 61 | 66 | 32 |
| 3 or more | 85 | 48 | 48 | 42 |
| Genotypic Sensitivity Score (GSS) * | ||||
| 0 | 116 | 39 | 65 | 5 |
| 1 | 177 | 62 | 95 | 26 |
| 2 | 111 | 61 | 49 | 53 |
| 3 or more | 51 | 49 | 23 | 35 |
16. How is Isentress supplied
ISENTRESS tablets 400 mg are pink, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets with "227" on one side. They are supplied as follows:
- NDC 82982-055-06 bottles of 6.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Distributed by: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC
Rahway, NJ 07065, USA
For patent information: www.msd.com/research/patent
uspi-mk0518-mf-2205r038
Repackaged by:
Pharmasource Meds, LLC
Tigard, OR 97223
| PATIENT INFORMATION | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised May 2022 | |||
| ISENTRESS
® (eye
sen tris)
(raltegravir) film-coated tablets | ISENTRESS
® (eye
sen tris)
(raltegravir) chewable tablets | |||
| ISENTRESS
® HD (eye
sen tris HD)
(raltegravir) film-coated tablets | ISENTRESS
® (eye
sen tris)
(raltegravir) for oral suspension | |||
| What are ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD? | ||||
| ISENTRESS is a prescription medicine used with other HIV-1 medicines to treat Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) infection in adults, and in children weighing at least 4.4 pounds (2 kg). HIV is the virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). | ||||
| ISENTRESS HD is a prescription medicine used with other HIV-1 medicines to treat HIV-1 infection in adults, and in children weighing at least 88 pounds (40 kg).
ISENTRESS should not be used in children who weigh less than 4.4 pounds (2 kg). |
||||
Before you take ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||||
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines interact with ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD.
|
||||
How should I take ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD?
If ISENTRESS for oral suspension is prescribed for your child, be sure to read the following information:
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD? | ||||
ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD can cause serious side effects including:
|
||||
|
|
|||
| Sometimes allergic reactions can affect body organs, such as your liver. Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following signs or symptoms of liver problems: | ||||
|
|
|||
|
||||
| The most common side effects of ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD include: | ||||
|
| |||
| Less common side effects of ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD include: | ||||
|
| |||
| Tell your doctor right away if you get unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness during treatment with ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD. These may be signs of a rare serious muscle problem that can lead to kidney problems. | ||||
| These are not all the possible side effects of ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD. | ||||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||||
| How should I store ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD? | ||||
ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD film-coated tablets:
|
||||
ISENTRESS chewable tablets:
|
||||
ISENTRESS for oral suspension:
|
||||
| Keep ISENTRESS and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD | ||||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information Leaflet. | ||||
| Do not use ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about ISENTRESS or ISENTRESS HD that is written for health professionals. | ||||
| What are the ingredients in ISENTRESS and ISENTRESS HD? | ||||
| ISENTRESS 400 mg film-coated tablets: | ||||
| Active ingredient: raltegravir | ||||
| Inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate dibasic anhydrous, hypromellose 2208, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, poloxamer 407 (contains 0.01% butylated hydroxytoluene as antioxidant), sodium stearyl fumarate. | ||||
| The film coating contains: black iron oxide, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol, red iron oxide, talc and titanium dioxide. | ||||
| ISENTRESS HD 600 mg film-coated tablets: | ||||
| Active ingredient: raltegravir | ||||
| Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose 2910, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose. | ||||
| The film coating contains: ferrosoferric oxide, hypromellose 2910, iron oxide yellow, lactose monohydrate, triacetin and titanium dioxide. | ||||
| The tablet may also contain trace amount of carnauba wax. | ||||
| ISENTRESS chewable tablets: | ||||
| Active ingredient: raltegravir | ||||
| Inactive ingredients: ammonium hydroxide, crospovidone, ethylcellulose 20 cP, fructose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose 2910/6cP, magnesium stearate, mannitol, medium chain triglycerides, monoammonium glycyrrhizinate, natural and artificial flavors (orange, banana, and masking that contains aspartame), oleic acid, PEG 400, saccharin sodium, sodium citrate dihydrate, sodium stearyl fumarate, sorbitol, sucralose and yellow iron oxide. The 100 mg chewable tablet also contains red iron oxide. | ||||
| ISENTRESS for oral suspension: | ||||
| Active ingredient: raltegravir | ||||
| Inactive ingredients: ammonium hydroxide, banana with other natural flavors, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, crospovidone, ethylcellulose 20 cP, fructose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose 2910/6cP, macrogol/PEG 400, magnesium stearate, maltodextrin, mannitol, medium chain triglycerides, microcrystalline cellulose, monoammonium glycyrrhizinate, oleic acid, sorbitol, sucralose and sucrose. | ||||
| Distributed by: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC
Rahway, NJ 07065, USA |
||||
| For patent information: www.msd.com/research/patent | ||||
| Copyright © 2007-2022 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and its affiliates. All rights reserved. | ||||
| usppi-mk0518-mf-2205r030
For more information go to www.ISENTRESS.com or call 1-800-622-4477. |
||||
Distributed by:
Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC
Rahway, NJ 07065, USA
For patent information: www.msd.com/research/patent
Copyright © 2013-2022 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and its affiliates.
All rights reserved.
ifu-mk0518-mf-2205r002
Repackaged by:
Pharmasource Meds, LLC
Tigard, OR 97223
Revised 2/2023
| ISENTRESS
raltegravir tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Pharmasource Meds, LLC (118772692) |





