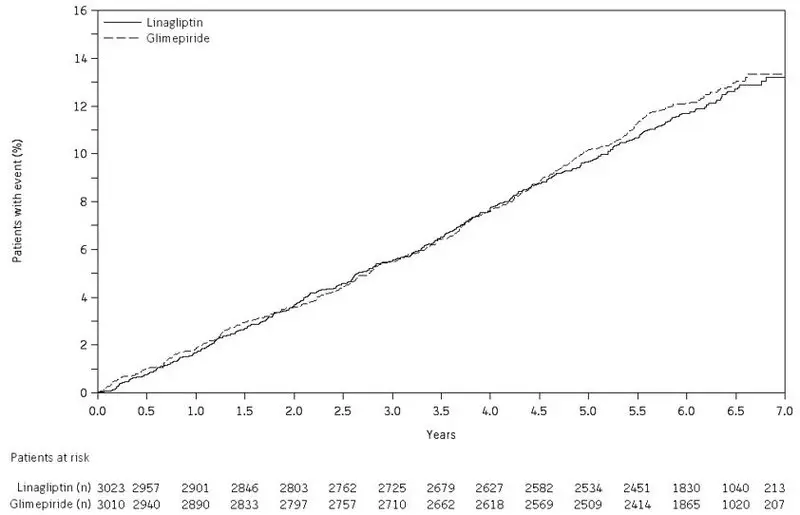
Drug Detail:Jentadueto (Linagliptin and metformin [ lin-a-glip-tin-and-met-for-min ])
Drug Class: Antidiabetic combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
JENTADUETO® (linagliptin and metformin hydrochloride tablets), for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias. Symptoms included malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, somnolence, and abdominal pain. Laboratory abnormalities included elevated blood lactate levels, anion gap acidosis, increased lactate/pyruvate ratio; and metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL. (5.1)
- Risk factors include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs, age ≥65 years old, radiological studies with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states, excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment. Steps to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis in these high risk groups are provided in the Full Prescribing Information. (5.1)
- If lactic acidosis is suspected, discontinue JENTADUETO and institute general supportive measures in a hospital setting. Prompt hemodialysis is recommended. (5.1)
Indications and Usage for Jentadueto
JENTADUETO is a combination of linagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and metformin hydrochloride (HCl), a biguanide, indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (1)
Limitations of Use
- Not recommended in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (1)
- Has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis (1)
Jentadueto Dosage and Administration
- Individualize the starting dosage of JENTADUETO based on the patient's current regimen (2.1)
- The maximum recommended dosage is 2.5 mg linagliptin/1,000 mg metformin HCl twice daily (2.1)
- Take orally twice daily with meals, with gradual dosage escalation to reduce the gastrointestinal effects due to metformin (2.1)
- Prior to initiation, assess renal function with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (2.2)
- Do not use in patients with eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Initiation is not recommended in patients with eGFR between 30 - 45 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Assess risk/benefit of continuing if eGFR falls below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Discontinue if eGFR falls below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2
- JENTADUETO may need to be discontinued at time of, or prior to, iodinated contrast imaging procedures (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets:
2.5 mg linagliptin/500 mg metformin HCl (3)
2.5 mg linagliptin/850 mg metformin HCl (3)
2.5 mg linagliptin/1,000 mg metformin HCl (3)
Contraindications
- Severe renal impairment (eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) (4)
- Metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis (4)
- Hypersensitivity to linagliptin, metformin, or any of the excipients in JENTADUETO (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Lactic acidosis: See boxed warning (5.1)
- Pancreatitis: There have been reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue JENTADUETO. (5.2)
- Hypoglycemia: Consider lowering the dosage of insulin secretagogue or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when initiating JENTADUETO (5.3)
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions) have occurred with JENTADUETO. If hypersensitivity reactions occur discontinue JENTADUETO, treat promptly, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. (5.4)
- Vitamin B12 deficiency: Metformin may lower vitamin B12 levels. Measure hematologic parameters annually and vitamin B12 at 2 to 3 year intervals and manage any abnormalities. (5.5)
- Arthralgia: Severe and disabling arthralgia has been reported in patients taking linagliptin. Consider as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate. (5.6)
- Bullous pemphigoid: There have been reports of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, discontinue JENTADUETO. (5.7)
- Heart failure: Heart failure has been observed with two other members of the DPP-4 inhibitor class. Consider risks and benefits of JENTADUETO in patients who have known risk factors for heart failure. Monitor for signs and symptoms. (5.8)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and more often than placebo) were nasopharyngitis and diarrhea (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors: May increase risk of lactic acidosis. Consider more frequent monitoring. (7)
- Drugs that Reduce Metformin Clearance: May increase risk of lactic acidosis. Consider benefits and risks of concomitant use. (7)
- Alcohol: Can potentiate the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake. (7)
- Strong P-glycoprotein/CYP3A4 Inducer: Efficacy may be reduced when administered in combination (e.g., rifampin). Use of alternative treatments is strongly recommended. (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Advise premenopausal females of the potential for an unintended pregnancy (8.3)
- Geriatric Use: Assess renal function more frequently (8.5)
- Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use in patients with hepatic impairment (8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 6/2023
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS
Postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias. The onset of metformin-associated lactic acidosis is often subtle, accompanied only by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, somnolence, and abdominal pain. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate levels (>5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), an increased lactate/pyruvate ratio; and metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs (e.g., carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as topiramate), age 65 years old or greater, having a radiological study with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states (e.g., acute congestive heart failure), excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment.
Steps to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis in these high risk groups are provided in the full prescribing information [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7), and Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7)].
If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, immediately discontinue JENTADUETO and institute general supportive measures in a hospital setting. Prompt hemodialysis is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Jentadueto
JENTADUETO is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
2. Jentadueto Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage and Administration
The dosage of JENTADUETO should be individualized on the basis of both effectiveness and tolerability, while not exceeding the maximum recommended dosage of 2.5 mg linagliptin/1,000 mg metformin hydrochloride (HCl), taken orally twice daily. JENTADUETO should be given twice daily with meals. Dosage escalation should be gradual to reduce the gastrointestinal (GI) side effects associated with metformin use.
Recommended starting dosage:
- In patients currently not treated with metformin HCl, initiate treatment with 2.5 mg linagliptin/500 mg metformin HCl twice daily.
- In patients already treated with metformin HCl, start with 2.5 mg linagliptin and the current dosage of metformin HCl taken at each of the two daily meals (e.g., a patient on metformin HCl 1,000 mg twice daily would be started on 2.5 mg linagliptin/1,000 mg metformin HCl twice daily with meals).
- Patients already treated with linagliptin and metformin HCl individual components may be switched to JENTADUETO containing the same dosages of each component.
2.2 Recommended Dosing in Renal Impairment
Assess renal function prior to initiation of JENTADUETO and periodically thereafter.
JENTADUETO is contraindicated in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Initiation of JENTADUETO in patients with an eGFR between 30-45 mL/min/1.73 m2 is not recommended.
In patients taking JENTADUETO whose eGFR later falls below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2, assess benefit/risk of continuing therapy.
Discontinue JENTADUETO if the patient's eGFR later falls below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.3 Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
Discontinue JENTADUETO at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m2; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure; restart JENTADUETO if renal function is stable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
JENTADUETO tablets are a combination of linagliptin and metformin HCl available as:
- 2.5 mg linagliptin/500 mg metformin HCl tablets are light yellow, oval, biconvex tablets debossed with "D2/500" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim symbol on the other side
- 2.5 mg linagliptin/850 mg metformin HCl tablets are light orange, oval, biconvex tablets debossed with "D2/850" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim symbol on the other side
- 2.5 mg linagliptin/1,000 mg metformin HCl tablets are light pink, oval, biconvex tablets debossed with "D2/1000" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim symbol on the other side
4. Contraindications
JENTADUETO is contraindicated in patients with:
- severe renal impairment (eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- hypersensitivity to linagliptin, metformin, or any of the excipients in JENTADUETO, reactions such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, exfoliative skin conditions, urticaria, or bronchial hyperreactivity have occurred with linagliptin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Lactic Acidosis
5.2 Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, has been reported in patients treated with linagliptin. In the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2)], acute pancreatitis was reported in 9 (0.3%) patients treated with linagliptin and in 5 (0.1%) patients treated with placebo. Two patients treated with linagliptin in the CARMELINA trial had acute pancreatitis with a fatal outcome. There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, in patients treated with linagliptin.
Take careful notice of potential signs and symptoms of pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue JENTADUETO and initiate appropriate management. It is unknown whether patients with a history of pancreatitis are at increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using JENTADUETO.
5.3 Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin and Insulin Secretagogues
Insulin secretagogues and insulin are known to cause hypoglycemia. The risk of hypoglycemia is increased when JENTADUETO is used in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Therefore, a lower dosage of the insulin secretagogue or insulin may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with JENTADUETO.
5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with linagliptin. These reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions. Onset of these reactions occurred predominantly within the first 3 months after initiation of treatment with linagliptin, with some reports occurring after the first dose. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction is suspected, discontinue JENTADUETO, assess for other potential causes for the event, and institute alternative treatment for diabetes mellitus.
Angioedema has also been reported with other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Use caution in a patient with a history of angioedema to another DPP-4 inhibitor because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to angioedema with JENTADUETO.
5.5 Vitamin B12 Deficiency
In metformin clinical trials of 29-week duration, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum vitamin B12 levels was observed in approximately 7% of metformin-treated patients. Such decrease, possibly due to interference with B12 absorption from the B12-intrinsic factor complex, may be associated with anemia but appears to be rapidly reversible with discontinuation of metformin or vitamin B12 supplementation. Certain individuals (those with inadequate vitamin B12 or calcium intake or absorption) appear to be predisposed to developing subnormal vitamin B12 levels. Measure hematologic parameters on an annual basis and vitamin B12 at 2 to 3 year intervals in patients on JENTADUETO and manage any abnormalities [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.6 Severe and Disabling Arthralgia
There have been postmarketing reports of severe and disabling arthralgia in patients taking linagliptin. The time to onset of symptoms following initiation of drug therapy varied from one day to years. Patients experienced relief of symptoms upon discontinuation of the medication. A subset of patients experienced a recurrence of symptoms when restarting the same drug or a different DPP-4 inhibitor. Consider DPP-4 inhibitors as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate.
5.7 Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid was reported in 7 (0.2%) patients treated with linagliptin compared to none in patients treated with placebo in the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2)], and 3 of these patients were hospitalized due to bullous pemphigoid. Postmarketing cases of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization have been reported with DPP-4 inhibitor use. In reported cases, patients typically recovered with topical or systemic immunosuppressive treatment and discontinuation of the DPP-4 inhibitor. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions while receiving JENTADUETO. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, JENTADUETO should be discontinued and referral to a dermatologist should be considered for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
5.8 Heart Failure
An association between DPP-4 inhibitor treatment and heart failure has been observed in cardiovascular outcomes trials for two other members of the DPP-4 inhibitor class. These trials evaluated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Consider the risks and benefits of JENTADUETO prior to initiating treatment in patients at risk for heart failure, such as those with a prior history of heart failure and a history of renal impairment, and observe these patients for signs and symptoms of heart failure during therapy. Advise patients of the characteristic symptoms of heart failure and to immediately report such symptoms. If heart failure develops, evaluate and manage according to current standards of care and consider discontinuation of JENTADUETO.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described below or elsewhere in the prescribing information:
- Lactic Acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin and Insulin Secretagogues [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Severe and Disabling Arthralgia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Bullous Pemphigoid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7. Drug Interactions
Table 2 describes clinically relevant interactions with JENTADUETO.
| Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact | Topiramate or other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., zonisamide, acetazolamide or dichlorphenamide) frequently cause a decrease in serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Concomitant use of these drugs with JENTADUETO may increase the risk of lactic acidosis. |
| Intervention | Consider more frequent monitoring of these patients. |
| Drugs that Reduce Metformin Clearance | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of drugs that interfere with common renal tubular transport systems involved in the renal elimination of metformin (e.g., organic cationic transporter-2 [OCT2] / multidrug and toxin extrusion [MATE] inhibitors such as ranolazine, vandetanib, dolutegravir, and cimetidine) could increase systemic exposure to metformin and may increase the risk for lactic acidosis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | Consider the benefits and risks of concomitant use. |
| Alcohol | |
| Clinical Impact | Alcohol is known to potentiate the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism. |
| Intervention | Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving JENTADUETO. |
| Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues | |
| Clinical Impact | The risk of hypoglycemia is increased when JENTADUETO is used in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin. |
| Intervention | Coadministration of JENTADUETO with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin may require lower dosages of the insulin secretagogue or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. |
| Drugs Affecting Glycemic Control | |
| Clinical Impact | Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia and may lead to loss of glycemic control. These drugs include the thiazides and other diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products, estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, calcium channel blocking drugs, and isoniazid. |
| Intervention | When such drugs are administered to a patient receiving JENTADUETO, the patient should be closely observed to maintain adequate glycemic control. When such drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving JENTADUETO, the patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia. |
| Inducers of P-glycoprotein or CYP3A4 Enzymes | |
| Clinical Impact | Rifampin decreased linagliptin exposure, suggesting that the efficacy of linagliptin may be reduced when administered in combination with a strong P-gp or CYP3A4 inducer. |
| Intervention | Use of alternative treatments is strongly recommended when linagliptin is to be administered with a strong P-gp or CYP3A4 inducer. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Data
Published clinical lactation studies report that metformin is present in human milk which resulted in infant doses approximately 0.11% to 1% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage and a milk/plasma ratio ranging between 0.13 and 1. However, the studies were not designed to definitely establish the risk of use of metformin during lactation because of small sample size and limited adverse event data collected in infants.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discuss the potential for unintended pregnancy with premenopausal women as therapy with metformin may result in ovulation in some anovulatory women.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of JENTADUETO have not been established in pediatric patients.
Effectiveness of linagliptin was not demonstrated in a 26-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT03429543) in 157 pediatric patients aged 10 to 17 years with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Linagliptin is minimally excreted by the kidney; however, metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of metformin accumulation and lactic acidosis increases with the degree of renal impairment.
JENTADUETO is contraindicated in severe renal impairment, patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
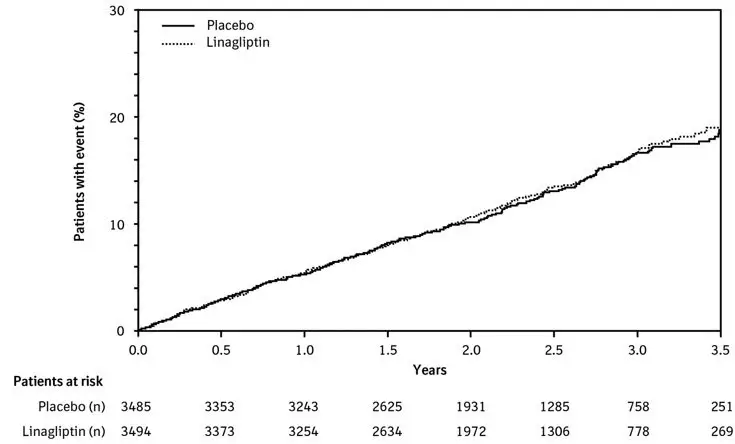
In the linagliptin treatment arm of the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2)], 2,200 (63%) patients had renal impairment (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2). Approximately 20% of the population had eGFR ≥45 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, 28% of the population had eGFR ≥30 to <45 mL/min/1.73 m2 and 15% had eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2. The overall incidence of adverse reactions were generally similar between the linagliptin and placebo treatment arms.
10. Overdosage
In the event of an overdose with JENTADUETO, consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations.
Overdose of metformin HCl has occurred, including ingestion of amounts greater than 50 grams. Lactic acidosis has been reported in approximately 32% of metformin overdose cases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Metformin is dialyzable with a clearance of up to 170 mL/min under good hemodynamic conditions. Therefore, hemodialysis may be useful for removal of accumulated drug from patients in whom metformin overdosage is suspected.
Removal of linagliptin by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is unlikely.
12. Jentadueto - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Specific Populations
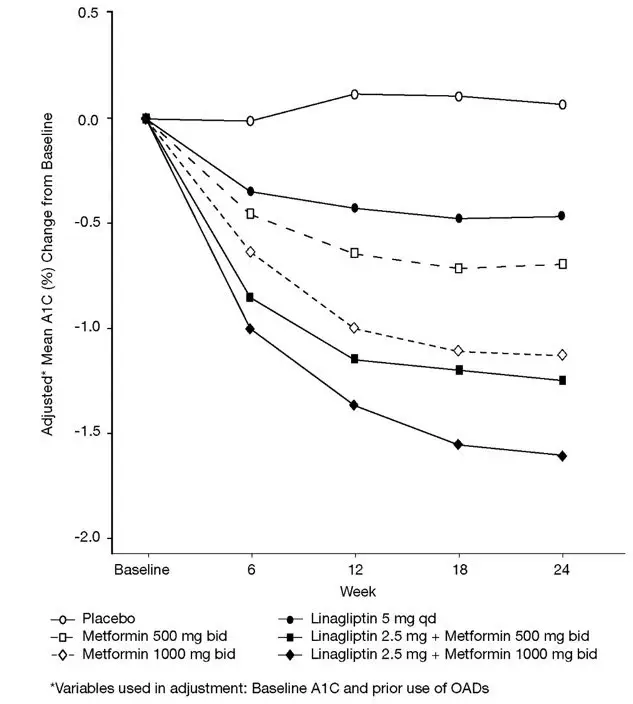
14. Clinical Studies
16. How is Jentadueto supplied
JENTADUETO (linagliptin and metformin HCl) tablets 2.5 mg/500 mg are light yellow, oval, biconvex tablets debossed with "D2/500" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim symbol on the other side, and are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 60 (NDC 0597-0146-60)
Bottles of 180 (NDC 0597-0146-18)
JENTADUETO (linagliptin and metformin HCl) tablets 2.5 mg/850 mg are light orange, oval, biconvex tablets debossed with "D2/850" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim symbol on the other side, and are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 60 (NDC 0597-0147-60)
Bottles of 180 (NDC 0597-0147-18)
JENTADUETO (linagliptin and metformin HCl) tablets 2.5 mg/1,000 mg are light pink, oval, biconvex tablets debossed with "D2/1000" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim symbol on the other side, and are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 60 (NDC 0597-0148-60)
Bottles of 180 (NDC 0597-0148-18)
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)
| MEDICATION GUIDE JENTADUETO® (JEN ta doo e toe) (linagliptin and metformin hydrochloride tablets) for oral use |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: June 2023 | ||||
|
What is the most important information I should know about JENTADUETO? |
|||||
JENTADUETO can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
|
||||
You have a higher chance of getting lactic acidosis with JENTADUETO if you:
|
|||||
| Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the problems in the list above. Tell your healthcare provider that you are taking JENTADUETO before you have surgery or x-ray tests. Your healthcare provider may decide to stop your JENTADUETO for a while if you have surgery or certain x-ray tests. JENTADUETO can have other serious side effects. See "What are the possible side effects of JENTADUETO?" | |||||
|
|||||
| Before you start taking JENTADUETO, tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had: | |||||
|
|
||||
| Stop taking JENTADUETO and call your healthcare provider right away if you have pain in your stomach area (abdomen) that is severe and will not go away. The pain may be felt going from your abdomen to your back. The pain may happen with or without vomiting. These may be symptoms of pancreatitis. | |||||
What is JENTADUETO?
|
|||||
Do not take JENTADUETO if you:
|
|||||
| What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking JENTADUETO? | |||||
Before taking JENTADUETO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
|||||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. JENTADUETO may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how JENTADUETO works. | |||||
| Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | |||||
How should I take JENTADUETO?
|
|||||
| What should I avoid while taking JENTADUETO?
Avoid drinking alcohol very often or drinking a lot of alcohol in a short period of time ("binge" drinking). It can increase your chances of getting serious side effects. |
|||||
JENTADUETO may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
||||
| If you have any of these symptoms, stop taking JENTADUETO and call your healthcare provider right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room. | |||||
|
|||||
The most common side effects of JENTADUETO include:
|
|||||
| These are not all the possible side effects of JENTADUETO. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. | |||||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |||||
How should I store JENTADUETO?
|
|||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of JENTADUETO. | |||||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use JENTADUETO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give JENTADUETO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. | |||||
| You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about JENTADUETO that is written for health professionals. | |||||
| What are the ingredients in JENTADUETO? | |||||
| Active Ingredients: linagliptin and metformin HCl | |||||
| Inactive Ingredients: arginine, colloidal silicon dioxide, copovidone, corn starch, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, propylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide | |||||
| 2.5 mg/500 mg and 2.5 mg/850 mg tablets also contain yellow ferric oxide. | |||||
| 2.5 mg/850 mg and 2.5 mg/1,000 mg tablets also contain red ferric oxide. | |||||
| Distributed by: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA. Licensed from: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Ingelheim, Germany. JENTADUETO is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. either owns or uses the Tradjenta®, CARMELINA®, and CAROLINA® trademarks under license. The other brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Copyright © 2023 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH ALL RIGHTS RESERVED |
|||||
| COL9414DF212023 | |||||
| For more information about JENTADUETO, including current prescribing information and Medication Guide, go to www.JENTADUETO.com, scan the code, or call Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| JENTADUETO
linagliptin and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| JENTADUETO
linagliptin and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| JENTADUETO
linagliptin and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Registrant - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH and Co. KG | 551147440 | MANUFACTURE(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) , API MANUFACTURE(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) , PACK(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) , LABEL(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| West-Ward Columbus Inc. | 058839929 | PACK(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) , LABEL(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Promeco, S.A. de C.V. | 812579472 | PACK(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) , LABEL(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) , MANUFACTURE(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| VISTIN Pharma AS | 671330697 | API MANUFACTURE(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sixarp, LLC | 016329513 | PACK(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) , LABEL(0597-0146, 0597-0147, 0597-0148) | |