Drug Detail:Kanjinti (Trastuzumab [ tras-too-zoo-mab ])
Drug Class:
Highlights of Prescribing Information
KANJINTI® (trastuzumab-anns) for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019
KANJINTI (trastuzumab-anns) is biosimilar* to HERCEPTIN® (trastuzumab)
WARNING: CARDIOMYOPATHY, INFUSION REACTIONS, EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY, and PULMONARY TOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
Cardiomyopathy: Trastuzumab products can result in subclinical and clinical cardiac failure manifesting as CHF, and decreased LVEF, with greatest risk when administered concurrently with anthracyclines. Evaluate cardiac function prior to and during treatment. Discontinue KANJINTI for cardiomyopathy. (2.3, 5.1)
Infusion Reactions, Pulmonary Toxicity: Discontinue KANJINTI for anaphylaxis, angioedema, interstitial pneumonitis, or acute respiratory distress syndrome. (5.2, 5.4)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Exposure to trastuzumab products during pregnancy can result in oligohydramnios, in some cases complicated by pulmonary hypoplasia and neonatal death. Advise patients of these risks and the need for effective contraception. (5.3, 8.1, 8.3)
Indications and Usage for Kanjinti Injection
KANJINTI is a HER2/neu receptor antagonist indicated for:
- the treatment of HER2 overexpressing breast cancer. (1.1, 1.2)
- the treatment of HER2 overexpressing metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. (1.3)
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved companion diagnostic for a trastuzumab product (1, 2.1).
Kanjinti Injection Dosage and Administration
For intravenous (IV) infusion only. Do not administer as an IV push or bolus. (2.2)
Do not substitute KANJINTI (trastuzumab-anns) for or with ado-trastuzumab emtansine. (2.2)
Perform HER2 testing using FDA-approved tests by laboratories with demonstrated proficiency. (1, 2.1)
Adjuvant Treatment of HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer (2.2)
Administer at either:
- Initial dose of 4 mg/kg over 90 minute IV infusion, then 2 mg/kg over 30 minute IV infusion weekly for 12 weeks (with paclitaxel or docetaxel) or 18 weeks (with docetaxel and carboplatin). One week after the last weekly dose of KANJINTI, administer 6 mg/kg as an IV infusion over 30−90 minutes every three weeks to complete a total of 52 weeks of therapy, or
- Initial dose of 8 mg/kg over 90 minutes IV infusion, then 6 mg/kg over 30–90 minutes IV infusion every three weeks for 52 weeks.
Metastatic HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer (2.2)
- Initial dose of 4 mg/kg as a 90-minute IV infusion followed by subsequent weekly doses of 2 mg/kg as 30 minute IV infusions.
Metastatic HER2-Overexpressing Gastric Cancer (2.2)
- Initial dose of 8 mg/kg over 90 minutes IV infusion, followed by 6 mg/kg over 30 to 90 minutes IV infusion every 3 weeks.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- For Injection: 150 mg lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution
- For Injection: 420 mg lyophilized powder in a multiple-dose vial for reconstitution
Contraindications
- None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Exacerbation of Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia. (5.5, 6.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Adjuvant Breast Cancer
- Most common adverse reactions (≥ 5%) are headache, diarrhea, nausea, and chills. (6.1)
Metastatic Breast Cancer
- Most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) are fever, chills, headache, infection, congestive heart failure, insomnia, cough, and rash. (6.1)
Metastatic Gastric Cancer
- Most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) are neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, anemia, stomatitis, weight loss, upper respiratory tract infections, fever, thrombocytopenia, mucosal inflammation, nasopharyngitis, and dysgeusia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amgen Medical Information at 1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Verify the pregnancy status of females prior to initiation of KANJINTI (8.3).
*Biosimilar means that the biological product is approved based on data demonstrating that it is highly similar to an FDA-approved biological product, known as a reference product, and that there are no clinically meaningful differences between the biosimilar product and the reference product. Biosimilarity of KANJINTI has been demonstrated for the condition(s) of use (e.g. indication(s), dosing regimen(s)), strength(s), dosage form(s), and route(s) of administration described in its Full Prescribing Information.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2022
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: CARDIOMYOPATHY, INFUSION REACTIONS, EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY, and PULMONARY TOXICITY
Cardiomyopathy
Trastuzumab products administration can result in sub-clinical and clinical cardiac failure. The incidence and severity was highest in patients receiving trastuzumab with anthracycline-containing chemotherapy regimens.
Evaluate left ventricular function in all patients prior to and during treatment with KANJINTI. Discontinue KANJINTI treatment in patients receiving adjuvant therapy and withhold KANJINTI in patients with metastatic disease for clinically significant decrease in left ventricular function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Infusion Reactions; Pulmonary Toxicity
Trastuzumab products administration can result in serious and fatal infusion reactions and pulmonary toxicity. Symptoms usually occur during or within 24 hours of administration. Interrupt KANJINTI infusion for dyspnea or clinically significant hypotension. Monitor patients until symptoms completely resolve. Discontinue KANJINTI for anaphylaxis, angioedema, interstitial pneumonitis, or acute respiratory distress syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Exposure to trastuzumab products during pregnancy can result in oligohydramnios and oligohydramnios sequence manifesting as pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities, and neonatal death. Advise patients of these risks and the need for effective contraception
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
1. Indications and Usage for Kanjinti Injection
1.1 Adjuvant Breast Cancer
KANJINTI is indicated for adjuvant treatment of HER2 overexpressing node positive or node negative (ER/PR negative or with one high risk feature [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]) breast cancer
- as part of a treatment regimen consisting of doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and either paclitaxel or docetaxel
- as part of a treatment regimen with docetaxel and carboplatin
- as a single agent following multi-modality anthracycline-based therapy.
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved companion diagnostic for a trastuzumab product [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
1.2 Metastatic Breast Cancer
KANJINTI is indicated:
- In combination with paclitaxel for first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer
- As a single agent for treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer in patients who have received one or more chemotherapy regimens for metastatic disease.
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved companion diagnostic for a trastuzumab product [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]
1.3 Metastatic Gastric Cancer
KANJINTI is indicated, in combination with cisplatin and capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil, for the treatment of patients with HER2 overexpressing metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma who have not received prior treatment for metastatic disease.
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved companion diagnostic for a trastuzumab product [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
2. Kanjinti Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients based on HER2 protein overexpression or HER2 gene amplification in tumor specimens [see Indications and Usage (1) and Clinical Studies (14)]. Assessment of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification should be performed using FDA-approved tests specific for breast or gastric cancers by laboratories with demonstrated proficiency. Information on the FDA-approved tests for the detection of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Assessment of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification in metastatic gastric cancer should be performed using FDA-approved tests specifically for gastric cancers due to differences in gastric vs. breast histopathology, including incomplete membrane staining and more frequent heterogeneous expression of HER2 seen in gastric cancers.
Improper assay performance, including use of suboptimally fixed tissue, failure to utilize specified reagents, deviation from specific assay instructions, and failure to include appropriate controls for assay validation, can lead to unreliable results.
2.2 Recommended Doses and Schedules
-
Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus. Do not mix KANJINTI with other drugs.
- Do not substitute KANJINTI (trastuzumab-anns) for or with ado-trastuzumab emtansine.
Adjuvant Treatment, Breast Cancer:
Administer according to one of the following doses and schedules for a total of 52 weeks of KANJINTI therapy:
During and following paclitaxel, docetaxel, or docetaxel and carboplatin:
- Initial dose of 4 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 90 minutes then at 2 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes weekly during chemotherapy for the first 12 weeks (paclitaxel or docetaxel) or 18 weeks (docetaxel and carboplatin).
- One week following the last weekly dose of KANJINTI, administer KANJINTI at 6 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 30–90 minutes every three weeks.
As a single agent within three weeks following completion of multi-modality, anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens:
- Initial dose at 8 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 90 minutes.
- Subsequent doses at 6 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 30-90 minutes every three weeks [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Extending adjuvant treatment beyond one year is not recommended [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Metastatic Treatment, Breast Cancer:
- Administer KANJINTI, alone or in combination with paclitaxel, at an initial dose of 4 mg/kg as a 90-minute intravenous infusion followed by subsequent once weekly doses of 2 mg/kg as 30-minute intravenous infusions until disease progression.
Metastatic Gastric Cancer:
- Administer KANJINTI at an initial dose of 8 mg/kg as a 90-minute intravenous infusion followed by subsequent doses of 6 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 30–90 minutes every three weeks until disease progression [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
2.3 Important Dosing Considerations
If the patient has missed a dose of KANJINTI by one week or less, then the usual maintenance dose (weekly schedule: 2 mg/kg; three-weekly schedule: 6 mg/kg) should be administered as soon as possible. Do not wait until the next planned cycle. Subsequent KANJINTI maintenance doses should be administered 7 days or 21 days later according to the weekly or three-weekly schedules, respectively.
If the patient has missed a dose of KANJINTI by more than one week, a re-loading dose of KANJINTI should be administered over approximately 90 minutes (weekly schedule: 4 mg/kg; three-weekly schedule: 8 mg/kg) as soon as possible. Subsequent KANJINTI maintenance doses (weekly schedule: 2 mg/kg; three-weekly schedule 6 mg/kg) should be administered 7 days or 21 days later according to the weekly or three-weekly schedules, respectively.
Infusion Reactions
[see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Decrease the rate of infusion for mild or moderate infusion reactions
- Interrupt the infusion in patients with dyspnea or clinically significant hypotension
- Discontinue KANJINTI for severe or life-threatening infusion reactions.
Cardiomyopathy
[see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) prior to initiation of KANJINTI and at regular intervals during treatment. Withhold KANJINTI dosing for at least 4 weeks for either of the following:
- ≥ 16% absolute decrease in LVEF from pre-treatment values
- LVEF below institutional limits of normal and ≥ 10% absolute decrease in LVEF from pre-treatment values.
KANJINTI may be resumed if, within 4–8 weeks, the LVEF returns to normal limits and the absolute decrease from baseline is ≤ 15%.
Permanently discontinue KANJINTI for a persistent (> 8 weeks) LVEF decline or for suspension of KANJINTI dosing on more than 3 occasions for cardiomyopathy.
2.4 Preparation for Administration
To prevent medication errors, it is important to check the vial labels to ensure that the drug being prepared and administered is KANJINTI (trastuzumab-anns) and not ado-trastuzumab emtansine.
420 mg Multiple-dose vial
Reconstitution
Reconstitute each 420 mg vial of KANJINTI with 20 mL of Bacteriostatic Water for Injection (BWFI), USP, containing 0.9% to 1.1% benzyl alcohol as a preservative to yield a multiple-dose solution containing 21 mg/mL trastuzumab-anns that delivers 20 mL (420 mg trastuzumab-anns). In patients with known hypersensitivity to benzyl alcohol, reconstitute with 20 mL of Sterile Water for Injection (SWFI) without preservative to yield a single use solution.
Use appropriate aseptic technique when performing the following reconstitution steps:
- Using a sterile syringe, slowly inject the 20 mL of diluent into the vial containing the lyophilized powder of KANJINTI, which has a cake-like appearance. The stream of diluent should be directed into the cake. The reconstituted vial yields a solution for multiple-dose use, containing 21 mg/mL trastuzumab-anns.
- Swirl the vial gently to aid reconstitution. DO NOT SHAKE.
- Slight foaming of the product may be present upon reconstitution. Allow the vial to stand undisturbed for approximately 5 minutes.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Inspect visually for particulates and discoloration. The solution should be free of visible particulates, clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow.
- Store reconstituted KANJINTI in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F); discard unused KANJINTI after 28 days. If KANJINTI is reconstituted with SWFI without preservative, use immediately and discard any unused portion. Do not freeze.
Dilution
- Determine the dose (mg) of KANJINTI [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Calculate the volume of the 21 mg/mL reconstituted KANJINTI solution needed, withdraw this amount from the vial and add it to an infusion bag containing 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
DO NOT USE DEXTROSE (5%) SOLUTION.
- Gently invert the bag to mix the solution.
- The solution of KANJINTI for infusion diluted in polyvinylchloride or polyethylene bags containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, should be stored at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours prior to use. Do not freeze.
150 mg Single-dose vial
Reconstitution
Reconstitute each 150 mg vial of KANJINTI with 7.4 mL of Sterile Water for Injection (SWFI) (not supplied) to yield a single-dose solution containing 21 mg/mL trastuzumab-anns that delivers 7.15 mL (150 mg trastuzumab-anns).
Use appropriate aseptic technique when performing the following reconstitution steps:
• Using a sterile syringe, slowly inject 7.4 mL of SWFI (not supplied) into the vial containing the lyophilized powder of KANJINTI, which has a cake-like appearance. The stream of diluent should be directed into the cake. The reconstituted vial yields a solution for single-dose use, containing 21 mg/mL trastuzumab-anns.
• Swirl the vial gently to aid reconstitution. DO NOT SHAKE.
• Slight foaming of the product may be present upon reconstitution. Allow the vial to stand undisturbed for approximately 5 minutes.
• Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Inspect visually for particulates and discoloration. The solution should be free of visible particulates, clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow.
• Use the KANJINTI solution immediately following reconstitution with SWFI, as it contains no preservatives and is intended for single-dose only. If not used immediately, store the reconstituted KANJINTI solution for up to 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F); discard any unused KANJINTI after 24 hours. Do not freeze.
Dilution
• Determine the dose (mg) of KANJINTI [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
• Calculate the volume of the 21 mg/mL reconstituted KANJINTI solution needed.
• Withdraw this amount from the vial and add it to an infusion bag containing 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
DO NOT USE DEXTROSE 5% SOLUTION.
• Gently invert the bag to mix the solution.
• The solution of KANJINTI for infusion diluted in polyvinylchloride or polyethylene bags containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, should be stored at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours prior to use. Discard after 24 hours. This storage time is additional to the time allowed for the reconstituted vials. Do not freeze.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiomyopathy
Trastuzumab products can cause left ventricular cardiac dysfunction, arrhythmias, hypertension, disabling cardiac failure, cardiomyopathy, and cardiac death [see Boxed Warning: Cardiomyopathy]. Trastuzumab products can also cause asymptomatic decline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF).
There is a 4–6 fold increase in the incidence of symptomatic myocardial dysfunction among patients receiving trastuzumab products as a single agent or in combination therapy compared with those not receiving trastuzumab products. The highest absolute incidence occurs when trastuzumab product is administered with an anthracycline.
Withhold KANJINTI for ≥ 16% absolute decrease in LVEF from pre-treatment values or an LVEF value below institutional limits of normal and ≥ 10% absolute decrease in LVEF from pre-treatment values [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. The safety of continuation or resumption of KANJINTI in patients with trastuzumab product-induced left ventricular cardiac dysfunction has not been studied.
Patients who receive anthracycline after stopping KANJINTI may also be at increased risk of cardiac dysfunction [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Cardiac Monitoring
Conduct thorough cardiac assessment, including history, physical examination, and determination of LVEF by echocardiogram or MUGA scan. The following schedule is recommended:
- Baseline LVEF measurement immediately prior to initiation of KANJINTI
- LVEF measurements every 3 months during and upon completion of KANJINTI
- Repeat LVEF measurement at 4 week intervals if KANJINTI is withheld for significant left ventricular cardiac dysfunction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]
- LVEF measurements every 6 months for at least 2 years following completion of KANJINTI as a component of adjuvant therapy.
In Study 1, 15% (158/1031) of patients discontinued trastuzumab due to clinical evidence of myocardial dysfunction or significant decline in LVEF after a median follow-up duration of 8.7 years in the AC-TH (anthracycline, cyclophosphamide, paclitaxel, and trastuzumab) arm. In Study 3 (one-year trastuzumab treatment), the number of patients who discontinued trastuzumab due to cardiac toxicity at 12.6 months median duration of follow-up was 2.6% (44/1678).In Study 4, a total of 2.9% (31/1056) of patients in the TCH (docetaxel, carboplatin, trastuzumab) arm (1.5% during the chemotherapy phase and 1.4% during the monotherapy phase) and 5.7% (61/1068) of patients in the AC-TH arm (1.5% during the chemotherapy phase and 4.2% during the monotherapy phase) discontinued trastuzumab due to cardiac toxicity.
Among 64 patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy (Studies 1 and 2) who developed congestive heart failure, one patient died of cardiomyopathy, one patient died suddenly without documented etiology and 33 patients were receiving cardiac medication at last follow-up. Approximately 24% of the surviving patients had recovery to a normal LVEF (defined as ≥ 50%) and no symptoms on continuing medical management at the time of last follow-up. Incidence of congestive heart failure (CHF) is presented in Table 1. The safety of continuation or resumption of KANJINTI in patients with trastuzumab product-induced left ventricular cardiac dysfunction has not been studied.
| Table 1
|
||||
| Incidence of Congestive Heart Failure in Adjuvant Breast Cancer Studies |
||||
| Study | Regimen | Incidence of CHF | ||
| Trastuzumab | Control | |||
| 1 & 2a | ACb→Paclitaxel+Trastuzumab | 3.2% (64/2000)c | 1.3% (21/1655) | |
| 3d | Chemo → Trastuzumab | 2% (30/1678) | 0.3% (5/1708) | |
| 4 | ACb→Docetaxel+Trastuzumab | 2% (20/1068) | 0.3% (3/1050) | |
| 4 | Docetaxel+Carbo+Trastuzumab | 0.4% (4/1056) | 0.3% (3/1050) | |
| a Median follow-up duration for Studies 1 and 2 combined was 8.3 years in the AC→TH arm. b Anthracycline (doxorubicin) and cyclophosphamide. c Includes 1 patient with fatal cardiomyopathy and 1 patient with sudden death without documented etiology. d Includes NYHA II-IV and cardiac death at 12.6 months median duration of follow-up in the one-year trastuzumab arm. |
||||
In Study 3 (one-year trastuzumab treatment), at a median follow-up duration of 8 years, the incidence of severe CHF (NYHA III & IV) was 0.8%, and the rate of mild symptomatic and asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction was 4.6%.
| Table 2 | |||||
| Incidence of Cardiac Dysfunctiona in Metastatic Breast Cancer Studies | |||||
| Incidence | |||||
| NYHA I-IV | NYHA III-IV | ||||
| Study | Event | Trastuzumab | Control | Trastuzumab | Control |
| 5 (AC)b | Cardiac Dysfunction | 28% | 7% | 19% | 3% |
| 5 (paclitaxel) | Cardiac Dysfunction | 11% | 1% | 4% | 1% |
| 6 | Cardiac Dysfunctionc | 7% | N/A | 5% | N/A |
| a Congestive heart failure or significant asymptomatic decrease in LVEF. b Anthracycline (doxorubicin or epirubicin) and cyclophosphamide. c Includes 1 patient with fatal cardiomyopathy. |
|||||
In Study 4, the incidence of NCI-CTC Grade 3/4 cardiac ischemia/infarction was higher in the trastuzumab-containing regimens (AC-TH: 0.3% (3/1068) and TCH: 0.2% (2/1056)) as compared to none in AC-T.
5.2 Infusion Reactions
Infusion reactions consist of a symptom complex characterized by fever and chills, and on occasion included nausea, vomiting, pain (in some cases at tumor sites), headache, dizziness, dyspnea, hypotension, rash, and asthenia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In post-marketing reports, serious and fatal infusion reactions have been reported. Severe reactions, which include bronchospasm, anaphylaxis, angioedema, hypoxia, and severe hypotension, were usually reported during or immediately following the initial infusion. However, the onset and clinical course were variable, including progressive worsening, initial improvement followed by clinical deterioration, or delayed post-infusion events with rapid clinical deterioration. For fatal events, death occurred within hours to days following a serious infusion reaction.
Interrupt KANJINTI infusion in all patients experiencing dyspnea, clinically significant hypotension, and intervention of medical therapy administered (which may include epinephrine, corticosteroids, diphenhydramine, bronchodilators, and oxygen). Patients should be evaluated and carefully monitored until complete resolution of signs and symptoms. Permanent discontinuation should be strongly considered in all patients with severe infusion reactions.
There are no data regarding the most appropriate method of identification of patients who may safely be retreated with trastuzumab products after experiencing a severe infusion reaction. Prior to resumption of trastuzumab infusion, the majority of patients who experienced a severe infusion reaction were pre-medicated with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids. While some patients tolerated trastuzumab infusions, others had recurrent severe infusion reactions despite pre-medications.
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Trastuzumab products can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In post-marketing reports, use of trastuzumab during pregnancy resulted in cases of oligohydramnios and oligohydramnios sequence manifesting as pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities, and neonatal death.
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of KANJINTI. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential that exposure to KANJINTI during pregnancy or within 7 months prior to conception can result in fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 7 months following the last dose of KANJINTI [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.4 Pulmonary Toxicity
Trastuzumab product use can result in serious and fatal pulmonary toxicity. Pulmonary toxicity includes dyspnea, interstitial pneumonitis, pulmonary infiltrates, pleural effusions, non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, pulmonary insufficiency and hypoxia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and pulmonary fibrosis. Such events can occur as sequelae of infusion reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Patients with symptomatic intrinsic lung disease or with extensive tumor involvement of the lungs, resulting in dyspnea at rest, appear to have more severe toxicity.
5.5 Exacerbation of Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia
In randomized, controlled clinical trials, the per-patient incidences of NCI-CTC Grade 3–4 neutropenia and of febrile neutropenia were higher in patients receiving trastuzumab in combination with myelosuppressive chemotherapy as compared to those who received chemotherapy alone. The incidence of septic death was similar among patients who received trastuzumab and those who did not [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infusion Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Pulmonary Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Exacerbation of Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
The most common adverse reactions in patients receiving trastuzumab products in the adjuvant and metastatic breast cancer setting are fever, nausea, vomiting, infusion reactions, diarrhea, infections, increased cough, headache, fatigue, dyspnea, rash, neutropenia, anemia, and myalgia. Adverse reactions requiring interruption or discontinuation of trastuzumab product treatment include CHF, significant decline in left ventricular cardiac function, severe infusion reactions, and pulmonary toxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
In the metastatic gastric cancer setting, the most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) that were increased (≥ 5% difference) in patients receiving trastuzumab as compared to patients receiving chemotherapy alone were neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, anemia, stomatitis, weight loss, upper respiratory tract infections, fever, thrombocytopenia, mucosal inflammation, nasopharyngitis, and dysgeusia. The most common adverse reactions which resulted in discontinuation of trastuzumab treatment in the absence of disease progression were infection, diarrhea, and febrile neutropenia.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adjuvant Breast Cancer Studies
The data below reflect exposure to one-year trastuzumab therapy across three randomized, open-label studies, Studies 1, 2, and 3, with (n = 3678) or without (n = 3363) trastuzumab in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer.
The data summarized in Table 3 below, from Study 3, reflect exposure to trastuzumab in 1678 patients; the median treatment duration was 51 weeks and median number of infusions was 18. Among the 3386 patients enrolled in the observation and one-year trastuzumab arms of Study 3 at a median duration of follow-up of 12.6 months in the trastuzumab arm, the median age was 49 years (range: 21 to 80 years), 83% of patients were Caucasian, and 13% were Asian.
| Table 3
Adverse Reactions for Study 3a, All Gradesb |
||
| Adverse Reaction | One-Year Trastuzumab (n = 1678) | Observation (n = 1708) |
| Cardiac | ||
| Hypertension | 64 (4%) | 35 (2%) |
| Dizziness | 60 (4%) | 29 (2%) |
| Ejection Fraction Decreased | 58 (3.5%) | 11 (0.6%) |
| Palpitations | 48 (3%) | 12 (0.7%) |
| Cardiac Arrhythmiasc | 40 (3%) | 17 (1%) |
| Cardiac Failure Congestive | 30 (2%) | 5 (0.3%) |
| Cardiac Failure | 9 (0.5%) | 4 (0.2%) |
| Cardiac Disorder | 5 (0.3%) | 0 (0%) |
| Ventricular Dysfunction | 4 (0.2%) | 0 (0%) |
| Respiratory Thoracic Mediastinal Disorders | ||
| Cough | 81 (5%) | 34 (2%) |
| Influenza | 70 (4%) | 9 (0.5%) |
| Dyspnea | 57 (3%) | 26 (2%) |
| URI | 46 (3%) | 20 (1%) |
| Rhinitis | 36 (2%) | 6 (0.4%) |
| Pharyngolaryngeal Pain | 32 (2%) | 8 (0.5%) |
| Sinusitis | 26 (2%) | 5 (0.3%) |
| Epistaxis | 25 (2%) | 1 (0.06%) |
| Pulmonary Hypertension | 4 (0.2%) | 0 (0%) |
| Interstitial Pneumonitis | 4 (0.2%) | 0 (0%) |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 123 (7%) | 16 (1%) |
| Nausea | 108 (6%) | 19 (1%) |
| Vomiting | 58 (3.5%) | 10 (0.6%) |
| Constipation | 33 (2%) | 17 (1%) |
| Dyspepsia | 30 (2%) | 9 (0.5%) |
| Upper Abdominal Pain | 29 (2%) | 15 (1%) |
| Musculoskeletal & Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
| Arthralgia | 137 (8%) | 98 (6%) |
| Back Pain | 91 (5%) | 58 (3%) |
| Myalgia | 63 (4%) | 17 (1%) |
| Bone Pain | 49 (3%) | 26 (2%) |
| Muscle Spasm | 46 (3%) | 3 (0.2%) |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Headache | 162 (10%) | 49 (3%) |
| Paresthesia | 29 (2%) | 11 (0.6%) |
| Skin & Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||
| Rash | 70 (4%) | 10 (0.6%) |
| Nail Disorders | 43 (2%) | 0 (0%) |
| Pruritus | 40 (2%) | 10 (0.6%) |
| General Disorders | ||
| Pyrexia | 100 (6%) | 6 (0.4%) |
| Edema Peripheral | 79 (5%) | 37 (2%) |
| Chills | 85 (5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Asthenia | 75 (4.5%) | 30 (2%) |
| Influenza-like Illness | 40 (2%) | 3 (0.2%) |
| Sudden Death | 1 (0.06%) | 0 (0%) |
| Infections | ||
| Nasopharyngitis | 135 (8%) | 43 (3%) |
| UTI | 39 (3%) | 13 (0.8%) |
| Immune System Disorders | ||
| Hypersensitivity | 10 (0.6%) | 1 (0.06%) |
| Autoimmune Thyroiditis | 4 (0.3%) | 0 (0%) |
| a Median follow-up duration of 12.6 months in the one-year trastuzumab treatment arm. b The incidence of Grade 3 or higher adverse reactions was <1% in both arms for each listed term. c Higher level grouping term. |
||
In Study 3, a comparison of 3-weekly trastuzumab treatment for two years versus one year was also performed. The rate of asymptomatic cardiac dysfunction was increased in the 2-year trastuzumab treatment arm (8.1% versus 4.6% in the one-year trastuzumab treatment arm). More patients experienced at least one adverse reaction of Grade 3 or higher in the 2-year trastuzumab treatment arm (20.4%) compared with the one-year trastuzumab treatment arm (16.3%).
The safety data from Studies 1 and 2 were obtained from 3655 patients, of whom 2000 received trastuzumab; the median treatment duration was 51 weeks. The median age was 49 years (range: 24–80); 84% of patients were White, 7% Black, 4% Hispanic, and 3% Asian.
In Study 1, only Grade 3–5 adverse events, treatment-related Grade 2 events, and Grade 2–5 dyspnea were collected during and for up to 3 months following protocol-specified treatment. The following non-cardiac adverse reactions of Grade 2–5 occurred at an incidence of at least 2% greater among patients receiving trastuzumab plus chemotherapy as compared to chemotherapy alone: fatigue (29.5% vs. 22.4%), infection (24.0% vs. 12.8%), hot flashes (17.1% vs. 15.0%), anemia (12.3% vs. 6.7%), dyspnea (11.8% vs. 4.6%), rash/desquamation (10.9% vs. 7.6%), leukopenia (10.5% vs. 8.4%), neutropenia (6.4% vs. 4.3%), headache (6.2% vs. 3.8%), pain (5.5% vs. 3.0%), edema (4.7% vs. 2.7%) and insomnia (4.3% vs. 1.5%). The majority of these events were Grade 2 in severity.
In Study 2, data collection was limited to the following investigator-attributed treatment-related adverse reactions: NCI-CTC Grade 4 and 5 hematologic toxicities, Grade 3–5 non-hematologic toxicities, selected Grade 2–5 toxicities associated with taxanes (myalgia, arthralgias, nail changes, motor neuropathy, sensory neuropathy) and Grade 1–5 cardiac toxicities occurring during chemotherapy and/or trastuzumab treatment. The following non-cardiac adverse reactions of Grade 2–5 occurred at an incidence of at least 2% greater among patients receiving trastuzumab plus chemotherapy as compared to chemotherapy alone: arthralgia (12.2% vs. 9.1%), nail changes (11.5% vs.6.8%), dyspnea (2.4% vs. 0.2%), and diarrhea (2.2% vs. 0%). The majority of these events were Grade 2 in severity.
Safety data from Study 4 reflect exposure to trastuzumab as part of an adjuvant treatment regimen from 2124 patients receiving at least one dose of study treatment [AC-TH: n = 1068; TCH: n = 1056]. The overall median treatment duration was 54 weeks in both the AC-TH and TCH arms. The median number of infusions was 26 in the AC-TH arm and 30 in the TCH arm, including weekly infusions during the chemotherapy phase and every three week dosing in the monotherapy period. Among these patients, the median age was 49 years (range: 22 to 74 years). In Study 4, the toxicity profile was similar to that reported in Studies 1, 2, and 3 with the exception of a low incidence of CHF in the TCH arm.
Metastatic Breast Cancer Studies
The data below reflect exposure to trastuzumab in one randomized, open-label study, Study 5, of chemotherapy with (n = 235) or without (n = 234) trastuzumab in patients with metastatic breast cancer, and one single-arm study (Study 6; n = 222) in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Data in Table 4 are based on Studies 5 and 6.
Among the 464 patients treated in Study 5, the median age was 52 years (range: 25–77 years). 89% were White, 5% Black, 1% Asian and 5% other racial/ethnic groups. All patients received 4 mg/kg initial dose of trastuzumab followed by 2 mg/kg weekly. The percentages of patients who received trastuzumab treatment for ≥ 6 months and ≥ 12 months were 58% and 9%, respectively.
Among the 352 patients treated in single agent studies (213 patients from Study 6), the median age was 50 years (range: 28–86 years), 86% were White, 3% were Black, 3% were Asian, and 8% in other racial/ethnic groups. Most of the patients received 4 mg/kg initial dose of trastuzumab followed by 2 mg/kg weekly. The percentages of patients who received trastuzumab treatment for ≥ 6 months and ≥ 12 months were 31% and 16%, respectively.
| Table 4
|
|||||
| Per-Patient Incidence of Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥5% of Patients in Uncontrolled Studies or at Increased Incidence in the Trastuzumab Arm (Studies 5 and 6) |
|||||
| Single Agenta n = 352 | Trastuzumab + Paclitaxel n = 91 | Paclitaxel Alone n = 95 | Trastuzumab+ ACb n = 143 | ACb Alone n = 135 |
|
| Body as a Whole | |||||
| Pain | 47% | 61% | 62% | 57% | 42% |
| Asthenia | 42% | 62% | 57% | 54% | 55% |
| Fever | 36% | 49% | 23% | 56% | 34% |
| Chills | 32% | 41% | 4% | 35% | 11% |
| Headache | 26% | 36% | 28% | 44% | 31% |
| Abdominal pain | 22% | 34% | 22% | 23% | 18% |
| Back pain | 22% | 34% | 30% | 27% | 15% |
| Infection | 20% | 47% | 27% | 47% | 31% |
| Flu syndrome | 10% | 12% | 5% | 12% | 6% |
| Accidental injury | 6% | 13% | 3% | 9% | 4% |
| Allergic reaction | 3% | 8% | 2% | 4% | 2% |
| Cardiovascular | |||||
| Tachycardia | 5% | 12% | 4% | 10% | 5% |
| Congestive heart failure | 7% | 11% | 1% | 28% | 7% |
| Digestive | |||||
| Nausea | 33% | 51% | 9% | 76% | 77% |
| Diarrhea | 25% | 45% | 29% | 45% | 26% |
| Vomiting | 23% | 37% | 28% | 53% | 49% |
| Nausea and vomiting | 8% | 14% | 11% | 18% | 9% |
| Anorexia | 14% | 24% | 16% | 31% | 26% |
| Heme & Lymphatic | |||||
| Anemia | 4% | 14% | 9% | 36% | 26% |
| Leukopenia | 3% | 24% | 17% | 52% | 34% |
| Metabolic | |||||
| Peripheral edema | 10% | 22% | 20% | 20% | 17% |
| Edema | 8% | 10% | 8% | 11% | 5% |
| Musculoskeletal | |||||
| Bone pain | 7% | 24% | 18% | 7% | 7% |
| Arthralgia | 6% | 37% | 21% | 8% | 9% |
| Nervous | |||||
| Insomnia | 14% | 25% | 13% | 29% | 15% |
| Dizziness | 13% | 22% | 24% | 24% | 18% |
| Paresthesia | 9% | 48% | 39% | 17% | 11% |
| Depression | 6% | 12% | 13% | 20% | 12% |
| Peripheral neuritis | 2% | 23% | 16% | 2% | 2% |
| Neuropathy | 1% | 13% | 5% | 4% | 4% |
| Respiratory | |||||
| Cough increased | 26% | 41% | 22% | 43% | 29% |
| Dyspnea | 22% | 27% | 26% | 42% | 25% |
| Rhinitis | 14% | 22% | 5% | 22% | 16% |
| Pharyngitis | 12% | 22% | 14% | 30% | 18% |
| Sinusitis | 9% | 21% | 7% | 13% | 6% |
| Skin | |||||
| Rash | 18% | 38% | 18% | 27% | 17% |
| Herpes simplex | 2% | 12% | 3% | 7% | 9% |
| Acne | 2% | 11% | 3% | 3% | < 1% |
| Urogenital | |||||
| Urinary tract infection | 5% | 18% | 14% | 13% | 7% |
| a Data for trastuzumab single agent were from 4 studies, including 213 patients from Study 6. b Anthracycline (doxorubicin or epirubicin) and cyclophosphamide. |
|||||
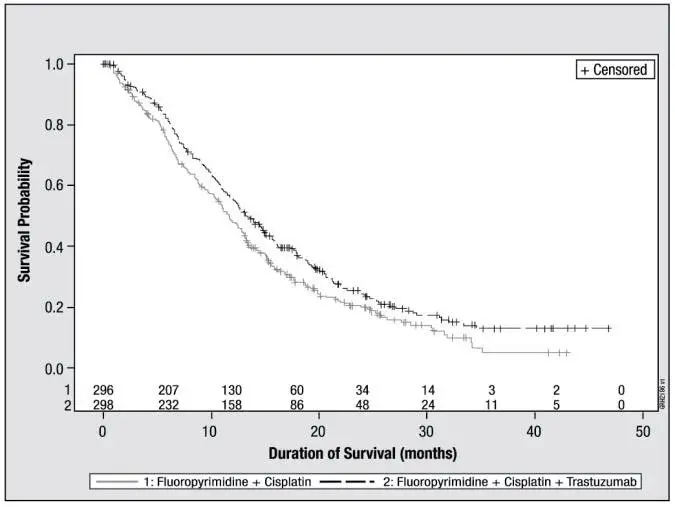
Metastatic Gastric Cancer
The data below are based on the exposure of 294 patients to trastuzumab in combination with a fluoropyrimidine (capecitabine or 5-FU) and cisplatin (Study 7). In the trastuzumab plus chemotherapy arm, the initial dose of trastuzumab 8 mg/kg was administered on Day 1 (prior to chemotherapy) followed by 6 mg/kg every 21 days until disease progression. Cisplatin was administered at 80 mg/m2 on Day 1 and the fluoropyrimidine was administered as either capecitabine 1000 mg/m2 orally twice a day on Days 1-14 or 5-fluorouracil 800 mg/m2/day as a continuous intravenous infusion Days 1 through 5.
Chemotherapy was administered for six 21-day cycles. Median duration of trastuzumab treatment was 21 weeks; median number of trastuzumab infusions administered was eight.
| Table 5 | |||||
| Study 7: Per-Patient Incidence of Adverse Reactions of All Grades (Incidence ≥ 5% between Arms) or Grade 3/4 (Incidence > 1% between Arms) and Higher Incidence in Trastuzumab Arm | |||||
| Trastuzumab + FC (N = 294) N (%) | FC (N = 290) N (%) |
||||
| Body System/Adverse Event | All Grades | Grades 3/4 | All Grades | Grades 3/4 | |
| Investigations | |||||
| Neutropenia | 230 (78) | 101 (34) | 212 (73) | 83 (29) | |
| Hypokalemia | 83 (28) | 28 (10) | 69 (24) | 16 (6) | |
| Anemia | 81 (28) | 36 (12) | 61 (21) | 30 (10) | |
| Thrombocytopenia | 47 (16) | 14 (5) | 33 (11) | 8 (3) | |
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | |||||
| Febrile Neutropenia | -- | 15 (5) | -- | 8 (3) | |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | |||||
| Diarrhea | 109 (37) | 27 (9) | 80 (28) | 11 (4) | |
| Stomatitis | 72 (24) | 2 (1) | 43 (15) | 6 (2) | |
| Dysphagia | 19 (6) | 7 (2) | 10 (3) | 1 (≤ 1) | |
| Body as a Whole | |||||
| Fatigue | 102 (35) | 12 (4) | 82 (28) | 7 (2) | |
| Fever | 54 (18) | 3 (1) | 36 (12) | 0 (0) | |
| Mucosal Inflammation | 37 (13) | 6 (2) | 18 (6) | 2 (1) | |
| Chills | 23 (8) | 1 (≤ 1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | |||||
| Weight Decrease | 69 (23) | 6 (2) | 40 (14) | 7 (2) | |
| Infections and Infestations | |||||
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infections | 56 (19) | 0 (0) | 29 (10) | 0 (0) | |
| Nasopharyngitis | 37 (13) | 0 (0) | 17 (6) | 0 (0) | |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | |||||
| Renal Failure and Impairment | 53 (18) | 8 (3) | 42 (15) | 5 (2) | |
| Nervous System Disorders | |||||
| Dysgeusia | 28 (10) | 0 (0) | 14 (5) | 0 (0) | |
The following subsections provide additional detail regarding adverse reactions observed in clinical trials of adjuvant breast cancer, metastatic breast cancer, metastatic gastric cancer, or post-marketing experience.
Cardiomyopathy
Serial measurement of cardiac function (LVEF) was obtained in clinical trials in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer. In Study 3, the median duration of follow-up was12.6 months (12.4 months in the observation arm; 12.6 months in the 1-year trastuzumab arm); and in Studies 1 and 2, 7.9 years in the AC-T arm, 8.3 years in the AC-TH arm. In Studies 1 and 2, 6% of all randomized patients with post-AC LVEF evaluation were not permitted to initiate trastuzumab following completion of AC chemotherapy due to cardiac dysfunction (LVEF < LLN or ≥ 16 point decline in LVEF from baseline to end of AC).
Following initiation of trastuzumab therapy, the incidence of new-onset dose-limiting myocardial dysfunction was higher among patients receiving trastuzumab and paclitaxel as compared to those receiving paclitaxel alone in Studies 1 and 2, and in patients receiving one-year trastuzumab monotherapy compared to observation in Study 3 (see Table 6, Figures 1 and 2). The per-patient incidence of new-onset cardiac dysfunction, as measured by LVEF, remained similar when compared to the analysis performed at a median follow-up of 2.0 years in the AC-TH arm. This analysis also showed evidence of reversibility of left ventricular dysfunction, with 64.5% of patients who experienced symptomatic CHF in the AC-TH group being asymptomatic at latest follow-up, and 90.3% having full or partial LVEF recovery.
| Table 6a | |||||
| Per-patient Incidence of New Onset Myocardial Dysfunction (by LVEF) Studies 1, 2, 3 and 4 | |||||
| LVEF < 50% and Absolute Decrease from Baseline | Absolute LVEF Decrease | ||||
| LVEF <50% | ≥10% decrease | ≥16% decrease | <20% and ≥10% | ≥20% | |
| Studies 1 & 2b,c | |||||
| AC→TH (n = 1856) | 23.1% (428) | 18.5% (344) | 11.2% (208) | 37.9% (703) | 8.9% (166) |
| AC→T (n = 1170) | 11.7% (137) | 7.0% (82) | 3.0% (35) | 22.1% (259) | 3.4% (40) |
| Study 3d | |||||
| Trastuzumab (n = 1678) | 8.6% (144) | 7.0% (118) | 3.8% (64) | 22.4% (376) | 3.5% (59) |
| Observation (n = 1708) | 2.7% (46) | 2.0% (35) | 1.2% (20) | 11.9% (204) | 1.2% (21) |
| Study 4e | |||||
| TCH (n = 1056) | 8.5% (90) | 5.9% (62) | 3.3% (35) | 34.5% (364) | 6.3% (67) |
| AC→TH (n = 1068) | 17% (182) | 13.3% (142) | 9.8% (105) | 44.3% (473) | 13.2% (141) |
| AC→T (n = 1050) | 9.5% (100) | 6.6% (69) | 3.3% (35) | 34% (357) | 5.5% (58) |
| a For Studies 1, 2 and 3, events are counted from the beginning of trastuzumab treatment. For Study 4, events are counted from the date of randomization. b Studies 1 and 2 regimens: doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel (AC→T) or paclitaxel plus trastuzumab (AC→TH). c Median duration of follow-up for Studies 1 and 2 combined was 8.3 years in the AC→TH arm. d Median follow-up duration of 12.6 months in the one-year trastuzumab treatment arm. e Study 4 regimens: doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (AC→T) or docetaxel plus trastuzumab (AC→TH); docetaxel and carboplatin plus trastuzumab (TCH). |
|||||
| Figure 1
Studies 1 and 2: Cumulative Incidence of Time to First LVEF Decline of ≥ 10 Percentage Points from Baseline and to Below 50% with Death as a Competing Risk Event |
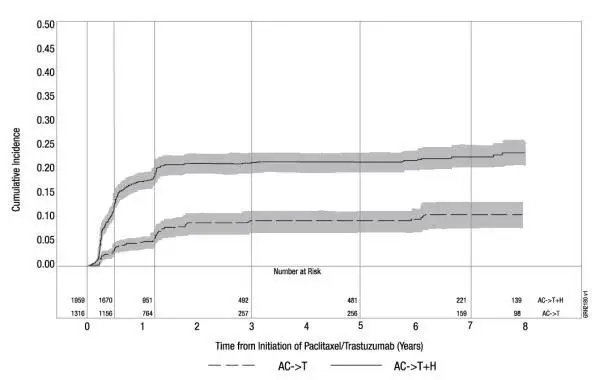 |
Time 0 is initiation of paclitaxel or trastuzumab + paclitaxel therapy.
| Figure 2
Study 3: Cumulative Incidence of Time to First LVEF Decline of ≥ 10 Percentage Points from Baseline and to Below 50% with Death as a Competing Risk Event |
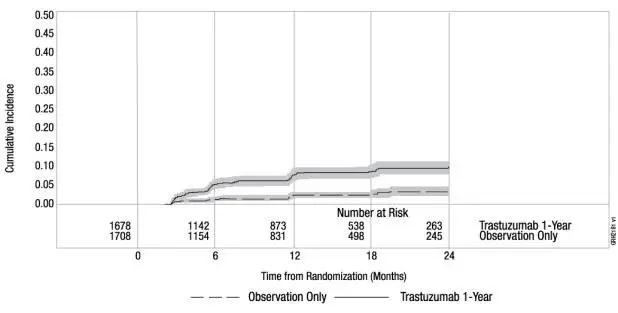 |
Time 0 is the date of randomization.
| Figure 3
Study 4: Cumulative Incidence of Time to First LVEF Decline of ≥10 Percentage Points from Baseline and to Below 50% with Death as a Competing Risk Event |
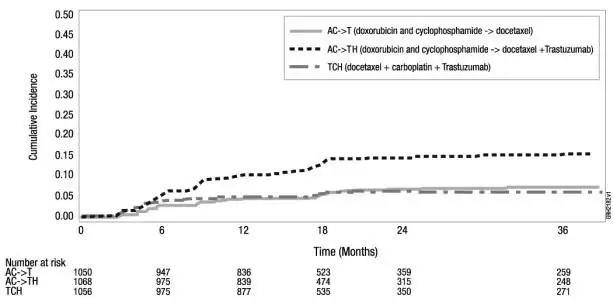 |
Time 0 is the date of randomization.
The incidence of treatment emergent congestive heart failure among patients in the metastatic breast cancer trials was classified for severity using the New York Heart Association classification system (I-IV, where IV is the most severe level of cardiac failure) (see Table 2). In the metastatic breast cancer trials, the probability of cardiac dysfunction was highest in patients who received trastuzumab concurrently with anthracyclines.
In Study 7, 5.0% of patients in the trastuzumab plus chemotherapy arm compared to 1.1% of patients in the chemotherapy alone arm had LVEF value below 50% with a ≥ 10% absolute decrease in LVEF from pre-treatment values.
Infusion Reactions
During the first infusion with trastuzumab, the symptoms most commonly reported were chills and fever, occurring in approximately 40% of patients in clinical trials. Symptoms were treated with acetaminophen, diphenhydramine, and meperidine (with or without reduction in the rate of trastuzumab infusion); permanent discontinuation of trastuzumab for infusion reactions was required in < 1% of patients. Other signs and/or symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, pain (in some cases at tumor sites), rigors, headache, dizziness, dyspnea, hypotension, elevated blood pressure, rash, and asthenia. Infusion reactions occurred in 21% and 35% of patients, and were severe in 1.4% and 9% of patients, on second or subsequent trastuzumab infusions administered as monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy, respectively. In the post-marketing setting, severe infusion reactions, including hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis, and angioedema have been reported.
Anemia
In randomized controlled clinical trials, the overall incidence of anemia (30% vs. 21% [Study 5]), of selected NCI-CTC Grade 2–5 anemia (12.3% vs. 6.7% [Study 1]), and of anemia requiring transfusions (0.1% vs. 0 patients [Study 2]) were increased in patients receiving trastuzumab and chemotherapy compared with those receiving chemotherapy alone. Following the administration of trastuzumab as a single agent (Study 6), the incidence of NCI-CTC Grade 3 anemia was < 1%. In Study 7 (metastatic gastric cancer), on the trastuzumab-containing arm as compared to the chemotherapy alone arm, the overall incidence of anemia was 28% compared to 21% and of NCI-CTC Grade 3/4 anemia was 12.2% compared to 10.3%.
Neutropenia
In randomized controlled clinical trials in the adjuvant setting, the incidence of selected NCI-CTC Grade 4–5 neutropenia (1.7% vs. 0.8% [Study 2]) and of selected Grade 2–5 neutropenia (6.4% vs. 4.3% [Study 1]) were increased in patients receiving trastuzumab and chemotherapy compared with those receiving chemotherapy alone. In a randomized, controlled trial in patients with metastatic breast cancer, the incidences of NCI-CTC Grade 3/4 neutropenia (32% vs. 22%) and of febrile neutropenia (23% vs. 17%) were also increased in patients randomized to trastuzumab in combination with myelosuppressive chemotherapy as compared to chemotherapy alone. In Study 7 (metastatic gastric cancer) on the trastuzumab-containing arm as compared to the chemotherapy alone arm, the incidence of NCI-CTC Grade 3/4 neutropenia was 36.8% compared to 28.9%; febrile neutropenia 5.1% compared to 2.8%.
Infection
The overall incidences of infection (46% vs. 30% [Study 5]), of selected NCI-CTC Grade 2–5 infection/febrile neutropenia (24.3% vs. 13.4% [Study 1]) and of selected Grade 3–5 infection/febrile neutropenia (2.9% vs. 1.4%) [Study 2]) were higher in patients receiving trastuzumab and chemotherapy compared with those receiving chemotherapy alone. The most common site of infections in the adjuvant setting involved the upper respiratory tract, skin, and urinary tract.
In Study 4, the overall incidence of infection was higher with the addition of trastuzumab to AC-T but not to TCH [44% (AC-TH), 37% (TCH), 38% (AC-T)]. The incidences of NCI-CTC Grade 3-4 infection were similar [25% (AC-TH), 21% (TCH), 23% (AC-T)] across the three arms.
In a randomized, controlled trial in treatment of metastatic breast cancer, the reported incidence of febrile neutropenia was higher (23% vs. 17%) in patients receiving trastuzumab in combination with myelosuppressive chemotherapy as compared to chemotherapy alone.
Pulmonary Toxicity
Adjuvant Breast Cancer
Among women receiving adjuvant therapy for breast cancer, the incidence of selected NCI-CTC Grade 2-5 pulmonary toxicity (14.3% vs. 5.4% [Study 1]) and of selected NCI-CTC Grade 3–5 pulmonary toxicity and spontaneous reported Grade 2 dyspnea (3.4% vs. 0.9% [Study 2]) was higher in patients receiving trastuzumab and chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone. The most common pulmonary toxicity was dyspnea (NCI-CTC Grade 2–5: 11.8% vs. 4.6% [Study 1]; NCI-CTC Grade 2–5: 2.4% vs. 0.2% [Study 2]).
Pneumonitis/pulmonary infiltrates occurred in 0.7% of patients receiving trastuzumab compared with 0.3% of those receiving chemotherapy alone. Fatal respiratory failure occurred in 3 patients receiving trastuzumab, one as a component of multi-organ system failure, as compared to 1 patient receiving chemotherapy alone.
In Study 3, there were 4 cases of interstitial pneumonitis in the one-year trastuzumab treatment arm compared to none in the observation arm at a median follow-up duration of 12.6 months.
Metastatic Breast Cancer
Among women receiving trastuzumab for treatment of metastatic breast cancer, the incidence of pulmonary toxicity was also increased. Pulmonary adverse events have been reported in the post-marketing experience as part of the symptom complex of infusion reactions. Pulmonary events include bronchospasm, hypoxia, dyspnea, pulmonary infiltrates, pleural effusions, non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, and acute respiratory distress syndrome. For a detailed description, [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Thrombosis/Embolism
In 4 randomized, controlled clinical trials, the incidence of thrombotic adverse events was higher in patients receiving trastuzumab and chemotherapy compared to chemotherapy alone in three studies (2.6% vs. 1.5% [Study 1], 2.5% and 3.7% vs. 2.2% [Study 4] and 2.1% vs. 0% [Study 5]).
Diarrhea
Among women receiving adjuvant therapy for breast cancer, the incidence of NCI-CTC Grade 2–5 diarrhea (6.7% vs. 5.4% [Study 1]) and of NCI-CTC Grade 3–5 diarrhea (2.2% vs. 0% [Study 2]), and of Grade 1–4 diarrhea (7% vs. 1% [Study 3; one-year trastuzumab treatment at 12.6 months median duration of follow-up]) were higher in patients receiving trastuzumab as compared to controls. In Study 4, the incidence of Grade 3–4 diarrhea was higher [5.7% AC-TH, 5.5% TCH vs. 3.0% AC-T] and of Grade 1–4 was higher [51% AC-TH, 63% TCH vs. 43% AC-T] among women receiving trastuzumab. Of patients receiving trastuzumab as a single agent for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, 25% experienced diarrhea. An increased incidence of diarrhea was observed in patients receiving trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy for treatment of metastatic breast cancer.
Renal Toxicity
In Study 7 (metastatic gastric cancer) on the trastuzumab-containing arm as compared to the chemotherapy alone arm the incidence of renal impairment was 18% compared to 14.5%. Severe (Grade 3/4) renal failure was 2.7% on the trastuzumab-containing arm compared to 1.7% on the chemotherapy only arm.
Treatment discontinuation for renal insufficiency/failure was 2% on the trastuzumab-containing arm and 0.3% on the chemotherapy only arm.
In the post-marketing setting, rare cases of nephrotic syndrome with pathologic evidence of glomerulopathy have been reported. The time to onset ranged from 4 months to approximately 18 months from initiation of trastuzumab therapy. Pathologic findings included membranous glomerulonephritis, focal glomerulosclerosis, and fibrillary glomerulonephritis. Complications included volume overload and congestive heart failure.
7. Drug Interactions
Patients who receive anthracycline after stopping trastuzumab products may be at increased risk of cardiac dysfunction because of trastuzumab's long washout period based on population PK analysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. If possible, physicians should avoid anthracycline-based therapy for up to 7 months after stopping trastuzumab products. If anthracyclines are used, the patient's cardiac function should be monitored carefully.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Trastuzumab products can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In post-marketing reports, use of trastuzumab during pregnancy resulted in cases of oligohydramnios and of oligohydramnios sequence, manifesting as pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities, and neonatal death [see Data]. Apprise the patient of the potential risks to a fetus. There are clinical considerations if trastuzumab products are used in a pregnant woman or if a patient becomes pregnant within 7 months following the last dose of a trastuzumab product [see Clinical Considerations].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Monitor women who received KANJINTI during pregnancy or within 7 months prior to conception for oligohydramnios. If oligohydramnios occurs, perform fetal testing that is appropriate for gestational age and consistent with community standards of care.
Data
Human Data
In post-marketing reports, use of trastuzumab during pregnancy resulted in cases of oligohydramnios and of oligohydramnios sequence, manifesting in the fetus as pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities and neonatal death. These case reports described oligohydramnios in pregnant women who received trastuzumab either alone or in combination with chemotherapy. In some case reports, amniotic fluid index increased after trastuzumab was stopped. In one case, trastuzumab therapy resumed after amniotic index improved, and oligohydramnios recurred.
Animal Data
In studies where trastuzumab was administered to pregnant cynomolgus monkeys during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 25 mg/kg given twice weekly (up to 25 times the recommended weekly human dose of 2 mg/kg), trastuzumab crossed the placental barrier during the early (Gestation Days 20 to 50) and late (Gestation Days 120 to 150) phases of gestation. The resulting concentrations of trastuzumab in fetal serum and amniotic fluid were approximately 33% and 25%, respectively, of those present in the maternal serum but were not associated with adverse developmental effects.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of KANJINTI.
Contraception
Females
Trastuzumab products can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered during pregnancy.
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KANJINTI and for 7 months following the last dose of KANJINTI [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
12. Kanjinti Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of trastuzumab was evaluated in a pooled population pharmacokinetic (PK) model analysis of 1,582 subjects with primarily breast cancer and metastatic gastric cancer (MGC) receiving intravenous trastuzumab. Total trastuzumab clearance increases with decreasing concentrations due to parallel linear and non-linear elimination pathways.
Although the average trastuzumab exposure was higher following the first cycle in breast cancer patients receiving the three-weekly schedule compared to the weekly schedule of trastuzumab, the average steady-state exposure was essentially the same at both dosages. The average trastuzumab exposure following the first cycle and at steady state as well as the time to steady state was higher in breast cancer patients compared to MGC patients at the same dosage; however, the reason for this exposure difference is unknown. Additional predicted trastuzumab exposure and PK parameters following the first trastuzumab cycle and at steady state exposure are described in Tables 7 and 8, respectively.
Population PK based simulations indicate that following discontinuation of trastuzumab, concentrations in at least 95% of breast cancer and MGC patients will decrease to approximately 3% of the population predicted steady-state trough serum concentration (approximately 97% washout) by 7 months [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
| Table 7
|
|||||
| Population Predicted Cycle 1 PK Exposures (Median with 5th – 95th Percentiles) in Breast Cancer and MGC Patients | |||||
| Schedule | Primary tumor type | N | Cmin
(µg/mL) | Cmax (µg/mL) | AUC0 - 21days
(µg.day/mL) |
| 8 mg/kg + 6 mg/kg q3w | Breast cancer | 1195 | 29.4 (5.8 - 59.5) | 178 (117 - 291) | 1373 (736 - 2245) |
| MGC | 274 | 23.1 (6.1 - 50.3) | 132 (84.2 - 225) | 1109 (588 - 1938) |
|
| 4 mg/kg + 2 mg/kg qw | Breast cancer | 1195 | 37.7 (12.3 - 70.9) | 88.3 (58 - 144) | 1066 (586 - 1754) |
| Table 8
|
|||||||
| Population Predicted Steady-State PK Exposures (Median with 5th - 95th Percentiles) in Breast Cancer and MGC Patients | |||||||
| Schedule | Primary
tumor type | N | Cmin,ssa
(µg/mL) | Cmax,ssb
(µg/mL) | AUCss, 0-21 days
(µg.day/mL) | Time
to steady- state (week) | Total CL
range at steady-state (L/day) |
|
8 mg/kg + 6 mg/kg q3w | Breast cancer | 1195 | 47.4 (5 - 115) | 179 (107 - 309) | 1794 (673 - 3618) | 12 | 0.173 - 0.283 |
|
MGC | 274 | 32.9 (6.1 - 88.9) | 131 (72.5 - 251) | 1338 (557 - 2875) | 9 | 0.189 - 0.337 | |
| 4 mg/kg + 2 mg/kg qw | Breast cancer | 1195 | 66.1 (14.9 - 142) | 109 (51.0 - 209) | 1765 (647 - 3578) | 12 | 0.201 - 0.244 |
| a Steady-state trough serum concentration of trastuzumab. b Maximum steady-state serum concentration of trastuzumab. |
|||||||
Specific Populations: Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, no clinically significant differences were observed in the pharmacokinetics of trastuzumab based on age (< 65 (n = 1294); ≥ 65 (n = 288)), race (Asian (n = 264); non-Asian (n = 1324)) and renal impairment (mild (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 60 to 90 mL/min) (n = 636) or moderate (CLcr 30 to 60 mL/min) (n = 133). The pharmacokinetics of trastuzumab products in patients with severe renal impairment, end-stage renal disease with or without hemodialysis, or hepatic impairment is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies:
There have been no formal drug interaction studies performed with trastuzumab products in humans. Clinically significant interactions between trastuzumab and concomitant medications used in clinical trials have not been observed.
Paclitaxel and doxorubicin: Concentrations of paclitaxel and doxorubicin and their major metabolites (i.e., 6-α hydroxyl-paclitaxel [POH], and doxorubicinol [DOL], respectively) were not altered in the presence of trastuzumab when used as combination therapy in clinical trials. Trastuzumab concentrations were not altered as part of this combination therapy.
Docetaxel and carboplatin: When trastuzumab was administered in combination with docetaxel or carboplatin, neither the plasma concentrations of docetaxel or carboplatin nor the plasma concentrations of trastuzumab were altered.
Cisplatin and capecitabine: In a drug interaction substudy conducted in patients in Study 7, the pharmacokinetics of cisplatin, capecitabine and their metabolites were not altered when administered in combination with trastuzumab.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Adjuvant Breast Cancer
The safety and efficacy of trastuzumab in women receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for HER2 overexpressing breast cancer were evaluated in an integrated analysis of two randomized, open-label, clinical trials (Studies 1 and 2) with a total of 4063 women at the protocol-specified final overall survival analysis, a third randomized, open-label, clinical trial (Study 3) with a total of 3386 women at definitive Disease-Free Survival analysis for one-year trastuzumab treatment versus observation, and a fourth randomized, open-label clinical trial with a total of 3222 patients (Study 4).
Studies 1 and 2
In Studies 1 and 2, breast tumor specimens were required to show HER2 overexpression (3+ by IHC) or gene amplification (by FISH). HER2 testing was verified by a central laboratory prior to randomization (Study 2) or was required to be performed at a reference laboratory (Study 1). Patients with a history of active cardiac disease based on symptoms, abnormal electrocardiographic, radiologic, or left ventricular ejection fraction findings or uncontrolled hypertension (diastolic > 100 mm Hg or systolic > 200 mm Hg) were not eligible.
Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel (AC→paclitaxel) alone or paclitaxel plus trastuzumab (AC→paclitaxel + trastuzumab). In both trials, patients received four 21-day cycles of doxorubicin 60 mg/m2 and cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m2.
Paclitaxel was administered either weekly (80 mg/m2) or every 3 weeks (175 mg/m2) for a total of 12 weeks in Study 1; paclitaxel was administered only by the weekly schedule in Study 2. Trastuzumab was administered at 4 mg/kg on the day of initiation of paclitaxel and then at a dose of 2 mg/kg weekly for a total of 52 weeks. Trastuzumab treatment was permanently discontinued in patients who developed congestive heart failure, or persistent/recurrent LVEF decline [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Radiation therapy, if administered, was initiated after the completion of chemotherapy. Patients with ER+ and/or PR+ tumors received hormonal therapy. The primary endpoint of the combined efficacy analysis was Disease-Free Survival (DFS), defined as the time from randomization to recurrence, occurrence of contralateral breast cancer, other second primary cancer, or death. The secondary endpoint was overall survival (OS).
A total of 3752 patients were included in the joint efficacy analysis of the primary endpoint of DFS following a median follow-up of 2.0 years in the AC→paclitaxel + trastuzumab arm. The pre-planned final OS analysis from the joint analysis included 4063 patients and was performed when 707 deaths had occurred after a median follow-up of 8.3 years in the AC→paclitaxel + trastuzumab arm. The data from both arms in Study 1 and two of the three study arms in Study 2 were pooled for efficacy analyses. The patients included in the primary DFS analysis had a median age of 49 years (range: 22–80 years; 6% > 65 years), 84% were white, 7% black, 4% Hispanic, and 4% Asian/Pacific Islander. Disease characteristics included 90% infiltrating ductal histology, 38% T1, 91% nodal involvement, 27% intermediate and 66% high grade pathology, and 53% ER+ and/or PR+ tumors. Similar demographic and baseline characteristics were reported for the efficacy evaluable population, after 8.3 years of median follow-up in the AC→paclitaxel + trastuzumab arm.
Study 3
In Study 3, breast tumor specimens were required to show HER2 overexpression (3+ by IHC) or gene amplification (by FISH) as determined at a central laboratory. Patients with node-negative disease were required to have ≥ T1c primary tumor. Patients with a history of congestive heart failure or LVEF < 55%, uncontrolled arrhythmias, angina requiring medication, clinically significant valvular heart disease, evidence of transmural infarction on ECG, poorly controlled hypertension (systolic > 180 mm Hg or diastolic > 100 mm Hg) were not eligible.
Study 3 was designed to compare one and two years of three-weekly trastuzumab treatment versus observation in patients with HER2 positive EBC following surgery, established chemotherapy and radiotherapy (if applicable). Patients were randomized (1:1:1) upon completion of definitive surgery, and at least four cycles of chemotherapy to receive no additional treatment, or one year of trastuzumab treatment or two years of trastuzumab treatment. Patients undergoing a lumpectomy had also completed standard radiotherapy. Patients with ER+ and/or PgR+ disease received systemic adjuvant hormonal therapy at investigator discretion. Trastuzumab was administered with an initial dose of 8 mg/kg followed by subsequent doses of 6 mg/kg once every three weeks. The main outcome measure was Disease-Free Survival (DFS), defined as in Studies 1 and 2.
A protocol specified interim efficacy analysis comparing one-year trastuzumab treatment to observation was performed at a median follow-up duration of 12.6 months in the trastuzumab arm and formed the basis for the definitive DFS results from this study. Among the 3386 patients randomized to the observation (n = 1693) and trastuzumab one-year (n = 1693) treatment arms, the median age was 49 years (range: 21–80), 83% were Caucasian, and 13% were Asian. Disease characteristics: 94% infiltrating ductal carcinoma, 50% ER+ and/or PgR+, 57% node positive, 32% node negative, and in 11% of patients, nodal status was not assessable due to prior neo-adjuvant chemotherapy. Ninety-six percent (1055/1098) of patients with node-negative disease had high risk features: among the 1098 patients with node-negative disease, 49% (543) were ER− and PgR−, and 47% (512) were ER and/or PgR + and had at least one of the following high risk features: pathological tumor size greater than 2 cm, Grade 2–3, or age < 35 years. Prior to randomization, 94% of patients had received anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens.
After the definitive DFS results comparing observation to one-year trastuzumab treatment were disclosed, a prospectively planned analysis that included comparison of one year versus two years of trastuzumab treatment at a median follow-up duration of 8 years was performed. Based on this analysis, extending trastuzumab treatment for a duration of two years did not show additional benefit over treatment for one year [Hazard Ratios of two-years trastuzumab versus one-year trastuzumab treatment in the intent to treat (ITT) population for Disease-Free Survival (DFS) = 0.99 (95% CI: 0.87, 1.13), p-value = 0.90 and Overall Survival (OS) = 0.98 (0.83, 1.15); p-value = 0.78].
Study 4
In Study 4, breast tumor specimens were required to show HER2 gene amplification (FISH+ only) as determined at a central laboratory. Patients were required to have either node-positive disease, or node-negative disease with at least one of the following high-risk features: ER/PR-negative, tumor size > 2 cm, age < 35 years, or histologic and/or nuclear Grade 2 or 3. Patients with a history of CHF, myocardial infarction, Grade 3 or 4 cardiac arrhythmia, angina requiring medication, clinically significant valvular heart disease, poorly controlled hypertension (diastolic > 100 mm Hg), any T4 or N2 or known N3 or M1 breast cancer were not eligible.
Patients were randomized (1:1:1) to receive doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (AC-T), doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel plus trastuzumab (AC-TH), or docetaxel and carboplatin plus trastuzumab (TCH). In both the AC-T and AC-TH arms, doxorubicin 60 mg/m2 and cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m2 were administered every 3 weeks for four cycles; docetaxel 100 mg/m2 was administered every 3 weeks for four cycles. In the TCH arm, docetaxel 75 mg/m2 and carboplatin (at a target AUC of 6 mg/mL/min as a 30- to 60-minute infusion) were administered every 3 weeks for six cycles. Trastuzumab was administered weekly (initial dose of 4 mg/kg followed by weekly dose of 2 mg/kg) concurrently with either T or TC, and then every 3 weeks (6 mg/kg) as monotherapy for a total of 52 weeks. Radiation therapy, if administered, was initiated after completion of chemotherapy. Patients with ER+ and/or PR+ tumors received hormonal therapy. Disease-Free Survival (DFS) was the main outcome measure.
Among the 3222 patients randomized, the median age was 49 (range: 22 to 74 years; 6% ≥ 65 years). Disease characteristics included 54% ER+ and/or PR+ and 71% node positive. Prior to randomization, all patients underwent primary surgery for breast cancer.
The results for DFS for the integrated analysis of Studies 1 and 2, Study 3, and Study 4 and OS results for the integrated analysis of Studies 1 and 2, and Study 3 are presented in Table 9. For Studies 1 and 2, the duration of DFS following a median follow-up of 2.0 years in the AC→TH arm is presented in Figure 4, and the duration of OS after a median follow-up of 8.3 years in the AC→TH arm is presented in Figure 5. The duration of DFS for Study 4 is presented in Figure 6. Across all four studies, at the time of definitive DFS analysis, there were insufficient numbers of patients within each of the following subgroups to determine if the treatment effect was different from that of the overall patient population: patients with low tumor grade, patients within specific ethnic/racial subgroups (Black, Hispanic, Asian/Pacific Islander patients), and patients > 65 years of age. For Studies 1 and 2, the OS hazard ratio was 0.64 (95% CI: 0.55, 0.74). At 8.3 years of median follow up [AC→TH], the survival rate was estimated to be 86.9% in the AC→TH arm and 79.4% in the AC→T arm. The final OS analysis results from Studies 1 and 2 indicate that OS benefit by age, hormone receptor status, number of positive lymph nodes, tumor size and grade, and surgery/radiation therapy was consistent with the treatment effect in the overall population. In patients ≤ 50 years of age (n = 2197), the OS hazard ratio was 0.65 (95% CI: 0.52, 0.81) and in patients > 50 years of age (n = 1866), the OS hazard ratio was 0.63 (95% CI: 0.51, 0.78). In the subgroup of patients with hormone receptor-positive disease (ER-positive and/or PR-positive) (n = 2223), the hazard ratio for OS was 0.63 (95% CI: 0.51, 0.78). In the subgroup of patients with hormone receptor-negative disease (ER-negative and PR-negative) (n = 1830), the hazard ratio for OS was 0.64 (95% CI: 0.52, 0.80). In the subgroup of patients with tumor size ≤ 2 cm (n = 1604), the hazard ratio for OS was 0.52 (95% CI: 0.39, 0.71). In the subgroup of patients with tumor size > 2 cm (n = 2448), the hazard ratio for OS was 0.67 (95% CI: 0.56, 0.80).
| Table 9
|
|||||
| Efficacy Results from Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer (Studies 1 + 2, Study 3, and Study 4) |
|||||
| DFS Hazard ratio | |||||
| DFS | (95% CI) | Deaths | OS Hazard ratio | ||
| events | p-value | (OS events) | p-value | ||
| Studies 1 + 2a | |||||
| AC→TH (n = 1872)b (n = 2031)c | 133b | 0.48b,d (0.39, 0.59) p ˂ 0.0001e | 289c | 0.64c,d
(0.55, 0.74) p ˂ 0.0001e |
|
| AC→T | 261b | 418c | |||
| (n = 1880)b | |||||
| (n = 2032)c | |||||
| Study 3f | |||||
| Chemo→ Trastuzumab (n = 1693) | 127 | 0.54 (0.44, 0.67) p ˂ 0.0001g | 31 | 0.75 p = NSh |
|
| Chemo→ | 219 | 40 | |||
| Observation | |||||
| (n = 1693) | |||||
| Study 4i | |||||
| TCH | 134 | 0.67 | 56 | ||
| (n = 1075) | (0.54 – 0.84) p = 0.0006e,j | ||||
| AC→TH | 121 | 0.60 | 49 | ||
| (n = 1074) | (0.48 – 0.76) p < 0.0001e,i | ||||
| AC→T (n = 1073) | 180 | 80 | |||
| CI = confidence interval. a Studies 1 and 2 regimens: doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel (AC→T) or paclitaxel plus trastuzumab (AC→TH). b Efficacy evaluable population, for the primary DFS analysis, following a median follow-up of 2.0 years in the AC→TH arm. c Efficacy evaluable population, for the final OS analysis, following 707 deaths (8.3 years of median follow-up in the AC→TH arm). d Hazard ratio estimated by Cox regression stratified by clinical trial, intended paclitaxel schedule, number of positive nodes, and hormone receptor status. e stratified log-rank test. f At definitive DFS analysis with median duration of follow-up of 12.6 months in the one-year trastuzumab treatment arm. g log-rank test. h NS = non-significant. i Study 4 regimens: doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (AC→T) or docetaxel plus trastuzumab (AC→TH); docetaxel and carboplatin plus trastuzumab (TCH). j A two-sided alpha level of 0.025 for each comparison. |
|||||
| Figure 4
Duration of Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer (Studies 1 and 2) |
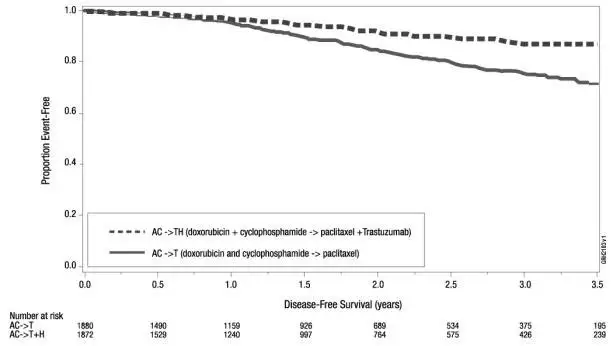 |
| Figure 5
Duration of Overall Survival in Patients with Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer (Studies 1 and 2) |
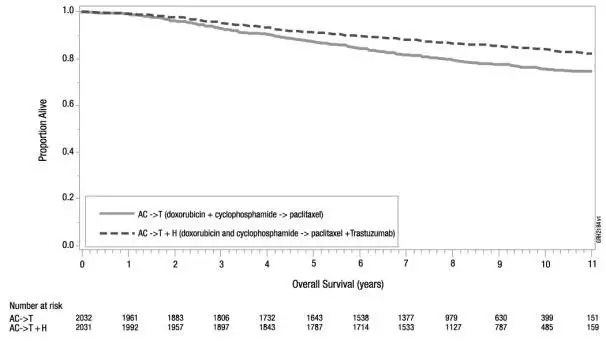 |
| Figure 6
Duration of Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer (Study 4) |
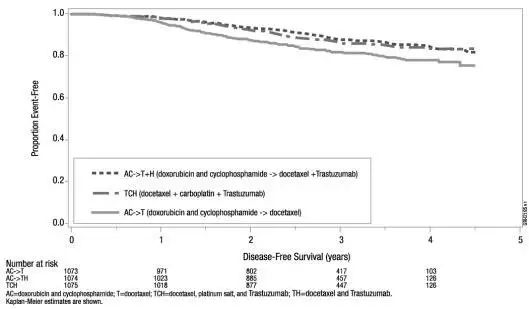 |
Exploratory analyses of DFS as a function of HER2 overexpression or gene amplification were conducted for patients in Studies 2 and 3, where central laboratory testing data were available. The results are shown in Table 10. The number of events in Study 2 was small with the exception of the IHC 3+/FISH+ subgroup, which constituted 81% of those with data. Definitive conclusions cannot be drawn regarding efficacy within other subgroups due to the small number of events. The number of events in Study 3 was adequate to demonstrate significant effects on DFS in the IHC 3+/FISH unknown and the FISH +/IHC unknown subgroups.
| Table 10
|
||||||
| Treatment Outcomes in Studies 2 and 3 as a Function of HER2 Overexpression or Amplification |
||||||
| Study 2 | Study 3c | |||||
| HER2 Assay Resulta | Number of Patients | Hazard Ratio DFS (95% CI) | Number of Patients | Hazard Ratio DFS (95% CI) |
||
| IHC 3+ | ||||||
| FISH (+) | 1170 | 0.42 | 91 | 0.56 | ||
| (0.27, 0.64) | (0.13, 2.50) | |||||
| FISH (-) | 51 | 0.71 | 8 | - | ||
| (0.04, 11.79) | ||||||
| FISH Unknown | 51 | 0.69 | 2258 | 0.53 | ||
| (0.09, 5.14) | (0.41, 0.69) | |||||
| IHC < 3+ / | 174 | 1.01 | 299b | 0.53 | ||
| FISH (+) | (0.18, 5.65) | (0.20, 1.42) | ||||
| IHC unknown / | - | - | 724 | 0.59 | ||
| FISH (+) | (0.38, 0.93) | |||||
| a IHC by HercepTest, FISH by PathVysion (HER2/CEP17 ratio ≥ 2.0) as performed at a central laboratory. b All cases in this category in Study 3 were IHC 2. c Median follow-up duration of 12.6 months in the one-year trastuzumab treatment arm. |
||||||
| KANJINTI
trastuzumab-anns injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| KANJINTI
trastuzumab-anns injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| KANJINTI
trastuzumab-anns kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Amgen Inc (039976196) |