Drug Detail:Keveyis (Dichlorphenamide [ dye-klor-fen-a-mide ])
Drug Class: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
KEVEYIS ® (dichlorphenamide) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1958
Indications and Usage for Keveyis
KEVEYIS is an oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of primary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis, primary hypokalemic periodic paralysis, and related variants ( 1)
Keveyis Dosage and Administration
- Initiate dosing at 50 mg by mouth once or twice daily ( 2.1)
- Titrate up or down dose based on individual response ( 2.1)
- The minimum recommended dosage is 50 mg daily, and the maximum recommended dosage is 200 mg daily ( 2.1)
- Evaluate response to KEVEYIS after 2 months of treatment ( 2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 50 mg ( 3)
Contraindications
- Hepatic insufficiency ( 4)
- Severe pulmonary obstruction ( 4)
- Hypersensitivity to dichlorphenamide or other sulfonamides ( 4)
- Concomitant use with high dose aspirin ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity and Other Life-Threatening Reactions: discontinue KEVEYIS at the first appearance of skin rash or any sign of immune-mediated or idiosyncratic adverse reaction ( 5.1)
- Hypokalemia: baseline and periodic measurements of serum potassium are recommended; if hypokalemia develops or persists, consider reducing the dose or discontinuing KEVEYIS and correcting potassium levels ( 5.3)
- Metabolic acidosis: baseline and periodic measurements of serum bicarbonate are recommended; if metabolic acidosis develops or persists, consider reducing the dose or discontinuing KEVEYIS ( 5.4)
- Falls: consider reducing the dose or discontinuing KEVEYIS in patients who experience falls ( 5.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence at least 10% and greater than placebo) include paresthesias, cognitive disorder, dysgeusia, and confusional state ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-855-324-8912, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Aspirin: anorexia, tachypnea, lethargy, and coma have been reported with concomitant use of dichlorphenamide and high-dose aspirin. The concomitant use of KEVEYIS and high-dose aspirin is contraindicated. KEVEYIS should be used with caution in patients receiving lower doses of aspirin ( 4, 5.2, 7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm ( 8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 5/2023
Related/similar drugs
dichlorphenamideFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Keveyis
KEVEYIS is indicated for the treatment of primary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis, primary hypokalemic periodic paralysis, and related variants.
2. Keveyis Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage Information
Initiate dosing at 50 mg by mouth once or twice daily. The dosage may be increased or decreased based on individual response, at weekly intervals (or sooner in case of adverse reaction). The minimum recommended total daily dosage is 50 mg, and the maximum recommended total daily dosage is 200 mg.
2.2 Monitoring to Assess Effectiveness
Primary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis, primary hypokalemic periodic paralysis, and related variants are a heterogeneous group of conditions, for which the response to KEVEYIS may vary. Therefore, prescribers should evaluate the patient's response to KEVEYIS after 2 months of treatment to decide whether KEVEYIS should be continued.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Round, white tablets, scored on one side, engraved with "D" above the score and "50" below the score, the other side is plain, 50 mg each.
4. Contraindications
KEVEYIS is contraindicated in the following circumstances:
- Hypersensitivity to dichlorphenamide or other sulfonamides [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Concomitant use of KEVEYIS and high dose aspirin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
- Severe pulmonary disease, limiting compensation to metabolic acidosis caused by KEVEYIS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatic insufficiency: KEVEYIS may aggravate hepatic encephalopathy.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity and Other Life-Threatening Reactions
Fatalities associated with the administration of sulfonamides have occurred because of adverse reactions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, fulminant hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia and other blood dyscrasias. Pulmonary involvement can occur in isolation or as part of a systemic reaction.
KEVEYIS should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any sign of immune-mediated or other life-threatening adverse reaction.
5.2 Concomitant Use of Aspirin or Other Salicylates
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, including KEVEYIS, can cause metabolic acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] , which can increase the risk of salicylate toxicity. Anorexia, tachypnea, lethargy, and coma have been reported with concomitant use of dichlorphenamide and high-dose aspirin. Therefore, the concomitant use of KEVEYIS and high-dose aspirin is contraindicated. Patients with concomitant use of KEVEYIS and low-dose aspirin should be carefully monitored.
5.3 Hypokalemia
KEVEYIS increases potassium excretion and can cause hypokalemia. The risk of hypokalemia is greater when KEVEYIS is used in patients with conditions associated with hypokalemia (e.g., adrenocortical excess, renal tubular acidosis type 1 and 2), and in patients receiving other drugs that may cause hypokalemia [see Drug Interactions (7.3)] .
Baseline and periodic measurements of serum potassium during KEVEYIS treatment is recommended.
If hypokalemia develops or persists, consideration should be given to reducing the dose or discontinuing KEVEYIS and correction of potassium levels.
5.4 Metabolic Acidosis
KEVEYIS can cause hyperchloremic non-anion gap metabolic acidosis. Concomitant use of KEVEYIS with other drugs that cause metabolic acidosis may increase the severity of acidosis. Concomitant use of KEVEYIS in compensated patients with respiratory acidosis, such as in advanced lung diseases, may lead to respiratory decompensation.
Baseline and periodic measurements of serum bicarbonate during KEVEYIS treatment are recommended.
If metabolic acidosis develops or persists, consideration should be given to reducing the dose or discontinuing KEVEYIS [see Drug Interactions (7.4)] .
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
- Hypersensitivity and Other Life-Threatening Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Metabolic Acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Falls [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In a 9-week randomized controlled trial in adults with hyperkalemic or hypokalemic periodic paralysis (Study 1), the most common adverse reactions in patients treated with KEVEYIS, with rates greater than placebo, were paresthesia, cognitive disorder, dysgeusia, and confusional state. The mean dose of KEVEYIS was 94 mg/day in patients with hypokalemic periodic paralysis and 82 mg/day in patients with hyperkalemic periodic paralysis.
Table 1 lists the incidence of adverse reactions that occurred in ≥ 5% of patients treated with KEVEYIS and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo in Study 1.
| Adverse Reaction | KEVEYIS
N = 36 (%) | Placebo
N = 29 (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Nervous system disorders | Paresthesia | 44 | 14 |
| Cognitive disorder * | 14 | 7 | |
| Dysgeusia | 14 | 0 | |
| Confusional state | 11 | 0 | |
| Headache | 8 | 7 | |
| Hypoesthesia | 8 | 0 | |
| Lethargy | 8 | 0 | |
| Dizziness | 6 | 0 | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Diarrhea | 6 | 3 |
| Nausea | 6 | 0 | |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Fatigue | 8 | 0 |
| Malaise | 6 | 0 | |
| Investigations | Weight decreased | 6 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Muscle spasms | 8 | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 6 | 3 | |
| Muscle twitching | 6 | 0 | |
| Respiratory | Dyspnea | 6 | 0 |
| Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 6 | 0 | |
| Skin | Rash | 8 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 6 | 0 | |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of dichlorphenamide. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following are adverse reactions which have been reported during postapproval use of dichlorphenamide and were serious or are not reported in the previous section of labeling [see Clinical Trials Experience (6.1)] : amnesia, cardiac failure, condition aggravated, convulsion, hallucination, nephrolithiasis, pancytopenia, psychotic disorder, renal tubular necrosis, stupor, syncope, tremor.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Aspirin and Other Salicylates
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, including KEVEYIS, can cause metabolic acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)], which can increase the risk of salicylate toxicity. Anorexia, tachypnea, lethargy, and coma have been reported with concomitant use of dichlorphenamide and high-dose aspirin. Therefore, concomitant use of KEVEYIS and high-dose aspirin is contraindicated. Patients with concomitant use of KEVEYIS and low-dose aspirin should be carefully monitored [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.2 Drugs that are Substrates of Organic Anion Transporter1 (OAT1)
In vitro, dichlorphenamide is an inhibitor of OAT1 transporters. The concomitant administration of KEVEYIS may increase the plasma exposures of OAT1 substrates. Use of KEVEYIS with drugs that are sensitive to OAT1 inhibition (e.g., methotrexate, famotidine, oseltamivir) is not recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Drugs that Cause Hypokalemia
The risk of hypokalemia is greater with coadministration of KEVEYIS and other drugs that can cause hypokalemia (e.g., loop diuretics, thiazide diuretics, laxatives, antifungals, penicillins, and theophylline) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
7.4 Drugs that Cause Metabolic Acidosis
Coadministration of KEVEYIS and other drugs that can cause metabolic acidosis may increase the severity of the acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
7.5 Drugs that are Inhibitors of OAT1 or OAT3
An in vitro transporter study indicated that dichlorphenamide is a substrate of human transporters OAT1 and OAT3 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Therefore, signs of dichlorphenamide toxicity should be monitored when administered with OAT1 or OAT3 inhibitors.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of dichlorphenamide in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for KEVEYIS and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from KEVEYIS or from the underlying maternal condition.
10. Overdosage
Symptoms of overdosage or toxicity may include drowsiness, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, ataxia, tremor, and tinnitus.
In the event of overdosage, induce emesis or perform gastric lavage. The electrolyte disturbances most likely to be encountered from overdosage are hypokalemia and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
11. Keveyis Description
KEVEYIS tablets contain dichlorphenamide, an oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Dichlorphenamide, a dichlorinated benzenedisulfonamide, is known chemically as 4, 5–dichloro-1,3-benzenedisulfonamide.
Its empirical formula is C 6H 6Cl 2N 2O 4S 2 and its structural formula is:
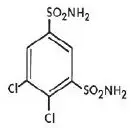
Dichlorphenamide USP is a white or practically white, crystalline compound with a molecular weight of 305.16. It is very slightly soluble in water but soluble in dilute solutions of sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide. Dilute alkaline solutions of dichlorphenamide are stable at room temperature.
KEVEYIS (dichlorphenamide) tablets are supplied as tablets, for oral administration, each containing 50 mg dichlorphenamide. Inactive ingredients are lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate and pregelatinized starch.
12. Keveyis - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dichlorphenamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. However, the precise mechanism by which dichlorphenamide exerts its therapeutic effects in patients with primary periodic paralysis is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
KEVEYIS can cause metabolic acidosis, which can increase the risk of salicylate toxicity with coadministration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. KEVEYIS-induced metabolic acidosis can also increase in severity with coadministration of other drugs that cause metabolic acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
After single-dose administration in healthy subjects in fasted state, dichlorphenamide C max and AUC increased in a dose-proportional manner within the range of 25 mg to 400 mg (2 times the maximum recommended dose). The steady-state is expected to be achieved within 10 days of twice-daily dosing.
Absorption
The median time to reach maximum concentration (T
max) of dichlorphenamide was about 1.5 to 3 hours postdose after both single and multiple dose administrations.
Distribution
The plasma protein binding of dichlorphenamide is approximately 88%.
Elimination
Following a single-dose administration, mean terminal half-life was in the range of 32 to 66 hours.
Metabolism
Dichlorphenamide is not a substrate for CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 isoforms when tested
in vitro.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme Inhibition
Dichlorphenamide is not an inhibitor for CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A4 enzymes when tested
in vitro.
Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme Induction
Dichlorphenamide is not an inducer for CYP1A2, 2B6, or 3A4 enzymes when tested
in vitro.
In vitro Assessment of Transporter-Drug Interactions
Dichlorphenamide is neither a substrate nor inhibitor for p-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT2, OAT4, OCT1, OCT2, MATE1, or MATE2-K when tested
in vitro.
Dichlorphenamide is not an inhibitor of OAT3, but is an inhibitor of OAT1 based on in vitro studies [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
Dichlorphenamide is a substrate for transporters OAT1 and OAT3 based on in vitro studies [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
In Vivo Drug Interactions
The use of dichlorphenamide in combination with high-dose aspirin is contraindicated as it may lead to salicylate toxicity. The mechanism(s) of this interaction is not known.
Specific Populations
Geriatrics
The pharmacokinetics of dichlorphenamide in the elderly has not been determined.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of KEVEYIS was evaluated in two clinical studies, Study 1 and Study 2.
16. How is Keveyis supplied
Each KEVEYIS (dichlorphenamide) tablet, 50 mg is round, white, scored on one side, engraved with "D" above the score and "50" below the score. The other side is plain.
KEVEYIS (dichlorphenamide) tablets are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 100.....NDC 72065-001-01
Distributed by:
Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
W Fulton St., Suite 1300
Chicago, IL 60607
KEVEYIS® is a registered trademark licensed exclusively in the US to Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a subsidiary of Xeris Biopharma, Inc.
XERIS PHARMACEUTICALS® and its associated logo are trademarks of Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
5200904-1021-02
| KEVEYIS
dichlorphenamide tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (609377135) |





