Drug Detail:Krazati (Adagrasib)
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antineoplastics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
KRAZATI™ (adagrasib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2022
Indications and Usage for Krazati
KRAZATI is an inhibitor of the RAS GTPase family indicated for the treatment of adult patients with KRAS G12C-mutated locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), as determined by an FDA approved test, who have received at least one prior systemic therapy. (1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR). Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of a clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s). (1)
Krazati Dosage and Administration
- Recommended dosage: 600 mg orally twice daily. (2.2)
- Swallow tablets whole with or without food. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 200 mg. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: Monitor patients for diarrhea, nausea and vomiting and provide supportive care as needed. Withhold, reduce the dose or permanently discontinue based on severity. (2.3, 5.1)
- QTc Interval Prolongation: Avoid concomitant use of KRAZATI with other products with a known potential to prolong the QTc interval. Monitor ECG and electrolytes in patients at risk, and in patients taking medications known to prolong the QT interval. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (2.3, 5.2)
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor liver laboratory tests prior to the start of KRAZATI and monthly for 3 months after and as clinically indicated. Reduce the dose, withhold, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (2.3, 5.3)
- Interstitial Lung Disease / Pneumonitis: Monitor for new or worsening respiratory symptoms. Withhold KRAZATI for suspected ILD/pneumonitis and permanently discontinue if no other potential causes of ILD/pneumonitis are identified. (2.3, 5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- The most common (≥ 25%) adverse reactions were nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, hepatotoxicity, renal impairment, edema, dyspnea, and decreased appetite. (6.1)
- The most common Grade 3 or 4 (≥ 2%) laboratory abnormalities were decreased lymphocytes, decreased hemoglobin, increased alanine aminotransferase, increased aspartate aminotransferase, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, increased lipase, decreased leukocytes, decreased neutrophils and increased alkaline phosphatase. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mirati Therapeutics, Inc. at 1-844-MIRATI-1 (1-844-647-2841) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
See full prescribing information for clinically significant drug interactions with KRAZATI. (7)
- Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid concomitant use. (7.1)
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use until adagrasib concentrations have reached steady state. (7.1)
- Sensitive CYP3A4 Substrates: Avoid concomitant use with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. (7.2)
- Sensitive CYP2C9 or CYP2D6 Substrates or P-gp Substrates: Avoid concomitant use with sensitive CYP2C9 or CYP2D6 substrates or P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions. (7.2)
- Drugs That Prolong QT Interval: Avoid concomitant use with KRAZATI. (7.3)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 12/2022
Related/similar drugs
Opdivo, Retevmo, Rybrevant, Lumakras, methotrexate, Keytruda, AvastinFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Krazati
KRAZATI is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with KRAS G12C-mutated locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), as determined by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)], who have received at least one prior systemic therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of a clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
2. Krazati Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment of locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with KRAZATI based on the presence of KRAS G12C mutation in plasma or tumor specimens [see Clinical Studies (14)]. If no mutation is detected in a plasma specimen, test tumor tissue.
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of a KRAS G12C mutation is available at: https://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of KRAZATI is 600 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Take KRAZATI at the same time every day with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Swallow tablets whole. Do not chew, crush or split tablets.
If vomiting occurs after taking KRAZATI, do not take an additional dose. Resume dosing at the next scheduled time.
If a dose is inadvertently missed, it should be skipped if greater than 4 hours have elapsed from the expected dosing time. Resume dosing at the next scheduled time.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Recommended dose reductions for adverse reactions are outlined in Table 1. If adverse reactions occur, a maximum of two dose reductions are permitted. Permanently discontinue KRAZATI in patients who are unable to tolerate 600 mg once daily.
| Dose Reduction | Dosage |
|---|---|
| First dose reduction | 400 mg twice daily |
| Second dose reduction | 600 mg once daily |
The recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
| Adverse reaction | Severity* | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|---|
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; ULN = upper limit of normal | ||
|
||
| Nausea or vomiting despite appropriate supportive care (including anti-emetic therapy) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Grade 3 or 4 |
|
| Diarrhea despite appropriate supportive care (including anti-diarrheal therapy) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Grade 3 or 4 |
|
| QTc Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | QTc absolute value greater than 500 ms or Greater than an increase of 60 ms from baseline |
|
| Torsade de pointes, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia or signs or symptoms of serious or life-threatening arrhythmia |
|
|
| Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Grade 2 AST or ALT |
|
| Grade 3 or 4 AST or ALT |
|
|
| AST or ALT > 3 × ULN with total bilirubin > 2 × ULN in the absence of alternative causes |
|
|
| Interstitial Lung Disease / Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | Any Grade |
|
| Other Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | Grade 3 or 4 |
|
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 200 mg, oval shaped, white to off-white, immediate release film coated tablets with "200" on one side and stylized "M" on the opposite side.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
KRAZATI can cause severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions.
In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], serious gastrointestinal adverse reactions observed were gastrointestinal bleeding in 3.8% including 0.8% Grade 3 or 4, gastrointestinal obstruction in 1.6% including 1.4% Grade 3 or 4, colitis in 0.5% including 0.3% Grade 3, ileus in 0.5%, and stenosis in 0.3%. In addition, nausea, diarrhea, or vomiting occurred in 89% of 366 patients, including 9% Grade 3. Nausea, diarrhea, or vomiting led to dosage interruption or dose reduction in 29% of patients and permanent discontinuation of adagrasib in 0.3%.
Monitor and manage patients using supportive care, including antidiarrheals, antiemetics, or fluid replacement, as indicated. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue KRAZATI based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 QTc Interval Prolongation
KRAZATI can cause QTc interval prolongation, which can increase the risk for ventricular tachyarrhythmias (e.g., torsades de pointes) or sudden death.
In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], 6% of 366 patients with at least one post-baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) assessment had an average QTc ≥ 501 ms and 11% of patients had an increase from baseline of QTc > 60 msec. KRAZATI causes concentration-dependent increases in the QTc interval [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Avoid concomitant use of KRAZATI with other products with a known potential to prolong the QTc interval. [see Drug Interactions (7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Avoid use of KRAZATI in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with concurrent QTc prolongation.
Monitor ECGs and electrolytes prior to starting KRAZATI, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, electrolyte abnormalities, and in patients who are unable to avoid concomitant medications that are known to prolong the QT interval. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue KRAZATI depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
KRAZATI can cause hepatotoxicity, which may lead to drug-induced liver injury and hepatitis.
In the pooled safety population of 366 patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], drug-induced liver injury was reported in 0.3% of patients, including 0.3% Grade 3. A total of 32% of patients who received adagrasib had increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT)/increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST); 5% were Grade 3 and 0.5% were Grade 4. The median time to first onset of increased ALT/AST was 3 weeks (range: 0.1 to 48). Overall hepatotoxicity occurred in 37%, and 7% were Grade 3 or 4. Hepatotoxicity leading to dose interruption or reduction occurred in 12% of patients. Adagrasib was discontinued due to hepatotoxicity in 0.5% of patients.
Monitor liver laboratory tests (AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase and total bilirubin) prior to the start of KRAZATI and monthly for 3 months or as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop transaminase elevations. Reduce the dose, withhold, or permanently discontinue KRAZATI based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.4 Interstitial Lung Disease /Pneumonitis
KRAZATI can cause interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis, which can be fatal.
In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], ILD/pneumonitis occurred in 4.1% of patients, 1.4% were Grade 3 or 4, and one case was fatal. The median time to first onset for ILD/pneumonitis was 12 weeks (range: 5 to 31 weeks). Adagrasib was discontinued due to ILD/pneumonitis in 0.8% of patients.
Monitor patients for new or worsening respiratory symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough, fever) during treatment with KRAZATI. Withhold KRAZATI in patients with suspected ILD/pneumonitis and permanently discontinue KRAZATI if no other potential causes of ILD/pneumonitis are identified [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- QTc Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to adagrasib as a single agent at 600 mg orally twice daily in 366 patients with NSCLC and other solid tumors enrolled in KRYSTAL-1 and KRYSTAL-12 (NCT04685135). Among 366 patients who received adagrasib, 39% of patients were exposed for 6 months or longer and 12% were exposed for greater than one year. In this pooled safety population the most common (≥ 25%) adverse reactions were nausea (70%), diarrhea (69%), vomiting (57%), fatigue (55%), musculoskeletal pain (38%), hepatotoxicity (37%), renal impairment (33%), edema (30%), dyspnea (26%), and decreased appetite (29%). In this pooled safety population, the most common Grade 3 or 4 (≥ 2%) laboratory abnormalities were decreased lymphocytes (20%), decreased hemoglobin (7%), increased alanine aminotransferase (4.5%), increased aspartate aminotransferase (4.2%), hypokalemia (3.6%), hyponatremia (3.4%), increased lipase (2.5%), decreased leukocytes (2.5%), decreased neutrophils (2.3%), and increased alkaline phosphatase (2.0%).
7. Drug Interactions
7.3 Drugs That Prolong QTc Interval
Avoid concomitant use of KRAZATI with other product(s) with a known potential to prolong the QTc interval. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, monitor electrocardiogram and electrolytes prior to starting KRAZATI, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Withhold KRAZATI if the QTc interval is > 500 ms or the change from baseline is > 60 ms [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Adagrasib causes QTc interval prolongation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Concomitant use of KRAZATI with other products that prolong the QTc interval may result in a greater increase in the QTc interval and adverse reactions associated with QTc interval prolongation, including Torsade de pointes, other serious arrythmias, and sudden death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
11. Krazati Description
Adagrasib is an irreversible inhibitor of KRAS G12C and belongs to the RAS GTPase family. The molecular formula is C32H35ClFN7O2 and the molecular weight is 604.1 g/mol. The chemical name is {(2S)-4-[7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-{[(2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]- methoxy}-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-(2-fluoroprop-2-enoyl)piperazin-2-yl}acetonitrile. Adagrasib has the following chemical structure:
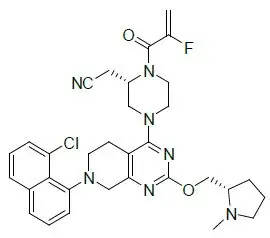
Adagrasib is a crystalline solid. The solubility of adagrasib in the aqueous media decreases over the range pH 1.2 to 7.4 from > 262 mg/mL to < 0.010 mg/mL.
KRAZATI (adagrasib) tablets for oral administration contain 200 mg of adagrasib. The following are inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate (vegetable sourced), mannitol, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet film coating contains hypromellose, maltodextrin, medium chain triglycerides (vegetable sourced), polydextrose, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12. Krazati - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Adagrasib is an irreversible inhibitor of KRAS G12C that covalently binds to the mutant cysteine in KRAS G12C and locks the mutant KRAS protein in its inactive state that prevents downstream signaling without affecting wild-type KRAS protein. Adagrasib inhibits tumor cell growth and viability in cells harboring KRAS G12C mutations and results in tumor regression in KRAS G12C-mutated tumor xenograft models with minimal off-target activity.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Adagrasib exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of adagrasib were studied in healthy subjects and in patients with KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC and are presented as mean (percent coefficient of variation) unless otherwise specified.
Adagrasib AUC and Cmax increase dose proportionally over the dose range of 400 mg to 600 mg (0.67 to 1 times the approved recommended dose). Adagrasib steady-state was reached within 8 days following administration of the approved recommended dosage and accumulation was approximately 6-fold.
Drug Interaction Studies
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with adagrasib.
Adagrasib was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not genotoxic in an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay or an in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
Fertility studies were not conducted with adagrasib. In toxicology studies of up to 13-weeks in duration in rats, oral administration of adagrasib induced phospholipidosis which increased vacuolation in female reproductive organs, including vacuolation in ovaries (corpora lutea, macrophage or interstitial cells) and uterus (glandular epithelium), and atrophy with mucification of the vaginal mucosa at doses ≥ 150 mg/kg (approximately equal to or greater than the human exposure at the recommended dose based on area under the curve [AUC]). These findings reversed after cessation of dosing in the 28-day study but in the 13-week study, pigmented macrophage aggregates were observed in the ovaries of female rats after the recovery period. In a 28-day repeat-dose toxicology study, oral administration of adagrasib to male rats induced atrophy and epithelial vacuolation of the prostate gland and seminal vesicles at 300 mg/kg (approximately 1.6 times the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC). These findings resolved after cessation of treatment.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Phospholipidosis (vacuolation and/or presence of foamy macrophages) was observed in multiple organs (e.g., lung, trachea, heart, skeletal, ovaries, uterus, adrenal gland, kidney, liver, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, and thyroid in rats; and heart and lung in dogs) after repeated oral administration of adagrasib in rats and dogs. In toxicology studies of up to 13-week duration in rats, phospholipidosis was observed at doses ≥ 150 mg/kg (approximately ≥ 2 times the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC). In a dog 28-day toxicity study, this effect was observed at 25 mg/kg (approximately equal to the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC). The extent of vacuolization and the presence of foamy macrophages were more prominent in the rat compared to dogs, and evidence of reversibility after cessation of treatment was noted for most organs. The significance of this finding in humans in unknown.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of adagrasib was evaluated in KRYSTAL-1 (NCT03785249), a multicenter, single-arm, open-label expansion cohort study. Eligible patients were required to have locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC who previously received treatment with a platinum-based regimen and an immune checkpoint inhibitor, an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) of 0 or 1, and at least one measurable lesion as defined by Response Evaluation criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST v1.1). Identification of a KRAS G12C mutation was prospectively determined by local testing using tissue specimens. Patients received adagrasib 600 mg orally twice daily until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. Tumor assessments were performed every 6 weeks. The major efficacy outcome measures were confirmed objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) as evaluated by blinded independent central review (BICR) according to RECIST v1.1.
In the efficacy population, KRAS G12C mutation status was determined by prospective local testing using tumor tissue specimens. Of the 112 patients with KRAS G12C mutation, tissue samples from 88% (98/112) patients were tested retrospectively using the QIAGEN therascreen KRAS RGQ PCR Kit. While 89% (87/98) of patients were positive for KRAS G12C mutation, 11% (11/98) did not have a KRAS G12C mutation identified. In addition, plasma samples from 63% (71/112) patients were tested retrospectively using Agilent Resolution ctDx FIRST assay. While 66% (47/71) of patients were positive for KRAS G12C mutation, 34% (24/71) did not have a KRAS G12C mutation identified.
A total of 112 patients had at least one measurable lesion at baseline as assessed by BICR according to RECIST v1.1.
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics in the efficacy population were: median age 64 years (range: 25 to 89), 55% female, 83% White, 8% were Black or African American, 4% Asian, 4% race not reported, 0.9% American Indian or Alaska Native, 16% Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) 0 and 83% ECOG PS 1. Tumor histology was 97% adenocarcinoma and 89% of patients had metastatic disease. Patients received a median of 2 prior systemic therapies (range 1 to 7); 43% received 1 prior line, 35% received 2 prior lines, 10% received 3 prior lines and 12% received 4 or more prior lines, 98% received both prior platinum and prior anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Sites of extra-thoracic disease included bone 42%, brain 30%, adrenals 21%, and liver 21%.
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 7.
| Efficacy Parameter | Adagrasib (n = 112) |
|---|---|
| CI = Confidence Interval | |
|
|
| Objective Response Rate (95% CI)* | 43 (34, 53) |
| Complete response rate, % | 0.9 |
| Partial response rate, % | 42 |
| Duration of Response* | |
| Median† in months (95% CI) | 8.5 (6.2, 13.8) |
| Patients with duration ≥ 6 months‡, % | 58 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| PATIENT INFORMATION KRAZATI™ (krah zah tee) (adagrasib) tablets |
||
|---|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: 12/2022 | |
| What is KRAZATI?
KRAZATI is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
It is not known if KRAZATI is safe and effective in children. |
||
Before taking KRAZATI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||
How should I take KRAZATI?
|
||
| What are possible side effects of KRAZATI? KRAZATI can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
| The most common side effects of KRAZATI include: | ||
|
|
|
| Certain abnormal laboratory test results are common with KRAZATI. Your healthcare provider will monitor you for abnormal laboratory tests, and treat you if needed. | ||
| KRAZATI may cause fertility problems in males and females, which may affect your ability to have children. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you. These are not all of the possible side effects of KRAZATI. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
How should I store KRAZATI?
|
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of KRAZATI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use KRAZATI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give KRAZATI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about KRAZATI that is written for health professionals. |
||
| What are the ingredients in KRAZATI? Active ingredient: adagrasib Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate (vegetable sourced), mannitol, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet film coating contains hypromellose, maltodextrin, medium chain triglycerides (vegetable sourced), polydextrose, talc, and titanium dioxide. Manufactured for: Mirati Therapeutics, Inc. 3545 Cray Court San Diego, CA 92121, U.S.A. © 2022 Mirati Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved For more information, go to www.KRAZATI.com or call 1-844-MIRATI-1 (1-844-647-2841) |
||
| KRAZATI
adagrasib tablet, coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Mirati Therapeutics, Inc (078870124) |





