Drug Detail:Kyzatrex (Testosterone oral [ tes-tos-ter-one ])
Drug Class: Androgens and anabolic steroids
Highlights of Prescribing Information
KYZATREX™ (testosterone undecanoate) capsules, for oral use, CIII Initial U.S. approval: 1953
WARNING: BLOOD PRESSURE INCREASES
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
- KYZATREX™ can cause blood pressure (BP) increases that can increase the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke and cardiovascular death ( 5.1, 5.3, 6.1).
- Before initiating KYZATREX™, consider the patient's baseline cardiovascular risk and ensure blood pressure is adequately controlled ( 5.1, 5.3).
- Periodically monitor for and treat new-onset hypertension or exacerbations of pre-existing hypertension and re-evaluate whether the benefits of KYZATREX™ outweigh its risks in patients who develop cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease on treatment ( 5.1, 5.3).
- Due to this risk, use KYZATREX™ only for the treatment of men with hypogonadal conditions associated with structural or genetic etiologies ( 1, 4).
Indications and Usage for Kyzatrex
KYZATREX™ is an androgen indicated for testosterone replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone ( 1).
Limitations of Use:
- Safety and efficacy of KYZATREX™ in males less than 18 years old have not been established ( 1, 8.4).
Kyzatrex Dosage and Administration
- KYZATREX™ is not substitutable with other oral testosterone undecanoate products ( 2.1).
- Prior to initiating KYZATREX™, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these concentrations are below the normal range ( 2.2).
- Take KYZATREX™ with food ( 2.3).
- Starting dosage: 200 mg orally once in the morning and once in the evening ( 2.3).
- Adjust the dosage to a minimum of 100 mg once in the morning and a maximum of 400 mg twice daily based on serum testosterone drawn 3 to 5 hours after the morning dose at least 7 days after starting treatment or following dose adjustment and periodically thereafter ( 2.3).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules: 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg ( 3).
Contraindications
- Carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate ( 5.4)
- Women who are pregnant. Testosterone may cause fetal harm ( 4, 5.7, 8.1)
- Hypersensitivity to KYZATREX™ or any of its ingredients ( 4)
- Hypogonadal conditions not associated with structural or genetic etiologies ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Polycythemia: Monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit approximately every 3 months to detect increased red blood cell mass and polycythemia. Discontinue KYZATREX™ if necessary ( 5.2).
- Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer: Monitor patients for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH. Evaluate patients for prostate cancer, including monitoring prostate specific antigen (PSA) prior to initiating and during treatment with androgens ( 5.4).
- Venous thromboembolism (VTE): VTE, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) have been reported in patients using testosterone. Discontinue KYZATREX™ if VTE is suspected and initiate appropriate workup and management ( 5.5).
- Abuse of Testosterone and Monitoring of Serum Testosterone: If testosterone use at doses higher than recommended for the approved indication and in combination with other anabolic androgenic steroids is suspected, check serum testosterone concentration ( 5.6).
- Potential for Adverse Effects on Spermatogenesis: KYZATREX™ may cause azoospermia ( 5.8).
- Edema: Edema, with or without congestive heart failure (CHF), may occur in patients with pre-existing cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease. Discontinue KYZATREX™ and initiate appropriate workup ( 5.10).
- Sleep Apnea: KYZATREX™ may potentiate sleep apnea in those with risk factors ( 5.11)
- Lipid Changes: KYZATREX™ may affect serum lipid profile. Monitor patient lipid concentrations periodically; if necessary, adjust dosage of lipid lowering drug(s) or discontinue KYZATREX™ ( 5.13).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2%): hypertension ( 6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Marius Pharmaceuticals at 1-833-949-5040 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Insulin: In patients with diabetes, concomitant use with KYZATREX™ may decrease blood glucose and insulin requirements ( 7.1).
- Oral Anticoagulants: Concomitant use with KYZATREX™ may cause changes in anticoagulant activity. Monitor International Normalized Ratio (INR) and prothrombin time (PT) frequently ( 7.2).
- Corticosteroids: Concomitant use with KYZATREX™ may result in increased fluid retention. Use with caution, particularly in patients with cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease ( 7.3).
- Drugs that May Also Increase Blood Pressure: Concomitant use with KYZATREX™ may lead to additional increases in blood pressure ( 7.4).
Use In Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients: Geriatric patients treated with androgens may also be at risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH and hypertension ( 8.5).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 9/2022
Related/similar drugs
testosterone, AndroGel, Depo-Testosterone, Xyosted, HCG, PregnylFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: BLOOD PRESSURE INCREASES
- KYZATREX™ can cause blood pressure (BP) increases that can increase the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke and cardiovascular death, with greater risk for MACE in patients with cardiovascular risk factors or established cardiovascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- Before initiating KYZATREX™, consider the patient's baseline cardiovascular risk and ensure blood pressure is adequately controlled [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- After initiating therapy, periodically monitor for and treat new-onset hypertension or exacerbations of pre-existing hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
- Re-evaluate whether the benefits of KYZATREX™ outweigh its risks in patients who develop cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease while on treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
- Due to this risk, use KYZATREX™ only for the treatment of men with hypogonadal conditions associated with structural or genetic etiologies [see Indications and Usage (1) and Contraindications (4)].
1. Indications and Usage for Kyzatrex
KYZATREX™ is indicated for testosterone replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
- Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): testicular failure due to conditions such as cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchiectomy, Klinefelter syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone concentrations and gonadotropins (folliclestimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH)) above the normal range.
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency, pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low serum testosterone concentrations but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range.
2. Kyzatrex Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Dosage Information
KYZATREX™ is not substitutable with other oral testosterone undecanoate products.
2.2 Confirmation of Hypogonadism Before Initiation of KYZATREX™
Prior to initiating KYZATREX™, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these testosterone concentrations are below the normal range.
2.3 Recommended Dosage and Administration
Individualize the dosage of KYZATREX™ based on the patient's serum testosterone concentration response to the drug.
The recommended starting dose is 200 mg orally twice daily, once in the morning and once in the evening. Take KYZATREX™ with food.
Dosage Adjustment
Check serum testosterone concentrations 7 days after starting treatment or after dosage adjustment, 3 to 5 hours after the morning dose. Adjust the KYZATREX™ dose as necessary as shown in Table 1. Thereafter, periodically monitor serum testosterone concentrations.
The minimum recommended dose is 100 mg once daily in the morning. The maximum recommended dose is 400 mg twice daily. For total daily doses greater than 100 mg, administer the same dose in the morning and evening.
| Serum Testosterone Concentration | Current KYZATREX™ Dosage | New KYZATREX™ Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 460 ng/dL | 100 mg with breakfast only | 100 mg twice daily with meals |
| 100 mg twice daily with meals | 200 mg twice daily with meals | |
| 200 mg twice daily with meals | 300 mg twice daily with meals | |
| 300 mg twice daily with meals | 400 mg twice daily with meals | |
| 460 to 971 ng/dL | No Dosage Change | |
| More than 971 ng/dL | 400 mg twice daily with meals | 300 mg twice daily with meals |
| 300 mg twice daily with meals | 200 mg twice daily with meals | |
| 200 mg twice daily with meals | 100 mg twice daily with meals | |
| 100 mg twice daily with meals | 100 mg with breakfast only | |
| 100 mg with breakfast only | Discontinue treatment | |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules:
- 100 mg, oval, opaque, white, imprinted with "MP100" in red ink
- 150 mg, oblong, opaque, white, imprinted with "MP150" in red ink
- 200 mg, oblong, opaque, white, imprinted with "MP200" in red ink
4. Contraindications
KYZATREX™ is contraindicated in:
- Patients with carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] .
- Women who are pregnant. Testosterone can cause virilization of the female fetus when administered to a pregnant woman [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to KYZATREX™ or any of its ingredients [see Description (11)] .
- Men with hypogonadal conditions, such as "age-related hypogonadism," that are not associated with structural or genetic etiologies. The efficacy of KYZATREX™ has not been established for these conditions, and KYZATREX™ can increase BP that can increase the risk of MACE [see Boxed Warning and Warning and Precautions (5.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Increase in Blood Pressure
In Study MRS-TU-2019EXT, KYZATREX™ increased 24-hour average systolic blood pressure (SBP) measured by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) by 1.7 mmHg from baseline after 4 months of treatment and 1.8 mmHg from baseline after 6 months of treatment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Three percent of KYZATREX™-treated patients were started on antihypertensive medications during the 6-month trial.
A history of antihypertensive treatment and diabetes mellitus at baseline were significant factors related to ambulatory SBP increases [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
Blood pressure (BP) increases can increase the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), with greater risk in patients with established cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease. In some patients, the increase in BP with KYZATREX™ may be too small to detect but can still increase the risk for MACE.
Before initiating KYZATREX™, consider the patient's baseline cardiovascular risk and ensure blood pressure is adequately controlled. Check BP periodically after initiating KYZATREX™ or increasing the dose and thereafter. Treat new-onset hypertension or exacerbations of pre-existing hypertension. Re-evaluate whether the benefits of continued treatment with KYZATREX™ outweigh its risks in patients who develop cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease.
5.2 Polycythemia
Androgens, including KYZATREX™, can cause increase in hemoglobin or hematocrit, reflective of increase in red blood cell mass. Check hematocrit prior to initiating KYZATREX™. An increase in red blood cell mass may increase the risk of thromboembolic events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] . Evaluate hematocrit approximately every 3 months while the patient is on KYZATREX™. If hematocrit becomes elevated, stop KYZATREX™ until the hematocrit decreases to an acceptable concentration. If KYZATREX™ is restarted and again causes hematocrit to become elevated, permanently discontinue KYZATREX™.
5.3 Cardiovascular Risk
Long-term clinical safety trials have not been conducted to assess the cardiovascular outcomes of testosterone replacement therapy in men. To date, epidemiologic studies and randomized controlled trials have been inconclusive for determining the risk of MACE, such as non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke, and cardiovascular death, with testosterone use compared to non-use. Some studies have reported an increased risk of MACE in association with use of testosterone replacement therapy in men.
KYZATREX™ can cause BP increases that can increase the risk of MACE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] . Patients should be informed of this possible risk when deciding whether to use or to continue to use KYZATREX™.
5.4 Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer
- Patients with BPH who are treated with androgens are at an increased risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH. Monitor patients with BPH for worsening signs and symptoms.
- Patients treated with androgens may be at increased risk for prostate cancer. Evaluate patients for prostate cancer prior to initiating and during treatment with androgens [see Contraindications (4)] .
5.5 Venous Thromboembolism
There have been post-marketing reports of venous thromboembolic events, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), in patients using testosterone replacement products such as KYZATREX™. Evaluate patients who report symptoms of pain, edema, warmth, and erythema in the lower extremity for DVT and those who present with acute shortness of breath for PE. If a venous thromboembolic event is suspected, discontinue KYZATREX™ and initiate appropriate workup and management [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.6 Abuse of Testosterone and Monitoring of Testosterone Concentrations
Testosterone has been subject to abuse, typically at doses higher than recommended for the approved indication and in combination with other anabolic androgenic steroids. Anabolic androgenic steroid abuse can lead to serious cardiovascular and psychiatric adverse reactions [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
If testosterone abuse is suspected, check testosterone concentrations to ensure they are within therapeutic range [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Testosterone levels may remain in the normal or subnormal range in men abusing synthetic testosterone derivatives. Counsel patients concerning the serious adverse reactions associated with abuse of testosterone and anabolic androgenic steroids. Also consider the possibility of testosterone and anabolic androgenic steroid abuse in suspected patients who present with serious cardiovascular or psychiatric adverse events.
5.7 Not for Use in Women
Due to lack of controlled studies in women and potential virilizing effects, KYZATREX™ is not indicated for use in women [see Contraindications (4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.2)].
5.8 Potential for Adverse Effects on Spermatogenesis
With large doses of exogenous androgens, including KYZATREX™, spermatogenesis may be suppressed through feedback inhibition of pituitary FSH, possibly leading to adverse effects on semen parameters including sperm count [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]. Inform patients of this possible risk when deciding whether to use or to continue to use KYZATREX™.
5.9 Hepatic Adverse Effects
KYZATREX™ is not a 17-alpha-alkyl androgen and is not known to cause hepatic adverse effects. However, prolonged use of high doses of orally active 17-alpha-alkyl androgens (e.g., methyltestosterone) has been associated with serious hepatic adverse effects (peliosis hepatis, hepatic neoplasms, cholestatic hepatitis, and jaundice). Peliosis hepatis can be a life-threatening or fatal complication. Long-term therapy with intramuscular testosterone enanthate has produced multiple hepatic adenomas. Patients should be instructed to report any signs or symptoms of hepatic dysfunction (e.g., jaundice). If these occur, promptly discontinue KYZATREX™ while the cause is evaluated.
5.10 Edema
Androgens, including KYZATREX™, may promote retention of sodium and water. Edema, with or without congestive heart failure, may be a serious complication in patients with pre-existing cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . In addition to discontinuation of the drug, diuretic therapy may be required.
5.11 Sleep Apnea
The treatment of hypogonadal men with testosterone may potentiate sleep apnea in some patients, especially those with risk factors such as obesity or chronic lung disease.
5.13 Lipid Changes
In clinical trials, patients receiving KYZATREX™ experienced reductions in lipid parameters, including total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Changes in the serum lipid profile may require dose adjustment of lipid lowering drugs or discontinuation of testosterone therapy. Monitor the lipid profile periodically, particularly after starting testosterone therapy.
5.14 Hypercalcemia
Androgens, including KYZATREX™, should be used with caution in cancer patients at risk of hypercalcemia (and associated hypercalciuria). Monitor serum calcium concentrations periodically during treatment with KYZATREX™ in these patients.
5.15 Decreased Thyroxine-binding Globulin
Androgens, including KYZATREX™, may decrease concentrations of thyroxin-binding globulin, resulting in decreased total T4 serum concentrations and increased resin uptake of T3 and T4. Free thyroid hormone concentrations remain unchanged, however, and there is no clinical evidence of thyroid dysfunction.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Increase in Blood Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Polycythemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiovascular Risk [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Venous Thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hepatic Adverse Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Sleep Apnea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Gynecomastia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Lipid Changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Hypercalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Decreased Thyroxine-binding Globulin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of KYZATREX™ was evaluated in Study MRS-TU-2019EXT in 155 hypogonadal males [see Clinical Studies (14)]. All patients initially received KYZATREX™ 200 mg orally twice daily. If needed, the dosage was titrated to 100 mg once daily in the morning or 100 mg, 300 mg, or 400 mg twice daily to achieve testosterone concentrations in the normal range . After the dosage titration period, patients continued their optimized dose for the remainder of the duration of the 6-month study. The mean duration of exposure was 168 days (range: 1 to 180 days). The median age was 52 years (range: 22 to 66 years); 77% were White, 19% were Black, 3% were Asian, and 2% were American Indian, Alaskan Native or Other.
Table 2 summarizes adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients in this 6-month study.
| Adverse Reaction | N = 155
n (%) |
|---|---|
|
|
| Hypertensión * | 4 (2.6) |
One (0.8%) patient who received KYZATREX™ experienced an adverse reaction (acne) that lead to premature discontinuation from the study.
In a 12-month, open-label study in hypogonadal adult males (N=212) who received KYZATREX™ 200 mg once daily to 400 mg twice daily (n=202) the following additional adverse reactions were reported: headache, arthralgia, diarrhea, hemoglobin increased, anxiety, constipation, peripheral edema, and PSA increased.
Blood Pressure Increases
Ambulatory (24-hour) and in-clinic (cuff) blood pressure Changes from Baseline for study MRS-TU-2019EXT are presented in Table 3 with 95% confidence intervals. No significant difference was observed between the 4-month and 6-month Changes from Baseline.
| Blood Pressure | Change from Baseline (95% CI) mm Hg | |
|---|---|---|
| Systolic | Diastolic | |
| 24-Hour Ambulatory | ||
| 4 Month | 1.7 (0.3 to 3.1) | 0.6 (-0.3 to 1.6) |
| 6 Month | 1.8 (0.3 to 3.2) | 0.6 (-0.4 to 1.6) |
| In-clinic (blood pressure cuff) | ||
| 4 Month | 2.7 (0.9 to 4.5) | 1.5 (0.3 to 2.6) |
| 6 Month | 2.4 (0.6 to 4.2) | 1.7 (0.5 to 2.9) |
A total of 5 of 155 patients (3.2%) in Study MRS-TU-2019EXT began taking new antihypertensive medications after study start. No patient had a dose increase in their antihypertensive medication by the end of treatment.
A history of antihypertensive treatment and diabetes mellitus at baseline were significant factors related to ambulatory SBP increases.
Table 4 presents the Least Squares Mean estimates of Change from Baseline, with 95% CI's, for sub-populations of subjects at study start either with or without hypertensive treatment or with or without diabetes mellitus.
| Subgroups | Ambulatory Systolic Blood Pressure Change from Baseline (95% CI), mm Hg |
|---|---|
| With hypertensive treatment at baseline (n=49) | |
| 4 Month | 3.4 (1.0 to 5.9) |
| 6 Month | 3.1 (0.6 to 5.6) |
| Without hypertensive treatment at baseline (n=90) | |
| 4 Month | 0.7 (-1.0 to 2.4) |
| 6 Month | 1.0 (-0.7 to 2.8) |
| With diabetes at baseline (n=29) | |
| 4 Month | 3.0 (-0.2 to 6.2) |
| 6 Month | 3.4 (0.2 to 6.7) |
| Without diabetes at baseline (n=110) | |
| 4 Month | 1.3 (-0.2 to 2.9) |
| 6 Month | 1.3 (-0.3 to 2.9) |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of testosterone. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular Disorders: myocardial infarction, stroke
Vascular Disorders: Venous thromboembolism
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Insulin
Changes in insulin sensitivity or glycemic control may occur in patients treated with androgens. In diabetic patients, the metabolic effects of androgens may decrease blood glucose and therefore necessitate a decrease in the dose of anti-diabetic medication.
7.2 Oral Vitamin K Antagonist Anticoagulants
Changes in anticoagulant activity may be seen with androgens; therefore, more frequent monitoring of international normalized ratio (INR) and prothrombin time are recommended in patients taking warfarin, especially at the initiation and termination of androgen therapy.
7.3 Corticosteroids
The concurrent use of testosterone with corticosteroids may result in increased fluid retention and requires careful monitoring particularly in patients with cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease.
7.4 Medications that May Also Increase Blood Pressure
Some prescription medications and nonprescription analgesic and cold medications contain drugs known to increase blood pressure. Concomitant administration of these medications with KYZATREX™ may lead to additional increases in blood pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of KYZATREX™ in pediatric patients less than 18 years old have not been established. KYZATREX™ is not recommended for use in patients less than 18 years of age because of the potential for acceleration of bone age and premature closure of epiphyses.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of KYZATREX™ did not include any patients 65 years of age and older. Therefore, it cannot be determined whether these patients respond differently from younger adult patients. Additionally, there are insufficient long-term safety data in geriatric patients to assess the potentially increased risk of cardiovascular disease and prostate cancer.
Geriatric patients treated with androgens including KYZATREX™ may be at risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] .
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
KYZATREX™ contains testosterone undecanoate, a Schedule III controlled substance
9.2 Abuse
Drug abuse is intentional non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological and physiological effects. Abuse and misuse of testosterone are seen in male and female adults and adolescents. Testosterone, often in combination with other anabolic androgenic steroids, and not obtained by prescription through a pharmacy, may be abused by athletes and bodybuilders. There have been reports of misuse by men taking higher doses of legally obtained testosterone than prescribed and continuing testosterone despite adverse events or against medical advice.
10. Overdosage
There is one report of acute overdosage with use of an approved injectable testosterone product: this subject had serum testosterone levels of up to 11,400 ng/dL with a cerebrovascular accident.
Treatment of overdosage consists of discontinuation of KYZATREX™ and appropriate symptomatic and supportive care.
11. Kyzatrex Description
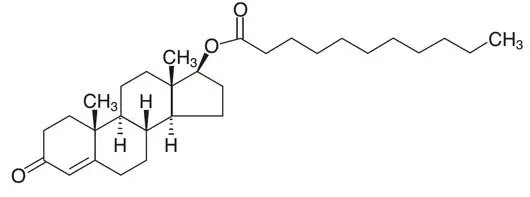
KYZATREX™ is provided as a gelatin capsule containing testosterone undecanoate, a fatty-acid ester of testosterone. Testosterone undecanoate is a white to off-white yellow crystalline powder. Testosterone, an androgen, is formed by cleavage of the ester side chain of testosterone undecanoate.
Testosterone undecanoate is chemically described as 17β-hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one undecanoate. It has the empirical formula of C 30H 48O 3 and a molecular weight of 456.7 g/mol. The structural formula for testosterone undecanoate is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Testosterone Undecanoate
KYZATREX™ (testosterone undecanoate) capsules for oral use are available in three dosage strengths- 100 mg, 150 mg, and 200 mg. The 100 mg strength is an opaque, white capsule imprinted with "MP100" in red ink. The 150 mg strength is an opaque white capsule imprinted with "MP150" in red ink. The 200 mg strength is an opaque white capsule imprinted with "MP200" in red ink. All capsule strengths also contain DL-alpha-tocopheryl acetate (Vitamin E), phytosterol esters, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and propylene glycol monolaurate as inactive ingredients.
Gelatin capsule shells are composed of the following inactive ingredients: gelatin, glycerin, purified water, sorbitol, and titanium dioxide.
12. Kyzatrex - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Endogenous androgens, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are responsible for the normal growth and development of the male sex organs and for maintenance of secondary sex characteristics. These effects include the growth and maturation of prostate, seminal vesicles, penis, and scrotum; the development of male hair distribution, such as facial, pubic, chest, and axillary hair; laryngeal enlargement; vocal cord thickening; alterations in body musculature; and fat distribution.
Male hypogonadism, a clinical syndrome resulting from insufficient secretion of testosterone, has two main etiologies. Primary hypogonadism is caused by defects of the gonads, such as Klinefelter syndrome or Leydig cell aplasia, whereas secondary hypogonadism (also known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism) is the failure of the hypothalamus (or pituitary gland) to produce sufficient gonadotropins (FSH, LH).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
There is insufficient data to characterize an exposure-response relationship or time course of pharmacodynamics.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
KYZATREX™ was taken orally at a starting dose of 200 mg twice per day with meals in a multicenter, open-label trial in hypogonadal males. The dose was adjusted, as needed, on Days 28 and 56 from a minimum dose of 100 mg (morning-only) to a maximum dose of 400 mg twice per day based on the plasma testosterone concentration obtained by a single blood draw collected 3 to 5 hours after the morning dose. The average daily NaF/EDTA plasma testosterone concentration was 393.3 (±113.6) ng/dL after 90 days of treatment (normal eugonadal range in NaF/EDTA plasma: 222-800 ng/dL. Note that the titration scheme for use in clinical practice is based on serum total testosterone [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] .
KYZATREX™ is expected to produce testosterone concentrations that approximate normal concentrations seen in healthy men.
Table 5 summarizes the pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters for plasma total testosterone in patients completing at least 90 days of KYZATREX™ treatment administered daily.
| PK Parameter | Plasma (N=130) | |
|---|---|---|
| PK = pharmacokinetic; C avg = 24-hour average concentration; C max = maximum concentration | ||
| C avg (ng/dL) | n | 127 |
| Mean | 393.3 | |
| SD | 113.6 | |
| C max (ng/dL) | n | 130 |
| Mean | 852.4 | |
| SD | 311.3 | |
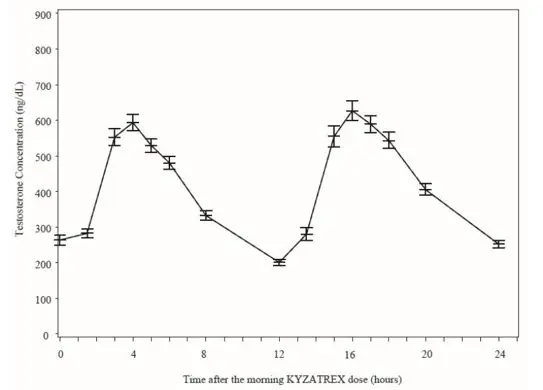
Figure 2 summarizes the mean plasma total testosterone profile at the final PK visit.
|
|
| SEM = standard error of the mean
Testosterone normal ranges: plasma = 222-800 ng/dL |
When KYZATREX™ was given with breakfast containing 16%, 33%, and 45% fat, the exposure (AUC 0-24 hr) of testosterone was increased by 37%, 87%, and 94%, respectively, compared to when given under fasted conditions. The primary efficacy and safety study was conducted under fed conditions regardless of the type of meals and the primary efficacy endpoint of achieving testosterone C avg in normal testosterone range was met.
There was no effect on testosterone PK when KYZATREX™ was administered with 20% alcohol along with a high-fat meal versus a high-fat meal alone.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
A 3-month repeat-dose oral toxicity study in male eugonadal dogs was conducted to evaluate whether phytosterol esters present in the KYZATREX™ formulation influenced target organ toxicity due to their structural similarities to sex steroids like testosterone. KYZATREX™ doses 2 times the MRHDD (based on mean AUC exposure to testosterone) produced similar effects on androgen-responsive tissues as testosterone undecanoate without phytosterol esters. These included mild to marked effects on the testes (decreased size, germ cell depletion, Leydig cell atrophy), epididymides (aspermia), adrenal glands (vacuolation in the zona fasciculata) and prostate (increased size and glandular hypertrophy/hyperplasia). Following a 4-week treatment-free period, findings in the testes, epididymides, and adrenal glands were not fully reversible at doses of 2 times the MRHDD of KYZATREX™ as compared to treatment with the excipients alone, including phytosterol esters. Reversibility was not assessed in testosterone undecanoate groups without phytosterol esters.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy and safety of KYZATREX™ were evaluated in Study MRS-TU-2019EXT (NCT04467697) a multi-center, open-label study of approximately 6 months of duration in 155 hypogonadal males.
Patients received KYZATREX™ at a starting dose of 200 mg twice daily with meals. The dosage was adjusted on Days 28 and 56 between a minimum dose of 100 mg (single morning dose) and a maximum dose of 800 mg (400 mg twice daily) based on plasma testosterone concentration from a single blood draw between 3 to 5 hours after the morning dose.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the percentage of KYZATREX™-treated patients with mean plasma total testosterone concentration (C avg) over 24-hours within the normal range of 222-800 ng/dL on the final PK visit of the study at Day 90.
The efficacy population consisted of 139 hypogonadal, males with a median age of 50 years (range 22 to 66 years), 79% were White, 16% were Black, 3% were Asian, and 2% were American Indian, Alaskan Native or Other.
Primary efficacy results are summarized in Table 6.
| Parameter | N=139 |
|---|---|
| C avg = 24-hour average concentration | |
| Patients (%) with Testosterone, C avg (ng/dL), 222-800 ng/dL | 122 (88%) |
| 95% Confidence Interval | (82%, 93%) |
Secondary endpoints were the percentage of patients with a maximum total testosterone concentration (C max) meeting three predetermined limits: less than or equal to 1.5 times the upper limit of normal range (ULN) (1200 ng/dL), between 1.8 and 2.5 times ULN (1440-2000 ng/dL), and greater than 2.5 times ULN (2000 ng/dL).
The percentage of patients who received KYZATREX™ and had testosterone Cmax threshold less than or equal to 1200 ng/dL, between 1440 and 2000 ng/dL, and greater than 2000 ng/dL at the final PK visit were 88%, 4%, and 0%, respectively.
16. How is Kyzatrex supplied
KYZATREX™ capsules are available in three strengths of 100 mg, 150 mg, and 200 mg packaged as 90 and 120 units in wide-mouth, round, white HDPE bottles with white, polypropylene, child resistant caps and induction-sealed liner.
100 mg: Oval, opaque, white capsules imprinted with "MP100" in red ink supplied in bottles; NDC 80603-101-11 for 90 capsules and NDC 80603-101-22 for 120 capsules.
150 mg: Oblong, opaque, white capsules imprinted with "MP150" in red ink supplied in bottles; NDC 80603-103-11 for 90 capsules and NDC 80603-103-22 for 120 capsules.
200 mg: Oblong, opaque, white capsules imprinted with "MP200" in red ink supplied in bottles; NDC 80603-105-11 for 90 capsules and NDC 80603-105-22 for 120 capsules.
| KYZATREX
testosterone undecanoate capsule, liquid filled |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| KYZATREX
testosterone undecanoate capsule, liquid filled |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| KYZATREX
testosterone undecanoate capsule, liquid filled |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Marius Pharmaceuticals (080572348) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Procaps S A | 880090568 | manufacture(80603-101, 80603-103, 80603-105) | |