Drug Detail:Liptruzet (Atorvastatin and ezetimibe [ a-tor-va-stat-in-and-e-zet-i-mibe ])
Drug Class: Antihyperlipidemic combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
LIPTRUZET™ (ezetimibe and atorvastatin) tablets for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2013
Indications and Usage for Liptruzet Tablets
LIPTRUZET, which contains a cholesterol absorption inhibitor and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin), is indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet to:
- reduce elevated total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C, and to increase HDL-C in patients with primary (heterozygous familial and non-familial) hyperlipidemia or mixed hyperlipidemia. (1.1)
- reduce elevated total-C and LDL-C in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH), as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments. (1.2)
Limitations of Use
- No incremental benefit of LIPTRUZET on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality over and above that demonstrated for atorvastatin has been established. LIPTRUZET has not been studied in Fredrickson Type I, III, IV, and V dyslipidemias. (1.3)
Liptruzet Tablets Dosage and Administration
- Dosage range is 10/10 mg/day through 10/80 mg/day. (2.1)
- Recommended starting dose is 10/10 mg/day or 10/20 mg/day. (2.1)
- Recommended starting dose is 10/40 mg/day for patients requiring a >55% reduction in LDL-C. (2.1)
- Dosing of LIPTRUZET should occur either ≥2 hours before or ≥4 hours after administration of a bile acid sequestrant. (2.3, 7.11)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets (ezetimibe mg/atorvastatin mg): 10/10, 10/20, 10/40, 10/80. (3)
Contraindications
- Active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations of hepatic transaminase levels. (4, 5.2)
- Hypersensitivity to any component of LIPTRUZET. (4, 6.2)
- Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant. (4, 8.1)
- Nursing mothers. (4, 8.3)
Warnings and Precautions
- Patients should be advised to report promptly any unexplained and/or persistent muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness. LIPTRUZET should be discontinued immediately if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. (5.1)
- Skeletal muscle effects (e.g., myopathy and rhabdomyolysis): Risks increase with higher doses and concomitant use of certain CYP3A4 inhibitors, fibric acid derivatives, and cyclosporine. Predisposing factors include advanced age (>65), uncontrolled hypothyroidism, and renal impairment. Rare cases of rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria have been reported. (5.1, 8.5)
- Liver enzyme abnormalities: Persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase can occur. Check liver enzyme tests before initiating therapy and as clinically indicated thereafter. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Common adverse reactions (incidence ≥2% and greater than placebo) are: increased ALT, increased AST, and musculoskeletal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
| Interacting Agents | Prescribing Recommendations for LIPTRUZET |
|---|---|
| Cyclosporine, HIV protease inhibitors (tipranavir plus ritonavir), hepatitis C protease inhibitor (telaprevir), gemfibrozil | Avoid LIPTRUZET |
| HIV protease inhibitor (lopinavir plus ritonavir) | Use with caution and lowest dose necessary. |
| Clarithromycin, itraconazole, HIV protease inhibitors (saquinavir plus ritonavir, darunavir plus ritonavir, fosamprenavir, fosamprenavir plus ritonavir) | Do not exceed 10/20 mg LIPTRUZET daily. |
| HIV protease inhibitor (nelfinavir), hepatitis C protease inhibitor (boceprevir) | Do not exceed 10/40 mg LIPTRUZET daily. |
- Other lipid-lowering medications: Use with fenofibrates or lipid-modifying doses (≥1 g/day) of niacin increases the risk of adverse skeletal muscle effects. Caution should be used when prescribing with LIPTRUZET. (7)
- Fenofibrates: Combination increases exposure of ezetimibe. If cholelithiasis is suspected in a patient receiving ezetimibe and a fenofibrate, gallbladder studies are indicated and alternative lipid-lowering therapy should be considered. (7.5, 12.3)
- Cholestyramine: Combination decreases exposure of ezetimibe. (2.3, 12.3)
- Digoxin: Patients should be monitored appropriately. (7.7)
- Oral contraceptives: Values for norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol may be increased. (7.8)
- Rifampin should be simultaneously coadministered with LIPTRUZET. (7.9)
Use In Specific Populations
- Hepatic impairment: Plasma concentrations of atorvastatin are markedly increased in patients with chronic alcoholic liver disease. (8.6, 12.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 5/2013
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Liptruzet Tablets
Therapy with lipid-altering agents should be only one component of multiple risk factor intervention in individuals at significantly increased risk for atherosclerotic vascular disease due to hypercholesterolemia. Drug therapy is indicated as an adjunct to diet when the response to a diet restricted in saturated fat and cholesterol and other nonpharmacologic measures alone has been inadequate.
1.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
LIPTRUZET™ is indicated for the reduction of elevated total cholesterol (total-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), apolipoprotein B (Apo B), triglycerides (TG), and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), and to increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in patients with primary (heterozygous familial and non-familial) hyperlipidemia or mixed hyperlipidemia.
2. Liptruzet Tablets Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosing
The dosage range of LIPTRUZET is 10/10 mg/day to 10/80 mg/day. The recommended starting dose of LIPTRUZET is 10/10 mg/day or 10/20 mg/day. LIPTRUZET can be administered as a single dose at any time of the day, with or without food. The recommended starting dose for patients who require a larger reduction in LDL-C (greater than 55%) is 10/40 mg/day. After initiation and/or upon titration of LIPTRUZET, lipid levels should be analyzed within 2 or more weeks and dosage adjusted accordingly.
Patients should swallow LIPTRUZET tablets whole. Tablets should not be crushed, dissolved, or chewed.
2.2 Patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
The dosage of LIPTRUZET in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia is 10/40 mg/day or 10/80 mg/day. LIPTRUZET should be used as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments (e.g., LDL apheresis) in these patients or if such treatments are unavailable.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- LIPTRUZET™ 10 mg/10 mg (ezetimibe 10 mg/atorvastatin 10 mg) tablets are white to off-white capsule-shaped, biconvex film-coated tablets with code "320" on one side.
- LIPTRUZET™ 10 mg/20 mg (ezetimibe 10 mg/atorvastatin 20 mg) tablets are white to off-white round, biconvex film-coated tablets with code "321" on one side.
- LIPTRUZET™ 10 mg/40 mg (ezetimibe 10 mg/atorvastatin 40 mg) tablets are white to off-white oval, biconvex film-coated tablets with code "322" on one side.
- LIPTRUZET™ 10 mg/80 mg (ezetimibe 10 mg/atorvastatin 80 mg) tablets are white to off-white capsule-shaped, biconvex film-coated tablets with code "323" on one side.
4. Contraindications
Active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations of hepatic transaminase levels.
Hypersensitivity to any component of LIPTRUZET [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant. LIPTRUZET may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy, and cholesterol or cholesterol derivatives are essential for fetal development. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process and discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on the outcome of long-term therapy of primary hypercholesterolemia. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of LIPTRUZET use during pregnancy; however in rare reports, congenital anomalies were observed following intrauterine exposure to statins. In rat and rabbit animal reproduction studies, atorvastatin revealed no evidence of teratogenicity. LIPTRUZET should be administered to women of childbearing age only when such patients are highly unlikely to conceive and have been informed of the potential hazards. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, LIPTRUZET should be discontinued immediately, and the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Nursing mothers. It is not known whether atorvastatin is excreted into human milk; however, a small amount of another drug in this class does pass into breast milk. Because statins have the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women who require LIPTRUZET treatment should not breast-feed their infants [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis
Atorvastatin
Rare cases of rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria have been reported with atorvastatin and with other drugs in this class. A history of renal impairment may be a risk factor for the development of rhabdomyolysis. Such patients merit closer monitoring for skeletal muscle effects.
Atorvastatin, like other statins, occasionally causes myopathy, defined as muscle aches or muscle weakness in conjunction with increases in creatine phosphokinase (CPK) values >10 times upper limit of normal (ULN). The concomitant use of higher doses of atorvastatin with certain drugs such as cyclosporine and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, itraconazole, and HIV protease inhibitors) increases the risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis.
There have been rare reports of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), an autoimmune myopathy, associated with statin use. IMNM is characterized by: proximal muscle weakness and elevated serum creatinine kinase, which persist despite discontinuation of statin treatment; muscle biopsy showing necrotizing myopathy without significant inflammation; improvement with immunosuppressive agents.
Myopathy should be considered in any patient with diffuse myalgias, muscle tenderness or weakness, and/or marked elevation of CPK. Patients should be advised to report promptly unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness, particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever or if muscle signs and symptoms persist after discontinuing LIPTRUZET. LIPTRUZET therapy should be discontinued if markedly elevated CPK levels occur or myopathy is diagnosed or suspected.
The risk of myopathy during treatment with statins is increased with concurrent administration of cyclosporine, fibric acid derivatives, erythromycin, clarithromycin, the hepatitis C protease inhibitor telaprevir, combinations of HIV protease inhibitors, including saquinavir plus ritonavir, lopinavir plus ritonavir, tipranavir plus ritonavir, darunavir plus ritonavir, fosamprenavir, and fosamprenavir plus ritonavir, niacin, or azole antifungals. Physicians considering combined therapy with LIPTRUZET and fibric acid derivatives, erythromycin, clarithromycin, a combination of saquinavir plus ritonavir, lopinavir plus ritonavir, darunavir plus ritonavir, fosamprenavir, or fosamprenavir plus ritonavir, azole antifungals, or lipid-modifying doses of niacin should carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks and should carefully monitor patients for any signs or symptoms of muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, particularly during the initial months of therapy and during any periods of upward dosage titration of either drug. Lower starting and maintenance doses of LIPTRUZET should be considered when taken concomitantly with the aforementioned drugs. [See Drug Interactions (7).] Periodic CPK determinations may be considered in such situations, but there is no assurance that such monitoring will prevent the occurrence of severe myopathy.
Prescribing recommendations for interacting agents are summarized in Table 1 [see also Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Interacting Agents | Prescribing Recommendations for LIPTRUZET |
|---|---|
|
|
| Cyclosporine, HIV protease inhibitors (tipranavir plus ritonavir), hepatitis C protease inhibitor (telaprevir), gemfibrozil | Avoid LIPTRUZET. |
| HIV protease inhibitor (lopinavir plus ritonavir) | Use with caution and lowest dose necessary. |
| Clarithromycin, itraconazole, HIV protease inhibitors (saquinavir plus ritonavir*, darunavir plus ritonavir, fosamprenavir, fosamprenavir plus ritonavir) | Do not exceed 10/20 mg LIPTRUZET daily. |
| HIV protease inhibitor (nelfinavir), hepatitis C protease inhibitor (boceprevir) | Do not exceed 10/40 mg LIPTRUZET daily. |
Cases of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, have been reported with atorvastatin coadministered with colchicine, and caution should be exercised when prescribing LIPTRUZET with colchicine [see Drug Interactions (7.10)].
LIPTRUZET therapy should be temporarily withheld or discontinued in any patient with an acute, serious condition suggestive of a myopathy or having a risk factor predisposing to the development of renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis (e.g., severe acute infection, hypotension, major surgery, trauma, severe metabolic, endocrine and electrolyte disorders, and uncontrolled seizures).
5.3 Endocrine Function
Increases in HbA1c and fasting serum glucose levels have been reported with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, including atorvastatin.
Statins interfere with cholesterol synthesis and theoretically might blunt adrenal and/or gonadal steroid production. Clinical studies have shown that atorvastatin does not reduce basal plasma cortisol concentration or impair adrenal reserve and that ezetimibe did not impair adrenocortical steroid hormone production. The effects of statins on male fertility have not been studied in adequate numbers of patients. The effects, if any, on the pituitary-gonadal axis in premenopausal women are unknown. Caution should be exercised if LIPTRUZET is administered concomitantly with drugs that may decrease the levels or activity of endogenous steroid hormones, such as ketoconazole, spironolactone, and cimetidine.
5.4 Use in Patients with Recent Stroke or TIA
In a post-hoc analysis of the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) study where atorvastatin 80 mg vs. placebo was administered in 4,731 subjects without CHD who had a stroke or TIA within the preceding 6 months, a higher incidence of hemorrhagic stroke was seen in the atorvastatin 80 mg group compared to placebo (55, 2.3% atorvastatin vs. 33, 1.4% placebo; HR: 1.68, 95% CI: 1.09, 2.59; p=0.0168). The incidence of fatal hemorrhagic stroke was similar across treatment groups (17 vs. 18 for the atorvastatin and placebo groups, respectively). The incidence of nonfatal hemorrhagic stroke was significantly higher in the atorvastatin (38, 1.6%) group as compared to the placebo group (16, 0.7%). Some baseline characteristics, including hemorrhagic and lacunar stroke on study entry, were associated with a higher incidence of hemorrhagic stroke in the atorvastatin group.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Rhabdomyolysis and myopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Liver enzyme abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Ezetimibe
In 10 double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials, 2396 patients with primary hyperlipidemia (age range 9-86 years, 50% women, 90% Caucasians, 5% Blacks, 3% Hispanics, 2% Asians) and elevated LDL-C were treated with ezetimibe 10 mg/day for a median treatment duration of 12 weeks (range 0 to 39 weeks).
Adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with ezetimibe and at an incidence greater than placebo regardless of causality assessment are shown in Table 3.
| Body System/Organ Class Adverse Reaction | Ezetimibe 10 mg (%) n=2396 | Placebo (%) n=1159 |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 4.1 | 3.7 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue | 2.4 | 1.5 |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Influenza | 2.0 | 1.5 |
| Sinusitis | 2.8 | 2.2 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 4.3 | 2.5 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Arthralgia | 3.0 | 2.2 |
| Pain in extremity | 2.7 | 2.5 |
Atorvastatin
In an atorvastatin placebo-controlled clinical trial database of 16,066 patients (8755 atorvastatin vs. 7311 placebo; age range 10–93 years, 39% women, 91% Caucasians, 3% Blacks, 2% Asians, 4% other) with a median treatment duration of 53 weeks, 9.7% of patients on atorvastatin and 9.5% of the patients on placebo discontinued due to adverse reactions regardless of causality.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥2% and greater than placebo) regardless of causality, in patients treated with atorvastatin in placebo controlled trials (n=8755) were: nasopharyngitis (8.3%), arthralgia (6.9%), diarrhea (6.8%), pain in extremity (6.0%), and urinary tract infection (5.7%).
Table 4 summarizes the frequency of clinical adverse reactions, regardless of causality, reported in ≥2% and at a rate greater than placebo in patients treated with atorvastatin (n=8755), from seventeen placebo-controlled trials.
| Adverse Reaction* | Any dose n=8755 | Atorvastatin 10 mg n=3908 | Atorvastatin 20 mg n=188 | Atorvastatin 40 mg n=604 | Atorvastatin 80 mg n=4055 | Placebo n=7311 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Nasopharyngitis | 8.3 | 12.9 | 5.3 | 7.0 | 4.2 | 8.2 |
| Arthralgia | 6.9 | 8.9 | 11.7 | 10.6 | 4.3 | 6.5 |
| Diarrhea | 6.8 | 7.3 | 6.4 | 14.1 | 5.2 | 6.3 |
| Pain in extremity | 6.0 | 8.5 | 3.7 | 9.3 | 3.1 | 5.9 |
| Urinary tract infection | 5.7 | 6.9 | 6.4 | 8.0 | 4.1 | 5.6 |
| Dyspepsia | 4.7 | 5.9 | 3.2 | 6.0 | 3.3 | 4.3 |
| Nausea | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 7.1 | 3.8 | 3.5 |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 3.8 | 5.2 | 3.2 | 5.1 | 2.3 | 3.6 |
| Muscle spasms | 3.6 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 5.1 | 2.4 | 3.0 |
| Myalgia | 3.5 | 3.6 | 5.9 | 8.4 | 2.7 | 3.1 |
| Insomnia | 3.0 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 5.3 | 2.8 | 2.9 |
| Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 2.3 | 3.9 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 0.7 | 2.1 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because the reactions below are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The additional events described below have been identified during post-approval use of ezetimibe and/or atorvastatin.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: thrombocytopenia
Nervous system disorders: headache; paresthesia; peripheral neuropathy
There have been rare postmarketing reports of cognitive impairment (e.g., memory loss, forgetfulness, amnesia, memory impairment, confusion) associated with statin use. These cognitive issues have been reported for all statins. The reports are generally nonserious, and reversible upon statin discontinuation, with variable times to symptom onset (1 day to years) and symptom resolution (median of 3 weeks).
Gastrointestinal disorders: pancreatitis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: angioedema; bullous rashes (including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis); rash; urticaria
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: myopathy/rhabdomyolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
There have been rare reports of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy associated with statin use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: tendon rupture
Immune system disorders: anaphylaxis; hypersensitivity reactions
Hepatobiliary disorders: hepatitis; cholelithiasis; cholecystitis; fatal and nonfatal hepatic failure
Psychiatric disorders: depression
Laboratory abnormalities: elevated creatine phosphokinase
7. Drug Interactions
[See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3).]
7.1 Strong Inhibitors of Cytochrome P450 3A4
Atorvastatin is metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4. Concomitant administration of atorvastatin with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 can lead to increases in plasma concentrations of atorvastatin. The extent of interaction and potentiation of effects depend on the variability of effect on CYP3A4. Because LIPTRUZET contains atorvastatin, the risk of myopathy during treatment with LIPTRUZET is increased with concurrent administration of:
- Clarithromycin: Atorvastatin AUC was significantly increased with concomitant administration of 80 mg atorvastatin with clarithromycin (500 mg twice daily) compared to that of atorvastatin alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, in patients taking clarithromycin, caution should be used when the LIPTRUZET dose exceeds 10/20 mg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Combination of Protease Inhibitors: Atorvastatin AUC was significantly increased with concomitant administration of atorvastatin with several combinations of HIV protease inhibitors, as well as with the hepatitis C protease inhibitor telaprevir, compared to that of atorvastatin alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, in patients taking the HIV protease inhibitor tipranavir plus ritonavir, or the hepatitis C protease inhibitor telaprevir, concomitant use of LIPTRUZET should be avoided. In patients taking the HIV protease inhibitor lopinavir plus ritonavir, caution should be used when prescribing LIPTRUZET and the lowest dose necessary should be used. In patients taking the HIV protease inhibitors saquinavir plus ritonavir, darunavir plus ritonavir, fosamprenavir, or fosamprenavir plus ritonavir, the dose of LIPTRUZET should not exceed 10/20 mg and should be used with caution [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. In patients taking the HIV protease inhibitor nelfinavir or the hepatitis C protease inhibitor boceprevir, the dose of LIPTRUZET should not exceed 10/40 mg daily and close clinical monitoring is recommended.
- Itraconazole: Atorvastatin AUC was significantly increased with concomitant administration of atorvastatin 40 mg and itraconazole 200 mg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, in patients taking itraconazole, do not use a LIPTRUZET dose that exceeds 10/20 mg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
7.2 Cyclosporine
Atorvastatin and atorvastatin-metabolites are substrates of the OATP1B1 transporter. Inhibitors of the OATP1B1 (e.g., cyclosporine) can increase the bioavailability of atorvastatin. Atorvastatin AUC was significantly increased with concomitant administration of atorvastatin 10 mg and cyclosporine 5.2 mg/kg/day compared to that of atorvastatin alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In addition, ezetimibe and cyclosporine used concomitantly can increase exposure to both ezetimibe and cyclosporine. The degree of increase in ezetimibe exposure may be greater in patients with severe renal impairment.
The coadministration of LIPTRUZET with cyclosporine should be avoided [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.3 Grapefruit Juice
Grapefruit juice contains one or more components that inhibit CYP3A4 and can increase plasma concentrations of atorvastatin, especially with excessive grapefruit juice consumption (>1.2 liters per day).
7.4 Gemfibrozil
Due to an increased risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis when HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors are coadministered with gemfibrozil, concomitant administration of LIPTRUZET with gemfibrozil should be avoided [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.5 Fenofibrates (e.g., fenofibrate and fenofibric acid)
Because it is known that the risk of myopathy during treatment with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors is increased with concurrent administration of fenofibrates, LIPTRUZET should be administered with caution when used concomitantly with a fenofibrate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Fenofibrates may increase cholesterol excretion into the bile, leading to cholelithiasis. If cholelithiasis is suspected in a patient receiving LIPTRUZET and a fenofibrate, gallbladder studies are indicated and alternative lipid-lowering therapy should be considered [see the product labeling for fenofibrate and fenofibric acid].
7.6 Niacin
The risk of skeletal muscle effects may be enhanced when LIPTRUZET is used in combination with niacin; a reduction in LIPTRUZET dosage should be considered in this setting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.7 Digoxin
When multiple doses of atorvastatin and digoxin were coadministered, steady state plasma digoxin concentrations increased by approximately 20%. Patients taking digoxin should be monitored appropriately.
7.8 Oral Contraceptives
Coadministration of atorvastatin and an oral contraceptive increased AUC values for norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. These increases should be considered when selecting an oral contraceptive for a woman taking LIPTRUZET.
7.9 Rifampin or Other Inducers of Cytochrome P450 3A4
Concomitant administration of atorvastatin with inducers of cytochrome P450 3A4 (e.g., efavirenz, rifampin) can lead to variable reductions in plasma concentrations of atorvastatin. Due to the dual interaction mechanism of rifampin, simultaneous coadministration of LIPTRUZET with rifampin is recommended, as delayed administration of atorvastatin after administration of rifampin has been associated with a significant reduction in atorvastatin plasma concentrations.
7.10 Colchicine
Cases of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, have been reported with atorvastatin coadministered with colchicine, and caution should be exercised when prescribing LIPTRUZET with colchicine.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Nursing Mothers
In rat studies, exposure to total ezetimibe in nursing pups was up to half of that observed in maternal plasma. It is not known whether ezetimibe is excreted into human breast milk.
It is not known whether atorvastatin is excreted in human milk, but a small amount of another drug in this class does pass into breast milk. Nursing rat pups had plasma and liver atorvastatin levels of 50% and 40%, respectively, of that in their mother's milk. Because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants, women taking LIPTRUZET should not breast-feed [see Contraindications (4)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the patients who received ezetimibe coadministered with atorvastatin in clinical studies, 1166 were 65 and older (this included 291 who were 75 and older). The effectiveness and safety of LIPTRUZET were similar between these patients and younger subjects. Greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. Since advanced age (≥65 years) is a predisposing factor for myopathy, LIPTRUZET should be prescribed with caution in the elderly. [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3).]
In geriatric patients, no dosage adjustment of LIPTRUZET is necessary.
11. Liptruzet Tablets Description
LIPTRUZET contains ezetimibe, a selective inhibitor of intestinal cholesterol and related phytosterol absorption, and atorvastatin, a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor.
The chemical name of ezetimibe is 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(R)-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(S)-hydroxypropyl]-4(S)-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone. The empirical formula is C24H21F2NO3. Its molecular weight is 409.4.
Ezetimibe is a white, crystalline powder that is freely to very soluble in ethanol, methanol, and acetone and practically insoluble in water. Its structural formula is:
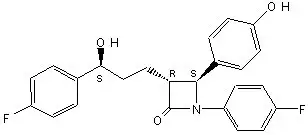
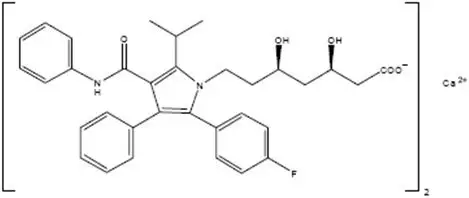
Atorvastatin is [R-(R*, R*)]-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-ß, δ-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-[(phenylamino) carbonyl]-1H-pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid, calcium salt (2:1).
Atorvastatin calcium is a white to off-white amorphous powder that is very slightly soluble in water, insoluble in acetonitrile, and soluble in methanol. The empirical formula of atorvastatin calcium is (C33H34FN2O5)2Ca. The molecular weight of atorvastatin calcium is 1155.37. Its structural formula is:
LIPTRUZET is available for oral use as tablets containing 10 mg of ezetimibe and: 10.34 mg of atorvastatin calcium, equivalent to 10 mg of atorvastatin (LIPTRUZET 10 mg/10 mg); 20.68 mg of atorvastatin calcium, equivalent to 20 mg of atorvastatin (LIPTRUZET 10 mg/20 mg); 41.37 mg of atorvastatin calcium, equivalent to 40 mg of atorvastatin (LIPTRUZET 10 mg/40 mg); or 82.73 mg of atorvastatin calcium, equivalent to 80 mg of atorvastatin (LIPTRUZET 10 mg/80 mg). Each film-coated tablet of LIPTRUZET contains the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, magnesium stearate, lactose anhydrous, hydroxypropyl cellulose, and sodium bicarbonate. In addition, the film coating contains the following inactive ingredients: hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, and carnauba wax.
12. Liptruzet Tablets - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Clinical studies have demonstrated that elevated levels of total-C, LDL-C and Apo B, the major protein constituent of LDL, promote human atherosclerosis. In addition, decreased levels of HDL-C are associated with the development of atherosclerosis. Epidemiologic studies have established that cardiovascular morbidity and mortality vary directly with the level of total-C and LDL-C and inversely with the level of HDL-C. Like LDL, cholesterol-enriched triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, including very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL), and remnants, can also promote atherosclerosis. The independent effect of raising HDL-C or lowering TG on the risk of coronary and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
Atorvastatin as well as some of its metabolites are pharmacologically active in humans. The liver is the primary site of action and the principal site of cholesterol synthesis and LDL clearance. Drug dosage, rather than systemic drug concentration, correlates better with LDL-C reduction. Individualization of drug dosage should be based on therapeutic response [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Specific Populations
Drug Interactions [See also Drug Interactions (7).]
No clinically significant pharmacokinetic interaction was seen when ezetimibe was coadministered with atorvastatin. Specific pharmacokinetic drug interaction studies with LIPTRUZET have not been performed.
Cytochrome P450: Ezetimibe had no significant effect on a series of probe drugs (caffeine, dextromethorphan, tolbutamide, and IV midazolam) known to be metabolized by cytochrome P450 (1A2, 2D6, 2C8/9 and 3A4) in a "cocktail" study of twelve healthy adult males. This indicates that ezetimibe is neither an inhibitor nor an inducer of these cytochrome P450 isozymes, and it is unlikely that ezetimibe will affect the metabolism of drugs that are metabolized by these enzymes.
Atorvastatin is metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4. Concomitant administration of LIPTRUZET with inhibitors of cytochrome P450 3A4 can lead to increases in plasma concentrations of the atorvastatin component of LIPTRUZET. The extent of interaction and potentiation of effects depends on the variability of effect on cytochrome P450 3A4.
Ezetimibe
| Coadministered Drug and Dosing Regimen | Total Ezetimibe* | |
|---|---|---|
| Change in AUC | Change in Cmax | |
|
||
| Cyclosporine-stable dose required (75-150 mg BID)†,‡ | ↑240% | ↑290% |
| Fenofibrate, 200 mg QD, 14 days‡ | ↑48% | ↑64% |
| Gemfibrozil, 600 mg BID, 7 days‡ | ↑64% | ↑91% |
| Cholestyramine, 4 g BID, 14 days‡ | ↓55% | ↓4% |
| Aluminum & magnesium hydroxide combination antacid, single dose§ | ↓4% | ↓30% |
| Cimetidine, 400 mg BID, 7 days | ↑6% | ↑22% |
| Glipizide, 10 mg, single dose | ↑4% | ↓8% |
| Statins | ||
| Lovastatin 20 mg QD, 7 days | ↑9% | ↑3% |
| Pravastatin 20 mg QD, 14 days | ↑7% | ↑23% |
| Atorvastatin 10 mg QD, 14 days | ↓2% | ↑12% |
| Rosuvastatin 10 mg QD, 14 days | ↑13% | ↑18% |
| Fluvastatin 20 mg QD, 14 days | ↓19% | ↑7% |
| Coadministered Drug and its Dosage Regimen | Ezetimibe Dosage Regimen | Change in AUC of Coadministered Drug | Change in Cmax
of Coadministered Drug |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Warfarin, 25 mg single dose on Day 7 | 10 mg QD, 11 days | ↓2% (R-warfarin) ↓4% (S-warfarin) | ↑3% (R-warfarin) ↑1% (S-warfarin) |
| Digoxin, 0.5 mg single dose | 10 mg QD, 8 days | ↑2% | ↓7% |
| Gemfibrozil, 600 mg BID, 7 days* | 10 mg QD, 7 days | ↓1% | ↓11% |
| Ethinyl estradiol & Levonorgestrel, QD, 21 days | 10 mg QD, Days 8-14 of 21 d oral contraceptive cycle | Ethinyl estradiol 0% Levonorgestrel 0% | Ethinyl estradiol ↓9% Levonorgestrel ↓5% |
| Glipizide, 10 mg on Days 1 and 9 | 10 mg QD, Days 2-9 | ↓3% | ↓5% |
| Fenofibrate, 200 mg QD, 14 days* | 10 mg QD, 14 days | ↑11% | ↑7% |
| Cyclosporine, 100 mg single dose Day 7* | 20 mg QD, 8 days | ↑15% | ↑10% |
| Statins | |||
| Lovastatin 20 mg QD, 7 days | 10 mg QD, 7 days | ↑19% | ↑3% |
| Pravastatin 20 mg QD, 14 days | 10 mg QD, 14 days | ↓20% | ↓24% |
| Atorvastatin 10 mg QD, 14 days | 10 mg QD, 14 days | ↓4% | ↑7% |
| Rosuvastatin 10 mg QD, 14 days | 10 mg QD, 14 days | ↑19% | ↑17% |
| Fluvastatin 20 mg QD, 14 days | 10 mg QD, 14 days | ↓39% | ↓27% |
Atorvastatin
| Coadministered Drug and Dosing Regimen | Atorvastatin | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dose (mg) | Change in AUC* | Change in Cmax* | |
|
|||
| Cyclosporine 5.2 mg/kg/day, stable dose† | 10 mg QD for 28 days | ↑8.7 fold | ↑10.7 fold |
| Tipranavir 500 mg BID/ritonavir 200 mg BID, 7 days† | 10 mg, SD | ↑9.4 fold | ↑8.6 fold |
| Telaprevir 750 mg q8h, 10 days† | 20 mg, SD | ↑7.88 fold | ↑10.6 fold |
| Saquinavir 400 mg BID/ritonavir 400 mg BID, 15 days†,‡ | 40 mg QD for 4 days | ↑3.9 fold | ↑4.3 fold |
| Clarithromycin 500 mg BID, 9 days† | 80 mg QD for 8 days | ↑4.4 fold | ↑5.4 fold |
| Darunavir 300 mg BID/ritonavir 100 mg BID, 9 days† | 10 mg QD for 4 days | ↑3.4 fold | ↑2.25 fold |
| Itraconazole 200 mg QD, 4 days† | 40 mg, SD | ↑3.3 fold | ↑20% |
| Fosamprenavir 700 mg BID/ritonavir 100 mg BID, 14 days† | 10 mg QD for 4 days | ↑2.53 fold | ↑2.84 fold |
| Fosamprenavir 1400 mg BID, 14 days† | 10 mg QD for 4 days | ↑2.3 fold | ↑4.04 fold |
| Nelfinavir 1250 mg BID, 14 days† | 10 mg QD for 28 days | ↑74% | ↑2.2 fold |
| Grapefruit Juice, 240 mL QD†,§ | 40 mg, SD | ↑37% | ↑16% |
| Diltiazem 240 mg QD, 28 days | 40 mg, SD | ↑51% | No change |
| Erythromycin 500 mg QID, 7 days | 10 mg, SD | ↑33% | ↑38% |
| Amlodipine 10 mg, single dose | 80 mg, SD | ↑15% | ↓12% |
| Cimetidine 300 mg QD, 4 weeks | 10 mg QD for 2 weeks | ↓Less than 1% | ↓11% |
| Colestipol 10 mg BID, 28 weeks | 40 mg QD for 28 weeks | Not determined | ↓26%¶ |
| Maalox TC® 30 mL QD, 17 days | 10 mg QD for 15 days | ↓33% | ↓34% |
| Efavirenz 600 mg QD, 14 days | 10 mg for 3 days | ↓41% | ↓1% |
| Rifampin 600 mg QD, 7 days (coadministered) †,# | 40 mg, SD | ↑30% | ↑2.7 fold |
| Rifampin 600 mg QD, 5 days (doses separated) †,# | 40 mg, SD | ↓80% | ↓40% |
| Gemfibrozil 600 mg BID, 7 days† | 40 mg, SD | ↑35% | ↓Less than 1% |
| Fenofibrate 160 mg QD, 7 days† | 40 mg, SD | ↑3% | ↑2% |
| Boceprevir 800 mg TID, 7 days | 40 mg, SD | ↑2.30 fold | ↑2.66 fold |
| Atorvastatin | Coadministered Drug and Dosing Regimen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug/Dose (mg) | Change in AUC | Change in Cmax | |
|
|||
| 80 mg QD for 15 days | Antipyrine, 600 mg SD | ↑3% | ↓11% |
| 80 mg QD for 14 days | Digoxin 0.25 mg QD, 20 days* | ↑15% | ↑20% |
| 40 mg QD for 22 days | Oral contraceptive QD, 2 months - norethindrone 1 mg - ethinyl estradiol 35 µg | ↑28% ↑19% | ↑23% ↑30% |
| 10 mg, SD | Tipranavir 500 mg BID/ritonavir 200 mg BID, 7 days | No change | No change |
| 10 mg QD for 4 days | Fosamprenavir 1400 mg BID, 14 days | ↓27% | ↓18% |
| 10 mg QD for 4 days | Fosamprenavir 700 mg BID/ritonavir 100 mg BID, 14 days | No change | No change |
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No animal carcinogenicity or fertility studies have been conducted with the combination of ezetimibe and atorvastatin. The combination of ezetimibe with atorvastatin did not show evidence of mutagenicity in vitro in a microbial mutagenicity (Ames) test with Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli with or without metabolic activation. No evidence of clastogenicity was observed in vitro in a chromosomal aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes with ezetimibe and atorvastatin with or without metabolic activation. There was no evidence of genotoxicity at doses up to 250 mg/kg with the combination of ezetimibe and atorvastatin (1:1) in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
LIPTRUZET – Lipid Efficacy
LIPTRUZET reduces total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C, and increases HDL-C in patients with hypercholesterolemia.
LIPTRUZET is effective in men and women with hyperlipidemia. Experience in non-Caucasians is limited and does not permit a precise estimate of the magnitude of the effects of LIPTRUZET.
In a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical study in patients with hyperlipidemia, 628 patients were treated for up to 12 weeks and 246 for up to an additional 48 weeks. Patients were randomized to receive placebo, ezetimibe (10 mg), atorvastatin (10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, or 80 mg), or coadministered ezetimibe and atorvastatin equivalent to LIPTRUZET (10/10, 10/20, 10/40, and 10/80) in the 12-week study. After completing the 12-week study, patients who agreed to participate in the study extension were assigned to coadministered ezetimibe and atorvastatin equivalent to LIPTRUZET (10/10-10/80) or atorvastatin (10-80 mg/day) for an additional 48 weeks.
The patient population was: 59% female; 85% Caucasian, 6% Black, 3% Asian, 5% Hispanic, 1% American Indian, <1% other; 18 to 86 years of age (mean age 57 years).
Patients receiving all doses of LIPTRUZET were compared to those receiving all doses of atorvastatin. LIPTRUZET lowered total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C, and increased HDL-C significantly more than atorvastatin alone. (See Table 9.)
| Treatment (Daily Dose) | N | Total-C [Baseline‡] | LDL-C [Baseline‡] | Apo B [Baseline‡] | TG*
[Baseline‡] | HDL-C [Baseline‡] | Non-HDL-C [Baseline‡] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
| Pooled data (All LIPTRUZET doses)§ | 255 | -41% [267] | -56% [182] | -45% [170] | -33% [165] | +7% [50.8] | -52% [217] |
| Pooled data (All atorvastatin doses)§ | 248 | -32% [269] | -44% [181] | -36% [168] | -24% [155] | +4% [53.7] | -41% [215] |
| Ezetimibe 10 mg | 65 | -14% [259] | -20% [177] | -15% [167] | -5% [145] | +4% [50.6] | -18% [209] |
| Placebo | 60 | +4% [262] | +4% [180] | +3% [168] | -6% [143] | +4% [50.4] | +4% [212] |
| LIPTRUZET by dose | |||||||
| 10/10 | 65 | -38% [262] | -53% [177] | -43% [165] | -31% [158] | +9% [51.9] | -49% [211] |
| 10/20 | 62 | -39% [269] | -54% [184] | -44% [174] | -30% [165] | +9% [49.3] | -50% [220] |
| 10/40 | 65 | -42% [271] | -56% [184] | -45% [173] | -34% [180] | +5% [51.1] | -52% [220] |
| 10/80 | 63 | -46% [267] | -61% [183] | -50% [169] | -40% [146] | +7% [50.9] | -58% [216] |
| Atorvastatin by dose | |||||||
| 10 mg | 60 | -26% [271] | -37% [185] | -28% [168] | -21% [153] | +6% [53.7] | -34% [217] |
| 20 mg | 60 | -30% [267] | -42% [177] | -34% [164] | -23% [147] | +4% [55.5] | -39% [211] |
| 40 mg | 66 | -32% [266] | -45% [180] | -37% [167] | -24% [159] | +4% [53.0] | -41% [213] |
| 80 mg | 62 | -40% [270] | -54% [184] | -46% [171] | -31% [163] | +3% [52.7] | -51% [218] |
The changes in lipid endpoints after an additional 48 weeks of treatment with LIPTRUZET (all doses) or with atorvastatin (all doses) were generally consistent with the 12-week data displayed above in the 245 subjects (out of the 576 who completed the 12-week study) who agreed to participate in the study extension.
A multicenter, double-blind, controlled, 14-week study was conducted in 621 patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH), coronary heart disease (CHD), or multiple cardiovascular risk factors (≥2), adhering to an NCEP Step I or stricter diet. All patients received atorvastatin 10 mg for a minimum of 4 weeks prior to randomization. Patients were then randomized to receive either coadministered ezetimibe and atorvastatin (equivalent to LIPTRUZET 10/10) or atorvastatin 20 mg/day monotherapy. Patients who did not achieve their LDL-C target goal after 4 and/or 9 weeks of randomized treatment were titrated to double the atorvastatin dose.
The patient population was: 47% female; 91% Caucasian, 2% Black, 2% Asian, 5% Hispanic, <1% other; 18 to 82 years of age (mean age 61 years).
LIPTRUZET 10/10 was significantly more effective than doubling the dose of atorvastatin to 20 mg in further reducing total-C, LDL-C, TG, and non-HDL-C. Results for HDL-C between the two treatment groups were not significantly different. (See Table 10.) In addition, at Week 4 significantly more patients receiving LIPTRUZET 10/10 attained LDL-C <100 mg/dL (<2.6 mmol/L) compared to those receiving atorvastatin 20 mg, 12% vs. 2%. The baseline mean LDL-C levels for patients receiving LIPTRUZET 10/10 and atorvastatin 20 mg were 186 mg/dL and 187 mg/dL, respectively.
| Treatment (Daily Dose) | N | Total-C [Baseline‡] | LDL-C [Baseline‡] | HDL-C [Baseline‡] | TG*
[Baseline‡] | Non-HDL-C [Baseline‡] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| LIPTRUZET 10/10 | 305 | -17%§
[262] | -24%§
[186] | +2% [50.0] | -9%§
[117] | -22%§
[212] |
| Atorvastatin 20 mg | 316 | -6% [264] | -9% [187] | +1% [49.9] | -4% [119] | -8% [214] |
The Titration of Atorvastatin Versus Ezetimibe Add-On to Atorvastatin in Patients with Hypercholesterolemia (TEMPO) study, a multicenter, double-blind, controlled, 6-week study, included 184 patients with an LDL-C level ≥100 mg/dL and ≤160 mg/dL (≥2.6 mmol/L and ≤4.1 mmol/L) and at moderate high risk for coronary heart disease (CHD). All patients received atorvastatin 20 mg for a minimum of 4 weeks prior to randomization. Patients not at the optional NCEP ATP III LDL-C level (<100 mg/dL [<2.6 mmol/L]) were randomized to receive either coadministered ezetimibe and atorvastatin (equivalent to LIPTRUZET 10/20) or atorvastatin 40 mg for 6 weeks.
The patient population was: 45% female; 60% Caucasian, 26% Multi-racial, 6% Black, 8% Asian, <1% American Indian or Alaska native; 24 to 78 years of age (mean age 58 years).
LIPTRUZET 10/20 was significantly more effective than doubling the dose of atorvastatin to 40 mg in further reducing total-C, LDL-C, Apo B and non-HDL-C. Results for HDL-C and TG between the two treatment groups were not significantly different. (See Table 11.) In addition, significantly more patients receiving LIPTRUZET 10/20 attained LDL-C <100 mg/dL (<2.6 mmol/L) compared to those receiving atorvastatin 40 mg, 84% vs. 49%.
| Treatment (Daily Dose) | N | Total-C [Baseline‡] | LDL-C [Baseline‡] | Apo B [Baseline‡] | HDL-C [Baseline‡] | TG*
[Baseline‡] | Non-HDL-C [Baseline‡] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
| LIPTRUZET 10/20 | 92 | -20%§
[203] | -31%§
[120] | -21%§
[123] | +3% [50.9] | -18% [155] | -27%§
[152] |
| Atorvastatin 40 mg | 92 | -7% [201] | -11% [118] | -8% [120] | +1% [52.1] | -6% [148] | -10% [149] |
The Ezetimibe Plus Atorvastatin Versus Atorvastatin Titration in Achieving Lower LDL-C Targets in Hypercholesterolemic Patients (EZ-PATH) study, a multicenter, double-blind, controlled, 6-week study, included 556 patients with an LDL-C level ≥70 mg/dL and ≤160 mg/dL (≥1.8 mmol/L and ≤4.1 mmol/L) and at high risk for coronary heart disease (CHD). All patients received atorvastatin 40 mg for a minimum of 4 weeks prior to randomization. Patients not at the optional NCEP ATP III LDL-C level <70 mg/dL (<1.8 mmol/L) were randomized to receive either coadministered ezetimibe and atorvastatin (equivalent to LIPTRUZET 10/40) or atorvastatin 80 mg for 6 weeks.
The patient population was: 39% female; 81% Caucasian, 11% Black, 6% Multi-racial, 2% Asian; 31 to 80 years of age (mean age 52 years).
LIPTRUZET 10/40 was significantly more effective than doubling the dose of atorvastatin to 80 mg in further reducing total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C. Results for HDL-C between the two treatment groups were not significantly different. (See Table 12.) In addition, significantly more patients receiving LIPTRUZET 10/40 attained LDL-C <70 mg/dL (<1.8 mmol/L) compared to those receiving atorvastatin 80 mg, 74% vs. 32%.
| Treatment (Daily Dose) | N | Total-C [Baseline‡] | LDL-C [Baseline‡] | Apo B [Baseline‡] | HDL-C [Baseline‡] | TG*
[Baseline‡] | Non-HDL-C [Baseline‡] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
| LIPTRUZET 10/40 | 277 | -17%§
[165] | -27%§
[89] | -18%§
[101] | 0% [47.7] | -12%§
[131] | -23%§
[117] |
| Atorvastatin 80 mg | 279 | -7% [165] | -11% [90] | -8% [102] | -1% [46.9] | -6% [136] | -9% [118] |
14.2 Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
A double-blind, randomized, 12-week study was performed in patients with a clinical and/or genotypic diagnosis of HoFH. Data were analyzed from a subgroup of patients (n=36) receiving atorvastatin 40 mg at baseline. Increasing the dose of atorvastatin from 40 to 80 mg (n=12) produced a reduction of LDL-C of 2% from baseline on atorvastatin 40 mg. Coadministered ezetimibe and atorvastatin equivalent to LIPTRUZET (10/40 and 10/80 pooled, n=24), produced a reduction of LDL-C of 19% from baseline on atorvastatin 40 mg. In those patients coadministered ezetimibe and atorvastatin equivalent to LIPTRUZET (10/80, n=12), a reduction of LDL-C of 25% from baseline on atorvastatin 40 mg was produced.
After completing the 12-week study, eligible patients (n=35), who were receiving atorvastatin 40 mg at baseline, were assigned to coadministered ezetimibe and atorvastatin equivalent to LIPTRUZET 10/40 for up to an additional 24 months. Following at least 4 weeks of treatment, the atorvastatin dose could be doubled to a maximum dose of 80 mg.
At the end of the 24 months, LIPTRUZET (10/40 and 10/80 pooled) produced a reduction of LDL-C that was consistent with that seen in the 12-week study.
16. How is Liptruzet Tablets supplied
Tablets LIPTRUZET 10 mg/10 mg are white to off-white capsule-shaped, biconvex film-coated tablets with code "320" on one side.
They are supplied as follows:
NDC 66582-320-30 unit of use packages of 30 (three foil pouches each containing one 10-count blister card)
NDC 66582-320-54 unit of use packages of 90 (nine foil pouches each containing one 10-count blister card)
Tablets LIPTRUZET 10 mg/20 mg are white to off-white round, biconvex film-coated tablets with code "321" on one side.
They are supplied as follows:
NDC 66582-321-30 unit of use packages of 30 (three foil pouches each containing one 10-count blister card)
NDC 66582-321-54 unit of use packages of 90 (nine foil pouches each containing one 10-count blister card)
Tablets LIPTRUZET 10 mg/40 mg are white to off-white oval, biconvex film-coated tablets with code "322" on one side.
They are supplied as follows:
NDC 66582-322-30 unit of use packages of 30 (three foil pouches each containing one 10-count blister card)
NDC 66582-322-54 unit of use packages of 90 (nine foil pouches each containing one 10-count blister card)
Tablets LIPTRUZET 10 mg/80 mg are white to off-white capsule-shaped, biconvex film-coated tablets with code "323" on one side.
They are supplied as follows:
NDC 66582-323-30 unit of use packages of 30 (three foil pouches each containing one 10-count blister card)
NDC 66582-323-54 unit of use packages of 90 (nine foil pouches each containing one 10-count blister card)
17. Patient Counseling Information
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information).
Patients should be advised to adhere to their National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP)-recommended diet, a regular exercise program, and periodic testing of a fasting lipid panel.
17.1 Muscle Pain
All patients starting therapy with LIPTRUZET should be advised of the risk of myopathy and told to report promptly any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever or if these muscle signs or symptoms persist after discontinuing LIPTRUZET. The risk of this occurring is increased when taking certain types of medication or consuming larger quantities (>1 liter) of grapefruit juice. Patients should discuss all medication, both prescription and over-the-counter, with their physician.
17.2 Liver Enzymes
It is recommended that liver enzyme tests be performed before the initiation of LIPTRUZET and if signs or symptoms of liver injury occur. All patients treated with LIPTRUZET should be advised to report promptly any symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine, or jaundice.
17.3 Pregnancy
Women of childbearing age should be advised to use an effective method of birth control to prevent pregnancy while using LIPTRUZET. Discuss future pregnancy plans with your patients, and discuss when to stop taking LIPTRUZET if they are trying to conceive. Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant they should stop taking LIPTRUZET and call their healthcare professional.
17.4 Breast-Feeding
Women who are breast-feeding should be advised to not use LIPTRUZET. Patients who have a lipid disorder and are breast-feeding should be advised to discuss the options with their healthcare professionals.
17.5 Important Storage and Administration Instructions
Patients should be advised to store LIPTRUZET at room temperature, 20-25°C (68-77°F). They should also be advised:
- not to open a pouch until they are ready to use LIPTRUZET
- that after the foil pouch is opened, LIPTRUZET should be protected from moisture and light, and stored in a dry place
- that for packages containing a plastic case (unit of use packages of 30 and 90), once they remove a tablet from the blister card, they should slide the blister card back into the plastic case
- to discard any unused tablets 30 days after the pouch is opened
Tablets should be swallowed whole. Do not crush, dissolve, or chew tablets.
If a dose is missed, the patient should not take an extra dose. Just resume the usual schedule.
Patient Information
LIPTRUZET™ (LIP-true-zett)
(ezetimibe and atorvastatin)
Tablets
Generic name: ezetimibe and atorvastatin tablets
Read this information carefully before you start taking LIPTRUZET™ and each time you get more LIPTRUZET. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment. If you have any questions about LIPTRUZET, ask your doctor. Only your doctor can determine if LIPTRUZET is right for you.
What is LIPTRUZET?
LIPTRUZET contains 2 cholesterol-lowering medications, ezetimibe and atorvastatin.
LIPTRUZET is a prescription medicine used to lower levels of total cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol and fatty substances called triglycerides in the blood. In addition, LIPTRUZET raises levels of HDL (good) cholesterol. LIPTRUZET is for patients who cannot control their cholesterol levels by diet and exercise alone. You should stay on a cholesterol-lowering diet while taking this medicine.
LIPTRUZET has not been shown to reduce heart attacks or strokes more than atorvastatin alone.
It is not known if LIPTRUZET is safe and effective in children.
Who should not take LIPTRUZET?
Do not take LIPTRUZET if you:
- have active liver problems or repeated blood tests showing possible liver problems.
- are allergic to ezetimibe or atorvastatin or any of the ingredients in LIPTRUZET. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in LIPTRUZET.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. LIPTRUZET may harm your unborn baby. If you are a woman of childbearing age, you should use an effective method of birth control while taking LIPTRUZET. Stop taking LIPTRUZET and call your doctor right away if you get pregnant while taking LIPTRUZET.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. LIPTRUZET can pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take LIPTRUZET. Do not breastfeed while taking LIPTRUZET.
What should I tell my doctor before taking LIPTRUZET?
Before you take LIPTRUZET, tell your doctor if you:
- have a thyroid problem
- have kidney problems
- have diabetes
- have unexplained muscle aches or weakness
- drink more than 2 glasses of alcohol daily or have or have had liver problems
- have any other medical conditions
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Taking LIPTRUZET with certain other medicines or substances can increase the risk of muscle problems or other side effects.
Especially tell your doctor if you take medicines for:
- your immune system
- cholesterol
- infections
- birth control
- heart failure
- HIV or AIDS
- hepatitis C
- gout
Also tell your doctor if you drink large amounts of grapefruit juice.
How should I take LIPTRUZET?
- Take LIPTRUZET exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Your doctor will tell you how much LIPTRUZET to take and when to take it.
- Your doctor may change your dose if needed.
- Do not open your LIPTRUZET pouch until you are ready to take LIPTRUZET.
- Take LIPTRUZET 1 time each day, with or without food. It may be easier to remember to take your dose if you do it at the same time every day, such as with breakfast, dinner, or at bedtime.
- Tablets should be swallowed whole. Do not crush, dissolve, or chew tablets.
- Keep taking LIPTRUZET unless your doctor tells you to stop. If you stop taking LIPTRUZET, your cholesterol may rise again.
- If you miss a dose, do not take an extra dose. Just resume your usual schedule.
- If you take too much LIPTRUZET, call your doctor or Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
- See your doctor regularly to check your cholesterol level and to check for side effects. Your doctor may do blood tests to check your liver before you start taking LIPTRUZET and during treatment.
What should I avoid while taking LIPTRUZET?
- Do not start any new medicines before talking to your doctor. This includes prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. LIPTRUZET and certain other medicines can interact causing serious side effects.
- Do not drink more than 2 glasses of alcohol daily.
- Do not get pregnant. If you get pregnant, stop taking LIPTRUZET right away and call your doctor.
What are the possible side effects of LIPTRUZET?
LIPTRUZET may cause serious side effects, including:
-
muscle problems. LIPTRUZET can cause serious muscle problems that can lead to kidney problems, including kidney failure. You have a higher chance for muscle problems if you are taking certain other medicines with LIPTRUZET.
Tell your doctor right away if:- you have unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, especially if you have a fever or feel more tired than usual, while you take LIPTRUZET.
- you have muscle problems that do not go away even after your doctor has advised you to stop taking LIPTRUZET. Your doctor may do further tests to diagnose the cause of your muscle problems.
-
liver problems. Your doctor should do blood tests to check your liver before you start taking LIPTRUZET and if you have symptoms of liver problems while you take LIPTRUZET. Call your doctor right away if you have the following symptoms of liver problems:
- feel tired or weak
- loss of appetite
- upper belly pain
- dark urine
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
Also call your doctor right away if you have:
- allergic reactions including swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and/or throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing which may require treatment right away
- nausea and vomiting
- passing brown or dark-colored urine
- you feel more tired than usual
- stomach pain
- allergic skin reactions
The most common side effects of LIPTRUZET include:
- muscle and body pain
- changes in your liver function tests
Additional side effects that have been reported in people taking LIPTRUZET, ezetimibe or atorvastatin in clinical studies or general use include: joint pain; diarrhea; tendon problems; memory loss; confusion; depression.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of LIPTRUZET. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store LIPTRUZET?
- Store LIPTRUZET at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep LIPTRUZET in the foil pouch until you are ready to take it.
- After you remove a LIPTRUZET tablet from the blister card, slide the blister card back into the case (where a case is provided) and store in a dry place.
- Write down the date the foil pouch was opened in the space provided.
- Keep LIPTRUZET tablets dry and out of the light.
- Safely throw away unused LIPTRUZET tablets 30 days after the foil pouch is opened.
Keep LIPTRUZET and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of LIPTRUZET.
LIPTRUZET may help to reduce your cholesterol in 2 ways. It reduces the cholesterol absorbed in your digestive tract, as well as the cholesterol your body makes by itself. LIPTRUZET does not help you lose weight.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not use LIPTRUZET for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give LIPTRUZET to other people, even if they have the same problem that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about LIPTRUZET. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about LIPTRUZET that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.LIPTRUZET.com or call 1-800-672-6372.
What are the ingredients in LIPTRUZET?
Active ingredients: ezetimibe and atorvastatin
Inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, magnesium stearate, lactose anhydrous, hydroxypropyl cellulose, sodium bicarbonate. The tablet film coating contains the following inactive ingredients: hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, and carnauba wax
| LIPTRUZET
ezetimibe and atorvastatin tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LIPTRUZET
ezetimibe and atorvastatin tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LIPTRUZET
ezetimibe and atorvastatin tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LIPTRUZET
ezetimibe and atorvastatin tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. (110456618) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSD International GmbH (Singapore Branch) | 894726637 | MANUFACTURE(66582-320, 66582-321, 66582-322, 66582-323) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSD International GmbH (Puerto Rico Branch) LLC | 967475950 | MANUFACTURE(66582-320, 66582-321, 66582-322, 66582-323) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Pharmaceuticals Inc. | 005286822 | MANUFACTURE(66582-320, 66582-321, 66582-322, 66582-323) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSD International GmbH (Puerto Rico Branch) LLC | 606266625 | MANUFACTURE(66582-320, 66582-321, 66582-322, 66582-323) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| DR. REDDY'S LABORATORIES LIMITED | 650443679 | API MANUFACTURE(66582-320, 66582-321, 66582-322, 66582-323) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSD International GmbH (Singapore Branch) | 595320830 | API MANUFACTURE(66582-320, 66582-321, 66582-322, 66582-323) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| AndersonBrecon Inc. | 053217022 | PACK(66582-320, 66582-321, 66582-322, 66582-323) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | 101740835 | PACK(66582-320, 66582-321, 66582-322, 66582-323) | |








