Drug Detail:Mektovi (Binimetinib [ bin-i-me-ti-nib ])
Drug Class: Multikinase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
MEKTOVI® (binimetinib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
Indications and Usage for Mektovi
MEKTOVI is a kinase inhibitor indicated, in combination with encorafenib, for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1, 2.1)
Mektovi Dosage and Administration
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to the initiation of MEKTOVI. (2.1)
- The recommended dose is 45 mg orally twice daily in combination with encorafenib. Take MEKTOVI with or without food. (2.2)
- For patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment the recommended dose is 30 mg orally twice daily. (2.4, 8.6)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
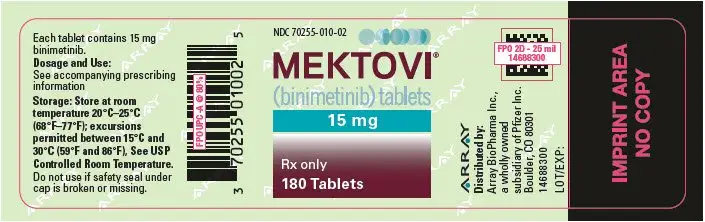
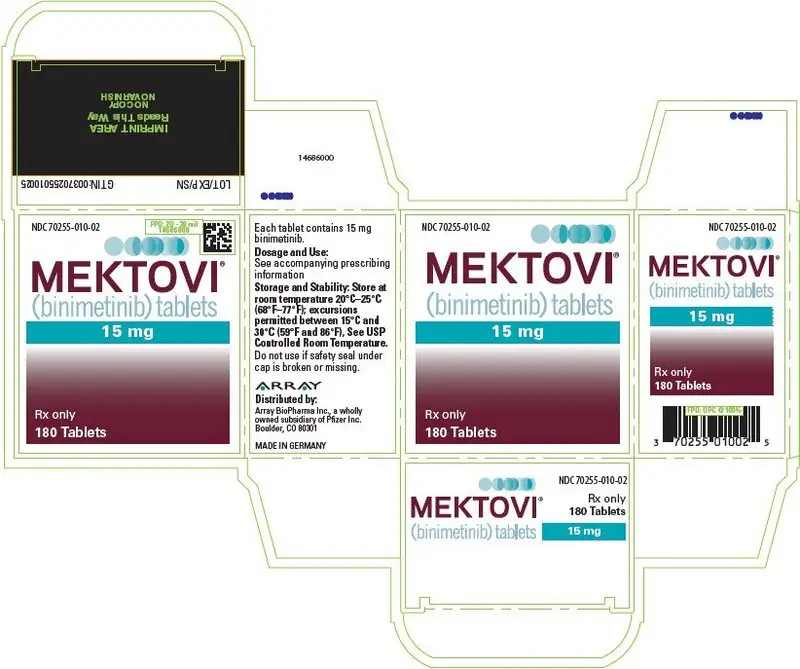
- Tablets: 15 mg. (3)
Contraindications
- None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Cardiomyopathy: Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before initiating treatment, after one month of treatment, then every 2 to 3 months thereafter. The safety of MEKTOVI has not been established in patients with LVEF below 50%. (5.1)
- Venous Thromboembolism: Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism can occur. (5.2)
- Ocular Toxicities: Serous retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion (RVO) and uveitis have occurred. Perform an ophthalmologic evaluation at regular intervals and for any visual disturbances. (5.3)
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD): Assess new or progressive unexplained pulmonary symptoms or findings for possible ILD. (5.4)
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor liver function tests before and during treatment and as clinically indicated. (5.5)
- Rhabdomyolysis: Monitor creatine phosphokinase and creatinine periodically and as clinically indicated. (5.6)
- Hemorrhage: Major hemorrhagic events can occur. (5.7)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females with reproductive potential of potential risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.8, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 25%) for MEKTOVI, in combination with encorafenib, are fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Array BioPharma at 1-844-792-7729 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 10/2020
Related/similar drugs
Keytruda, pembrolizumab, nivolumab, Opdivo, dabrafenib, YervoyFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Mektovi
MEKTOVI® is indicated, in combination with encorafenib, for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
2. Mektovi Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection
Confirm the presence of a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiating MEKTOVI [Clinical Studies (14)]. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600E and V600K mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of MEKTOVI is 45 mg orally taken twice daily, approximately 12 hours apart, in combination with encorafenib until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Refer to the encorafenib prescribing information for recommended encorafenib dosing information.
MEKTOVI may be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Do not take a missed dose of MEKTOVI within 6 hours of the next dose of MEKTOVI.
Do not take an additional dose if vomiting occurs after MEKTOVI administration but continue with the next scheduled dose.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
If encorafenib is permanently discontinued, discontinue MEKTOVI.
Dose reductions for adverse reactions associated with MEKTOVI are presented in Table 1.
| Action | Recommended Dose |
|---|---|
| First Dose Reduction | 30 mg orally twice daily |
| Subsequent Modification | Permanently discontinue if unable to tolerate MEKTOVI 30 mg orally twice daily |
Dosage modifications for adverse reactions associated with MEKTOVI are presented in Table 2.
| Severity of Adverse Reaction* | Dose Modification for MEKTOVI |
|---|---|
|
|
| Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | |
| Withhold MEKTOVI for up to 4 weeks, evaluate LVEF every 2 weeks. Resume MEKTOVI at a reduced dose if the following are present:
|
| Permanently discontinue MEKTOVI. |
| Venous Thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | |
| Withhold MEKTOVI.
|
| Permanently discontinue MEKTOVI. |
| Serous Retinopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | |
| Withhold MEKTOVI for up to 10 days.
|
| Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | |
| Permanently discontinue MEKTOVI. |
| Uveitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | |
| If Grade 1 or 2 does not respond to specific ocular therapy, or for Grade 3 uveitis, withhold MEKTOVI for up to 6 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue MEKTOVI. |
| Interstitial Lung Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | |
| Withhold MEKTOVI for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue MEKTOVI. |
| Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | |
| Maintain MEKTOVI dose.
|
| See Other Adverse Reactions. |
| Rhabdomyolysis or Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] | |
| Withhold MEKTOVI dose for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Dermatologic | |
| If no improvement within 2 weeks, withhold MEKTOVI until Grade 0-1. Resume at same dose if first occurrence or reduce dose if recurrent. |
| Withhold MEKTOVI until Grade 0-1. Resume at same dose if first occurrence or reduce dose if recurrent. |
| Permanently discontinue MEKTOVI. |
| Other Adverse Reactions (including: Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)])† | |
| Withhold MEKTOVI for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue MEKTOVI, or Withhold MEKTOVI for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Consider permanently discontinuing MEKTOVI. |
| Permanently discontinue MEKTOVI. |
Refer to the encorafenib prescribing information for dose modifications for adverse reactions associated with encorafenib.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Moderate or Severe Hepatic Impairment
For patients with moderate (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 and less than or equal to 3 × ULN and any AST) or severe (total bilirubin levels greater than 3 × ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment, the recommended dosage is 30 mg orally taken twice daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 15 mg, yellow/dark yellow, unscored biconvex oval film-coated tablets debossed with a stylized "A" on one side and "15" on the other side.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy, manifesting as left ventricular dysfunction associated with symptomatic or asymptomatic decreases in ejection fraction, has been reported in patients treated with MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib. In COLUMBUS, evidence of cardiomyopathy (decrease in LVEF below the institutional LLN with an absolute decrease in LVEF ≥ 10% below baseline as detected by echocardiography or MUGA) occurred in 7% of patients receiving MEKTOVI plus encorafenib. Grade 3 left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 1.6% of patients. The median time to first occurrence of left ventricular dysfunction (any grade) in patients receiving MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib was 3.6 months (range 0 to 21 months). Cardiomyopathy resolved in 87% of patients receiving MEKTOVI plus encorafenib.
Assess ejection fraction by echocardiogram or MUGA scan prior to initiating treatment, one month after initiating treatment, and then every 2 to 3 months during treatment. The safety of MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib has not been established in patients with a baseline ejection fraction that is either below 50% or below the institutional lower limit of normal (LLN). Patients with cardiovascular risk factors should be monitored closely when treated with MEKTOVI.
Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Venous Thromboembolism
In COLUMBUS, venous thromboembolism (VTE) occurred in 6% of patients receiving MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib, including 3.1% of patients who developed pulmonary embolism. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.4 Interstitial Lung Disease
In patients with BRAF mutation-positive melanoma receiving MEKTOVI with encorafenib (n=690), 2 patients (0.3%) developed interstitial lung disease (ILD), including pneumonitis.
Assess new or progressive unexplained pulmonary symptoms or findings for possible ILD. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.5 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity can occur when MEKTOVI is administered in combination with encorafenib. In COLUMBUS, the incidence of Grade 3 or 4 increases in liver function laboratory tests in patients receiving MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib was 6% for alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 2.6% for aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and 0.5% for alkaline phosphatase. No patient experienced Grade 3 or 4 serum bilirubin elevation.
Monitor liver laboratory tests before initiation of MEKTOVI, monthly during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.6 Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis can occur when MEKTOVI is administered in combination with encorafenib. In COLUMBUS, elevation of laboratory values of serum CPK occurred in 58% of patients treated with MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib. In patients with BRAF mutation-positive melanoma receiving MEKTOVI with encorafenib (n=690), rhabdomyolysis was reported in 1 patient (0.1%).
Monitor CPK and creatinine levels prior to initiating MEKTOVI, periodically during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.7 Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage can occur when MEKTOVI is administered in combination with encorafenib. In COLUMBUS, hemorrhage occurred in 19% of patients receiving MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib. Grade 3 or greater hemorrhage occurred in 3.2% of patients. The most frequent hemorrhagic events were gastrointestinal, including rectal hemorrhage (4.2%), hematochezia (3.1%), and hemorrhoidal hemorrhage (1%). Fatal intracranial hemorrhage in the setting of new or progressive brain metastases occurred in 1.6% of patients.
Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.8 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, MEKTOVI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Binimetinib was embryotoxic and abortifacient when administered to rabbits during the period of organogenesis at doses greater than or equal to those resulting in exposures approximately 5 times the human exposure at the recommended clinical dose of 45 mg twice daily.
Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MEKTOVI and for at least 30 days after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Venous Thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Ocular Toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Interstitial Lung Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Rhabdomyolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described in Warnings and Precautions [see Warnings and Precautions (5)] reflect exposure of 192 patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma to MEKTOVI (45 mg twice daily) in combination with encorafenib (450 mg once daily) in a randomized open-label, active-controlled trial (COLUMBUS) or, for rare events, exposure of 690 patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma to MEKTOVI (45 mg twice daily) in combination with encorafenib at doses between 300 mg and 600 mg once daily across multiple clinical trials.
The data described below reflect exposure of 192 patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma to MEKTOVI (45 mg twice daily) in combination with encorafenib (450 mg once daily) in COLUMBUS.
The COLUMBUS trial [see Clinical Studies (14)] excluded patients with a history of Gilbert's syndrome, abnormal left ventricular ejection fraction, prolonged QTc (> 480 msec), uncontrolled hypertension, and history or current evidence of retinal vein occlusion. The median duration of exposure was 11.8 months for patients treated with MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib and 6.2 months for patients treated with vemurafenib.
The most common (≥ 25%) adverse reactions in patients receiving MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib were fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Adverse reactions leading to dose interruptions of MEKTOVI occurred in 33% of patients receiving MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib; the most common were left ventricular dysfunction (6%) and serous retinopathy (5%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of MEKTOVI occurred in 19% of patients receiving MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib; the most common were left ventricular dysfunction (3%), serous retinopathy (3%), and colitis (2%). Five percent (5%) of patients receiving MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib experienced an adverse reaction that resulted in permanent discontinuation of MEKTOVI. The most common adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of MEKTOVI were hemorrhage in 2% and headache in 1% of patients.
Table 3 and Table 4 present adverse drug reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, identified in COLUMBUS. The COLUMBUS trial was not designed to demonstrate a statistically significant difference in adverse reaction rates for MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib, as compared to vemurafenib, for any specific adverse reaction listed in Table 3.
| Adverse Reaction | MEKTOVI with encorafenib N=192 | Vemurafenib N=186 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4†
(%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4†
(%) |
|
|
||||
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Fatigue‡ | 43 | 3 | 46 | 6 |
| Pyrexia‡ | 18 | 4 | 30 | 0 |
| Peripheral edema‡ | 13 | 1 | 15 | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 41 | 2 | 34 | 2 |
| Diarrhea | 36 | 3 | 34 | 2 |
| Vomiting‡ | 30 | 2 | 16 | 1 |
| Abdominal pain‡ | 28 | 4 | 16 | 1 |
| Constipation | 22 | 0 | 6 | 1 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Rash‡ | 22 | 1 | 53 | 13 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Dizziness‡ | 15 | 3 | 4 | 0 |
| Visual Disorders | ||||
| Visual impairment‡ | 20 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Serous retinopathy/RPED‡ | 20 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Vascular Disorders | ||||
| Hemorrhage‡ | 19 | 3 | 9 | 2 |
| Hypertension‡ | 11 | 6 | 11 | 3 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions occurring in < 10% of patients who received MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib were:
Gastrointestinal disorders: Colitis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Panniculitis
Immune system disorders: Drug hypersensitivity
| Laboratory Abnormality | MEKTOVI with encorafenib N=192 | Vemurafenib N=186 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) |
|
|
||||
| Hematology | ||||
| Anemia | 36 | 3.6 | 34 | 2.2 |
| Leukopenia | 13 | 0 | 10 | 0.5 |
| Lymphopenia | 13 | 2.1 | 30 | 7 |
| Neutropenia | 13 | 3.1 | 4.8 | 0.5 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Increased Creatinine | 93 | 3.6 | 92 | 1.1 |
| Increased Creatine Phosphokinase | 58 | 5 | 3.8 | 0 |
| Increased Gamma Glutamyl Transferase | 45 | 11 | 34 | 4.8 |
| Increased ALT | 29 | 6 | 27 | 2.2 |
| Increased AST | 27 | 2.6 | 24 | 1.6 |
| Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 21 | 0.5 | 35 | 2.2 |
| Hyponatremia | 18 | 3.6 | 15 | 0.5 |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of MEKTOVI have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 690 patients with BRAF mutation-positive melanoma who received MEKTOVI (45 mg twice daily) in combination with encorafenib at doses between 300 mg and 600 mg once daily across multiple clinical trials, 20% were aged 65 to 74 years and 8% were aged 75 years and older. No overall differences in the safety or effectiveness of MEKTOVI plus encorafenib were observed in elderly patients as compared to younger patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Binimetinib concentrations may increase in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment. Dose adjustment for MEKTOVI is not recommended in patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 1 and ≤ 1.5 × ULN and any AST or total bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN). Reduce the dose of MEKTOVI for patients with moderate (total bilirubin > 1.5 and ≤ 3 × ULN and any AST) or severe (total bilirubin levels > 3 × ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
Since binimetinib is 97% bound to plasma proteins, hemodialysis is likely to be ineffective in the treatment of overdose with MEKTOVI.
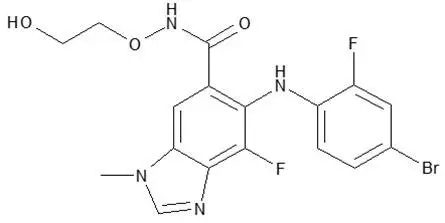
11. Mektovi Description
Binimetinib is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name is 5-[(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide. The molecular formula is C17H15BrF2N4O3 and the molecular weight is 441.2 daltons. The chemical structure of binimetinib is shown below:
Binimetinib is a white to slightly yellow powder. In aqueous media, binimetinib is slightly soluble at pH 1, very slightly soluble at pH 2, and practically insoluble at pH 4.5 and higher.
MEKTOVI (binimetinib) tablets for oral use contain 15 mg of binimetinib with the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate (vegetable source), and colloidal silicon dioxide. The coating contains polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide, talc, ferric oxide yellow, and ferrosoferric oxide.
12. Mektovi - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Binimetinib is a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2 activity. MEK proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway. In vitro, binimetinib inhibited extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) phosphorylation in cell-free assays as well as viability and MEK-dependent phosphorylation of BRAF-mutant human melanoma cell lines. Binimetinib also inhibited in vivo ERK phosphorylation and tumor growth in BRAF-mutant murine xenograft models.
Binimetinib and encorafenib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Compared to either drug alone, coadministration of encorafenib and binimetinib resulted in greater anti-proliferative activity in vitro in BRAF mutation-positive cell lines and greater anti-tumor activity with respect to tumor growth inhibition in BRAF V600E mutant human melanoma xenograft studies in mice. Additionally, the combination of binimetinib and encorafenib delayed the emergence of resistance in BRAF V600E mutant human melanoma xenografts in mice compared to either drug alone.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of binimetinib was studied in healthy subjects and patients with solid tumors. After twice-daily dosing, the accumulation is 1.5-fold and the coefficient of variation (CV%) of the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) is < 40% at steady state. The systemic exposure of binimetinib is approximately dose proportional.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with binimetinib have not been conducted. Binimetinib was not genotoxic in studies evaluating reverse mutations in bacteria, chromosomal aberrations in mammalian cells, or micronuclei in bone marrow of rats.
No dedicated fertility studies have been conducted with binimetinib in animals. In general toxicology studies in rats and monkeys, there were no remarkable findings in male or female reproductive organs.
14. Clinical Studies
MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib was evaluated in a randomized, active-controlled, open-label, multicenter trial (COLUMBUS; NCT01909453). Eligible patients were required to have BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma, as detected using the bioMerieux THxID™BRAF assay. Patients were permitted to have received immunotherapy in the adjuvant setting and one prior line of immunotherapy for unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease. Prior use of BRAF inhibitors or MEK inhibitors was prohibited. Randomization was stratified by American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Stage (IIIB, IIIC, IVM1a or IVM1b, versus IVM1c), Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (0 versus 1), and prior immunotherapy for unresectable or metastatic disease (yes versus no).
Patients were randomized (1:1:1) to receive MEKTOVI 45 mg twice daily in combination with encorafenib 450 mg once daily (MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib), encorafenib 300 mg once daily, or vemurafenib 960 mg twice daily. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Only the results of the approved dosing (MEKTOVI 45 mg in combination with encorafenib 450 mg) are described below.
The major efficacy outcome measure was progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by a blinded independent central review, to compare MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib with vemurafenib. Additional efficacy measures included overall survival (OS), as well as objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR) which were assessed by central review.
A total of 577 patients were randomized, 192 to the MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib arm, 194 to the encorafenib arm, and 191 to the vemurafenib arm. Of the 383 patients randomized to either the MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib or the vemurafenib arms, the median age was 56 years (20 to 89 years), 59% were male, 91% were White, and 72% had baseline ECOG performance status of 0. Ninety-five percent (95%) had metastatic disease, 65% were Stage IVM1c, and 4% received prior CTLA-4, PD-1, or PD-L1 directed antibodies. Twenty-eight percent (28%) had elevated baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), 45% had ≥ 3 organs with tumor involvement at baseline, and 3% had brain metastases. Based on centralized testing, 100% of patients' tumors tested positive for BRAF mutations; BRAF V600E (88%), BRAF V600K (11%), or both (< 1%).
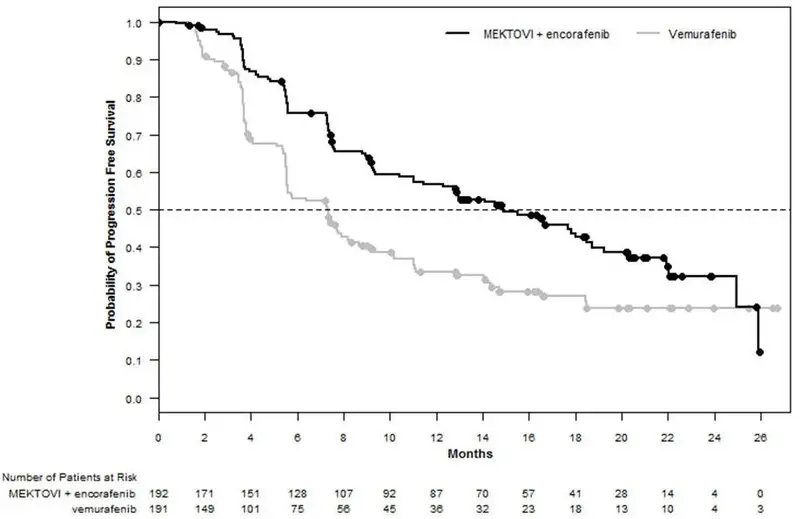
MEKTOVI in combination with encorafenib demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS compared to vemurafenib. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 5 and Figure 1.
| MEKTOVI with encorafenib N=192 | Vemurafenib N=191 |
|
|---|---|---|
| CI = Confidence interval; CR = Complete response; DoR = Duration of response; HR = Hazard ratio; NE = Not estimable; ORR = Overall response rate; OS = Overall survival; PFS = Progression-free survival; PR = Partial response. | ||
|
||
| Progression-Free Survival | ||
| Number of events (%) | 98 (51) | 106 (55) |
| Progressive disease | 88 (46) | 104 (54) |
| Death | 10 (5) | 2 (1) |
| Median PFS, months (95% CI) | 14.9 (11, 18.5) | 7.3 (5.6, 8.2) |
| HR (95% CI)* | 0.54 (0.41, 0.71) | |
| P value† | < 0.0001 | |
| Overall Survival‡ | ||
| Number of events (%) | 105 (55) | 127 (67) |
| Median OS, months (95% CI) | 33.6 (22.4, 39.2) | 16.9 (14.0, 24.5) |
| HR (95% CI)* | 0.61 (0.47, 0.79) | |
| Overall Response Rate | ||
| ORR (95% CI) | 63% (56%, 70%) | 40% (33%, 48%) |
| CR | 8% | 6% |
| PR | 55% | 35% |
| Duration of Response | ||
| Median DoR, months (95% CI) | 16.6 (12.2, 20.4) | 12.3 (6.9, 16.9) |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Progression-Free Survival in COLUMBUS
16. How is Mektovi supplied
MEKTOVI (binimetinib) is supplied as 15 mg yellow/dark yellow, unscored biconvex oval film-coated tablets debossed with a stylized "A" on one side and "15" on the other side, available in bottles of 180 tablets (NDC 70255-010-02).
| MEKTOVI
binimetinib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Array BioPharma Inc. (004047838) |
| Registrant - Pfizer Inc (113480771) |