Drug Detail:Menquadfi (Meningococcal conjugate vaccine [ me-nin-je-kok-al-kon-je-gate-vax-een ])
Drug Class:
Highlights of Prescribing Information
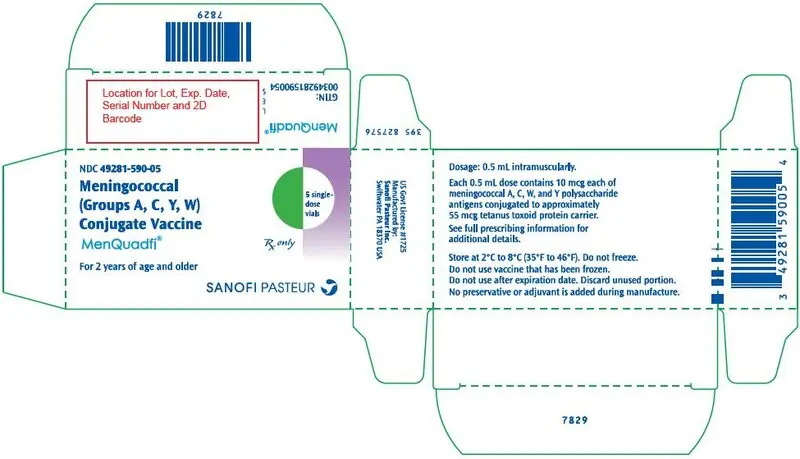
MenQuadfi, Meningococcal (Groups A, C, Y, W) Conjugate Vaccine
Solution for Intramuscular Injection
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration, Dose and Schedule (2.2) | 06/2023 |
Indications and Usage for MenQuadfi
MenQuadfi is a vaccine indicated for active immunization for the prevention of invasive meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, W, and Y. MenQuadfi is approved for use in individuals 2 years of age and older. (1)
MenQuadfi does not prevent N. meningitidis serogroup B disease.
MenQuadfi Dosage and Administration
0.5 mL dose for intramuscular injection. (2)
Primary Vaccination
- Individuals 2 years of age and older: a single dose.
Booster Vaccination
- A single dose of MenQuadfi may be administered to individuals 13 years of age and older who are at continued risk for meningococcal disease if at least 3 years have elapsed since a prior dose of meningococcal (groups A, C, W, Y) conjugate vaccine.
Vaccination Following Prior Dose of Meningococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine
- A single dose of MenQuadfi may be administered if at least 3 years have elapsed since a prior dose of meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Solution for injection in 0.5 mL single-dose vial. (3)
Contraindications
Severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine, or after a previous dose of MenQuadfi or any other tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine. (4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most commonly reported adverse reactions (≥10%) following a primary dose were as follows:
- Children 2 through 9 years of age, pain (38.6%), erythema (22.6%), and swelling (13.8%) at the injection site; malaise (21.1%), myalgia (20.1%), and headache (12.5%). (6)
- Adolescents aged 10 through 17 years of age, injection site pain (34.8%–45.2%), myalgia (27.4%–35.3%), headache (26.5%–30.2%), and malaise (19.4%–26.0%). (6)
- Adults aged 18 through 55 years, injection site pain (41.9%), myalgia (35.6%), headache (29.0%), and malaise (22.9%). (6)
- Adults 56 years of age and older, pain at the injection site (25.5%), myalgia (21.9%), headache (19.0%), and malaise (14.5%). (6)
In adolescents and adults, rates of solicited adverse reactions following a booster dose were comparable to those observed following primary vaccination. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sanofi Pasteur Inc., Discovery Drive, Swiftwater, PA 18370 at 1-800-822-2463 (1-800-VACCINE) or VAERS at 1-800-822-7967 or www.vaers.hhs.gov.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for MenQuadfi
MenQuadfi® is a vaccine indicated for active immunization for the prevention of invasive meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, W, and Y. MenQuadfi is indicated for use in individuals 2 years of age and older.
MenQuadfi does not prevent N. meningitidis serogroup B disease.
2. MenQuadfi Dosage and Administration
2.1 Preparation for Administration
MenQuadfi is a clear, colorless solution.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and/or discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. If any of these conditions exist, the vaccine should not be administered. Discard the vial with any unused portion.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
MenQuadfi is a sterile solution for intramuscular injection supplied in 0.5 mL single-dose vials.
4. Contraindications
Severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine, or after a previous dose of MenQuadfi or any other tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine [see Description (11)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Management of Acute Allergic Reactions
Appropriate observation and medical treatment should always be readily available in case of an anaphylactic event following the administration of the vaccine.
5.3 Syncope
Syncope (fainting) can occur following, or even before, vaccination with MenQuadfi.
Procedures should be in place to prevent falling and injury and to manage syncope.
5.4 Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) has been reported in temporal relationship following administration of another U.S.-licensed meningococcal quadrivalent polysaccharide conjugate vaccine. The decision by the healthcare professional to administer MenQuadfi to persons with a history of GBS should take into account the expected benefits and potential risks.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trial(s) of a vaccine cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trial(s) of another vaccine and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of a single dose of MenQuadfi in individuals 2 years of age and older was evaluated in seven randomized, active-controlled, multi-center clinical studies conducted in the US and Puerto Rico. In these studies, a total of 5,787 participants received either a primary dose (N = 4517), a booster dose (N = 1119) of MenQuadfi following priming with a meningococcal conjugate vaccine, or a dose of MenQuadfi following a prior dose of meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine (N = 151) and were included in the safety analyses.
Booster Vaccination Following Priming with a Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine; Vaccination Following a Prior Dose of a Meningococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine
Adolescents and adults 13 through 26 years of age
The safety of MenQuadfi in previously vaccinated adolescents and adults 13 through 26 years of age was evaluated in Study 6 (NCT04084769). All randomized participants had received a primary dose of either MenQuadfi or Menveo 3-6 years previously. The safety analysis set included 370 participants who received a booster dose of MenQuadfi alone (median age: 15.0 years for subjects primed with MenQuadfi and 16.0 years for subjects primed with Menveo) and 185 participants who received MenQuadfi concomitantly with Trumenba® [Meningococcal Group B Vaccine] (N=93, median age: 15.0 years) or Bexsero® [Meningococcal Group B Vaccine] (N=92, median age: 15.0 years). Of the participants who received a booster dose of MenQuadfi, 47.2% were female, 88.1% were White, 8.2% were Black, 3.8% were of other racial groups, and 14.4% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
The rates and severity of the solicited adverse reactions that occurred within 7 days following a booster dose of MenQuadfi alone or concomitantly with Trumenba or Bexsero in Study 6 (NCT04084769) are presented in Table 5.
The majority of solicited reactions were Grade 1 or 2 and resolved within 3 days after vaccination.
There were no reported SAEs that were assessed as vaccine related.
| MenQuadfi in MenQuadfi-primed (N=186) % | MenQuadfi in Menveo-primed (N=184) % | MenQuadfi and Trumenba in MenQuadfi-primed (N=93) % | MenQuadfi and Bexsero in MenQuadfi-primed (N=92) % |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reactions | Any | Grade 3 | Any | Grade 3 | Any | Grade 3 | Any | Grade 3 |
| N: number of participants in the safety analysis set | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Local Reactions† | ||||||||
| Injection Site Pain | 38.2 | 0.5 | 33.7 | 1.1 | 48.9 | 5.4 | 56.5 | 0 |
| Injection Site Erythema | 6.5 | 0.5 | 5.4 | 0 | 1.1 | 0 | 6.5 | 1.1 |
| Injection Site Swelling | 5.4 | 0 | 1.6 | 0 | 2.2 | 0 | 5.4 | 1.1 |
| Systemic Reactions | ||||||||
| Myalgia | 32.8 | 1.6 | 34.8 | 1.1 | 65.2 | 7.6 | 63.0 | 4.3 |
| Headache | 36.0 | 1.1 | 34.8 | 1.6 | 42.4 | 4.3 | 39.1 | 2.2 |
| Malaise | 26.9 | 2.2 | 25.5 | 2.2 | 39.1 | 5.4 | 40.2 | 3.3 |
| Fever | 0 | 0 | 2.2 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 0 | 4.4 | 0 |
Older adults ≥ 59 years of age
The safety of MenQuadfi in previously vaccinated older adults ≥ 59 years of age was evaluated in Study 7 (NCT04142242). All randomized participants had received a prior dose of either MenQuadfi (N=162) or Menomune (N=151) at a median interval of 3.34 and 3.35 years, respectively. The safety analysis set included 313 participants who received a dose of MenQuadfi (median age: 69.0 years for subjects primed with MenQuadfi and 70.0 years for subjects who received a prior dose of Menomune); 62.6% were female, 90.4% were White, 8.6% were Black, 0.3% were of other racial groups, and 10.5% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
The rates and severity of the solicited adverse reactions that occurred within 7 days following a dose of MenQuadfi in Study 7 (NCT04142242) are presented in Table 6.
The majority of solicited reactions were Grade 1 or 2 and resolved within 3 days after vaccination.
There were no reported SAEs that were assessed as vaccine related.
| MenQuadfi-primed (N=162) % | Prior dose of Menomune (N=151) % |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reactions | Any | Grade 3 | Any | Grade 3 |
| N: number of participants in the safety analysis set | ||||
|
||||
| Local Reactions | ||||
| Injection Site Pain | 16.7 | 0 | 21.2 | 0.7 |
| Injection Site Erythema | 3.7 | 0 | 7.3 | 0 |
| Injection Site Swelling | 3.7 | 0 | 4.6 | 0 |
| Systemic Reactions | ||||
| Myalgia | 21.6 | 2.5 | 19.9 | 1.3 |
| Headache | 18.5 | 0 | 13.9 | 0 |
| Malaise | 13.6 | 1.9 | 14.6 | 2.6 |
| Fever | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Concomitant Administration with Other Vaccines
In a clinical trial in adolescents 10 through 17 years of age, MenQuadfi was administered concomitantly with Tdap and HPV [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Lower geometric mean antibody concentrations (GMCs) for antibodies to the pertussis antigens filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA), pertactin (PRN) and fimbriae (FIM) were observed when MenQuadfi was co-administered with Tdap and HPV, compared to concomitant administration of Tdap and HPV (without MenQuadfi) [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Data
Animal Data
In a developmental toxicity study, female rabbits received a human dose of MenQuadfi by intramuscular injection on five occasions: 30 days and 10 days prior to mating, gestation days 6, 12 and 27. No adverse effects on pre-weaning development up to post-natal day 35 were observed. There were no vaccine-related fetal malformations or variations observed.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of MenQuadfi have not been established in individuals younger than 2 years of age in the US.
8.5 Geriatric Use
A total of 249 participants 65 years of age and older, including 71 participants 75 years of age or older, in Study 4 received one dose of MenQuadfi [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
MenQuadfi recipients ≥ 65 years of age had lower GMTs and seroresponse rates for all serogroups compared to MenQuadfi recipients 56 through 64 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
11. MenQuadfi Description
MenQuadfi is a sterile liquid vaccine administered by intramuscular injection that contains Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A, C, W, and Y capsular polysaccharide antigens that are individually conjugated to tetanus toxoid protein. N. meningitidis A, C, W, and Y strains are cultured on Mueller Hinton agar medium and grown in Watson Scherp medium. The polysaccharides are extracted from the N. meningitidis cells and purified by centrifugation, detergent precipitation, alcohol precipitation, solvent extraction, and diafiltration. To prepare the polysaccharides for conjugation, Serogroup A is activated with carbonyldiimidazole (CDI), derivatized with adipic acid dihydrazide (ADH), and purified by diafiltration. Serogroups C, W, and Y are depolymerized, activated with periodate, and purified by diafiltration.
Clostridium tetani is fermented in media to generate tetanus toxin, which is purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation to yield purified tetanus toxin (PTT) and detoxified with formaldehyde to yield purified tetanus protein (PTP). The PTP is then concentrated and filtered to yield concentrated tetanus protein (CTP). The activated/derivatized polysaccharides are covalently linked to tetanus toxoid and purified by chromatography and serial diafiltration. The four meningococcal components, present as individual serogroup-specific glycoconjugates, compose the final formulated vaccine.
MenQuadfi is manufactured as a sterile, clear, colorless solution. Each 0.5 mL dose of vaccine contains 10 microgram each of meningococcal A, C, W, and Y polysaccharide antigens conjugated to approximately 55 micrograms tetanus toxoid protein carrier; 3.35 mg sodium chloride (0.67%), and 1.23 mg sodium acetate (30 mM). Potency of MenQuadfi is determined by quantifying the amount of each polysaccharide antigen that is conjugated to tetanus toxoid protein and the amount of unconjugated polysaccharide present.
No preservative or adjuvant is added during manufacture. Each 0.5 mL dose may contain residual amounts of formaldehyde of less than 3 mcg/mL, by calculation.
The vial in which the vaccine components are contained is composed of USP Type I borosilicate glass. The vial stopper is a chlorobutyl synthetic polyisoprene blend stopper (not made with natural rubber latex).
12. MenQuadfi - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Invasive meningococcal disease (IMD) is caused by the bacterium N. meningitidis, a gram-negative diplococcus found exclusively in humans. The presence of bactericidal anti-capsular meningococcal antibodies in serum has been associated with protection from IMD. MenQuadfi induces the production of bactericidal antibodies specific to the capsular polysaccharides of N. meningitidis serogroups A, C, W, and Y.
14. Clinical Studies
To infer effectiveness of MenQuadfi, the immunogenicity in persons 2 years of age and older was evaluated using a serogroup-specific serum bactericidal assay with exogenous human complement (hSBA). The hSBA responses following a single dose of MenQuadfi for primary vaccination were assessed in four studies, and the hSBA responses following a single dose of MenQuadfi for booster vaccination were assessed in two studies. The hSBA responses following a single dose of MenQuadfi were also assessed in one study that enrolled a group of participants who had received a prior dose of meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine. Serum was collected at baseline and 30 days post-vaccination to measure antibodies with hSBA. The hSBA geometric mean titers (GMTs) and proportion of participants who achieved hSBA seroresponse (defined below) were evaluated.
- Seroresponse rate for each serogroup: the proportion of participants with an hSBA
- pre-vaccination titer < 1:8 who achieved a post-vaccination titer ≥ 1:16, or
- pre-vaccination titer ≥ 1:8 who achieved a post-vaccination titer at least 4-fold greater than the pre-vaccination titer.
14.2 Booster Vaccination Following Priming with a Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine; Vaccination Following a Prior Dose of a Meningococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine
Immunogenicity in Adolescents and Adults 13 through 26 Years of Age
Immunogenicity of a booster dose of MenQuadfi was evaluated in Study 6 (NCT04084769). The study enrolled participants 13 through 26 years of age who had received a primary dose of MenQuadfi or Menveo 3–6 years previously in Study 2 or Study 3.
For a description of study design and number of participants, see section 6.1 Booster Vaccination Following Priming with a Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine; Vaccination Following a Prior Dose of a Meningococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine. The primary immunogenicity endpoints were hSBA seroresponse to each serogroup 30 days following a booster vaccination with MenQuadfi given to participants who received a prior dose of MenQuadfi or Menveo 3–6 years previously (Table 11). The other endpoints included hSBA GMTs for each serogroup. These endpoints were also evaluated at 6 days post vaccination in a subset (Per-Protocol Analysis Set 1).
| †Endpoint by Serogroup | MenQuadfi-primed (95% CI) N=174 | Menveo-primed (95% CI) N=176 |
|---|---|---|
| N: number of subjects in Per-Protocol Analysis Set 2 (D30) with valid serology results. | ||
|
||
| A | ||
| % Participants achieving Seroresponse | 94.8 (90.4; 97.6) | 93.2 (88.4; 96.4) |
| C | ||
| % Participants achieving Seroresponse | 97.1 (93.4; 99.1) | 98.9 (96.0; 99.9) |
| W | ||
| % Participants achieving Seroresponse | 97.7 (94.2; 99.4) | 98.9 (96.0; 99.9) |
| Y | ||
| % Participants achieving Seroresponse | 98.9 (95.9; 99.9) | 100 (97.9; 100) |
Seroresponse rates at Day 6 following booster dose with MenQuadfi were 82.6%, 89.1%, 97.8%, and 95.7% for serogroups A, C, W, and Y, respectively, in MenQuadfi-primed participants (N=46) and 77.8%, 93.3%, 88.9%, and 91.1% for serogroups A, C, W, and Y, respectively, in Menveo-primed participants (N=45).
Following a booster dose of MenQuadfi, the hSBA GMTs at Day 6 were 289, 3799, 1928, and 1658 for MenQuadfi-primed participants (N=46) and 161, 919, 708, and 800 for Menveo-primed participants (N=45) for serogroups A, C, W, and Y, respectively. At D30, the hSBA GMTs were 502, 3708, 2290, and 2308 for MenQuadfi-primed participants (N=174) and 399, 2533, 2574, and 3036 for Menveo-primed participants (N=176).
Prior to booster vaccination, the percentage of subjects with hSBA titers ≥1:8 for serogroups A, C, W, and Y were 71.3%, 87.9%, 86.2%, and 79.9% for those who received a prior dose of MenQuadfi 3-6 years earlier (N=174), and 71.0%, 50.6%, 77.8%, and 52.8% for those who received a prior dose of Menveo 3-6 years earlier (N=176).
Immunogenicity in Older Adults ≥ 59 Years of Age
Immunogenicity of a dose of MenQuadfi was evaluated in Study 7 (NCT04142242). The study enrolled participants ≥ 59 years of age who had received a prior dose of MenQuadfi or Menomune at least 3 years previously in Study 4 (NCT02842866).
For a description of study design and number of participants, see section 6.1 Booster Vaccination Following Priming with a Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine; Vaccination Following a Prior Dose of a Meningococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine. The primary immunogenicity endpoint was hSBA seroresponse to each serogroup 30 days following vaccination with MenQuadfi in participants who had received a prior dose of Menomune 3 years previously. Additionally, hSBA seroresponse 30 days following vaccination with MenQuadfi in MenQuadfi-primed participants was also assessed (Table 12). The other endpoints included the hSBA GMTs for each serogroup. These endpoints were also evaluated at 6 days post vaccination in a subset (Per-Protocol Analysis Set 2).
| †Endpoint by Serogroup | MenQuadfi- primed (95% CI) | Prior dose of Menomune (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| N: number of subjects in Per-Protocol Analysis Set 1 (D30) with valid serology results. | ||
|
||
| A | N=145 | N=130 |
| % Participants achieving Seroresponse | 79.3 (71.8; 85.6) | 60.8 (51.8; 69.2) |
| C | ||
| % Participants achieving Seroresponse | 93.1 (87.7; 96.6) | 55.0 (46.0; 63.8) |
| W | ||
| % Participants achieving Seroresponse | 90.3 (84.3; 94.6) | 49.2 (40.4; 58.1) |
| Y | ||
| % Participants achieving Seroresponse | 92.4 (86.8; 96.2) | 49.2 (40.4; 58.1) |
Seroresponse rates at Day 6 following vaccination with MenQuadfi were 36.2%, 77.6%, 70.7%, and 72.4% for serogroups A, C, W, and Y, respectively, in MenQuadfi-primed participants (N=58) and 8.1%, 8.1%, 6.5%, and 8.1% for serogroups A, C, W, and Y, respectively, in participants who received a prior dose of Menomune (N=62). Following vaccination with MenQuadfi, the hSBA GMTs at Day 6 were 44, 206, 118, and 151 for MenQuadfi-primed participants (N=58) and 13, 11, 10, and 11 for participants who received a prior dose of Menomune (N=62) for serogroups A, C, W, and Y, respectively. At D30, the hSBA GMTs were 162, 638, 419, and 566 for MenQuadfi-primed participants (N=145) and 57, 56, 31, and 41 for participants who received a prior dose of Menomune (N=130).
Prior to MenQuadfi vaccination, the percentage of subjects with hSBA titers ≥1:8 for serogroups A, C, W, and Y were 64.8%, 73.8%, 66.9%, and 72.4% for those who received a prior dose of MenQuadfi at least 3 years earlier (N=145), and 65.4%, 49.2%, 40.0%, and 41.5% for those who received a prior dose of Menomune at least 3 years earlier (N=130).
14.3 Immunogenicity of Concomitantly Administered Vaccines
Concomitant administration of MenQuadfi with Tdap and HPV in adolescents 10 through 17 years was evaluated in Study 2 (NCT02199691). In this randomized study, 503 participants received MenQuadfi alone, 392 received MenQuadfi coadministered with Tdap and HPV, 296 received Tdap and HPV alone. A fourth group received Menveo alone (N=501).
No evidence of interference in hSBA seroresponse rates was observed when MenQuadfi was coadministered with Tdap and HPV. Antibody responses to HPV, and to the tetanus and diphtheria antigens were similar when Tdap and HPV were administered with and without MenQuadfi. Anti-pertussis GMC responses were non-inferior for the pertussis toxoid antigen, but did not meet non-inferiority for the FHA, PRN, and FIM antigens. The clinical relevance of the diminished responses to the pertussis antigens is unknown.
16. How is MenQuadfi supplied
MenQuadfi is supplied in a single-dose vial (NDC 49281-590-58):
in packages of 1 vial (NDC 49281-590-01);
in packages of 5 vials (NDC 49281-590-05);
in packages of 10 vials (NDC 49281-590-10).
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
The vial stopper is not made with natural rubber latex.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Vaccine Information Statements are required by the National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act of 1986 to be given prior to immunization to the patient, parent, or guardian. These materials are available free of charge at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website (www.cdc.gov/vaccines). Inform the patients, parents or guardians about:
- Potential benefits and risks of immunization with MenQuadfi.
- Potential for adverse reactions that have been temporally associated with administration of MenQuadfi or other vaccines containing similar components.
- Reporting any adverse reactions to their healthcare provider.
- The Sanofi Pasteur Inc. Pregnancy Registry, as appropriate [see Pregnancy (8.1)].
| MENQUADFI
neisseria meningitidis group a capsular polysaccharide tetanus toxoid conjugate antigen, neisseria meningitidis group c capsular polysaccharide tetanus toxoid conjugate antigen, neisseria meningitidis group y capsular polysaccharide tetanus toxoid conjugate antigen, and neisseria meningitidis group w-135 capsular polysaccharide tetanus toxoid conjugate antigen injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Sanofi Pasteur Inc. (086723285) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanofi Pasteur Inc. | 086723285 | MANUFACTURE | |